Spatio-Temporal Characteristics of Land Subsidence and Driving Factors Analysis in Shenzhen
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Study Area
3. Material and Methods
3.1. Datasets
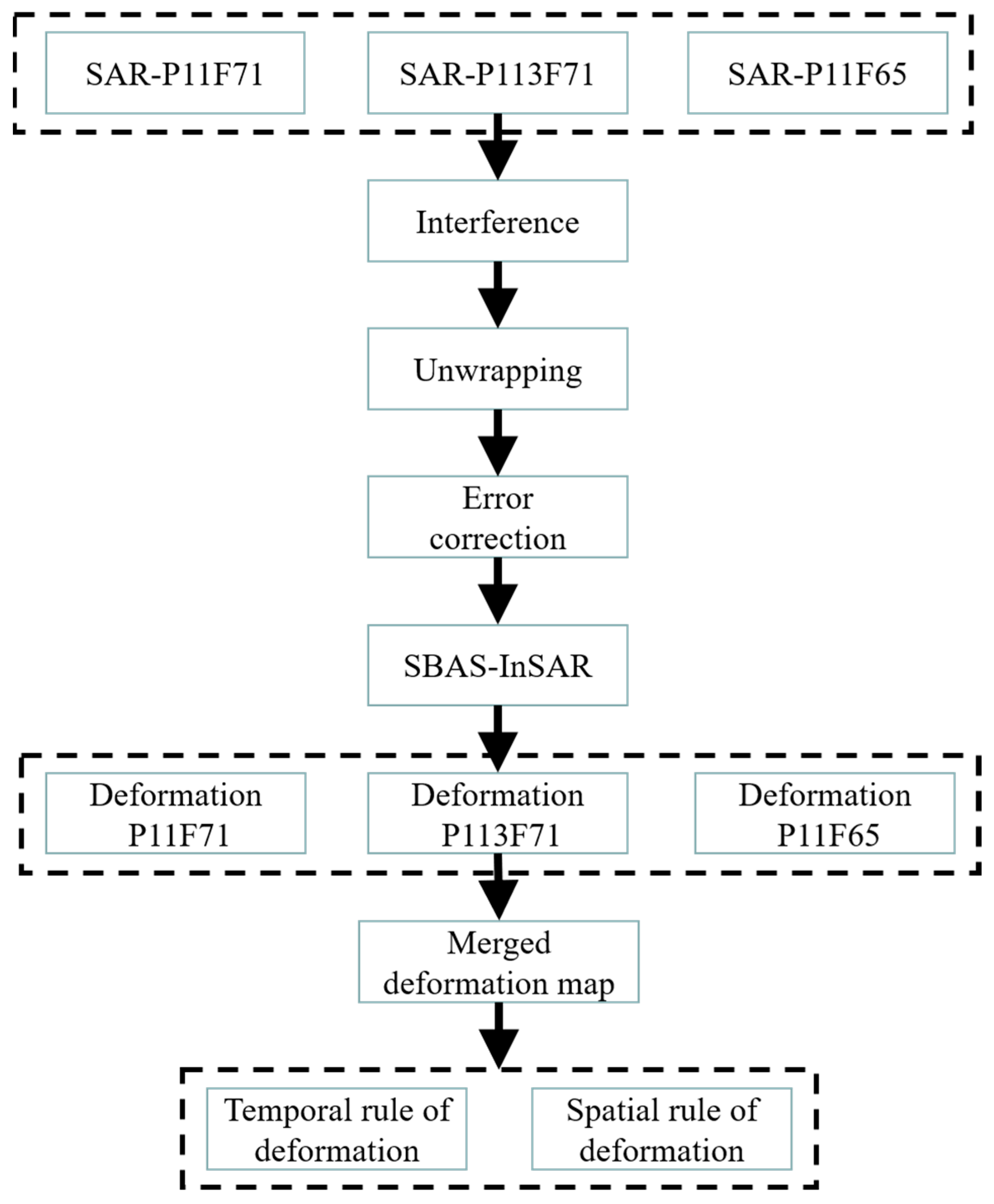
3.2. MT-InSAR
3.3. The Merging of Subsidence Rate Maps
4. Results
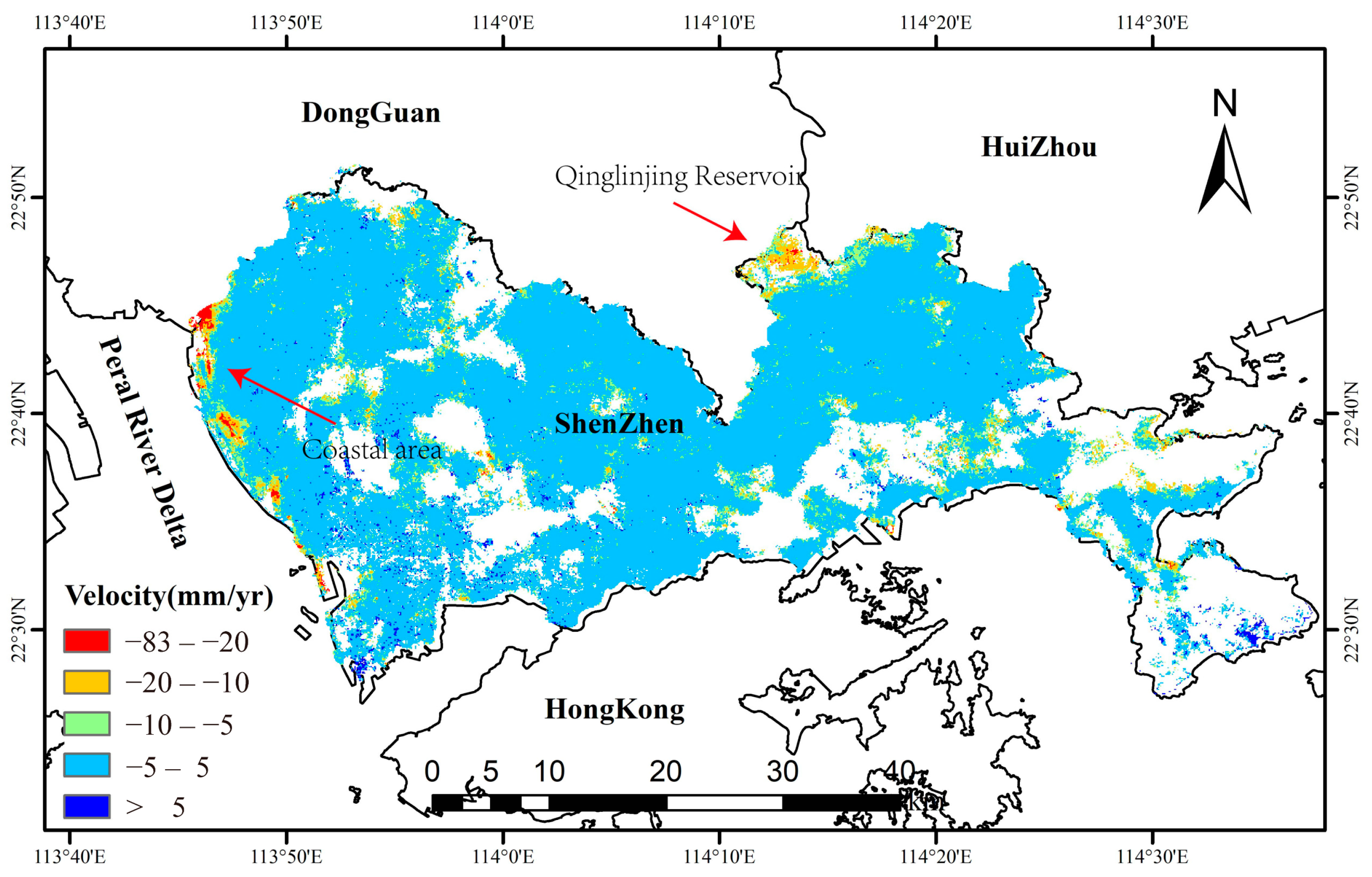
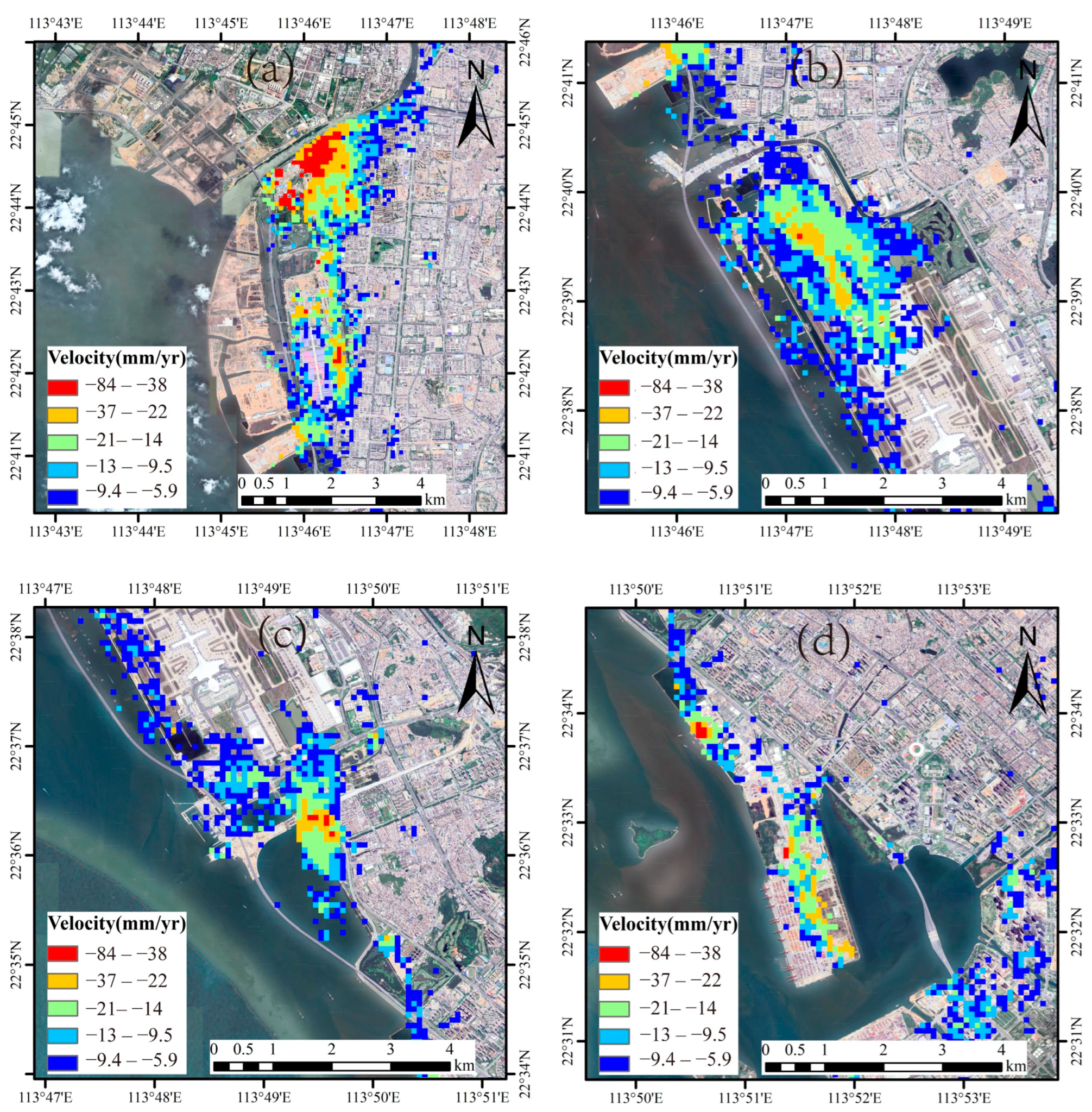
4.1. Land Subsidence Rate Map
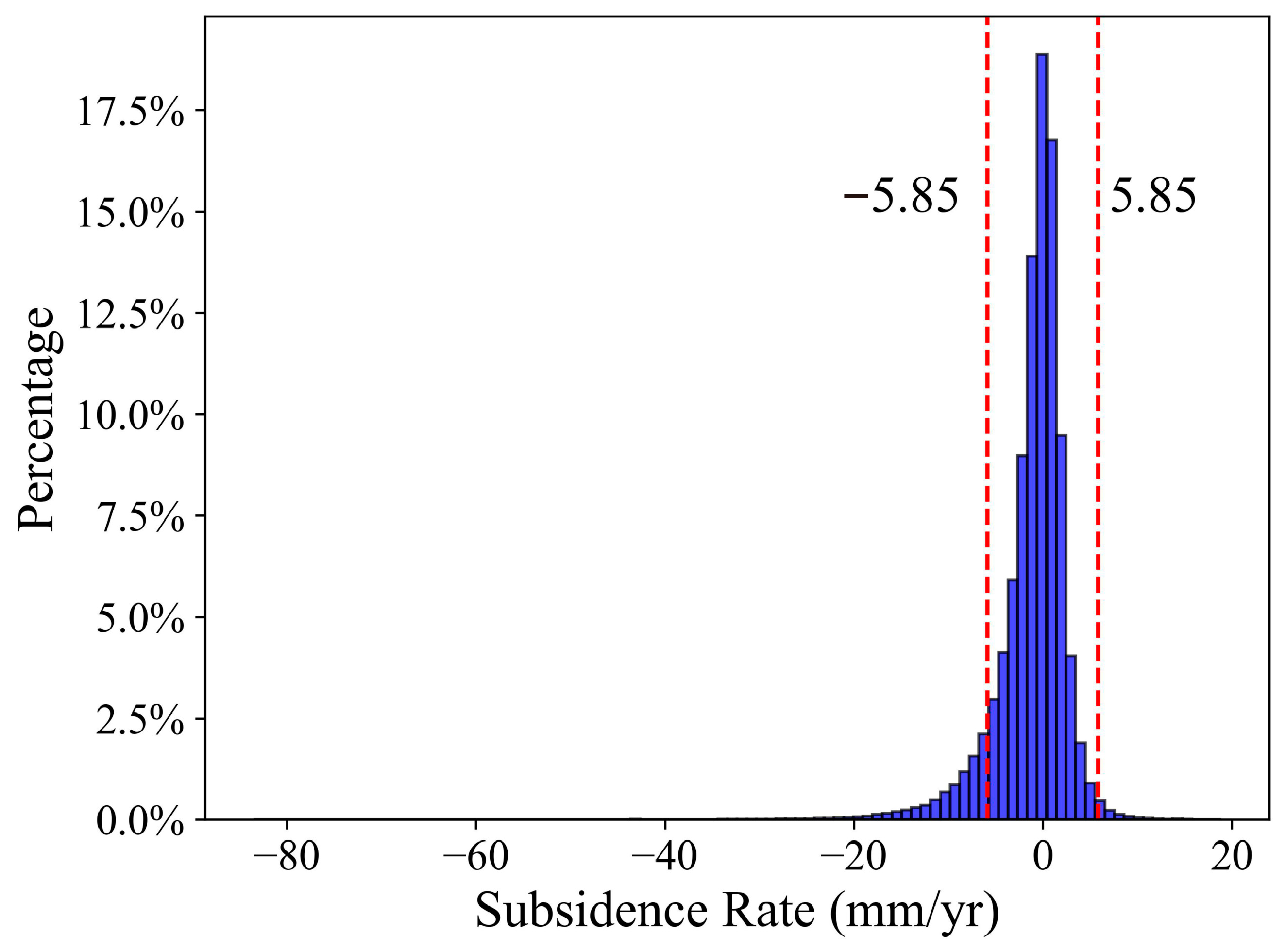
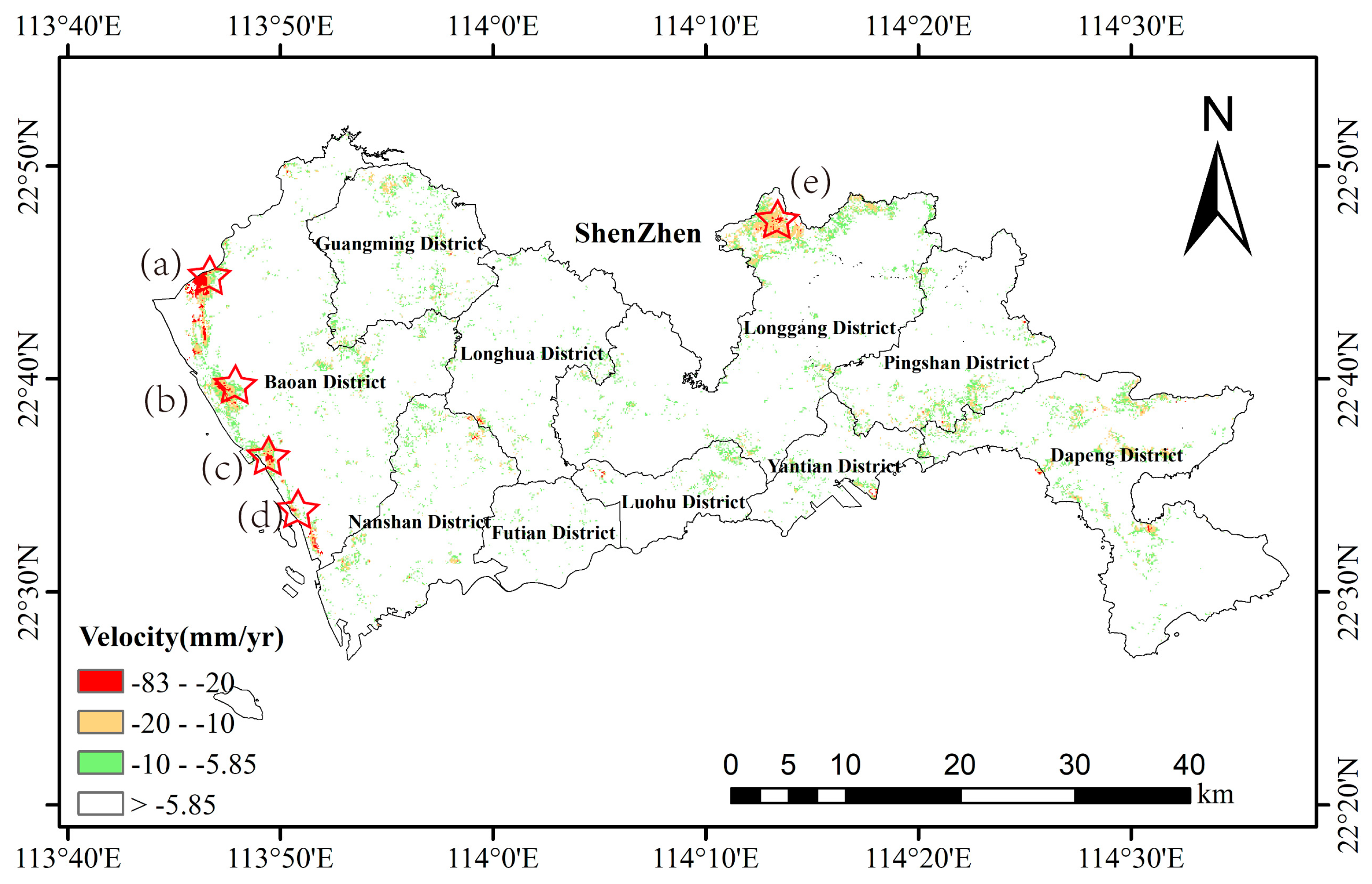
4.2. Reliable Subsidence Regions
5. Discussion
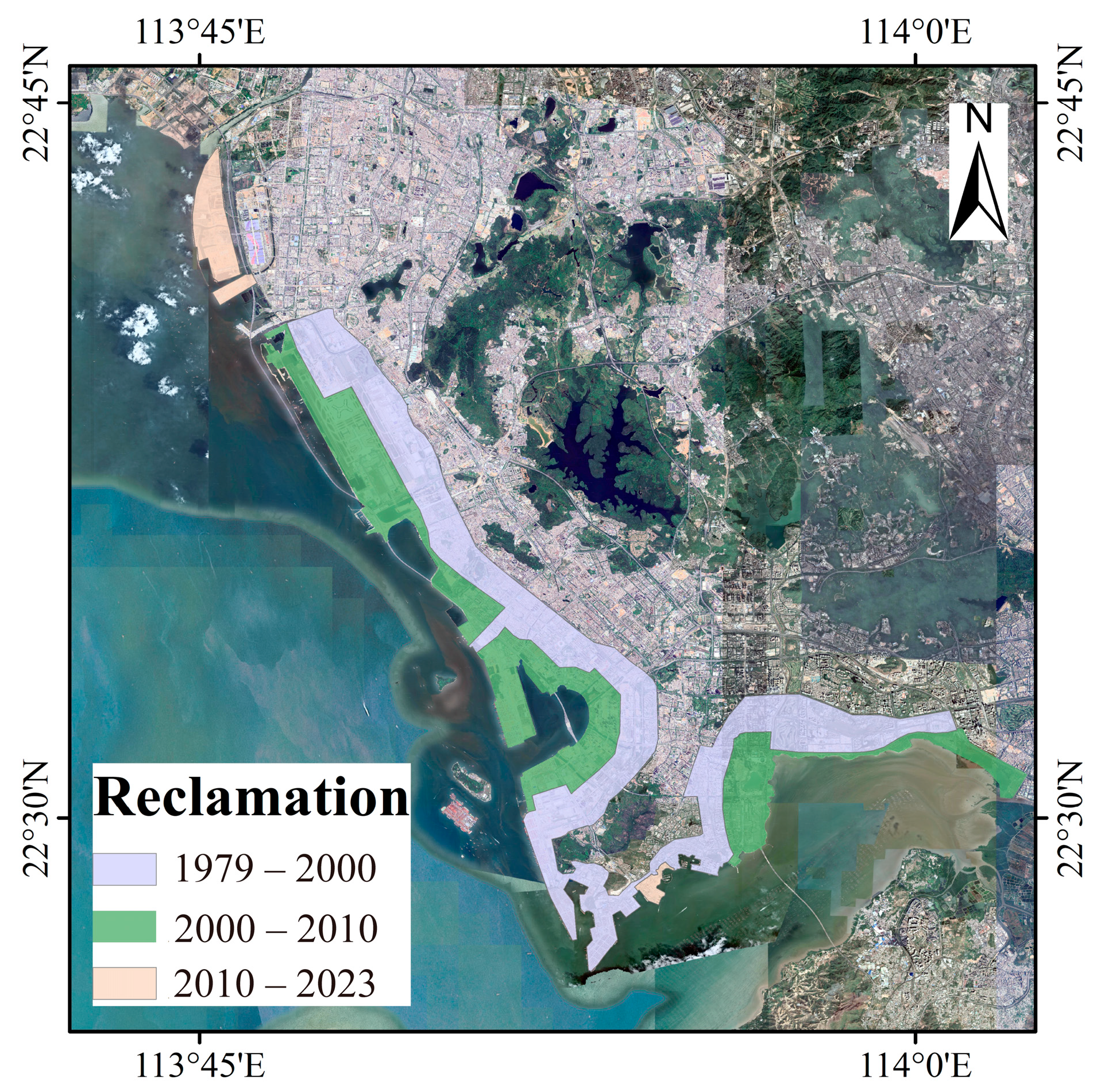
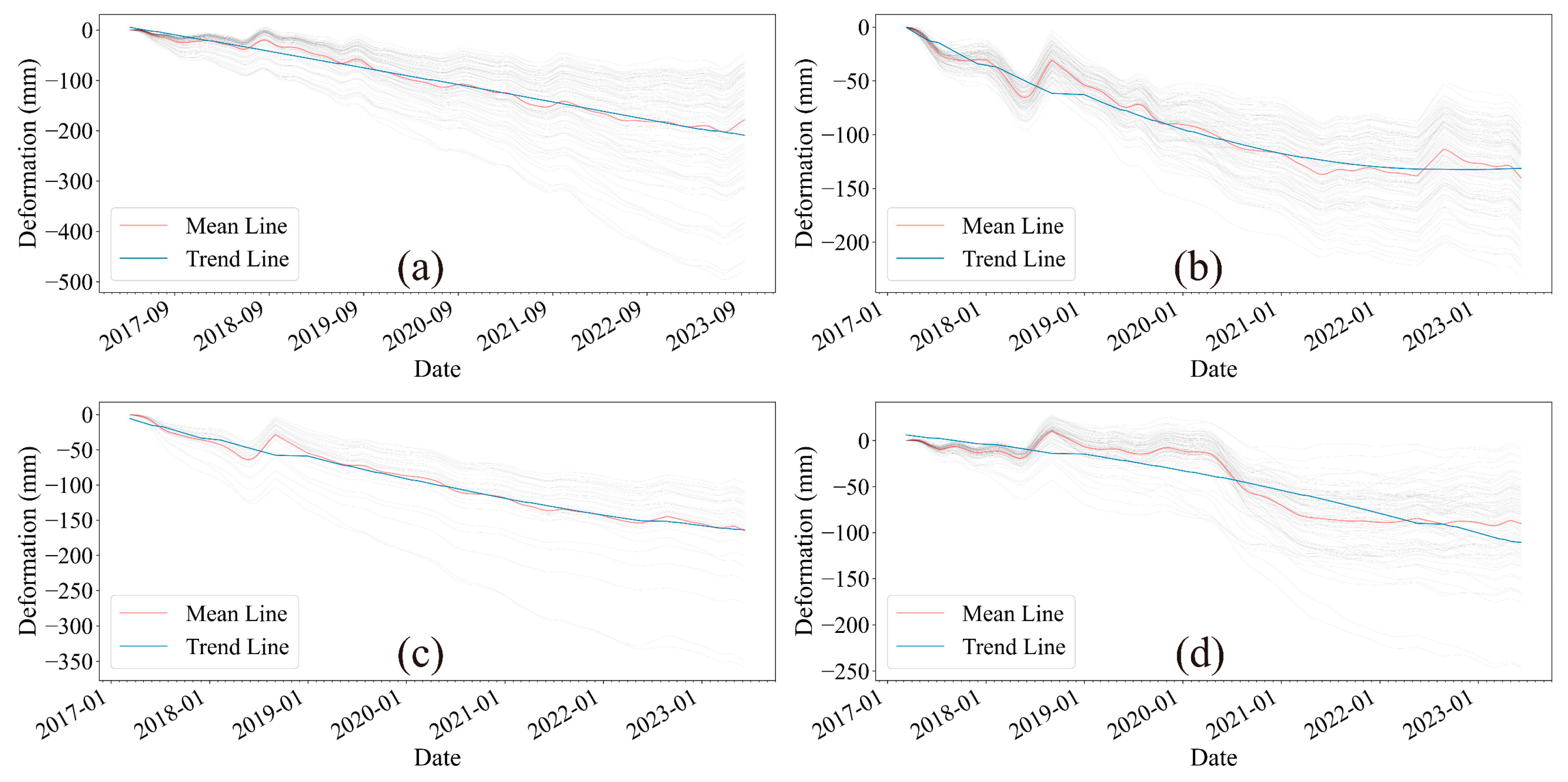
5.1. Land Subsidence in Reclamation Areas and Its Causal Analysis
5.2. Construction-Related Subsidence
5.3. Land Subsidence and Factor Analysis of Qinglinjing Reservoir
5.4. Destructive Impacts of Land Subsidence and Countermeasures
5.5. Limitation of This Study
6. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Kulp, S.A.; Strauss, B.H. New elevation data triple estimates of global vulnerability to sea-level rise and coastal flooding. Nat. Commun. 2019, 10, 4844. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cazenave, A.; Cozannet, G.L. Sea level rise and its coastal impacts. Earth’s Future 2014, 2, 15–34. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Williams, S.J. Sea-Level Rise Implications for Coastal Regions. J. Coast. Res. 2013, 63, 184–196. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Allison, M.; Yuill, B.; Törnqvist, T.; Amelung, F.; Dixon, T.; Erkens, G.; Stuurman, R.; Jones, C.; Milne, G.; Steckler, M.; et al. Global risks and research priorities for coastal subsidence. Eos Trans. Am. Geophys. Union 2016, 97, 22–27. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chini, M.; Pulvirenti, L.; Pierdicca, N. Analysis and Interpretation of the COSMO-SkyMed Observations of the 2011 Japan Tsunami. IEEE Geosci. Remote Sens. Lett. 2012, 9, 467–471. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nicholls, R.J.; Cazenave, A. Sea-Level Rise and Its Impact on Coastal Zones. Science 2010, 328, 1517–1520. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nicholls, R.J.; Lincke, D.; Hinkel, J.; Brown, S.; Vafeidis, A.T.; Meyssignac, B.; Hanson, S.E.; Merkens, J.-L.; Fang, J. A global analysis of subsidence, relative sea-level change and coastal flood exposure. Nat. Clim. Chang. 2021, 11, 338–342. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, G.; Li, P.; Li, Z.; Ding, D.; Qiao, L.; Xu, J.; Li, G.; Wang, H. Coastal Dam Inundation Assessment for the Yellow River Delta: Measurements, Analysis and Scenario. Remote Sens. 2020, 12, 3658. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gracia, V.; Sierra, J.P.; Gómez, M.; Pedrol, M.; Sampé, S.; García-León, M.; Gironella, X. Assessing the impact of sea level rise on port operability using LiDAR-derived digital elevation models. Remote Sens. Environ. 2019, 232, 111318. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gebremichael, E.; Sultan, M.; Becker, R.; El Bastawesy, M.; Cherif, O.; Emil, M. Assessing Land Deformation and Sea Encroachment in the Nile Delta: A Radar Interferometric and Inundation Modeling Approach. J. Geophys. Res. Solid Earth 2018, 123, 3208–3224. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Syvitski, J.P.M.; Kettner, A.J.; Overeem, I.; Hutton, E.W.H.; Hannon, M.T.; Brakenridge, G.R.; Day, J.; Vorosmarty, C.; Saito, Y.; Giosan, L.; et al. Sinking Deltas due to Human Activities. Nat. Geosci. 2009, 2, 681–686. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shirzaei, M.; Bürgmann, R. Global climate change and local land subsidence exacerbate inundation risk to the San Francisco Bay Area. Sci. Adv. 2018, 4, eaap9234. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yin, J.; Zhao, Q.; Yu, D.; Lin, N.; Kubanek, J.; Ma, G.; Liu, M.; Pepe, A. Long-term flood-hazard modeling for coastal areas using InSAR measurements and a hydrodynamic model: The case study of Lingang New City, Shanghai. J Hydrol. 2019, 571, 593–604. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Syvitski, J.; Ángel, J.R.; Saito, Y.; Overeem, I.; Vörösmarty, C.J.; Wang, H.; Olago, D. Earth’s sediment cycle during the Anthropocene. Nat. Rev. Earth Environ. 2022, 3, 179–196. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Herrera-García, G.; Ezquerro, P.; Tomás, R.; Béjar-Pizarro, M.; López-Vinielles, J.; Rossi, M.; Mateos, R.M.; Carreón-Freyre, D.; Lambert, J.; Teatini, P.; et al. Mapping the global threat of land subsidence. Science 2021, 371, 34–36. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, P.; Wang, G.; Liang, C.; Wang, H.; Li, Z. InSAR-derived Coastal Subsidence Reveals New Inundation Scenarios over the Yellow River Delta. IEEE J. Sel. Top. Appl. Earth Obs. Remote Sens. 2023, 16, 8431–8441. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hallegatte, S.; Green, C.; Nicholls, R.J.; Corfee-Morlot, J. Future flood losses in major coastal cities. Nat. Clim. Chang. 2013, 3, 802–806. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, B.; Chu, Z.; Shen, F.; Tang, W.; Wang, B.; Wang, X. Land subsidence (2004–2013) in Changzhou in Central Yangtze River delta revealed by MT-InSAR. Nat. Hazards 2019, 97, 379–394. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, G.; Li, P.; Li, Z.; Liang, C.; Wang, H. Coastal subsidence detection and characterization caused by brine mining over the Yellow River Delta using time series InSAR and PCA. Int. J. Appl. Earth Obs. Geoinf. 2022, 114, 103077. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, G.; Li, P.; Li, Z.; Liu, J.; Zhang, Y.; Wang, H. InSAR and machine learning reveal new understanding of coastal subsidence risk in the Yellow River Delta, China. Sci. Total Environ. 2024, 915, 170203. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Y.; Liu, J.; Xia, X.; Bi, H.; Huang, H.; Ding, R.; Zhao, L. Land subsidence of the Yellow River Delta in China driven by river sediment compaction. Sci. Total Environ. 2021, 750, 142165. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, H.; Wright, T.J.; Yu, Y.; Lin, H.; Jiang, L.; Li, C.; Qiu, G. InSAR reveals coastal subsidence in the Pearl River Delta, China. Geophys. J. Int. 2012, 191, 1119–1128. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qiang, Y.J.; Zhang, L.M.; He, J.; Xiao, T.; Huang, H.H.; Wang, H.J. Urban flood analysis for Pearl River Delta cities using an equivalent drainage method upon combined rainfall-high tide-storm surge events. J. Hydrol. 2021, 597, 126293. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Su, G.; Wu, Y.; Zhan, W.; Zheng, Z.; Chang, L.; Wang, J. Spatiotemporal evolution characteristics of land subsidence caused by groundwater depletion in the North China plain during the past six decades. J. Hydrol. 2021, 600, 126678. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, M.; Ge, D.; Zhang, L.; Guo, X.; Liu, B.; Wang, Y.; Wu, Q. Assessment of the temporal–spatial evolution of subsidence and its driving mechanism in the Beijing Plain (China) by using SAR interferometry and geological data. Geomat. Nat. Hazards Risk 2021, 12, 2708–2735. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, B.; Feng, G.; Li, Z.; Wang, Q.; Wang, C.; Xie, R. Coastal Subsidence Monitoring Associated with Land Reclamation Using the Point Target Based SBAS-InSAR Method: A Case Study of Shenzhen, China. Remote Sens. 2016, 8, 652. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Du, Y.; Feng, G.; Li, Z.; Peng, X.; Zhu, J.; Ren, Z. Effects of External Digital Elevation Model Inaccuracy on StaMPS-PS Processing: A Case Study in Shenzhen, China. Remote Sens. 2017, 9, 1115. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, P.; Chen, X.; Li, Z.; Zhang, Z.; Xu, J.; Feng, W.; Wang, C.; Hu, Z.; Tu, W.; Li, H. Resolving Surface Displacements in Shenzhen of China from Time Series InSAR. Remote Sens. 2018, 10, 1162. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, M.; Du, Y.A.; Liu, Q.Y.; Feng, G.C.; Peng, X.; Liao, C.H. Understanding the Spatial-Temporal Characteristics of Land Subsidence in Shenzhen under Rapid Urbanization Based on MT-InSAR. IEEE J. Sel. Top. Appl. Earth Obs. Remote Sens. 2023, 16, 4153–4166. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, L.; Liu, S.G.; Li, J.H.; Pan, Y.J.; Wang, C.; Huang, L.K.; Huang, L. Investigating Surface Deformation and Its Intrinsic Mechanism in Shenzhen, China Using Sentinel-1A SAR Imagery. Earth Space Sci. 2023, 10, e2023EA002905. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, G.M.; Xia, P.J.; Zhang, Y.Y.; Shi, Q.M.; Jun, L.; Song, P.F.; Tan, Z.W.; Hao, L.; Ze, C. Land Lapse Phenomenon and Surface Subsidence Law of Shield Tunnel Passing through Rock-Bearing Formation. Front. Earth Sci. 2022, 10, 934360. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- He, Y.F.; Xu, G.C.; Kaufmann, H.; Wang, J.T.; Ma, H.; Liu, T. Integration of InSAR and LiDAR Technologies for a Detailed Urban Subsidence and Hazard Assessment in Shenzhen, China. Remote Sens. 2021, 13, 2366. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liang, H.Y.; Zhang, L.; Li, X. Enhancing MTInSAR Phase Unwrapping in Decorrelating Environments by Spatiotemporal Observation Optimization. IEEE Geosci. Remote Sens. Lett. 2023, 20, 4002505. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, W.Q.; Cui, H.T.; Hu, J.; Yao, L.N. Detection and 3D Visualization of Deformations for High-Rise Buildings in Shenzhen, China from High-Resolution TerraSAR-X Datasets. Appl. Sci. 2019, 9, 3818. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ding, J.Z.; Zhao, Q.; Tang, M.C.; Calò, F.; Zamparelli, V.; Falabella, F.; Liu, M.; Pepe, A. On the Characterization and Forecasting of Ground Displacements of Ocean-Reclaimed Lands. Remote Sens. 2020, 12, 2971. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Berardino, P.; Fornaro, G.; Lanari, R.; Sansosti, E. A new algorithm for surface deformation monitoring based on small baseline differential SAR interferograms. IEEE Trans. Geosci. Remote Sens. 2002, 40, 2375–2383. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ge, D.Q.; Zhang, L.; Wang, Y.; Guo, X.F.; Xia, Y. Merging Multi-Track Psi Result for Land Subsidence Mapping over Very Extended Area. In Proceedings of the 2010 IEEE International Geoscience and Remote Sensing Symposium, Honolulu, HI, USA, 25–30 July 2010; pp. 3522–3525. [Google Scholar]
- Fernández-Torres, E.A.; Cabral-Cano, E.; Solano-Rojas, D.; Salazar-Tlaczani, L.; Gárcia-Venegas, J.; Marquez-Azúa, B.; Graham, S.; Villarnobo-Gonzalez, K.M. Country-scale assessment of urban areas, population, and households exposed to land subsidence using Sentinel-1 InSAR, and GPS time series. Nat. Hazards 2024, 120, 1577–1601. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tomás, R.; Pagán, J.I.; Navarro, J.A.; Cano, M.; Pastor, J.L.; Riquelme, A.; Cuevas-González, M.; Crosetto, M.; Barra, A.; Monserrat, O.; et al. Semi-Automatic Identification and Pre-Screening of Geological–Geotechnical Deformational Processes Using Persistent Scatterer Interferometry Datasets. Remote Sens. 2019, 11, 1675. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, L.; Shi, X.; Ren, C.; Huang, Y.; Zhu, Z. Monitoring and Analysis of Land Subsidence in Shenzhen reclamation area Based on Sentinel-1A Interferometric Synthetic Aperture Radar. Sci. Technol. Eng. 2021, 21, 8765–8769. [Google Scholar]
- Li, D.; Li, B.; Zhang, Y.; Fan, C.; Xu, H.; Hou, X. Spatial and temporal characteristics analysis for land subsidence in Shanghai coastal reclamation area using PS-InSAR method. Front. Mar. Sci. 2022, 9, 1000523. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, Y.-S.; Wu, H.-N.; Wang, B.Z.-F.; Yang, T.-L. Dewatering induced subsidence during excavation in a Shanghai soft deposit. Environ. Earth Sci. 2017, 76, 351. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chang, T.G.; Li, B.H.; Zeng, X.X. Prediction and verification of earthquakes induced by the Xiluodu hydropower station reservoir. Earthq. Sci. 2022, 35, 387–397. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, L.F.; Gahalaut, K.; Liao, W.L.; Zhao, Y.N.; Yao, Y.S.; Li, J.G.; Qin, W.B.; Wei, G.C.; Zhou, Z.Y. Application of spectral analysis to the reservoir-triggered earthquakes in Three Gorges reservoir region, China. Nat. Hazards 2023, 118, 479–494. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, L.; Li, J.; Sun, X.; Liao, W.; Zhao, Y.; Wei, G.; He, C. A Possible Mechanism of Reservoir-Induced Earthquakes in the Three Gorges Reservoir, Central China. Bull. Seismol. Soc. Am. 2018, 108, 3016–3028. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lei, H.F.; Wang, Q.C.; Zhao, C.P.; Zhao, C.; Zhang, J.C.; Li, J. Seismic analysis of the Xiluodu reservoir area and insights into the geometry of seismogenic faults. Earthq. Sci. 2022, 35, 371–386. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]






| Interferometric Processing Coverage | Temporal Analysis Coverage | |
|---|---|---|
| P11F71 | 12 March 2017–13 September 2023 (190) | 20 September 2017–9 June 2023 (169) |
| P113F71 | 27 September 2017–27 August 2023 (184) | 27 September 2017–16 June 2023 (156) |
| P11F65 | 12 March 2017–9 June 2023 (160) | 20 September 2017–9 June 2023 (146) |
| Parameters | P11F71 | P113F71 | P11F65 |
|---|---|---|---|
| Temporal baseline | 12–60 days | 12–84 days | 12–144 days |
| The max perpendicular baseline | 1–321 m | 1–336 m | 1–328 m |
| Unwrapping coherence threshold | 0.4 | 0.4 | 0.4 |
| Multi-looking | 20 × 5 | 20 × 5 | 20 × 5 |
| Unwrapping method | MCF | MCF | MCF |
| DEM and resolution | SRTM 30 m with height datum of WGS84 | SRTM 30 m with height datum of WGS84 | SRTM 30 m with height datum of WGS84 |
| Precise orbital data | Yes | Yes | Yes |
| Filter method | Gaussian filter | Gaussian filter | Gaussian filter |
| Number of interferograms | 502 | 477 | 471 |
| Orbital Ramp Remove | YES | YES | YES |
| Atmospheric correction | ERA5 | ERA5 | ERA5 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Wang, S.; Wang, G.; Huang, M.; Song, J.; Yang, X.; Zhang, T.; Ji, W.; Zhang, S.; Wu, W.; Wei, C.; et al. Spatio-Temporal Characteristics of Land Subsidence and Driving Factors Analysis in Shenzhen. Water 2024, 16, 1200. https://doi.org/10.3390/w16091200
Wang S, Wang G, Huang M, Song J, Yang X, Zhang T, Ji W, Zhang S, Wu W, Wei C, et al. Spatio-Temporal Characteristics of Land Subsidence and Driving Factors Analysis in Shenzhen. Water. 2024; 16(9):1200. https://doi.org/10.3390/w16091200
Chicago/Turabian StyleWang, Shuanglong, Guoyang Wang, Min Huang, Jun Song, Xiaoyu Yang, Tingyu Zhang, Wenyu Ji, Shuai Zhang, Weili Wu, Chengwen Wei, and et al. 2024. "Spatio-Temporal Characteristics of Land Subsidence and Driving Factors Analysis in Shenzhen" Water 16, no. 9: 1200. https://doi.org/10.3390/w16091200
APA StyleWang, S., Wang, G., Huang, M., Song, J., Yang, X., Zhang, T., Ji, W., Zhang, S., Wu, W., Wei, C., & Xiao, J. (2024). Spatio-Temporal Characteristics of Land Subsidence and Driving Factors Analysis in Shenzhen. Water, 16(9), 1200. https://doi.org/10.3390/w16091200






