Study on Impeller Optimization and Operation Method of Variable Speed Centrifugal Pump with Large Flow and Wide Head Variation
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Hydraulic Design
2.1. Pump Station Parameter Analysis
2.2. Impeller Optimization Design
3. Performance Estimation Method
3.1. CFD Numerical Calculation Method
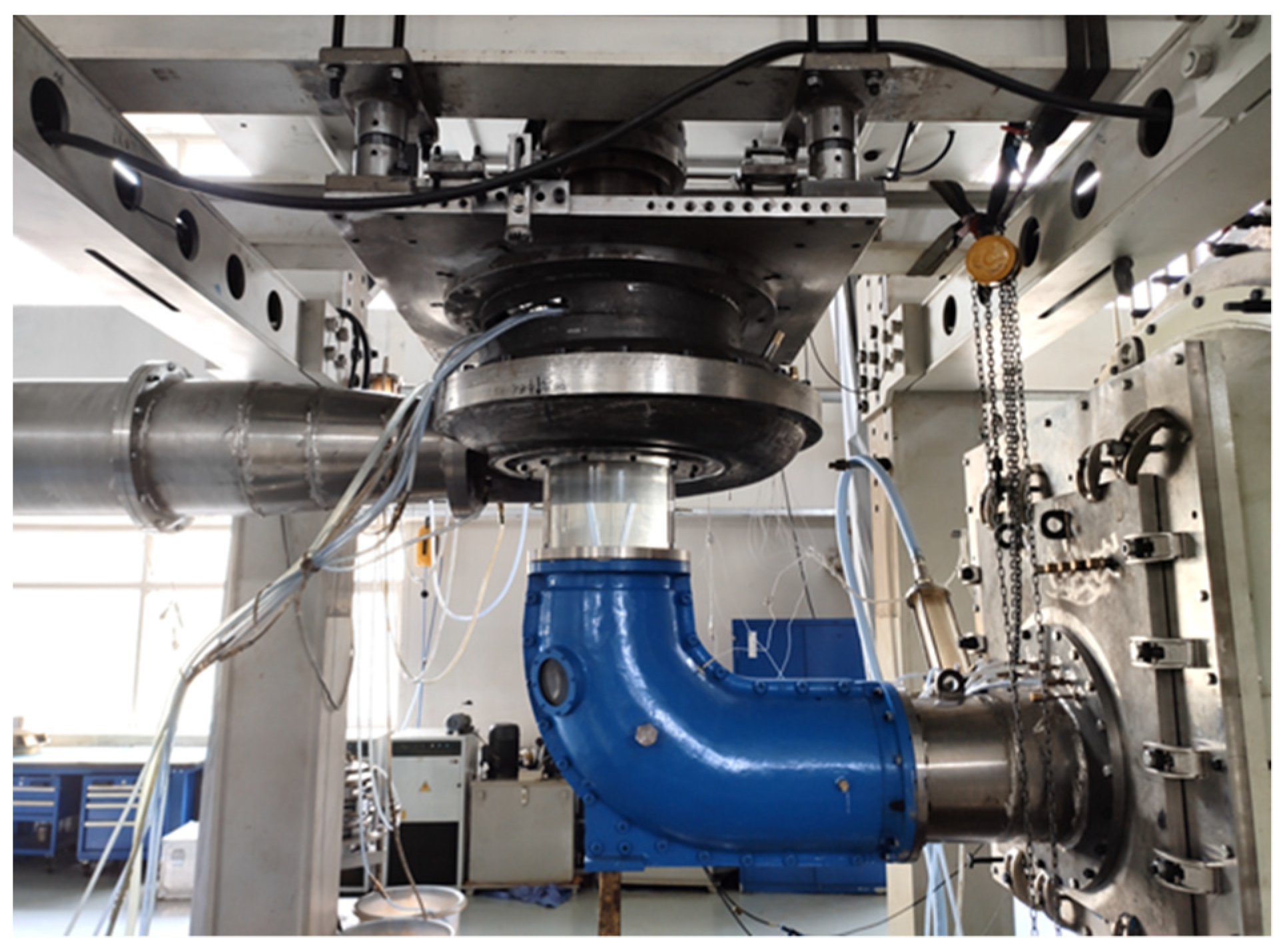
3.2. Model Test Validation Method
4. Performance Evaluation and Result Analysis
4.1. Centrifugal Pump Performance Evaluation
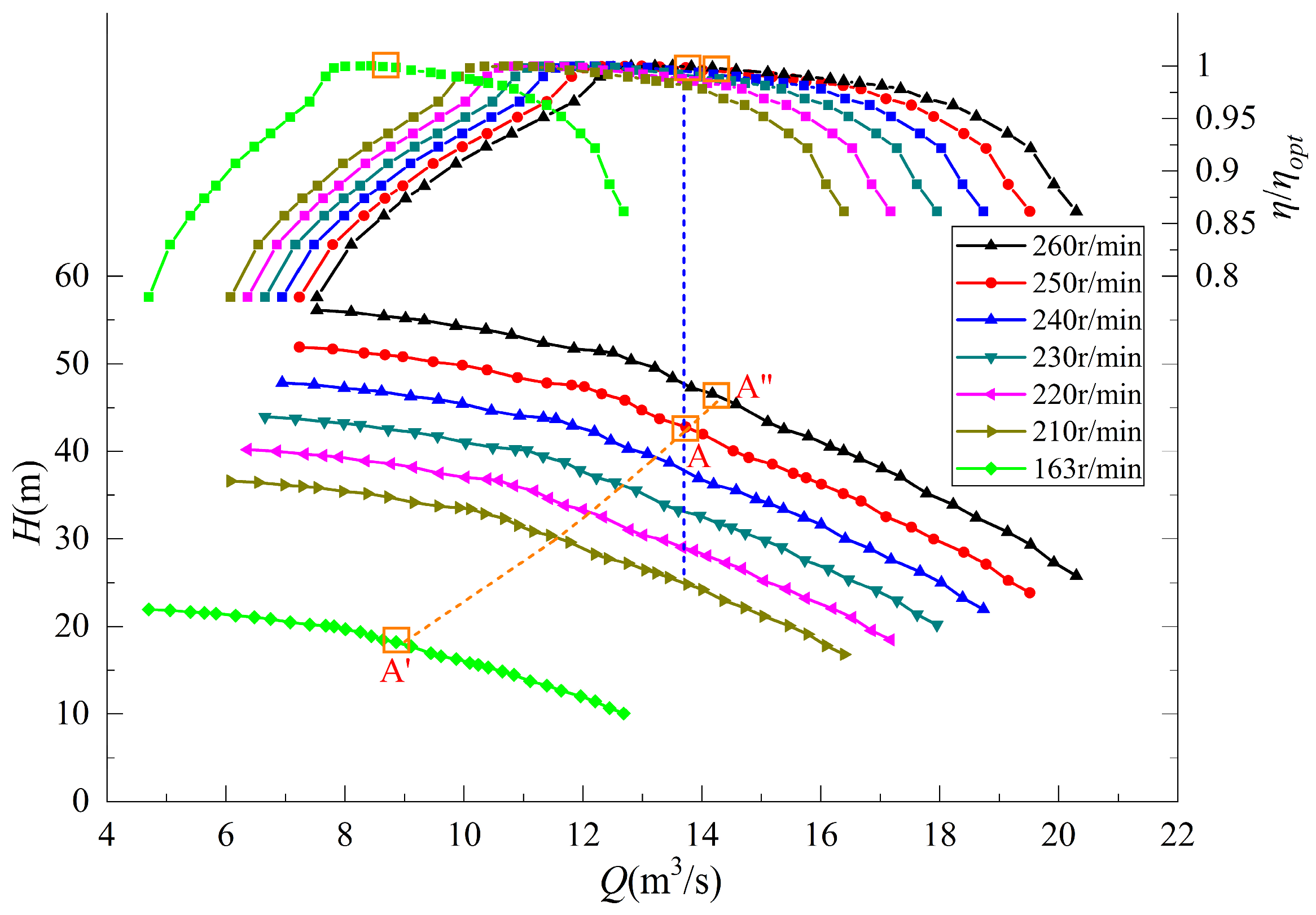
4.2. Variable Speed Operating Characteristics Analysis
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Shi, X.; Lu, J.; Zhao, L. Investigations on the influence of tandem blades on inner flow and performance characteristics of centrifugal pump. Proc. Inst. Mech. Eng. Part E J. Process Mech. Eng. 2020, 234, 46–55. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Torii, D.; Nagahara, T.; Okihara, T. Suppression of the secondary flow in a suction channel of a large centrifugal pump. IOP Conf. Ser. Mater. Sci. Eng. 2013, 52, 032005. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ramirez, R.; Avila, E.; Lopez, L.; Bula, A.; Forero, J.D. CFD characterization and optimization of the cavitation phenomenon in dredging centrifugal pumps. Alex. Eng. J. 2020, 59, 291–309. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- AI-Obaidi, A.R.; Towsyfyan, H. An experimental study on vibration signatures for detecting incipient cavitation in centrifugal pumps based on envelope spectrum analysis. J. Appl. Fluid Mech. 2019, 12, 2057–2067. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, D.; Liu, Z.; Han, W. Study on improving cavitation performance of centrifugal Pump by Perforation at the Front Cover Plate. Int. J. Fluid Mach. Syst. 2020, 13, 668. [Google Scholar]
- Hesamedin, K.; Abdolah, S.; Siamak, H. Improvement of the centrifugal pump performance by restricting the cavitation phenomenon. Chem. Eng. Trans. 2018, 71, 1369–1374. [Google Scholar]
- Song, P.; Wei, Z.; Zhen, H.; Liu, M.; Ren, J. Effects of pre-whirl and blade profile on the hydraulic and cavitation performance of a centrifugal pump. Int. J. Multiph. Flow 2022, 157, 104261. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, G.; Shen, X.; Shi, L.; Zhang, D.; Zhao, X.; van Esch, B.P.M. Numerical investigation of hump characteristic improvement in a large vertical centrifugal pump with special emphasis on energy loss mechanism. Energy 2023, 273, 127163. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ye, C.; Wang, C.; Yan, H.; Wang, F.; Zheng, Y.; van Esch, B.P.M. Investigation on transition characteristics of laminar separation bubble on a hydrofoil. Phys. Fluids 2023, 35, 105154. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ye, C.; Tang, Y.; An, D.; Wang, F.; Zheng, Y.; van Esch, B.P.M. Investigation on stall characteristics of marine centrifugal pump considering transition effect. Ocean Eng. 2023, 280, 114823. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Feng, J.; Ge, Z.; Yang, H.; Zhu, G.; Li, C.; Luo, X. Rotating stall characteristics in the vaned diffuser of a centrifugal pump. Ocean Eng. 2021, 229, 108955. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.; Ding, Z. Optimization design of hump phenomenon of low specific speed centrifugal pump based on CFD and orthogonal test. Sci. Rep. 2022, 12, 12121. [Google Scholar]
- Li, P.; Li, N.; Tao, R.; Lu, Z.; Zhu, D.; Liu, W.; Yao, Z.; Xiao, R. Quantitative investigation of the head-hump of large-scale vaned-voluted centrifugal pump. Proc. Inst. Mech. Eng. Part C J. Mech. Eng. Sci. 2022, 236, 10779–10791. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- De Donno, R.; Ghidoni, A.; Noventa, G.; Rebay, S. Shape optimization of the ERCOFTAC centrifugal pump impeller using open-source software. Optim. Eng. 2019, 20, 929–953. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.; Zhou, L.; Han, M.; Shen, L. Performance Prediction of an Optimized Centrifugal Pump with High Efficiency. Fluid Dyn. Mater. Process. 2023, 19, 2215–2228. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, R.; Zhang, Z.; Zhang, W.; Mou, J.; Zhou, P.; Wang, Y. Energy performance prediction of the centrifugal pumps by using a hybrid neural network. Energy 2020, 213, 119005. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ramadhan, A.A.; Ali, Q. Effect of outlet impeller diameter on performance prediction of centrifugal pump under single-phase and cavitation flow conditions. Int. J. Nonlinear Sci. Numer. Simul. 2022, 23, 1203–1229. [Google Scholar]
- Dong, J.; Li, W. Numerical simulation of centrifugal pump cavitation based on ANSYS. J. Phys. Conf. Ser. 2023, 2450, 012031. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mahdi, M.T.; Amin, D.A.; Ahmad, H.; Mohamed BB, H.; Mohsen, I. MLP and optimized FCM-ANFIS models pro-posed for inlet turbulent flow under ultrasonic vibration. J. Therm. Anal. Calorim. 2023, 148, 13995–14009. [Google Scholar]
- Morteza, E.; Amin, D.A.; Ali, J. Optimization of ultrasonic-excited double-pipe heat exchanger with machine learning and PSO. Int. Commun. Heat Mass Transf. 2023, 147, 106985. [Google Scholar]
- Li, L.; Xu, W.; Tan, Y.; Yang, Y.; Yang, J.; Tan, D. Fluid-induced vibration evolution mechanism of multiphase free sink vortex and the multi-source vibration sensing method. Mech. Syst. Signal Process. 2023, 189, 110058. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cao, W.; Wang, H.; Yang, X.; Leng, X. Optimization of Guide Vane Centrifugal Pumps Based on Response Surface Methodology and Study of Internal Flow Characteristics. J. Mar. Sci. Eng. 2023, 11, 1917. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, G.; Zhao, X.; Zhang, D.; Geng, L.; Yang, X.; Gao, X. Hydraulic components’ matching optimization design and entropy production analysis in a large vertical centrifugal pump. J. Mech. Sci. Technol. 2021, 35, 5033–5048. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yuan, Y.; Jin, R.; Tang, L.; Lin, Y. Optimization Design for the Centrifugal Pump under Non-Uniform Elbow Inflow Based on Orthogonal Test and GA_PSO. Processes 2022, 10, 1254. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, X.; Zhu, R.; Wang, J.; Li, Y. Effect analysis of centrifugal pump parameters optimization design on performance. J. Phys. Conf. Ser. 2023, 2599, 012034. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, J.; Pei, J.; Wang, W. Effect of impeller and diffuser matching optimization on broadening operating range of storage pump. J. Energy Storage 2023, 72, 108737. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, Z.; Cheng, Y.; Liu, D.; Chen, H.; Ji, B.; Ding, J. Broadening the operating range of pump-turbine to deep-part load by runner optimization. Renew. Energy 2023, 207, 73–88. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Iliev, I.; Trivedi, C.; Dahlhaug, O.G. Variable-speed operation of Francis turbines: A review of the perspectives and challenges. Renew. Sustain. Energy Rev. 2019, 103, 109–121. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Badshah, M.; Badshah, S.; Jan, S. Comparison of computational fluid dynamics and fluid structure interaction models for the performance prediction of tidal current turbines. J. Ocean Eng. Sci. 2020, 5, 164–172. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nasir, U.; Iqbal, Z.; Rasheed, M.; Minxiao, H. Active and reactive power control of a variable speed pumped storage system. In Proceedings of the 2015 IEEE 15th International Conference on Environment and Electrical Engineering (EEEIC), Rome, Italy, 10–13 June 2015; pp. 6–11. [Google Scholar]
- Li, Y.; Yang, W.; Huang, Y.; Ma, W.; Zhao, Z.; Yang, J.; Yang, J. Variation law of pressure pulsation during variable speed operation of pumped storage units. IOP Conf. Ser. Earth Environ. Sci. 2022, 1079, 012111. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mercier, T.; Hardy, C.; Van Tichelen, P.; Olivier, M.; De Jaeger, E. Control of variable-speed pumps used as turbines for flexible grid-connected power generation. Electr. Power Syst. Res. 2019, 176, 105962. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Salome, D.M.; Meirelles, G.L.; Melo, B.B.; Bezerra, D.B. Optimal pump selection for variable speed operation in water distribution network. RBRH-Rev. Bras. Recur. Hidreicos 2020, 25. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gevorkov, L.; Rassõlkin, A.; Kallaste, A.; Vaimann, T. Simulation study of mixed pressure and flow control systems for optimal operation of centrifugal pumping plants. Electr. Control. Commun. Eng. 2018, 14, 89–94. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, X.; Liu, S.; Wang, Y. Optimal control study of solar-air source heat pump coupled heating system operation. J. Phys. Conf. Ser. 2023, 2474, 012015. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Amul, G.; Atmaram, K.; Lal, P.B.; Sailesh, C.; Prasad, H.N. Numerical analysis of francis turbine being operated in variable speed from sediment erosion perspective. J. Phys. Conf. Ser. 2023, 2629, 012006. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, H.; Ma, Z. Regulation Characteristics and Load Optimization of Pump-Turbine in Variable-Speed Operation. Energies 2021, 14, 8484. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Delgado, J.; Ferreira, J.P.; Covas DI, C.; Avellan, F. Variable speed operation of centrifugal pumps running as tur-bines. Experimental investigation. Renew. Energy 2019, 142, 437–450. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Selçuk; Arslan, S. Comparison of energy efficiencies of a small centrifugal pump at constant and variable speed operations. Tarim Bilim. Derg. 2016, 22, 444–454. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Edson, B.; Zulcy, S.; Augusto, V.; Helcio, V.; Ângelo, R.; Roberto, S.; Rafael, B.; José, B. The benefits of variable speed operation in hydropower plants driven by francis turbines. Energies 2019, 12, 3719. [Google Scholar]
- Becker, M.R.; Torres TC, J.; Matías, D. Adaptive control of M3C-based variable speed drive for multiple permanent-magnet-synchronous-motor-drive centrifugal pumps. Machines 2023, 11, 884. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mercier, T.; Olivier, M.; Dejaeger, E. Operation ranges and dynamic capabilities of variable-speed pumped-storage hydropower. J. Physics Conf. Ser. 2017, 813, 012004. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]

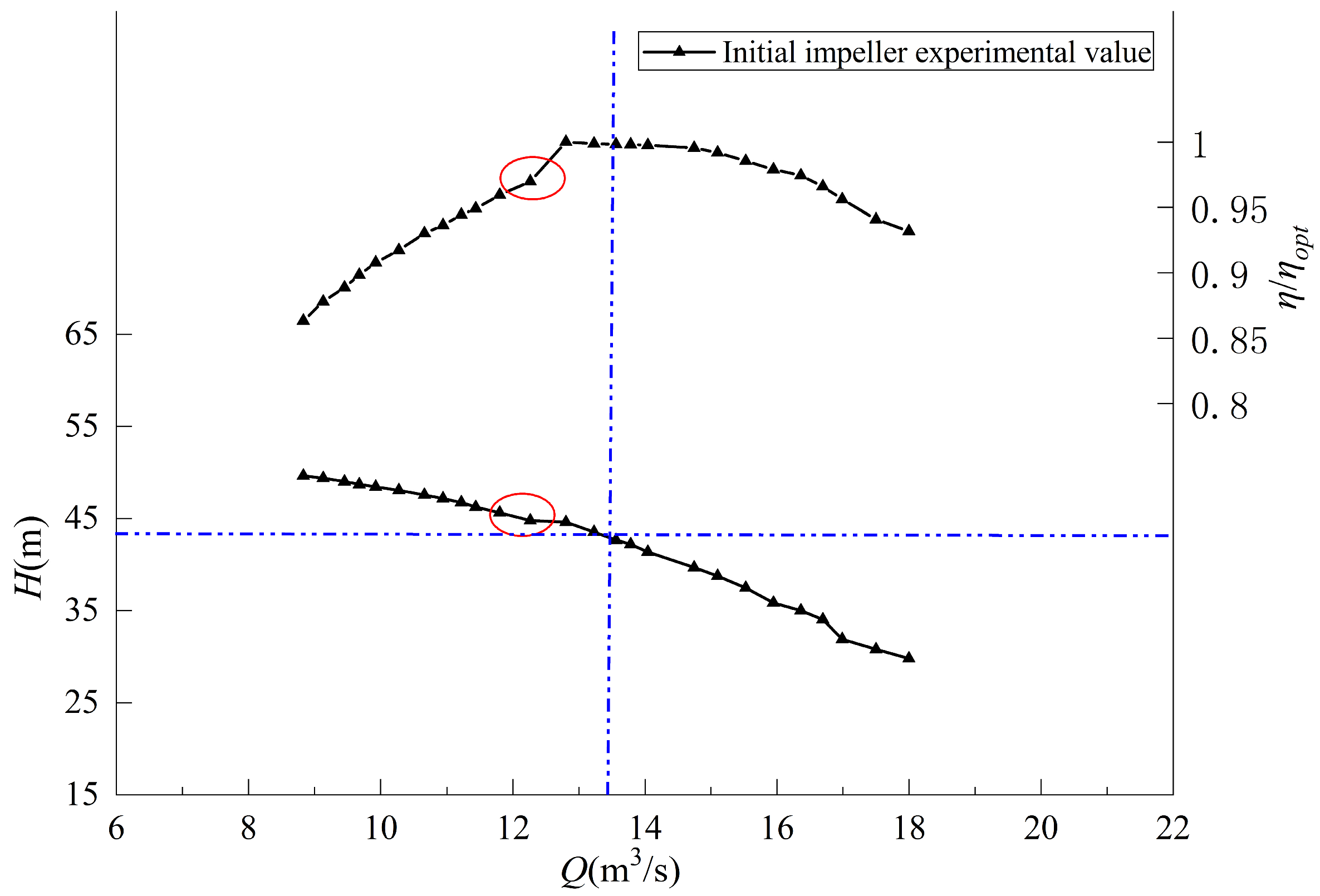

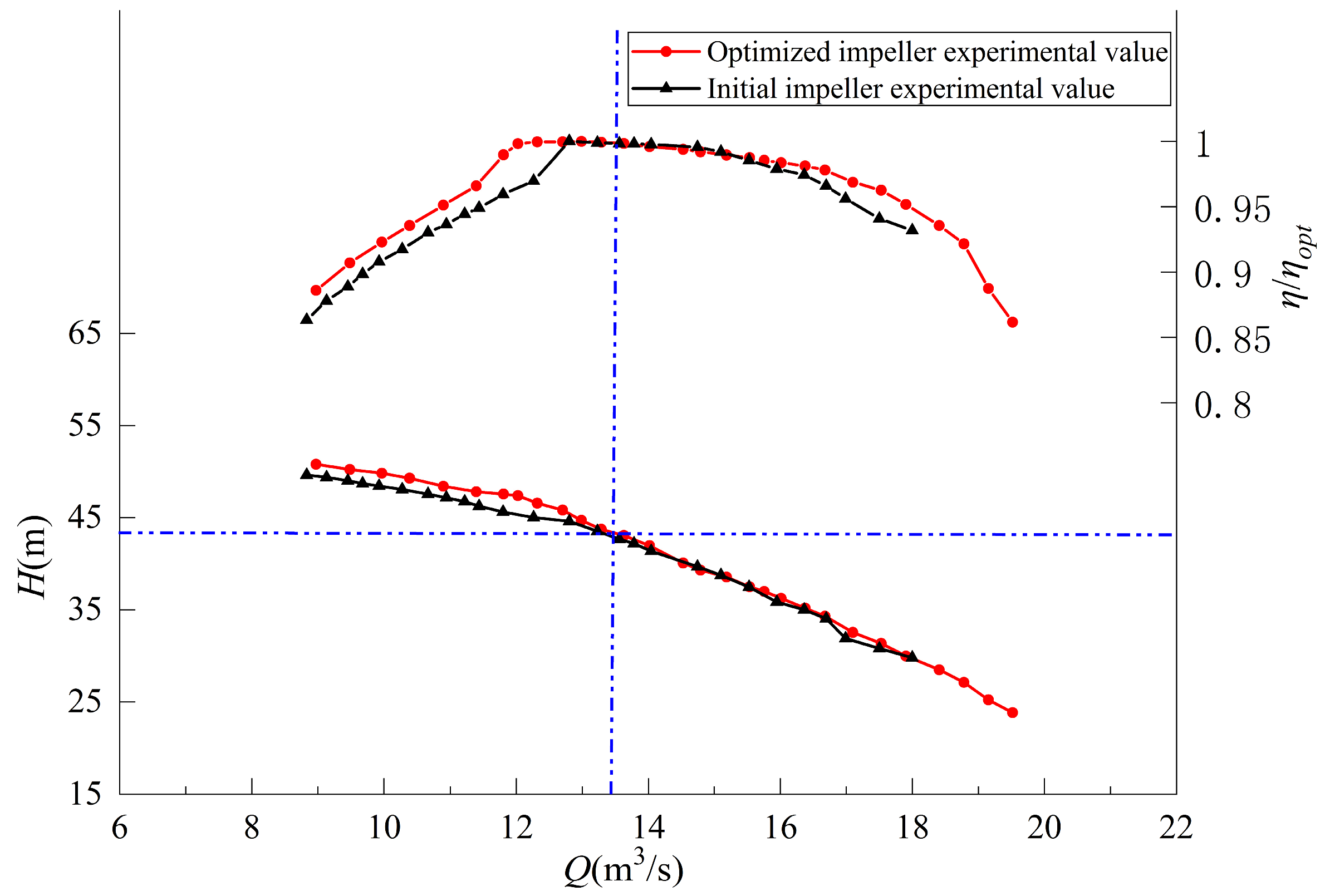
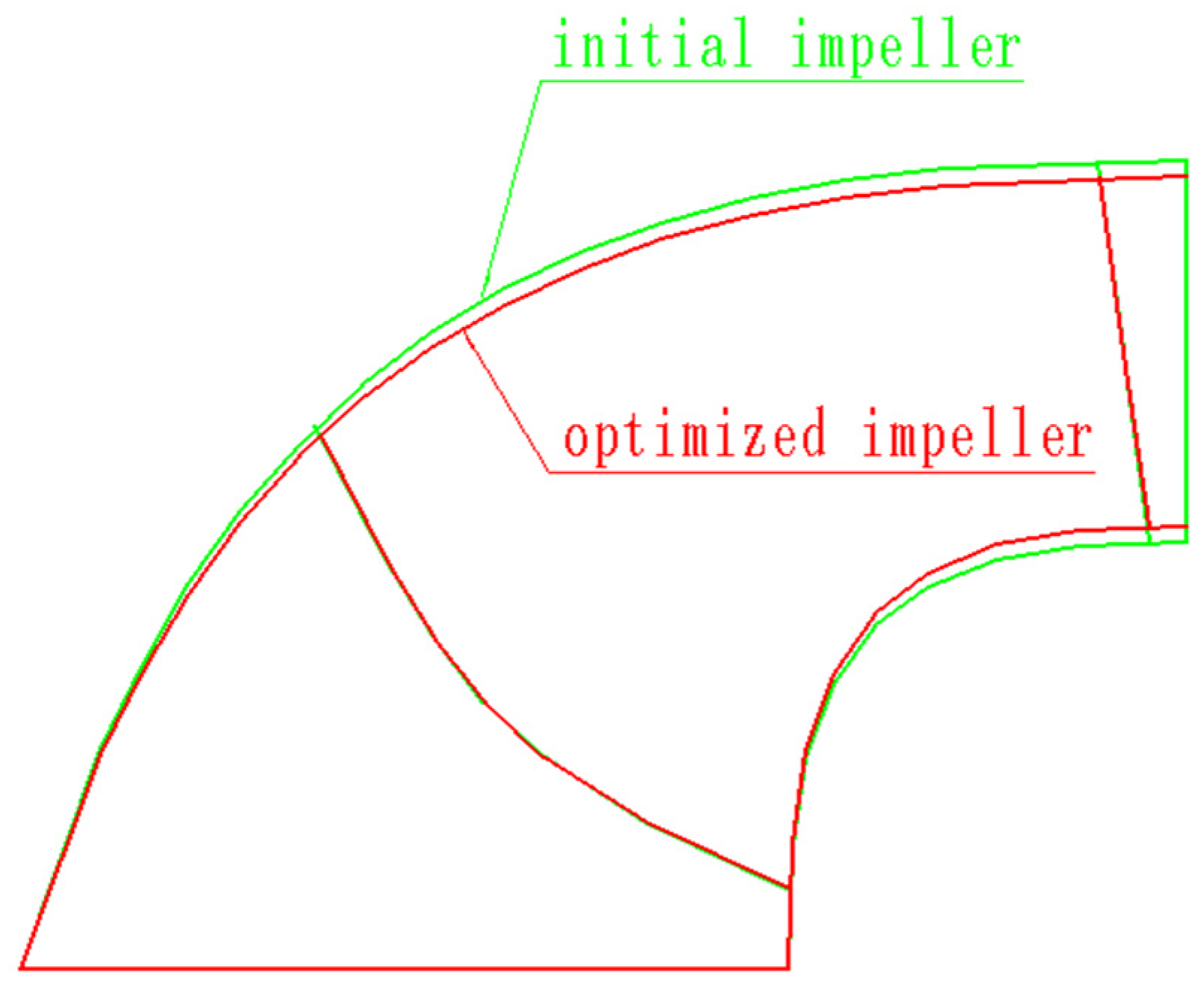
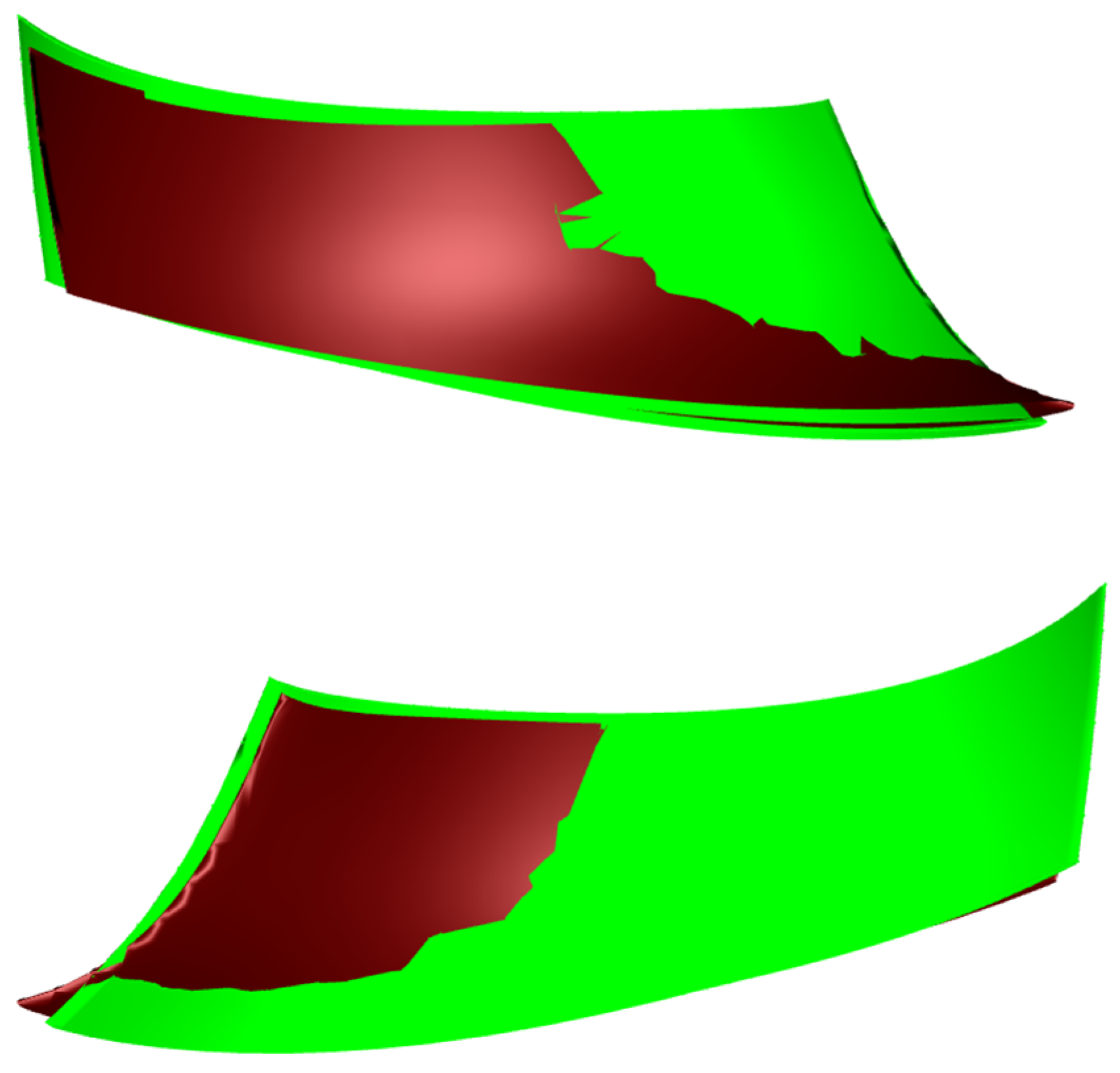
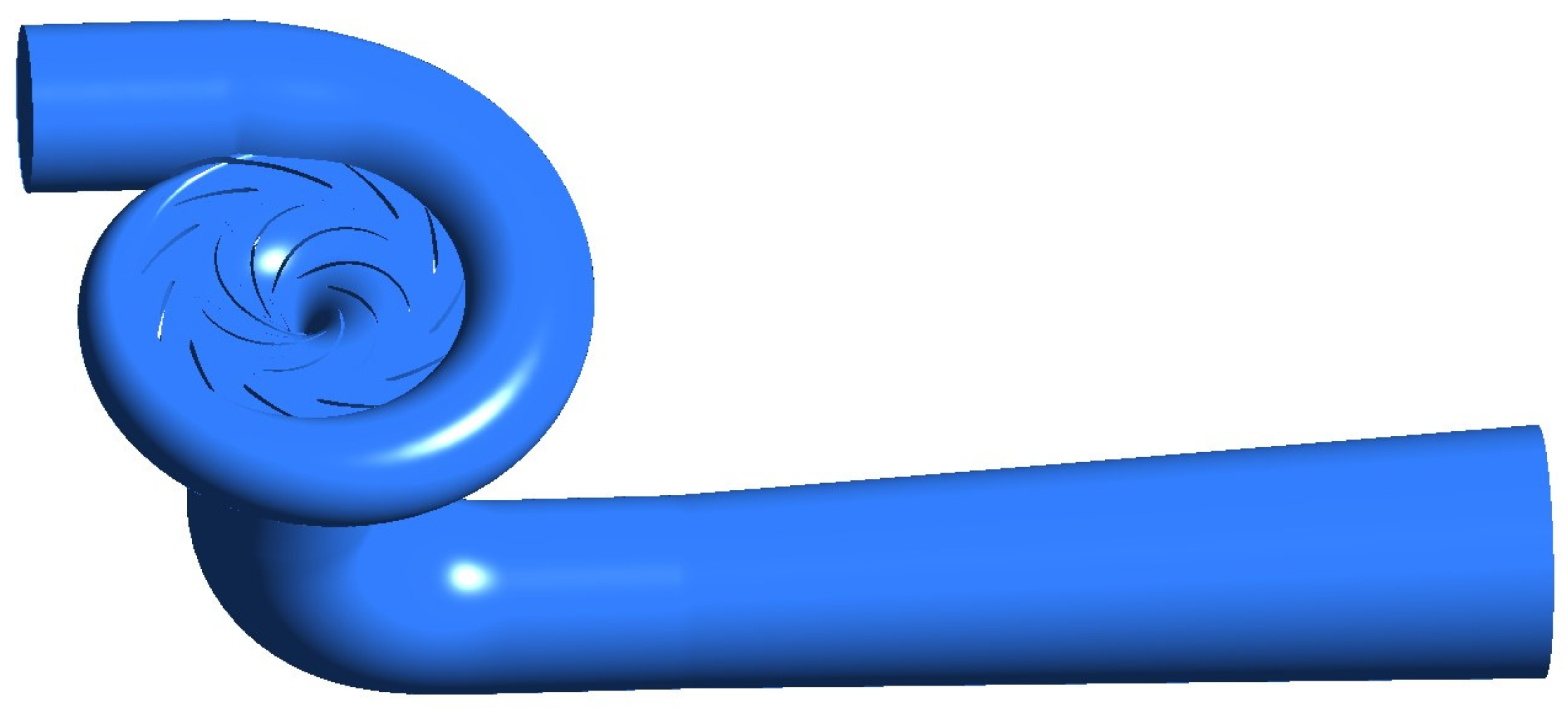


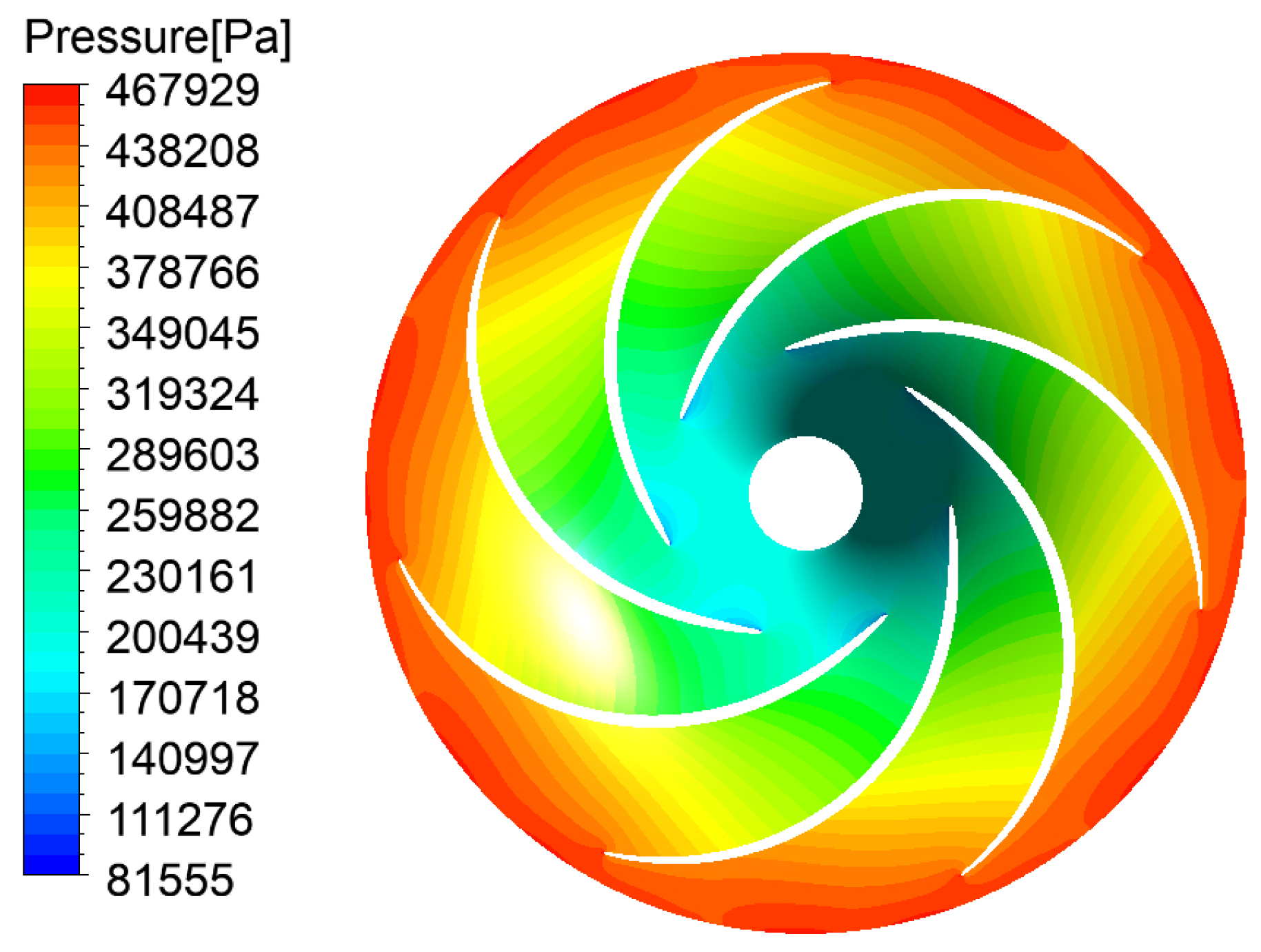

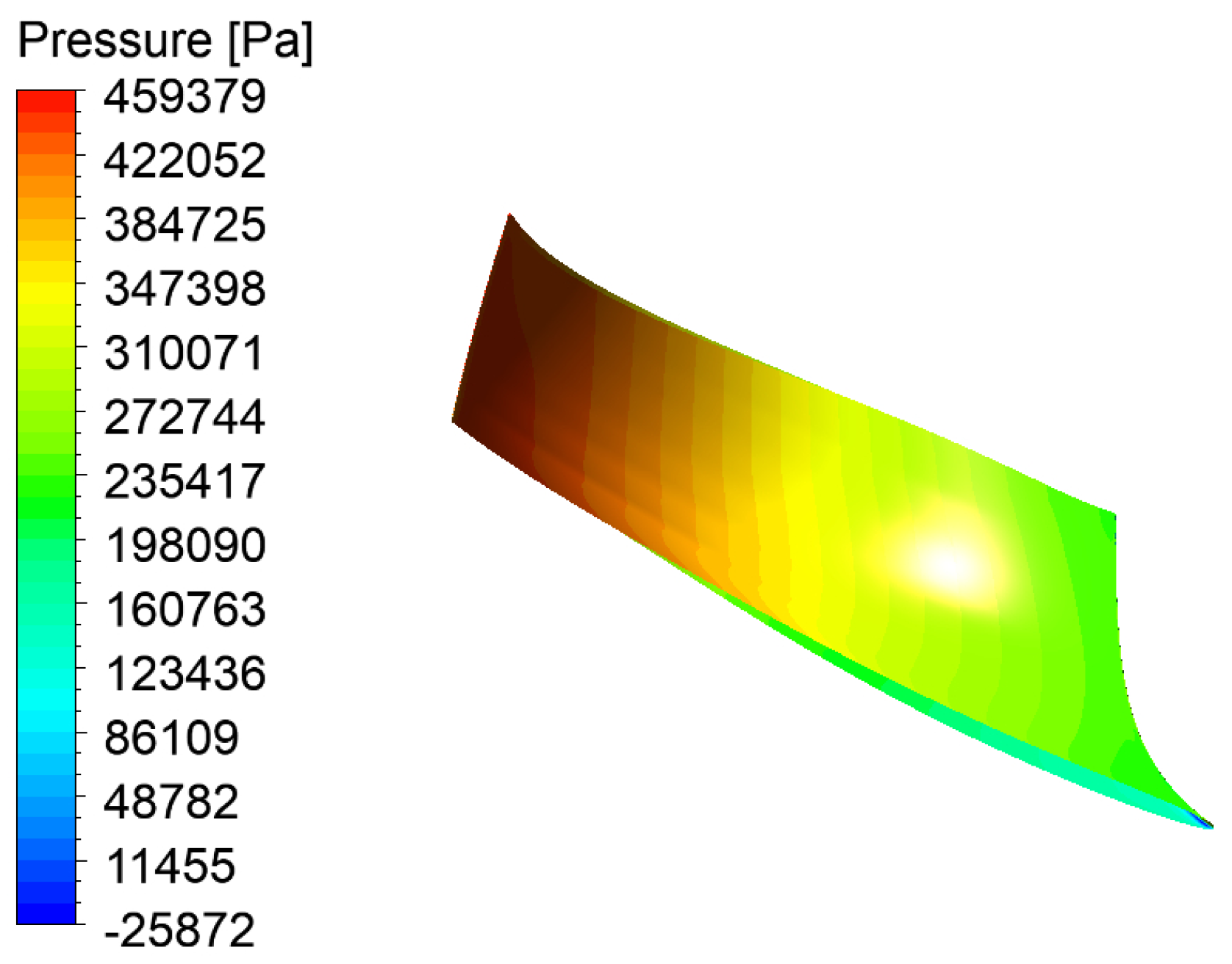

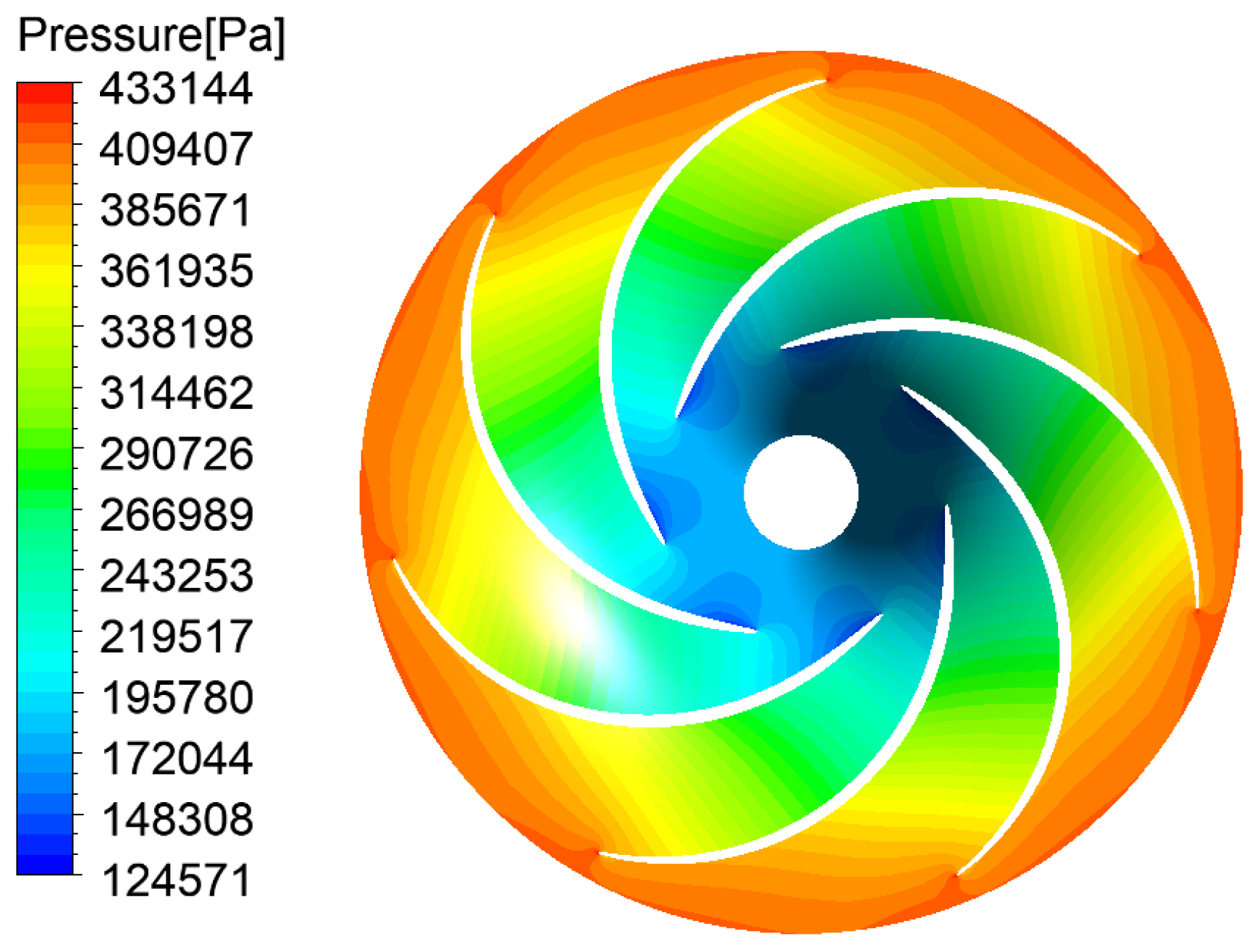
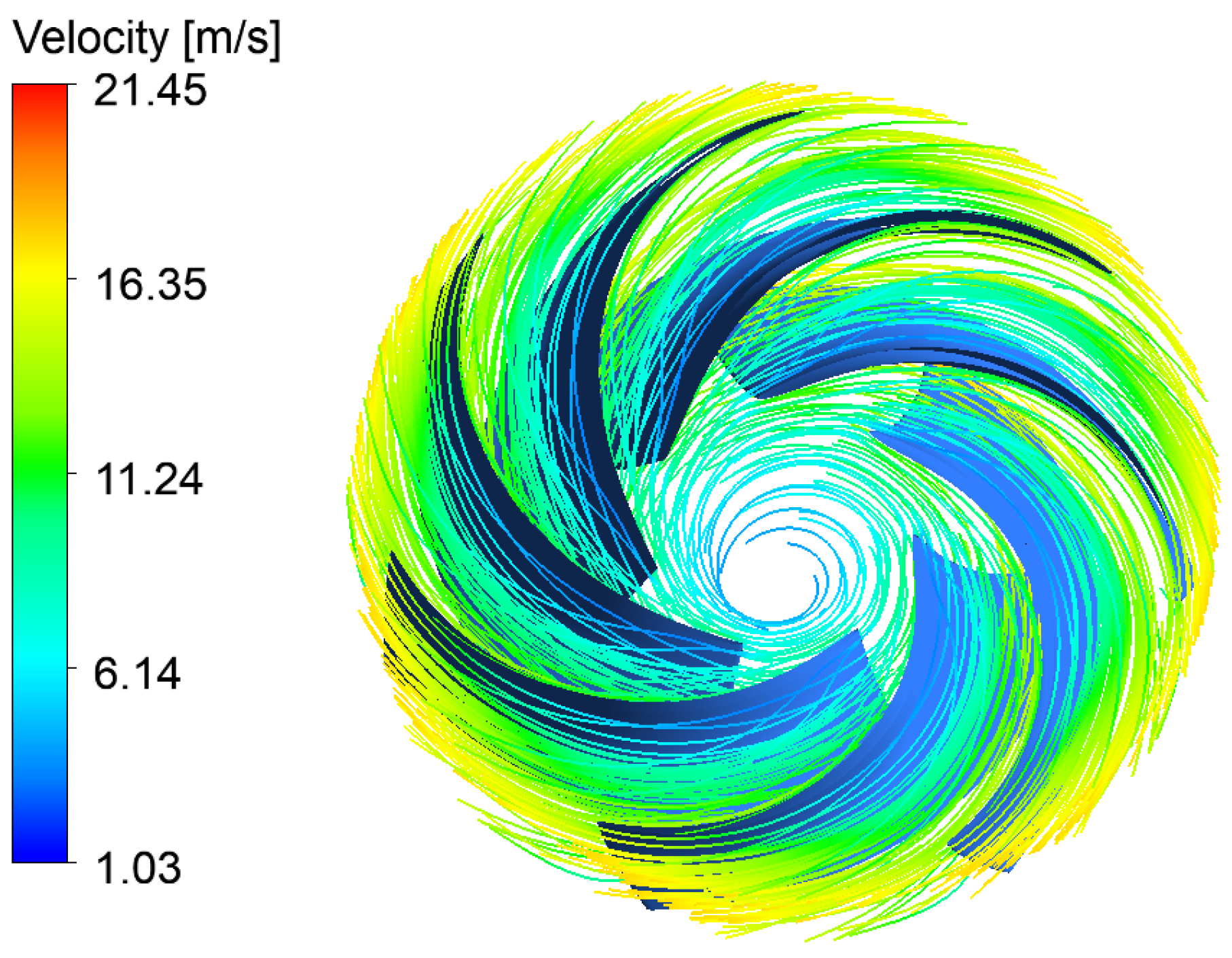



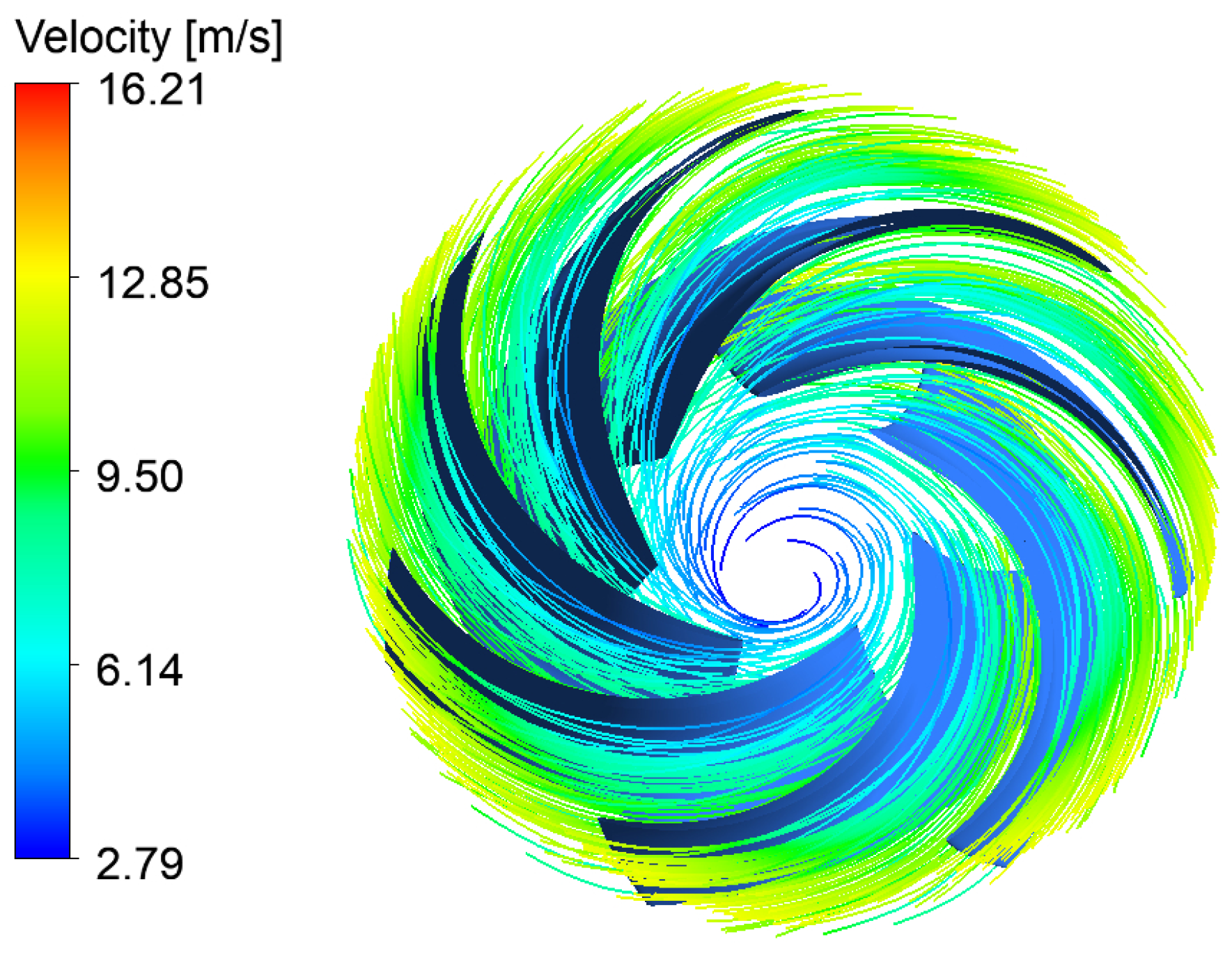

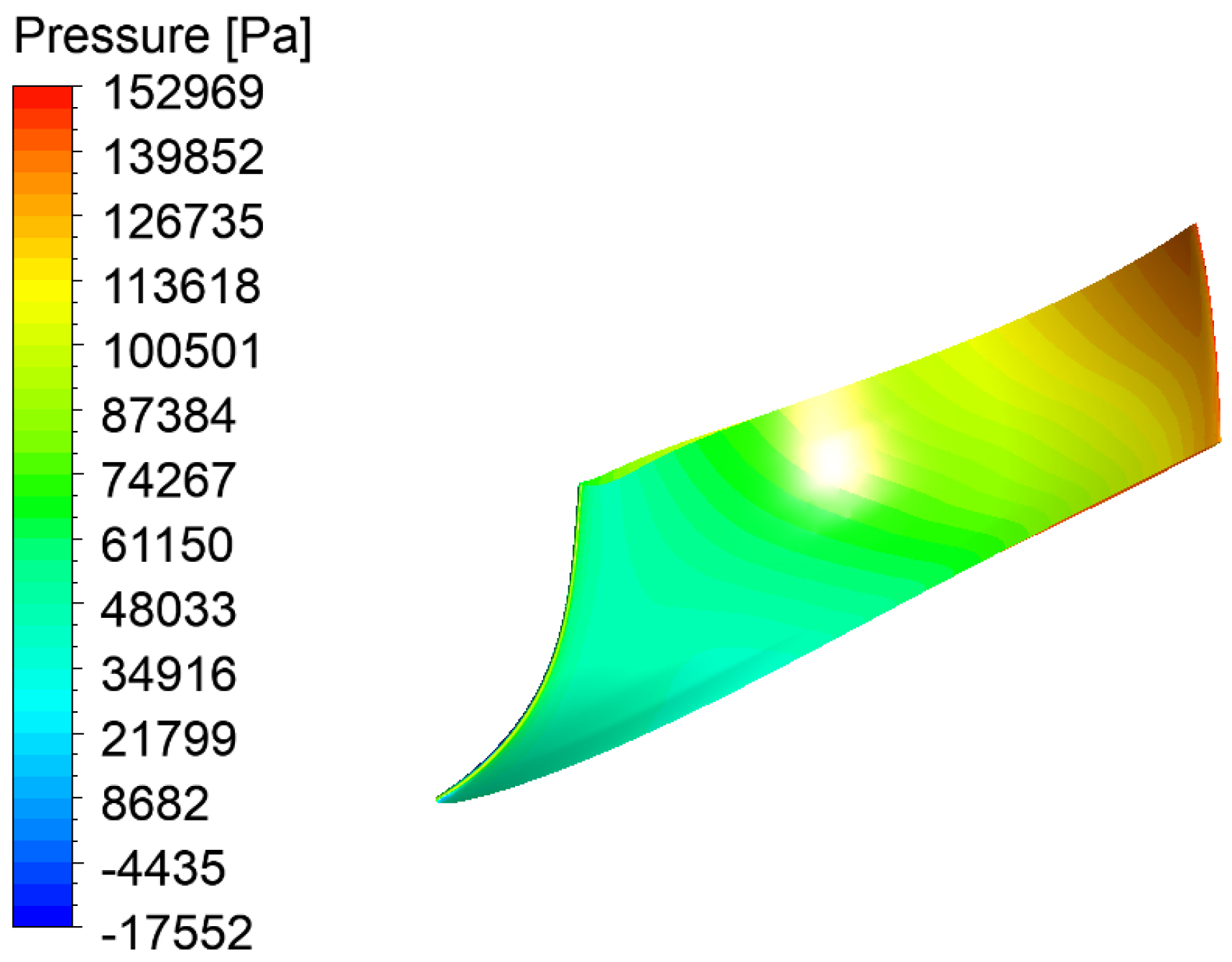

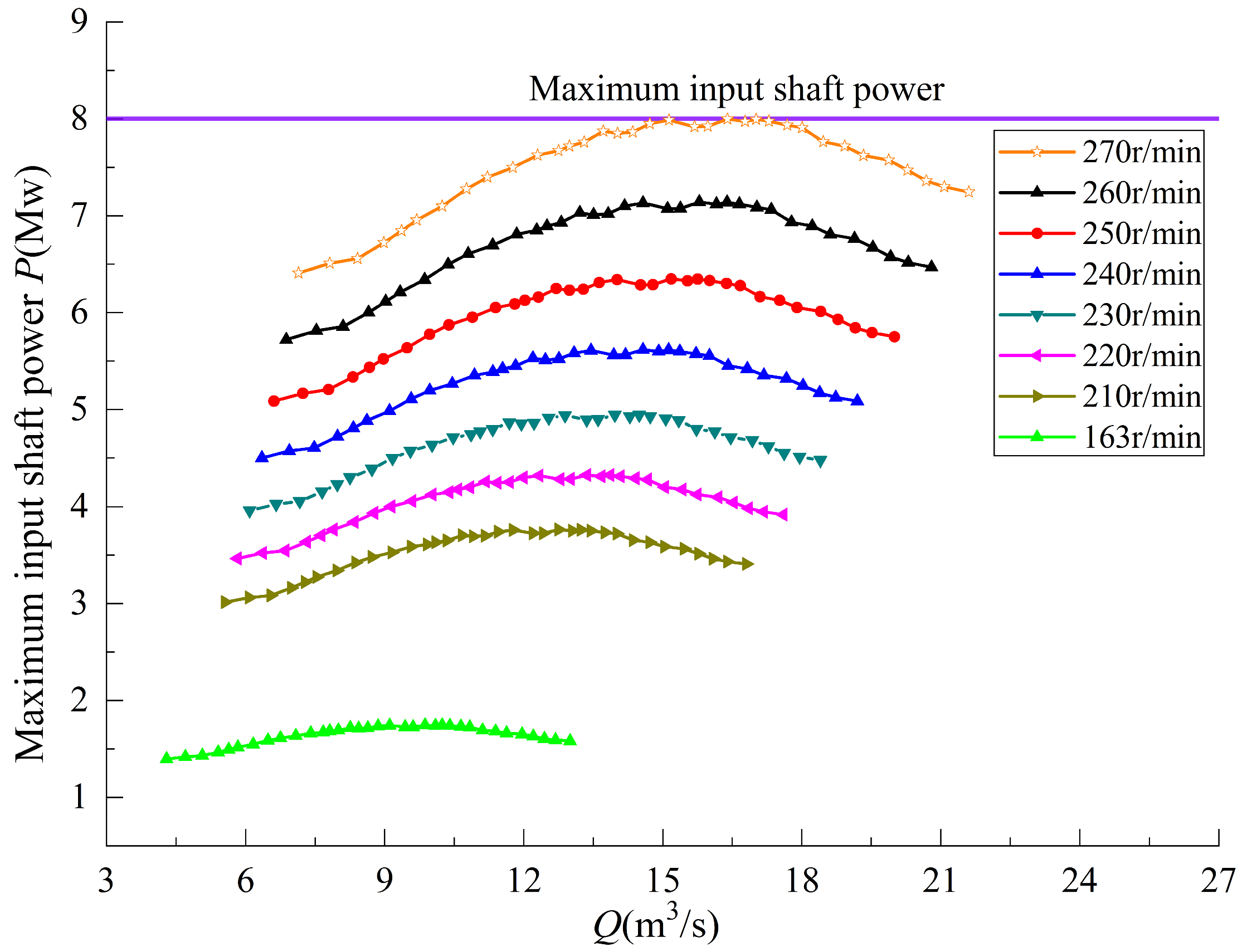

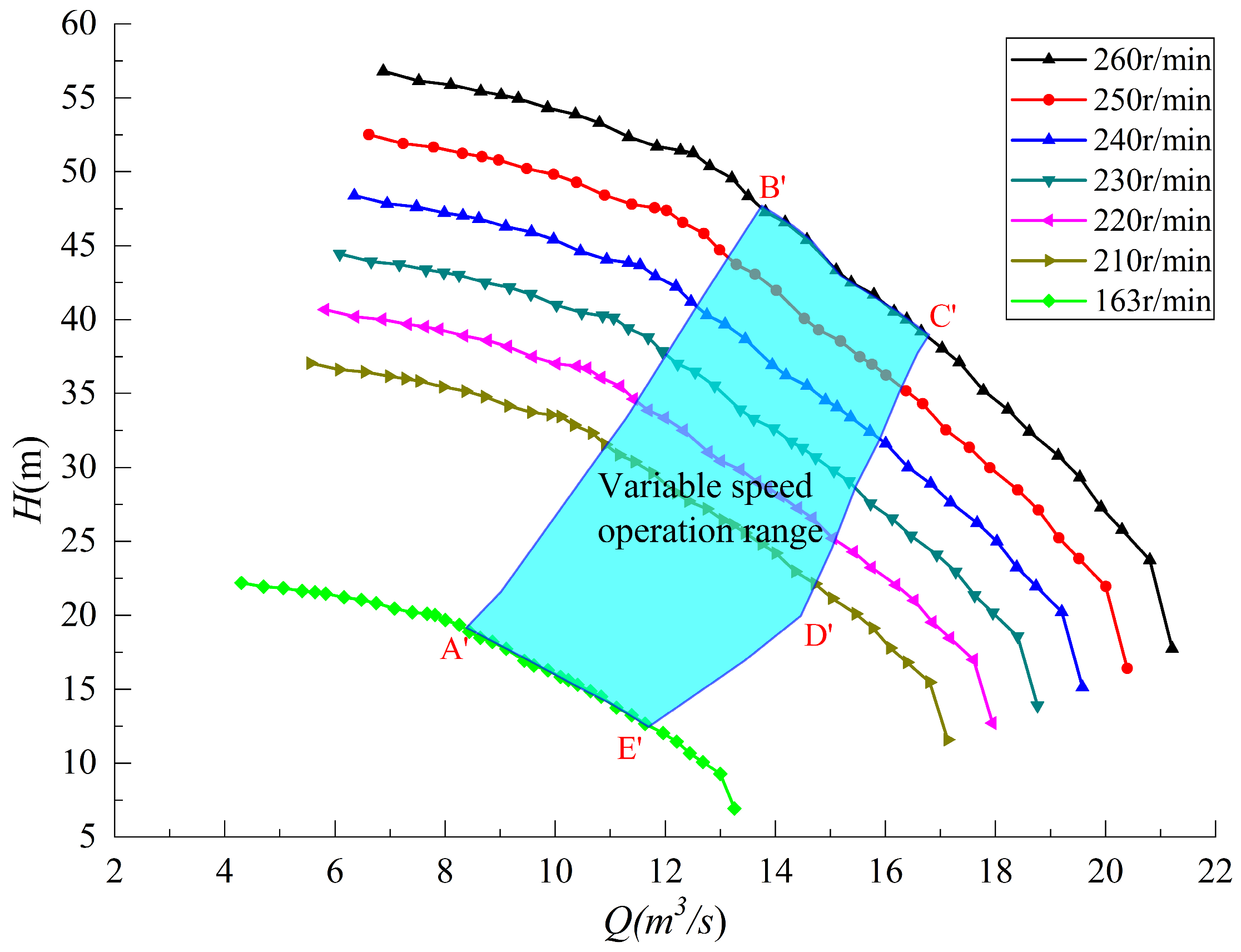

| Physical Quantity | Measure Value | Physical Quantity | Measure Value |
|---|---|---|---|
| Maximum head Hmax (m) | 48 | Design flow, Q (m3/s) | 13.5 |
| Design head Hr (m) | 42.2 | Rated speed, n (r/min) | 250 |
| Minimum head Hmin (m) | 16.3 | Head variation ratio | 2.945 |
| Hump margin | ≥2% | Variable speed range | (0.65~1.04)n |
| Physical Quantity | Measure Value | Physical Quantity | Measure Value |
|---|---|---|---|
| Impeller blade number | 7 | High-pressure edge diameter (mm) | 427 |
| Inlet liquid flow angle (°) | 15.1 | Low-pressure edge diameter (mm) | 300 |
| Inlet liquid flow angle (°) | 17.8 | Guide vane high (mm) | 74 |
| Physical Quantity | Measure Value | Physical Quantity | Measure Value |
|---|---|---|---|
| Impeller blade number | 7 | High pressure edge diameter (mm) | 427 |
| Inlet liquid flow Angle (°) | 16.5 | High pressure edge diameter (mm) | 300 |
| Inlet liquid flow Angle (°) | 18.7 | Guide vane high (mm) | 68 |
| Condition Point | Rated Speed n (r/min) | Mass Flow Q (m3/s) | Head H (m) |
|---|---|---|---|
| T1 Prototype (Hmax) | 250 | 11.48 | 48.48 |
| T1 Model (Hmax) | 1200 | 0.29 | 33.79 |
| T2 Prototype (Hr) | 250 | 13.86 | 42.47 |
| T2 Model (Hr) | 1200 | 0.35 | 29.60 |
| T3 Prototype (Hmin) | 162.5 | 10.29 | 16.6 |
| T3 Model (Hmin) | 780 | 0.26 | 11.57 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Zheng, Y.; Meng, L.; Zhang, G.; Xue, P.; Wang, X.; Zhang, C.; Tian, Y. Study on Impeller Optimization and Operation Method of Variable Speed Centrifugal Pump with Large Flow and Wide Head Variation. Water 2024, 16, 812. https://doi.org/10.3390/w16060812
Zheng Y, Meng L, Zhang G, Xue P, Wang X, Zhang C, Tian Y. Study on Impeller Optimization and Operation Method of Variable Speed Centrifugal Pump with Large Flow and Wide Head Variation. Water. 2024; 16(6):812. https://doi.org/10.3390/w16060812
Chicago/Turabian StyleZheng, Yang, Long Meng, Guang Zhang, Peng Xue, Xin Wang, Chiye Zhang, and Yajuan Tian. 2024. "Study on Impeller Optimization and Operation Method of Variable Speed Centrifugal Pump with Large Flow and Wide Head Variation" Water 16, no. 6: 812. https://doi.org/10.3390/w16060812
APA StyleZheng, Y., Meng, L., Zhang, G., Xue, P., Wang, X., Zhang, C., & Tian, Y. (2024). Study on Impeller Optimization and Operation Method of Variable Speed Centrifugal Pump with Large Flow and Wide Head Variation. Water, 16(6), 812. https://doi.org/10.3390/w16060812






