Abstract
This study provides a comprehensive analysis of the groundwater potential of hard rock aquifers in five diverse African case study areas: Lake Tana Basin and Beles Basin in northwestern Ethiopia and Mount Meru in northern Tanzania (comprising volcanic aquifers); the Mekelle area in northern Ethiopia and Jifarah Plain in Libya (consisting of sedimentary aquifers). The evaluation of recharge, transmissivity, and water quality formed the basis of qualitative and quantitative assessment. Multiple methods, including water table fluctuation (WTF), chloride mass balance (CMB), physical hydrological modeling (WetSpass), baseflow separation (BFS), and remote sensing techniques like GRACE satellite data, were employed to estimate groundwater recharge across diverse hydrogeological settings. Topographic contrast, fractured orientation, lineament density, hydro-stratigraphic connections, hydraulic gradient, and distribution of high-flux springs were used to assess IGF from Lake Tana to Beles Basin. The monitoring, sampling, and pumping test sites took into account the high hydromorphological and geological variabilities. Recharge rates varied significantly, with mean values of 315 mm/year in Lake Tana Basin, 193 mm/year in Mount Meru, and as low as 4.3 mm/year in Jifarah Plain. Transmissivity ranged from 0.4 to 6904 m2/day in Lake Tana Basin, up to 790 m2/day in Mount Meru’s fractured lava aquifers, and reached 859 m2/day in the sedimentary aquifers of the Mekelle area. Water quality issues included high TDS levels (up to 3287 mg/L in Mekelle and 11,141 mg/L in Jifarah), elevated fluoride concentrations (>1.5 mg/L) in 90% of Mount Meru samples, and nitrate pollution in shallow aquifers linked to agricultural practice. This study also highlights the phenomenon of inter-basin deep groundwater flow, emphasizing its role in groundwater potential assessment and challenging conventional water balance assumptions. The findings reveal that hard rock aquifers, particularly weathered/fractured basalt aquifers in volcanic regions, exhibit high potential, while pyroclastic aquifers generally demonstrate lower potential. Concerns regarding high fluoride levels are identified in Mount Meru aquifers. Among sedimentary aquifers in the Mekelle area and Jifarah Plain, limestone intercalated with marl or dolomite rock emerges as having high potential. However, high TDS and high sulfate concentrations are quality issues in some of the areas, quite above the WHO’s and each country’s drinking water standards. The inter-basin groundwater flow, investigated in this study of Beles Basin, challenges the conventional water balance assumption that the inflow into a hydrological basin is equivalent to the outflow out of the basin, by emphasizing the importance of considering groundwater influx from neighboring basins. These insights contribute novel perspectives to groundwater balance and potential assessment studies, challenging assumptions about groundwater divides.
1. Introduction
Groundwater plays a critical role in addressing some of Africa’s most pressing challenges, including climate change, population growth, and natural resource degradation [1]. Climate change, with its unpredictable rainfall patterns and increasing frequency of droughts, exacerbates water scarcity across the continent [2]. At the same time, Africa’s rapidly growing population places increasing pressure on both surface and groundwater resources, leading to overextraction and degradation of aquifers [3]. According to Gaye and Tindimugaya [3], managing groundwater in Africa is essential, as more than 50% of the population depends on it for drinking water and agriculture. Furthermore, the degradation of natural resources, including groundwater, through overexploitation, pollution, and unsustainable agricultural practices, further diminishes water availability [4]. Consequently, understanding the quantity and quality of groundwater is essential for its sustainable management, especially given projected increases in demand and potential climate-induced shifts [5]. Groundwater potential assessment fosters awareness among decision makers, guiding effective use, management, and protection without compromising future demand [6]. According to Kebede [7], groundwater potential is assessed by (1) recharge rate and mechanism, (2) aquifer storage and transmission properties, (3) water quality suitability, and (4) the response of the aquifer to changes such as climate, seasonality, and exploitation. As the amount of recharge water and transmissivity directly determines the amount of groundwater in an aquifer, water quality, particularly total dissolved solids (TDS), is a key aspect of groundwater sustainability. High TDS levels often indicate poor water quality as they result from dissolved salts and minerals. Elevated TDS values can impair water’s suitability for consumption and irrigation, with high concentrations of ions such as calcium, sulfate, and fluoride being of particular concern [5].
As stated by Macdonald and Davies [4], groundwater distribution across Africa is primarily associated with four distinct aquifer systems: Precambrian basement rocks, volcanic rocks, unconsolidated sediments, and consolidated sedimentary rocks. In basement rocks, groundwater typically resides within the uppermost layers of weathered rock. Within volcanic rocks, groundwater is found in highly permeable zones between lava flows. Consolidated sedimentary rocks contain groundwater within pore spaces of sandstones or fractures and weathered zones within limestones. Unconsolidated sediments are widespread throughout Africa, contributing to groundwater resources across the continent. Limited observational data are the source of considerable uncertainty in the knowledge of freshwater availability and withdrawals in the African continent [8]. Despite the literature highlighting that there is a high potential for groundwater resource development, there remains a lack of quantitative understanding regarding its potential [3]. In particular, the exploration of groundwater in hard rock terrains is a complex task [9] due to the high heterogeneity of aquifer characteristics.
In this study, groundwater potential in the hard rocks of volcanic and sedimentary aquifers of Africa has been assessed by considering five case study areas: Lake Tana Basin and Beles Basin, both in northwest Ethiopia, and the Mekelle area in northern Ethiopia; Mount Meru in northern Tanzania and Jifarah Plain in northwest Libya. The case studies represent different geological settings and climatological characteristics.
The objectives of this study are (1) to quantitatively assess the groundwater potential of volcanic and sedimentary hard rock aquifers across five case study areas by evaluating aquifer transmissivity, groundwater recharge, and water quality criteria; (2) to explore the role of inter-basin groundwater flow as an evaluation parameter in assessing groundwater potential, as demonstrated in the Beles Basin case study. In this paper, the fourth criterion of Kebede [7], which includes the external stress factors, is not considered as an independent potential assessment criteria. This paper presents a synthesis of existing studies alongside primary data analyses results from the case study areas. Due to the extensive diversity in climatology, geology, and hydrogeology across Africa, these selected study areas may not entirely encapsulate the continent’s groundwater potential on a larger scale. However, given that these study areas are found in different geoenvironmental and climatological settings of the continent, they offer insights into the potential of Africa’s different main volcanic and sedimentary aquifers.
2. Location, Geology, and Hydrogeology
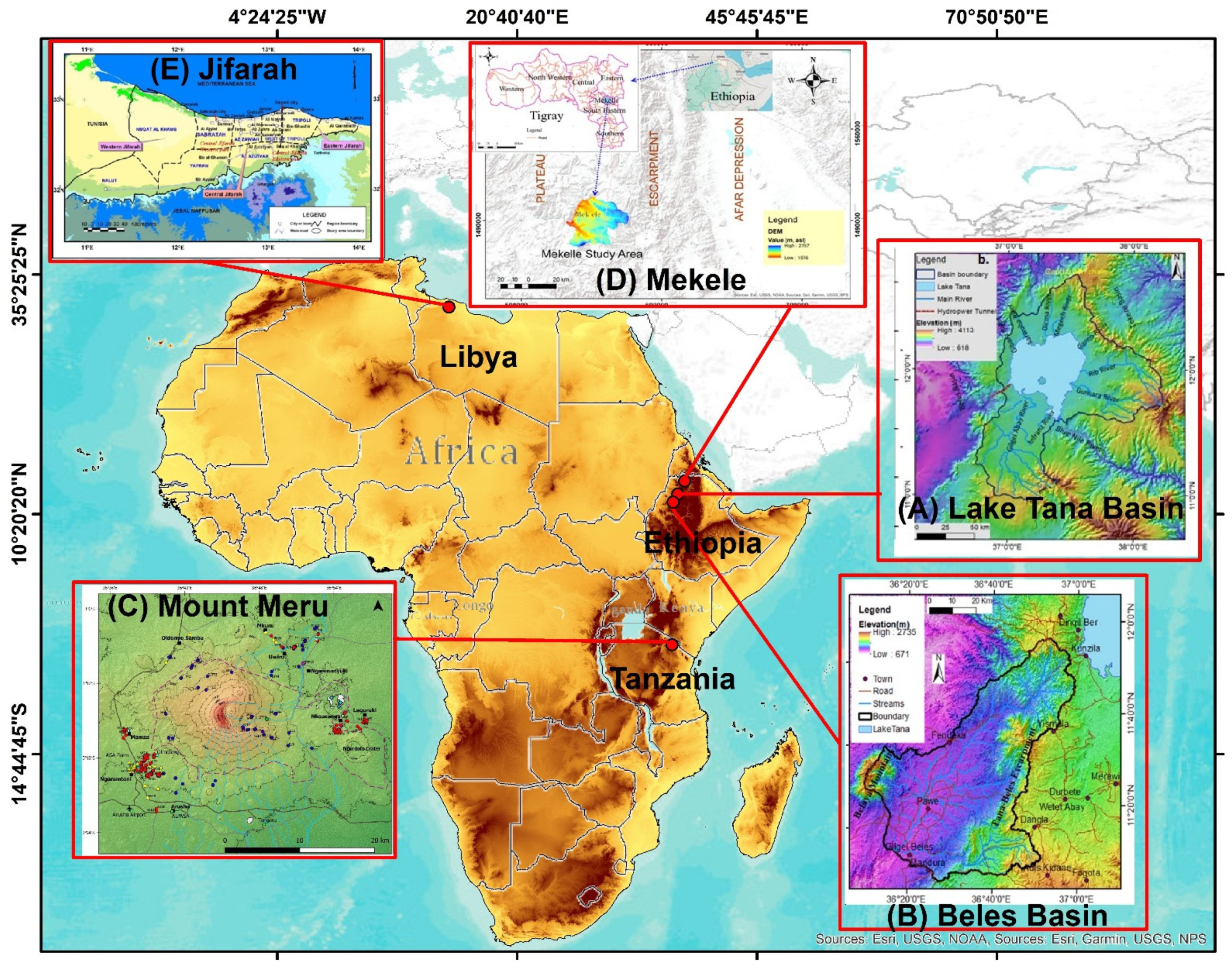
In this study, five case study areas are included (Figure 1), representing hard rock aquifers in volcanic, sedimentary, and, to some extent, metamorphic rocks. Lake Tana Basin (Figure 1A) and Beles Basin (Figure 1B), located in northwest Ethiopia, and Mount Meru (Figure 1C), located in northern Tanzania, represent volcanic rock aquifers, whereas the Mekelle area (Figure 1D) in northern Ethiopia and Jifarah Plain (Figure 1E), northwest Libya, represent sedimentary rock aquifers. The lower part of Beles Basin also contains metamorphic rocks.
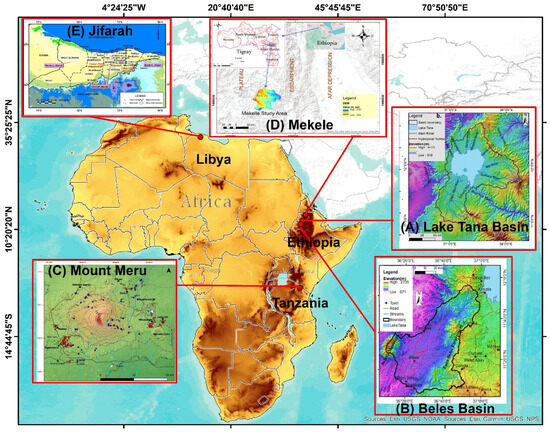
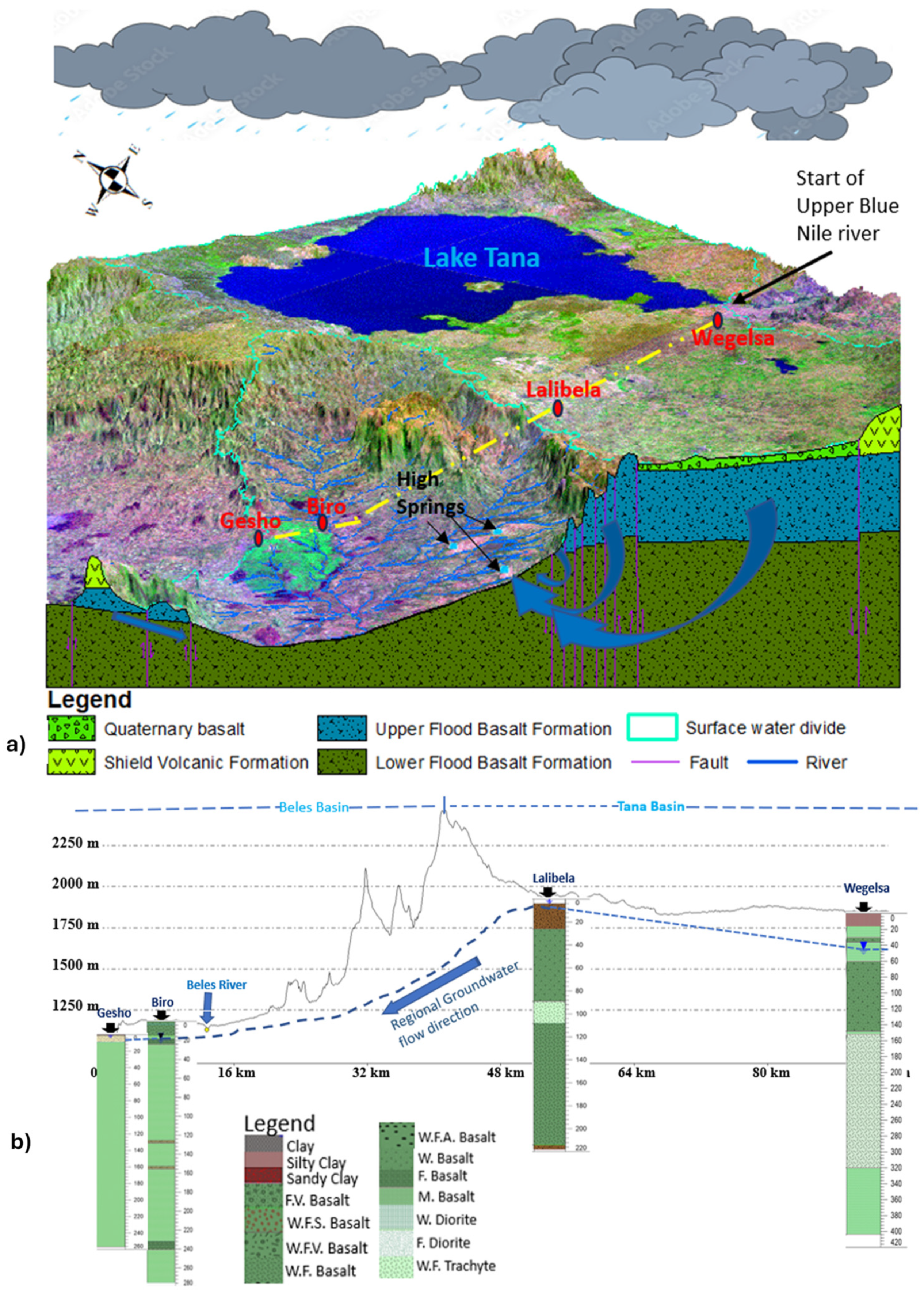
Figure 1.
Location map of the five case study areas: (A) Lake Tana Basin; (B) Beles Basin; (C) Mount Meru; (D) Mekelle Basin; (E) Jifarah Plain.
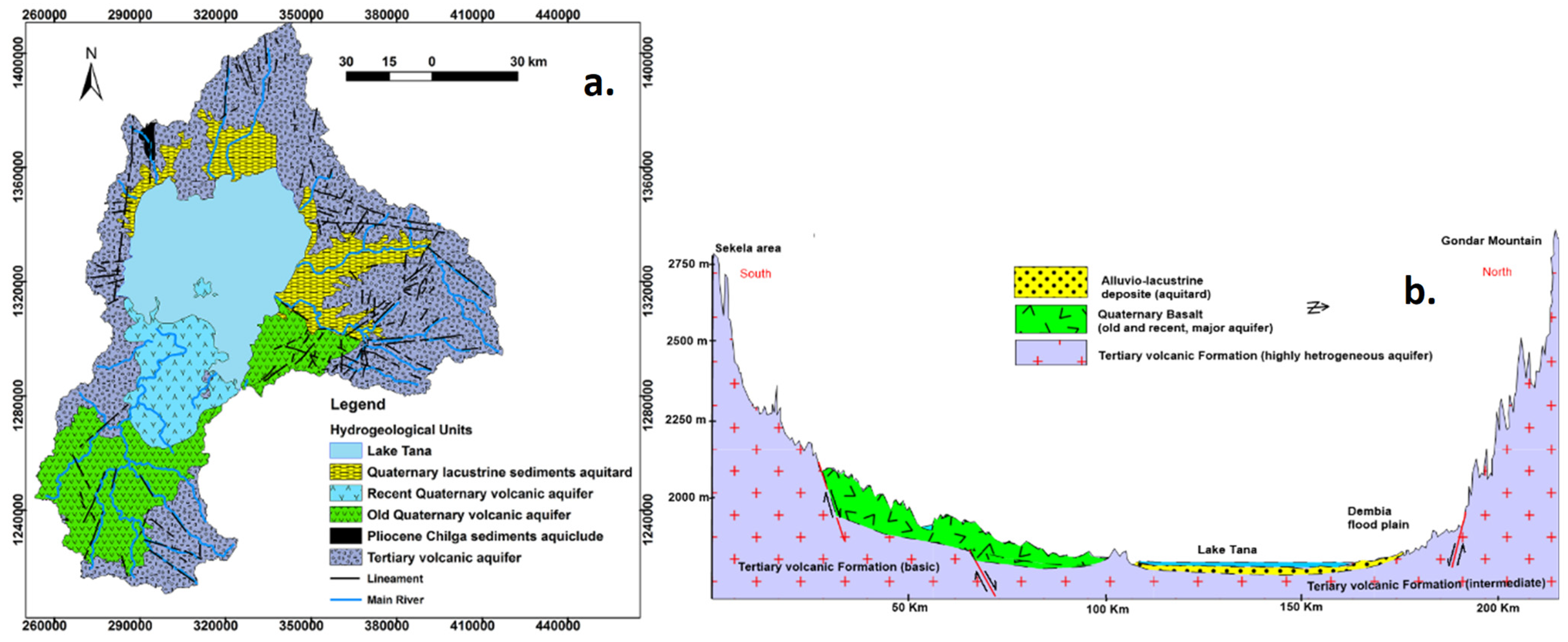
Lake Tana Basin, with a drainage area of approximately 15,077 km2, serves as the source of the Upper Blue Nile Basin. This basin consists of Lake Tana (Figure 1A), the largest lake in Ethiopia covering 3069 km2, and is fed by around 40 rivers from various directions. It is renowned as one of the country’s agricultural growth corridors. The geology of Lake Tana Basin is characterized by Tertiary flood basalt, shield volcanoes, Quaternary volcanic flows, and alluvial–lacustrine deposits, as illustrated in Figure 2a (e.g., [10,11]). The basin is considered as an uplifted dome, potentially associated with the Afar mantle plume [12]. It is believed to be formed by the confluence of three grabens [13,14] through rifting [15]. This geologic unit consists of highly variable volcanic flows and pyroclastic deposits.
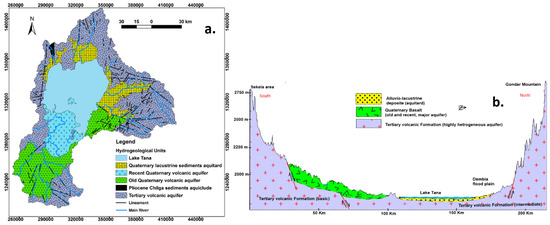
Figure 2.
(a) Hydrogeological map of Lake Tana Basin; (b) hydrogeological cross-section of Lake Tana Basin from the southern tip to the north.
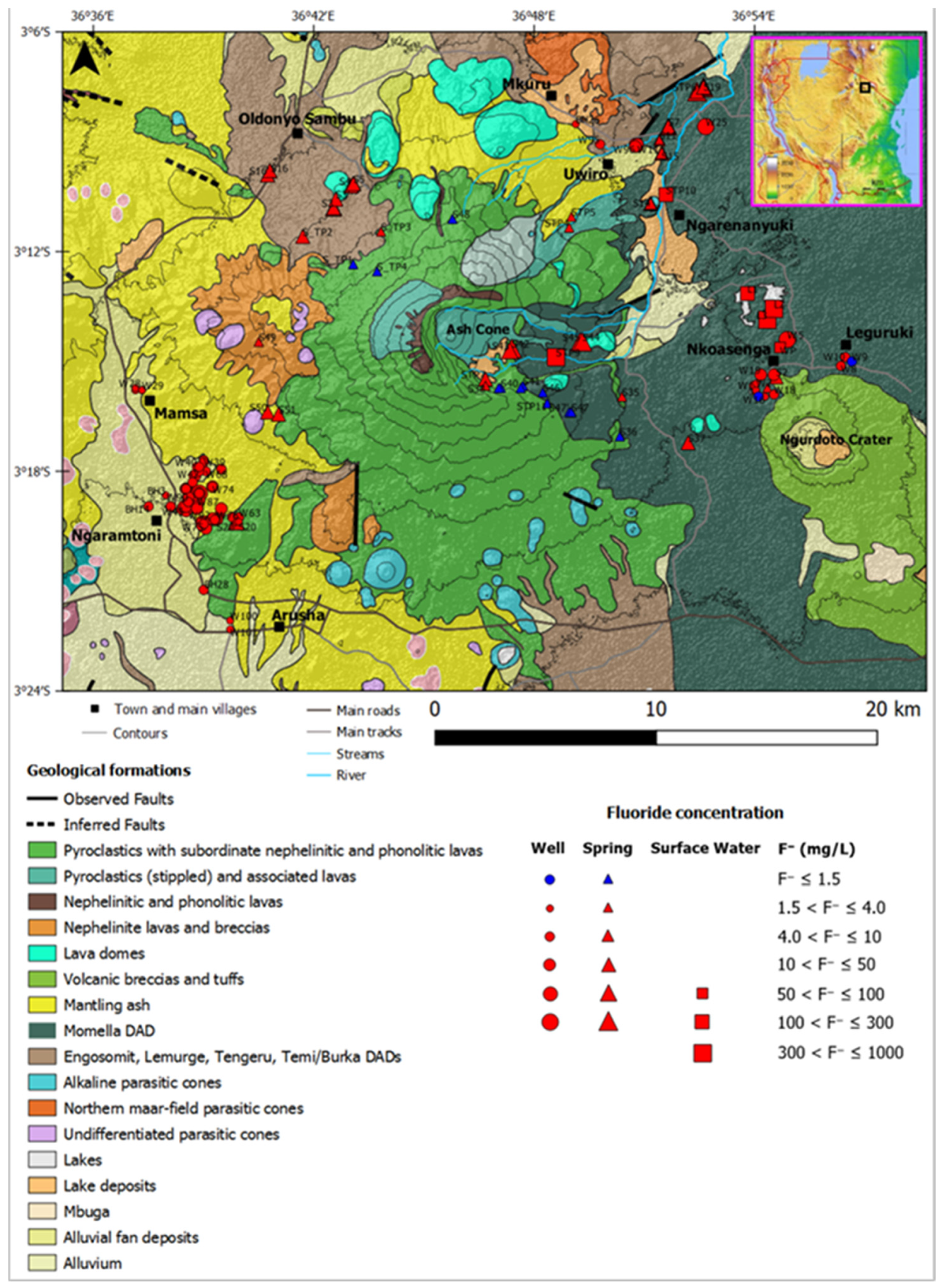
Similarly, the Mount Meru case study area includes the flanks of Mount Meru in the Arusha volcanic region of northern Tanzania (Figure 1C). The landscape is dominated by Mount Meru, with several parasitic cones in the area. Most of the rocks of Mount Meru are Miocene–Pliocene volcanic sedimentary sequences, but younger sequences are of Pleistocene origin [16,17]. The lithology of the study area is defined by pyroclastics, debris avalanches, and volcanic rocks from Mount Meru, with some alluvial fan, alluvium, and lake deposits at the base of the mountain (Figure 3).
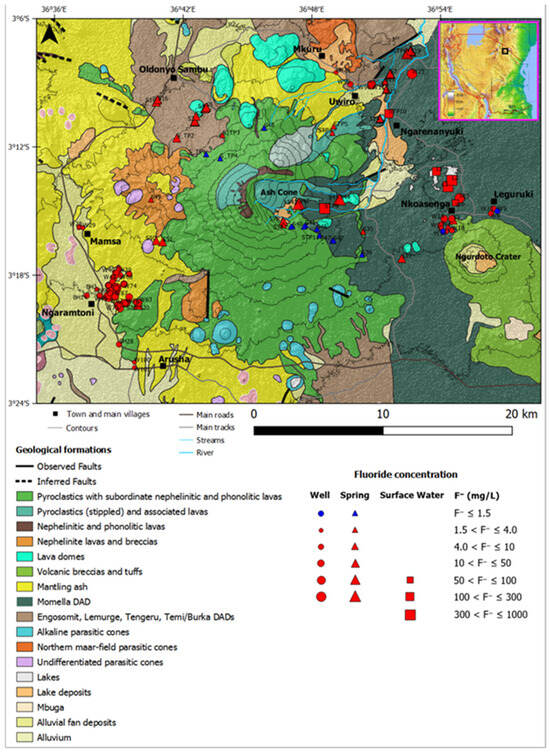
Figure 3.
Geological map showing the various geological formations and the spatial distribution of F− concentrations at the sampled water points around Mount Meru (adapted from Bennett et al. [18]).
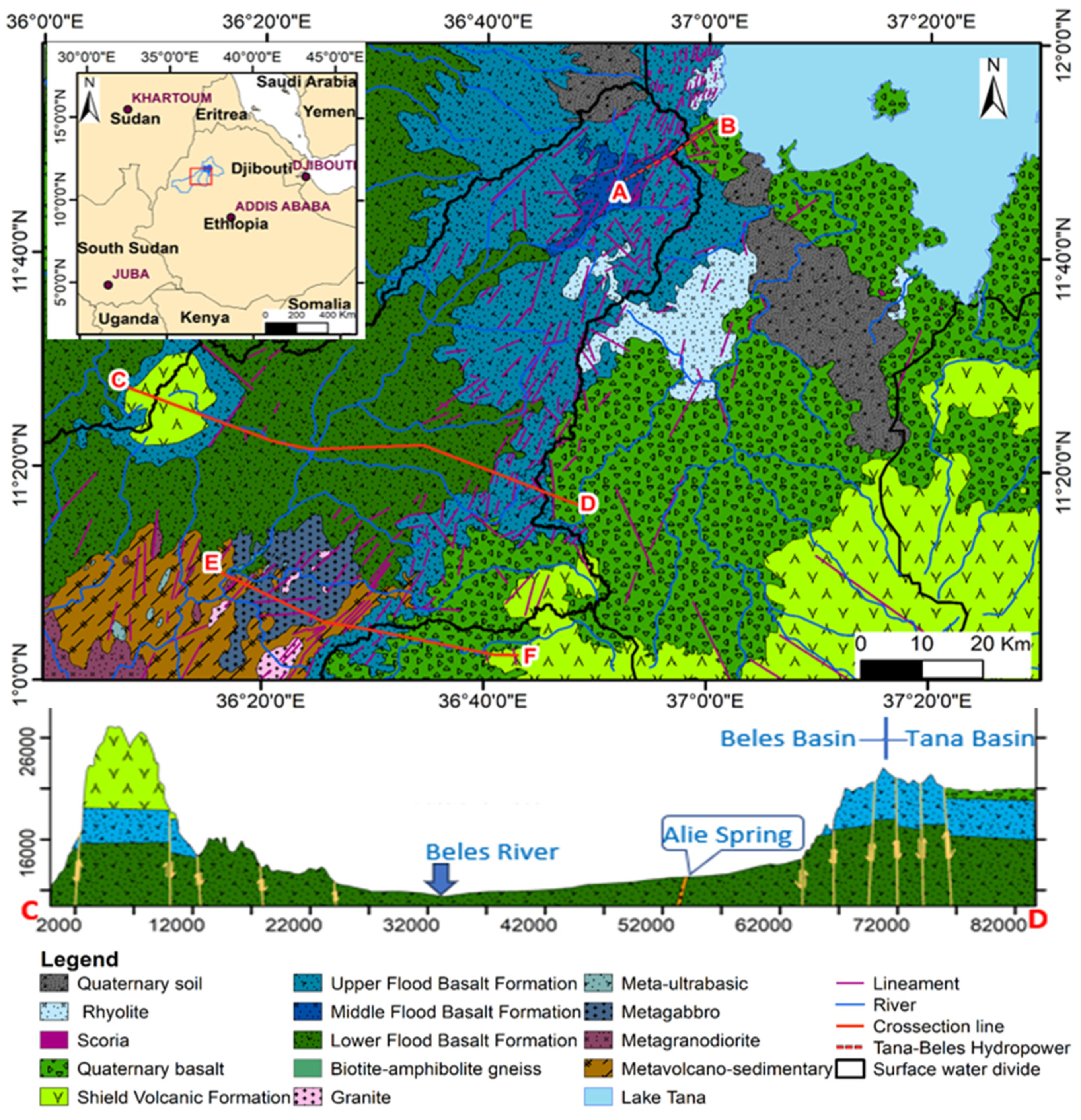
Upper Beles Basin is located at the northwestern margin of the Ethiopia plateau (Figure 1B), characterized as a valley surrounded by volcanic mountain chains, particularly on the side of Tana Basin, and a flat landform in the central part with alluvial soil, with a highly diverse climate attributed to the large physiographic differences. The evolution of the Tana-Beles basins is the result of geotectonic events of the uplift of the plateau caused by the rising of the Afar plume and subsidence in the Lake Tana area, which resulted from the faulting of mid-Tertiary basalts followed by surface processes (erosion); and are stratigraphically and structurally complex [19].
Similar to the Lake Tana Basin and Mount Meru case study areas, the geology is a result of multi-episodes of volcanic strata that have undergone multi-phase uplifting, doming, and collapse processes. The geology of the area consists of Oligocene–Miocene flood basalts of the Trap sequence (one of the world’s large igneous provinces (LIP)), Quaternary basalt flows, and basement rocks exposed at the lower Beles Basin [11,20,21,22,23,24] (Figure 4). The flood basalt flows in the area are grouped into three main flood basalt formations: lower, middle, and upper flood basalt formations, overlain by Miocene shield volcanic rocks and Quaternary basaltic rocks [21].
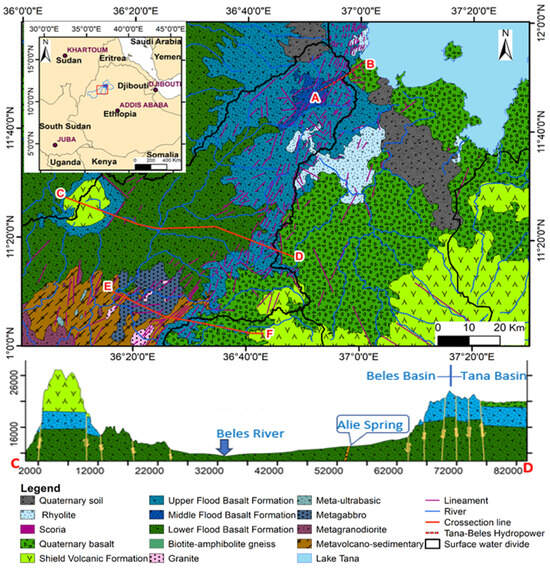
Figure 4.
Geological map and lithological cross-section view of the study area, showing the spatial distribution of complex volcanic rock system at Tana and Beles Basin (modified after Belay et al. [20]).
The hydrogeological setting of the volcanic aquifers in the three case studies is very similar. The aquifers are complex and spatially variable. Lake Tana Basin consists of fractured and weathered volcanic aquifers and an alluvial aquifer in the lowland flood plains (Figure 2). However, the volcanic aquifer unit covers a wider area with multiple aquifer layers with different water yielding capacity. The aquifer system comprises alternating layers of massive rock, pyroclastic material, and volcanic tuffs. Additionally, paleosols, clay layers, and ashes are intercalated between different layers of volcanic flows, which affect the groundwater flow system. The aquifers within this volcanic formation can be broadly categorized into confined, semi-confined, and unconfined aquifers. In Mount Meru, volcanic debris avalanche deposits, pyroclastic deposits, and weathered and fractured lava are identified as major aquifers. The aquifer system in the area is a sloping aquifer similar to the highland areas of Lake Tana and Beles Basins. The aquifer types of Mount Meru are semi-confined on the west and northeastern flanks, consisting of weathered fractured lava, and unconfined on the southwestern flank, consisting of several layers of pyroclastics and fractured lava with different degrees of weathering (Figure 5). The aquifer is unconfined at the far east of the eastern flank and consists of debris avalanche deposits. Groundwater flows are determined by the area’s geomorphology, with flows occurring in multiple directions from high to low areas [22].
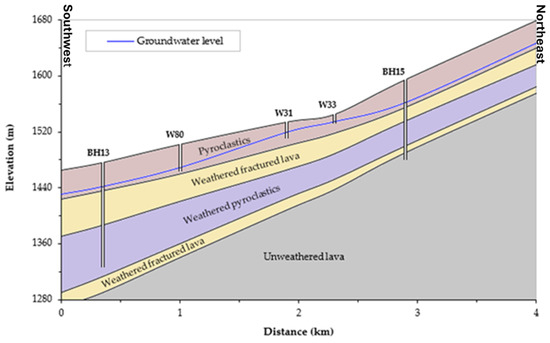
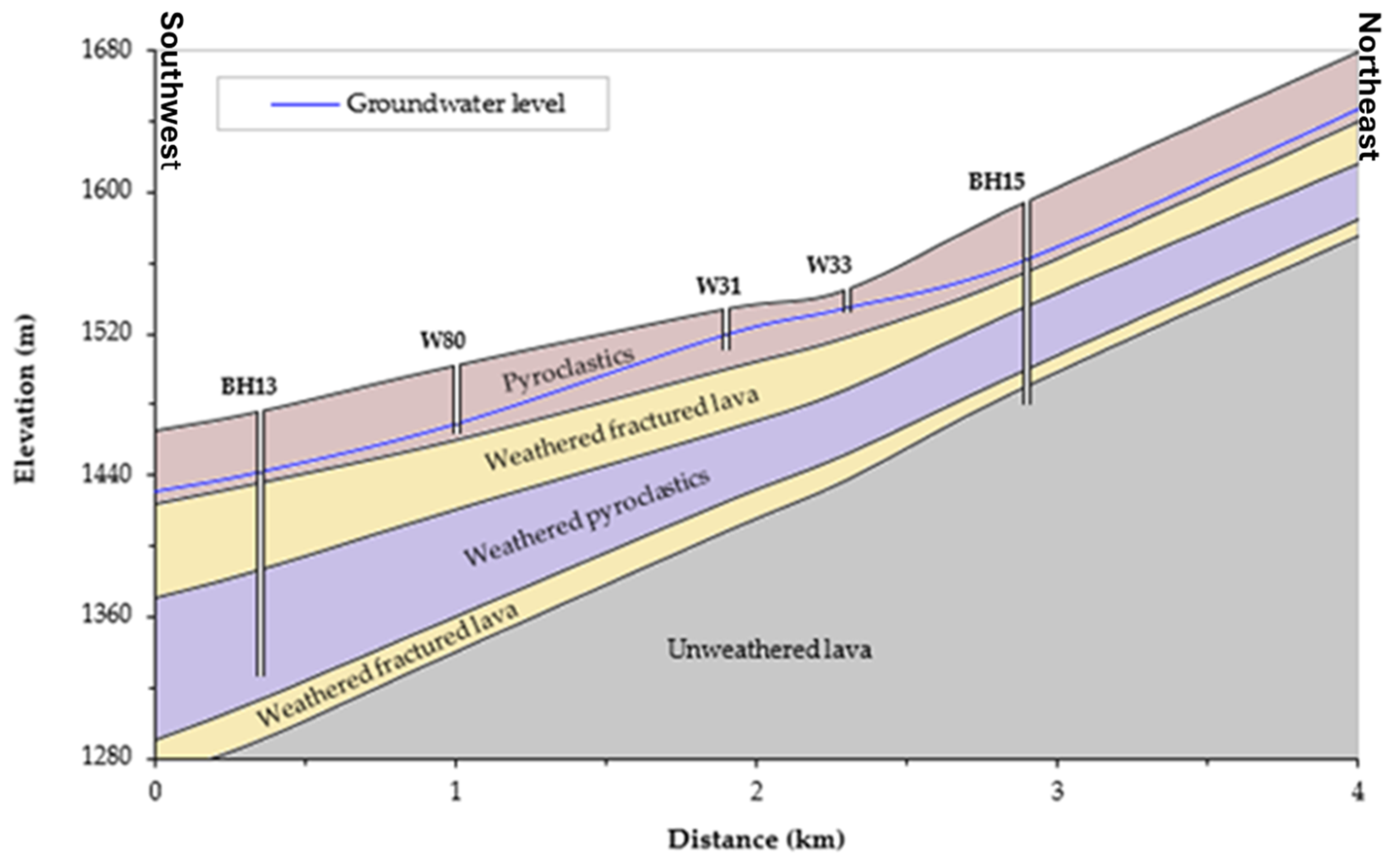
Figure 5.
Litho-hydrostratigraphy of the southwestern flank of Mount Meru in Ngaramtoni showing the aquifer structure [22]. BH stands for boreholes and W stands for shallow hand-dug wells.
The spatial distribution of water resources in Ethiopia is highly sporadic and affected by complex geology and topography [7]. The Tana-Beles contact area, situated within this volcanic landscape, holds significant importance in terms of groundwater resources in the region. However, the heterogeneous nature of volcanic deposits introduces considerable variability in groundwater resources, aquifer characteristics, and groundwater dynamics. There is a high spatial variability of water resources in Beles Basin. In some places, access to water for the household is a severe problem, whereas in other places, high-discharge springs supply tens of thousands of people (Figure 6). The nature of groundwater flow characteristics and boundary conditions of aquifers are mainly controlled by the lithostratigraphic and structural framework of geologic formations [22,23].

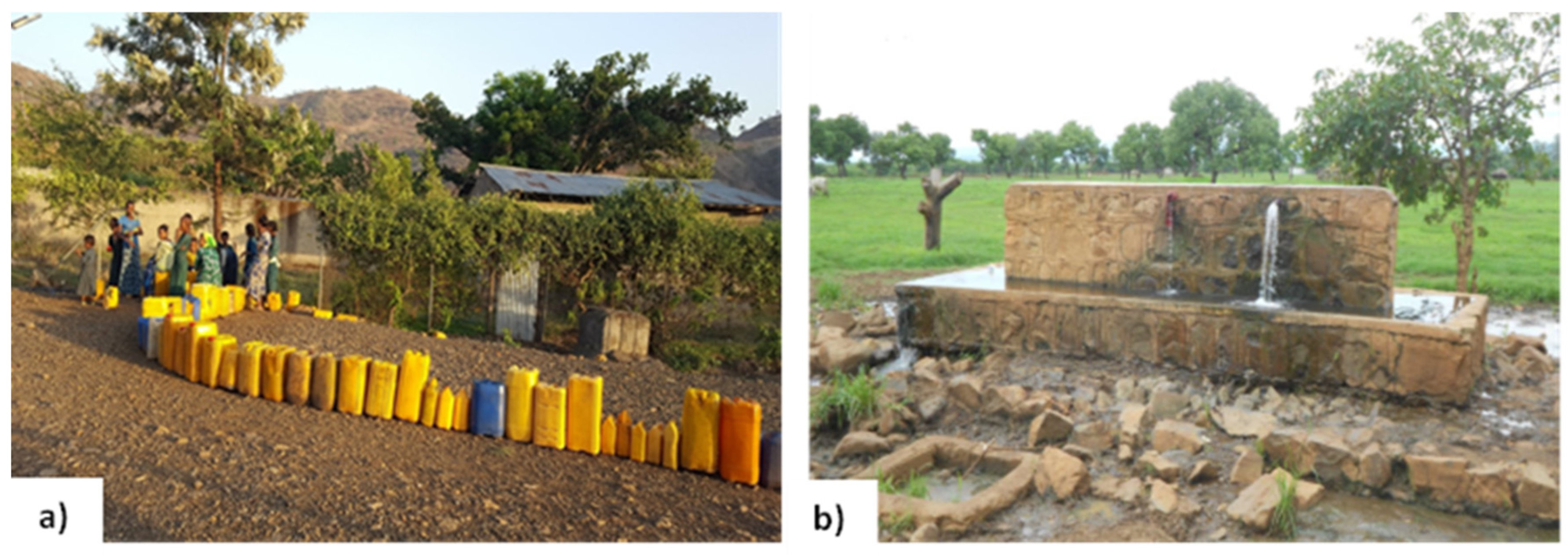
Figure 6.
The spatial variability of water resources in Beles Basin. (a) Photo showing the difficulty of access to water in most Upper Beles areas, where precipitation is higher, and (b) photo showing the middle of Beles Basin (precipitation relatively lower), with relative water supply abundance from high-discharge springs.
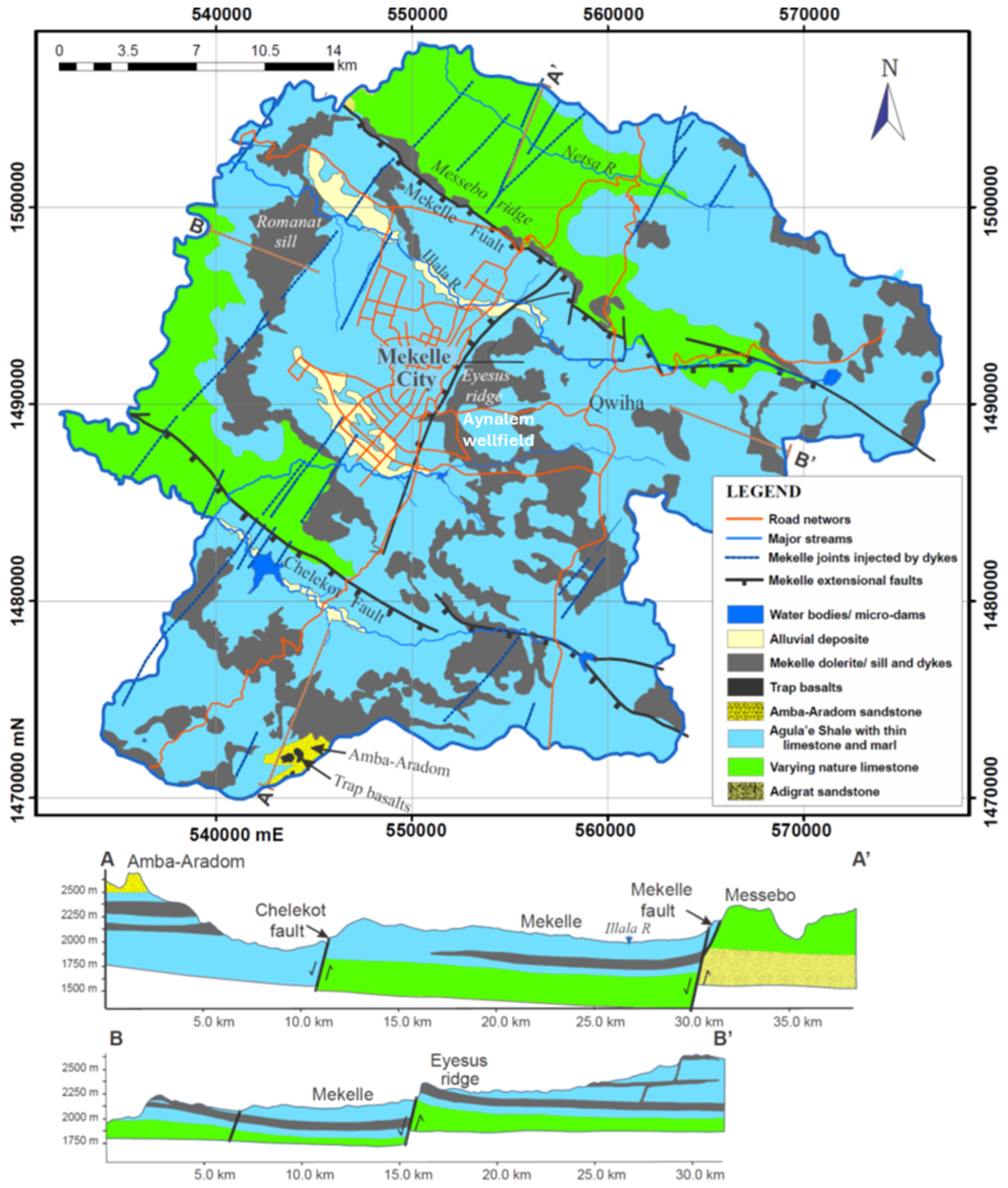
The Mekelle case study area (Figure 1D) is within the Mekelle Outlier which is a terrestrial and shallow marine sedimentary rock-filled basin, bounded by NNW-SSE oriented post-depositional major faults [24]. The area has a rugged topography with a degraded landscape of Mesozoic sedimentary rocks and Cenozoic dolerite intrusions shaped by tectonic and erosional forces. Prominent morphologic features in the area include deep gorges and cliffs of limestone and sandstone, plateaus and basins of marl–shale–limestone intercalations, and ridges of dolerite sills and dykes. The study area is drained by four main ephemeral rivers that are tributaries of the Geba river, which drain to the Tekeze (Atbara in Sudan) river. The major lithological units in the area include dolerites, sandstones, limestone, and shale and marl with intercalations of gypsum (Figure 7). The Cenozoic dolerite intrusions, occurring within the Mesozoic to Paleozoic sedimentary strata [25], mainly intrude at the upper part of the Jurassic limestone–shale succession (Agulae shale) and display a generally concordant to sub-concordant relationship with the flat-laying sedimentary rocks. The main Mesozoic sedimentary rocks in the area are the Adigrat sandstone and the Antalo super sequence (a limestone–shale–marl intercalation). The Antalo super sequence is grouped as the Antalo sequence and the Agulae shale [26]. Agulae shale represents the topmost part of the super sequence and is composed of finely laminated black shale, marl, limestone, and local evaporite units mainly composed of gypsum. The lower section of the Antalo super sequence is a sequence of limestone and marl, with occasional shale and calcareous sandstone layers.
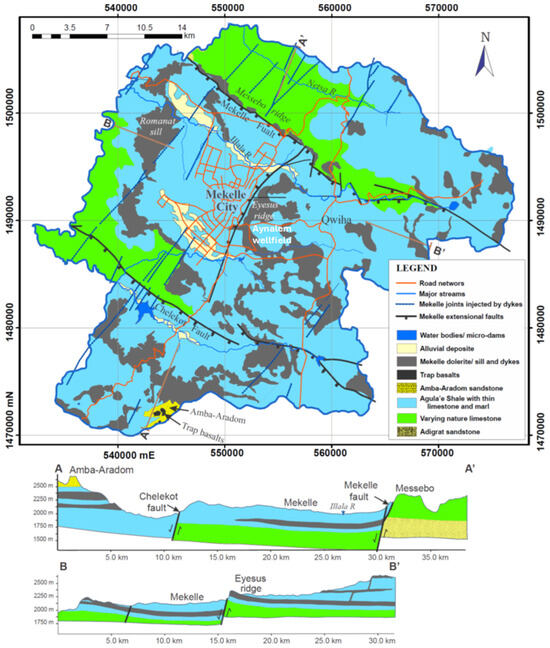
Figure 7.
Geological map and cross-sections along east-to-west and north-to-south directions through the Mekelle area.
A wide range of lithologic units and tectonic disturbances such as major faults and sag folds has resulted in the quite complex hydrogeological setting of the Mekelle area. The main aquifers in the area are sandstone, fractured limestone, and weathered and fractured dolerite [27]. The groundwater flow in the Mekelle area is generally controlled by fractures, faults, and dolerite dykes and sills. The sandstone in the study area is deeply buried under the Antalo super sequence, and, thus, is out of reach of most wells, except in a small area along the Geba river valley in the northwestern and western parts. The limestone with inter-beds of shale–marl intercalation and occasionally with thin gypsum layers is the most common aquifer in the Mekelle area. Studies indicate the presence of three E-W trending groundwater flow systems (shallow, intermediate, and deep) and inter-catchment groundwater transfer through the synthetic faults connecting adjacent sub-basins like the Ilala and Aynalem catchments [28]. Given the tectonic and volcanic disturbance of the area, the aquifer system, in general, is in an unconfined condition regionally, and in a semi-confined condition at some places such as the Aynalem well field (Figure 7).
The total area of the Jifarah Plain in Libya is about 20,000 km2, starting from the Tunisian border in the west and extending east to Al Khums at the foot of the mountain, from the Mediterranean Sea in the north and southward to Jebal Naffusah, where the elevation ranges from 400 to 900 m above sea level (Figure 1E). It is divided into two areas from north to south. The first is the coastal strip, which runs parallel to the sea shore, varying from 15 to 25 km wide. This strip is one of the most important agricultural areas in Libya. The second or inner part is the plain, which extends from the coastal strip to the southern mountains; within this plain, there are valleys varying in elevation and width. Most of these wadis are found in the south-eastern and south-central parts of the plain. The sediments of Jifarah Plain have been deposited since early Mesozoic times in a near-shore lagoonal environment. In Jifarah Plain, the rocks are classified into lithostratigraphic units, with their age ranging from Permian to Quaternary. A north-south hydrogeological cross-section through Jifarah Plain is represented in Figure 8.
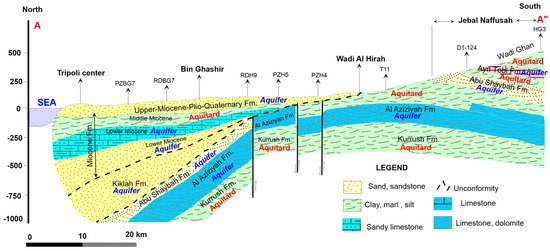
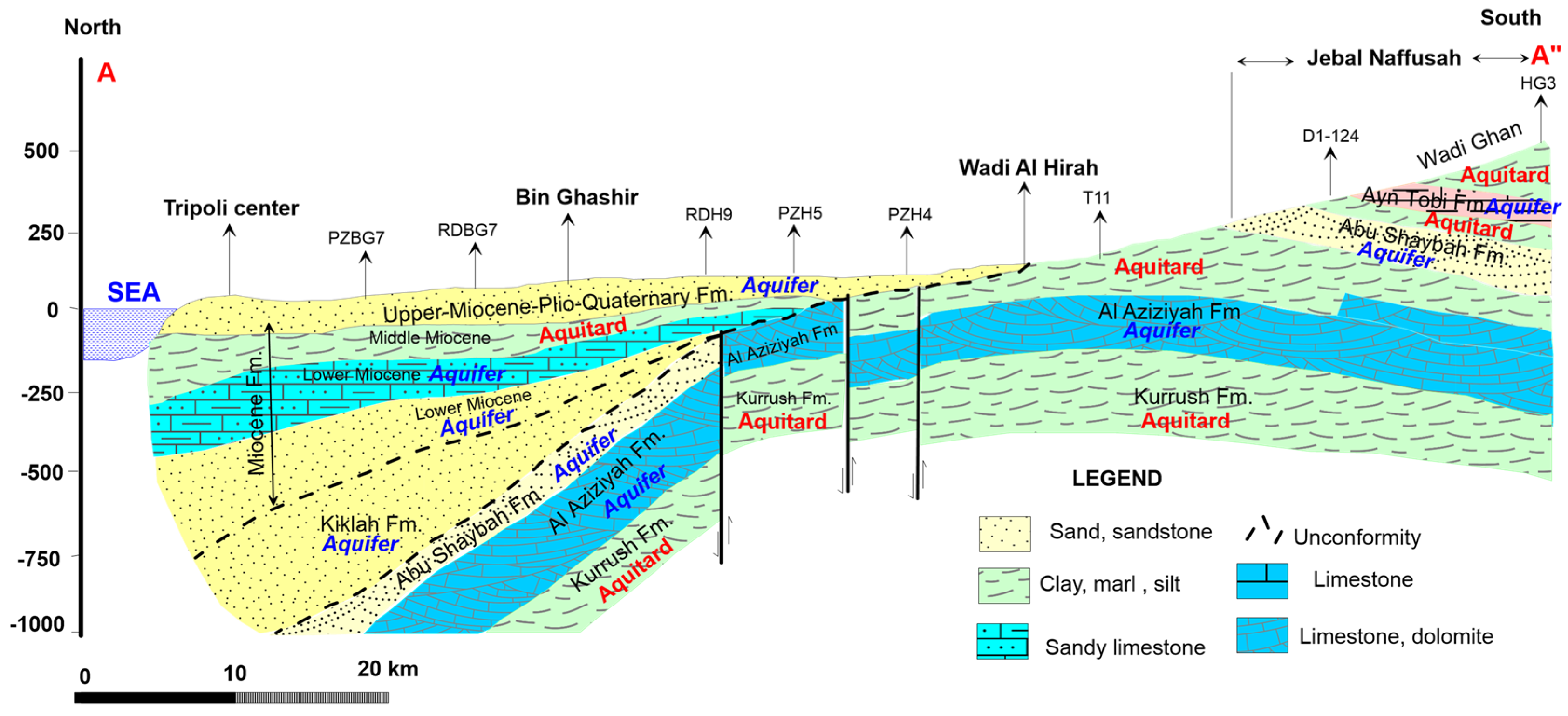
Figure 8.
Geological cross-section in the coastal area of Jifarah Plain, including Tripoli region [29]. The cross-section shows the hydrostratigraphy of the Jifarah Plain main groundwater aquifer system. The labels with codes PZBG7, RDBG7, etc. are the wells along the A-A” profile line.
The main aquifers in the Jifarah Plain are Ras Hamia aquifer, Al Aziziyah aquifer, Abu Shaybah aquifer, Middle and Lower Miocene aquifers, and Upper Miocene–Pliocene–Quaternary aquifers, from oldest to youngest (Figure 8). The Lower Triassic Ras Hamia Formation is the oldest formation investigated for its water resources in the plain. It consists mainly of multicolored sandy clay with alternating red and green sandstone layers and dolomitic layers. This aquifer occurs under the entire Jifarah Plain, overlaying the Permian Ouled Chebbi aquitard of Lower Triassic age. The Middle Triassic Al Aziziyah aquifer usually shows a number of distinct aquifers formed through karstification of the formation. It consists of dolomitic limestone, dolomite, and limestone intercalated by clay and/or marl. This aquifer is everywhere confined to semi-confined, except in the south central part at the foothills of Naffusah mountain. In this area, the aquifer is unconfined (Figure 8). In central Jifarah, the aquifer is rather deep-seated, generally 300 to 400 m. It reaches 1000 m below ground in the Tripoli area. Abu Shaybah aquifer is a thick series of sand and sandstones intercalated with red clay and shale at the bottom. It overlies Al Aziziyah aquifer in the central and eastern part of the plain. The upper part of this sandstone series often directly underlies the Miocene sandy limestone and calcareous sandstone. The thickness of the aquifer complex ranges from 100 to 350 m.
The Middle and Lower Miocene aquifers are built up by a series of limestone, sandy limestone, dolomitic limestone, sandstone, and clay. These aquifers are semi-confined, extending from central Jifarah in the south to the coast in the north (Figure 8). The Middle Miocene aquifer is well developed in western Jifarah and in the western central part of the plain, where the top of the aquifer is found at 70–150 m below the surface, with a thickness of 125–200 m. Middle Miocene clay layers separate this aquifer from the upper aquifer and Lower Miocene aquifer. The Upper Miocene–Pliocene–Quaternary aquifer is also called the upper aquifer. Clayey sand series and marl divide the aquifer into a number of aquifer horizons, all considered as one unconfined unit. It is separated from the lower aquifers by Middle Miocene clays (Figure 8). The lithology of the aquifer varies widely and includes detrital limestone, gravel, marl, clay, silt, sand, sandstone, limestone of Alkums formation, gypsum, and calcarenite. The bottom of the upper aquifer varies between 30 and 180 m deep; the depths of the wells that are utilized in this aquifer are between 30 and 160 m.
3. Methodology and Data
Different methods were employed to estimate groundwater recharge and aquifer transmissivity, and to characterize water quality. Secondary datasets and findings from previous studies served as the primary information sources for the chosen evaluation metrics. In some of the study areas, newly collected data were integrated with secondary sources, while, in others, the analyses relied solely on prior research results. The following sections briefly describe the methods and data used in this study.
Depending on the aquifer type and recharging mechanism, the groundwater potential of an area may be related to the recharge rate; unconfined aquifer systems depend on recharge, while deep and confined systems such as the lower aquifers of Jifarah Plain do not, and the groundwater in such hydrogeological systems is assumed non-renewable [30].
Different methods such as chloride mass balance (CMB), water table fluctuation (WTF), soil moisture balance (SMB), and baseflow separation (BFS) and hydrological models such as WetSpass were applied to estimate groundwater recharge in these case study areas (Table 1). Both CMB and WTF are widely used and well-established methods [31,32]. The CMB method is based on the difference of chloride concentration in shallow groundwater compared with the rainfall as a result of evapo-concentration. The WTF method estimates recharge from the rise of the water table. The SMB method is based on the water balance in the vadose zone, as stated in detail by Bakundukize et al. [33]. Baseflow separation (BFS) is a technique that separates baseflow (groundwater contributions) from quick flow or direct runoff in a stream hydrograph [34]. The WetSpass (water and energy transfer in soil, plants, and atmosphere under quasi-steady state) model is a spatially distributed physically based model that gives the long-term average recharge together with the other water balance components of the vadose zone at a catchment scale [35]. In this study, the groundwater recharge estimations in the Lake Tana and Beles Basins were based on the WTF, CMB, and WetSpass methods (Table 1). About 138 groundwater and 25 rainfall samples for CMB and 65 groundwater levels measured at daily and half-hour time scale intervals for WTF were used for Lake Tana Basin. Similarly, 21 wells for WTF and 56 for CMB were used for Beles Basin (Table 1). WTF and BFS techniques were applied to Mount Meru, where 5 monitoring wells for WTF and 4 river gauging stations for BFS were used for the estimation of recharge. Groundwater recharge for the Mekelle area was compiled from 16 studies in the area that had used WetSpass, WetSpa, and WATERBAL water balance models, and SMB, WTF, and CMB methods. On the other hand, the GRACE satellite was used to estimate the groundwater recharge of Jifarah Plain. The Gravity Recovery and Climate Experiment (GRACE) satellites were used to estimate groundwater recharge by measuring changes in Earth’s gravity field, which reflected variations in terrestrial water storage (TWS) [36,37]. GRACE was particularly useful for large-scale assessments of groundwater recharge in regions with limited in situ monitoring, such as the arid Jifarah Plain.

Table 1.
Number of data points and minimum, maximum, mean, median, and standard deviation values of the three groundwater potential assessment parameters for each case study area. The methods applied for groundwater recharge, transmissivity values for aquifers of a case study area together or per aquifer type, and TDS for each study area are reported. Recharge as a percentage of rainfall is also mentioned.
Transmissivity of the case studies’ aquifers was mainly estimated by pumping tests and slug tests. The number of wells, where pumping tests were interpreted, are shown in Table 1. The slug test involves a rapid change in water level within a well, either by adding or removing a volume of water, followed by monitoring the water level recovery over time. In this study, slug tests were conducted on the shallow aquifers of Lake Tana and Mount Meru. Water in the large-diameter hand-dug wells was instantly pumped out, and the recovery was recorded with automatic pressure transducers. The slug test is suitable for low-storage aquifers like weathered basalt regolith and pyroclastic materials, where fast drawdown and long recovery make slug tests more practical. The Bouwer and Rice [38] method, commonly used for unconfined aquifers, was used to analyze and estimate the transmissivity. The pumping test was used for both deep and shallow aquifers of all case studies. A constant pumping test, withdrawing water at a constant rate from a well and recording the drawdown and recovery in the same well, was the technique applied in this study. Analysis for large-diameter wells on fractured basaltic aquifers was found to be significantly affected by wellbore storage water; hence, methods that took into account its effect on analysis such as Papadopoulos and Cooper [39] for confined aquifers and Moench [40] for unconfined aquifers were applied. For the recovery phase, Theis’ [41] recovery method was applied, which was particularly effective in estimating transmissivity. Pumping tests are more applicable to high-storage aquifers like Quaternary basalt, which exhibit steady-state drawdown behavior compared with slug-test basalt regolith pyroclastic aquifers. Transmissivity of aquifers in the deep wells was typically estimated using pumping tests, specifically constant rate and recovery tests. Data were secondary data collected from drilling companies, consultants, and governmental water offices, where slug tests and pumping tests on large-diameter hand-dug wells showed primary data. Analytical methods applied included the Theis solution for confined aquifers [41], the Neuman method for unconfined aquifers [42], and the Hantush–Jacob method for leaky aquifers [43]. These analyses relied on time–drawdown data, which were plotted on log-log and semi-log graphs to determine radial flow conditions and fit diagnostic curves [44]. Additionally, transmissivity estimation from recovery data employed the Theis residual drawdown method [41]. Advanced diagnostic tools, such as logarithmic derivative plots, were also used to identify flow regimes and refine model selection [45].
Groundwater quality was assessed for each of the case study areas, mostly based on water samples that were analyzed at Ghent University. Nigate et al. [46] used a total of 301 groundwater samples for chemistry and 88 for stable isotope analysis collected from various sources, including deep and shallow wells, hand-dug wells, springs, rivers, rainwater, and lake water from Lake Tana Basin. The water quality of the Mekelle area was computed from 196 water samples (Table 1) that were analyzed at Mekelle University (Ethiopia), Ghent University (Belgium), and the Technical University of Darmstadt (Germany). On the other hand, the Jifarah Plain study was based on groundwater samples from 134 shallow and deep wells (mostly 30–180 m deep) (Table 1) located in the coastal area of the plain, at different distances from the Mediterranean Sea, which were analyzed at Ghent University. They were selected from profiles perpendicular to the coastline. The sampling was performed during dry periods from March to July in 2007 and from September to November of 2008. Water samples, both added for this study as primary data and collected as secondary, were collected in 250 mL HDPE bottles, cooled, filtered through a 0.45 μm membrane, and acidified to pH = 2 with HNO3 for major cation analysis. In situ and lab measurements were made for pH, EC, and temperature. The detailed analytical methods applied to this study were thoroughly explained by Nigate et al. [46], Bennett et al. [47], Kahsay [28], and Belay et al. [20].
4. Results
4.1. Groundwater Recharge
Recharge rates for the five different case studies were estimated using one or several of the methods. The estimated groundwater recharge values varied not only from case study to case study but also different methods that had different ranges of recharge values (Table 1). These variations among the methods applied could be (1) due to the assumptions of the different methods versus hydrogeological, climatological, and topographical characteristics of the aquifer types; or (2) due to variability in data type, data scale, measurement accuracy, and representativity. The mean annual recharge in Lake Tana Basin was found to be highly variable, ranging from 125 mm to 778 mm, and with an average value of 315 mm (22% of rainfall amount) [48] (Table 1). The main recharging mechanism was the diffuse type by direct rainfall. However, the focused recharging (preferential flows) along rock fractures also contributed. In steep-sloping topography aquifers, where low recharge was expected, higher recharge values were estimated, as in flat floodplain areas where the recharge was small. Similarly, an annual groundwater recharge ranging from 192 mm to 802 mm, and with a mean value of 364 mm (Table 1) and similar recharging mechanisms, was noted for the Beles Basin. The spatial distribution of recharge was highly variable and controlled by land use in the lowlands and by slope, soil, and rainfall in the highland areas.
On the other hand, debris avalanche deposits (DADs) of Mount Meru generally showed low infiltration rates under homogeneous recharge conditions compared with pyroclastic deposits with heterogeneous recharge conditions; thus, areas covered by pyroclastic deposits had potential for targeted surface runoff recharge. On the northeastern slope (leeward side), which consisted of DADs, and the southwestern slope (windward side), which consisted of pyroclastic deposits (Figure 1C), the groundwater recharge values were 90 mm/year and 544 mm/year, respectively (Table 1). This recharge amounted to, on average, 13% and 53% of the annual rainfall for each slope. On the northwestern slope (leeward side), which consisted of pyroclastic deposits, and the southeastern slope (windward side), which consisted of DADs, the groundwater recharge values were 54 mm/year and 88 mm/year, respectively. This amounted to around 7% and 12% of the annual rainfall on each slope, respectively. Generally, the annual recharge rate over the Mount Meru study area was highly variable, ranging from 33 mm to 1320 mm, with mean and median values of 193 mm and 95 mm, respectively.
On the other hand, generally, a lower groundwater recharge was observed in the Mekelle area. Values of 6 to 283 mm/year by CMB, with a mean of 51 mm/year and standard deviation of 24 mm/year by the physical hydrological models, were reported for the Mekelle case study area (Table 1), the variation of which was partly due to different estimation approaches employed. For arid climates like in Libya in general, and in Jifarah Plain in particular, the renewable water resource was limited due to low rainfall rates, high evaporation, and no reliable surface water resources, suggesting the very low recharge amount. Gonçalvès et al. [49] estimated the groundwater recharge of the Jifarah Plain with average, minimum, and maximum values of 4.3 mm/year, 1.6 mm/year, and 7 mm/year, respectively (Table 1). Furthermore, the major aquifers of Jifarah were deep and confined, where the effect of recharge on the groundwater potential was low or negligible.
4.2. Hydraulic Transmissivities
The shallow aquifers where significant amounts of water were being exploited mainly by large-diameter hand-dug wells in Lake Tana Basin were unconsolidated lithological materials and outside the scope of this paper. However, the highly fractured Quaternary basalt was often exposed to the surface, and thus, the pumping test and slug test results were within the scope of this paper. Transmissivity for this shallow Quaternary basalt aquifer, analyzed from 12 large-diameter hand-dug wells, ranged from 117 to 1064 m2/d. Hand-dug wells situated in highly fractured Quaternary basalt yielded substantial water, often coinciding with high-discharge springs [50]. Transmissivity (T) of the deep volcanic aquifers in Lake Tana Basin (consisting of Quaternary and/or Tertiary basalt) was assessed at various locations. Pumping test data from 31 wells in the Quaternary basalt and 36 wells in the Tertiary basalt (flood basalt and shield volcanoes) (Table 1) were analyzed to estimate the transmissivity of the deep aquifers. Results, revealing variable values ranging from 0.38 m2/d to 860 m2/d (average and standard deviation of 101 m2/d and 184 m2/d, respectively) in flood basalt and shield volcanoes, and from 2 m2/d to 18,000 m2/d (average and standard deviation of 510 m2/d and 1308 m2/d, respectively) in young basalt (Quaternary basalts), were found by this study. This strong aquifer heterogeneity affected the groundwater flow system and groundwater potential in the study area.
Similarly, transmissivity of the different volcanic aquifers identified in Mount Meru such as volcanic debris avalanche deposits, pyroclastic deposits, and weathered and fractured lava were determined from pumping tests. Pumping test data from 11 wells were used for this study (Table 1). On the southwestern slope of the mountain, both shallow and deep aquifers consisting of pyroclastic deposits had the potential for local water supply. The range of transmissivity for the shallow aquifer was 0.3–19 m2/d, while for the deep aquifer, the range of T was 9–43 m2/d. On the northeastern slope of the mountain, the aquifer consisting of weathered and fractured lava had potential for local water supply for the shallow aquifer (range of T: 1.3–35 m2/d), while the deep aquifer had potential for regional water supply (T = 790 m2/d) [22]. Moreover, the debris avalanche deposits on the northeastern slope contained some perched aquifers in the area. The slug tests conducted in the shallow wells in these deposits did not yield reliable results due to the slow water recovery, but these deposits showed a very low response to rainfall, indicating low hydraulic properties. In addition, compared with pyroclastic deposits with heterogeneous recharge conditions, debris avalanche deposits exhibited low infiltration rates under homogeneous recharge conditions; thus, areas covered by pyroclastic deposits had the potential for targeted surface runoff recharge.
The Mekelle and Jifarah Plain case studies comprised basically sedimentary rock aquifers and some magmatic-like dolerites (Mekelle area). The main aquifers in the Mekelle area were sandstone, fractured limestone and weathered and fractured dolerite [27]. In total, pumping test data from about 44 boreholes were used in the estimation of transmissivity in the Mekelle area (Table 1). Average T values for the main aquifers in the Mekelle area were 1 m2/d for deep massive dolerite, 6 m2/d for shallow weathered and fractured dolerite, 48 m2/d for shale–marl–limestone intercalations, 306 m2/d for sandstone, 539 m2/d for marl–limestone intercalation, and 859 m2/d for limestone–marl intercalation [51]. On the other hand, in Jifarah Plain, transmissivities for the five different sedimentary rock aquifers were determined. The thickness of the Ras Hamia Formation varied from 450 to 600 m, but only a small part was considered an aquifer, with usually low transmissivity (0.9 m2/d or less), according to Kruseman and Floegel [52]. Al Aziziyah aquifer, generally having depths of 300 to 400 m, had T that varied from 1728 m2/d in the eastern part of the plain to 4320 m2/d in the western part [52]. According to the results of the pumping tests in central Jifarah, the aquifer had average T values of 82 m2/d. Referring to Kruseman and Floegel [52], the storage coefficient of the unconfined aquifer was from 1 to 5%, whereas it was 0.001 where the aquifer was confined. On the other hand, the T of Abu Shaybah aquifer was in the order of 432 m2/d and the storage coefficient was about 0.0001, according to Kruseman and Floegel [52]. The transmissivity values resulting from the analysis of pumping tests fell within a close range, with an average value of 182 m2/d. Kruseman and Floegel [52] also estimated T for Lower Miocene and for the Upper Miocene–Pliocene–Quaternary aquifers. Kruseman and Floegel [52] found T of 43 m2/d for the former, and T ranging from 100 to 8001 m2/d for the latter; whereas, in this study, average T values of 77 m2/d for the former and 51 m2/d for the latter were estimated.
4.3. Water Quality
TDS of the groundwater over the whole Lake Tana Basin ranged from 79 mg/L to 3388 mg/L, and had mean and median values of 709 mg/L and 203 mg/L, respectively (Table 1). Based on chemical and stable isotope analyses, the groundwater of Lake Tana Basin was classified into (1) low TDS (~130 mg/L) Ca-HCO3 and Ca-Mg-HCO3 recharge-type water resulting from low rock–water interaction; (2) high TDS (reaching up to 3000 mg/L), brackish Mg-Na-Ca-HCO3-type water resulting from strong water–rock interaction; and (3) low TDS (~420 mg/L) Na-HCO3-type water. Similarly, three flow systems (shallow, intermediate, and deep) were identified. The stable hydrogen and oxygen isotopes helped to support the extent of rock–water interaction, concluded by the chemistry to identify the recharge mechanism. Expected water quality problems such as high fluoride concentration were less prevalent in Lake Tana Basin. Flow systems were identified as shallow, intermediate, and deep flow systems. Some water samples from the shallow aquifer exhibited high nitrate concentrations (>50 mg/L), surpassing the WHO standard [46].
Deep groundwater in volcanic aquifers and shallow groundwater in metamorphic rock aquifers of the Beles Basin exhibited relatively higher TDS ranging from 500 to 700 mg/L (mean was 249 mg/L and median was 219 mg/L), whereas most of the shallow groundwater on the volcanic rock formation showed TDS values of less than 500 mg/L. The higher nitrate levels in shallow groundwater compared with deep groundwater indicated that the shallow groundwater was probably polluted from agricultural practices. The dominant types of water in the study area were Ca–HCO3, Ca–Mg–CO3, and Na–HCO3.
On the other hand, the main groundwater type in the Mount Meru aquifer was high-fluoride Na-HCO3, with an average pH of 7.8, i.e., alkaline groundwater. The low Ca2+ in this water type allowed for high F− in solution. Most of the groundwater samples, about 90% of the samples (n = 175), showed elevated fluoride (F−) values above the WHO health-based guideline for drinking water (1.5 mg/L); F− values range from 0.15 to 301 mg/L. Almost 40% of the samples showed Na+ concentrations above the WHO taste-based guideline of 200 mg/L [47]. The debris avalanche deposits (DADs) contained poor-quality groundwater, with elevated F− levels above the WHO limit (1.5 mg/L) and the Tanzanian limit (4.0 mg/L) (Figure 3), which may have adverse effects on the local population. The deep aquifer consisting of weathered and fractured lava had F− values that met the Tanzanian limit (4 mg/L) [47]. Total dissolved solids (TDS) values in the groundwater over the whole case study area ranged from 117 to 4214 mg/L (mean = 987 mg/L and median = 867 mg/L) (Table 1). The highest TDS values came from hydrothermal springs near the ash cone. Deep wells showed low mineralization, with an average TDS value of 653 mg/L compared with shallow wells, with average TDS values ranging from 744 to 1188 mg/L. Therefore, the deep aquifer around Mount Meru, which consisted of weathered and fractured lava, was potentially better than other aquifers, because it had good productivity and good water quality; additionally, the aquifer had the potential for providing a regional water supply.
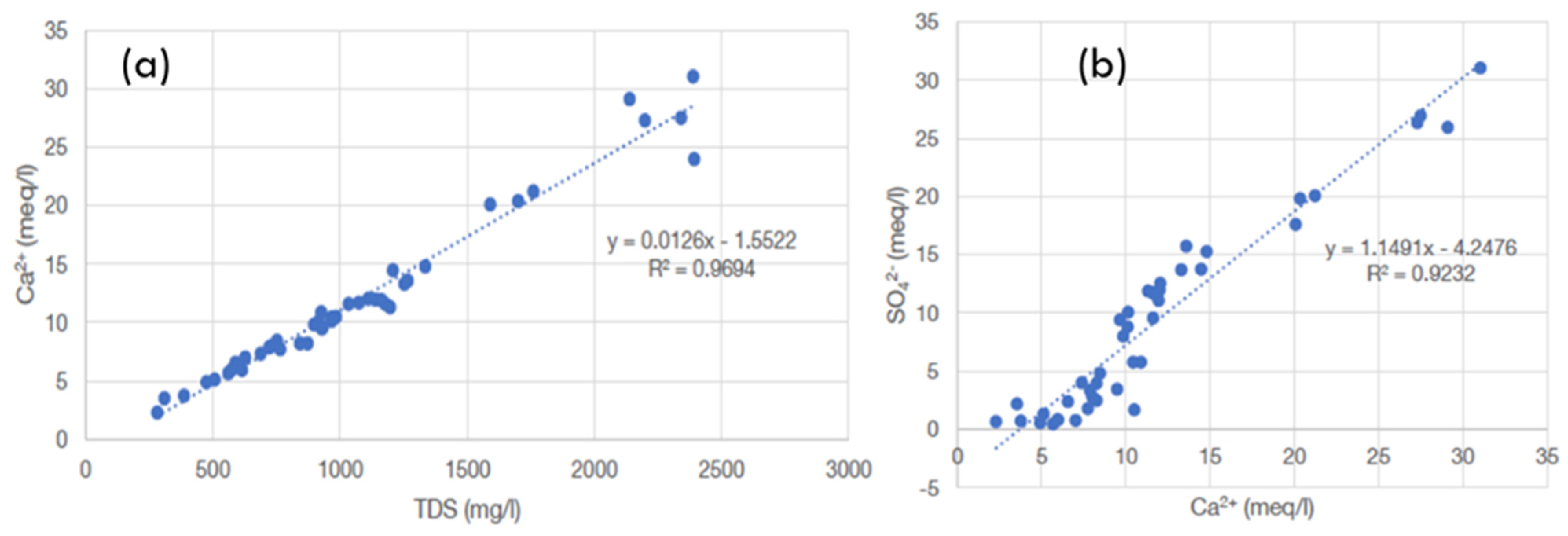
In the sedimentary rock aquifers of the Mekelle area and the Jifarah Plain, high TDS and high sulfate concentrations were the major problems with regard to water quality. The TDS in the Mekelle area was very high due to the high dissolution of gypsum and carbonate rocks. The TDS in the area ranged from 251 mg/L to 3287 mg/L (a mean = 1806 mg/L, and a median = 1224 mg/L (Table 1). According to Kahsay [28], 32.8% of the water samples from the aquifers in the Mekelle area showed TDS concentrations exceeding the permissible limit of the Ethiopian drinking water standards, which was 1500 mg/l. Kahsay [28] and several other studies reported that the common groundwater types in the Mekelle area were Ca-HCO3-SO4 and Ca-SO4-HCO3, followed by Ca-SO4 type. Ca-Mg-HCO3, Ca-Mg-HCO3-SO4, and Ca to mixed cation-HCO3 were also common in the dolerite, limestone, and sandstone aquifers of the area (Figure 7), respectively. The high concentrations of both calcium and sulfate ions were strongly correlated with shale (with gypsum beds) and shale–marl limestone geological formations. There was a strong correlation of Ca2+ vs. TDS and SO42− vs. Ca2+ (Figure 9).
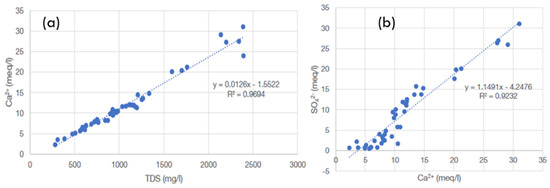
Figure 9.
Cross-plot of Ca2+ vs. TDS (a) and of SO42− vs. Ca2+ (b).
Similarly, high TDS and high sulfate concentrations, far above the allowable WHO limits, were also major issues in the case study of the Jifarah Plain aquifers. In general, the sulfate concentration ranged from 27 mg/L to 2238 mg/L across the entire Jifarah Plain. In the Ras Hamia aquifer, the poor hydraulic characteristics of this aquifer and the high salinity (TDS of 2700–8000 mg/L) made the aquifer unimportant and made further investigation not worthwhile, as stated by Pallas [53]. The Al Aziziyah aquifer was characterized by a TDS range of 3000–7000 mg/L, with groundwater temperatures ranging from 40 to 72 °C. The high temperature was attributed to its substantial depth. Notably, this aquifer is renowned for its exceptionally high sulfate concentration. There were groundwater samples with a sulfate concentration of 2238 mg/L in the aquifer. Moreover, its considerable depth posed challenges for exploitation, resulting in limited utilization. The water quality of Abu Shaybah aquifer was good in the south but deteriorated towards the north and was very poor in the west. TDS generally ranged from 1000 to 3000 mg/L, with high sulfate concentrations. The aquifer has been exploited for many governmental agricultural projects. The groundwater temperature for the aquifer was between 33 and 44 °C. The Middle and Lower Miocene aquifers had TDS of about 2000 to 4000 mg/L and, according to Stuyfzand [54], the groundwater was a fresh brackish very hard MgMix water type in the coastal part. The upper aquifer had TDS ranging from 2000 to 10,000 mg/l. Types of water in the upper aquifer (Figure 8) included NaCl, MgCl, and CaCl, which were the typical water types, indicating salinization. Groundwater with a Na+ concentration of 2749 mg/L and Cl− concentration of 5285 mg/L were noted in this aquifer. Generally, TDS in the aquifers of Jifarah Plain ranged from 360 mg/L to 11,141 mg/L. Pollution with a very high nitrate concentration (>45 mg/L) was found in many locations along the coast. The nitrate concentration in the Jifarah Plain generally ranged from 0.2 mg/L to 160 mg/L.
4.4. Inter-Basin Groundwater Flow
Another factor that may determine the groundwater potential of a given aquifer system is inter-basin groundwater flow. Deep aquifer systems within a basin may receive replenishment from the deep groundwater of neighboring basins through deep fractures that extend across basin boundaries. The Beles Basin case study emphasized the crucial role of this phenomenon in groundwater potential assessment and groundwater balance studies. Hydro-stratigraphic, groundwater water level, presence of high discharge springs, fracture orientation and density, topography, and hydrochemistry were used to detect the presence or absence of inter-basin flow.
The nature of the aquifer in the Tana/Beles Basins area is controlled by the litho-stratigraphy and effect of geological structures [7]. The high topographic contrast, the extension of the fractured basaltic aquifer, the high lineament density, the fracture distribution and orientation along the basin contact, the connection of hydro-stratigraphic units (Figure 1B), the high hydraulic gradient (Figure 10b), and the spatial distribution of high-flux springs (Figure 10a) were evidence of the existence of inter-basin groundwater flow (IGF) from Tana Basin to Beles Basin (Figure 10a) [20]. In most groundwater potential studies, IGF is not considered; however, in some cases, like the Beles Basin, IGF has a significant role in the groundwater potential of the basin. The high flux springs like Ali Spring (Figure 6b and Figure 10a), which are the main water sources in this study area, might be the result of regional IGF. Hence, in groundwater potential and water balance studies in fractured hard rock aquifers systems, which have undergone a series of geotectonic events, regional groundwater flow like IGF may have a significant role.
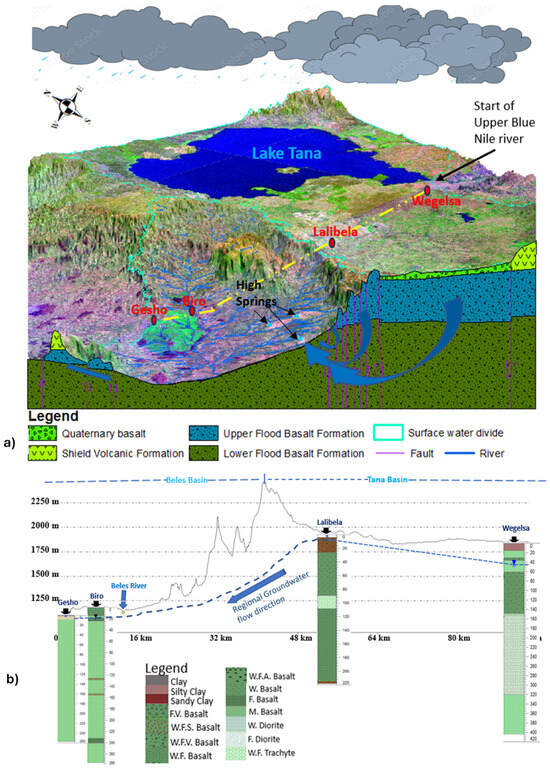
Figure 10.
(a) Schematic of conceptualized regional groundwater flow system of Tana-Beles basins contact (Landsat image with a false color composite of RGB band 7, 5, and 1, respectively, with lithostratigraphy cross-section). Blue arrows represent local and regional flow paths and location of high-flux springs that are the result of IGF. (b) Cross-section showing the relation of groundwater level at the deep boreholes to the land surface topography along a perpendicular axis to the Tana-Beles basin boundary (a), modified after [20].
5. Discussion
The summary of this study, the main results, and the concluding remarks, are shown in Table 2. The high groundwater recharge estimated using the water table fluctuation (WTF) method in the sloping aquifers of the Lake Tana and Beles basins may be attributed to additional recharge from lateral groundwater flow (mountain block recharge) in combination with diffuse recharge. Furthermore, preferential percolation through specific flow paths, as highlighted by Yenehun et al. [55], could also play a significant role. Markovich et al. [56] similarly found that lateral groundwater flow in mountainous and volcanic regions can significantly influence recharge rates. This is supported by the volcanic rock fractures observed during fieldwork. Conversely, the low recharge observed in the flat floodplain areas can be explained by the limited storage capacity of the aquifer. In these areas, the aquifer becomes fully recharged during the early to middle stages of the recharge period, after which excess water primarily contributes to runoff and evaporation. According to this study, the major controlling factors of the groundwater recharge rate in the Mekelle area are the soil texture and topography, which are directly related to the bedrock geology or the lithology and the geological structures, respectively.

Table 2.
Summary of the key parameter values and properties across case study areas.
Offodile [57], and subsequently Kwami et al. [58], attempted to establish a correlation between transmissivity (T) and aquifer potential in hard rock aquifers. They proposed that aquifers with a T greater than 500 m2/d are to be classified as high potential, while those with T less than 0.5 m2/d are to be considered negligible. On the other hand, aquifers with T ranging from 0.5 to 5 m2/d, 5 to 50 m2/d, and 50 to 500 m2/d are to be classified as very low, low, and medium potential aquifers, respectively. Both shallow and deep aquifers of the Quaternary basalt in the Lake Tana Basin, and the deep aquifer of the weathered and fractured lava of Mount Meru are found to list alongside high potential aquifers. According to Jalludin and Razack [59], transmissivities for the Adolei basalts in Djibouti ranged from 6 m2/d to 220 m2/d (average 122 m2/d), while this study found an average value of 101 m2/day for similar Tertiary flood basalts. Similarly, they estimated T values ranging from 13 m2/d to 27,120 m2/d (average 5347 m2/d) for the Quaternary Gulf and stratiform basalts, while it was described to range from 2 m2/d to 18,000 m2/d (average 510 m2/d) by this study for the Quaternary basalt in Lake Tana Basin. The difference in the average value must be due to the relatively small thickness in Lake Tana Basin (it is on average about 20 m in thickness). In general, both studies confirmed that the recent Quaternary basalt geological unit was the more transmissive, showing the more intensively fractured nature of the Quaternary basalt compared with the Tertiary period volcanic aquifers. On the other hand, the shallow aquifers of pyroclastic material intercalated with lava flows in Mount Meru and Lake Tana Basin were in the range of very low to low potential aquifers. In general, the fractured quaternary basalt in Lake Tana Basin, and weathered and fractured lava (mostly basaltic) in both of the case study areas, were potentially better than other aquifers because they had good productivity and good water quality; therefore, the aquifers have the potential for providing a regional water supply. In addition, the Tertiary deep-weathered and fractured lava aquifer in both case studies also showed a similar potential to the weathered and fractured bedrock aquifers in Ilorin, Nigeria (range of T: 3–1200 m2/d) [60].
There was no reported high fluoride problem in Lake Tana and Beles Basin volcanic aquifers, in contrast with the debris avalanche deposits (DADs) of Mount Meru. This could be related to the prevalence of Ca2+ in most water types, inhibiting high F− concentrations, which would lead to the precipitation of the mineral fluorite (CaF2). Among the 100 countries of the world where fluoride is observed as a geogenic groundwater pollutant, 38 are African countries [61]; nearly 81 million Africans are using water sources with a fluoride concentration above 1.5 mg/L. High fluoride levels in water can stem from volcanic activities, thermal waters (especially those with high-pH sources), gas emissions, and granitic or gneissic rocks [62]. This issue is particularly severe in the East African Rift Valley area in nations such as Kenya, Tanzania, and Ethiopia, where Mount Meru lies, and where groundwater is characterized by Na+-dominated water types, unlike the two volcanic case study areas of Ethiopia that are located on the old volcanic plateau, with Ca2+-dominated water types. Similar high fluoride concentrations have been studied by Coetsiers et al. [63] in Nairobi, Kenya.
The high-potential aquifers in the Mekelle area are the limestone–marl and marl–limestone (Antalo limestone formation) aquifers. According to the Offodile [57] aquifer potential classification, they are regarded as high-potential aquifers, whereas the deep Adigrat sandstone has moderate potential. The shale–marl–limestone intercalation has low potential but supplies the rural community through large hand-dug wells. Its productivity depends on the thickness of the bedded and fractured limestone. The dolerite intrusion, which has a limited areal extent, is also used as an aquifer, with a potential ranging from very low to low. However, the high TDS and high sulfate concentrations (in some of the wells where gypsum evaporite exists) of groundwater in the Mekelle area are major water quality issues. The strong correlation of Ca2+ vs. TDS and SO42− vs. Ca2+ (Figure 9) indicates that Ca2+, the dominant cation in the water, is the primary ion contributing to TDS, originating from calcite and/or gypsum dissolution [64,65]. It is worthwhile to note, based on Figure 9, that, for low Ca2+, the correlation with SO42− is poor; here, the Ca2+ is due to calcite dissolution. However, for high Ca2+ (>12 meq/L), there is a high correlation with Ca2+; here, the Ca2+ is due to gypsum dissolution. HCO3− is the dominant anion, followed by SO42−, in most samples, indicating calcite and gypsum dissolution being the primary geochemical processes in the study area. These findings are consistent with global studies on geogenic contamination in regions with gypsum or evaporite deposits, such as India’s arid zones [66] and Libya’s coastal aquifers [29], where high TDS is linked to evaporite dissolution and salinity.
Also, the relatively low recharge compared with the studied volcanic aquifers, and the high seasonal variability of the recharging period (short recharging and long dry), lowers the potential of the shallow shale–marl–limestone intercalation aquifer during the later dry months.
The deepest aquifer of the Jifarah case study area, the Ras Hamia formation, has very low potential, according to the Offodile [57] classification, while the Al Aziziyah aquifer has high potential in the eastern and western part, and moderate potential in the center. Abu Shaybah, Lower Miocene, and Upper Miocene–Pliocene–Quaternary aquifers have, on average, moderate potential. The Mesozoic sandstone of Mekelle has moderate potential, while its similar era formation of Ras Hamia in Jifarah Plain has very low potential. Dominantly, limestone rock aquifers of both case study areas, limestone–marl in Mekelle and limestone–dolomite–marl Al Aziziyah aquifer in Jifarah Plain, are high potential aquifers, where karstification might play a role in increasing transmissivities. However, the high TDS values are quality concerns.
The high nitrate concentrations observed in some of the shallow hard rock aquifers in the studies have also been noted in wells of villages, towns, and agricultural fields, as seen in the studies of Lake Tana and Beles Basins. Similarly, Lapworth et al. [5] observed high nitrate concentrations in the towns of Sub-Saharan countries, for which municipal wastes and agricultural additives are the main causes. Aquifer boundaries are usually defined based on the surface topography; hence, inter-basin groundwater transfer (IGF) is seldom taken into account in most groundwater studies [67]. Investigating IGF holds significance due to its implications for watershed hydrology, water quality, ecology, water balance, and management [68]. IGF plays a crucial role in shaping our comprehension of groundwater flow systems, impacting factors such as aquifer dimensions, residence times, boundary conditions, and sustainability in relation to abstraction practices [69]. An IGF, as observed from Lake Tana Basin to Beles Basin, has also been seen by the study of Kahsay [28] in the Mekelle area. Groundwater is inferred as being exchanged between the aquifers of the Ilala and Aynalem catchments through synthetic faults connecting these adjacent catchments; similar geological structures are found to be a way of groundwater transfer from Lake Tana Basin to Beles Basin. The presence of IGF emphasizes the interconnected nature of groundwater systems, transcending basin boundaries. Assessing and considering IGF as groundwater balance and potential assessment, and thus management plans, is crucial for ensuring sustainable utilization of groundwater resources, especially in regions where regional flow dynamics significantly influence groundwater availability. Previous studies, such as by Han et al. [70], Frisbee et al. [71], and Genereux et al. [68], have similarly emphasized the importance of IGF in understanding groundwater systems, which can play a critical role in overall water resource management.
The primary limitation of this study lies in the lack of data at the required spatial scale. The significant spatial variation of key parameters, both within and across the case study areas, highlights the need for more extensive data collection to improve the understanding of these parameters across the aquifers. Finer spatial scale data on transmissivity, recharge, and water quality samples could yield a different range of values for the various aquifers. While this study has maximized available data by incorporating both the published and the unpublished literature, the interpretation and conclusions drawn are still subject to the constraints imposed by the data limitations.
6. Conclusions
This study investigates the groundwater aquifer potential in five African case study areas, encompassing volcanic, sedimentary, and partially metamorphic hard rock aquifers. The assessment of recharge, transmissivity, and water quality forms the basis of the qualitative evaluation. The variability in recharge rates, hydraulic transmissivities, and water quality highlights the need for site-specific assessments and management strategies. This study also highlights a unique phenomenon of deep groundwater flow from Lake Tana to Beles Basins and between the Ilala and Aynalem catchments in the Mekelle area, illustrating the dependency of groundwater potential on such distinct occurrences. The findings indicate that hard rock aquifers serve as the primary groundwater source in volcanic regions where weathered/fractured basalt aquifers exhibit high potential, while pyroclastic aquifers typically demonstrate lower potential. High fluoride levels present a water quality concern in Mount Meru aquifers, as is noted in the Rift Valley region of many other African countries. Among the sedimentary aquifer types studied in the Mekelle area and Jifarah Plain, limestone, intercalated with marl or dolomite, emerges as a high-potential aquifer, but high mineralization and high sulfate may be water quality issues.
This study of Beles Basin offers a fresh perspective on groundwater potential assessment by emphasizing the importance of considering groundwater influx from neighboring basins alongside catchment-level recharge and discharge dynamics. It challenges the conventional notion that groundwater within confined or unconfined aquifers of a catchment or basin remains solely within its respective aquifers. This insight is crucial for refining water balance models and improving water resource management by accounting for groundwater transfer between adjacent basins.
Finally, while this study provides valuable insights, data limitations remain a key challenge, particularly in terms of spatial scale. The significant spatial variation in parameters like transmissivity, recharge, and water quality underscores the importance of collecting more fine-scale data to gain a deeper understanding of aquifer behavior. This study, by integrating available published and unpublished data, contributes to the understanding of groundwater resources, but further research is needed to refine these findings and enhance groundwater management strategies.
Author Contributions
Conceptualization, K.W., A.Y., G.B. (George Bennett), N.A., T.G. and F.N.; methodology, K.W., G.B. (George Bennett), N.A., T.G., G.B. (Gebremedhin Berhane), F.N., A.S.B. and A.Y.; software, G.B. (George Bennett), N.A., T.G., F.N., A.S.B., A.Y. and A.B.; validation, K.W., G.B. (George Bennett), M.H., A.H. and A.Y.; formal analysis, K.W., A.Y., G.B. (George Bennett), N.A., T.G., G.B. (Gebremedhin Berhane), F.N. and A.S.B.; investigation, K.W., G.B. (George Bennett), N.A. and T.G.; resources, K.W.; data curation, G.B. (George Bennett), N.A., T.G., F.N., A.S.B., G.B. (Gebremedhin Berhane) and A.Y.; writing—original draft preparation, K.W., G.B. (George Bennett), N.A., T.G., G.B. (Gebremedhin Berhane), F.N., A.S.B. and A.Y.; writing—review and editing, K.W., A.Y. and A.B.; visualization, A.B., A.Y., G.B. (George Bennett), M.H., T.G., F.N., A.S.B. and N.A.; supervision, K.W., N.A., T.G. and F.N.; project administration, K.W.; funding acquisition, K.W. All authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript.
Funding
Parts of this research were funded by VLIR-UOS, the university development cooperation branch of the Flemish Interuniversity Council, through various projects with Ghent University and the Global South partners.
Data Availability Statement
Data are available with respective authors.
Acknowledgments
We express our gratitude to the Flemish Interuniversity Council-University Development Cooperation (VLIR-UOS) for providing funding support for the field and laboratory work conducted in the case studies. This support was facilitated through VLIR-UOS TEAM projects with Ghent University and partner universities in the Global South, NSS (North-South-South) projects, and Short Initiative (SI) projects. Additionally, we extend our appreciation to Jill Van Reybrouck for executing the water analyses at the Laboratory for Applied Geology and Hydrogeology, Ghent University.
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare no conflicts of interest.
References
- Carter, R.C.; Parker, A. Climate Change, Population Trends and Groundwater in Africa Climate Change, Population Trends and Groundwater in Africa. Hydrol. Sci. J. 2009, 54, 676–689. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rosegrant, M.W.; Perez, N.D. Water Resources Development in Africa: A Review and Synthesis of Issues, Potentials, and Strategies for the Future; International Food Policy Research Institute: Washington, DC, USA, 1997. [Google Scholar]
- Gaye, C.B.; Tindimugaya, C. Review: Challenges and Opportunities for Sustainable Groundwater Management in Africa. Hydrogeol. J. 2019, 27, 1099–1110. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Macdonald, A.M.; Davies, J. A Brief Review of Groundwater for Rural Water Supply in Sub-Saharan; Technical Report WC/00/33 for Overseas Geology Series; BGS International: Nottingham, UK, 2000. [Google Scholar]
- Lapworth, D.J.; Nkhuwa, D.C.W.; Pedley, S.; Stuart, M.E. Urban Groundwater Quality in Sub-Saharan Africa: Current Status and Implications for Water Security and Public Health. Hydrogeol. J. 2017, 25, 1093–1116. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tessema, A.; Nzotta, U.; Chirenje, E. Assessment of Groundwater Potential in Fractured Hard Rocks around Vryburg, North West Province, South Africa; Report; Water Research Commission: Pretoria, South Africa, 2014. [Google Scholar]
- Kebede, S. Groundwater in Ethiopia: Features, Numbers and Opportunities; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2012; ISBN 9783642303913. [Google Scholar]
- Taylor, R.G.; Koussis, A.D.; Tindimugaya, C. Groundwater and Climate in Africa—A Review. Hydrol. Sci. J. 2009, 54, 655–664. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Srinivasa Rao, Y.; Jugran, D.K. Delineation of Groundwater Potential Zones and Zones of Groundwater Quality Suitable for Domestic Purposes Using Remote Sensing and GIS. Hydrol. Sci. J. 2003, 48, 821–833. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abbate, E.; Bruni, P.; Peter, M.; Delmer, C.; Ada, M.; Hagos, M.; Bedri, O.; Rook, L.; Sagri, M.; Libsekal, Y. The East Africa Oligocene Intertrappean Beds: Regional Distribution, Depositional Environments and Afro/Arabian Mammal Dispersals. J. Afr. Earth Sci. 2014, 99, 463–489. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Prave, A.R.; Bates, C.R.; Donaldson, C.H.; Toland, H.; Condon, D.J.; Mark, D.; Raub, T.D. Geology and Geochronology of the Tana Basin, Ethiopia: LIP Volcanism, Super Eruptions and Eocene–Oligocene Environmental Change. Earth Planet. Sci. Lett. 2016, 443, 1–8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pik, R.; Marty, B.; Carignan, J.; Lavé, J. Stability of the Upper Nile Drainage Network (Ethiopia) Deduced from (U-Th)/He Thermochronometry: Implications for Uplift and Erosion of the Afar Plume Dome. Earth Planet. Sci. Lett. 2003, 215, 73–88. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chorowicz, J.; Collet, B.; Bonavia, F.F.; Mohr, P.; Parrot, J.F.; Korme, T. The Tana Basin, Ethiopia: Intra-Plateau Uplift, Rifting and Subsidence. Tectonophysics 1998, 295, 351–367. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zanettin, B. Evolution of the Ethiopian Volcanic Province. Accad. Naz. Lincei 1992, 1, 155–181. [Google Scholar]
- Mohr, P.A. Ethiopian Rift and Plateaus: Some Volcanic Petrochemical Differences. J. Geophys. Res. 1971, 76, 1967–1984. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ghiglieri, G.; Balia, R.; Oggiano, G.; Pittalis, D. Prospecting for Safe (Low Fluoride) Groundwater in the Eastern African Rift: The Arumeru District (Northern Tanzania). Hydrol. Earth Syst. Sci. 2010, 14, 1081–1091. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wilkinson, P.; Downie, C.; Cattermole, P.J.; Mitchell, J.G. Arusha, Geological Survey of Tanzania; Quarter Degree Sheet 55; Royal Museum for Central Africa: Tervuren, Belgium, 1983. [Google Scholar]
- Bennett, G.; Van Reybrouck, J.; Shemsanga, C.; Kisaka, M.; Tomašek, I.; Fontijn, K.; Kervyn, M.; Walraevens, K. Hydrochemical Characterisation of High-Fluoride Groundwater and Development of a Conceptual Groundwater Flow Model Using a Combined Hydrogeological and Hydrochemical Approach on an Active Volcano: Mount Meru, Northern Tanzania. Water 2021, 13, 2159. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pik, R.; Deniel, C.; Coulon, C.; Yirgu, G.; Hofmann, C.; Ayalew, D. The Northwestern Ethiopian Plateau Flood Basalts: Classification and Spatial Distribution of Magma Types. J. Volcanol. Geotherm. Res. 1998, 81, 91–111. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Belay, A.S.; Yenehun, A.; Nigate, F.; Nigussie, W.; Tilahun, S.A.; Dessie, M.; Moges, M.M.; Chen, M.; Adgo, E.; Fentie, D.; et al. Investigation of Interbasin Groundwater Flow Using Multiple Approaches: The Case of the Tana and Beles Basins, Ethiopia. Hydrogeol. J. 2023, 31, 2251–2270. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abbate, E.; Bruni, P.; Sagri, M. Geology of Ethiopia: A Review and Geomorphological Perspectives. In Landscapes and Landforms of Ethiopia; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2015; ISBN 9789401780261. [Google Scholar]
- Bennett, G.; Van Camp, M.; Shemsanga, C.; Kervyn, M.; Walraevens, K. Delineation of the Aquifer Structure and Estimation of Hydraulic Properties on the Flanks of Mount Meru, Northern Tanzania. J. Afr. Earth Sci. 2022, 196, 104673. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ayenew, T.; Demlie, M.; Wohnlich, S. Hydrogeological Framework and Occurrence of Groundwater in the Ethiopian Aquifers. J. Afr. Earth Sci. 2008, 52, 97–113. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alemu, T.; Abdelsalam, M.G.; Dawit, E.L.; Atnafu, B.; Mickus, K.L. The Paleozoic and Mesozoic Mekele Sedimentary Basin in Ethiopia: An Example of an Exhumed IntraCONtinental Sag (ICONS) Basin. J. Afr. Earth Sci. 2018, 143, 40–58. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Küster, D.; Dwivedi, S.B.; Kabeto, K.; Mehari, K.; Matheis, G. Petrogenetic Reconnaissance Investigation of Mafic Sills Associated with Flood Basalts, Mekelle Basin, Northern Ethiopia: Implications for Ni–Cu Exploration. J. Geochem. Explor. 2005, 85, 63–79. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bosellini, A.; Russo, A.; Fantozzi, P.L.; Getaneh, A.; Tadesse, S. The Mesozoic Succession of the Mekele Outlier (Tigre Province, Ethiopia). Mem. DELLA Soc. Ital. 1997, 49, 95–116. [Google Scholar]
- TAHAL. Mekelle Water Supply Development Project Groundwater Assessment for Additional Well Fields; Technical Report; TAHAL: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 2007. [Google Scholar]
- Kahsay, H. Groundwater Recharge Estimation, Source and Flow System Identification Using Stable Isotope Hydrogeochemistry and Hydrogeochemical Modeling, Case of Mekelle Area, Tigray, Northern Ethiopia. Ph.D. Thesis, Mekelle University, Mekelle, Ethiopia, 2023. [Google Scholar]
- Alfarrah, N.; Berhane, G.; Bakundukize, C.; Walraevens, K. Degradation of Groundwater Quality in Coastal Aquifer of Sabratah. Environ. Earth Sci. 2017, 76, 664. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bierkens, M.F.P.; Wada, Y. Non-Renewable Groundwater Use and Groundwater Depletion: A Review. Environ. Res. Lett. 2019, 14, 063002. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Healy, R.W.; Cook, P.G. Using Groundwater Levels to Estimate Recharge. Hydrogeol. J. 2002, 10, 91–109. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Somaratne, N.; Smettem, K.R.J. Theory of the Generalized Chloride Mass Balance Method for Recharge Estimation in Groundwater Basins Characterised by Point and Diffuse Recharge. Hydrol. Earth Syst. Sci. Discuss. 2014, 11, 307–332. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bakundukize, C.; Van Camp, M.; Walraevens, K. Estimation of Groundwater Recharge in Bugesera Region (Burundi) Using Soil Moisture Budget Approach. Geol. Belg. 2011, 14, 85–102. [Google Scholar]
- Arnold, J.G.; Allen, P.M.; Muttiah, R.; Bernhardt, G. Automated Base Flow Separation and Recession Analysis Techniques. Groundwater 1995, 33, 1010–1018. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Batelaan, O.; De Smedt, F. GIS-Based Recharge Estimation by Coupling Surface–Subsurface Water Balances. J. Hydrol. 2007, 337, 337–355. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Long, D.; Longuevergne, L.; Scanlon, B.R. Global Analysis of Approaches for Deriving Total Water Storage Changes from GRACE Satellites. Water Resour. Res. 2015, 54, 2574–2594. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rodell, M.; Velicogna, I.; Famiglietti, J.S. Satellite-Based Estimates of Groundwater Depletion in India. Nature 2009, 460, 999–1002. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bouwer, H.; Rice, R.C. A Slug Test for Determining Hydraulic Conductivity of Unconfined Aquifers with Completely or Partially Penetrating Wells. Water Resour. Res. 1976, 12, 423–428. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Papadopulos, I.S.; Cooper, H.H. Drawdown in a Well of Large Diameter. WATER Resour. Res. 1967, 3, 241–244. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moench, A.F. Flow to a Well of Finite Diameter in a Homogeneous, Anisotropic Water Table Aquifer. Water Resour. Res. 1997, 33, 1397–1407. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Theis, C.V. The Relation between the Lowering of the Piezometric Surface and the Rate and Duration of Discharge of a Well Using Ground-Water Storage. Am. Geophys. Union 1935, 16, 519–524. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Neuman, S.P. Effect of Partial Penetration on Flow in Unconfined Aquifers Considering Delayed Gravity Response. Water Resour. Res. 1974, 10, 303–312. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hantush, M.S.; Jacob, C. Non-Steady Radial Flow in an Infinite Leaky Aquifer. Eos Trans. Am. Geophys. Union 1955, 36, 95–100. [Google Scholar]
- Bourdet, D.; Ayoub, J.A.; Pirard, Y.M. Use of Pressure Derivative in Well-Test Interpretation. SPE Form. Eval. 1989, 4, 293–302. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Razack, M.; Huntley, D. Assessing Transmissivity from Specific Capacity in a Large and Heterogeneous Alluvial Aquifer. Groundwater 1991, 29, 856–861. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nigate, F.; Yenehun, A.; Belay, A.S.; Van Camp, M.; Walraevens, K. Hydrogeochemical Processes and Groundwater Evolution in Complex Volcanic Highlands and Alluvio-Lacustrine Deposits (Upper Blue Nile), Ethiopia. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 2023, 30, 63953–63974. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bennett, G.; Van Reybrouck, J.; Shemsanga, C.; Kisaka, M.; Tomašek, I.; Fontijn, K.; Kervyn, M.; Walraevens, K. Identification of Low Fluoride Areas Using Conceptual Groundwater Flow Model and Hydrogeochemical System Analysis in the Aquifer System on the Flanks of an Active Volcano: Mount Meru, Northern Tanzania. Sci. Total Environ. 2022, 814, 152682. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yenehun, A.; Dessie, M.; Nigate, F.; Belay, A.S.; Azeze, M.; Van Camp, M.; Taye, D.F.; Kidane, D.; Adgo, E.; Nyssen, J.; et al. Spatial and Temporal Simulation of Groundwater Recharge and Cross-Validation with Point Estimations in Volcanic Aquifers with Variable Topography. J. Hydrol. Reg. Stud. 2022, 42, 101142. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gonçalvès, J.; Séraphin, P.; Stieglitz, T.; Chekireb, A.; Hamelin, B.; Deschamps, P. Coastal Aquifer Recharge and Groundwater–Seawater Exchanges Using Downscaled GRACE Data: Case Study Of the Djeffara Plain (Libya–Tunisia). C. R. Géosci. 2021, 353, 297–318. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nigate, F.; Van Camp, M.; Kebede, S.; Walraevens, K. Hydrologic Interconnection Between the Volcanic Aquifer and Springs, Lake Tana Basin on the Upper Blue Nile. J. Afr. Earth Sci. 2016, 121, 154–167. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- WWDSE. Evaluation of Aynalem Well Field and Selection of Additional Prospective Boreholes for Mekelle Town Water Supply Source. In Volume II: Evaluation of Groundwater Potential; Study Report; WWDSE: Addis Ababa, Ethiopia, 2007. [Google Scholar]
- Kruseman, G.P.; Floegel, H. Hydrogeology of the Jifarah Plain, NW-Libya. In The Geology of Libya; Salem, M., Pusrewil, M., Eds.; Al Fateh University: Tripoli, Libya, 1978; pp. 763–777. [Google Scholar]
- Pallas, P. Water Resources of the Socialist People’s Libyan Arab Jamahiriya. In The Geology of Libya, Proceedings of the Second Symposium on the Geology of Libya, Tripoli, Libya, 16–21 September 1978; Academic Press: Tripoli, Libya, 1980; pp. 539–593. [Google Scholar]
- Stuyfzand, P. A New Hydrochemical Classification of Water Types: Principles and Application to the Coastal Dunes Aquifer System of the Netherlands. In Proceedings of the 9th Salt Water Intrusion Meeting, Delft, The Netherlands, 12–16 May 1986; pp. 12–16. [Google Scholar]
- Yenehun, A.; Nigate, F.; Belay, A.S.; Desta, M.T.; Van Camp, M.; Walraevens, K. Groundwater Recharge and Water Table Response to Changing Conditions for Aquifers at Different Physiography: The Case of a Semi-Humid River Catchment, Northwestern Highlands of Ethiopia. Sci. Total Environ. 2020, 748, 142243. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Markovich, K.H.; Manning, A.H.; Condon, L.E. Mountain-Block Recharge: A Review of Current Understanding. Water Resour. Res. 2019, 55, 8278–8304. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Offodile, M.E. The Occurrence and Exploitation of Groundwater in Nigeria Basement Rocks. J. Min. Geol. 1983, 2, 131–146. [Google Scholar]
- Kwami, I.A.; Ishaku, J.M.; Mukkafa, S.; Haruna, A.I.; Ankidawa, B.A. Delineation of Aquifer Potential Zones Using Hydraulic Parameters in Gombe and Environs, North-Eastern, Nigeria. Heliyon 2019, 5, e01927. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jalludin, M.; Razack, M. Assessment of Hydraulic Properties of Sedimentary and Volcanic Aquifer Systems under Arid Conditions in the Republic of Djibouti (Horn of Africa). Hydrogeol. J. 2004, 12, 159–170. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Raji, W.O.; Abdulkadir, K.A. Evaluation of Groundwater Potential of Bedrock Aquifers in Geological Sheet 223 Ilorin, Nigeria, Using Geo-Electric Sounding. Appl. Water Sci. 2020, 10, 220. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shaji, E.; Sarath, K.V.; Santosh, M.; Krishnaprasad, P.K.; Arya, B.K.; Babu, M.S. Fluoride Contamination in Groundwater: A Global Review of the Status, Processes, Challenges, and Remedial Measures. Geosci. Front. 2024, 15, 101734. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Malago, J.; Makoba, E.; Muzuka, A.N.N. Fluoride Levels in Surface and Groundwater in Africa: A Review. Am. J. Water Sci. Eng. 2017, 3, 1–17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Coetsiers, M.; Kilonzo, F.; Walraevens, K. Hydrochemistry and Source of High Fluoride in Groundwater of the Nairobi Area, Kenya. Hydrol. Sci. J. 2008, 53, 1230–1240. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Van den Broeck, S. The Sustainability of the Aynalem Well Field, Mekelle Ethiopia: A Hydrogeological Study. Master’s Thesis, Ghent University, Ghent, Belgium, 2019. [Google Scholar]
- Lear, D. Hydrogeology of the Aynalem Well Field, Tigray, Northern Ethiopia: Assessment and Modeling. Master’s Thesis, Ghent University, Ghent, Belgium, 2020. [Google Scholar]
- Anoubam, D.; Madhuri, S.; Tirumalesh, S.R. Evaluation of Groundwater Quality and Suitability for Irrigation and Drinking Purposes in Southwest Punjab, India Using Hydrochemical Approach. Appl. Water Sci. 2017, 7, 3137–3150. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pellicer-Martínez, F.; Martínez-Paz, J.M. Assessment of Interbasin Groundwater Flows between Catchments Using a Semi-Distributed Water Balance Model. J. Hydrol. 2014, 519, 1848–1858. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Genereux, D.P.; Jordan, M. Interbasin Groundwater Flow and Groundwater Interaction with Surface Water in a Lowland Rainforest, Costa Rica: A Review. J. Hydrol. 2006, 320, 385–399. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nelson, S.T.; Mayo, A.L. The Role of Interbasin Groundwater Transfers in Geologically Complex Terranes, Demonstrated by the Great Basin in the Western United States. Hydrogeol. J. 2014, 22, 807–828. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Han, P.; Wang, X.; Zhou, Y.; Yang, Z.; Wan, L.; Chen, J.; Jiang, X. Three-Dimensional Inter-Basin Groundwater Flow Toward a Groundwater-Fed Stream: Identification, Partition, and Quantification. J. Hydrol. 2024, 629, 130524. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Frisbee, M.D.; Tysor, E.H.; Stewart-Maddox, N.S.; Tsinnajinnie, L.M. Is There a Geomorphic Expression of Interbasin Groundwater Flow in Watersheds? Interactions between Interbasin Groundwater Flow, Springs, Streams, and Geomorphology. Geophys. Res. Lett. 2016, 43, 1158–1165. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).