Effects of a Fishing Ban on the Ecosystem Stability and Water Quality of a Plateau Lake: A Case Study of Caohai Lake, China
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
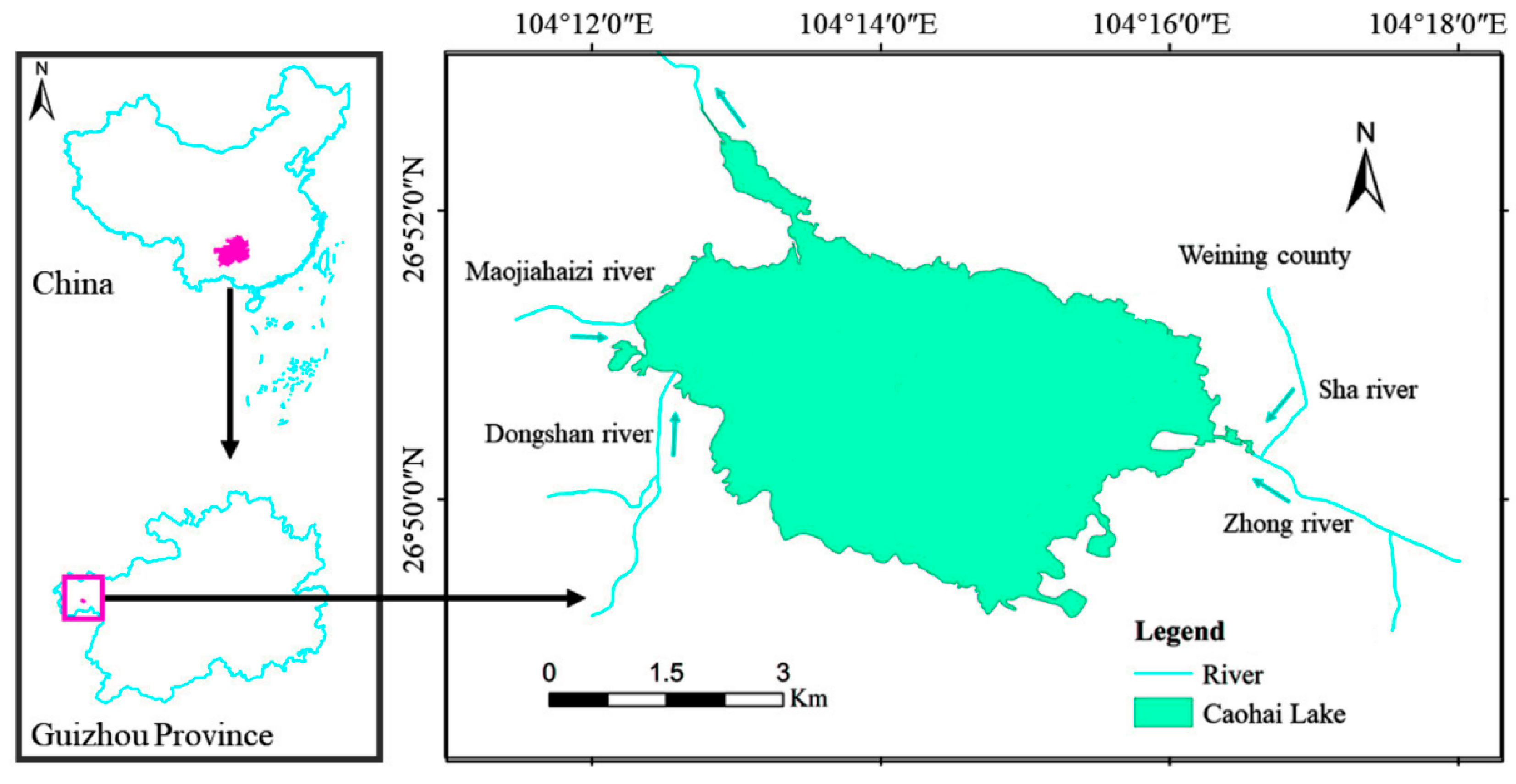
2.1. Study Area
2.2. Samples
2.3. Ecopath Model
2.4. Parameter Determination
2.5. Model Equilibrium
3. Results and Discussion
3.1. Ecosystem Structure and Energy Flow Distribution
3.2. Energy Conversion Efficiency and Trophic Relationships
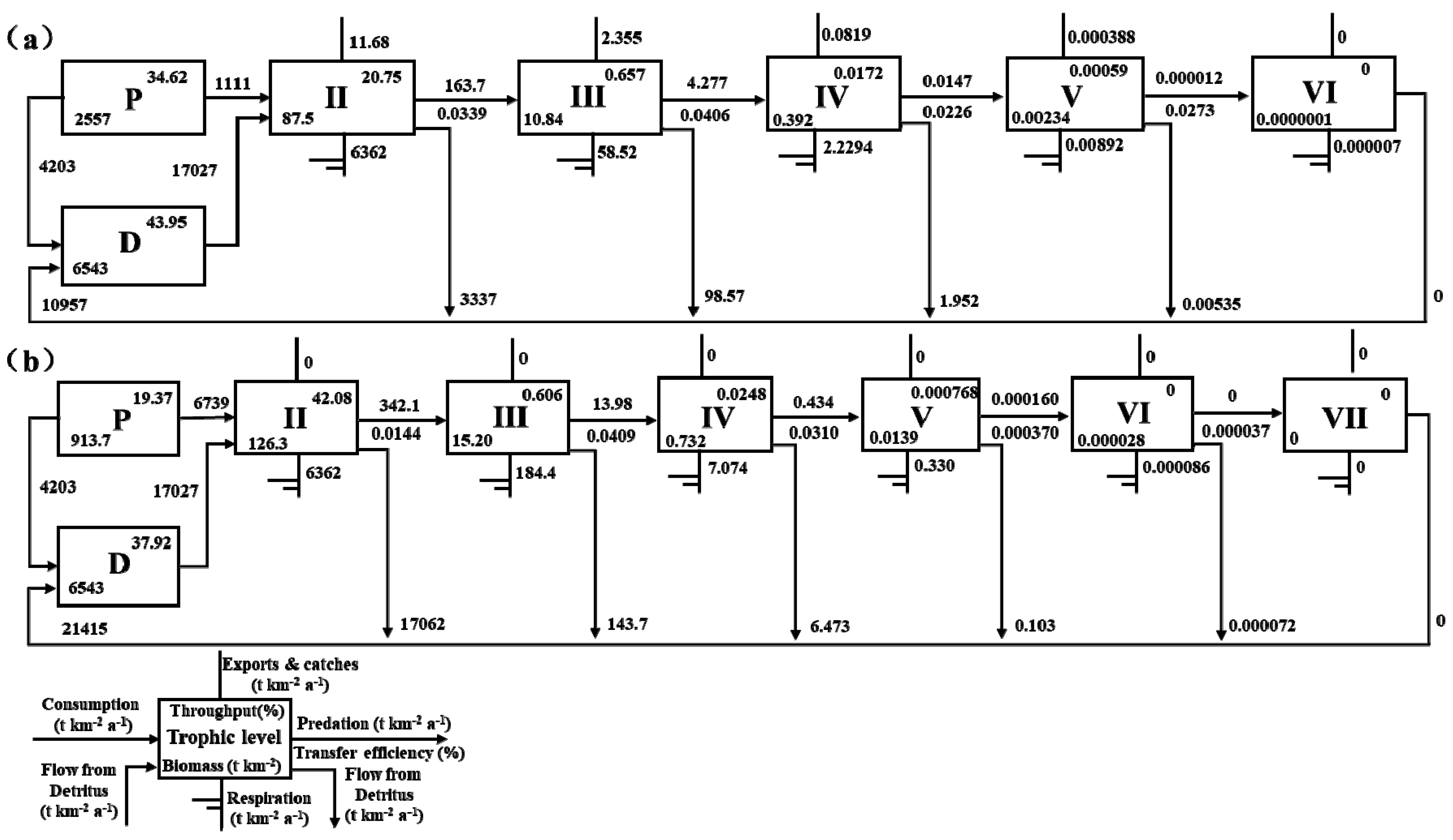
3.2.1. Lindeman Energy Flow Diagram
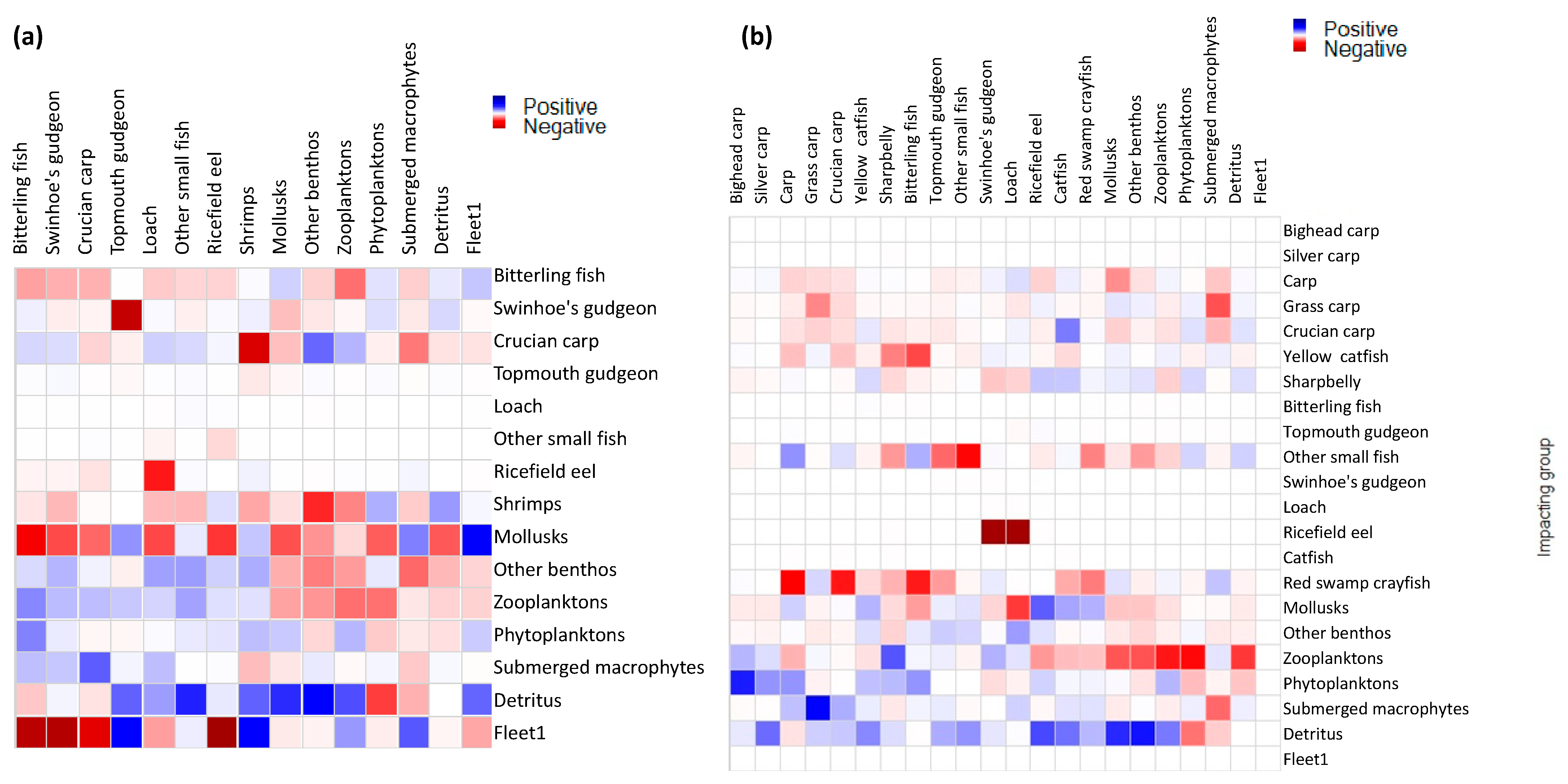
3.2.2. Transfer Efficiency and Mixed Nutritional Effects
3.3. Characterization of System’s Energy Flow
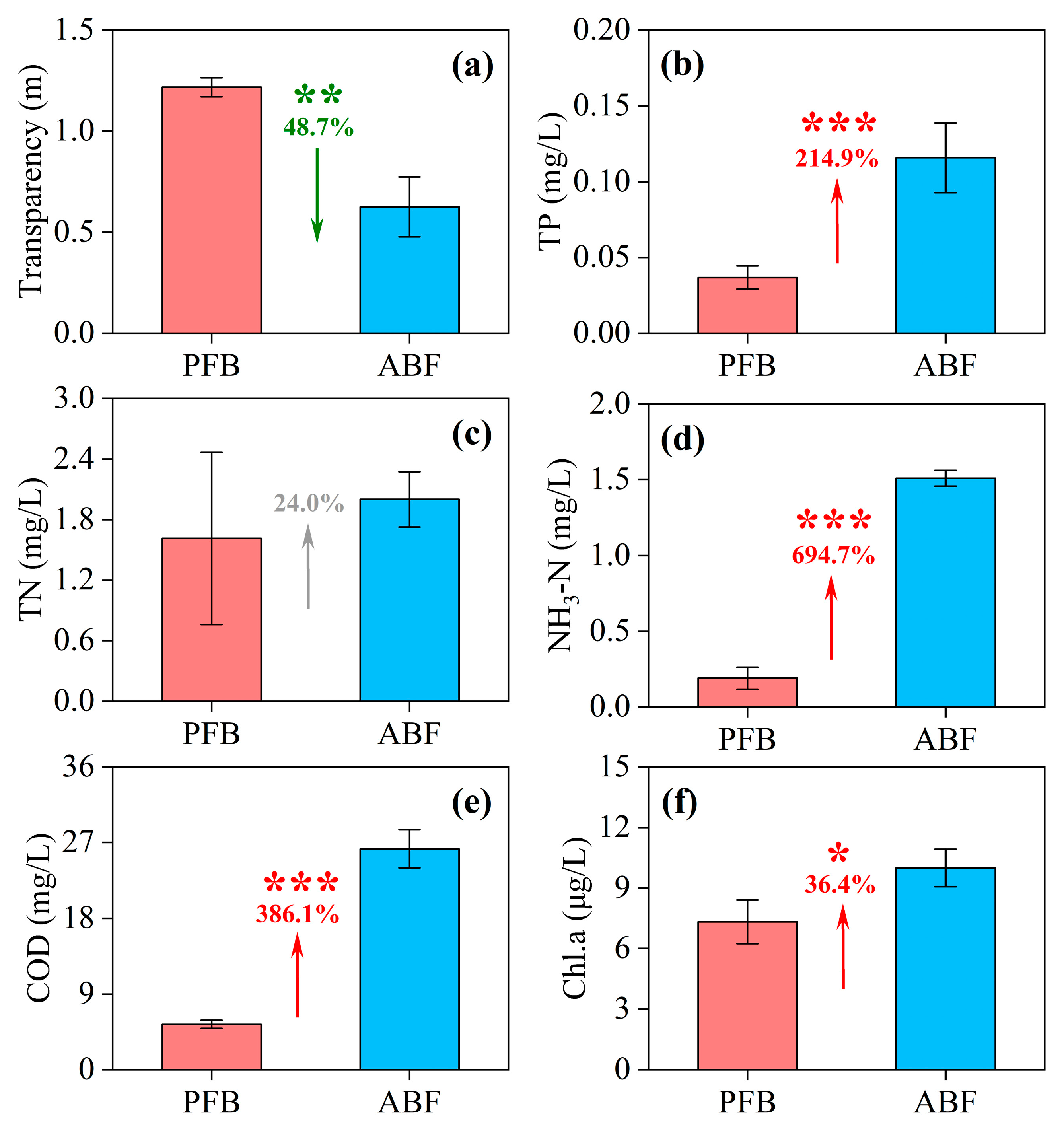
3.4. Water Quality Changes
4. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Williamson, C.E.; Saros, J.E.; Vincent, W.F.; Smol, J.P. Lakes and reservoirs as sentinels, integrators, and regulators of climate change. Limnol. Oceanogr. 2009, 54, 2273–2282. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiang, X.; Ding, C.; Brosse, S.; Pan, B.; Lu, Y.; Xie, Z. Local rise of phylogenetic diversity due to invasions and extirpations leads to a regional phylogenetic homogenization of fish fauna from Chinese isolated plateau lakes. Ecol. Indicat. 2019, 101, 388–398. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Su, G.; Logez, M.; Xu, J.; Tao, S.; Villéger, S.; Brosse, S. Human impacts on global freshwater fish biodiversity. Science 2021, 371, 835–838. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ding, C.; Jiang, X.; Xie, Z.; Brosse, S. Seventy-five years of biodiversity decline of fish assemblages in Chinese isolated plateau lakes: Widespread introductions and extirpations of narrow endemics lead to regional loss of dissimilarity. Divers. Distrib. 2017, 23, 171–184. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tao, J.; Ding, C.; Chen, J.; Ding, L.; Brosse, S.; Heino, J.; Hermoso, V.; Wu, R.; Wang, Z.; Hu, J.; et al. Boosting freshwater fish conservation with high resolution distribution mapping across a large territory. Conserv. Biol. 2023, 37, e14036. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, X.; Qin, J.; Xu, Y.; Ouyang, S.; Wu, X. Biodiversity decline of fish assemblages after the impoundment of the three gorges dam in the Yangtze River basin, China. Rev. Fish Biol. Fish 2019, 29, 177–195. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, H.; Kang, M.; Shen, L.; Wu, J.; Li, J.; Du, H.; Wang, C.; Yang, H.; Zhou, Q.; Liu, Z.; et al. Rapid change in Yangtze fisheries and its implications for global freshwater ecosystem management. Fish Fish. 2020, 21, 601–620. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, L.; Li, Y. An overview of fishing ban measures and research in the Yangtze River basin in the context of Yangtze River protection. China Fish. 2022, 63–67. [Google Scholar]
- Cao, W. Ten-year fishing ban is an important step for the protection of the Yangtze River. J. Aquat. Biol. 2022, 46, 1. [Google Scholar]
- Jiang, T.; Yang, J.; Xuan, Z. Preliminary report on the effects of resource recovery on anadromous Coilia nasus in Poyang Lake under the national 10-year fishing ban. Prog. Fish. Sci. 2022, 43, 24–30. [Google Scholar]
- Liu, F.; Yu, F.; Xia, Z.; Qin, Q.; Xu, C.; Wang, J.; Liu, H. Changes in fish assemblages following the implementation of a complete fishing closure in the Chishui River. Fish. Res. 2021, 243, 106099. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xie, C.; Dai, B.; Wu, J.; Liu, Y.; Jiang, Z. Initial recovery of fish faunas following the implementation of pen-culture and fishing bans in floodplain lakes along the Yangtze River. J. Environ. Manag. 2022, 319, 115743. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mai, Y.; Wang, X.; Peng, S.; Tie, H.; Cai, Y.; Chen, H.; Peng, M.; Wang, Y.; Li, H.; Zeng, Y.; et al. Supporting Evidence for the “Ten-Year Fishing Ban”: Different Modes of Fishing and Pollution Induce a Fish Diversity Decline between the Pearl River and Its Estuary. ACS EST Water 2023, 8, 2590–2603. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, W. Research on the Mechanism of Endogenous Phosphorus Release and In Situ Control Technology in Caohai Lake; Guizhou Normal University: Guiyang, China, 2022. [Google Scholar]
- Yang, Z.; Ren, J.T.; Ren, F. Surface cover information extraction and change monitoring in Caohai Lake protected area based on PE-Engine. Sci. Technol. Innov. 2023, 3, 10–14. [Google Scholar]
- Zhou, X. Assessment of Nitrogen and Phosphorus Pollution Loads from Agricultural Surface Sources in Caohai Lake Watershed Based on SWAT Model; Southwest University: El Paso, TX, USA, 2023. [Google Scholar]
- Xu, L.; Guo, Y.M.; Liu, D. Analysis of water quality changes and influencing factors of Caohai Lake in Guizhou from 2013 to 2022. Environ. Prot. Sci. 2024, 2, 1–8. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, H.; Wang, P.; Xu, C.; Shi, L.; Zhou, L.; Jeppesen, E.; Chen, J.; Xie, P. Can the “10-year fishing ban” rescue biodiversity of the Yangtze River? Innovation 2022, 3, 100235. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dai, L.; Yuan, Q.; Liu, W.; Lü, J.; Yuan, G. Flora characteristics and geographical distribution of aquatic plants in Caohai Wetland of Guizhou. Life Sci. 2022, 40, 6–14. [Google Scholar]
- Tang, J.G.; Li, W.; Zhou, C.Y. Study on aquatic plant diversity changes in Caohai plateau wetland. Guihaia 2014, 34, 601–607. [Google Scholar]
- Wu, H.; Zhang, J.; Yu, L.; Yuan, C.; Yan, L. Classification of Plant Functional Groups Based on Water-holdingFeatures in Caohai Water Functional District. Res. Soil Water Conserv. 2014, 21, 138–143. [Google Scholar]
- Qin, H.C.; Zhu, L.; Long, H.W.; Xiang, Y.; Li, Y.; Li, Q.; Li, F. Species composition and community diversity of Caohai Lake fishes. Guizhou Sci. 2021, 4, 7–12. [Google Scholar]
- Hessen, D.O.; Faafeng, B.A.; Brettum, P.; Andersen, T. Nutrient Enrichment and Planktonic Biomass Ratios in Lakes. Ecosystems 2006, 4, 516–527. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, W.; Huang, X.; Zhou, W. Methods of Lake Ecosystem Observation; China Environmental Science Press: Beijing, China, 2005. [Google Scholar]
- NIGLAS Nanjing Institute of Geography and Lakes, Chinese Academy of Sciences. Technical Regulations for Lake Survey; Science Press: Beijing, China, 2015. [Google Scholar]
- Jin, X.; Tu, Q. Specification for the Investigation of Eutrophication in Lakes Second Edition; China Environmental Science Press: Beijing, China, 1990. [Google Scholar]
- SEPA State Environmental Protection Administration. Analytical Methods for Water and Wastewater Monitoring, 4th ed.; China Environmental Science Press: Beijing, China, 2002. [Google Scholar]
- Fasham, M.; Ducklow, H.; Mckelvie, S. A nitrogen-based model of plankton dynamics in theoceanic mixed layer. J. Mar. Res. 1990, 48, 591–639. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Baretta, J.W.; Ebenhoh, W.; Ruardij, P. The European Regional Seas Ecosystem Model, a complex marine ecosystem model. Neth. J. Sea Res. 1995, 33, 233–246. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Christensen, V.; Walters, C.J.; Pauly, D. Ecopath with Ecosim: A User’s Guide; Fisheries Centre University of British Columbia: Vancouver, BC, Canada, 2005. [Google Scholar]
- Li, H.; Shen, H.; Li, S.J.; Liang, Y.; Lu, C.; Zhang, L. Effects of eutrophication on the benthic-pelagic coupling food web in Baiyangdian Lake. Acta Ecol. Sin. 2018, 38, 2017–2030. [Google Scholar]
- Feng, D.X.; Chen, L.; Li, Y.K.; Yu, N.; Chen, L. Structure and energy flow of Dianshan Lake ecosystem based on the Ecopath model. J. Fish. Sci. China 2011, 8, 867–876. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jia, P.P. Construction of Ecopath Model and Ecological Effect of Bighead and Silver Carp Stocking in Seine Net in Lake Ge Hu; Shanghai Ocean University: Shanghai, China, 2012. [Google Scholar]
- Yan, Y.J.; Liang, Y.L. Energy flow of macrozoobenthic community in a macrophytic lake, Biandantang Lake. Acta Ecol. Sin. 2003, 23, 527–538. [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, T.; Cui, Y. Methods and progress of fish productivity studies. J. Aquat. Sci. 1999, 23, 409–414. [Google Scholar]
- Pauly, D. On the interrelationships between natural mortality, growth parameters and mean environmental temperature in 175 fish stock. ICES J. Mar. Sci. 1980, 32, 175–192. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kwak, I.S.; Park, Y.S. Food Chains and Food Webs in Aquatic Ecosystems. Appl. Sci. 2020, 14, 5012. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Symondson, W.O.C. Molecular identification of prey in predator diets. Mol. Ecol. 2002, 11, 627–641. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ma, X.L.; Liu, C.Q.; Liu, L.S. Study on the food web of fish in Baiyangdian Lake based diet analysis. J. Hydro Ecol. 2011, 32, 85–90. [Google Scholar]
- Xu, C.; Wang, S.K.; Zhao, F.; Zhao, G.; Zhuang, P. Trophic structure of food web and its variation on aquatic animals in the Yangtze Estuary. Acta Hydrobiol. Sin. 2019, 43, 155–164. [Google Scholar]
- Morissette, L.; Hammill, M.; Savenkoff, C. The trophic role of marine mammals in the Northern Gulf of St. Lawrence. Mar. Mammal Sci. 2006, 22, 74–103. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, D.; Zhang, M.; Liu, K. Changes in fishery biodiversity in the Anqing section of the Yangtze River before and after the spring ban. J. Anhui Agric. Univ. 2006, 33, 76–80. [Google Scholar]
- Abdul, J.K.U.; Usha, V.P.; Aiswarya, G.; Chippy, K.; Ganesh, T.; Sanjeevan, V.N.; Shunmugaraj, T.; Anil, K.V.; Gupta, G.V.M. Evaluation of changes in macrobenthic standing stock and polychaete community structure along the south eastern Arabian Sea shelf during the monsoon trawl-ban. Cont. Shelf. Res. 2015, 102, 9–18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lindeman, R.L. The Trophic—Dynamic Aspect of Ecology. Ecology 1942, 23, 399–417. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Q.G. Aquatic Environment Protection Oriented AEPO Fishery in L. Qiandaohu and Its Influences on the Lake Ecosystem; East China Normal University: Shanghai, China, 2005; pp. 85–96. [Google Scholar]
- Li, Y.K.; Liu, E.S.; Wang, H.; Gong, Y. Analysis on the ecosystem structure and function of Lake Taihu based on Ecopath model. Chin. J. Appl. Ecol. 2014, 25, 2033–2040. [Google Scholar]
- Li, Y.; Chen, Y.; Song, B.; Olson, D.; Yu, N.; Chen, L. Ecosystem structure and functioning of Lake Taihu China and the impacts of fishing. Fish. Res. 2009, 95, 309–324. [Google Scholar]
- Yin, C.; Gong, L.; Chen, Y.; Ni, L.; Pitcher, T.J.; Kang, B.; Guo, L. Modeling ecosystem impacts of the invasive Japanese smelt Hypomesus nipponensis in Lake Erhai, southwestern China. Ecol. Inform. 2022, 67, 101488. [Google Scholar]
- Yu, S.; Li, H. Advances in sediment resuspension-heavy metal release mechanism. J. Ecol. Environ. 2010, 19, 1724–1731. [Google Scholar]
- Graham, N.D.; Bouffard, D.; Loizeau, J.L. The influence of bottom boundary layer hydrodynamics on sediment focusing in a contaminated bay. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 2016, 23, 25412–25426. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Meerhoff, M.; Clemente, J.M.; Mello, F.T.D.; Iglesias, C.; Pedersen, A.R.; Jeppesen, E. Can warm climate-related structure of littoral predator assemblies weaken the clear water state in shallow lakes? Global. Change Biol. 2010, 13, 1888–1897. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, S.; He, Y.; Qi, Y. Analysis of water transparency and main influencing factors in Fuxian Lake. J. Environ. Sci. 2022, 41, 1–6. [Google Scholar]
- Yang, L.; Pan, M.; Sun, J.; Cui, Y.; Dong, J.; Yang, J.; Ji, S.; Tao, J.; Ding, C. Short-term responses of macroinvertebrate assemblages 446 to the “ten-year fishing ban” in the largest highland lake of the Yangtze basin. J. Environ. Manag. 2023, 343, 118160. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
| Functional Group | Group with the Main Species |
|---|---|
| Bitterling fish | Acheilognathus macropterus (A. macropterus) |
| Swinhoe’s gudgeon | Hypseleotris swinhonis (H. swinhonis) |
| Crucian carp | Carassius auratus (C. auratus) |
| Topmouth gudgeon | Pseudorasbora parva (P. parva) |
| Loach | Misgurnus anguillicaudatus (M. anguillicaudatus) |
| Other small fishes | Yunnanilus caohaiensis (Y. caohaiensis), Yunnanilus nigromaculatus (Y. nigromaculatus) |
| Ricefield eel | Monopterus albus (C. auratus) |
| Shrimps | Panulirus ornatus (C. auratus) |
| Mollusks | Cipangopaludina cathayensis (C. cathayensis), Parafossarulus striatulus (P. striatulus), Anodonta woodiana (A. woodiana), etc. |
| Other benthos | Pelopia, Monopylephoruslimosus, Cricotopus, etc. |
| Zooplanktons | Sinodiaptomus sarsi (S. sarsi), Limnoithona sinensis (L. sinensis), etc. |
| Phytoplanktons | Microcystis aeruginosa (M. aeruginosa), Synedra acusvar (S. acusvar), etc. |
| Submerged macrophytes | Submerged macrophytes |
| Detritus | Detritus |
| Functional Group | Group with the Main Species |
|---|---|
| Bighead carp | Hypophthalmichthys nobilis (H. nobilis) |
| Silver carp | Hypophthalmichthys molitrix (H. molitrix) |
| Carp | Cyprinus carpio (C. carpio) |
| Grass carp | Ctenopharyngodon idellus (C. idellus) |
| Crucian carp | Carassius auratus |
| Yellow catfish | Pelteobagrus fulvidraco (P. fulvidraco) |
| Sharpbelly | Hemiculter leucisculus (H. leucisculus) |
| Bitterling fish | A. macropterus |
| Topmouth gudgeon | P. parva |
| Other small fishes | Y. caohaiensis, Y. nigromaculatus |
| Swinhoe’s gudgeon | H. swinhonis |
| Loach | M. anguillicaudatus |
| Ricefield eel | M. albus |
| Catfish | Clarias gariepinus (C. gariepinus) |
| Red swamp crayfish | Procambarus clarkii (P. clarkii) |
| Mollusks | C. cathayensis, P. striatulus, A. woodiana, etc. |
| Other benthos | Pelopia, Monopylephoruslimosus, Cricotopus, etc. |
| Zooplanktons | S. sarsi, L. sinensis, etc. |
| Phytoplanktons | M. aeruginosa, S. acusvar, etc. |
| Submerged macrophytes | Submerged macrophytes |
| Functional Group | Trophic Level | Biomass (t·km−2) | Production/Biomass (a−1) | Consumption/Biomass (a−1) | Eco Trophic Efficiency | Production/Consumption (a−1) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Bitterling fish | 2.4 | 4.06 | 4.2 | 21.70 | 0.060 | 0.194 |
| Bony fishes | 2.7 | 4.49 | 1.2 | 6.20 | 0.190 | 0.194 |
| Crucian carp | 2.6 | 4.32 | 1.13 | 12.30 | 0.218 | 0.092 |
| Topmouth gudgeon | 2.8 | 0.93 | 1.2 | 6.20 | 0.345 | 0.194 |
| Loach | 2.5 | 0.156 | 1.2 | 6.20 | 0.090 | 0.194 |
| Other small fishes | 3.0 | 0.002 | 1.33 | 34.70 | 0 | 0.038 |
| Ricefield eel | 2.8 | 0.201 | 1.2 | 6.20 | 0.044 | 0.194 |
| Shrimps | 2.7 | 4.53 | 4.5 | 24.70 | 0.330 | 0.182 |
| Mollusks | 2.0 | 71.5 | 2.4 | 33.10 | 0.241 | 0.073 |
| Other benthos | 2.0 | 6.22 | 12 | 201.50 | 0.735 | 0.060 |
| Zooplanktons | 2.0 | 2.32 | 62.25 | 617.00 | 0.524 | 0.101 |
| Phytoplanktons | 1.0 | 4.69 | 420 | 0.538 | ||
| Submerged macrophytes | 1.0 | 2552 | 2.61 | 0.008 | ||
| Detritus | 1.0 | 6543 | 0.371 |
| Functional Group | Trophic Level | Biomass (t·km−²) | Production/Biomass (a−1) | Consumption/Biomass (a−1) | Eco Trophic Efficiency | Production/Consumption (a−1) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Bighead carp | 2.6 | 0.048 | 1.299 | 7.53 | 0 | 0.173 |
| Silver carp | 2.5 | 0.08 | 1.503 | 10.19 | 0 | 0.147 |
| Carp | 2.4 | 4.224 | 3.5 | 31.00 | 0.440 | 0.113 |
| Grass carp | 2.1 | 2.814 | 1.2 | 45.00 | 0 | 0.027 |
| Crucian carp | 2.4 | 8.672 | 1.13 | 15.00 | 0.840 | 0.075 |
| Yellow catfish | 2.9 | 2.262 | 1.47 | 5.70 | 0 | 0.258 |
| Sharpbelly | 2.8 | 2.09 | 4.4 | 15.00 | 0.361 | 0.293 |
| Bitterling fish | 2.4 | 0.07 | 4.2 | 21.70 | 0.600 | 0.194 |
| Topmouth gudgeon | 2.8 | 0.31 | 1.2 | 6.20 | 0.824 | 0.194 |
| Other small fishes | 2.8 | 5.2 | 1.33 | 34.70 | 0.156 | 0.038 |
| Bony fishes | 2.9 | 0.01 | 1.2 | 6.20 | 0.004 | 0.194 |
| Loach | 2.5 | 0.007 | 1.2 | 6.20 | 0.006 | 0.194 |
| Ricefield eel | 2.8 | 0.008 | 1.2 | 6.20 | 0 | 0.194 |
| Catfish | 3.1 | 0.016 | 1.4 | 6.60 | 0 | 0.212 |
| Red swamp crayfish | 2.7 | 4.53 | 4.5 | 24.70 | 0.728 | 0.182 |
| Mollusks | 2.0 | 73.4 | 2.4 | 33.10 | 0.801 | 0.073 |
| Other benthos | 2.0 | 6.64 | 12 | 201.50 | 0.780 | 0.060 |
| Zooplanktons | 2.0 | 31.82 | 62.25 | 617.00 | 0.063 | 0.101 |
| Phytoplanktons | 1.0 | 20.5 | 420 | 0.761 | ||
| Submerged macrophytes | 1.0 | 893.2 | 2.61 | 0.080 | ||
| Detritus | 1.0 | 6543 | 0.795 |
| Source\Trophic Level | PFB | ABF | ||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| II | III | IV | V | VI | II | III | IV | V | VI | |
| Producer (%) | 3.496 | 3.853 | 2.262 | 2.723 | 1.193 | 4.251 | 2.794 | 0.037 | ||
| Detritus (%) | 3.363 | 4.105 | 2.256 | 2.727 | 1.537 | 4.036 | 3.2 | 0.037 | ||
| All flows (%) | 3.391 | 4.051 | 2.257 | 2.726 | 0.619 | 1.44 | 4.086 | 3.101 | 0.037 | 0.004 |
| Proportion of total flow originating from detritus (%) | 61 | 69 | ||||||||
| Transfer efficiencies from primary producers (%) | 3.12 | 2.42 | ||||||||
| Transfer efficiencies from detritus (%) | 3.15 | 2.71 | ||||||||
| Total transfer efficiencies (%) | 3.14 | 2.63 | ||||||||
| Trophic Level | PFB | ABF | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Consumption by Predators | Flow to Detritus | Throughput | Consumption by Predators | Flow to Detritus | Throughput | |
| VI | 0 | 0.000001 | 0.000002 | 0 | 0.00002 | 0.00004 |
| V | 0 | 0.0011 | 0.0029 | 0 | 0.0228 | 0.0955 |
| IV | 0.003 | 0.393 | 0.862 | 0.096 | 1.515 | 3.419 |
| III | 0.86 | 20.91 | 35.67 | 3.419 | 34.58 | 80.42 |
| II | 36 | 678 | 1111 | 80.42 | 4819 | 6739 |
| I | 1111 | 7520 | 8631 | 6739 | 4203 | 10,941 |
| Sum | 1147 | 8219 | 9778 | 6823 | 9058 | 17,764 |
| Parameter | Unit | PFB | ABF | Variation |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Sum of all consumptions | t·km−2·a−1 | 534.4 | 24,129.5 | 352% |
| Sum of all exports | 6909.5 | 4387.4 | −37% | |
| Sum of all respiratory flows | 1720.9 | 6553.7 | 281% | |
| Sum of all flows to detritus | 10,957.1 | 21,414.8 | 95% | |
| Total system throughput | 24,928.0 | 56,485.6 | 127% | |
| Sum of all productions | 9070.4 | 13,246.5 | 46% | |
| Calculated total net primary production | 8630.5 | 10,941.2 | 27% | |
| Total primary production/total respiration | / | 5.0 | 1.6 | −67% |
| Net system production | t·km−2·a−1 | 6909.6 | 4387.4 | |
| Total primary production/total biomass | 3.2 | 10.3 | ||
| Total biomass/total throughput | 0.106 | 0.018 | ||
| Total biomass (excluding detritus) | t·km−2 | 2655.4 | 1055.9 | |
| Connectance index | / | 0.386 | 0.275 | |
| System omnivory index (SOI) | 0.143 | 0.151 | ||
| Shannon diversity index | 0.21 | 0.69 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Yang, T.; Li, D.; Xu, Q.; Zhu, Y.; Zhu, Z.; Leng, X.; Zhao, D.; An, S. Effects of a Fishing Ban on the Ecosystem Stability and Water Quality of a Plateau Lake: A Case Study of Caohai Lake, China. Water 2024, 16, 782. https://doi.org/10.3390/w16050782
Yang T, Li D, Xu Q, Zhu Y, Zhu Z, Leng X, Zhao D, An S. Effects of a Fishing Ban on the Ecosystem Stability and Water Quality of a Plateau Lake: A Case Study of Caohai Lake, China. Water. 2024; 16(5):782. https://doi.org/10.3390/w16050782
Chicago/Turabian StyleYang, Tangwu, Dianpeng Li, Qing Xu, Yijia Zhu, Zhengjie Zhu, Xin Leng, Dehua Zhao, and Shuqing An. 2024. "Effects of a Fishing Ban on the Ecosystem Stability and Water Quality of a Plateau Lake: A Case Study of Caohai Lake, China" Water 16, no. 5: 782. https://doi.org/10.3390/w16050782
APA StyleYang, T., Li, D., Xu, Q., Zhu, Y., Zhu, Z., Leng, X., Zhao, D., & An, S. (2024). Effects of a Fishing Ban on the Ecosystem Stability and Water Quality of a Plateau Lake: A Case Study of Caohai Lake, China. Water, 16(5), 782. https://doi.org/10.3390/w16050782








