Technical Analysis and Application Prospects of Magnetic Source Transient Electromagnetic Coil Devices in Hydrogeological Survey of Mining Area
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Classification and Summary of Coil Devices
2.1. Classification Methods for Various Coil Devices
2.2. Fixed Source Devices
2.2.1. The Large Fixed-Source Loop
2.2.2. The Ground-Hole TEM
2.3. Dynamic Source Devices
2.3.1. The Central Loop Method
2.3.2. The Overlapping Loop
2.3.3. The Transient Electromagnetic Dipole Device
2.3.4. The Well-Ground TEM
2.3.5. Magnetic Induction Probes
2.3.6. Bucking Coils
2.3.7. The Opposing Coils
2.3.8. Others
3. Analysis and Discussion of Different Coil Device Characteristics
3.1. Characteristics
3.1.1. Detection Depth
3.1.2. Resolution
3.1.3. Detection Blind Zone
3.2. Discussion
4. Conclusions
- (1)
- The TEM coil devices are categorized into fixed source devices and mobile source devices based on whether the transmitter is stationary. Fixed source devices typically offer higher resolution and greater detection depth. Mobile source devices exhibit strong environmental adaptability, are easy to transport and operate, and are effective in acquiring abundant geological information.
- (2)
- Fixed-source TEM devices are typically larger in size and possess strong emission currents, enabling substantial detection depths and high resolution. However, these devices are cumbersome to install, have low construction efficiency, provide limited data, and incur higher costs. In contrast, moving-source devices are generally smaller, easier, and quicker to install, with weaker emission currents and limited detection depth.
- (3)
- Large fixed-source loops and well-ground devices utilize substantial emission coils to generate strong magnetic fields. Central loops, with their simple structure, facilitate optimal coupling with targets. Overlapping loops possess larger emission and reception magnetic moments. Dipole devices have been largely replaced by newer technologies. Well-ground devices employ multi-turn small loops for emission coils, providing large magnetic moments and extensive receiving units for deep detection. Magnetic induction probes effectively address the “one-hole view” limitation in borehole detection. Bucking coils and equivalent reverse magnetic flux devices reduce primary field interference to obtain higher quality response signals, with the latter theoretically eliminating detection blind zones.
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Xue, G.Q.; Li, X.; Di, Q.Y. The progress of TEM in theory and application. Prog. Geophys. 2007, 22, 1195–1200. [Google Scholar]
- Farquharson, C.G.; Hu, X.; Huang, Q.; Li, X.; Li, J.; Xue, G.; Yin, C. Advances in Transient Electromagnetic Methods. J. Geophys. Eng. 2023, 20, 1305–1307. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kassie, L.N.; Chang, P.-Y.; Zeng, J.-R.; Huang, H.-H.; Chen, C.-S.; Doyoro, Y.G.; Lin, D.-J.; Puntu, J.M.; Amania, H.H. Mapping Hydrogeological Structures Using Transient Electromagnetic Method: A Case Study of the Choushui River Alluvial Fan in Yunlin, Taiwan. Water 2023, 15, 1703. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Feng, Q.; Li, C.; Hao, S.; Li, D.; Liu, T.; Sun, Z.; Zhou, L. Hydrogeological Investigation of a Goaf and Subsidence Area Based on a Ground-to-Air Transient Electromagnetic Sounding Method. Water 2024, 16, 1067. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lu, Y.; Tao, J.; Cao, C.; Liu, H.; Liu, Y.; Ge, Z. Detection of Landfill Leachate Leakage Based on ERT and OCTEM. Water 2023, 15, 1778. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lu, T.; Liu, H.; Jia, H.; Wang, B. A Geophysical-Drilling-Hydrochemical Coupled Method for Accurate Detection of Concealed Water-Conducting Faults in Coal Mines. Water 2024, 16, 2619. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, K.; Sun, H.F.; Su, C.X.; Li, S.C.; Tang, P.Y.; Qi, Z.P. Comparison of transient electromagnetic configuration in prediction of water bearing structures in tunnels. Chin. J. Rock Mech. Eng. 2017, 36, 3164–3173. [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, Y.Y.; Li, X. Research progress on ground-airborne transient electromagnetic method. Prog. Geophys. 2017, 32, 1735–1741. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, J.; Wang, L.; Wang, X.G.; Cai, M.; Fu, L.; Shang, X.L. Research and development on the air-core coil sensor for mine transient electromagnetic exploration. Chin. J. Geophys. 2016, 59, 721–730. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, L.; Zhang, S.; Chen, S.; Jiang, H. Fast Localization of Underground Targets by Magnetic Gradient Tensor and Gaussian-Newton Algorithm with a Portable Transient Electromagnetic System. IEEE Access 2021, 9, 148469–148478. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiang, Z.; Liu, S.; Malekian, R. Analysis of a Whole-Space Transient Electromagnetic Field in 2.5-Dimensional FDTD Geoelectric Modeling. IEEE Access 2017, 5, 18707–18714. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, H.; Chen, S.; Yue, J.; Li, F.; Zhang, H. Transient Electromagnetic Response with a Ramp Current Excitation Using Conical Source. IEEE Access 2019, 7, 63829–63836. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barsukov, P.O.; Fainberg, E.B. Mapping Bedrock Topography and Moraine Deposits by Transient Electromagnetic Sounding: Oslo Graben, Norway. Near Surf. Geophys. 2020, 18, 123–133. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- QI, Z.; Li, X.; Zhu, H.W.; Ma, B.-z.; Zhang, J.; Wu, Q. Definition of apparent resistivity for non-center vertical component of Large-loop TEM configuration. Prog. Geophys. 2011, 26, 1350–1358. [Google Scholar]
- Han, Z.Q.; Liu, T.; Ou, Y.J.; Luo, J. Application of large rectangular loop source TEM all-time apparent resistivity on colliery goaf exploration. Prog. Geophys. 2015, 30, 343–349. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pan, J.S.; Zhang, X.; Chen, S.Z.; Zhang, J.L.; Zhang, Y.T. Application of transient electromagnetic method with large fixed source loop device in detection of coal mine goaf. Technol. Innov. Appl. 2024, 14, 137–140. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bai, J.; Yao, J.; Yang, Z.; Guo, Y.; Wang, L. Transient Electromagnetic Weak Signal Extraction Method Based on Multi-Scale Combined Difference Product Morphological Filtering. IEEE Access 2022, 10, 22140–22149. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, X.; Pan, D.M.; Yu, J.C. Review in the geophysical methods for coalmine goaf prospecting. Prog. Geophys. 2022, 37, 1197–1206. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xue, G.Q.; Li, H.; Chen, W.Y.; Yu, C.T.; Chang, J.H.; Yu, J.C. Progress of transient electromagnetic detection technology for water-bearing bodies in coal mines. J. China Coal Soc. 2021, 46, 77–85. [Google Scholar]
- Su, B.Y.; Yu, J.C.; Wang, Y.Z.; Tang, Y.; Yang, H.Y.; Li, M.F.; Li, H.H.; Sun, S.Y. Characteristics and application of ground-borehole transient electromagnetic response to coal seam roof separated layer water. J. Min. Saf. Eng. 2023, 40, 572–577. [Google Scholar]
- Sun, H.F.; Zhang, Y.Y.; Zhao, Y.C.; Liu, Y.C.; Zhao, H.L. Present study situation review of borehole transient electromagnetic method. Coal Geol. Explor. 2022, 50, 85–97. [Google Scholar]
- Boyd, G.W.; Wiles, C.J. The Newmont Drill-hole EMP System—Examples from Eastern Australia. Geophysics 1984, 49, 949–956. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bishop, J.R.; Lewis, R.J.G.; Macnae, J.C. Down-Hole Electromagnetic Surveys at Renison Bell, Tasmania. Explor. Geophys. 1987, 18, 265–277. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, J.; Deng, X.H.; Guo, X.; Wu, J.J.; Wang, X.C. Typical cases of applying borehole tem to deep prospecting in crisis mines. Geophys. Geochem. Explor. 2013, 37, 30–34. [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, J.Z.; Hu, F.H.; Liu, H.X.; Xing, G.Z. TEM response characteristics of borehole in goaves of old coal mines. Geophys. Geochem. Explor. 2022, 46, 191–197. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Song, F. Study on Forward and Inversion of Transient Electromagnetic Method for Central Loop Devices. Master’s Thesis, Chongqing University, Chongqing, China, 2018. [Google Scholar]
- Chen, X.H. Study About 1D Forward and Inversion Algorithm of Central-Loop TEM Data. Master’s Thesis, Chengdu University of Technology, Chengdu, China, 2012. [Google Scholar]
- Xian, Y.; Lan, R.; Liu, Y.; Li, D.; Yang, J.; Sun, H. Improved Adaptive Thin-Layer Inversion for Semi-Airborne Transient Electromagnetic Method. J. Geophys. Eng. 2023, 20, 915–926. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yan, S.; Chen, M.S.; Shi, X.X. Transient Electromagnetic Sounding Using a 5 m Square Loop. Explor. Geophys. 2009, 40, 193–196. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, S.X.; Liu, J.; Lei, Z. The relationship between the loop size and the optimal detecting depth in in-loop TEM. Comput. Tech. Geophys. Geochem. Explor. 2012, 34, 548–551. [Google Scholar]
- Liu, C.S.; Lin, J.; Zhou, F.D. Transient response characteristics of central loop configuration on seafloor. Chin. J. Radio Sci. 2010, 25, 195–200. [Google Scholar]
- Vrbancich, J. Airborne Electromagnetic Bathymetry Investigations in Port Lincoln, South Australia—Comparison with an Equivalent Floating Transient Electromagnetic System. Explor. Geophys. 2011, 42, 167–175. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Z.G. Application of Central Loop Transient Electromagnetic Method in an Underground Tunnel Exploration. Site Investig. Sci. Technol. 2019, 4, 55–57. [Google Scholar]
- Guo, S.W.; Yan, Q. Application of Transient Electromagnetic Methods in Water Exploration of the West of Ming’an Town in Wulateqianqi, Inner Mongolia. Sci. Technol. Eng. 2020, 20, 2564–2572. [Google Scholar]
- Zhao, H.; Wang, H.; Zhou, X.G. Application of TEM in Detecting Goaf of Shallow Coal Seam. Mod. Chem. Res. 2023, 18, 125–127. [Google Scholar]
- Jiang, Z.H.; Yue, J.H.; Liu, S.C. Mine transient electromagnetic observation system of small multi-turn coincident configuration. J. China Coal Soc. 2007, 32, 1152–1156. [Google Scholar]
- Liu, T. Application of small-wireframe overlapping loop TEM in geological exploration. New Tech. Prod. China 2024, 4, 114–116. [Google Scholar]
- Spies, B.R. The Dual Loop Configuration of the Transient Electromagnetic Method. Geophysics 1975, 40, 1051–1057. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cheng, K. Inversion Methods and Experimental Study of Fixed-loop Transient Electromagnetic in Tunnels. Master’s Thesis, Shandong University, Jinan, China, 2022. [Google Scholar]
- Liu, J.P.; Che, H.Q.; Zhu, H.; Liu, F.; Sun, Y. Transient Electromagnetic Response for a Coincident Loop in a Full-space Layered Medium. Sci. Technol. Ind. 2023, 23, 289–295. [Google Scholar]
- Yang, H.Y.; Wu, X.M.; Zhang, H. Delay Correction Technique of Underground Transient Electromagnetic Method with Coincident Loop. J. East China Univ. Technol., Nat. Sci. 2016, 39, 362–368. [Google Scholar]
- Maurya, P.K.; Christiansen, A.V.; Pedersen, J.; Auken, E. High Resolution 3D Subsurface Mapping Using a Towed Transient Electromagnetic System—tTEM: Case Studies. Near Surf. Geophys. 2020, 18, 249–259. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, S.D. Research on Zero Mutual Inductance Overlapping Loop Transient Electromagnetic Method. Master’s Thesis, Zhejiang University, Hanzhou, China, 2019. [Google Scholar]
- Zhuang, D.Y. Application of Overlap Loop Transient Electromagnetic Method in Goaf Exploration. China Plant Eng. 2021, 2, 135–137. [Google Scholar]
- Guo, R.P.; Zhang, K.; Tian, J.H.; Cheng, B.; Zhang, H.T. Small Multi-turn Coincident with Large Current Transient Electromagnetics Method Application Effect in Geotechnical Engineering Investigation. Chin. J. Eng. Geophys. 2021, 18, 503–512. [Google Scholar]
- Ying, Y. Transient Electromagnetic Structure Radar Research. Adv. Geosci. 2019, 9, 218–229. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, C.S.; Lin, J.; Ji, Y.J.; Wu, G.Q. On model experiments of TEM dipole configuration. Geophys. Geochem. Explor. 2006, 30, 430–434. [Google Scholar]
- Jiao, J.M. Physical Simulation and Application of TEM Dipole Device on Concealed Water Source in Coal Mine. Master’s Thesis, China University of Mining and Technology, Xuzhou, China, 2018. [Google Scholar]
- Chen, G. Ability of dipole devices to reflect IP anomalies. Geophys. Geochem. Explor. 1986, 10, 398–400. [Google Scholar]
- Xue, G.Q.; Yan, S.; Zhou, N.N. Theoretical study on the errors caused by dipole hypothesis of large-loop TEM response. Chin. J. Geophys. 2011, 54, 2389–2396. [Google Scholar]
- Maher, M.J. Transient Electromagnetic Surveys in the Okiep District. Geophysics 1992, 57, 736–744. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, H.Y.; Zhao, Y.H. Application effect and improvement of technology of coal mine dipole transient electromagnetic. China Coal 2014, 40, 37–39+72. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, X.F.; Wu, G.R.; Zhang, T.; Guo, L.C. On application of NanoTEM in detection of troubles in canal banks. Shanxi Archit. 2016, 42, 223–224. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shi, C.H.; Liu, L.D.; Jia, X.Y. Advanced Geological Prediction Method and Application of TEM Based on Coaxial Dipole Device. Chin. J. Eng. Geophys. 2021, 18, 579–588. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, P. Study on floating coefficient space intersection and equivalent current loop inversion of Downhole TEM. Ph.D. Thesis, China University of Geosciences, Wuhan, China, 2017. [Google Scholar]
- Yang, Y.; Dang, R.R.; Ren, Z.P. Research on transient electromagnetic method in borehole. Pet. Instr. 2009, 23, 99. [Google Scholar]
- Wu, Q.; Zhi, Q.Q.; Wu, J.J.; Wang, X.C. Study on the approximation between equivalent current field and pure anomaly field of borehole-ground joint transient electromagnetic method. Comput. Tech. Geophys. Geochem. Explor. 2022, 44, 224–234. [Google Scholar]
- Yang, H.Y.; Yue, J.H.; Liu, Z.X. Theoretical Study of Inductance Effect With Multi-axial Coils for TEM in Underground Mine. J. Jilin Univ. Earth Sci. Ed. 2006, 36, 168–171. [Google Scholar]
- Ren, Z.; Kalscheuer, T. Uncertainty and Resolution Analysis of 2D and 3D Inversion Models Computed from Geophysical Electromagnetic Data. Surv. Geophys. 2020, 41, 47–112. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, P.; Li, M.; Yao, W.; Su, C.; Wang, Y.; Wang, Q. Detection of Abandoned Water-Filled Mine Tunnels Using the Downhole Transient Electromagnetic Method. Explor. Geophys. 2020, 51, 667–682. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shi, H. Application of comprehensive geophysical prospecting methods in groundwater exploration in thick overburden areas. Hydrogeol. Eng. Geol. 2005, 32, 101–104. [Google Scholar]
- Wu, J.J.; Liu, B.; Zhi, Q.Q.; Deng, X.H.; Wang, X.C.; Yang, Y.; Liu, D.M.; Qiu, J.Z. Application of surface and borehole TEM joint exploration in 2000 m deep mineral exploration. Coal Geol. Explor. 2022, 50, 70–78. [Google Scholar]
- Shao, Y.Q.; Cheng, D.F.; Wang, Y.Z.; Zhang, F. Research of high sensitivity inductive magnetic sensor. Chin. J. Sci. Instrum. 2012, 33, 349–355. [Google Scholar]
- Vallianatos, F. A Non Extensive View of Electrical Resistivity Spatial Distribution Estimated Using Inverted Transient Electromagnetic Responses in a Karstified Formation (Keritis Basin, Crete, Greece). Physica A 2018, 505, 171–178. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Simard, P.T.; Chesnaux, R.; Rouleau, A.; Daigneault, R.; Cousineau, P.A.; Roy, D.W.; Lambert, M.; Poirier, B.; Poignant-Molina, L. Imaging Quaternary Glacial Deposits and Basement Topography Using the Transient Electromagnetic Method for Modeling Aquifer Environments. J. Appl. Geophy. 2015, 119, 36–50. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, K.B. Research of mining induction probe of TEM detection system. J. Xi’an Univ. Sci. Technol. 2013, 33, 336–342. [Google Scholar]
- Fan, T.; Zhao, Z.; Wu, H.; Lu, J.J.; Wang, J.K. Research on inductance effect removing and curve offset for mine TEM with multi small loops. J. China Coal Soc. 2014, 39, 932–940. [Google Scholar]
- Fan, T. Experimental study on the exploration of coal mine goaf by dynamic source and fixed reception Roadway-Borehole TEM detection method. J. China Coal Soc. 2017, 42, 3229–3238. [Google Scholar]
- Xiao, P.; Shi, Z.; Wu, X.; Fang, G. Improved Bucking Coil Design in Helicopter Transient Electromagnetic System. Prog. Electromagn. Res. M 2017, 60, 131–139. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, J.; Pi, S.; Zhang, Y.; Lin, T. Weak Coupling Technology with Noncoplanar Bucking Coil in a Small-Loop Transient Electromagnetic System. IEEE Trans. Ind. Electron. 2022, 69, 3151–3160. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Witherly, K.; Witherly, K. Mapping Targets of High Conductance with the VTEM Airborne EM System. ASEG Ext. Abstr. 2007, 2007, 1–4. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kuzmin, P.V.; Morrison, E.B. Bucking Coil and B-Field Measurement System and Apparatus for Time Domain Electromagnetic Measurements. U.S. Patent 8,400,157, 19 March 2013. [Google Scholar]
- Liang, Q.H. The Technology and Application of Mine Full-Space Transient Electromagnetic Detection by Small Coil. Ph.D. Thesis, Central South University, Changsha, China, 2012. [Google Scholar]
- Jiang, J. Application of Towed TEM Method in Shallow Waters Geotechnical Investigation. Coal Geol. China 2019, 31, 103–107. [Google Scholar]
- Long, X.; Xi, Z.Z.; Zhou, S.; Hou, H.T.; Wang, L.; Xue, J.P. Detection capability of opposing coils transient electromagnetic method for thin layers. Prog. Geophys. 2020, 35, 753–759. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.; Xi, Z.Z.; Jiang, H.; Hou, H.T.; Zhou, S.; Fan, F.L. The application research on the detection of karst disease of airport runway based on OCTEM. Geophys. Geochem. Explor. 2017, 41, 360–363. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fan, X.Y. Development and Application of Self-balancing Opposing Coils Transient Electromagnetics Instrument. Master’s Thesis, South-Central University for Nationalities, Wuhan, China, 2021. [Google Scholar]
- Zhao, S.W. Application of shallow TEM in the exploration of water filled karst cave in southwest Custer area. Railw. Investig. Surv. 2017, 43, 102–105. [Google Scholar]
- Zhou, L.; Cao, C.H.; Deng, Z.; Tan, J.L.; Long, X. Case Study of Geophysical Prospecting Water under the Condition of Limited Site in Urban Areas. Urban Geol. 2019, 14, 97–102. [Google Scholar]
- Zhou, C.; Qiao, H.Q.; Zhao, S.W.; Zhao, W.L. Application of shallow transient electromagnetic method in concealed fault exploration of subway project. Geotech. Investig. Survey. 2018, 46, 74–78. [Google Scholar]
- He, Y. Application of high-density electrical method and equivalent reverse flux transient electromagnetic method in exploration of a certain mining area. China Metal Bull. 2019, 6, 201–202. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, T.T.; Wang, Y.; Ren, J.; Zhang, Z.H. Application of equivalent inverse flux transient electromagnetic method in the detection of leakage hidden danger of the Yangtze River dike. Jiangsu Water Res. 2024, 2, 58–62. [Google Scholar]
- Kang, F.P.; Deng, Y.; Cao, C.H.; Jing, J.; Liu, C.M.; Peng, J.; Zhou, L. Application of Opposing Coils Transient Electromagnetic Method in Leakage Detection of Urban Domestic Waste Landfills. Chin. J. Eng. Geophys. 2023, 20, 725–732. [Google Scholar]
- Zhao, D.D.; Chen, J.W.; Zong, Q.B.; Zhang, B.D.; Di, B.Y.; Zhu, H.B.; Wang, J.L. Application of Opposing Coils Transient Electromagnetic Method in Metro Shielding Boulder Detection. Chin. J. Eng. Geophys. 2021, 18, 495–502. [Google Scholar]
- Liu, J.X. Application of Equivalent Reverse Flux Transient Electromagnetic Method to Underwater Detection. Chin. J. Eng. Geophys. 2019, 16, 764–769. [Google Scholar]
- Lin, J.; Chen, J.; Liu, F.; Zhang, Y. The Helicopter Time-Domain Electromagnetic Technology Advances in China. Surv. Geophys. 2021, 42, 585–624. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yan, L. Advancements in Controlled Source Electromagnetic Methods for Prospecting Unconventional Hydrocarbon Resources in China. Surv. Geophys. 2024, 45, 239–276. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bai, Y.; Zhang, J.; Zhang, M.; Rao, W. Flexible Liquid Metal Electromagnetic Shielding Materials. Sci. China Technol. Sci. 2023, 66, 2757–2774. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, G.C.; Xu, Y.K.; Zhao, Z.T.; Wang, Y.; Hu, J. Simulation and Analysis of 8-shaped Coils Structure for Electromagnetic Transmitter Based on MAXWELL. Sci. Technol. Eng. 2013, 13, 10481–10484, 10500. [Google Scholar]
- Xie, S.W.; Yang, H.Y.; Liu, S.G.; Xu, Z.Y.; Dong, M.M.; Deng, J.Z.; Zhang, H.; Tang, H.Z. The comparative with single loop and the loop of type 8 of transient electromagnetic method. Prog. Geophys. 2015, 30, 1354–1360. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, H.Y.; Li, F.P.; Yue, J.H.; Liu, X.H.; Zhao, H.J. Optimal transient electromagnetic inversionof conical field source based on smoke ring theory. J. China Univ. Min. Technol. 2016, 45, 1230–1237. [Google Scholar]
- Yang, H.Y.; Li, F.P.; Yue, J.H.; Guo, F.S.; Liu, X.H.; Zhang, H. Cone-shaped source characteristics and inductance effect of transient electromagnetic method. Appl. Geophys. 2017, 14, 165–174, 192. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, H.Y.; Liu, Z.X.; Zhang, H.; Chen, X.; Li, Z.; Wang, L.; Yang, F.J. Experimental study on transient electromagnetic method with a conical source. Coal Geol. Explor. 2021, 49, 107–112. [Google Scholar]
- Hu, X.W.; Chen, R.J.; Zhang, P.S.; Wu, R.C.; Fu, M.R.; Zhou, H.Y. Development and experiment of transient electromagnetic common centerzero-flux coil. J. China Coal Soc. 2023, 48, 918–930. [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, Z.; Liu, S. Two-Dimensional Whole Space Transient Electromagnetic Forward Response of Magnetic Moment in Arbitrary Direction. IEEE Access 2021, 9, 82462–82470. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chang, J.; Yu, J.; Li, J.; Xue, G.; Malekian, R.; Su, B. Diffusion Law of Whole-Space Transient Electromagnetic Field Generated by the Underground Magnetic Source and Its Application. IEEE Access 2019, 7, 63415–63425. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ji, Y.; Li, D.; Yuan, G.; Lin, J.; Du, S.; Xie, L.; Wang, Y. Noise Reduction of Time Domain Electromagnetic Data: Application of a Combined Wavelet Denoising Method. Radio Sci. 2016, 51, 680–689. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xue, G.Q.; Yan, Y.J.; Li, X.; Di, Q.Y. Transient Electromagnetic S-Inversion in Tunnel Prediction. Geophys. Res. Lett. 2007, 34, L18403. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xue, G.Q.; Yan, Y.J.; Li, X. Pseudo-Seismic Wavelet Transformation of Transient Electromagnetic Response in Engineering Geology Exploration. Geophys. Res. Lett. 2007, 34, L16405. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moorkamp, M. Integrating Electromagnetic Data with Other Geophysical Observations for Enhanced Imaging of the Earth: A Tutorial and Review. Surv. Geophys. 2017, 38, 935–962. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]






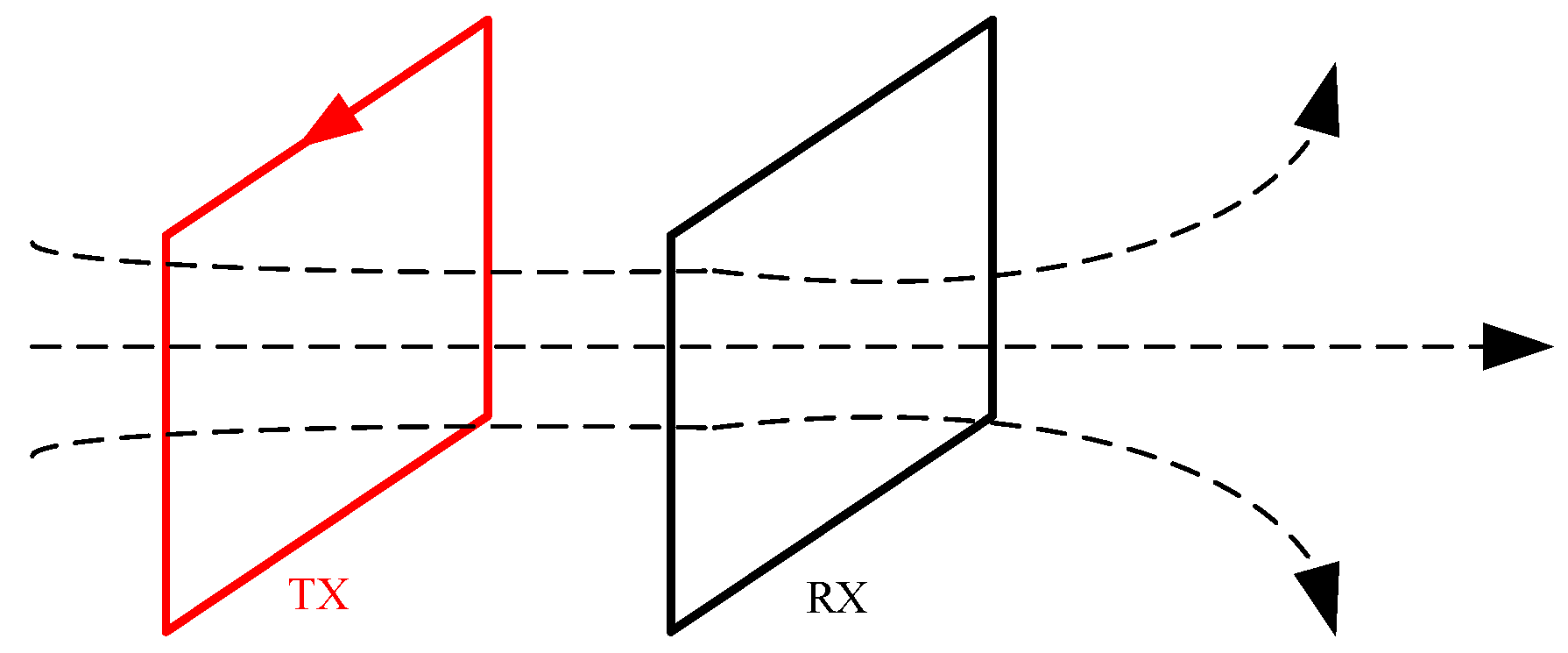





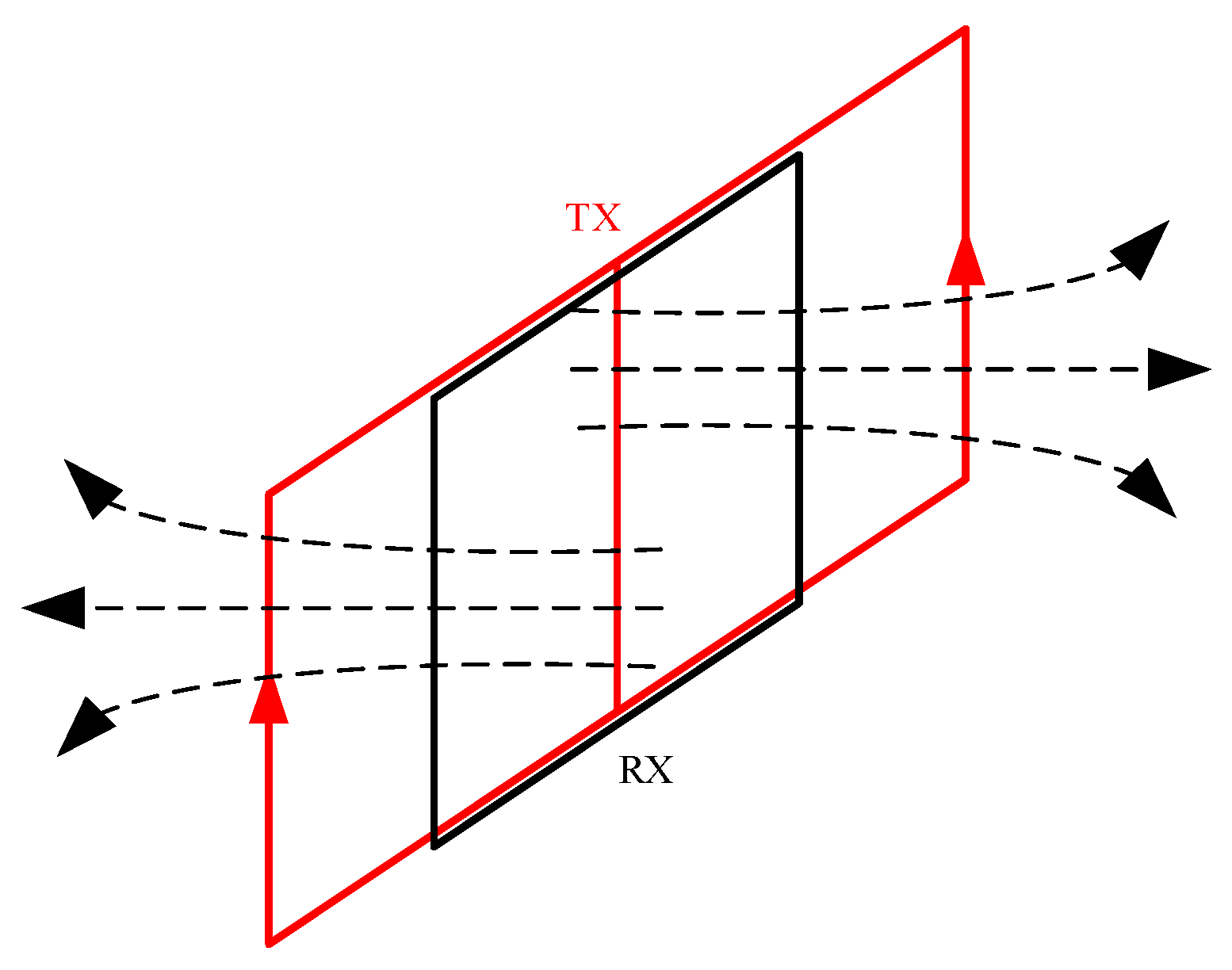



| Device Classification | Meaning | Coil Structure | Advantages | Disadvantages | Application |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Fixed-source devices | Fixed source location | The large fixed-source loop, the ground-hole TEM | High resolution and deep detection depth, facilitating detailed geological structure analysis in specific areas | Inconvenient construction, low construction efficiency, and high costs | Oil exploration, detection of deep hidden mineral deposits and goaf areas |
| Dynamic source devices | Flexible source location | The central loop method, the transient electromagnetic dipole device, the well-ground TEM, magnetic induction probes, bucking coils, the opposing coils, and others | Meeting diverse detection requirements, adapting to various environmental conditions, facilitating portability and operation, and enabling the acquisition of abundant geological information | Convenient construction, high construction efficiency, and rich data | Engineering surveys, hydrological surveys, advance detection in mine shafts and shallow coal seam goaf |
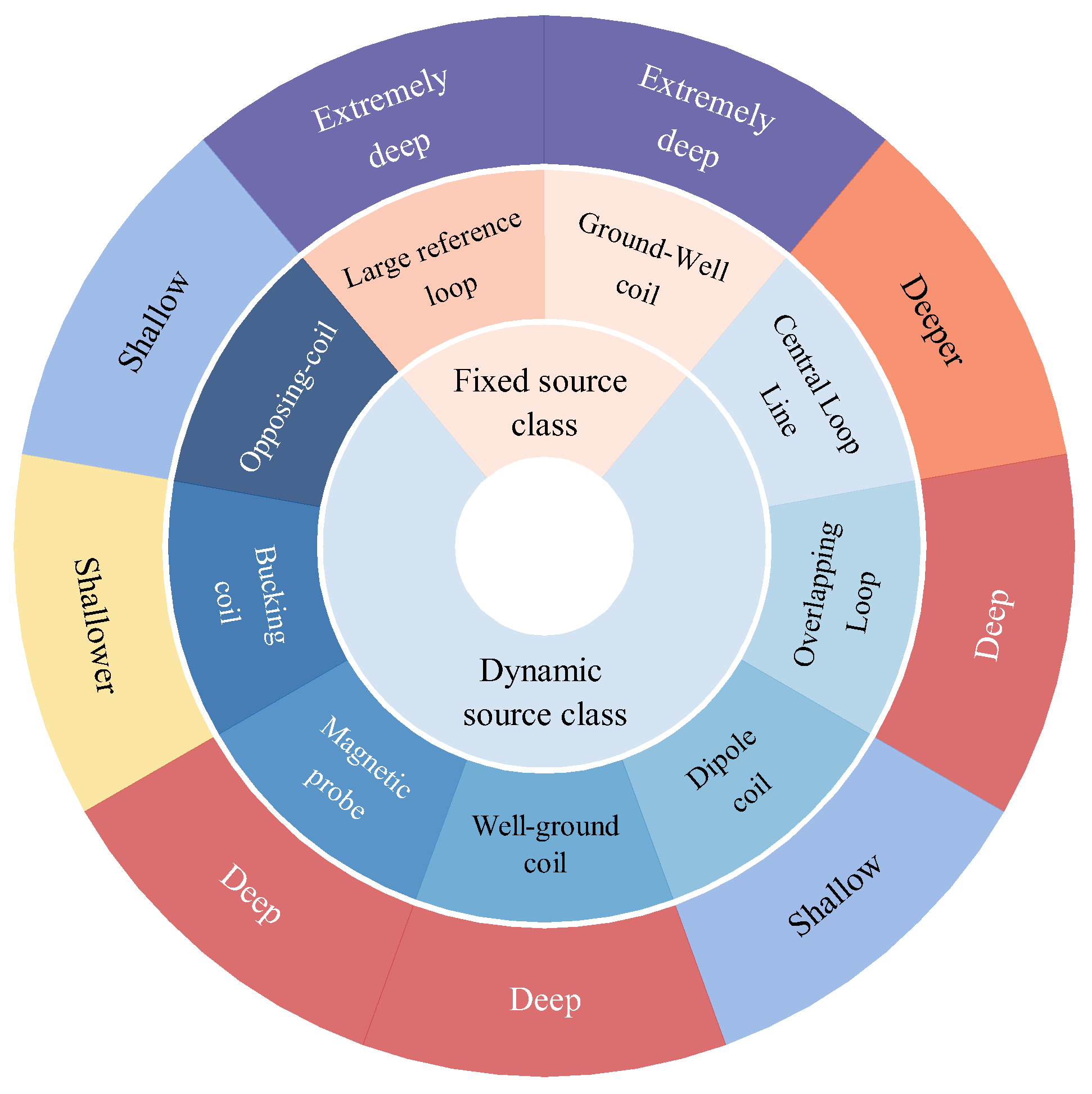
| Detection Depth Metric | Specified Range |
|---|---|
| Extremely deep | >2000 m |
| Deep | 200~2000 m |
| Deeper | 100~200 m |
| Shallower | 50~100 m |
| Shallow | <50 m |
| Detection Blind Zone Metric | Specified Range |
|---|---|
| Very large | >200 m |
| Large | 150~200 m |
| Relatively large | 100~150 m |
| Medium | 50~100 m |
| Relatively small | 30~50 m |
| Small | 10~30 m |
| Very small | <10 m |
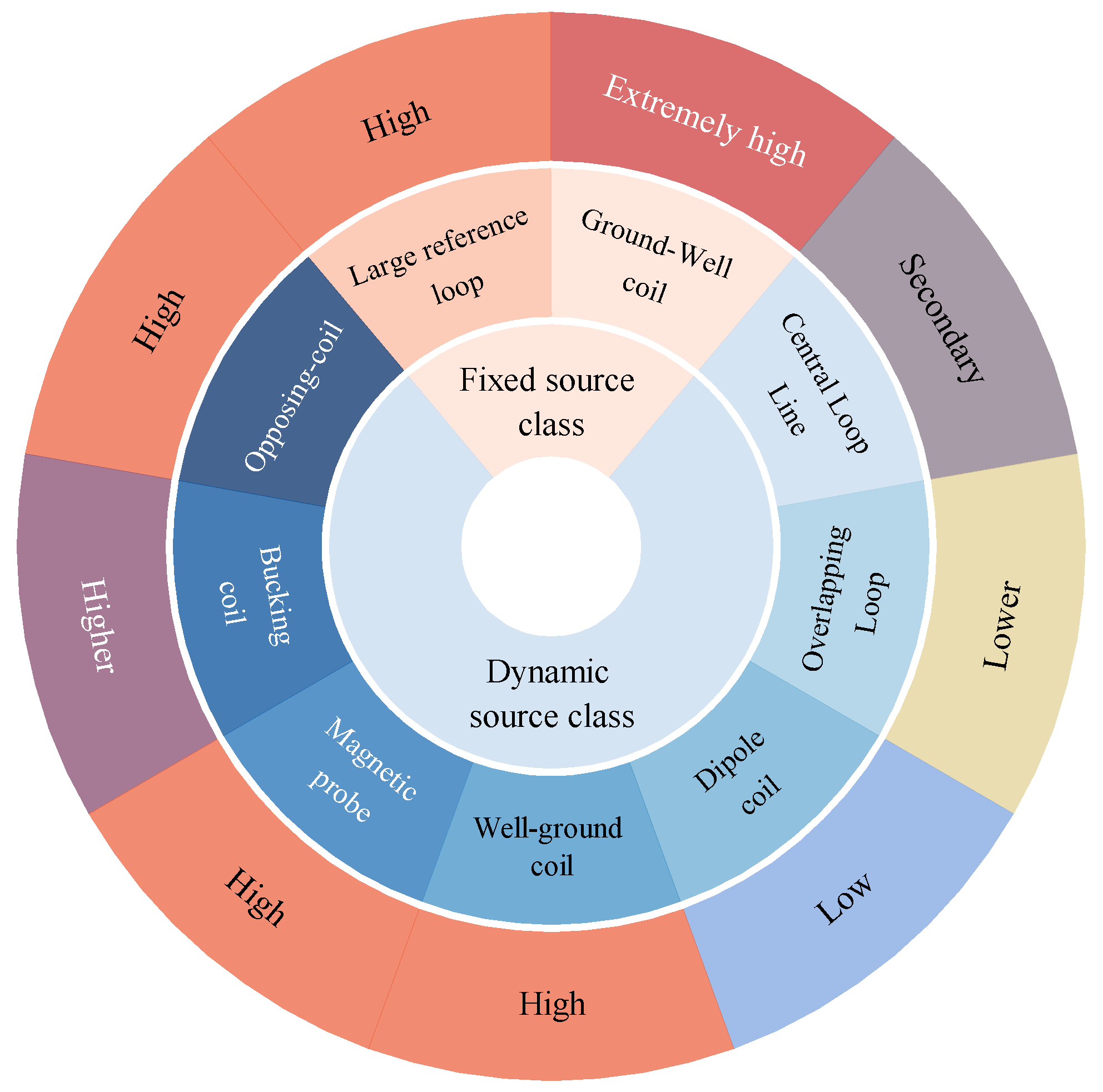
| Device Classification | Detection Depth | Resolution | Detection Blind Zone |
|---|---|---|---|
| The large fixed-source loop | Extremely deep | High | Large |
| The ground-hole TEM | Extremely deep | Extremely high | Very large |
| The central loop method | Deeper | Medium | Medium |
| Overlapping Coils | Deep | Lower | Relatively large |
| The transient electromagnetic dipole device | Shallow | Low | Small |
| The well-ground TEM | Deep | High | Relatively large |
| Magnetic induction probes | Deep | High | Relatively small |
| Bucking coils | Shallower | Higher | Very small |
| The opposing coils | Shallow | High | Very small |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Yang, Y.; Yang, F.; Wang, B.; Qian, W.; Wang, Y.; Zuo, Y. Technical Analysis and Application Prospects of Magnetic Source Transient Electromagnetic Coil Devices in Hydrogeological Survey of Mining Area. Water 2025, 17, 171. https://doi.org/10.3390/w17020171
Yang Y, Yang F, Wang B, Qian W, Wang Y, Zuo Y. Technical Analysis and Application Prospects of Magnetic Source Transient Electromagnetic Coil Devices in Hydrogeological Survey of Mining Area. Water. 2025; 17(2):171. https://doi.org/10.3390/w17020171
Chicago/Turabian StyleYang, Yang, Fei Yang, Bo Wang, Wangping Qian, Ying Wang, and Yuanbin Zuo. 2025. "Technical Analysis and Application Prospects of Magnetic Source Transient Electromagnetic Coil Devices in Hydrogeological Survey of Mining Area" Water 17, no. 2: 171. https://doi.org/10.3390/w17020171
APA StyleYang, Y., Yang, F., Wang, B., Qian, W., Wang, Y., & Zuo, Y. (2025). Technical Analysis and Application Prospects of Magnetic Source Transient Electromagnetic Coil Devices in Hydrogeological Survey of Mining Area. Water, 17(2), 171. https://doi.org/10.3390/w17020171







