Abstract
The feeding characteristics of the chub mackerel, Scomber japonicus from Jeju Island waters and the Yellow Sea were compared by analyzing the stomach contents. Large and small purse seines were used to collect 1437 individuals from Jeju Island waters and 1066 individuals from the Yellow Sea. The fork length of S. japonicus ranged from 21.0 to 43.6 cm for individuals from Jeju Island waters and 19.6 to 41.5 cm for those from the Yellow Sea. Based on the index of relative importance and variation in stomach contents according to fish size, S. japonicus was identified as a piscivore and a spatiotemporally opportunistic feeder. The proportion of fish in the diet increased as the body sizes of S. japonicus from both Jeju Island waters and the Yellow Sea increased, whereas the proportion of copepods, amphipods, and euphausiids gradually decreased. Differences in stomach content compositions were observed due to interactions between size and location. Thus, the feeding characteristics of S. japonicus are affected by the abundance and composition of prey in its habitat.
1. Introduction
The distribution and migration of fish prey species are greatly influenced by the physical and chemical conditions of the ocean, which in turn significantly shapes the composition of prey communities across various habitats. The waters around the Jeju Island and the Yellow Sea have distinct oceanographic characteristics and are key fishing grounds for Scomber japonicus (Chub mackerel), a major commercial species. The Jeju region is influenced by both the Tsushima Warm Current and the Yellow Sea Cold Water Mass, which cause seasonal variations in the occurrence and distribution of various migratory fish species such as S. japonicus, Trachurus japonicus (Japanese jack mackerel), Seriola quinqueradiata (Japanese amberjack), and Scomberomorus niphonius (Japanese Spanish mackerel) [1,2]. In contrast, the Yellow Sea exhibits high productivity due to nutrient input from rivers in China and Korea. This region, under the combined influence of the Yellow Sea Warm Current and the Cold Water Mass, provides favorable environmental conditions for the habitation of S. japonicus [3].
Ongoing global climate change has increased ocean warming and significantly affected coastal and offshore waters around the Korean Peninsula [4]. Traditional fishing areas have changed significantly as a result of the increased poleward migration of both cold- and warm-water fish species. Consequently, the abundance, distribution, productivity, and seasonal variability of marine resources have all increased. These changes not only alter the location and extent of fishing grounds but also influence the composition of fish prey communities, indicating that these factors will play a critical role in future resource management strategies [5,6,7]. In particular, major migratory species such as S. japonicus are highly responsive to changes in oceanographic conditions; thus, variations in their feeding grounds, migration routes, and prey composition are likely to occur [8].
S. japonicus is a representative pelagic fish species commonly harvested in Korea, China, and Japan and is widely distributed throughout temperate and subtropical marine waters [9]. It has a high density in the North Pacific, particularly along the coasts of Korea and Japan and the East China Sea, with seasonal variation in distribution. In February and March, S. japonicus enters the waters around Jeju Island, from where some of the populations migrate northward to the East Sea and others move into the Yellow Sea to form distinct seasonal fishing grounds. These spatial distributions are primarily influenced by oceanographic factors, particularly sea surface temperature [10,11]. This seasonal migration pattern is closely associated with the formation of purse seine fishing grounds in Korean coastal waters. In these areas, S. japonicus is predominantly harvested via large-scale purse seine fisheries. Fishing grounds begin to develop around Jeju in May to June and expand into the Yellow Sea in August. The catch per unit effort (CPUE) reaches its peak in November, indicating a seasonal aggregation of S. japonicus and a critical period for purse seine operations [12].
To promote the sustainable management of S. japonicus resources, the Republic of Korea introduced a Total Allowable Catch (TAC) system in 1999, in addition to other regulatory measures such as voluntary fishing moratoriums, a minimum catch size limit (≤21.0 cm), and seasonal fishing bans (one-month closures between April and June) [13]. The average catch of S. japonicus has shown a decreasing trend since the introduction of the TAC system (184,852 tons from 2002–2006 to 122,320 tons from 2015–2019) because of its seasonal fluctuations in production, indicating the need for further efforts in resource management [14]. Accordingly, research on feeding ecology is essential as it provides information on interspecific predator–prey relationships and food web structures and serves as fundamental data for ecosystem-based fisheries resource assessment and management. In particular, information on the feeding characteristics and trophic levels of key species in resource assessments can enable more precise predictions of population responses to changes in prey organisms and interspecies interactions [15]. Notably, comparative studies of dietary habits across different sea areas can help identify the types and distribution of the primary prey of mackerel and provide crucial information for understanding the feeding patterns.
Previous studies on the feeding ecology of S. japonicus in the North Pacific have primarily focused on the Yellow Sea, the South Sea, and the waters around Jeju Island in Korea, and research in Japan has mainly been on the Satsunan and Seto Inland Sea regions [16,17,18,19,20,21]. Hence, comparative studies on prey composition that account for spatiotemporal variability across different habitats remain limited. Investigating the diet composition and feeding characteristics of S. japonicus in the Jeju and Yellow Sea regions can reveal the patterns of regional prey utilization and highlight the differences in the primary prey species. The findings can contribute to a more comprehensive understanding of the ecological role of species and their interspecific interactions within marine ecosystems. Therefore, the present study aimed to identify the major prey species of S. japonicus in the Jeju and Yellow Sea regions and comparatively analyze the composition of the stomach content according to ontogenetic stages and seasonal variations.
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Study Area and Sampling
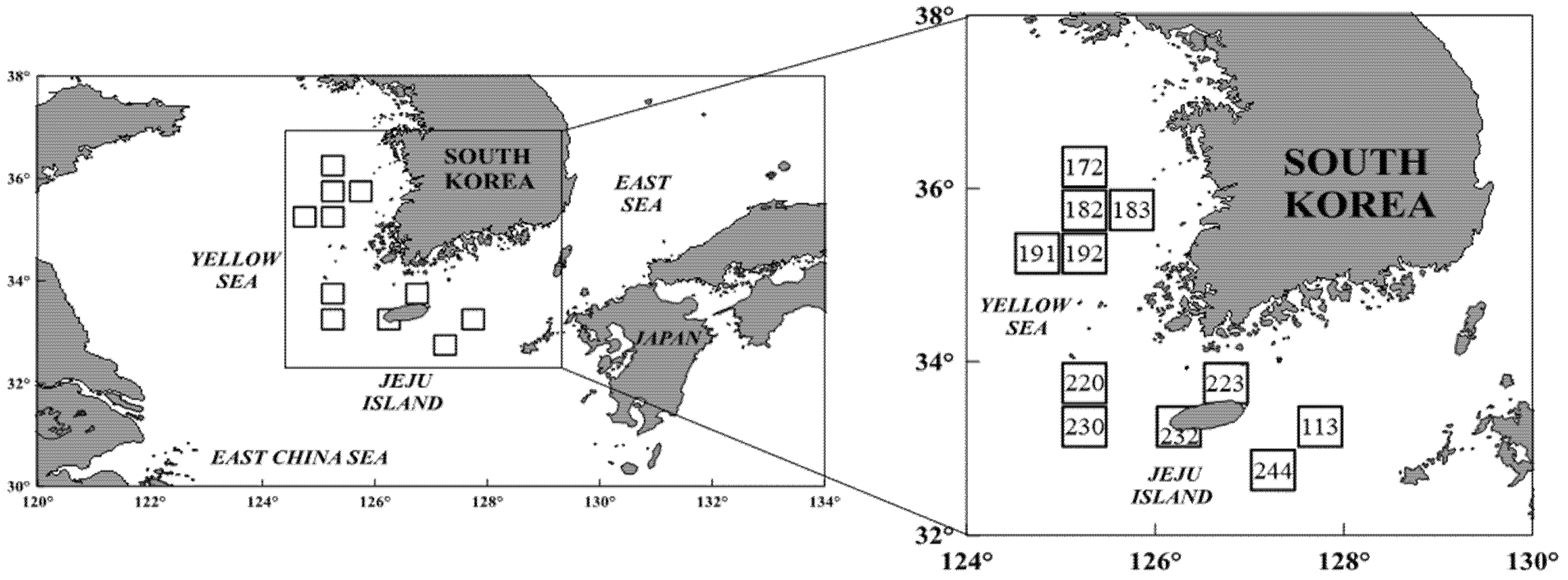
Specimens of S. japonicus from the Jeju region were collected in October–December 2021 (subareas 223, 230, and 244), August–September and November–December 2022 (subareas 220, 223, and 232), and September–December 2023 (subareas 113 and 232). Samples from the Yellow Sea were collected in October–December 2021 (subareas 172, 182, and 191), September–November 2022 (subareas 182, 191, and 192), and August–September 2023 (subareas 182 and 183). The fish were obtained from both large- and small-scale purse seine fisheries, which included a fleet of six vessels (one main vessel, two auxiliary boats, and three transport vessels), and also purchased from the Busan Cooperative Fish Market for analysis [12] (Figure 1). To prevent misidentification with the closely related species Scomber australasicus (Blue mackerel), all specimens were accurately identified using the taxonomic key provided by Kim et al. [22]. The total length (TL), fork length (FL), and body weight (BW) of each specimen were measured to the nearest 0.1 cm and 0.1 g, accordingly. The stomach of each fish was dissected and preserved in 10% formalin solution. Prey items were identified under a dissecting microscope, as precisely as possible to the species level. For quantitative analysis, the number of individual prey items was counted, and their weight was measured to the nearest 0.0001 g.
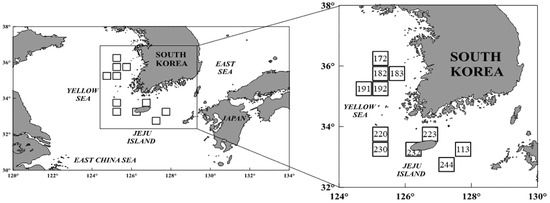
Figure 1.
A map showing the fishing areas where the chub mackerel, Scomber japonicus, were collected from the waters around Jeju Island and in the Yellow Sea of Korea.
2.2. Stomach Content Analysis
Stomach content analysis was expressed in terms of frequency of occurrence (%F), numerical composition (%N), and weight composition (%W) and calculated using the following formulas [23].
where Ai represents the number of mackerel individuals in which the specific prey item was found, N is the total number of mackerel that had consumed prey, and Ni and Wi denote the number and weight of the specific prey item, respectively. Ntotal and Wtotal represent the total number and weight of all prey items found. The index of relative importance (IRI) of the analyzed prey items was calculated using the formula by Pinkas et al. [24] and was then converted into a percentage to represent the percentage index of relative importance (%IRI).
%F = Ai/N × 100
%N = Ni/Ntotal × 100
%W = Wi/Wtotal × 100
IRI = (%N +%W) × %F
To assess the spatiotemporal variations in the biological characteristics of the samples, which may be influenced by various environmental factors such as water temperature and prey availability, major prey items were classified and compared between the Jeju and Yellow Sea regions. Temporally, the samples were grouped into three categories: Group A (2021), Group B (2022), and Group C (2023), and the results were analyzed both individually and in total across years.
To examine the ontogenetic changes in diet composition, specimens were categorized into two size classes based on fork length: small (<34.0 cm) and large (≥34.0 cm). Seasonal variations in stomach contents were analyzed by grouping the data into three seasons: summer (August), autumn (September–November), and winter (December).
2.3. Trophic Level
To evaluate the ecological status of mackerel, the trophic level (TLk) was calculated based on the formula by Cortés [25]. The formula is as follows:
where Pj represents the percentage index of relative importance (%IRI) of prey item category j, and TLj represents the trophic level of prey item category j. The trophic level values for each prey item category were derived as average values based on previous studies by Pauly et al. [26], Cortés [25], and Ebert and Bizzarro [27].
2.4. Multivariate Analysis of Stomach Contents
To determine the significant effects of mackerel size class, sea area, and their interaction (Size class × Area) on the stomach content composition, a two-way Permutational Multivariate Analysis of Variance (PERMANOVA) was performed. When significant differences were detected in the PERMANOVA analysis, a Canonical Analysis of Principal Coordinate (CAP) analysis was employed to assess which prey organisms exhibited high correlation coefficients with the results. Prey organisms with correlation coefficients ≥ 0.4 were displayed on the first and second axes of the CAP plot. For these analyses, individuals belonging to each sea area and size class were randomly divided into subgroups of 3–6 individuals, and the average weight proportion of consumed prey item categories was calculated for each subgroup. To reduce the bias caused by dominant prey items, a square root transformation was applied to the average weight proportions, and a similarity matrix was generated based on Bray–Curtis similarity for subsequent analysis. All analyses were conducted using Microsoft Excel 2014, the PRIMER v6 multivariate statistics package (www.primer-e.com, accessed on 4 February 2025), and the PERMANOVA+ add-on module [28].
3. Results
3.1. Oceanographic Variability
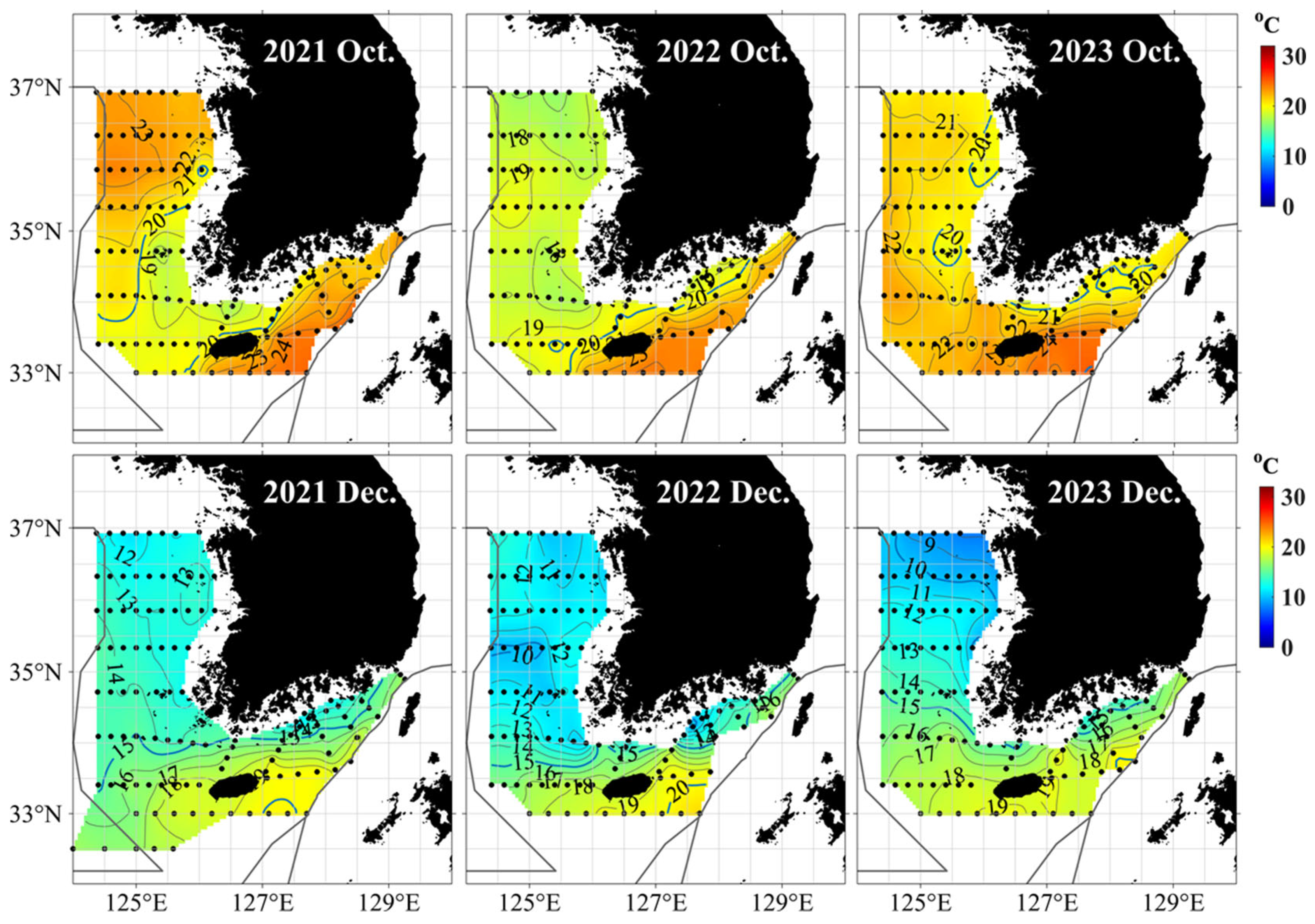
Stable S. japonicus samples were obtained from the Jeju region from August to December, but the S. japonicus collected from the Yellow Sea in December were limited to 2021. To investigate the temporal variability in samples collected from the Yellow Sea, the regional sea surface temperature (SST) fluctuations during August–December 2021–2023 were examined. Temperature data from each subarea were compared using in situ SST observations from the National Fisheries Research and Development Institute (NFRDI) marine surveys, as provided by the Korea Ocean Data Center (KODC). The relatively higher SSTs observed in the Yellow Sea until December 2021 likely facilitated the collection of S. japonicus samples in that year (Figure 2).
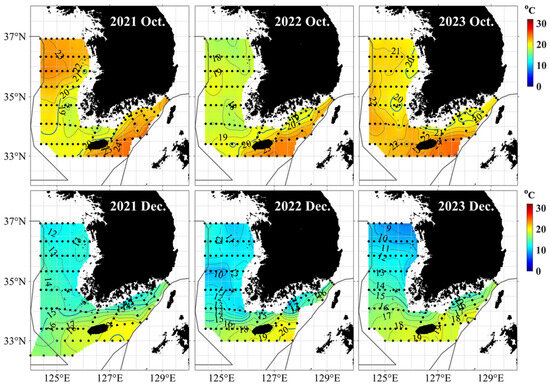
Figure 2.
Horizontal sea surface temperature distribution around the Korean Peninsula provided by the Korea Oceanographic Data Center (KODC) of the National Institute of Fisheries Science (NIFS).
3.2. Fork Length Distribution
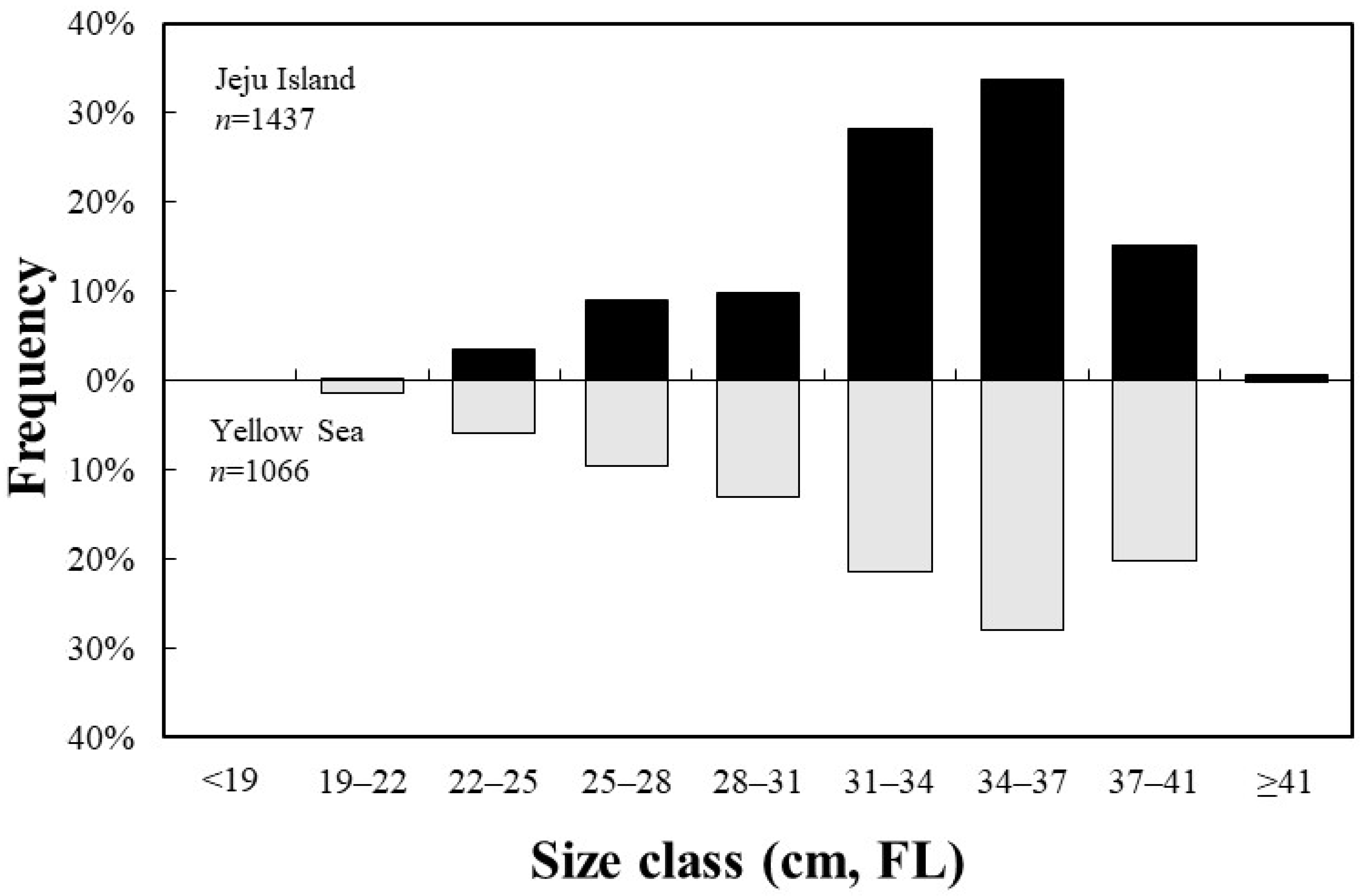
A total of 1437 S. japonicus specimens were collected from the Jeju region, with an average fork length of 33.2 cm, ranging from 21.0 to 43.6 cm. A total of 1066 specimens were collected from the Yellow Sea, with an average fork length of 32.8 cm, ranging from 19.6 to 41.5 cm (Figure 3).
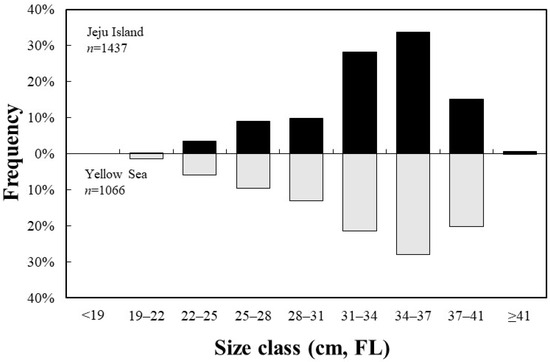
Figure 3.
Length–frequency distribution of the chub mackerel, Scomber japonicus, collected from the waters around Jeju Island and in the Yellow Sea of Korea (FL, fork length).
3.3. Stomach Content Composition and Trophic Levels
The stomach content compositions of S. japonicus collected from the Jeju and Yellow Sea regions were analyzed separately and categorized as Group A, B, C, and total (Table 1 and Table 2). In the Jeju region, analysis of stomach contents from 225 out of 358 specimens in Group A revealed that the most important prey item was fish, and it accounted for 57.3% of the frequency of occurrence, 7.6% of the numerical composition, and 88.3% of the weight composition, which resulted in a relative importance index of 59.9%. Engraulis japonicus (anchovy) was the most dominant among the fish species, followed by the euphausiids, which contributed to 26.0% of the relative importance index and the second most important prey item. Other prey items were amphipods, copepods, and brachyuran larvae, but their relative importance indices were very low, each accounting for less than 8.6% of the relative importance index. In Group B, analysis of stomach contents of 102 out of 479 specimens revealed that fish accounted for 35.3% of the frequency of occurrence, 6.9% of the numerical composition, and 93.9% of the weight composition, which resulted in a relative importance index of 46.7%. E. japonicus was the most dominant among the fish, followed by euphausiids, which contributed to 35.6% of the relative importance index and the second most important prey item. Other prey items were amphipods and copepods, but each contributed less than 13.9% of the relative importance index. In Group C, analysis of stomach contents of 281 of 600 specimens revealed that fish accounted for 44.1% of the frequency of occurrence, 9.4% of the numerical composition, and 88.9% of the weight composition, yielding a relative importance index of 66.5%. Champsodon snyderi (Crocodile toothfishes) was the most dominant among the fish, followed by euphausiids, which contributed to 23.8% of the relative importance index. Other prey items were copepods, cephalopods, and caridean shrimp, but each contributed less than 4.1% of the relative importance index. When the data from all three years were combined, analysis of stomach contents of 608 out of 1437 specimens showed that the most important prey item for S. japonicus was fish, and it accounted for 47.5% of the frequency of occurrence, 7.9% of the numerical composition, and 89.9% of the weight composition, resulting in a relative importance index of 88.4%. E. japonicus was the most dominant among the fish. Other prey items were amphipods, brachyuran larvae, and caridean shrimp, but each accounted for less than 9.3% of the relative importance index.

Table 1.
Composition of the stomach contents of the chub mackerel, Scomber japonicus, collected around Jeju Island of Korea, showing the frequency of occurrence (%F), number (%N), wet weight (%W), and index of relative importance (%IRI) for four periods: (Group A) 2021, (Group B) 2022, (Group C) 2023, and (total) 2021 to 2023.

Table 2.
Composition of the stomach contents of chub mackerel, Scomber japonicus, collected in the Yellow Sea of Korea, showing frequency of occurrence (%F), number (%N), wet weight (%W), and index of relative importance (%IRI) for four periods: (Group A) 2021, (Group B) 2022, (Group C) 2023, and (total) 2021 to 2023.
To assess the ecological role of S. japonicus in the Jeju waters, the trophic levels were estimated separately for Groups A, B, and C and the total dataset (Table 1). The trophic level was 3.76 in Group A, 3.66 in Group B, and 3.82 in Group C. When the data from the three years were combined, the trophic level was calculated to be 4.0, ranging from 3.66 to 4.0.
In the Yellow Sea region (Table 2), a total of 351 S. japonicus specimens were collected in Group A, of which stomach contents were observed in 261 individuals. Analysis of the prey items showed that fish were the most dominant prey group, accounting for 60.5% in frequency of occurrence, 6.9% in numerical composition, and 96.5% in weight composition. These values resulted in a relative importance index of 63.1%, with E. japonicus identified as the most dominant fish species. Following fish, copepods were the second most important prey group, contributing 24.3% to the IRI%. Other prey items, such as amphipods and cephalopods, were also found, but each accounted for less than 11.4% of the IRI%, indicating their minor contribution to the overall diet. In Group B, a total of 476 S. japonicus were collected, among which 194 individuals had identifiable stomach contents. The analysis revealed that fish were the dominant prey group, comprising 50.5% of the frequency of occurrence, 3.8% of the numerical composition, and 94.2% of the weight composition, resulting in a relative importance index of 65.8%. Among the identified fish, E. japonicus was the most dominant species, followed by euphausiids, which contributed 15.0% to the IRI% and indicate their position as the second most important prey group. Other prey organisms, such as amphipods and copepods, were also present but contributed less than 14.9% each to the IRI%, suggesting a relatively minor role in the diet. In Group C, 239 individuals were collected, and stomach contents were observed in 58 specimens. Fish were clearly the predominant prey, accounting for 81.0% in frequency of occurrence, 75.7% in numerical composition, and 98.6% in weight composition, leading to a remarkably high IRI% of 98.7%. E. japonicus again dominated among the fish species. Other prey items, such as carideans and cephalopods, were found in the diet, but each contributed less than 1.0% to the IRI%, indicating minimal dietary significance. When the data from the three-year sampling period were combined, a total of 1066 S. japonicus specimens were analyzed, with stomach contents observed in 513 individuals. Fish emerged as the primary prey group, accounting for 59.1% in frequency of occurrence, 6.6% in numerical composition, and 96.3% in weight composition, resulting in an overall IRI% of 71.5%. E. japonicus was again the most dominant species among the fish. Amphipods were the second most important prey group, accounting for 30.8% in frequency, 33.1% in numerical composition, and 0.2% in weight, contributing to 12.1% of the IRI%. Other prey groups, such as copepods, euphausiids, and cephalopods, were also identified, but each accounted for less than 11.8% of the IRI%, indicating a relatively minor contribution to the diet.
To evaluate the ecological trophic position of S. japonicus in the Yellow Sea, trophic levels were estimated for Groups A, B, C, and the total dataset (Table 2). The trophic level was calculated to be 3.80 for Group A, 3.82 for Group B, and 4.05 for Group C. When the data from all three years were combined, the overall trophic level was determined to be 3.87, ranging from 3.80 to 4.05.
3.4. Changes in Stomach Content Composition Based on Size Class
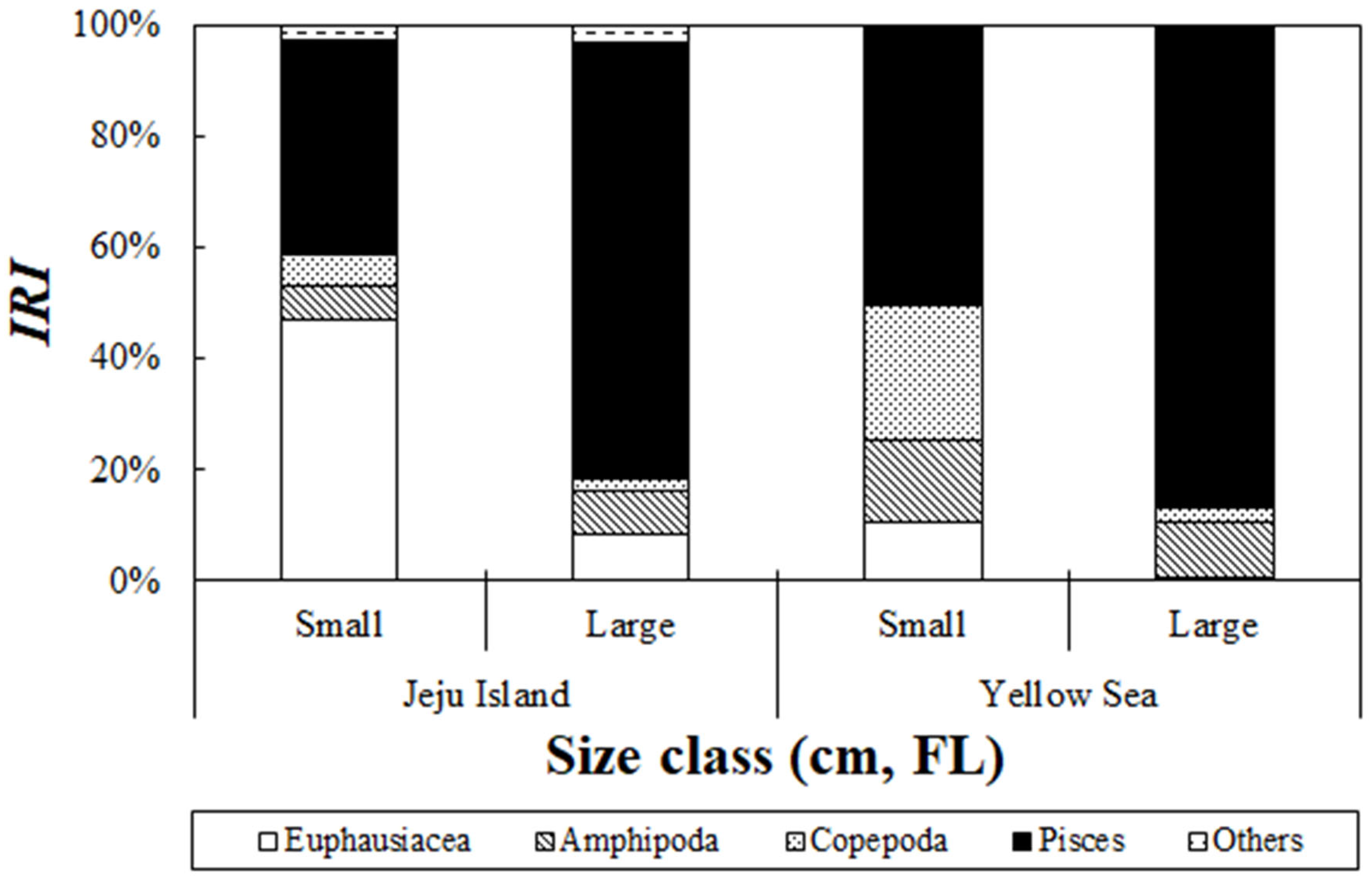
An analysis of the stomach content composition of S. japonicus collected from the Jeju Sea based on size group revealed significant differences (Figure 4). In the small-size group, euphausiids accounted for the highest relative importance index at 47.0%, followed by fish, which contributed 38.8%. In contrast, the large-sized group showed a dominant presence of fish, which accounted for 78.8% of the relative importance index. Fish contribution showed an increasing trend as the body size increased. However, as the fish grew, the relative importance index of euphausiids in the large-size group gradually dropped to 8.5%. An analysis of the stomach content composition of S. japonicus collected from the Yellow Sea based on size group revealed significant differences (Figure 4). In the small-size group, fish dominated with a relative importance index of 49.9%, followed by copepods, which contributed 24.3%. Additionally, amphipods and euphausiids accounted for relative importance indices of 15.0% and 10.5%, respectively. In the large-size group, fish accounted for the highest proportion at 86.3%, showing a clear trend of increasing fish contribution with growth. However, amphipods, copepods, and euphausiids decreased in relative importance to 9.9%, 2.7%, and 0.7%, respectively, as the fish grew.
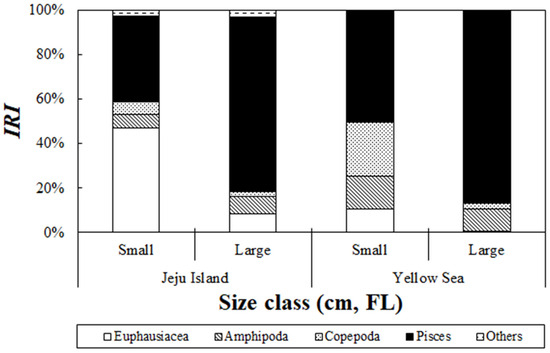
Figure 4.
Ontogenetic changes in the composition of chub mackerel, Scomber japonicus, from the waters around Jeju Island and the Yellow Sea based on the index of relative importance (%IRI) across size classes (small: 34.0 cm; large: ≥34.0 cm). In Jeju waters, small individuals primarily consumed euphausiids, whereas large individuals consumed a higher proportion of fish. In the Yellow Sea, fish were dominant in both size classes, with small individuals consuming more copepods and amphipods compared to large individuals.
These results indicate that in the small-size group, S. japonicus primarily consumes relatively small prey items but changes its feeding patterns as it grows, with fish becoming the dominant prey item.
3.5. Analysis of Feeding Patterns Based on Sea Area and Size Class
The results of a two-way PERMANOVA analysis, conducted to test the statistical significance in feeding relationships between habitats and size groups of S. japonicus collected from Jeju and the Yellow Sea (Table 3), showed significant differences in prey composition between size groups (p = 0.001) and habitats (p = 0.001) (p < 0.05). In addition, significant interaction was observed between these two factors (p = 0.008) (p < 0.05).

Table 3.
Degrees of freedom (df), sum of squares (SS), mean squares (MS), pseudo-F ratios, and significance levels (p) for PERMANOVA tests that compared the feeding characteristics based on area and size.
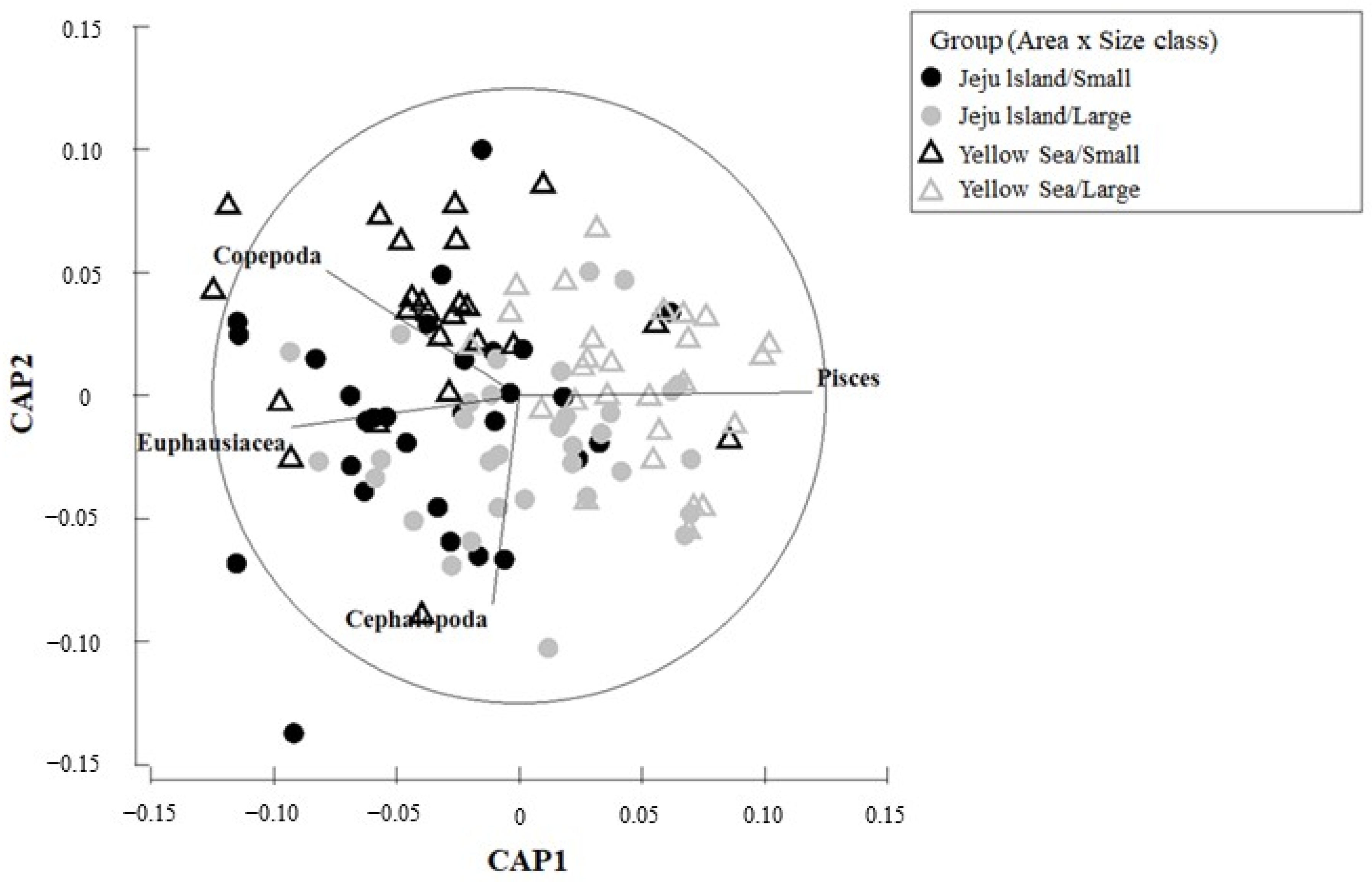
In the CAP analysis for habitats and size groups (Figure 5), copepods, euphausiids, and cephalopods were the primary contributing factors in the Jeju small-size group, whereas copepods and euphausiids were the main contributing factors in the Yellow Sea small-size group. In both Jeju and Yellow Sea large-size groups, fish were the major contributing factor, indicating that similar prey resources were formed in both habitats.
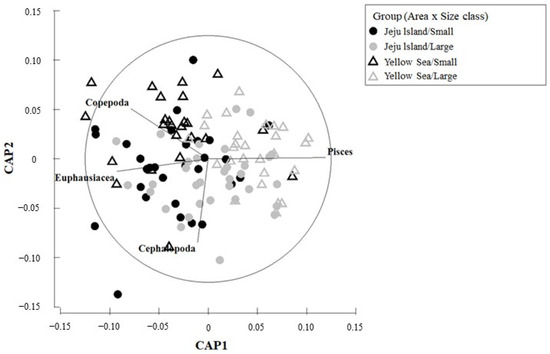
Figure 5.
Canonical analysis of principal coordinate (CAP) ordination plot of feeding characteristics of the chub mackerel, Scomber japonicus, from the waters around Jeju Island and the Yellow Sea of Korea used to assess differences between area and size class. Copepods, euphausiids, and cephalopods mainly contribute to the diet of small fish in Jeju, while fish dominate the diet of large fish in both regions.
3.6. Changes in Stomach Content Composition Based on Season
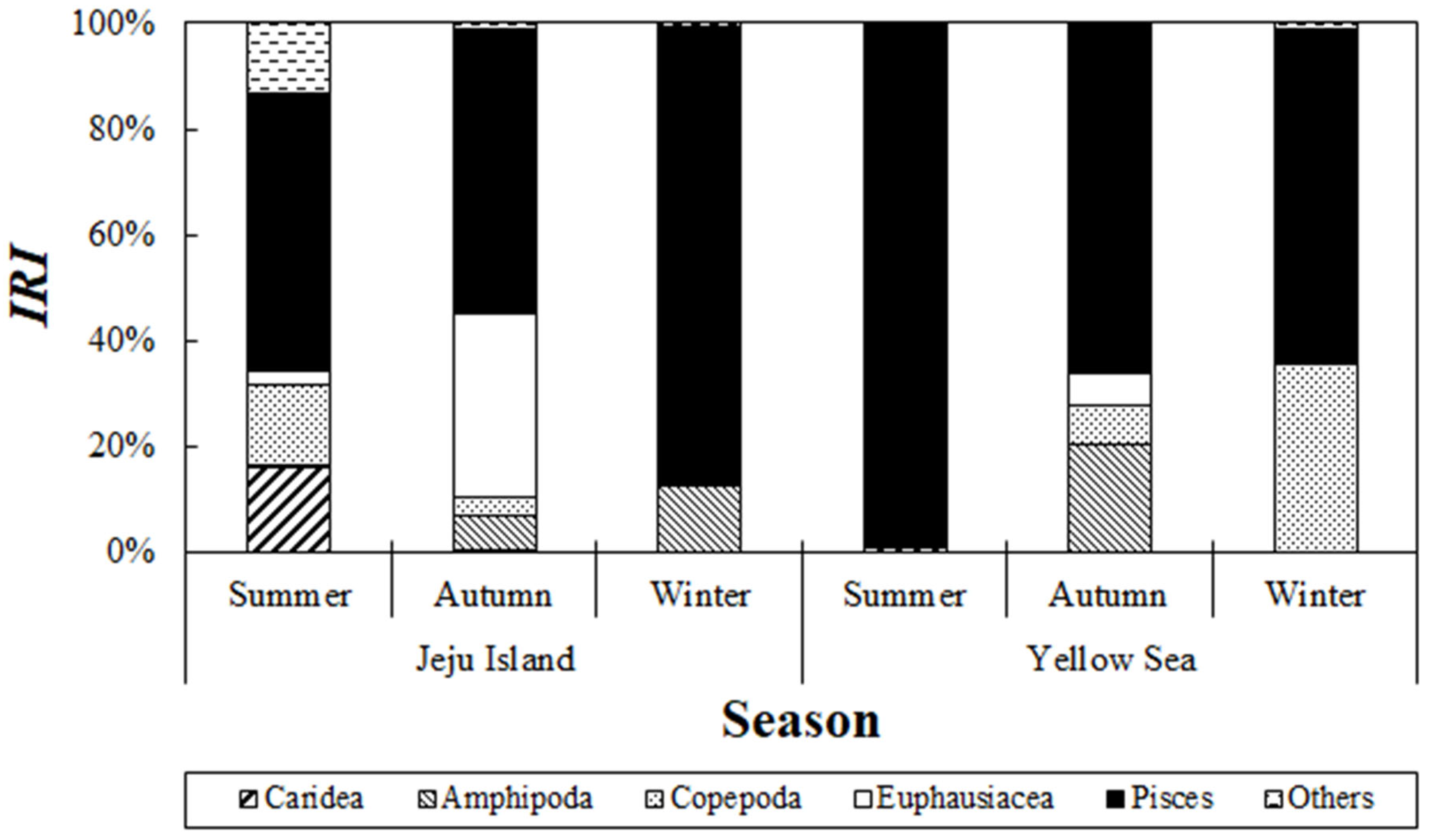
The seasonal variation in the composition of stomach contents of S. japonicus collected from the Jeju Sea was analyzed (Figure 6). During the summer, fish accounted for 52.5% of the relative importance index, making them the most dominant prey, followed by caridean shrimp (16.3%) and copepods (15.3%). In autumn, fish maintained their dominance with a relative importance index of 53.5%, followed by euphausiids with 34.8%. In winter, fish were the most dominant prey, with a relative importance index of 86.9%.
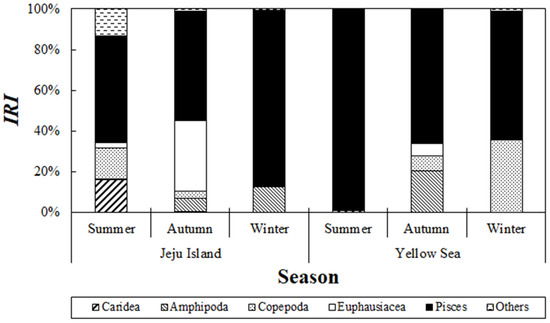
Figure 6.
Seasonal changes in the composition of chub mackerel, Scomber japonicus, from the waters around Jeju Island and the Yellow Sea based on the index of relative importance (%IRI) across seasons: Summer: August; Autumn: September to November; Winter: December. Fish were the dominant prey item in the diet across all seasons.
The seasonal variation in the composition of stomach contents of S. japonicus collected from the Yellow Sea was examined (Figure 6). In summer, fish accounted for 98.8% of the relative importance index, making them the most significant prey item. In autumn, fish comprised 65.7% of the relative importance index, followed by amphipods with 20.2%. In winter, fish remained the most dominant prey, contributing 86.9% to the relative importance index.
3.7. Changes in Stomach Content Composition Based on Size Class and Season
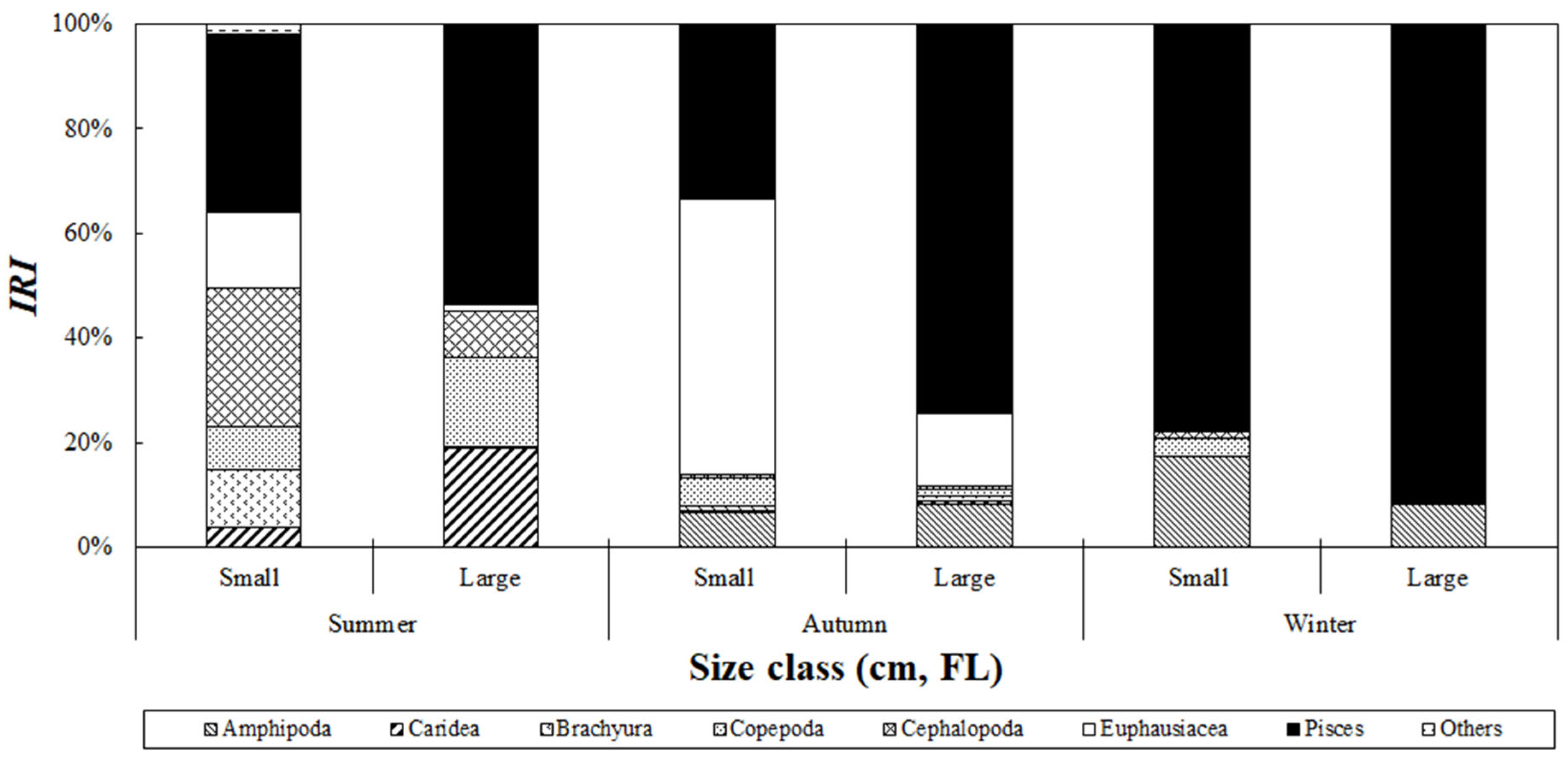
Analysis of the seasonal variation in the composition of stomach contents based on the size class of S. japonicus collected from the Jeju Sea revealed differences in prey composition based on season and size class (Figure 7). In the summer, fish accounted for 34.0% of the relative importance index in the small-size class, making it the most dominant prey item, and then followed by cephalopods and euphausiids, which contributed 26.5% and 14.7%, respectively. In the large-size class, fish also dominated and accounted for 53.5%, followed by caridean shrimp and copepods at 18.8% and 16.9%, respectively. In autumn, euphausiids dominated the small-size class with 52.7% of the relative importance index, whereas fish remained the primary prey in the large-size class, accounting for 74.5%. In winter, fish were the dominant prey item in all size classes, contributing 78.0% and 91.3% in the small- and large-size classes, respectively.
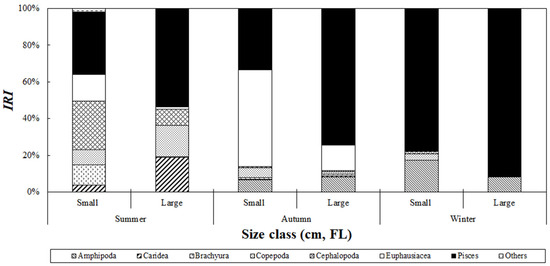
Figure 7.
Index of relative importance (%IRI) of prey composition of chub mackerel, Scomber japonicus collected from the waters around Jeju Island based on fish size and season. Season is defined as follows: Summer: August; Autumn: September to November; Winter: December. During summer and autumn, smaller-size classes primarily consumed amphipods and hyperiid amphipods, shifting to fish consumption as they grew. In winter, fish were the predominant prey across all size classes.
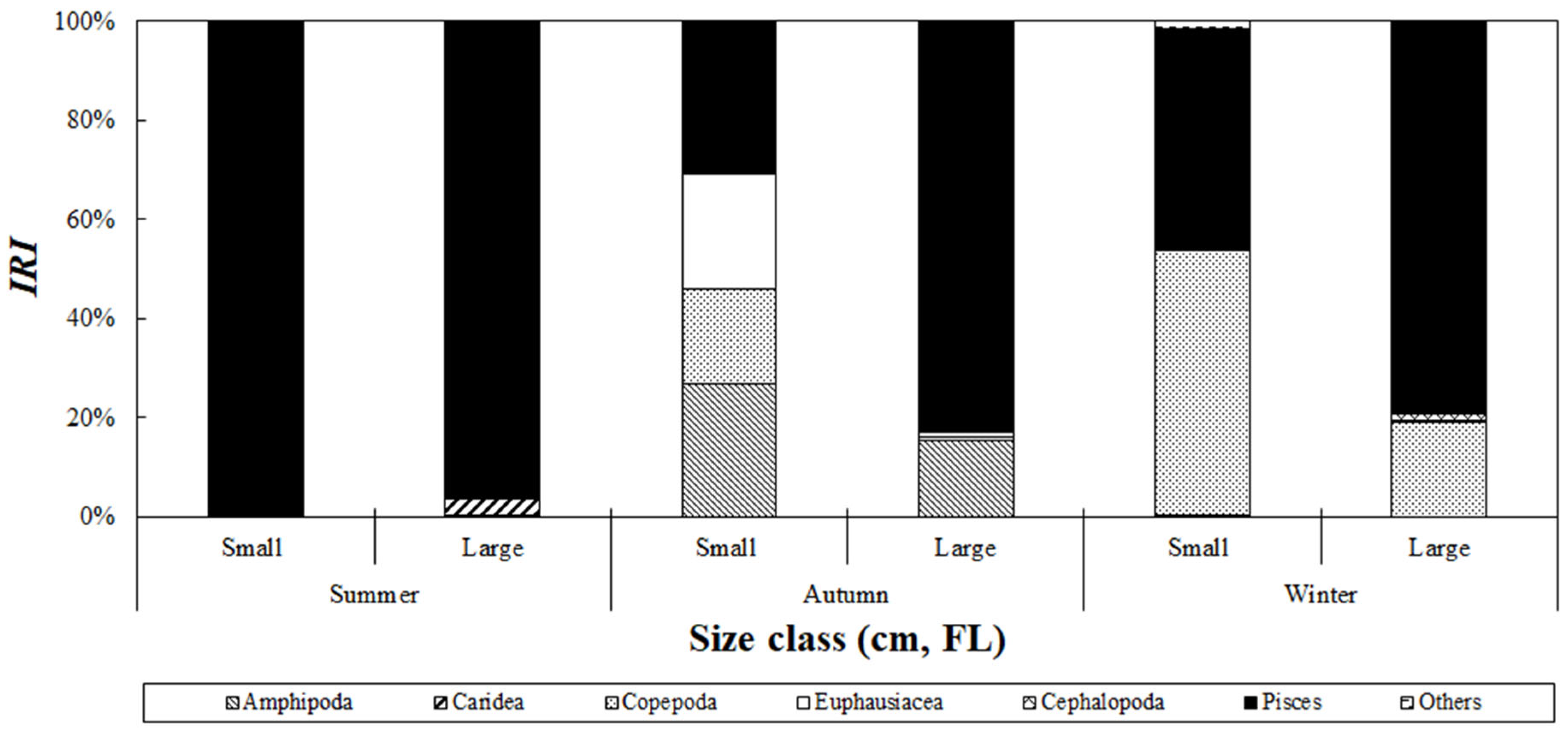
The seasonal variation in the composition of stomach contents of S. japonicus collected from the Yellow Sea was analyzed based on size class (Figure 8). In summer, fish accounted for 99.7% and 96.1% of the relative importance index in the small- and large-size classes, respectively, making them the dominant prey items in all size classes. In autumn, fish contributed 30.6% of the relative importance index in the small-size class. In addition to fish, amphipods, euphausiids, and copepods accounted for 26.9%, 23.1%, and 19.1%, respectively. In the large-size class, fish dominated with 82.9%, whereas amphipods, euphausiids, and copepods contributed 15.3%, 0.8%, and 0.8%, respectively, showing a decreasing trend in the consumption of these prey as the fish size increased. In winter, copepods became the most important prey in the small-size class, with 53.3% of the relative importance index, whereas in the large-size class, fish consumption increased to 79.0%, and the proportion of copepods decreased to 19.2%.
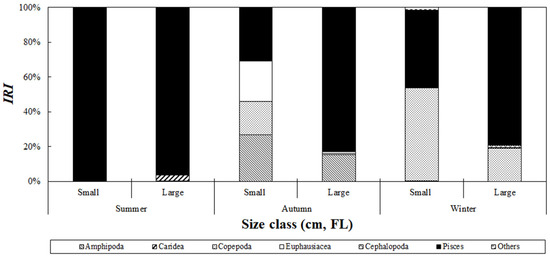
Figure 8.
Index of relative importance (%IRI) of prey composition of chub mackerel, Scomber japonicus, collected from the Yellow Sea based on fish size and season. Season is defined as follows: Summer: August; Autumn: September to November; Winter: December. During summer, fish were consumed across all size classes, whereas in autumn and winter, smaller size classes primarily fed on amphipods and copepods, shifting to fish consumption as they grew.
Overall, the prey selection of S. japonicus varied depending on the season and size class, with a tendency for the proportion of fish consumption to gradually increase as the size of the fish increases (Table 4).

Table 4.
Summary of feeding characteristics of chub mackerel, Scomber japonicus, from Jeju Island and the Yellow Sea by trophic level, size class, and season.
4. Discussion
4.1. Water Temperature Fluctuations and Mackerel Distribution Density
Analysis of temperature fluctuations showed that relatively high water temperatures persisted until December 2021 in the Yellow Sea, providing suitable habitat conditions for S. japonicus until late autumn. S. japonicus typically inhabits waters with temperatures of 7–25 °C and moves southward as temperatures drop [29]. The faster temperature decline in 2022 and 2023 likely reduced its distribution and catchability. The findings indicate that the seasonal distribution of S. japonicus is highly sensitive to water temperature changes, highlighting the need for future surveys to consider temperature conditions more closely.
4.2. Major Prey Species, Feeding Characteristics, and Trophic Level
An analysis of the feeding ecology of S. japonicus collected from the Jeju and Yellow Sea regions across Groups A, B, and C, and three years of sampling revealed that fish, especially E. japonicus, are the main prey. The Jeju region, influenced by seasonal cold-water masses and ocean currents, provides a suitable habitat for E. japonicus. Similarly, the Yellow Sea region, enriched by nutrients from river runoff and high primary productivity, creates favorable conditions for the growth of small fish populations such as E. japonicus [30,31,32,33]. After August, warm currents along the southern coast cause E. japonicus schools to migrate northward into the Yellow Sea, increasing their density and promoting their consumption by S. japonicus [34]. Both regions have high plankton productivity, favoring E. japonicus growth and reproduction, and E. japonicus mainly inhabit the surface layer (0–25 m) and are highly gregarious [35,36,37,38]. In contrast, S. japonicus found in the Jeju Sea region in 2023 fed on major prey species, particularly C. snyderi. Previous studies by Kim et al. [39] and Yoo et al. [40] have reported that juvenile C. snyderi are the dominant species in the Jeju coastal waters. C. snyderi drifts along the bottom while feeding and migrates vertically to the surface at night [41,42]. Conversely, S. japonicus is more active at night, often rising to 20–25 m depth, making it vulnerable to nighttime purse seine fishing [43]. S. japonicus is an opportunistic feeder relying on strong swimming and schooling behavior to prey mainly on small fish, feeding mostly around 25 m depth, which is favorable for feeding on E. japonicus and C. snyderi. E. japonicus is a primary prey for various predators, including Xiphias gladius (Swordfish), Thunnus orientalis (Pacific bluefin tuna), and Todarodes pacificus (Common Squid). E. japonicus in Jeju and the Yellow Sea serve as prey for many species, such as Sarda orientalis (Oriental Bonito) and T. japonicus [44,45,46,47]. Studies suggest a similar ecological relationship between E. japonicus and S. niphonius, highlighting the importance of E. japonicus as prey during spawning, which likely applies to S. japonicus as well [48,49]. Feeding patterns of S. japonicus vary seasonally with prey availability and density, influenced by regional environmental factors. Studies conducted in the South Sea of Korea by Cha et al. [50], Yoon et al. [17], Seong et al. [19], and Kim [51], as well as in the Yellow Sea by Park et al. [20], have all identified E. japonicus as the primary prey of S. japonicus, consistent with the findings of the present study. However, Park et al. [21] reported euphausiids as the main prey in waters around Jeju Island, likely due to differences in sampling periods. Whereas previous studies collected samples throughout all four seasons, the present study only included summer, autumn, and winter, excluding spring. During spring, S. japonicus migrates inshore for spawning and feeds on crustacean larvae and euphausiids [17]. In particular, euphausiids become highly abundant at night in spring in the southern waters of Jeju Island. In contrast, during winter, which is a common sampling period in both the current and previous studies, the composition of dominant prey species was similar. S. japonicus exhibits opportunistic predation, selecting prey based on availability, using a “feed-on-the-fly” strategy to track and capture prey in real time with sharp vision and speed adjusted to prey size [52,53,54]. Both the present and previous studies confirm S. japonicus as a strong exploratory opportunistic feeder, preying mainly on species frequenting specific habitats.
Trophic levels generally range from 2.0 (Herbivory/Detritivory) to 5.0 (Carnivory/Piscivory) [55,56]. The trophic level of S. japonicus in Jeju and Yellow Sea waters ranged from 3.76 to 4.05, consistent with previous studies in the South and Yellow Seas (3.65–4.00) [17,19,20,51]. Compared to other species, T. orientalis had a trophic level of 4.44, and Lophius litulon (Yellow goosefish) and Neophocaena phocaenoides (Finless porpoise) had levels of 4.04 and 4.20, respectively [57,58,59]. This indicates that S. japonicus occupies an intermediate trophic level, serving as an important link between top predators and lower food webs in Korean pelagic ecosystems.
4.3. Ontogenetic Diet Shift
Fish prefer larger prey with higher trophic levels for greater energy efficiency as they grow due to changes in body shape and ecological characteristics. Migratory species like S. japonicus minimize energy expenditure in foraging by consuming abundant prey in their habitat, reducing inter- and intraspecific competition, and promoting efficient growth [51]. In the present study, as S. japonicus in both Jeju and Yellow Sea waters grew, consumption of copepods, amphipods, and euphausiids decreased, whereas consumption of fish increased. Previous studies in Korean waters have similarly observed dietary shifts from zooplankton such as amphipods and euphausiids to fish with growth [17,20,21,50]. Comparable patterns have also been reported by Castro [60], Yokota et al. [61], and Lipskaya [62] in other regions, where smaller fish primarily consume copepods and larger fish shift to small fish. Other Korean species such as Lateolabrax japonicus (Sea bass), T. japonicus, and Doederleinia berycoides (Blackthroat seaperch) also transition from zooplankton in early stages to fish as they grow [47,63,64]. The findings suggest that S. japonicus shifts its diet from euphausiids, copepods, and amphipods in smaller size groups to higher trophic level prey such as small fish like E. japonicus as it grows.
4.4. Seasonal Characteristics
Seasonal analysis of the stomach contents revealed that the proportion of fish as diet in Jeju was relatively higher during the winter, whereas in the Yellow Sea, the proportion of fish was relatively higher in the summer, with E. japonicus being the primary prey item among fish. According to Ko et al. [65], E. japonicus were the dominant species in the fishing grounds around Jeju during the low-temperature winter period. Additionally, a study by Cha et al. [66] conducted along the Yellow Sea coast reported that 97.3% of the fish collected during the survey period were E. japonicus, with large numbers entering the fishing grounds at the time. Therefore, the high E. japonicus abundance in the winter fishing grounds of Jeju and the summer fishing grounds of the Yellow Sea likely served as a major food resource for S. japonicus, influencing its feeding ecology. A more detailed analysis of the seasonal ecological characteristics of S. japonicus based on size groups showed that as the seasons changed from summer to fall and winter, larger individuals tended to consume a higher proportion of fish. Notably, during fall in the Jeju Sea, small-size groups were predominantly feeding on euphausiids. According to Lee [67], both juvenile and adult euphausiids were reported to be present in high densities during the period. However, in the Yellow Sea, small-size groups of S. japonicus predominantly consumed copepods during the winter. A study by Lim et al. [68] observed that copepods were the most dominant group during the autumn and winter survey periods, with copepods accounting for 83.33% of the total zooplankton community from late autumn to early spring. The findings suggest that small-size groups of S. japonicus feed primarily on the dominant prey species present in that period and region. This study indicates that the enlargement of the mouth and improved swimming ability of the individuals as they grow have an impact on their feeding ecology and suggests that S. japonicus efficiently utilizes available food resources in different environments based on its size group. In conclusion, the feeding ecology of S. japonicus is highly responsive to seasonal factors and regional environmental characteristics, with the consumption of specific prey species in certain seasons being closely related to the environmental features of the respective habitats [69]. Furthermore, since S. japonicus feeds primarily on small fish such as E. japonicus, it is likely that copepods and amphipods present in the stomachs of E. japonicus are also consumed during feeding, a natural occurrence in the feeding process of S. japonicus.
The present study provides essential foundational data on the feeding ecology of S. japonicus in the Jeju and Yellow Sea regions, contributing to sustainable fisheries management and future research. It is the first to compare and analyze stomach contents based on trophic levels in the regions, offering valuable input data and model validation material for fisheries ecosystem models using S. japonicus, an amphidromous apex predator. However, research on growth and seasonal prey variation remains insufficient. This study excluded individuals smaller than 19.3 cm and did not include spring samples, limiting the analysis scope. Observed variations in sample availability related to regional sea temperature distributions highlight the need for a more planned sampling strategy accounting for sea temperature in seasonal feeding ecology studies. Future research should encompass the entire size range of S. japonicus and year-round sampling to comprehensively analyze feeding habits across growth stages in relation to marine environmental factors.
Author Contributions
Conceptualization, H.-S.P. and S.H.S.; methodology, H.-S.P.; software, H.-S.P.; validation, S.H.S. and J.M.J.; formal analysis, H.-S.P.; investigation, H.-S.P.; resources, C.K.; data curation, H.-S.P.; writing—original draft preparation, H.-S.P.; writing—review and editing, S.H.S., J.M.J., J.H.Y. and C.K.; visualization, H.-S.P.; supervision, C.K.; project administration, C.K.; funding acquisition, J.H.Y. All authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript.
Funding
This research was supported by the National Institute of Fisheries Science, Korea (R2025007).
Data Availability Statement
The oceanic environmental data used in this study were published by the Korea Ocean Data Center (KODC) and can be accessed at https://www.nifs.go.kr/kodc/eng/index.kodc, accessed on 4 February 2025.
Acknowledgments
This research was funded by a grant from the National Institute of Fisheries Science, Korea (R2025007). We would like to thank the reviewers and editors for their thoughtful review of this paper.
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare no conflicts of interest.
Abbreviations
The following abbreviations are used in this manuscript:
| IRI | Index of Relative Importance |
| PERMANOVA | Permutational Multivariate Analysis of Variance |
| CAP | Canonical Analysis of Principal Coordinate |
| KODC | Korea Ocean Data Center |
References
- Kim, D.G.; Jeong, J.M.; Lee, S.J.; Kang, S.Y.; Seong, G.C.; Kang, D.Y.; Jin, S.Y.; Baeck, G.W. Comparison of stomach contents of yellow goosefish Lophius litulon, in the South Sea and Yellow Sea, Korea. Korean J. Fish. Aquat. Sci. 2022, 55, 714–720. [Google Scholar]
- Park, K.A.; Park, J.E.; Choi, B.J.; Lee, S.H.; Lee, E.I.; Byun, D.S.; Kim, Y.T. An analysis of oceanic current maps of the Yellow Sea and the East China Sea in secondary school science textbooks. J. Korean Earth Sci. Soc. 2014, 35, 439–466. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kondo, M. Oceanographic investigations of fishing grounds in the East China Sea and the Yellow Sea-I, Characteristics of the mean temperature and salinity distributions measured at 50 m and near the bottom. Bull. Seikai Reg. Fish. Res. Lab. 1985, 62, 19–66. [Google Scholar]
- Kim, C.S.; Han, I.S.; Lee, J.S.; Yang, J.Y. Establishment of a foundation for risk assessment in fisheries issues and identification of the impact of marine climate change, 2024. J. Clim. Change Res. 2024, 15, 909–918. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kang, Y.H.; Ju, S.J.; Park, Y.G. Predicting impacts of climate change on Sinjido marine food web. Ocean Polar Res. 2012, 34, 239–251. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lu, H.J.; Lee, H.L. Changes in the fish species composition in the coastal zones of the Kuroshio Current and China Coastal Current during periods of climate change: Observations from the set-net fishery (1993–2011). Fish. Res. 2014, 155, 103–113. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Payne, M.R.; Kudahl, M.; Engelhard, G.H.; Peck, M.A.; Pinnegar, J.K. Climate risk to European fisheries and coastal communities. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2021, 118, e2018086118. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, S. Changes in fisheries resources in relation to variability of oceanic environments. J. Korean Fish. Soc. 2003, 6, 11–20. [Google Scholar]
- FAO. Fishery and Aquaculture Statistics; FAO: Rome, Italy, 2016. [Google Scholar]
- Yang, Y.J.; Kim, S.H.; Rho, H.K.; Jeong, D.G. Relationship between SST fronts and purse-seine fishing grounds in the South-West Sea of Korea and the northern area of the East China Sea. Korean J. Fish. Aquat. Sci. 1999, 32, 618–623. [Google Scholar]
- Hwang, S.D.; Baik, C.I.; Park, J.H.; Choi, K.H. Seasonal and annual variations of catch by large purse seine off Korea. J. Korean Soc. Oceanogr. 2001, 6, 164–179. [Google Scholar]
- Lee, H.N.; Kim, H.S. Variation of fisheries conditions of mackerel (Scomber japonicus) fishing ground for large purse seine fisheries. J. Korean Soc. Fish. Ocean. Technol. 2011, 47, 108–117. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, S.R.; Kim, J.J.; Park, H.W.; Kang, S.K.; Cha, H.K.; Baek, H.J. Maturity and spawning of the chub mackerel Scomber japonicus in the Korean waters. Korean J. Fish. Aquat. Sci. 2020, 53, 9–18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jang, Y.S.; Park, K.S.; Lee, J.P. A study of fisheries distribution margin and performance; focused on the case of mackerel. J. Fish. Bus. Adm. 2015, 46, 143–161. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Melnychuk, M.C.; Peterson, E.; Elliott, M.; Hilborn, R. Fisheries management impacts on target species status. Proc. Nat. Acad. Sci. USA 2017, 114, 178–183. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shoji, J.; Tanaka, M.; Maehara, T. Comparative diets and growth of two scombrid larvae, chub mackerel Scomber japonicus and Japanese Spanish mackerel Scomberomorus niphonius, in the central Seto Inland Sea, Japan. Ecol. Aquac. Species Enhanc. Stock. 2001, 30, 93–103. [Google Scholar]
- Yoon, S.J.; Kim, D.H.; Baeck, G.W.; Kim, J.W. Feeding habits of chub mackerel (Scomber japonicus) in the South Sea of Korea. Korean J. Fish. Aquat. Sci. 2008, 41, 26–31. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kume, G.; Shigemura, T.; Okanishi, M.; Hirai, J.; Shiozaki, K.; Ichinomiya, M.; Komorita, T.; Habano, A.; Makino, F.; Kobari, T. Distribution, feeding habits, and growth of chub Mackerel, Scomber japonicus, larvae during a high-stock period in the Northern Satsunan Area, Southern Japan. Front. Mar. Sci. 2021, 8, 725227. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Seong, G.C.; Kim, D.G.; Jin, S.Y.; Soh, H.Y.; Baeck, G.W. Diet composition of the chub mackerel Scomber japonicus in the coastal waters of the South Sea of Korea. Korean J. Fish. Aquat. Sci. 2021, 54, 73–79. [Google Scholar]
- Park, H.S.; Kim, C.S.; Yang, J.H.; Song, S.H. Feeding characteristics of chub mackerel Scomber japonicus in the Yellow Sea of Korea in autumn. Korean J. Ichthyol. 2023, 35, 278–284. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Park, H.S.; Kim, S.R.; Song, S.H.; Kim, C.S. Diet composition of chub mackerel, Scomber japonicus in coastal waters of Jeju Island, Korea. Korean J. Ichthyol. 2023, 35, 113–120. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, I.S.; Choi, Y.; Lee, C.L.; Lee, Y.J.; Kim, B.J.; Kim, J.H. Illustrated Book of Korean Fishes; Kyo-Hak Publishing Co., Ltd.: Seoul, Korea, 2005; pp. 420–443. [Google Scholar]
- Hyslop, E.J. Stomach contents analysis: A review of methods and their application. J. Fish Biol. 1980, 17, 411–429. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pinkas, L.; Oliphant, M.S.; Iverson, I.L.K. Food habits of albacore, bluefin tuna, and bonito in California waters. Fish. Bull. 1971, 152, 1–105. [Google Scholar]
- Cortés, E. Standardized diet compositions and trophic levels of sharks. ICES J. Mar. Sci. 1999, 56, 707–717. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pauly, D.; Trites, A.W.; Capuli, E.; Christensen, V. Diet composition and trophic levels of marine mammals. ICES J. Mar. Sci. 1998, 55, 467–481. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ebert, D.A.; Bizzarro, J.J. Standardized diet compositions and trophic levels of skates (Chondrichthyes: Rajiformes: Rajoidei). Environ. Biol. Fish. 2007, 80, 221–237. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Anderson, M.J.; Gorley, R.N.; Clarke, K.R. PERMANOVA + for PRIMER: Guide to Software and Statistical Methods; PRIMER-E: Albany, New Zealand; Plymouth Marine Laboratory: Plymouth, UK, 2008. [Google Scholar]
- NIFS (National Institute of Fisheries Science). Ecology and Fishing Ground of Fisheries Resources in Korean Waters; NIFS: Busan, Republic of Korea, 2017; p. 411. [Google Scholar]
- Kim, D.S.; Sim, J.H.; Lee, J.A.; Kang, Y.C. The distribution of nutrients and chlorophyll in the northern East China Sea during the spring and summer. Ocean Polar Res. 2005, 27, 251–263. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, S.H.; Pang, I.C. Distribution and characteristic of transport mechanism of eggs and larvae of anchovy, Engraulis japonica, in the southwestern sea of Korea in July and November, 2001. Korean J. Fish. Aquat. Sci. 2005, 38, 331–341. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ko, J.C.; Yoo, J.T.; Rho, H.K. Environmental factors and the distribution of eggs and larvae of the anchovy, Engraulis japonica in the coastal waters of Jeju Island. Korean J. Fish. Aquat. Sci. 2007, 40, 394–410. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Youn, B.I.; Choi, D.H.; Im, Y.J.; Kim, J.N.; Kim, M.J. A study on the characteristics of fish community in the coastal water of the Five West Sea Islands in Korea. J. Korean Soc. Fish. Ocean Technol. 2020, 56, 213–222. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chang, S.D.; Hong, S.Y.; Park, C.K.; Chin, P.; Lee, B.G.; Lee, T.Y.; Kang, Y.J.; Gong, Y. Studies on the migration of anchovy Engraulis japonica in Korean waters. Publ. Inst. Mar. Sci. Nat. Fish. Univ. Busan 1980, 12, 1–38. [Google Scholar]
- Suh, H.L.; Soh, H.Y. Zooplankton in the waters around Cheju Island: A brief overview. Bull. Mar. Res. Inst. 1993, 17, 57–67. [Google Scholar]
- Bacha, M.; Amara, R. Spatial, temporal and ontogenetic variation in diet of anchovy (Engraulis encrasicolus) on the Algerian coast (SW Mediterranean). Estuar. Coast. Shelf Sci. 2009, 85, 257–264. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Seo, M.H.; Shin, K.S.; Jang, M.C.; Soh, H.Y. Occurrence patterns of zooplankton present in ports of Korea during summer. Korean J. Environ. Biol. 2013, 31, 448–457. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, C.I.; Jang, L.H.; Park, S.E. Influence of water temperature during the main spawning period on anchovy catch. Korean J. Fish. Aquat. Sci. 2009, 42, 297–301. [Google Scholar]
- Kim, Y.U.; Kang, C.B.; Kim, J.K.; Jung, G.A.; Myoung, J.G. New records of two species, Megalaspis cordyla and Champsodon snyderi (Pisces: Perciformes) from Korea. Kor. J. Ichthyol. 1995, 7, 101–108. [Google Scholar]
- Yoo, J.M.; Kim, S.; Lee, E.K.; Kim, Y.U. Studies on the fish larvae community in the sea around Cheju Island in November, 1986. J. Korean Soc. Oceanogr. 1998, 3, 71–79. [Google Scholar]
- Smith, J.L.B. The Sea Fishes of Southern Africa; Central News Agency: Cape Town, South Africa, 1953. [Google Scholar]
- Morohoshi, Y.; Sasaki, K. Intensive cannibalism and feeding on bregmacerotids in Champsodon snyderi (Champsodontidae): Evidence for pelagic predation. Ichthyol. Res. 2003, 50, 387–390. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cho, J.H.; Hong, S.G.; Oh, S.T.; Jung, M.S.; Lee, S.M. Optimal Exploitation of Mackerel Stocks in Korea: An Application of Bioeconomic Model; Basic report; Korea Maritime Institute: Busan, Republic of Korea; p. 15.
- Odate, S. Studies on the larval fish of the Japanese anchovy, Engraulis japonica (Houttuyn), in the northeastern sea area of Japan. Bull. Tohoku Reg. Fish. Res. Lab. 1957, 9, 111–128. [Google Scholar]
- Hayashi, S. A note on the biology and fishery of the Japanese anchovy Engraulis japonica (Houttuyn). CalCOFI Rep. 1966, 11, 44–57. [Google Scholar]
- Kim, H.J.; Jeong, J.M. Diet composition of oriental bonito (Sarda orientalis) in coastal waters of Jeju Island, Korea. Korean J. Ichthyol. 2020, 32, 8–13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, D.G.; Seong, G.C.; Jin, S.Y.; Soh, H.Y.; Baeck, G.W. Diet composition and trophic level of jack mackerel, Trachurus japonicus, in the South Sea of Korea. J. Korean Soc. Fish. Ocean Technol. 2021, 57, 117–126. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, W.K. The mouth structure and feeding habits of Scomberomorus niphonius. Acta Oceanol. Sin. 1987, 9, 525–530. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar]
- Ye, M.Z.; Zhang, Z. The distribution and behaviour of Engraulis japonicus Temminck and Schlegel and its detection in the North China Seas (Hwang-hai and Po-hai). J. Fish. China 1965, 2, 27–34, (In Chinese, English abstract). [Google Scholar]
- Cha, B.Y.; Gong, Y.G.; Lee, C.H.; Kim, D.H. Feeding ecology of pacific mackerel, Scomber japonicus in Korean waters. J. Korean Soc. Fish. Res. 2004, 6, 14–22. [Google Scholar]
- Kim, D.G. Study on Population Ecology of Chub Mackerel, Scomber japonicus, in the South Sea, Korea. Ph.D. Dissertation, Gyeongsang National University, Jinju, Republic of Korea, 2024. [Google Scholar]
- Folkvord, A.; Hunter, J.R. Size-specific vulnerability of northern anchovy Engraulis mordax larvae to predation by fishes. Fish. Bull. US 1986, 84, 859–869. [Google Scholar]
- Pepin, P.; Koslow, J.A.; Pearre, S. Laboratory study of foraging by atlantic mackerel, Scomber scombrus, on natural zooplankton assemblages. Can. J. Fish. Aquat. Sci. 1988, 45, 879–887. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Macy, W.K.; Sutherland, S.J.; Durbin, E.G. Effects of zooplankton size and concentration and light intensity on the feeding behavior of Atlantic mackerel, Scomber scombrus. Mar. Ecol. Prog. Ser. 1998, 172, 89–100. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pauly, D.; Christensen, V.; Dalsgaard, J.; Froese, R.; Torres, F. Fishing down marine food webs. Science 1998, 279, 860–863. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pauly, D.; Palomares, M.L. Approaches for dealing with three sources of bias when studying the fishing down marine food web phenomenon. In Fishing Down the Mediterranean Food Webs; Briand, F., Ed.; CIESM Workshop Series; Kerkyra, Greece, 26–30 July 2000; CIESM: Monaco, 2000; Volume 12, pp. 61–66. [Google Scholar]
- Park, K.J. Feeding Habits of Finless Porpoise, Neophocaena phocaenoides, in the Yellow Sea. Master’s Thesis, Pukyoung National University, Busan, Republic of Korea, 2002. [Google Scholar]
- Jo, H.J.; Lee, S.I.; Kim, D.N.; Lee, M.K. Feeding habits of the pacific bluefin tuna, Thunnus orientalis, in Korean waters. J. Korean Soc. Fish. Ocean Technol. 2019, 55, 20–28. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, D.G.; Kim, H.J.; Lee, S.J.; Baeck, G.W. Feeding habits and trophic level of blackthroat seaperch, Doederleinia berycoides, in the South Sea of Korea. Korean J. Ichthyol. 2022, 34, 172–178. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Castro, J.J. Feeding ecology of chub mackerel Scomber japonicus in the Canary Islands area. S. Afr. J. Mar. Sci. 1993, 13, 323–328. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yokota, T.; Toriyama, M.; Kanai, F.; Nomura, S. Studies on the feeding habit of fishes. Bull. Nankai Reg. Fish. Res. Lab. 1961, 14, 1–234, (In Japanese with English abstract). [Google Scholar]
- Lipskaya, N.Y. The feeding of larvae of the chub mackerel, Scomber japonicus (Scombridae), from the southeastern Pacific. J. Ichthyol. 1982, 22, 97–104. [Google Scholar]
- Huh, S.H.; Park, J.M.; Park, S.C.; Jeong, D.; Park, C.I.; Baeck, G.W. Feeding habits of Lateolabrax japonicus in the coastal waters off Dolsan-do, Yeosu. Korean J. Ichthyol. 2009, 21, 23–27. [Google Scholar]
- Kim, J.T.; No, H.G.; Kim, S.H. Studies on the forming mechanism of the fishing ground of yellowtail, Seriola quinqueradiata in the adjacent sea of Jeju Island. Bull. Korean Soc. Fish. Technol. 2002, 38, 20–35. [Google Scholar]
- Ko, J.C.; Kim, B.Y.; Kim, M.J.; Park, S.E.; Kim, J.B.; Cho, H.K. A seasonal characteristic of marine environment and fish assemblage in the coastal waters of Jeju Island, Korea from 2012 to 2013. J. Fish. Mar. Sci. Educ. 2015, 27, 327–352. [Google Scholar]
- Cha, B.Y.; Im, Y.J.; Jo, H.S.; Kwo, D.H. A fish community caught by a stow net in the water off Hwaseong City, the West Sea, Korea. Korean J. Ichthyol. 2013, 25, 119–134. [Google Scholar]
- Lee, B.R. Distribution of Euphausiids and Population Structure of Euphausia pacifica in Korea Waters. Ph.D. Dissertation, Pukyoung National University, Busan, Republic of Korea, 2021. [Google Scholar]
- Lim, D.H.; Yoon, W.D.; Yang, J.Y.; Lee, Y. The spatio-temporal distribution of zooplankton communities in the northern Yellow Sea during autumn and winter. J. Korean Soc. Mar. Environ. Saf. 2009, 15, 339–344. [Google Scholar]
- Bang, M.Y.; Sohn, D.W.; Kim, J.J.; Choi, W.K.; Hazen, E.L.; Kang, S.K.; Kim, S.G.; Jang, C.J. Projected changes in seasonal potential distribution of chub mackerel (Scomber japonicus) under continued ocean warming in Korean waters. Mar. Ecol. Prog. Ser. 2024, 751, 133–152. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).