Soil–Plant Carbon Pool Variations Subjected to Agricultural Drainage in Xingkai Lake Wetlands
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Study Area
2.2. Soil Sample Collections and Laboratory Analyses
2.3. Statistical Analysis
3. Results
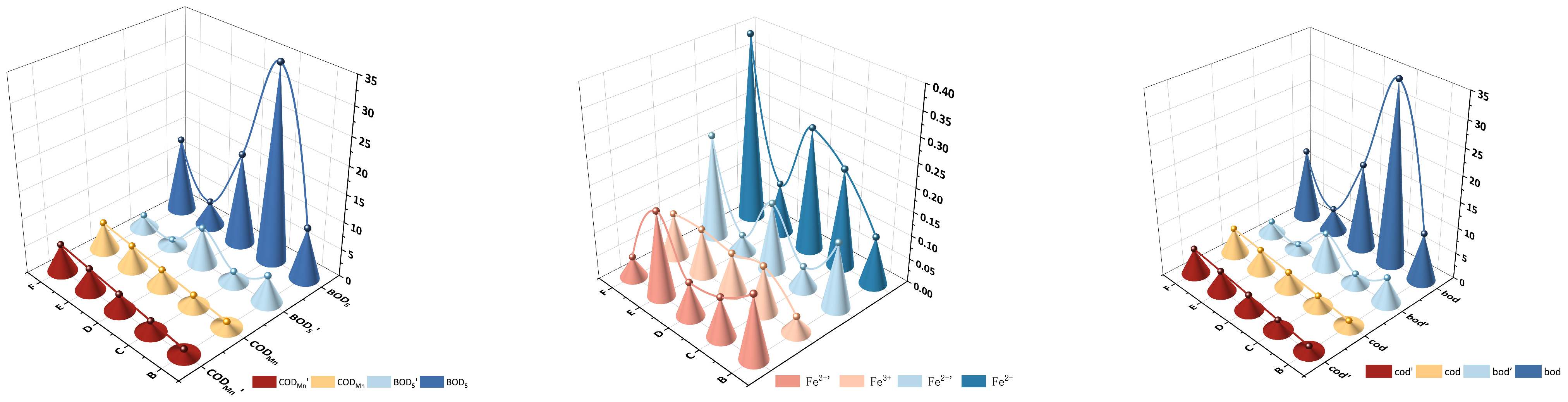
3.1. The Variations in Surface Water Quality Characteristics Across Wetlands with Different Drainage Duration
3.2. Variation in Plant Biomass Across Wetlands with Different Drainage Duration
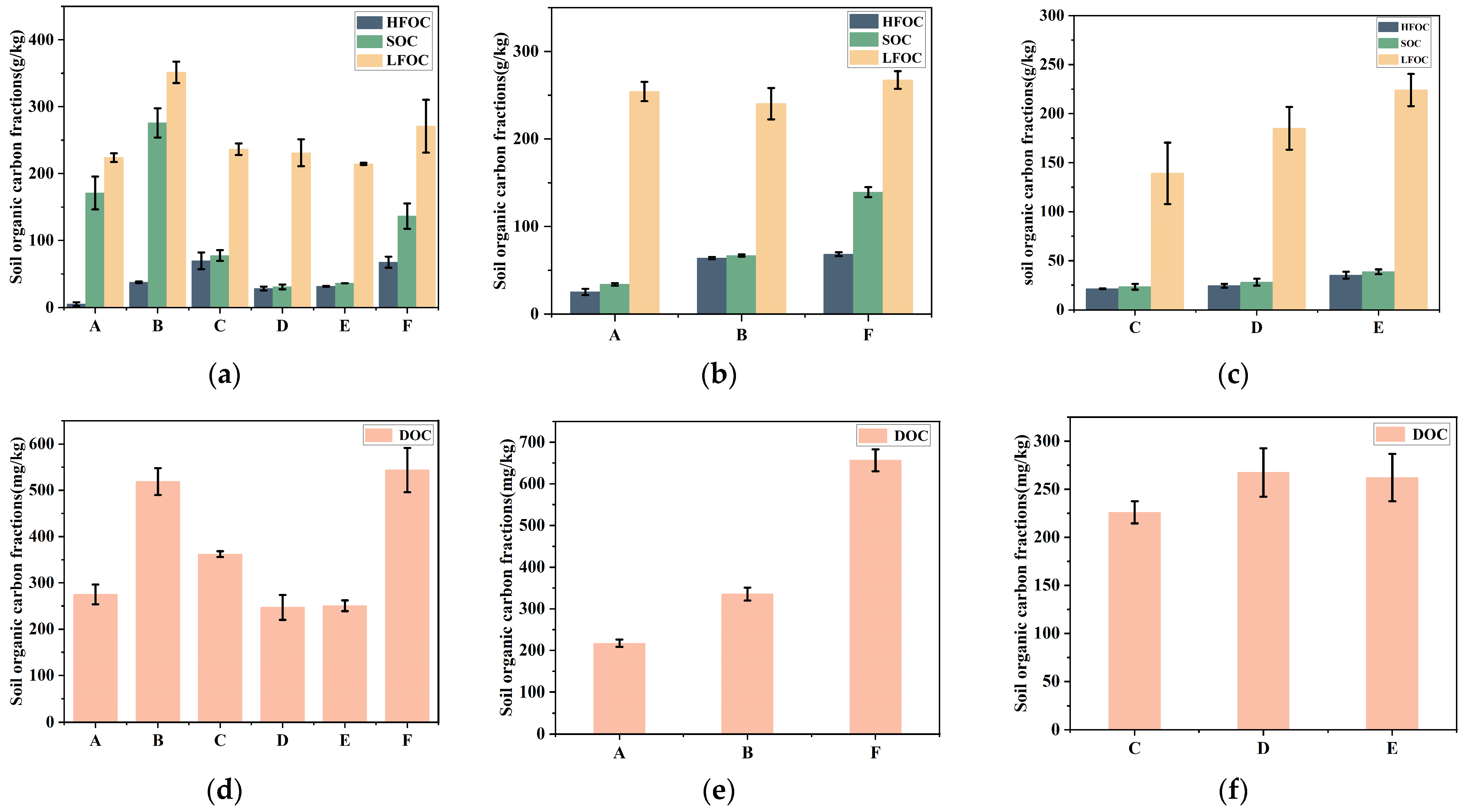
3.3. Changes in Organic Carbon Content in the Topsoil (0–20 cm) of Dominant Plant Communities Across Varying Water Recession Durations
3.3.1. Variation in Soil Physicochemical Parameters
3.3.2. Dynamic Changes in the Organic Carbon Components of Surface Soil in Wetland Plants
3.3.3. Temporal Dynamics of Microbial Biomass Variations
3.3.4. Variation in the Concentrations of Total Iron (TFe) and Available Iron (Afe) in the Soil
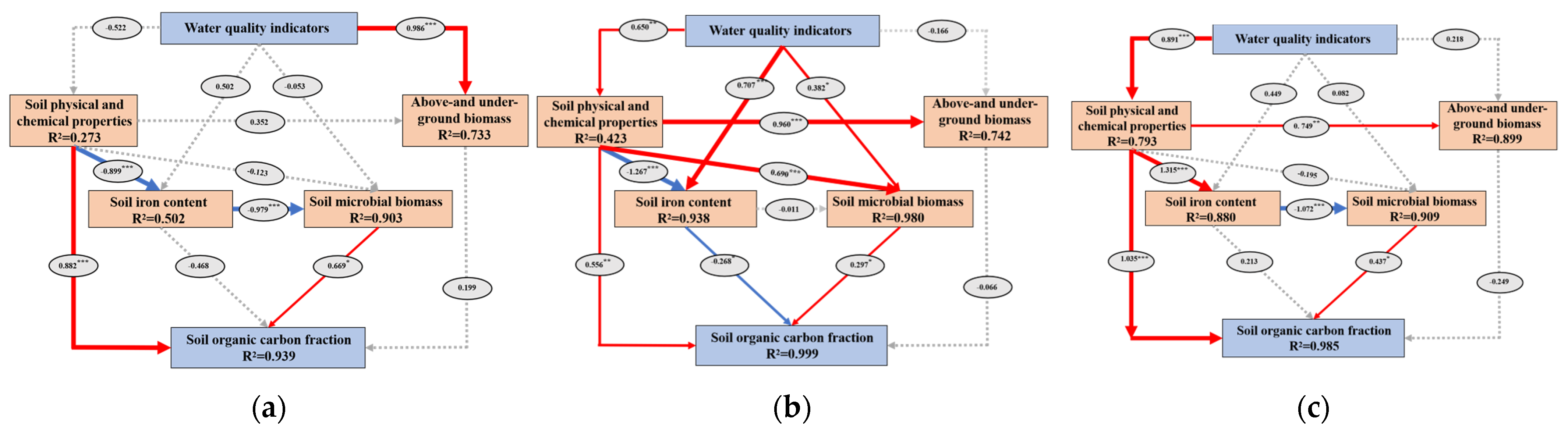
3.4. Correlation Analysis of Soil Parameters for the Three Plant Species During the Water Recession Process
3.5. Quantitative Analysis of the Soil Organic Carbon Fractions Associated with the Three Plant Species During the Water Recession Process
4. Discussion
4.1. Response of Plant Biomass Characteristics to Rice Paddy Water Withdrawal
4.2. Response of Soil Properties Characteristics to Rice Paddy Water Withdrawal
4.3. Effects of Plant Biomass and Soil Properties on Soil Organic Carbon Component Changes
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Dargie, G.C.; Lewis, S.L.; Lawson, I.T.; Page, S.E.; Bocko, Y.E. Age, extent and carbon storage of the central Congo Basin peatland complex. Nature 2017, 542, 86–90. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Post, W.M.; Emanue, W.R.; Zinke, P.J. Soil carbon pools and world life zones. Nature 1982, 298, 156–159. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mitra, S.; Wassmann, R.; Vlek, P.L.G. An appraisal of global wetland area and its organic carbon stock. Curr. Sci. 2005, 88, 25–35. [Google Scholar]
- Deng, W.; Hu, J. Development of Wetland Hydrology Research and Key Scientific Issues. Wetl. Sci. 2003, 1, 12–20. [Google Scholar]
- Kopol, A.R.; Ahn, C.; Noe, G.B. Richness, biomass, and nutrient content of a wetland macrophyte community affect soil nitrogen cycling in a diversity-ecosystem functioning experiment. Ecol. Eng. 2016, 95, 252–265. [Google Scholar]
- Bai, C.B. A review of research on the impact of global climate change on wetland ecological hydrology. Sci. Technol. Innov. 2014, 10, 29. [Google Scholar]
- Wantzen, K.M.; Rothhaupt, K.O.; Mortl, M.; Cantonati, M.; László, G.T.; Fischer, P. Ecological effects of water-level fluctuations in lakes: An urgent issue. Hydrobiologia 2008, 613, 1–4. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shen, R.C.; Lan, Z.C.; Fang, C.G.; Chen, J.K. The dikes of the sub-lakes change soil carbon cycle in the littoral wetland in Poyang Lake. J. Lake Sci. 2018, 30, 1260–1270. [Google Scholar]
- Wei, Y.; Lu, H.; Wang, J.; Wang, X.; Sun, J. Dual Influence of Climate Change and Anthropogenic Activities on the Spatiotemporal Vegetation Dynamics over the Qinghai-Tibetan Plateau from 1981 to 2015. Earth’s Future 2022, 10, e2021EF002566. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shi, J.; Yang, L.; Liao, Y.; Li, J.W.; Jiao, S.; Shangguan, Z.P.; Deng, L. Soil labile organic carbon fractions mediate microbial community assembly processes during long-term vegetation succession in a semiarid region. iMeta 2023, 2, e142. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kannenberg, S.A.; Anderegg, W.R.L.; Barnes, M.L.; Dannenberg, M.P.; Knapp, A.K. Dominant role of soil moisture in mediating carbon and water fluxes in dryland ecosystems. Nat. Geosci. 2024, 17, 38–43. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiang, M.D.; Li, H.L.; Zhang, W.; Liu, J.B.; Zhang, Q. Effects of climate change and grazing on the soil organic carbon stock of alpine wetlands on the Tibetan Plateau from 2000 to 2018. Catena 2024, 238, 107870. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Y.H.; Liu, C.; Fu, Z.Y.; Chen, H.S.; He, C.H.; Wang, K.L.; Li, P. Optical properties and molecular compositions of dissolved organic matter in multiple runoff components during rainfalls on the karst hillslope. Water Res. 2024, 257, 121664. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Su, X.L.; Su, X.; Zhou, G.Y.; Du, Z.G.; Yang, S.C.; Ni, M.Y.; Qin, H.; Huang, Z.Q.; Zhou, X.H.; Deng, J. Drought accelerated recalcitrant carbon loss by changing soil aggregation and microbial communities in a subtropical forest. Soil Biol. Biochem. 2020, 148, 107898. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, X.Q.; Liu, H.R.; Zhang, Y.S.; Chen, G.; Li, Z.H.; Zhang, M.C. Straw return drives soil microbial community assemblage to change metabolic processes for soil quality amendment in a rice-wheat rotation system. Soil Biol. Biochem. 2023, 185, 109131. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, X.Q.; Liu, H.R.; Zhang, Y.S.; Chen, G.; Li, Z.H.; Zhang, M.C. Effects of vegetation on soil temperature and water content: Field monitoring and numerical modelling. J. Hydrol. 2019, 571, 494–502. [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, Q.J.; Wang, Z.S.; Xia, S.X.; Zhang, G.S.; Li, S.X.; Yu, D.K.; Yu, X.B. Hydrologic-induced concentrated soil nutrients and improved plant growth increased carbon storage in a floodplain wetland over wet-dry alternating zones. Sci. Total Environ. 2022, 822, 153512. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Huang, Y.; Song, X.; Wang, Y.P.; Josep, G.C.; Luo, Y.Q.; Philippe, C.; Chen, A.P.; Hong, S.B.; Wang, Y.G.; Zhang, L.Z. Size, distribution, and vulnerability of the global soil inorganic carbon. Science 2024, 384, 233–239. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, J.Q.; Jiang, M.K.; Pei, J.M.; Fang, C.M.; Li, B.; Nie, M. Convergence of carbon sink magnitude and water table depth in global wetlands. Ecol. Lett. 2023, 26, 797–804. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fu, L.; Zhou, Y.M.; Liu, G.; Song, K.S.; Tao, H.; Zhao, F.R.; Li, S.J.; Shi, S.Q.; Shang, Y.X. Retrieval of Chla Concentrations in Lake Xingkai Using OLCI Images. Remote Sens. 2023, 15, 3809. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moore, J.M.; Klose, S.; Tabatabal, M.A. Soil microbial biomass carbon and nitrogen as affected by cropping systems. Biol. Fertil. Soils 2000, 31, 200–210. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tan, Z.; Lal, R.; Owens, L.; Izaurralde, R.C. Distribution of light and heavy fractions of soil organic carbon as related to land use and tillage practice. Soil Tillage Res. 2007, 92, 53–59. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Avgyan, A.; Runkle, B.R.K.; Kutzbach, L. Application of high-resolution spectral absorbance measurements to determine dissolved organic carbon concentration in remote areas. J. Hydrol. 2014, 517, 435–446. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, N.; Xin, H.N.; Lai, N.; Li, Y.F.; Lyu, C.X.; Geng, Q.L.; Duan, J.J.; Chen, S.H. Effects of different land-use methods on the organic carbon composition and soil microbial biomass carbon of farmland soil. Arid. Zone Res. 2014, 41, 1789–1796. [Google Scholar]
- Guo, W.W.; Huang, S.Z.; Huang, Q.; Leng, G.Y.; Mu, Z.X.; Han, Z.M.; Wei, X.T.; She, D.X.; Wang, H.Y.; Wang, Z.X. Drought trigger thresholds for different levels of vegetation loss in China and their dynamics. Agric. For. Meteorol. 2023, 331, 109349. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liao, L.; Wang, J.; Dijkstra, F.A.; Lei, S.L.; Zhang, L.; Wang, X.J.; Liu, G.B.; Zhang, C. Nitrogen enrichment stimulates rhizosphere multi-element cycling genes via mediating plant biomass and root exudates. Soil Biol. Biochem. 2024, 190, 109306. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, J.J.; Yang, C.; Liu, X.L.; Shao, X.Q. Inconsistent stoichiometry response of grasses and forbs to nitrogen and water additions in an alpine meadow of the Qinghai-Tibet Plateau. Agric. Ecosyst. Environ. 2019, 279, 178–186. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Deng, Q.; Hui, D.; Dennis, S.; Reddy, K.C. Responses of terrestrial ecosystem phosphorus cycling to nitrogen addition: A meta-analysis. Glob. Ecol. Biogeogr. 2017, 26, 713–728. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hou, S.L.; Hattenschwiler, S.; Yang, J.J.; Sistla, S.; Wei, H.W.; Zhang, Z.W.; Hu, Y.Y.; Wang, R.Z.; Cui, S.Y.; Lü, X.T.; et al. Increasing rates of long-term nitrogen deposition consistently increased litter decomposition in a semi-arid grassland. New Phytol. 2021, 229, 296–307. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Qin, W.K.; Feng, J.G.; Zhang, Q.F.; Yuan, X.; Ren, F.; Zhou, H.K.; Zhu, B. Different responses of priming effects in long-term nitrogen- and phosphorus-fertilized soils to exogenous carbon inputs. Plant Soil 2024, 500, 647–663. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hou, E.Q.; Luo, Y.Q.; Kuang, Y.W.; Chen, C.R.; Lu, X.K.; Jiang, L.F.; Luo, X.Z.; Wen, D.Z. Global meta-analysis shows pervasive phosphorus limitation of aboveground plant production in natural terrestrial ecosystems. Nat. Commun. 2020, 11, 637. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jiang, J.; Wang, Y.P.; Yang, Y.H.; Yu, M.X.; Wang, C.; Yan, J.H. Interactive effects of nitrogen and phosphorus additions on plant growth vary with ecosystem type. Plant Soil 2019, 440, 523–537. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tariq, A.; Graciano, C.; Sardans, J.; Zeng, F.J.; Hughes, A.C.; Ahmed, Z.; Ullah, A.; Ali, S.; Gao, Y.J.; Peñuelas, J. Plant root mechanisms and their effects on carbon and nutrient accumulation in desert ecosystems under changes in land use and climate. New Phytol. 2024, 242, 916–934. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, C.F.; Cai, Y.M.; Zhang, T.; He, T.B.; Li, J.; Li, X.Y.; Zhao, Q.X. Litter removal increases the plant carbon input to soil in a Pinus massoniana plantation. Eur. J. For. Res. 2022, 141, 833–843. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, Y.; Tilman, D.; Furey, G.; Lehman, C. Soil carbon sequestration accelerated by restoration of grassland biodiversity. Nat. Commun. 2019, 10, 718. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xiao, J.N.; Dong, S.K.; Shen, H.; Li, S.; Zhi, Y.L.; Mu, Z.Y.; Ding, C.X. Phosphorus addition promotes Nitrogen retention in alpine grassland plants while increasing N deposition. CATENA 2022, 210, 105887. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fang, H.J.; Geng, J.; Cheng, S.L.; Xu, M.; Lu, M.Z.; Yu, G.X.; Cao, Z.C. Effects of Nitrogen and Phosphorus Enrichment on Carbon Sequestration in Forest Soils: A Review. Acta Pedol. Sin. 2018, 56, 1–11. [Google Scholar]
- Terrer, C.; Jackson, R.B.; Prentice, I.C.; Keenan, T.F.; Kaiser, C.; Vicca, S.; Fisher, J.B.; Reich, P.B.; Stocker, B.D.; Hungate, B.A.; et al. Nitrogen and phosphorus constrain the CO2 fertilization of global plant biomass. Nat. Clim. Change 2019, 9, 684. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, X.L.; Sheng, Y.Z.; Wang, G.C.; Zhou, P.P.; Liao, F.; Mao, H.R.; Zhang, H.Y.; Qiao, Z.Y.; Wei, Y.Q. Spatiotemporal successions of N, S, C, Fe, and As cycling genes in groundwater of a wetland ecosystem: Enhanced heterogeneity in wet season. Water Res. 2024, 251, 121105. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, X.D.; Qiao, Y.N.; Zhou, G.Y. Controlling action of soil organic matter on soil moisture retention and its availability. Chin. J. Plant Ecol. 2011, 35, 1209–1218. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lepore, E.; Schmidt, O.; Fenton, O.; Tracy, S.; Bondi, G.; Wall, D.P. Traffic induced compaction and physical quality of grassland soil under different soil moisture deficits. Soil Tillage Res. 2024, 244, 106205. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, W.P.; Fornara, D.; Yang, H.; Yu, R.P.; Callaway, R.M.; Li, L. Plant litter strengthens positive biodiversity–ecosystem functioning relationships over time. Trends Ecol. Evol. 2023, 38, 473–484. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhao, T.; Jiang, Y.L.; Yan, H.; Huang, Y.M. Research advances on microbial function in soil ammonifying process. Chin. J. Appl. Environ. Biol. 2014, 20, 315–321. [Google Scholar]
- Hu, H.L.; Zhao, L.; Tan, W.B.; Wang, G.A.; Xi, B.D. Discrepant responses of soil organic carbon dynamics to nitrogen addition in different layers: A case study in an agroecosystem. Front. Agric. Sci. Eng. 2024, 11, 314–325. [Google Scholar]
- Sun, T.; Mao, X.L.; Han, K.F.; Wang, X.J.; Cheng, Q.; Liu, X.; Zhou, J.J.; Ma, Q.X.; Ni, Z.H.; Wu, L.H. Nitrogen addition increased soil particulate organic carbon via plant carbon input whereas reduced mineral−associated organic carbon through attenuating mineral protection in agroecosystem. Sci. Total Environ. 2023, 899, 165705. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lange, M.; Eisenhauer, N.; Chen, H.M.; Gleixner, G. Increased soil carbon storage through plant diversity strengthens with time and extends into the subsoil. Glob. Change Biol. 2023, 29, 2627–2639. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.; Jianming Wang, J.M.; Qu, M.J.; Shao, S.; Li, J.W. Soil fungal guilds as important integrators linking plant richness and carbon, nitrogen and phosphorus stocks in oasis–desert ecosystems. Soil Biol. Biochem. 2023, 177, 108930. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Han, B.; Geng, Y.Y.; Deng, Y.F.; Wang, Y.F.; Zhou, H.K.; Shao, X.Q.; Li, Z.W. Effects of Nitrogen Addition on Soil Phosphorus Fractions in an Alpine Meadow of Qinghai-Tibet Plateau. Acta Agrestia Sin. 2022, 30, 2721–2728. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, S.Q.; Song, M.H.; Wang, C.M.; Dou, X.M.; Wang, X.Q.; Li, X.Y. Mechanisms underlying soil microbial regulation of available phosphorus in a temperate forest exposed to long-term nitrogen addition. Sci. Total Environ. 2023, 904, 166403. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wu, W.C.; Wang, F.; Xia, A.Q.; Zhang, Z.J.; Wang, Z.S.; Wang, K.; Dong, J.F.; Li, T.; Wu, Y.B.; Che, R.X. Meta-analysis of the impacts of phosphorus addition on soil microbes. Agric. Ecosyst. Environ. 2022, 340, 108180. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiang, Y.Y.; Yang, X.D.; Ni, K.; Ma, L.F.; Shi, Y.Z.; Wang, Y.; Cai, Y.J.; Ma, Q.X.; Ruan, J.Y. Nitrogen addition reduces phosphorus availability and induces a shift in soil phosphorus cycling microbial community in a tea (Camellia sinensis L.) plantation. J. Environ. Manag. 2023, 342, 118207. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, X.L.; Chen, H.Y.H.; Chang, S.X. Meta-analysis shows that plant mixtures increase soil phosphorus availability and plant productivity in diverse ecosystems. Nat. Ecol. Evol. 2022, 6, 1112–1121. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Qiu, L.H.; He, J.H.; Yue, C.; Ciais, P.; Zheng, C.M. Substantial terrestrial carbon emissions from global expansion of impervious surface area. Nat. Commun. 2024, 15, 6456. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, F.; Wang, Z.H.; Hou, J.F.; Li, X.Q.; Wang, D.; Yang, W.Q. The changes in soil organic carbon stock and quality across a subalpine forest successional series. For. Ecosyst. 2024, 11, 100203. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, S.; Delgado-Baquerizo, M.; Ding, J.X.; Hu, H.; Huang, W.G.; Sun, Y.S.; Ni, H.W.; Kuang, Y.Y.; Yuan, M.M.; Zhou, J.Z.; et al. Intrinsic microbial temperature sensitivity and soil organic carbon decomposition in response to climate change. Glob. Change Biol. 2024, 30, e17395. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xiao, Y.; Huang, Z.G.; Li, Y.F.; Ling, Y.L.; Xiao, H.X. Dynamics Variation of Soil Labile Organic Carbon Fractions in Different Wetland Types of Dongting Lake under Seasonal Water Level Fluctuation. Sustainability 2021, 13, 13836. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Song, X.; Tan, T.; Lu, Y. Microscopic analyses of the reinforcement mechanism of plant roots in different morphologies on the stability of soil slopes under heavy rainfall. Catena 2024, 241, 108018. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, H.; Dai, Q.H.; Yan, Y.J.; He, J.; Yang, Y.; Zhang, Y.; Hu, Z.Y.; Meng, W.P.; Wang, C.Y. Litter input promoted dissolved organic carbon migration in karst soil. Appl. Soil Ecol. 2024, 202, 105606. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, K.; Zhu, J.J.; Zhang, W.W.; Zhang, Q.; Lu, D.L.; Zhang, Y.K.; Zheng, X.; Xu, S.; Wang, G.G. Litter decomposition and nutrient release from monospecific and mixed litters: Comparisons of litter quality, fauna and decomposition site effects. J. Ecol. 2022, 110, 1673–1686. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Feng, J.G.; He, K.Y.; Zhang, Q.F.; Han, M.G.; Zhu, B. Changes in plant inputs alter soil carbon and microbial communities in forest ecosystems. Glob. Change Biol. 2022, 28, 3426–3440. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dong, J.Y.; Wang, W.; Zhao, D.; Zhang, C.; Fang, J.H.; Wang, L.F.; Zhang, Q.Z.; Liu, J. A novel organic carbon accumulation mechanism in croplands in the Yellow River Delta, China. Sci. Total Environ. 2022, 806, 150629. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, F.F.; Tao, Y.R.; Yang, S.C.; Cao, W.Z. Warming and flooding have different effects on organic carbon stability in mangrove soils. J. Soils Sediments 2024, 24, 60–69. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Q.; Liu, J.L.; Liu, H.F.; Liang, L.Q.; Cai, Y.P.; Wang, X.; Li, C.H. Vegetation dynamics under water-level fluctuations: Implications for wetland restoration. J. Hydrol. 2020, 581, 124418. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liao, C.; Long, C.Y.; Zhang, Q.; Cheng, X.L. Stronger effect of litter quality than micro-organisms on leaf and root litter C and N loss at different decomposition stages following a subtropical land use change. Funct. Ecol. 2022, 36, 896–907. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Patoine, G.; Eisenhauer, N.; Cesarz, S.; Phillips, H.R.P.; Xu, X.F.; Zhang, L.H.; Guerra, C.A. Drivers and trends of global soil microbial carbon over two decades. Nat. Commun. 2022, 13, 4195. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, S.E.; Plaza, C.; Ochoa-Hueso, R.; Trivedi, C.; Wang, J.T.; Trivedi, P.; Zhou, G.Y.; Piñeiro, J.; Martins, C.S.C.; Singh, B.K.; et al. Litter and soil biodiversity jointly drive ecosystem functions. Glob. Change Biol. 2023, 29, 6276–6285. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, D.; Xiao, X.; Sun, B.; Liang, Y.T. Co-occurrence network of bacterial communities in mollisol soils under increasing hydrothermal conditions. Acta Microbiol. Sin. 2021, 61, 1715–1727. [Google Scholar]
- Huang, X.Y.; Li, Y.X.; Lin, H.Y.; Wen, X.T.; Liu, J.; Yuan, Z.F.; Fu, C.; Zheng, B.F.; Gong, L.Q.; Zhan, H.Y.; et al. Flooding dominates soil microbial carbon and phosphorus limitations in Poyang Lake wetland, China. CATENA 2023, 232, 107468. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, Y.Q.; Zou, D.S.; Wang, A.D.; Zou, J.C.; Zheng, Z.G. Effects of rice-fish integrated farming on soil nutrients and enzyme activities under long-term flooding. Res. Agric. Mod. 2022, 43, 911–920. [Google Scholar]
- Cotrufo, M.F.; Wallenstein, M.D.; Boot, C.M.; Denef, K.; Paul, E. The Microbial Efficiency-Matrix Stabilization (MEMS) framework integrates plant litter decomposition with soil organic matter stabilization: Do labile plant inputs form stable soil organic matter? Glob. Change Biol. 2013, 19, 988–995. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, Z.W.; Wang, Y.T.; Li, H.K.; Dong, Y.M.; Wang, Z.C.; Liu, Z.P.; Liu, S.S.; Sun, D.J.; Zhao, H.Y.; Wang, S.Z. Soil moisture and bacterial carbon limitation regulate the soil organic carbon in mountain peatlands. CATENA 2024, 234, 107610. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, R.X.; Luo, H.Q.; Yu, J.L.; Luo, L.; He, Y.; Deng, S.H.; Deng, O.P.; Shi, D.Z.; He, J.S.; Xiao, H.; et al. The importance of moisture in regulating soil organic carbon content based on a comparison of? enzymic latch? and? iron gate? in Zoige Plateau peatland. CATENA 2023, 225, 107019. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nie, X.Q.; Wang, D.; Zhou, G.Y.; Xiong, F.; Du, Y.G. Soil microbial biomass carbon, nitrogen, phosphorus and their stoichiometric characteristics in alpine wetlands in the Three Rivers Sources Region. Chin. J. Plant Ecol. 2021, 45, 996–1005. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lange, M.; Azizi-Rad, M.; Dittmann, G.; Lange, D.F.; Orme, A.M.; Schroeter, S.A.; Simon, C.; Gleixner, G. Stability and carbon uptake of the soil microbial community is determined by differences between rhizosphere and bulk soil. Soil Biol. Biochem. 2024, 189, 109280. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Quan, Q.; He, N.P.; Zhang, R.Y.; Wang, J.S.; Luo, Y.Q.; Ma, F.F.; Pan, J.X.; Wang, R.M.; Liu, C.C.; Zhang, J.H.; et al. Plant height as an indicator for alpine carbon sequestration and ecosystem response to warming. Nat. Plants 2024, 10, 890–900. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, Y.; Dou, Y.X.; Wang, B.R.; Wang, Y.Q.; Liang, C.; An, S.S.; Soromotin, A.; Kuzyakov, Y. Increasing contribution of microbial residues to soil organic carbon in grassland restoration chronosequence. Soil Biol. Biochem. 2022, 170, 108688. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, Y.; Zhou, Q.X.; Tao, Z.X.; Zheng, T.; Wu, K.Y.; Zhang, J.L.; Ouyang, S.H. Research Progress in Reducing Pollution and Sequestration of Carbon by Carbon Neutral Plants. Environ. Sci. 2024, 45, 3446–3458. [Google Scholar]
- Jackson, R.B.; Lajtha, K.; Crow, S.E.; Hugelius, G.; Kramer, M.G.; Piñeiro, G. The Ecology of Soil Carbon: Pools, Vulnerabilities, and Biotic and Abiotic Controls. Annu. Rev. 2017, 48, 419–445. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dang, P.F.; Zhang, M.M.; Chen, X.L.; Loreau, M.; Duffy, J.E.; Li, X.E.; Wen, S.Y.; Han, X.Q.; Liao, L.C.; Huang, T.T.; et al. Plant diversity decreases greenhouse gas emissions by increasing soil and plant carbon storage in terrestrial ecosystems. Ecol. Lett. 2024, 27, e14469. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xu, Y.; Zhou, J.; Liu, C.Y.; Jia, R.; Ji, H.J.; Dippold, M.A.; Zhao, T.; Pavinato, P.S.; Peixoxo, L.; Yang, Y.D.; et al. Long-term rotational and perennial cropping benefit soil organic carbon stocks and ecosystem multifunctionality. Ind. Crops Prod. 2024, 209, 117980. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bai, B.; Liu, W.D.; Qiu, X.Y.; Zhang, J.; Zhang, J.Y.; Bai, Y. The root microbiome: Community assembly and its contributions to plant fitness. J. Integr. Plant Biol. 2022, 64, 230–243. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]







Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Wang, W.; Sheng, L.; Yu, X.; Zhang, J.; Su, P.; Zou, Y. Soil–Plant Carbon Pool Variations Subjected to Agricultural Drainage in Xingkai Lake Wetlands. Water 2025, 17, 125. https://doi.org/10.3390/w17010125
Wang W, Sheng L, Yu X, Zhang J, Su P, Zou Y. Soil–Plant Carbon Pool Variations Subjected to Agricultural Drainage in Xingkai Lake Wetlands. Water. 2025; 17(1):125. https://doi.org/10.3390/w17010125
Chicago/Turabian StyleWang, Wei, Lianxi Sheng, Xiaofei Yu, Jingyao Zhang, Pengcheng Su, and Yuanchun Zou. 2025. "Soil–Plant Carbon Pool Variations Subjected to Agricultural Drainage in Xingkai Lake Wetlands" Water 17, no. 1: 125. https://doi.org/10.3390/w17010125
APA StyleWang, W., Sheng, L., Yu, X., Zhang, J., Su, P., & Zou, Y. (2025). Soil–Plant Carbon Pool Variations Subjected to Agricultural Drainage in Xingkai Lake Wetlands. Water, 17(1), 125. https://doi.org/10.3390/w17010125







