Evaluation of Hydraulic Performance of Sewage Pipe Networks
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Methodology
2.1. Indicators for Assessing Hydraulic Performance
2.1.1. Pipe Flow Velocity
2.1.2. Pipe Fullness
2.1.3. Manhole Fullness
2.1.4. Pipe Network Comprehensive Score
2.2. Research Object
2.3. SWMM Pipe Network Model
2.3.1. SWMM
2.3.2. Model Run Indicators
2.3.3. Drainage Curves for Drainage Households
3. Result and Discussion
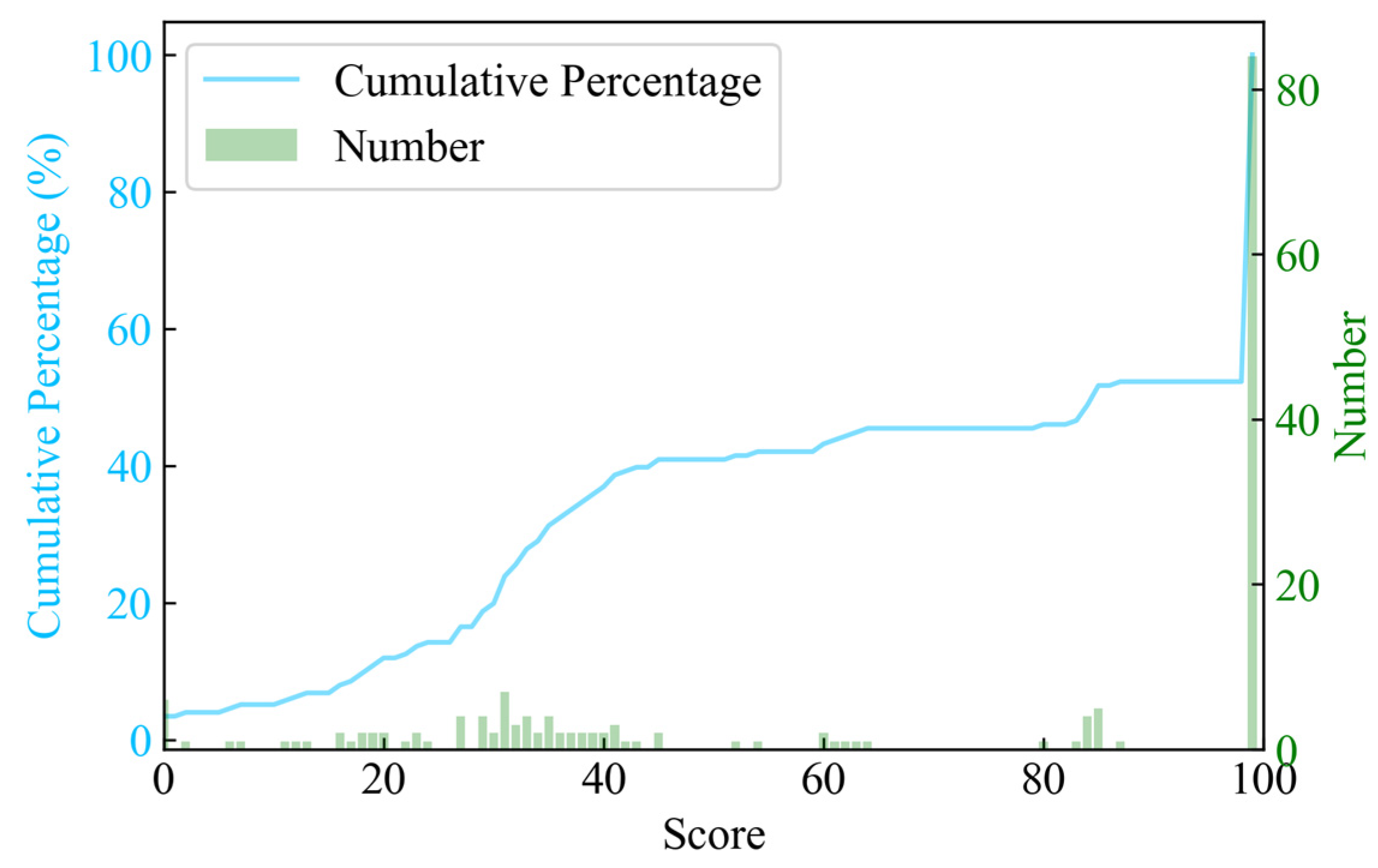
3.1. Pipe Flow Velocity Evaluation
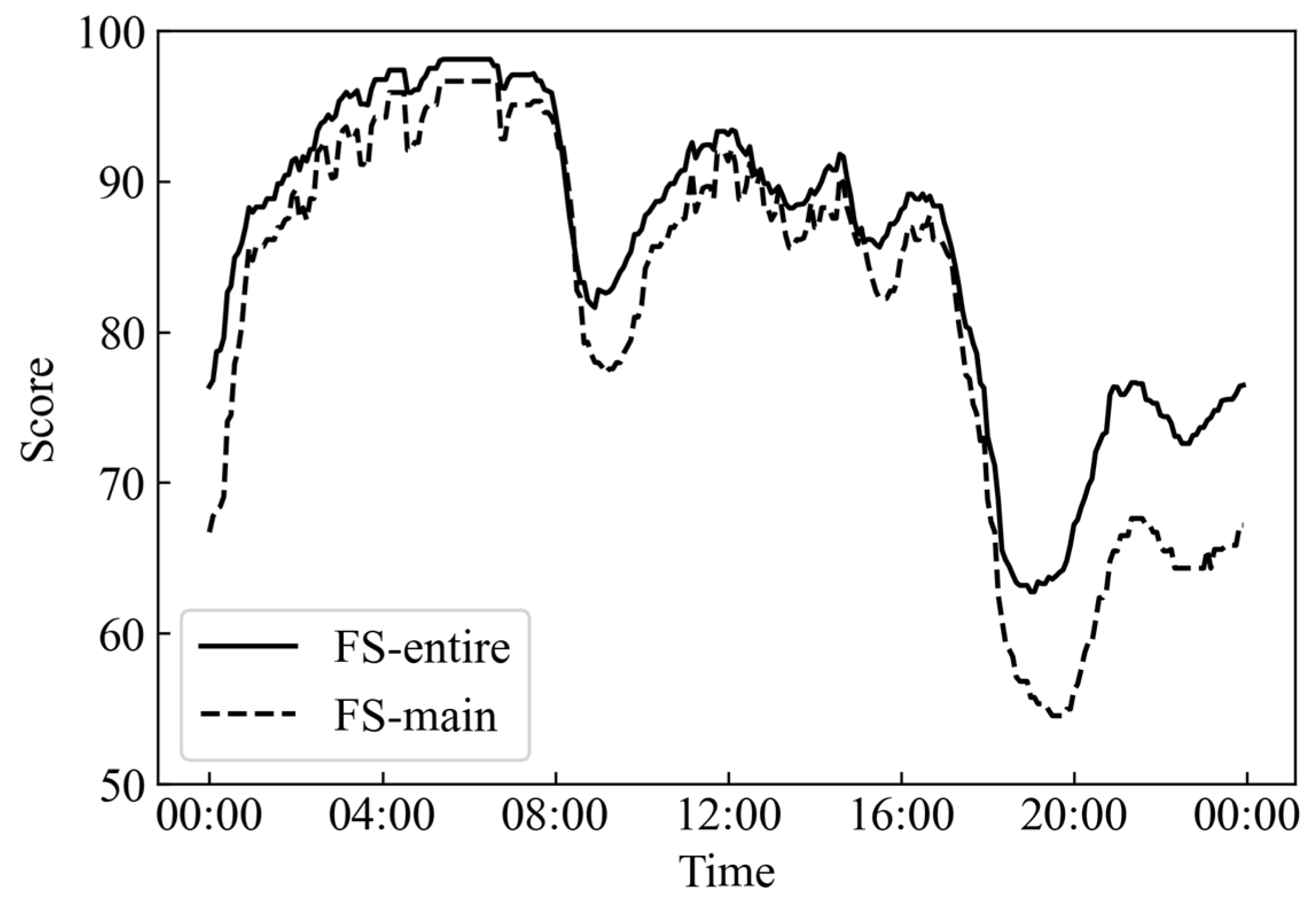
3.2. Pipe Fullness Evaluation
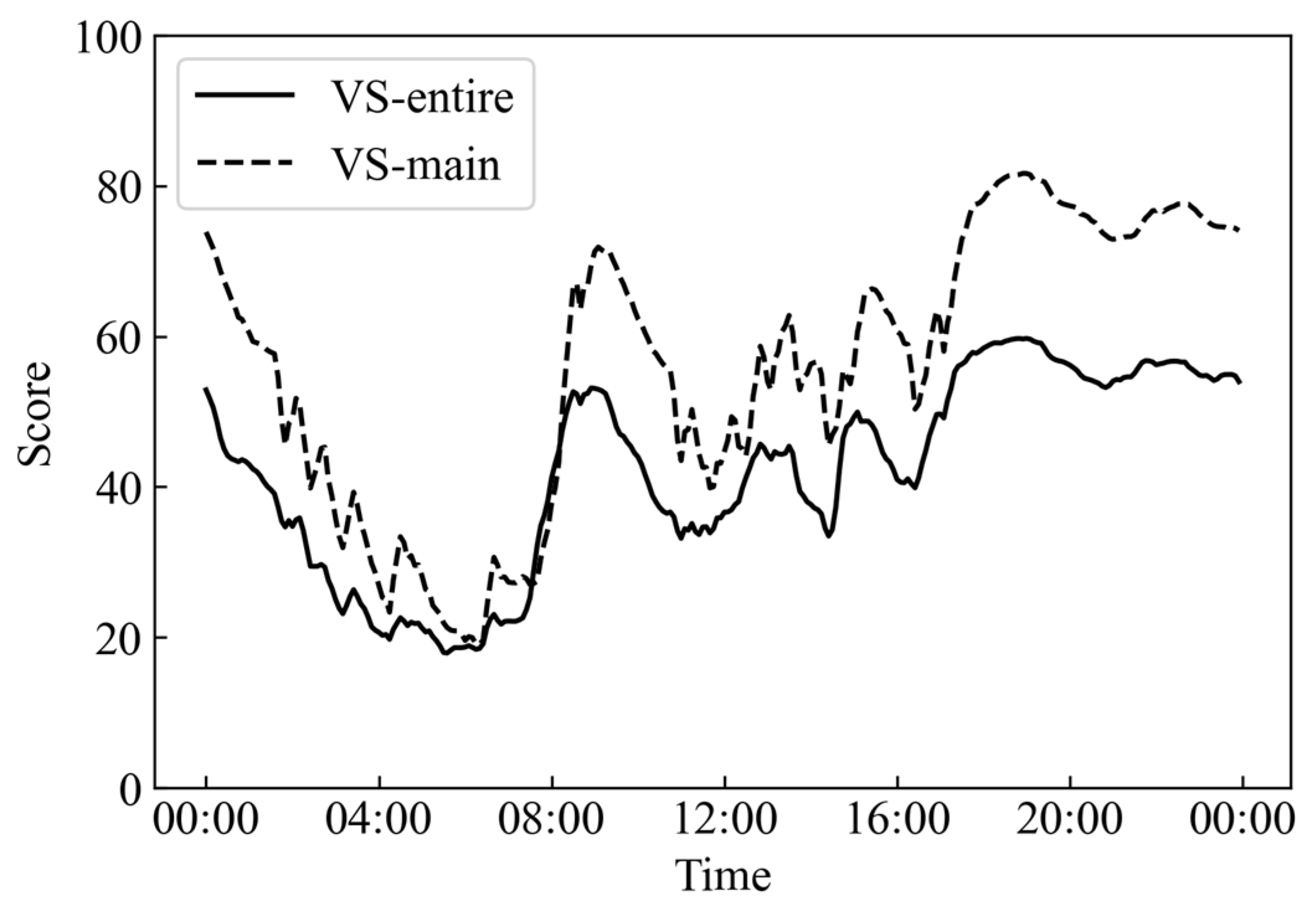
3.3. Manhole Fullness Evaluation
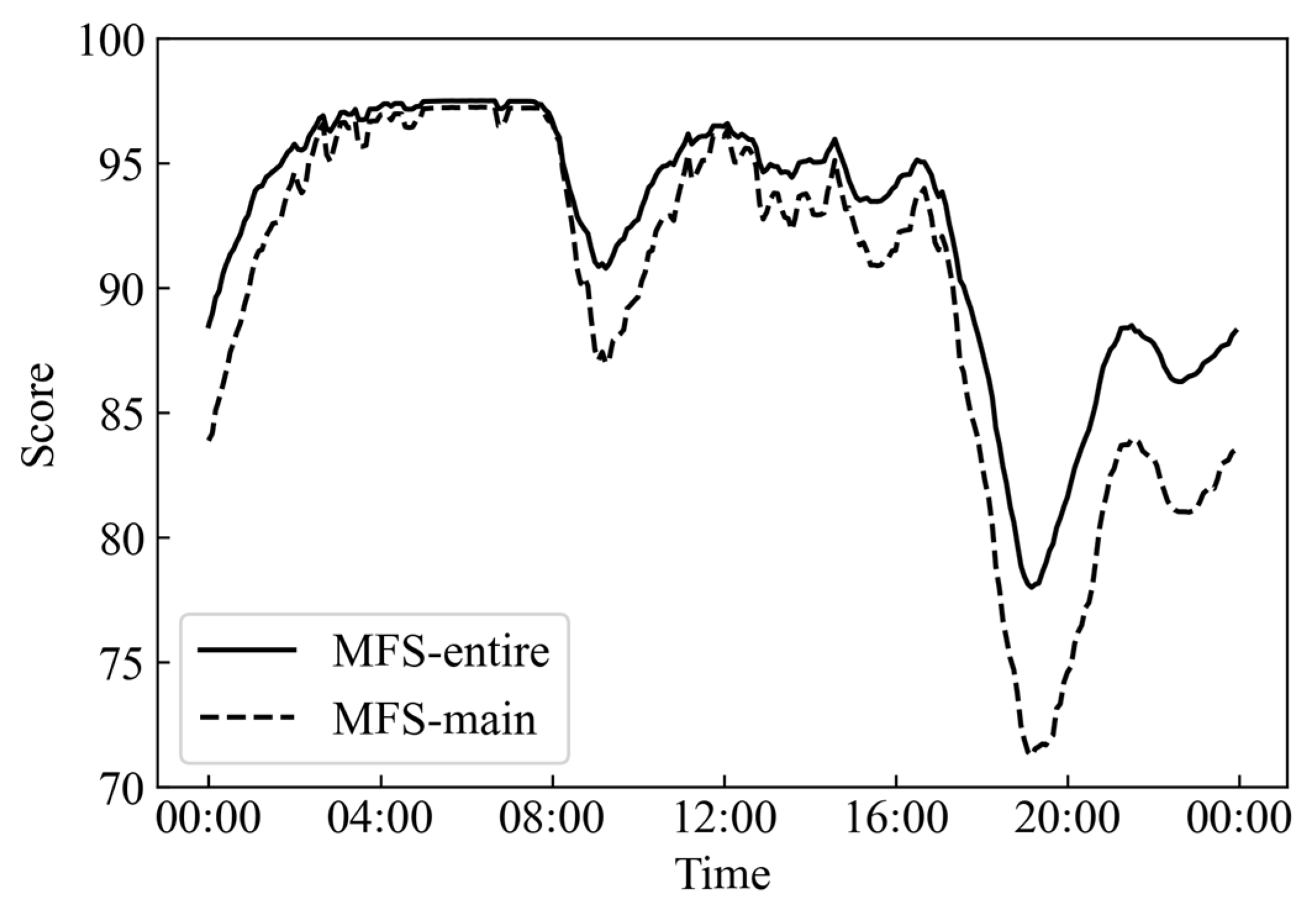
3.4. Comprehensive Hydraulic Performance Evaluation and Pipeline Renovation Recommendations
3.5. Indicator Correlation Analysis
3.6. Implications for Future Work in Sewage and Pipe Network
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- China City Statistical Yearbook 2022. Available online: https://www.mohurd.gov.cn/gongkai/fdzdgknr/sjfb/index.html (accessed on 26 September 2024).
- Chocat, B.; Ashley, R.; Marsalek, J.; Matos, M.R.; Rauch, W.; Schilling, W.; Urbonas, B. Toward the sustainable management of urban storm-water. Indoor Built Environ. 2007, 16, 273–285. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Larsen, T.A.; Gujer, W. The concept of sustainable urban water management. Water Sci. Technol. 1997, 35, 3–10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khan, Z.; Zayed, T.; Moselhi, O. Simulating impact of factors affecting sewer network operational condition. In Proceedings of the CSCE 2009 Annual General Conference, Montreal, QC, Canada, 27–30 May 2009; pp. 285–294. [Google Scholar]
- Zhou, Q. A review of sustainable urban drainage systems considering the climate change and urbanization impacts. Water 2014, 6, 976–992. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, J.; Liu, G.; Wang, J.; Xu, X.; Shao, Y.; Zhang, Q.; Liu, Y.; Qi, L.; Wang, H. Current status, existent problems, and coping strategy of urban drainage pipeline network in China. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. Int. 2021, 28, 43035–43049. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barbosa, A.; Fernandes, J.; David, L. Key issues for sustainable urban stormwater management. Water Res. 2012, 46, 6787–6798. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fletcher, D.T.; Shuster, W.; Hunt, F.W.; Ashley, R.; Butler, D.; Arthur, S.; Trowsdale, S.; Barraud, S.; Semadeni-Davies, A.; Bertrand, J.-L.; et al. SUDS, LID, BMPs, WSUD and more–The evolution and application of terminology surrounding urban drainage. Urban Water J. 2015, 12, 525–542. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moss, T. “Cold spots” of urban infrastructure: “Shrinking” processes in Eastern Germany and the modern infrastructural ideal. Int. J. Urban Reg. Res. 2008, 32, 436–451. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Notice of the Ministry of Housing and Urban-Rural Development and Other Four Departments on Strengthening the Construction and Operation & Maintenance of Urban Domestic Sewage Pipe Networks. Available online: https://www.gov.cn/zhengce/zhengceku/202403/content_6940086.htm (accessed on 26 September 2024).
- Chang, N.; Lu, J.; Chui, M.F.T.; Hartshorn, N. Global policy analysis of low impact development for stormwater management in urban regions. Land Use Policy 2018, 70, 368–383. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ellis, J.; Deutsch, J.; Mouchel, J.; Scholes, L.; Revitt, M.D. Multicriteria decision approaches to support sustainable drainage options for the treatment of highway and urban runoff. Sci. Total Environ. 2004, 334, 251–260. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hoang, L.; Fenner, R. System interactions of stormwater management using sustainable urban drainage systems and green infrastructure. Urban Water J. 2016, 13, 739–758. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Katharina, T.; Elodie, B.; Fanny, F.; Cherqui, F.; Nielsen, J.E.; Brüggemann, T.; Naismith, I.; Goerke, M.; López, J.S.; Rieckermann, J.; et al. European stakeholders’ visions and needs for stormwater in future urban drainage systems. Urban Water J. 2023, 20, 831–843. [Google Scholar]
- Bach, M.P.; Rauch, W.; Mikkelsen, S.P.; McCarthy, D.T.; Deletic, A. A critical review of integrated urban water modelling–Urban drainage and beyond. Environ. Model. Softw. 2014, 54, 88–107. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Einfalt, T.; Arnbjerg-Nielsen, K.; Golz, C.; Jensen, N.-E.; Quirmbach, M.; Vaes, G.; Vieux, B. Towards a roadmap for use of radar rainfall data in urban drainage. J. Hydrol. 2004, 299, 186–202. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rauch, W.; Seggelke, K.; Brown, R.; Krebs, P. Integrated approaches in urban storm drainage: Where do we stand? Environ. Manag. 2005, 35, 396–409. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dhakal, P.K.; Chevalier, R.L. Managing urban stormwater for urban sustainability: Barriers and policy solutions for green infrastructure application. J. Environ. Manag. 2017, 203, 171–181. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Berardi, L.; Giustolisi, O.; Savic, D.A.; Kapelan, Z. An effective multi-objective approach to prioritization of sewer pipe inspection. Water Sci. Technol. 2009, 60, 841–850. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mu, H.; Xiong, J.; Hu, J. Assessment and rehabilitation plan for the health condition of sewage pipeline networks in a city in the Pearl River Delta. Munic. Eng. Technol. 2024, 42, 169–175. (in Chinese). [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, S.; Guo, Z.; Li, Y. Practice in the reconstruction and rehabilitation of sewage pipeline networks in Liaoyuan City. Water Supply Drain. 2023, 59, 141–147. [Google Scholar]
- Soroush, B.; Mojtaba, G.H.; Meysam, G.; Movahedinia, M.; Shahdany, S.M.H. A practical method for rehabilitation of stormwater collecting system by node flooding detection and regional hydraulic redesign: A case study of eastern Tehran metropolis. Water Sci. Technol. 2022, 86, 1759–1773. [Google Scholar]
- Martínez, C.; Sanchez, A.; Toloh, B.; Vojinovic, Z. Multi-objective evaluation of urban drainage networks using a 1D/2D flood inundation model. Water Resour. Manag. 2018, 32, 4329–4343. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, J.; Xiong, Y.; Zhang, X.; Deng, Y. Evaluation of urban drainage pipeline network condition and operational efficiency based on the AHP-Fuzzy comprehensive evaluation method: A case study of Huaian District, Huaian City. J. Environ. Eng. Technol. 2022, 12, 1162–1169. (in Chinese). [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, X.; Zhao, S.; Zhao, D.; Sheng, Z.; Luo, R.; Lu, L.; Zhang, L. Introduction to urban drainage pipeline network simulation systems. China Water Wastewater 2015, 31, 104–108. (in Chinese). [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hou, J.; Dong, M.; Li, D.; Ma, Y.; Ju, G.; Zhang, S. Drainage performance of urban stormwater pipeline networks under extreme rainfall: A case study of Fengxi New City, Xi’an. J. Earth Sci. Environ. 2023, 45, 427–436. (in Chinese). [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiang, T.; Xing, H. Research on the drainage pipeline network condition assessment system based on the analytic hierarchy process. Intell. City 2022, 8, 53–55. [Google Scholar]
- Huang, X.; Li, H.; Zhang, Y.; Yang, X.; Chen, S. Development and vulnerability assessment of an urban flooding vulnerability evaluation system for Xi’an City based on PSR and AHP methods. J. Nat. Disasters 2019, 28, 167–175. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khan, Z.; Zayed, T.; Moselhi, O. Structural condition assessment of sewer pipelines. J. Perform. Constr. Facil. 2010, 24, 170–179. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ashley, R.; Hopkinson, P. Sewer systems and performance indicators—Into the 21st century. Urban Water 2002, 4, 123–135. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wei, X.; Suo, X.; Cui, X. Discussion on the star rating management method for urban drainage pipeline network projects. Adv. Environ. Prot. 2024, 14, 1141–1148. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yan, M.; Wang, H.; Liu, Z.; Palace, E.; Dai, X. Construction and research of an evaluation indicator system for the operational efficiency of urban drainage systems. J. Environ. Eng. 2023, 17, 3124–3136. (in Chinese). [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Saaty, T.L. How to make a decision–The analytic hierarchy process. Eur. J. Oper. Res. 1990, 48, 9–26. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ho, W.; Ma, X. The state-of-the-art integrations and applications of the analytic hierarchy process. Eur. J. Oper. Res. 2018, 267, 399–414. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ghavami, S.M.; Borzooei, Z.; Maleki, J. An effective approach for assessing risk of failure in urban sewer pipelines using a combination of GIS and AHP-DEA. Process Saf. Environ. Prot. 2020, 133, 275–285. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rani, H.A.; Syammaun, T.; Adamy, A.; Fadillah, A. The alternative of drainage construction technology selection by using analytical hierarchy process method. Elkawanie J. Islam. Sci. Technol. 2022, 7, 368–381. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Savitri, Y.R.; Kakimoto, R.; Begum, R.A.; Wardoyo, N.A.W.; Suryani, E. The application of AHP to determine the priority drainage system on flood mitigation in Surabaya, Indonesia. J. Disaster Res. 2022, 17, 431–443. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, G.; Liu, L.; Shi, P.; Zhang, G.; Liu, J. Flood risk assessment of metro system using improved trapezoidal fuzzy AHP: A case study of Guangzhou. Remote Sens. 2021, 13, 5154. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sepehri, M.; Malekinezhad, H.; Hosseini, Z.S.; Ildoromi, A. Assessment of flood hazard mapping in urban areas using entropy weighting method: A case study in Hamadan city, Iran. Acta Geophys. 2019, 67, 1435–1449. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chae, M.J.; Abraham, D.M. Neuro-fuzzy approaches for sanitary sewer pipeline condition assessment. Water Sci. Technol. 2024, 41, 4–14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wei, L.; Wanli, C.; Mingji, C.; Hu, Q.; Song, Z. Operation safety risk assessment of water distribution networks based on the combined weighting method (CWM). KSCE J. Civ. Eng. 2023, 27, 2116–2130. [Google Scholar]
- Zhou, Y.; Dong, Y.; Sun, T. Evaluation of operational efficiency of urban sewage systems: A case study of a district in Shanghai. Urban Roads Bridges Flood Control 2024, 144, 18–19, 136–139. [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, W.; Zhang, X.; Liu, Y. Analysis and simulation of drainage capacity of urban pipe network. Res. J. Appl. Sci. Eng. Technol. 2013, 6, 387–392. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bennis, S.; Bengassem, J.; Lamarre, P. Hydraulic performance index of a sewer network. J. Hydraul. Eng. 2003, 129, 504–510. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mohammadi, M.M.; Najafi, M.; Kermanshachi, S.; Kaushal, V.; Serajiantehrani, R. Factors influencing the condition of sewer pipes: State-of-the-art review. J. Pipeline Syst. Eng. Pract. 2020, 11, 03120002. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, J.; Pang, Y.; Wang, H.; Du, W.; Zeng, P.; Yi, Z. Health assessment method for urban sewage pipelines integrating hydrodynamic simulation. J. Beijing Univ. Technol. 2024, 50, 1458–1467. [Google Scholar]
- Dong, L.; Zhao, D.; Liu, X.; Tang, L. Drainage pipeline network performance evaluation system based on monitoring and simulation technology. China Water Wastewater 2014, 30, 150–154. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dong, N. Evaluation indicator system for smart municipal pipeline network operations. Surv. Spatial Geogr. Inf. 2024, 47, 1–4. [Google Scholar]
- Di, D.; Li, T.; Fang, H.; Xiao, L.; Du, X.; Sun, B.; Zhang, J.; Wang, N.; Li, B. A CFD-DEM investigation into hydraulic transport and retardation response characteristics of drainage pipeline siltation using intelligent model. Tunneling Undergr. Space Technol. 2024, 152, 105964. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Montes, C.; Bohorquez, J.; Borda, S.; Saldarriaga, J.G. Criteria of minimum shear stress vs. minimum velocity for self-cleaning sewer pipes design. Procedia Eng. 2017, 186, 69–75. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ebtehaj, I.; Bonakdari, H.; Sharifi, A. Design criteria for sediment transport in sewers based on self-cleansing concept. J. Zhejiang Univ. Sci. A 2014, 15, 914–924. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- May, R.W.; Ackers, J.C.; Butler, D.; John, S.C. Development of design methodology for self-cleansing sewers. Water Sci. Technol. 1996, 33, 195–205. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Montes, C.; Kapelan, Z.; Saldarriaga, J. Impact of self-cleansing criteria choice on the optimal design of sewer networks in South America. Water 2019, 11, 1148. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Safari, S.J.M.; Mohammadi, M.; Ghani, A.A. Experimental studies of self-cleansing drainage system design: A review. J. Pipeline Syst. Eng. Pract. 2018, 9, 04018017. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vongvisessomjai, N.; Tingsanchali, T.; Babel, S.M. Non-deposition design criteria for sewers with part-full flow. Urban Water J. 2010, 7, 61–77. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Merritt, L.B.; Enfinger, K.L. Tractive force: A key to solids transport in gravity flow drainage pipes. Water Sci. Technol. 2019, 33, 349–358. [Google Scholar]
- Enfinger, K.L.; Mitchell, P.S. Scattergraph principles and practice: Evaluating self-cleansing in existing sewers using the tractive force method. Water Sci. Technol. 2012, 33, 4458–4467. [Google Scholar]
- Pina, R.; Ochoa-Rodriguez, S.; Simões, N.E.; Mijic, A.; Marquesm, A.S.; Maksimovi, C. Semi- vs. fully-distributed urban stormwater models: Model setup and comparison with two real case studies. Water 2016, 8, 58. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, F.T.; Hong, H.Z.; Chang, W.L.; Di, N.T.; Bao, L.W.; Yan, H.L.; Zong, Q.Z.; Yan, P.L. Studies on the integration of geographic information system (GIS) and drainage pipe network model. Adv. Mater. Res. 2011, 1380, 317–319. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Garcia, S.G. A Real-Time Flood Forecasting and Simulation System Based on GIS and DEM: Analysis of Sensitivity to Scale Factors. Ph.D. Thesis, Universidad Politécnica de Valencia, Valencia, Spain, 2000. [Google Scholar]
- Takaijudin, H.; Zaaba, S.I. Performance of integrated urban drainage simulation model using XP-SWMM software. Water Sci. Technol. 2012, 65, 1–10. [Google Scholar]
- Campbell, W.C.; Sean, M.S. Simulating time-varying cave flow and water levels using the Storm Water Management Model. Eng. Geol. 2002, 65, 100–110. [Google Scholar]
- Temprano, J.; Arango, O.; Cagiao, J.; Suárez, J.; Tejero, I. Stormwater quality calibration by SWMM: A case study in Northern Spain. Water SA 2006, 32, 55–63. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Koudelak, P.; West, S. Sewerage network modelling in Latvia, use of InfoWorks CS and Storm Water Management Model 5 in Liepaja city. Water Environ. J. 2008, 22, 81–87. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rubinato, M.; Shucksmith, J.; Saul, A.J.; Shepherd, W. Comparison between InfoWorks hydraulic results and a physical model of an urban drainage system. Water Sci. Technol. 2013, 68, 372–379. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Khodashenas, S.R.; Tajbakhsh, M. Management of urban drainage system using integrated MIKE SWMM and GIS. J. Water Resour. Hydraul. Eng. 2016, 5, 36–45. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, X.; Wang, K.; Wang, T. SWMM-based assessment of the improvement of hydrodynamic conditions of urban water system connectivity. Water Resour. Manag. 2021, 35, 4519–4534. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hamouz, V.; Muthanna, T.M. Hydrological modelling of green and grey roofs in cold climate with the SWMM model. J. Environ. Manag. 2019, 249, 109350. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, Z.; Chen, Y.; Zeng, Z.; Chen, X.; Li, X.; Jiang, X.; Lai, C. A tight coupling model for urban flood simulation based on SWMM and TELEMAC-2D and the uncertainty analysis. Sustain. Cities Soc. 2024, 114, 105794. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kun, Z.; Chui, T.F.M.; Yang, Y. Simulating the hydrological performance of low impact development in shallow groundwater via a modified SWMM. J. Hydrol. 2018, 566, 313–331. [Google Scholar]
- Tanim, A.H.; Smith-Lewis, C.; Downey, A.R.; Imran, J.; Goharian, E. Bayes_Opt-SWMM: A Gaussian process-based Bayesian optimization tool for real-time flood modeling with SWMM. Environ. Model. Softw. 2024, 179, 106122. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, Y.; Li, J.; Huang, Q.; Xia, J.; Li, J.; Liu, D.; Tan, Q. Performance assessment of sponge city infrastructure on stormwater outflows using isochrone and SWMM models. J. Hydrol. 2021, 597, 126151. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sui, Z.; Li, Z. Simulation of urban rainstorm waterlogging and pipeline network drainage process based on SWMM. J. Phys. Conf. Ser. 2019, 1213, 52–61. [Google Scholar]
- Song, Y.; Tu, M.; Traver, R. Predicting Sedimentation in Urban Sewer Conduits. Water 2018, 10, 462. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cong, Z.; Ning, L.; Kun, C.; Ren, F. Study on Drainage Mode and Anti-Clogging Performance of New Waterproofing and Drainage System in a Tunnel. Sci. Rep. 2023, 13, 5354. [Google Scholar]
- Tu, M.; Traver, R. Clogging Impacts on Distribution Pipe Delivery of Street Runoff to an Infiltration Bed. Water 2018, 10, 1045. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jin, P.K.; Hao, X.Y.; Wang, B.B.; Guo, H. Characteristics of Water Quality Variation in Urban Sewage Pipeline Networks. Chin. J. Environ. Eng. 2015, 9, 1009–1014. [Google Scholar]
- Zan, F.; Tang, W.; Jiang, F.; Chen, G. Diversion of Food Waste into the Sulfate-Laden Sewer: Interaction and Electron Flow of Sulfidogenesis and Methanogenesis. Water Res. 2021, 202, 117437. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gu, D.; Liu, Y.; Zhao, W.; Qiu, S.; Cui, N.; Hu, X.; Zhao, P. Status of Research on Greenhouse Gas Emissions from Wastewater Collection Systems. Water 2023, 15, 2512. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sokáč, M.; Velísková, Y. Impact of Sediment Layer on Longitudinal Dispersion in Sewer Systems. Water 2021, 13, 3168. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kitsikoudis, V.; Velísková, Y.; Erpicum, S.; Rubinato, M.; Shucksmith, J.D.; Archambeau, P.; Pirotton, M.; Dewals, B. Exchange between Drainage Systems and Surface Flows during Urban Flooding: Quasi-Steady and Dynamic Modelling in Unsteady Flow Conditions. J. Hydrol. 2021, 602, 126628. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]









| Diameter (mm) | Vsc (m/s) | ||
|---|---|---|---|
| d50 (mm) | 10 | 1 | 0.1 |
| (lb/ft2) | 0.0343 | 0.0181 | 0.0096 |
| 100 | 0.56 | 0.40 | 0.29 |
| 200 | 0.62 | 0.45 | 0.33 |
| 300 | 0.67 | 0.49 | 0.35 |
| 400 | 0.70 | 0.51 | 0.37 |
| 500 | 0.73 | 0.53 | 0.38 |
| 600 | 0.75 | 0.54 | 0.40 |
| 700 | 0.77 | 0.56 | 0.41 |
| 800 | 0.79 | 0.57 | 0.42 |
| 900 | 0.80 | 0.58 | 0.42 |
| 1000 | 0.82 | 0.59 | 0.43 |
| 1100 | 0.83 | 0.60 | 0.44 |
| 1200 | 0.84 | 0.61 | 0.44 |
| Diameter (mm) | Maximum Design Fullness |
|---|---|
| 200~300 | 0.55 |
| 350~450 | 0.65 |
| 500~900 | 0.70 |
| ≥1000 | 0.75 |
| Grade | Excellent | Good | Medium + | Medium − | Poor |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| PNCS range | 90–100 | 80–90 | 70–80 | 60–70 | 0–60 |
| Diameter (mm) | 200 | 300 | 400 | 500 | 600 | 800 | 1000 | 1200 | 1500 | Total |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Length (m) | 50 | 2517 | 7686 | 4452 | 3640 | 4190 | 1799 | 2444 | 132 | 26,910 |
| Percentage | 0.2% | 9.4% | 28.6% | 16.5% | 13.5% | 15.6% | 6.7% | 9.1% | 0.5% | 100% |
| Sections | VS | FS | Up MFS 1 | Down MFS 2 | D0 3 (mm) | D1 4 (mm) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| WS167 | 100 | 95 | 78.3 | 76.8 | 600 | 800 |
| WS170 | 100 | 84 | 69.6 | 78.3 | 600 | 800 |
| WS171 | 100 | 53 | 60.8 | 69.6 | 600 | 800 |
| WS172 | 100 | 43 | 53.7 | 60.8 | 600 | 800 |
| WS175 | 100 | 43 | 49.4 | 53.7 | 600 | 800 |
| WS178 | 100 | 46 | 48.3 | 49.4 | 600 | 800 |
| WS179 | 100 | 45 | 38.1 | 48.3 | 600 | 800 |
| WS180 | 100 | 42 | 37.7 | 38.1 | 600 | 800 |
| WS181 | 100 | 6 | 29.7 | 37.7 | 600 | 800 |
| WS183 | 100 | 0 | 28.8 | 29.7 | 600 | 800 |
| WS162 | 100 | 1 | 30.6 | 28.8 | 600 | 800 |
| WS327 | 100 | 50 | 27.6 | 31.7 | 800 | 1200 |
| WS332 | 100 | 45 | 31.7 | 29.0 | 800 | 1200 |
| WS333 | 100 | 23 | 29.0 | 26.8 | 800 | 1200 |
| WS335 | 100 | 49 | 26.8 | 34.3 | 800 | 1200 |
| WS336 | 100 | 80 | 34.3 | 33.0 | 800 | 1200 |
| WS337 | 100 | 49 | 33.0 | 28.2 | 800 | 1200 |
| WS338 | 100 | 6 | 28.2 | 30.9 | 800 | 1200 |
| WS339 | 100 | 29 | 30.9 | 56.5 | 800 | 1200 |
| WS317 | 100 | 66 | 56.5 | 72.7 | 800 | 1200 |
| Indicators | Before | After | ||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Entire Network | Main Pipeline | Entire Network | Main Pipeline | |||||
| Score | Grade | Score | Grade | Score | Grade | Score | Grade | |
| Velocity | 51.6 | Poor | 69.3 | Medium − | 51.2 | Poor | 67.0 | Medium − |
| Pipe fullness | 80.0 | Good | 74.4 | Medium + | 84.2 | Good | 81.8 | Good |
| Manhole fullness | 47.7 | Medium | 35.8 | Medium | 77.8 | Medium + | 76.9 | Medium + |
| Total | 59.8 | Poor | 59.8 | Poor | 70.8 | Medium + | 75.1 | Medium + |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Li, P.; Zhang, Y.; Zhao, P.; Gu, D.; Wang, S. Evaluation of Hydraulic Performance of Sewage Pipe Networks. Water 2025, 17, 159. https://doi.org/10.3390/w17020159
Li P, Zhang Y, Zhao P, Gu D, Wang S. Evaluation of Hydraulic Performance of Sewage Pipe Networks. Water. 2025; 17(2):159. https://doi.org/10.3390/w17020159
Chicago/Turabian StyleLi, Peng, Yitao Zhang, Peng Zhao, Dongmei Gu, and Shaohua Wang. 2025. "Evaluation of Hydraulic Performance of Sewage Pipe Networks" Water 17, no. 2: 159. https://doi.org/10.3390/w17020159
APA StyleLi, P., Zhang, Y., Zhao, P., Gu, D., & Wang, S. (2025). Evaluation of Hydraulic Performance of Sewage Pipe Networks. Water, 17(2), 159. https://doi.org/10.3390/w17020159








