Utilizing Cement Kiln Dust as an Efficient Adsorbent for Heavy Metal Removal in Wastewater Treatment
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Research Methodology Outline
2.2. Cement Kiln Dust (CKD)
2.3. Sewage Sludge Samples
2.4. Wastewater Adsorption Treatment Experiments
2.5. Quality Control Aspect
2.6. Removal and Adsorption of Heavy Metals
- C0: initial concentration of heavy metal ions in the test solution, in mg/L.
- C: final equilibrium concentration of the test solution, in mg/L.
2.7. Sorption Isotherm Model
3. Results and Discussion
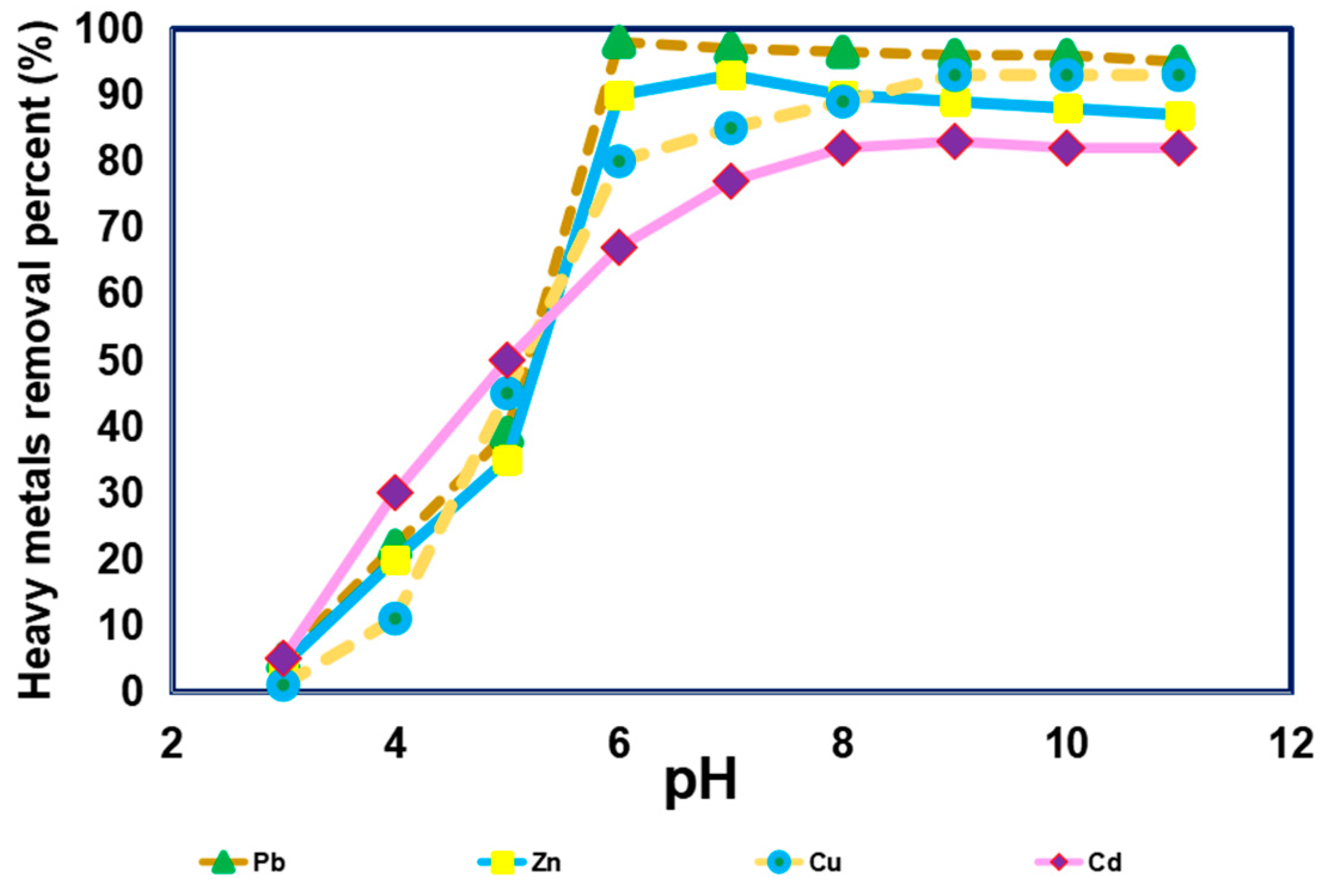
3.1. Impact of pH on Removal of Different Heavy Metals from Simulated Sewage Sludge
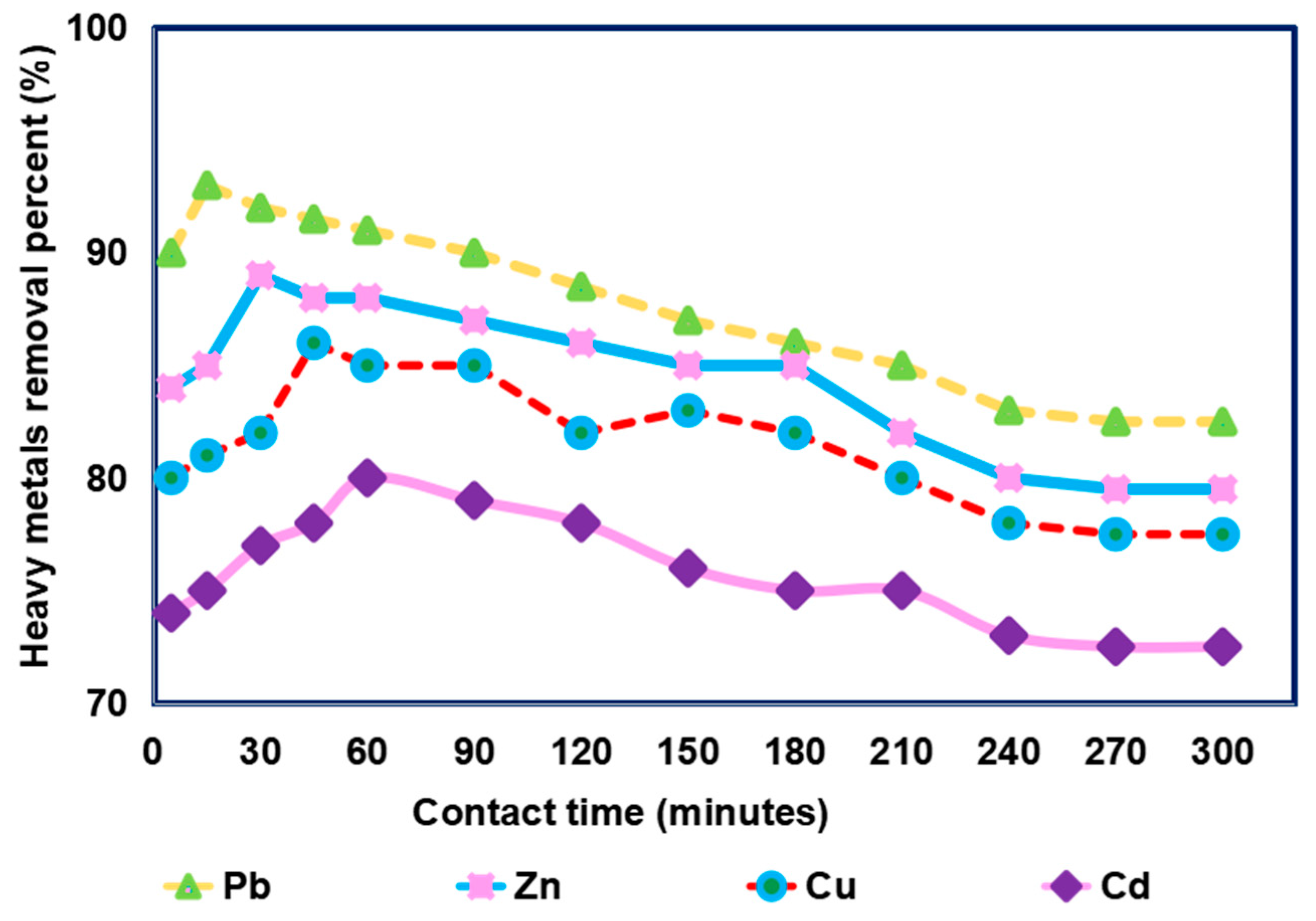
3.2. Impact of Contact Time on Removal of Different Heavy Metals from Simulated Sewage Sludge
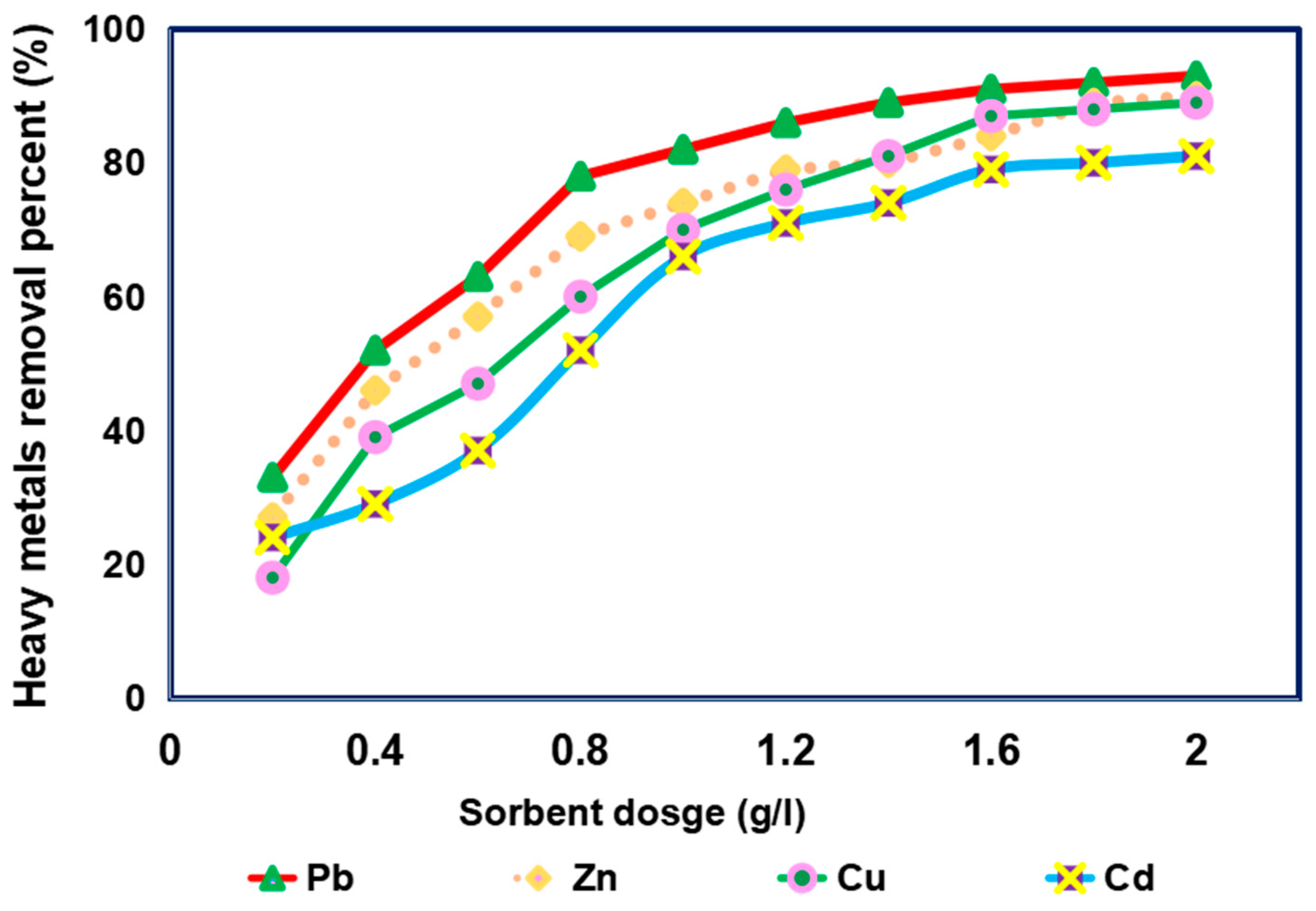
3.3. Impact of Sorbent Dose on Removal of Different Heavy Metals from Simulated Sewage Sludge
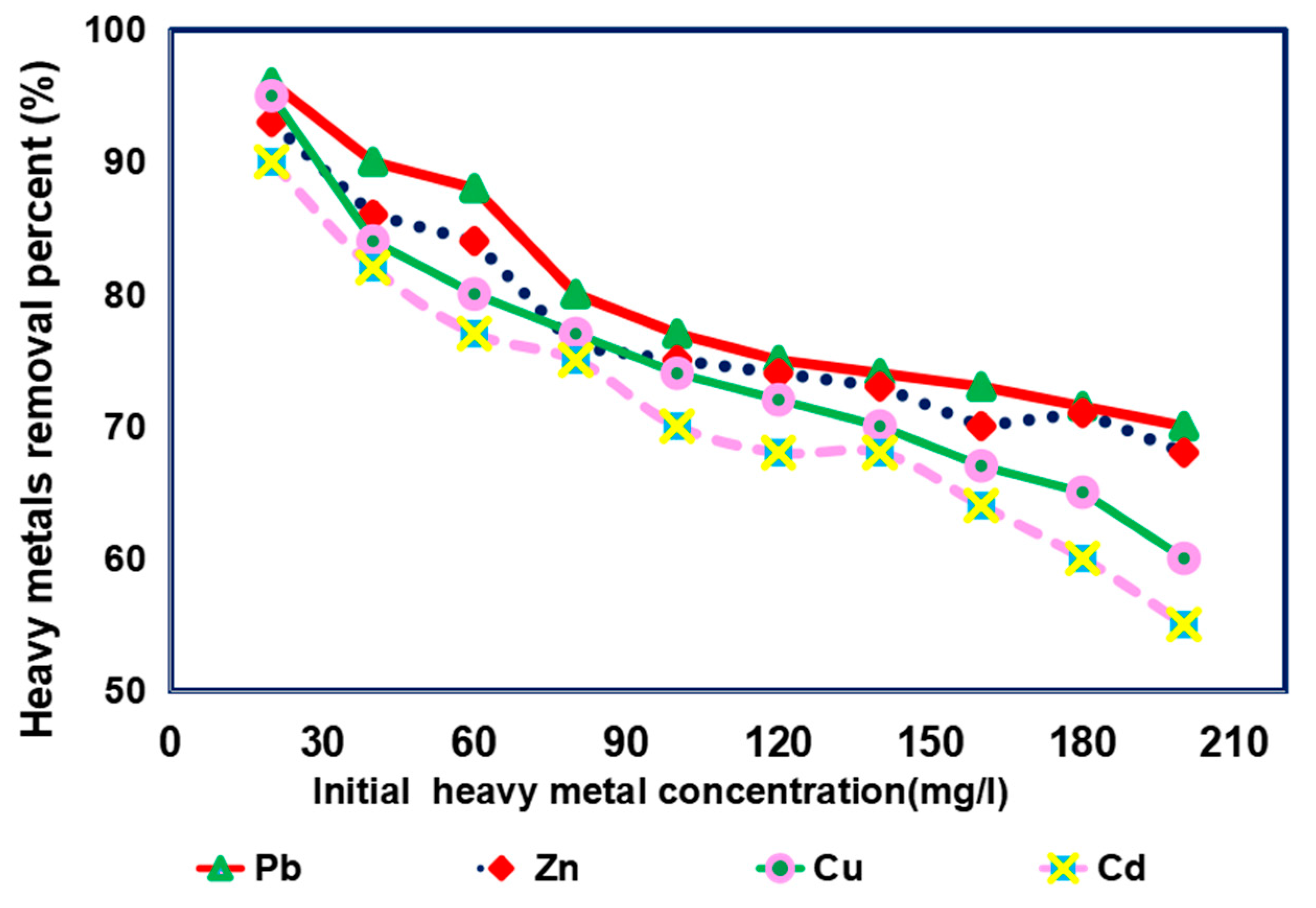
3.4. Impact of Initial Concentrations on Removal of Different Heavy Metals from Simulated Sewage Sludge
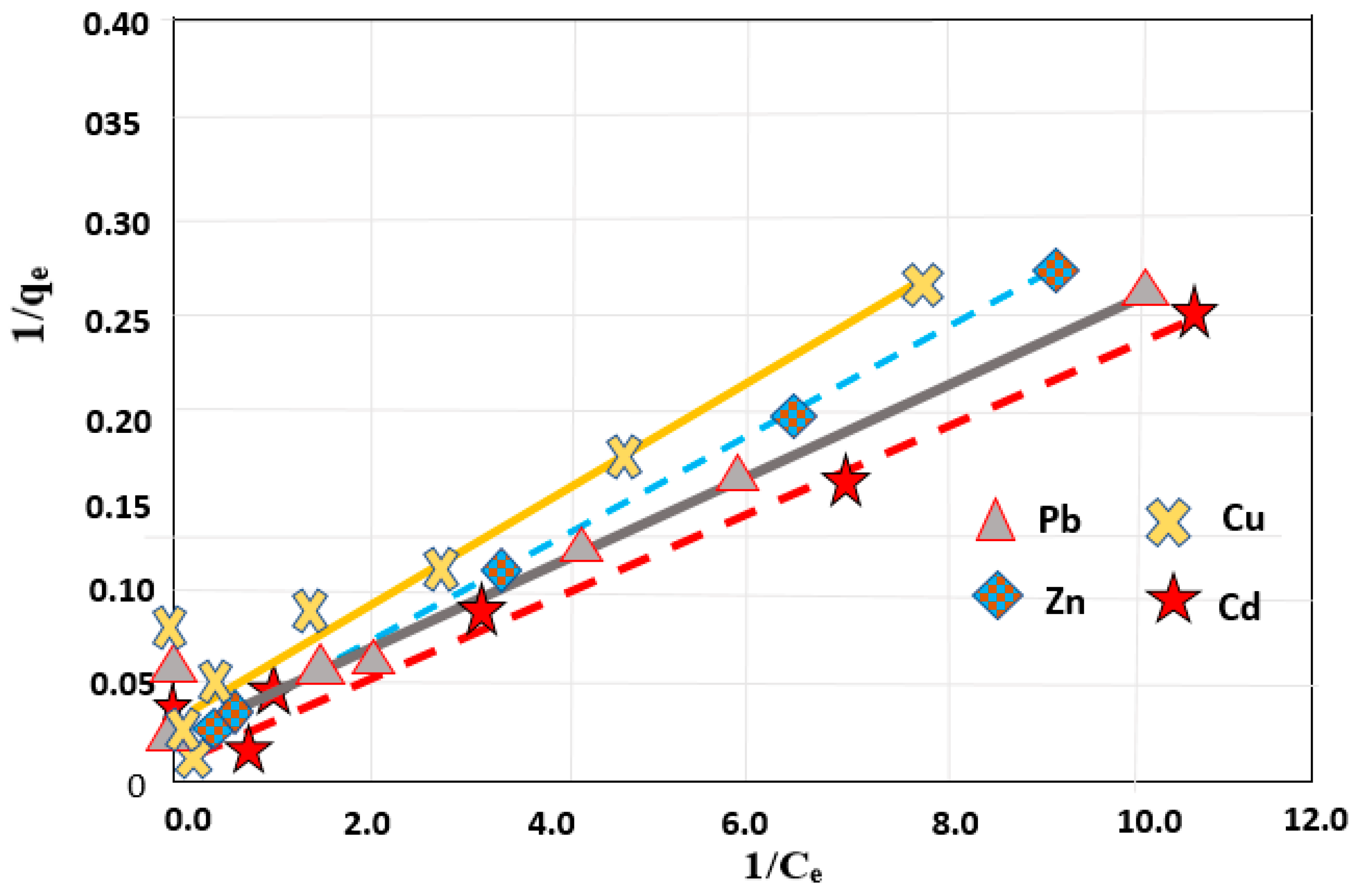
3.5. Adsorption Isotherm for Removal of Different Heavy Metals from Simulated Sewage Sludge
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Barakat, M.A. New Trends in Removing Heavy Metals from Industrial Wastewater. Arab. J. Chem. 2011, 4, 361–377. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- El-Gawad, H.A.; Hassan, G.K.; Aboelghait, K.M.; Mahmoud, W.H.; Mohamed, R.M.; Afify, A.A. Removal of Chromium from Tannery Industry Wastewater Using Iron-Based Electrocoagulation Process: Experimental; Kinetics; Isotherm and Economical Studies. Sci. Rep. 2023, 13, 19597. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abidli, A.; Ben Rejeb, Z.; Zaoui, A.; Naguib, H.E.; Park, C.B. Comprehensive Insights into the Application of Graphene-Based Aerogels for Metals Removal from Aqueous Media: Surface Chemistry, Mechanisms, and Key Features. Adv. Colloid Interface Sci. 2025, 335, 103338. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Briffa, J.; Sinagra, E.; Blundell, R. Heavy Metal Pollution in the Environment and Their Toxicological Effects on Humans. Heliyon 2020, 6, e04691. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Albayati, N.; Mohammed, M.; Ahmed, H.; Kadhom, M. The Potential of Gundelia Seeds Waste as an Emerging Sustainable Adsorbent for Methylene Blue-Polluted Water Treatment. Prog. Color. Color. Coat. 2024, 18, 53–71. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, S.; Pan, Y.; Wang, W.; Lin, R.; Liu, X. Carboxylated Cellulose-Based Aerogel with Cellular Pores Prepared by Stir Freezing for Cationic Dye Adsorption. Process Saf. Environ. Prot. 2023, 177, 807–817. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Saleh, T.A.; Mustaqeem, M.; Khaled, M. Water Treatment Technologies in Removing Heavy Metal Ions from Wastewater: A Review. Environ. Nanotechnol. Monit. Manag. 2022, 17, 100617. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chowdhury, S.; Mazumder, M.A.J.; Al-Attas, O.; Husain, T. Heavy Metals in Drinking Water: Occurrences, Implications, and Future Needs in Developing Countries. Sci. Total Environ. 2016, 569–570, 476–488. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zaimee, M.Z.A.; Sarjadi, M.S.; Rahman, M.L. Heavy Metals Removal from Water by Efficient Adsorbents. Water 2021, 13, 2659. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abukhadra, M.R.; Bakry, B.M.; Adlii, A.; Yakout, S.M.; El-Zaidy, M.E. Facile Conversion of Kaolinite into Clay Nanotubes (KNTs) of Enhanced Adsorption Properties for Toxic Heavy Metals (Zn2+, Cd2+, Pb2+, and Cr6+) from Water. J. Hazard. Mater. 2019, 374, 296–308. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abollino, O.; Aceto, M.; Malandrino, M.; Sarzanini, C.; Mentasti, E. Adsorption of Heavy Metals on Na-Montmorillonite. Effect of PH and Organic Substances. Water Res. 2003, 37, 1619–1627. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ben Bouabdallah, A.; Djelali, N.E. Study of the Effect of Various Parameters on the Adsorption of Heavy Metals by Bentonite-Polypyrrole Composite. Iran. J. Chem. Chem. Eng. 2023, 42, 786–800. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Franus, M.; Bandura, L.; Madej, J. Mono and Poly-Cationic Adsorption of Heavy Metals Using Natural Glauconite. Minerals 2019, 9, 470. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhong, Z.; Li, J.; Ma, Y.; Yang, Y. The Adsorption Mechanism of Heavy Metals from Coal Combustion by Modified Kaolin: Experimental and Theoretical Studies. J. Hazard. Mater. 2021, 418, 126256. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, J.-M.; Zhao, J.; Qin, X.-Z.; Wang, Z. Theoretical Study of Adsorption Mechanism of Heavy Metals As and Pb on the Calcite (104) Surface. Mater. Today Commun. 2021, 26, 101742. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, X.; Zhu, D.; Jian, Q.; Wang, X.; Zheng, X.; Xue, G.; Liu, Y.; Li, X.; Hassan, G.K. Treatment of Industrial Ferric Sludge through a Facile Acid-Assisted Hydrothermal Reaction: Focusing on Dry Mass Reduction and Hydrochar Recyclability Performance. Sci. Total Environ. 2023, 869, 161879. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Takarina, N.D.; Matsue, N.; Johan, E.; Adiwibowo, A.; Rahmawati, M.F.N.K.; Pramudyawardhani, S.A.; Wukirsari, T. Machine Learning Using Random Forest to Model Heavy Metals Removal Efficiency Using a Zeolite-Embedded Sheet in Water. Glob. J. Environ. Sci. Manag. 2024, 10, 321–336. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ahmed, H.M.; Hefni, M.A.; Ahmed, H.A.M.; Saleem, H.A. Cement Kiln Dust (CKD) as a Partial Substitute for Cement in Pozzolanic Concrete Blocks. Buildings 2023, 13, 568. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Seo, M.; Lee, S.-Y.; Lee, C.; Cho, S.-S. Recycling of Cement Kiln Dust as a Raw Material for Cement. Environments 2019, 6, 113. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kunal; Siddique, R.; Rajor, A. Use of Cement Kiln Dust in Cement Concrete and Its Leachate Characteristics. Resour. Conserv. Recycl. 2012, 61, 59–68. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kiran, S.; Nosheen, S.; Abrar, S.; Anjum, F.; Gulzar, T.; Naz, S. Advanced Approaches for Remediation of Textile Wastewater: A Comparative Study. In Advanced Functional Textiles and Polymers: Fabrication, Processing and Applications; Wiley: Hoboken, NJ, USA, 2019; ISBN 9781119605843. [Google Scholar]
- Faisal, A.A.H.; Jasim, H.K.; Naji, L.A.; Naushad, M.; Ahamad, T. Cement Kiln Dust-Sand Permeable Reactive Barrier for Remediation of Groundwater Contaminated with Dissolved Benzene. Sep. Sci. Technol. 2021, 56, 870–883. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kosajan, V.; Wen, Z.; Fei, F.; Doh Dinga, C.; Wang, Z.; Zhan, J. The Feasibility Analysis of Cement Kiln as an MSW Treatment Infrastructure: From a Life Cycle Environmental Impact Perspective. J. Clean. Prod. 2020, 267, 122113. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hasaballah, A.F.; Hegazy, T.A.; Ibrahim, M.S.; El-Emam, D.A. Cement Kiln Dust as an Alternative Technique for Wastewater Treatment. Ain Shams Eng. J. 2021, 12, 4201–4209. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- El-Sayed, G.; Waly, A.; Dakroury, A.M.; El-Sayed, G.O.; El-Salam, S.A. Assessment Removal of Heavy Metals Ions from Wastewater by Cement Kiln Dust (CKD). J. Am. Sci. 2010, 6, 910–917. [Google Scholar]
- Hung, D.Q.; Dinh, L.X.; Van Tung, N.; Huong, L.T.M.; Lien, N.T.; Minh, P.T.; Le, T.-H. The Adsorption Kinetic and Isotherm Studies of Metal Ions (Co2+, Sr2+, Cs+) on Fe3O4 Nanoparticle of Radioactive Importance. Results Chem. 2023, 6, 101095. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mahmoud, E.; Hammad, W.; Hakami, O. Effect of Water Treatment Residuals and Cement Kiln Dust on Cod Adsorption and Heavy Metals from Textile Wastewater. Desalin. Water Treat. 2020, 205, 336–342. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, Y.H.; Yang, H.; Lee, S.M.; Kim, S.S. Surface Properties of Cement Kiln Dust with Water Treatment for Selective Extraction of Calcium and Potassium. ACS Omega 2020, 5, 24351–24355. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vardhan, K.H.; Kumar, P.S.; Panda, R.C. A Review on Heavy Metal Pollution, Toxicity and Remedial Measures: Current Trends and Future Perspectives. J. Mol. Liq. 2019, 290, 111197. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shamohammadi, S.; Khajeh, M.; Fattahi, R.; Kadkhodahosseini, M. Introducing the New Model of Chemical Adsorption for Heavy Metals by Jacobi Activated Carbon Adsorbents, Iranian Activated Carbon and Blowy Sand. Case Stud. Chem. Environ. Eng. 2022, 6, 100220. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pang, F.M.; Kumar, P.; Teng, T.T.; Mohd Omar, A.K.; Wasewar, K.L. Removal of Lead, Zinc and Iron by Coagulation–Flocculation. J. Taiwan Inst. Chem. Eng. 2011, 42, 809–815. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aklil, A.; Mouflih, M.; Sebti, S. Removal of Heavy Metal Ions from Water by Using Calcined Phosphate as a New Adsorbent. J. Hazard. Mater. 2004, 112, 183–190. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mahmoud, E.K. Textile Wastewater Treatment by Using Cement Kiln Dust and Biochar Filter. Desalin. Water Treat. 2018, 120, 180–184. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Senthil Kumar, P.; Kirthika, K. Kinetics and Equilibrium Studies of Zn2+ Ions Removal from Aqueous Solutions by Use of Natural Waste. Electron. J. Environ. Agric. Food Chem. 2010, 9, 64. [Google Scholar]
- Hafshejani, L.D.; Nasab, S.B.; Gholami, R.M.; Moradzadeh, M.; Izadpanah, Z.; Hafshejani, S.B.; Bhatnagar, A. Removal of Zinc and Lead from Aqueous Solution by Nanostructured Cedar Leaf Ash as Biosorbent. J. Mol. Liq. 2015, 211, 448–456. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Anitha, T.; Senthil Kumar, P.; Sathish Kumar, K. Binding of Zn(II) Ions to Chitosan–PVA Blend in Aqueous Environment: Adsorption Kinetics and Equilibrium Studies. Environ. Prog. Sustain. Energy 2015, 34, 15–22. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Senthil Kumar, P.; Sai Deepthi, A.S.L.; Bharani, R.; Prabhakaran, C. Adsorption of Cu(II), Cd(II) and Ni(II) Ions from Aqueous Solution by Unmodified Strychnos Potatorum Seeds. Eur. J. Environ. Civ. Eng. 2013, 17, 293–314. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Saravanan, A.; Senthil Kumar, P.; Mugilan, R. Ultrasonic-Assisted Activated Biomass (Fishtail Palm Caryota Urens Seeds) for the Sequestration of Copper Ions from Wastewater. Res. Chem. Intermed. 2016, 42, 3117–3146. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gossuin, Y.; Vuong, Q.L. NMR Relaxometry for Adsorption Studies: Proof of Concept with Copper Adsorption on Activated Alumina. Sep. Purif. Technol. 2018, 202, 138–143. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mahmood-ul-Hassan, M.; Suthar, V.; Rafique, E.; Ahmad, R.; Yasin, M. Kinetics of Cadmium, Chromium, and Lead Sorption onto Chemically Modified Sugarcane Bagasse and Wheat Straw. Environ. Monit. Assess. 2015, 187, 470. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Senthilkumar, P.; Gayathri, R. Study on removal of cadmium from aqueous solutions by adsorption on bael tree leaf powder. Environ. Eng. Manag. J. 2010, 9, 429–434. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gupta, V.K.; Jain, C.K.; Ali, I.; Sharma, M.; Saini, V.K. Removal of Cadmium and Nickel from Wastewater Using Bagasse Fly Ash—A Sugar Industry Waste. Water Res. 2003, 37, 4038–4044. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]

| Components | Average (%) |
|---|---|
| SiO2 | 21.5 ± 1.9 |
| Al2O3 | 7.4 ± 0.6 |
| Fe2O3 | 4.5 ± 0.2 |
| CaO | 43.5 ± 2.4 |
| MgO | 2.8 ± 0.2 |
| K2O | 6.3 ± 0.3 |
| Na2O | 6.3 ± 0.4 |
| TiO2 | 1.1 ± 0.1 |
| Heavy Metals | Langmuir Constants | |
|---|---|---|
| Qm (mg/g) | KL(L/mg) | |
| Pb | 0.011 | 0.489 |
| Zn | 0.024 | 0.373 |
| Cu | 0.271 | 0.047 |
| Cd | 0.041 | 1.112 |
| Heavy Metals | MAErel | PBIAS | NSE |
|---|---|---|---|
| Pb | 0.10 | 0.13 | 0.95 |
| Zn | 0.09 | 0.11 | 0.92 |
| Cu | 0.07 | 0.10 | 0.96 |
| Cd | 0.08 | 0.08 | 0.94 |
| Adsorbents | Metal | Langmuir Monolayer Adsorption Capacity, qm (mg/g) | Ref. |
|---|---|---|---|
| Cedar leaf ash | Zn | 4.8 | [35] |
| Bael tree leaf powder | Zn | 2.1 | [34] |
| Chitosan–PVA blend | Zn | 5.9 | [36] |
| Cement kiln dust | Zn | 1.9 | This study |
| Unmodified Strychnos potatorum seeds | Cu | 8.6 | [37] |
| Raw Caryota urens seeds | Cu | 5.0 | [38] |
| Activated alumina | Cu | 4.3 | [39] |
| Cement kiln dust | Cu | 1.9 | This study |
| Spruce wood | Cd | 2.0 | [40] |
| Bael tree leaf powder | Cd | 1.8 | [41] |
| Bagasse fly ash | Cd | 1.2 | [42] |
| Cement kiln dust | Cd | 1.8 | This study |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Elmaadawy, K.; Hamed, M.R.; Al-Hazmi, H.; Hassan, G.K. Utilizing Cement Kiln Dust as an Efficient Adsorbent for Heavy Metal Removal in Wastewater Treatment. Water 2025, 17, 40. https://doi.org/10.3390/w17010040
Elmaadawy K, Hamed MR, Al-Hazmi H, Hassan GK. Utilizing Cement Kiln Dust as an Efficient Adsorbent for Heavy Metal Removal in Wastewater Treatment. Water. 2025; 17(1):40. https://doi.org/10.3390/w17010040
Chicago/Turabian StyleElmaadawy, Khaled, Mohamed R. Hamed, Hussein Al-Hazmi, and Gamal K. Hassan. 2025. "Utilizing Cement Kiln Dust as an Efficient Adsorbent for Heavy Metal Removal in Wastewater Treatment" Water 17, no. 1: 40. https://doi.org/10.3390/w17010040
APA StyleElmaadawy, K., Hamed, M. R., Al-Hazmi, H., & Hassan, G. K. (2025). Utilizing Cement Kiln Dust as an Efficient Adsorbent for Heavy Metal Removal in Wastewater Treatment. Water, 17(1), 40. https://doi.org/10.3390/w17010040






