Treatment of Acid Mine Water from the Breiner-Băiuț Area, Romania, Using Iron Scrap
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
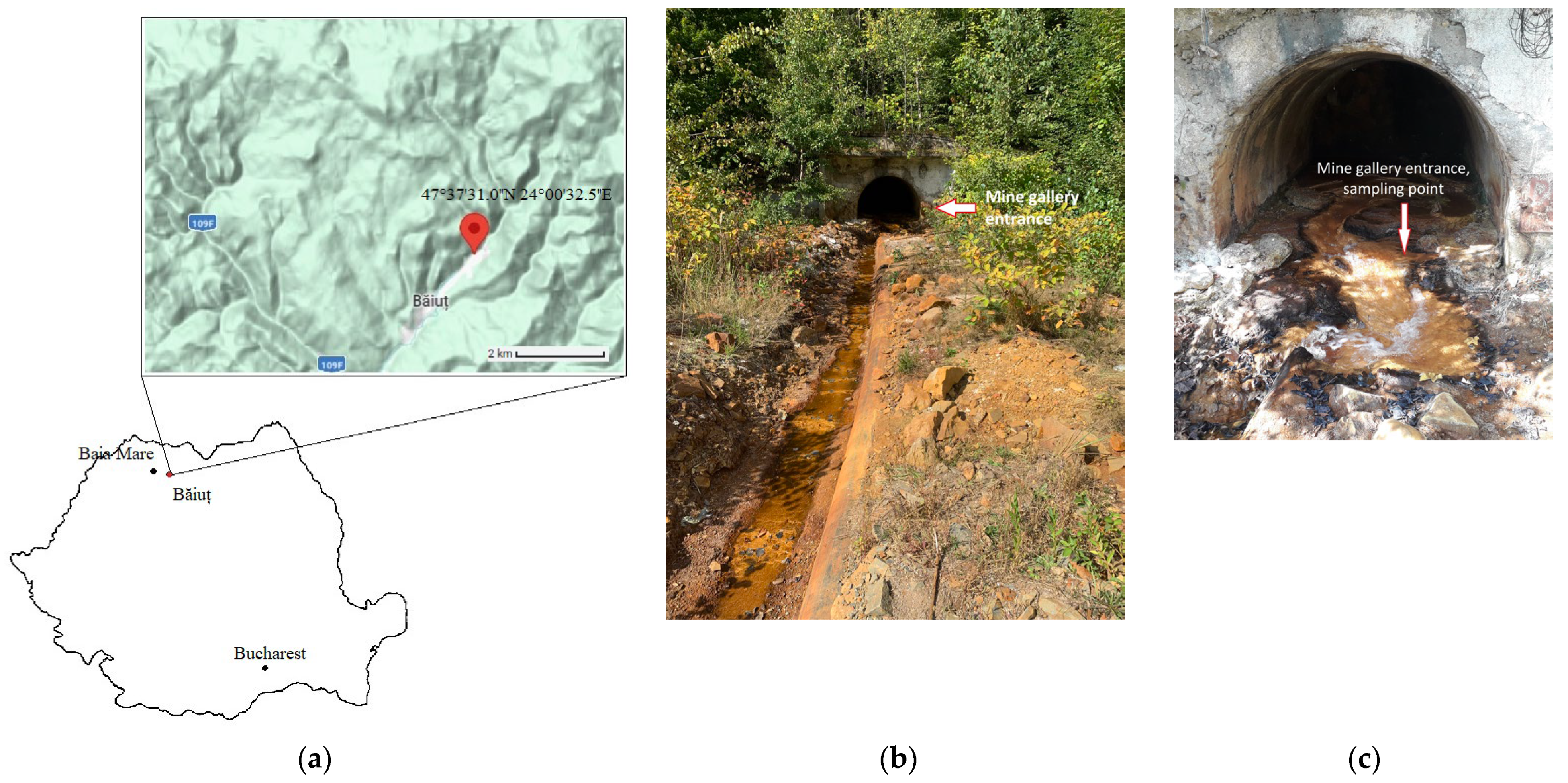
Site Description
3. Results and Discussion
3.1. Water Analysis
3.2. Sludge Analysis
3.2.1. Chemical Analysis
3.2.2. XRD Analysis
3.3. Microscopic Analysis of Iron Shavings
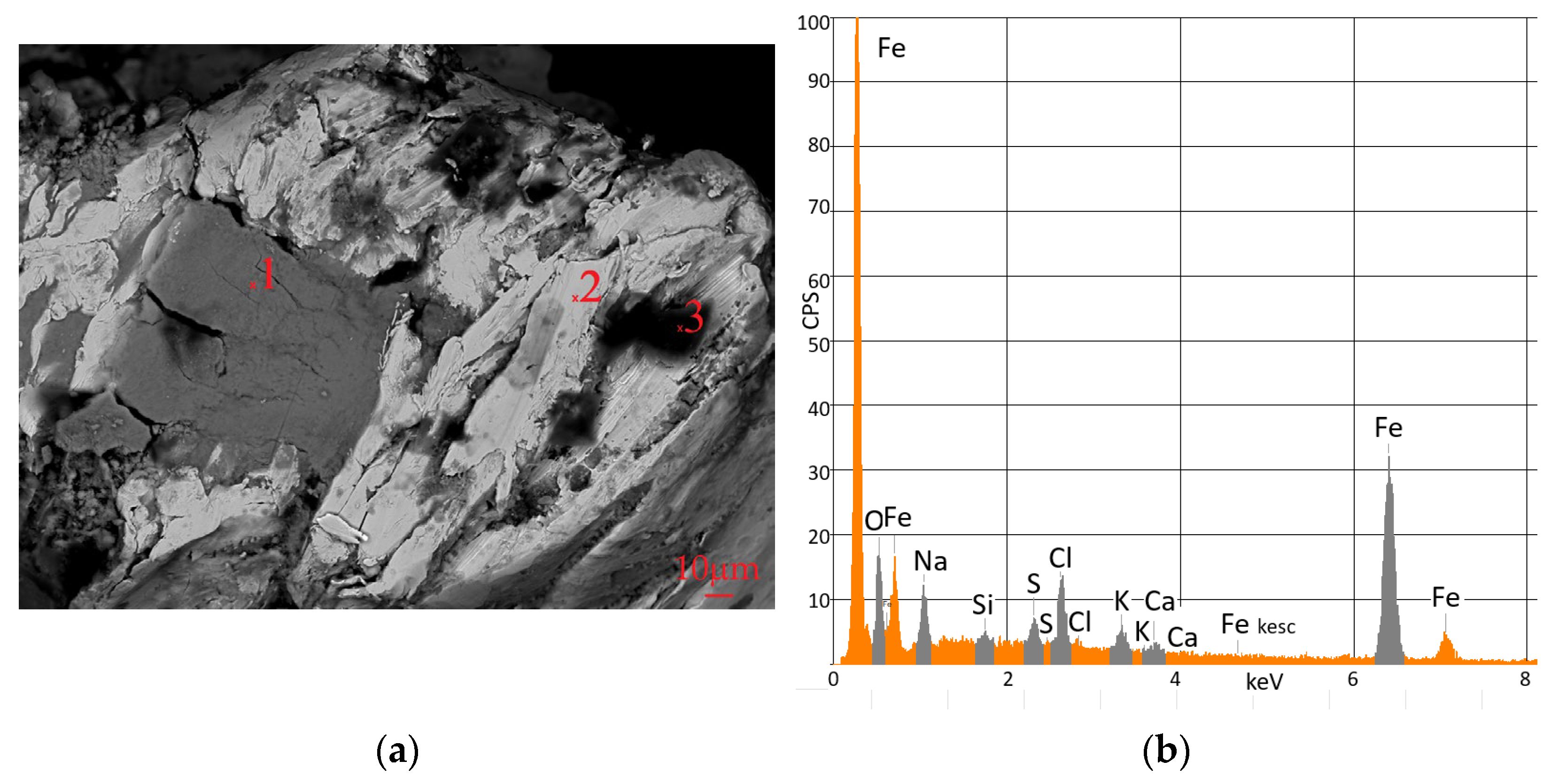
Electron Probe Analyses
4. Discussion and Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Valente, T.M.; Gomes, C.L. Occurrence, properties and pollution potential of environmental minerals in acid mine drainage. Sci. Total Environ. 2009, 407, 1135–1152. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Schwertmann, U. The effect of pedogenic environments on iron oxide minerals. Adv. Soil Sci. 1985, 1, 172–200. [Google Scholar]
- Regenspurg, S.; Brand, A.; Peiffer, S. Formation and stability of schwertmannite in acidic mining lakes. Geochim. Cosmochim. Acta 2004, 68, 1185–1197. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Accornero, M.; Marini, L.; Ottonello, G.; Vetuschi Zuccolini, M. The fate of major constituents and chromium and other trace elements when acid waters from the derelict Libiola mine (Italy) are mixed with stream waters. Appl. Geochem. 2005, 20, 1368–1390. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Blowes, D.W.; Ptacek, C.J.; Jambor, J.L.; Weisner, C.G. The geochemistry of acid mine drainage. In Treatise on Geochemistry; Lollar, B.S., Environmental Geochemistry, Holland, H.D., Turekian, K.K., Eds.; Elsevier–Pergamon: Oxford, UK, 2005; Volume 9, pp. 149–204. [Google Scholar]
- Nagy-Korodi, I.; Ionescu, C.; Forray, L.F.; Hoeck, V.; Tippelt, G. Environmental Impact and Polymetallic Mining in the Nistru-Băiţa, North Romania. Ph.D. Thesis, BABEŞ-BOLYAI” University of Cluj-Napoca, Cluj-Napoca, Romania, 2009. [Google Scholar]
- Nagy, I.; Weiszburg, G.T.; Fodorpataki, L.; Bartha, A. Environmental impact of acid mine drainage in the Turţ Creek. Satu Mare County, Romania. Acta Mineral. Petrogr. 2006, 5, 80. [Google Scholar]
- Hammarstrom, J.M.; Seal, R.R., II; Meier, A.L.; Kornfeld, J.M. Secondary sulfate minerals associated with acid drainage in the eastern US: Recycling of metals and acidity in surficial environments. Chem. Geol. 2005, 215, 407–431. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jordan, G.; D’Alessandro, M. Mining, Mining Waste and Related Environmental Issues: Problems and Solutions in the Central and Eastern European Candidate Countries; Joint Research Centre of the European Commission: Ispra, Italy, 2004; LB-NA-20868-EN-C. [Google Scholar]
- Poggere, G.; Gasparina, A.; Barbosa, J.Z.; Meloc, G.W.; Corrêa, R.S.; Motta, A.C.V. Soil contamination by copper: Sources, ecological risks, and mitigation strategies in Brazil. J. Trace Elem. Miner. 2023, 4, 100059. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Larsson, M.; Nosrati, A.; Kaur, S.; Wagner, J.; Baus, U.; Nydén, M. Copper removal from acid mine drainage-polluted water using glutaraldehyde-polyethyleneimine modified diatomaceous earth particles. Heliyon 2018, 4, e00520. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kortei, N.K.; Heymann, M.E.; Essuman, E.K.; Kpodo, F.M.; Akonor, P.T.; Lokpo, S.Y.; Boadi, N.O.; Ayim-Akonor, M.; Tettey, C. Health risk assessment and levels of toxic metals in fishes (Oreochromis noliticus and Clarias anguillaris) from Ankobrah and Pra basins: Impact of illegal mining activities on food safety. Toxicol. Rep. 2020, 7, 360–369. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Erasmus, J.H.; Malherbe, W.; Zimmermann, S.; Lorenz, A.W.; Nachev, M.; Wepener, V.; Sures, B.; Smit, N.J. Metal accumulation in riverine macroinvertebrates from a platinum mining region. Sci. Total Environ. 2020, 703, 134738. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Naidoo, S. An assessment of the impacts of acid mine drainage on socio-economic development in the Witwatersrand: South Africa, Environment. Dev. Sustain. 2015, 17, 1045–1063. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stylianou, M.; Gavriel, I.; Vogiatzakis, I.N.; Zorpas, A.; Agapiou, A. Native plants for the remediation of abandoned sulphide mines in Cyprus: A preliminary assessment. J. Environ. Manag. 2020, 274, 110531. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Reinhardt, C.H. Acid Mine Drainage in Pennsylvania Streams: “Ironing Out” the Problem, Restorasion and Reclamation Review; University of Minnesota: Minneapolis, MN, USA, 1999; Volume 5, pp. 1–10. [Google Scholar]
- Kuyucak, N. Water in Mining and Environment for Sustainability. Mine Water Environ. 2021, 40, 815–817. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kaur, G.; Couperthwaite, S.J.; Hatton-Jones Bradley, W.; Millar Graeme, J. Alternative neutralisation materials for acid mine drainage treatment. J. Water Process Eng. 2018, 22, 46–58. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lei, L.-Q.; Song, C.-A.; Xie, X.-L.; Li, Y.-H.; Wang, F. Acid mine drainage and heavy metal contamination in groundwater of metal sulfide mine at arid territory (BS mine, Western Australia). Trans. Nonferrous Met. China 2010, 20, 1488–1493. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Adamovic, D.; Ishiyama, D.; Kawaraya, H.; Ogawa, Y.; Stevanovic, Z. Geochemical characteristics and estimation of groundwater pollution in catchment areas of Timok and Pek Rivers, Eastern Serbia: Determination of early-stage groundwater pollution in mining areas. Groundw. Sustain. Dev. 2022, 16, 100719. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Weiersbye, I.M.; Witkowski, E.T.F. Impacts of acid mine drainage on the regeneration potential of highveld phreatophytes. In Conference: Multiple Use Management of Natural Forests and Woodlands: Policy Refinements and Scientific Progress; Department of Water Affairs and Forestry of South Africa: Pretoria, South Africa, 2007; pp. 224–237. [Google Scholar]
- Tipping, E.; Jarvis, A.P.; Kelly, M.G.; Lofts, S.; Merrix, F.L.; Ormerod, S.J. Ecological Indicators for Abandoned Mines, Phase 1: Review of the Literature Centre for Ecology and Hydrology Report; SC030136/R49; Environment Agency: Bristol, UK, 2009.
- Matebese, F.M.; Mosai, A.K.; Tutu, H.; Tsentu, Z.R. Mining wastewater treatment technologies and resource recovery techniques: A review. Heliyon 2024, 10, e24730. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wildeman, T.R.; Schmiermund, R. Mining influenced waters: Their chemistry and methods of treatment. In Proceedings of the America Society of Mining and Reclamation and the 25th West Virginia Surface Mine Drainage Task Force, Morgantown, WV, USA, 18–24 April 2004; ASMR: Lexington, KY, USA, 2004; Volume 40502, pp. 2001–2013. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Akcil, A.; Koldas, S. Acid Mine Drainage (AMD): Causes, treatment and case studies. J. Clean. Prod. 2006, 14, 1139–1145. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hansen, E.; Collins, A.; Zegre, S.; Hereford, A. The Benefits of Acid Mine Drainage Remediation on the North Branch Potomac River, Downstream Strategies, Water Quality Advisory; Committee Garrett County, Maryland Economic Development Office: Oakland, MD, USA, 2010.
- RoyChowdhury, A.; Sarkar, D.; Datta, R. Remediation of acid mine drainage-impacted water. Water Pollut. 2015, 1, 131–141. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kefeni, K.; Msagati, T.; Mamba, B. Acid mine drainage: Prevention, treatment options, and resource recovery: A review. J. Clean. Prod. 2017, 151, 475–493. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Skousen Jeffrey, G.; Alan, S.; Ziemkiewicz Paul, F. Acid Mine Drainage Control And Treatment Reprinted from 2000. In Reclamation of Drastically Disturbed Lands; American Society of Agronomy: Madison, WI, USA; American Society for Surface Mining and Reclamation: Butte, MT, USA, 2000. [Google Scholar]
- Moreno, N.; Querol, X.; Ayora, C.; Fernández-Pereira, C.; Janssen-Jurkovicová, M. Utilization of zeolites synthesized from coal fly ash for the purification of acid mine waters. Environ. Sci. Technol. J. 2001, 35, 3526–3534. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wingenfelder, U.; Hansen, C.; Furrer, G.; Schulin, R. Removal of Heavy Metals from Mine Waters by Natural Zeolites. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2005, 39, 12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xue, C.; Zhang, Q.; Li, W.; Ownes, G.; Chen, Z. Removal mechanism of Sb(V) by a hybrid ZIF-8@FeNPs and used for treatment of mining wastewater. Chem. Eng. J. 2023, 451, 138691. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Damian, F.; Damian, G.; Lăcătușu, R.; Postolache, C.; Iepure, G.; Jelea, M.; Nasui, D. The heavy metals immobilization in polluted soils from Romania by the natural zeolites use. Carpathian J. Earth Environ. Sci. 2013, 8, 231–250. [Google Scholar]
- Damian, F.; Damian, G. Geochemical characterization of some old mine waste dumps from Baia Mare area and their influence on the natural vegetation. Carpathian J. Earth Environ. Sci. 2006, 1, 63–72. [Google Scholar]
- Pop, A.; Vida-Simiti, I.; Damian, G.S.; Iepure, G. Removal of heavy metals from wastewater by using zeolitic tuff. Carpathian J. Earth Environ. Sci. 2012, 7, 239–248. [Google Scholar]
- Udayabhanu, G.; Prasad, B. Studies on environmental impact of acid mine drainage generation and its treatment: An appraisa. Indian J. Environ. Prot. 2010, 30, 953–967. [Google Scholar]
- Lawrence, R.; Philippe, R.; Fleming, C. Sulphide and ion exchange technologies for metal recovery and water treatment in the copper mining industry. In Proceedings of the HydroCopper Conference in Santiago, Vina del Mar, Chile, 16–18 May 2007. [Google Scholar]
- Ayangbenro, A.S.; Olanrewaju, O.S.; Babalola, O.O. Sulfate-Reducing Bacteria as an Effective Tool for Sustainable Acid Mine Bioremediation. Front. Microbiol. 2018, 9, 1986. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Meseldzija, S.; Petrovic, J.; Onjia, A.; Volkov-Husovic, T.; Nesic, A.; Vukelic, N. Utilization of agro-industrial waste for removal of copper ions from aqueous solutions and mining-wastewater. J. Ind. Eng. Chem. 2019, 75, 246–252. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Benavente, M.; Moreno, L.; Martinez, J. Sorption of heavy metals from gold mining wastewater using chitosan. J. Taiwan Inst. Chem. Eng. 2011, 42, 976–988. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rambabu, K.; Banat, F.; Pham, Q.M.; Ho, S.-H.; Ren, N.-Q.; Show, P.L. Biological remediation of acid mine drainage: Review of past trends and current outlook. Environ. Sci. Ecotechnol. 2020, 2, 100024. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bachtlin, A. Acid Mine Drainage and the Techniques to Cleanup This Issue. DU Quark 2019, 3, 28–34. [Google Scholar]
- Grossi, L.B.; Magalhaes, N.C.; Araujo, B.M.; De Carvalho, F.; Andrade, L.H.; Amaral, M.C.S. Water conservation in mining industry by integrating pressureoriented membrane processes for nitrogen-contaminated wastewater treatment: Bench and pilot-scale studies. J. Environ. Chem. Eng. 2021, 9, 104779. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Naidu, G.; Ryu, S.; Thiruvenkatachari, R.; Choi, Y.; Jeong, S.; Vigneswaran, S. A critical review on remediation, reuse, and resource recovery from acid mine drainage. Environ. Pollut. 2019, 247, 1110–1124. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Samaei, S.M.; Gato-Trinidad, S.; Altaee, A. Performance evaluation of reverse osmosis process in the post-treatment of mining wastewaters: Case study of Costerfield mining operations, Victoria, Australia. J. Water Process Eng. 2020, 34, 101116. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sukmana, H.; Bellahsen, N.; Pantoja, F.; Hodur, C. Adsorption and coagulation in wastewater treatment—Review. Prog. Agric. Eng. Sci. 2021, 17, 49–68. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- De Gisi, S.; Lofrano, G.; Grassi, M.; Notarnicola, M. Characteristics and adsorption capacities of low-cost sorbents for wastewater treatment: A review. Sustain. Mater. Technol. 2016, 9, 10–40. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Acheampong, M.A.; Okwaning Ansa, E.D. Low-Cost Technologies for Mining Wastewater Treatment. J. Environ. Sci. Eng. 2017, 6, 391–405. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fashola, M.O.; Ngole-Jeme, V.M.; Babalola, O.O. Heavy metal pollution from gold mines: Environmental effects and bacterial strategies for resistance. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2016, 13, 1047. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nordstrom, D.K.; Blowes, D.W.; Ptacek, C.J. Hydrogeochemistry and microbiology of mine drainage: An update. Appl. Geochem. 2015, 57, 3–16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hosseinpour, M.; Osanloo, M.; Azimi, Y. Evaluation of positive and negative impacts of mining on sustainable development by a semi-quantitative method. J. Clean. Prod. 2022, 366, 132955. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, X.; Di, J.; Dong, Y.; Yang, Y.; Liang, B.; Meng, F.; Wang, T.; An, W.; Li, Z.; Guo, J. The dynamic experiment on treating acid mine drainage with iron scrap and sulfate reducing bacteria using biomass materials as carbon source. J. Renew. Mater. 2021, 9, 163–177. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, R.; Walder, I.; Leiviska, T. Pilot-scale field study for vanadium removal from mining-influenced waters using an iron-based sorbent. J. Hazard. Mater. 2021, 416, 125961. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Temur, H.; Yartaşi, A.; Kocakerim, M.M. A study on the optimum conditions of the cementation of copper in chlorination solution of chalcopyrite concentrate by iron scraps. BAÜ Fen Bil. Enst. Derg. 2006, 8, 63–73. [Google Scholar]
- Shahrivar, E.; Karamoozian, M.; Gharabaghi, M. Modeling and optimization of oxide copper cementation kinetics. Appl. Sci. 2020, 2, 469. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pozo-Antonio, S.; Puente-Luna, I.; Lagüela-López, S.; Veiga-Ríos, M. Techniques to correct and prevent acid mine drainage: A review. DYNA 2014, 81, 73–80. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chira, I.; Gh, D.; Chira, R. Spatial distribution of heavy metals in the soils of Băiuţ area, Maramureş County, Romania. Carpathian J. Earth Environ. Sci. 2014, 9, 269–278. [Google Scholar]
- Costin, D. Major Elements Geochemistry of the Breiner Baiut Ore Deposits (Gutai Mts. Eastern Carpathians). Stud. UBB Geol. 2000, 45, 55–66. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Borcoş, M. Neogene Volcanicity—Metallogeny in the Oaş—Gutâi Mts., Plate Tectonics and Metallogeny in the East Carpathians and Apuseni Mts.; Borcoş, M., Vlad, Ş., Eds.; Springer Science and Business Media LLC.: Berlin, Germany, 1994; pp. 20–22. [Google Scholar]
- Damian, F.; Damian, G. Mineral parageneses of the hydrothermal ore deposits from Baia Mare area, Romania. Bul. Ştiinţific Univeritatii Nord. Baia Mare Ser. D Mine Prep. Geoogie Ing. Mediu. Metal. 2004, 18, 155–170. [Google Scholar]
- Thomas, G.; Sheridan, C.; Holm, P.E. A critical review of phytoremediation for acid mine drainage-impacted environments. Sci. Total Environ. 2022, 811, 152230. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Neniţescu, C.D. Chimie Generală; Editura Didactica si Pedagogica, Bucureşti: București, Romania, 1985. [Google Scholar]
- Gâdea, S.; Rău, A.; Oprea, F.; Tripşa, I.; Geru, N. Manualul Inginerului Metalurg; Tehnică Bucureşti: Bucharest, Romania, 1978; Volume I. [Google Scholar]
- SR EN 10025-2:2004; Hot Rolled Construction Steel Products (Produse Laminate la Cald din Oţeluri de Construcţii). British Standards Institution: London, UK, 2004.
- NTPA 001/2005; The Regulation Regarding the Establishment of Pollutant Loading Limits for Industrial and Urban Wastewater Discharges into Natural Receivers. Editura Academica Brâncuşi: Târgu Jiu, Romania, 2005.
- Law 161/2006; Normative Regarding the Classification of Water Quality Surface in Order to Establish the Ecological Status of Water Bodies. Statute Law Database: Online, 2006.
- Johnson, D.B.; Hallberg, K.B. Acid mine drainage remediation options: A review. Sci. Total Environ. 2005, 338, 3–14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Moalla, S.M.N.; Rashed, M.N.; El Aziz, A.A.; Maghazy, M.A. Determination of Cd2+, Cu2+, Mn2+, Pb2+, and Zn2+ in aqueous solution after their separation and preconcentation as metal—Dithizone complexes on activated carbon. Aswan Univ. J. Environ. Stud. 2020, 1, 157–170. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, J.; Zhao, J.; Du, J.; Peng, S.; Tan, S.; Zhang, W.; Yan, X.; Wang, H.; Lin, Z. Machine learning predicts heavy metal adsorption on iron (oxyhydr)oxides: A combined insight into the adsorption efficiency and binding configuration. Sci. Total Environ. 2024, 950, 175370. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Skousen, J.; Zipper, C.E.; Rose, A.; Ziemkiewicz, P.F.; Nairn, R.; McDonald, L.M.; Kleinmann, R.L. Review of Passive Systems for Acid Mine Drainage Treatment. Mine Water Environ. 2017, 36, 133–153. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- ASTM. Powder Difraction File, Alphabetical Index (Chemical and Mineral Name), International Center for Difraction Data; American Society for Testing and Materials: West Conshohocken, PA, USA, 1987. [Google Scholar]
- Nemecz, E. Agyagásványok (Clay Minerals); Akadémiai Kiadó Bp.: Budapest, Hungary, 1973; p. 507. [Google Scholar]
- Miler, M.; Bavec, S.; Gosar, M. The environmental impact of historical Pb-Zn mining waste deposits in Slovenia. J. Environ. Manag. 2022, 308, 114580. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Eltaweel Yehia, A.; Nassef Ehssan, M.; Hazza Riham, A. Recovery of Copper from Wastewater by Cementation Technique. World Environ. 2014, 4, 199–205. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Toro, N.; Pérez, K.; Saldaña, M.; Salinas-Rodríguez, E.; Hernández, P. Treatment of black copper with the use of iron scrap—Part l. Hem. Ind. 2020, 74, 237–245. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Loibl, A.; Tercero Espinoza, L.A. Current challenges in copper recycling: Aligning insights from material flow analysis with technological research developments and industry issues in Europe and North America, Resources. Conserv. Recycl. 2021, 169, 105462. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, Y.; Dai, W.; Zheng, P.; Zheng, X.; He, S.; Zhao, M. Iron scraps enhance simultaneous nitrogen and phosphorus removal in subsurface flow constructed wetlands. J. Hazard. Mater. 2020, 395, 122612. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sánchez-España, J.; Ilin, A.; Yusta, I. Metallic Copper (Cu [0]) Obtained from Cu2+-Rich Acidic Mine Waters by Two Different Reduction Methods: Crystallographic and Geochemical Aspects. Minerals 2022, 12, 322. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
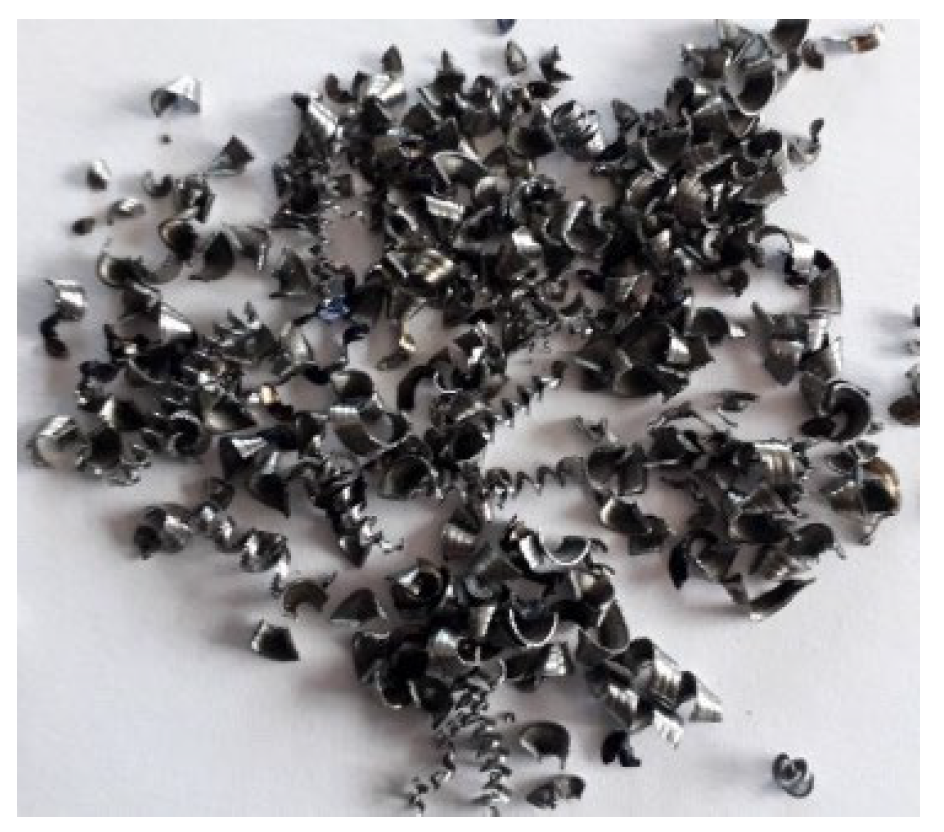







| Cemented Metal | Reducing Metal | Difference Between Electrode Potentials | Anion Present in the Solution from Which the Metal is Cemented |
|---|---|---|---|
| Cu | Zn | 1.10 | SO42−, Cl−, NO3− |
| Fe | 0.78 | SO42−, Cl−, NO3− | |
| Cd | 0.74 | SO42− | |
| As | Fe | 0.69 | SO42−, Cl− |
| Pb | Zn | 0.63 | SO42−, Cl− |
| Fe | 0.31 | Cl− | |
| Sn | Zn | 0.62 | SO42−, Cl− |
| Fe | 0.30 | SO42− | |
| Cd | Zn | 0.36 | SO42− |
| Hg | Cu | 0.35 | SO42− |
| Steel Type | Fe, % | C, % | Mn, % | S, % | P, % | N % |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| S235 (OL37) | 97.72 | 0.17 | 1.4 | 0.35 | 0.35 | 0.012 |
| Parameter | Concentrations—Metals in Mine Water Before Treatment [mg/L] | Allowed Concentrations (NTPA001/2005) |
|---|---|---|
| pH | 2.75 | 6.5–8.5 |
| Zn | 42.5 | 0.5 |
| Cu | 71.1 | 0.1 |
| Pb | 0.004 | 0.2 |
| Fe | 122.5 | 5.0 |
| Cd | 0.042 | 0.2 |
| Sample no. | Treatment Variant (Sample—Iron Shavings) | Cu (mg/L) | Zn (mg/L) | Pb (mg/L) | Fe (mg/L) | Cd (mg/L) | pH | CE (mS/cm) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | P1-200 g | 0.005 | 1.221 | <LOQ | 275 | 0.003 | 4.91 | 2.97 |
| 2 | P2-400 g | 0.001 | 1.091 | <LOQ | 302 | 0.002 | 4.83 | 2.98 |
| 3 | P3-600 g | <LOQ | 0.932 | <LOQ | 385 | 0.003 | 4.82 | 2.96 |
| NTPA001/2005 | 0.1 | 0.5 | 0.2 | 5.0 | 0.2 | 6.5–8.5 | - |
| Sample | Na | Mg | Al | K | Ca | Cr | Mn | Fe | Co | Ni | Cu | Zn | As | Mo | Cd | Tl | Pb |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| P1-200 | 991.8 | 428.7 | 2034.3 | 179.7 | 348.3 | 378.6 | 4154.4 | 599,287.2 | 69.6 | 872.4 | 833.7 | 4182.3 | 68.7 | 79.8 | 5.1 | 4.5 | 28.2 |
| P2-400 | 1109.7 | 273.9 | 3561 | 41.4 | 300 | 342.9 | 3382.5 | 556,343.7 | 75.6 | 799.2 | 1034.4 | 10,347.3 | 145.2 | 71.1 | 10.2 | 3.9 | 14.4 |
| P3-600 | 1114.2 | 306 | 2038.2 | 44.1 | 298.2 | 348 | 3899.1 | 571,009.2 | 70.5 | 832.2 | 872.1 | 5886 | 81.6 | 69.9 | 5.4 | 2.7 | 9 |
| Analysis no. | CaO wt,% | K2O wt,% | P2O5 wt,% | Al2O3 wt,% | SiO2 wt,% | Na2O wt,% | MgO wt,% | BaO wt,% | SrO wt,% | FeO wt,% | MnO wt,% | TiO2 wt,% | Cl wt,% | Cr2O3 wt,% | Total wt,% |
| 1 | 0.12 | 9.39 | - | 35.983 | 50.014 | 0.144 | 0.451 | 0.018 | 0 | 0.247 | 0 | 0.102 | - | - | 96.469 |
| 2 | 0.129 | 9.279 | - | 35.412 | 49.834 | 0.138 | 0.39 | 0.052 | 0.033 | 0.248 | 0.031 | - | - | - | 95.546 |
| 3 | 0.163 | 9.093 | 0.013 | 35.615 | 50.24 | 0.199 | 0.431 | 0.042 | 0.052 | 0.204 | - | - | - | - | 96.052 |
| 4 | 0.153 | 9.131 | - | 35.549 | 49.837 | 0.164 | 0.416 | 0.028 | - | 0.23 | 0.053 | 0.102 | - | - | 95.663 |
| 5 | 0.143 | 9.125 | - | 36.15 | 49.798 | 0.133 | 0.459 | - | - | 0.258 | 0.048 | - | 0.002 | 0.005 | 96.121 |
| 6 | 0.134 | 8.946 | - | 36.309 | 50.264 | 0.106 | 0.436 | - | - | 0.246 | 0.11 | - | 0.004 | - | 96.555 |
| 7 | 0.165 | 9.062 | - | 35.659 | 49.452 | 0.11 | 0.412 | - | - | 0.221 | 0.013 | 0.045 | 0.01 | 0.011 | 95.16 |
| 8 | 0.193 | 9.032 | - | 36.074 | 50.175 | 0.099 | 0.368 | - | - | 0.16 | - | 0.113 | 0.004 | 0.011 | 96.229 |
| 9 | 0.212 | 8.94 | - | 36.251 | 50.293 | 0.147 | 0.449 | - | - | 0.225 | 0.013 | 0.079 | 0.003 | 0.085 | 96.697 |
| 10 | 0.098 | 9.232 | - | 36.28 | 49.434 | 0.075 | 0.378 | - | - | 0.156 | 0.079 | - | - | 0.079 | 95.811 |
| Average | 0.151 | 9.123 | 0.003 | 35.928 | 49.934 | 0.132 | 0.419 | 0.035 | 0.021 | 0.220 | 0.035 | 0.044 | 0.004 | 0.032 | - |
| Point | Element/Formula | Fe | O | Cl | Na2O | SiO2 | SO3 | K2O | CaO | FeO |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | wt% | 60.12 | 39.88 | - | - | - | - | - | - | - |
| Atom, % | 30.16 | 69.84 | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | |
| 2 | wt% | 100 | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - |
| Atom, % | 100 | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | |
| 3 | wt% | - | - | 5.43 | 11.01 | 1.39 | 4.46 | 2.21 | 1.15 | 74.35 |
| Atom % | - | - | 10.29 | 11.93 | 1.56 | 3.74 | 1.58 | 1.38 | 69.52 |
| Point | Element/Formula | Fe | Si | Cr | Na2O | SiO2 | SO3 | K2O | CaO | FeO | ZnO | MgO | Al2O3 | Cr2O3 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | wt% | 87.88 | 0.55 | 11.57 | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - |
| Atom, % | 86.66 | 1.08 | 11.57 | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | |
| 2 | wt% | 100 | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - |
| Atom, % | 100 | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | |
| 3 | wt% | - | - | - | 2.54 | 1.22 | 1.28 | 0.45 | 0.48 | 89.30 | 4.74 | - | - | - |
| mol% | - | - | - | 2.94 | 1.45 | 1.15 | 0.35 | 0.61 | 89.31 | 4.19 | - | - | - | |
| 4 | wt% | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | 89.63 | 10.37 | - | - | - |
| mol% | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | 90.73 | 9.27 | - | - | - | |
| 5 | wt% | - | - | - | - | 1.04 | 0.94 | - | 0.49 | 91.13 | 3.91 | 0.75 | 0.18 | 1.56 |
| mol% | - | - | - | - | 1.25 | 0.85 | - | 0.63 | 91.59 | 3.47 | 1.34 | 0.13 | 0.74 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Iepure, G.; Pop, A. Treatment of Acid Mine Water from the Breiner-Băiuț Area, Romania, Using Iron Scrap. Water 2025, 17, 225. https://doi.org/10.3390/w17020225
Iepure G, Pop A. Treatment of Acid Mine Water from the Breiner-Băiuț Area, Romania, Using Iron Scrap. Water. 2025; 17(2):225. https://doi.org/10.3390/w17020225
Chicago/Turabian StyleIepure, Gheorghe, and Aurica Pop. 2025. "Treatment of Acid Mine Water from the Breiner-Băiuț Area, Romania, Using Iron Scrap" Water 17, no. 2: 225. https://doi.org/10.3390/w17020225
APA StyleIepure, G., & Pop, A. (2025). Treatment of Acid Mine Water from the Breiner-Băiuț Area, Romania, Using Iron Scrap. Water, 17(2), 225. https://doi.org/10.3390/w17020225






