Diurnal Variation of Carbon Dioxide Concentration and Flux in a River–Lake Continuum of a Mega City
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
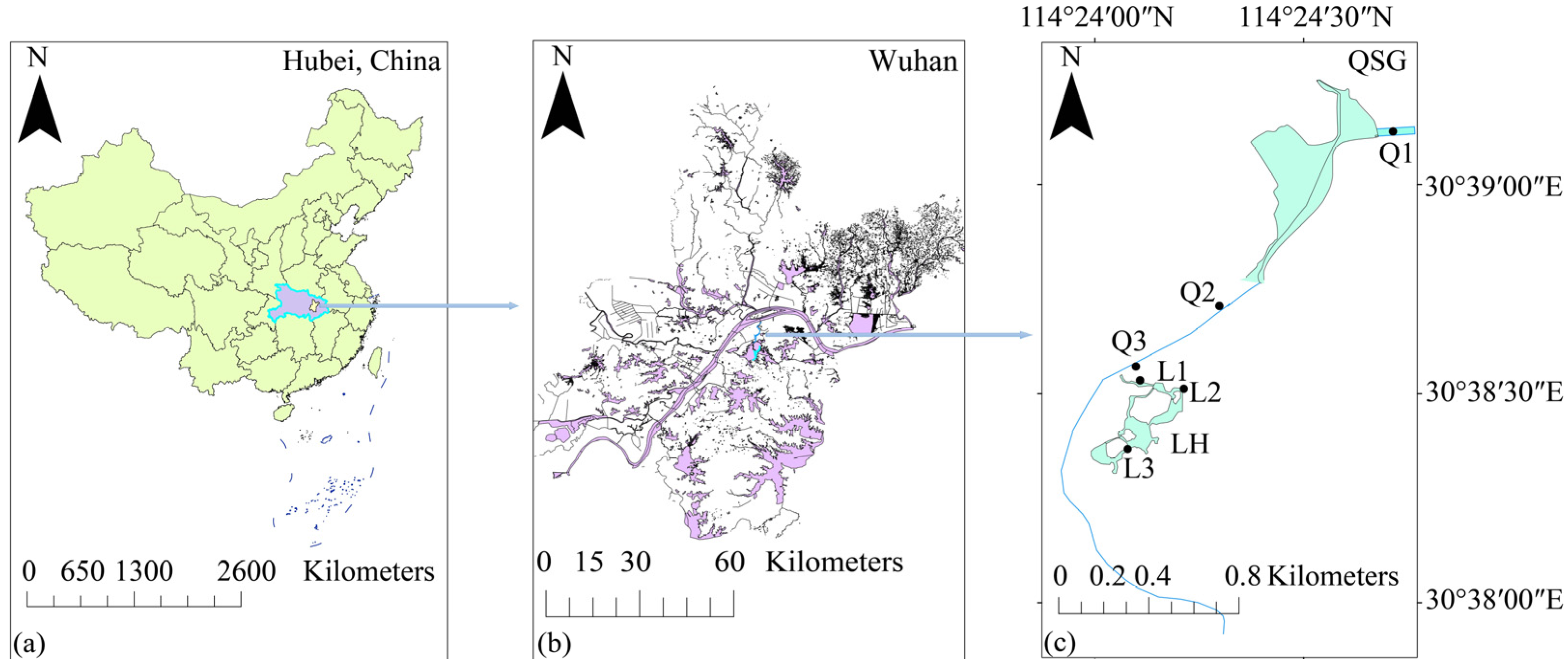
2.1. Study Area
2.2. Sampling and Analyses
2.3. Water Chemical Parameters Measurements
2.4. Continuous CO2 Measurements
2.5. CO2 Flux Estimations
2.6. Statistical Analysis
3. Results
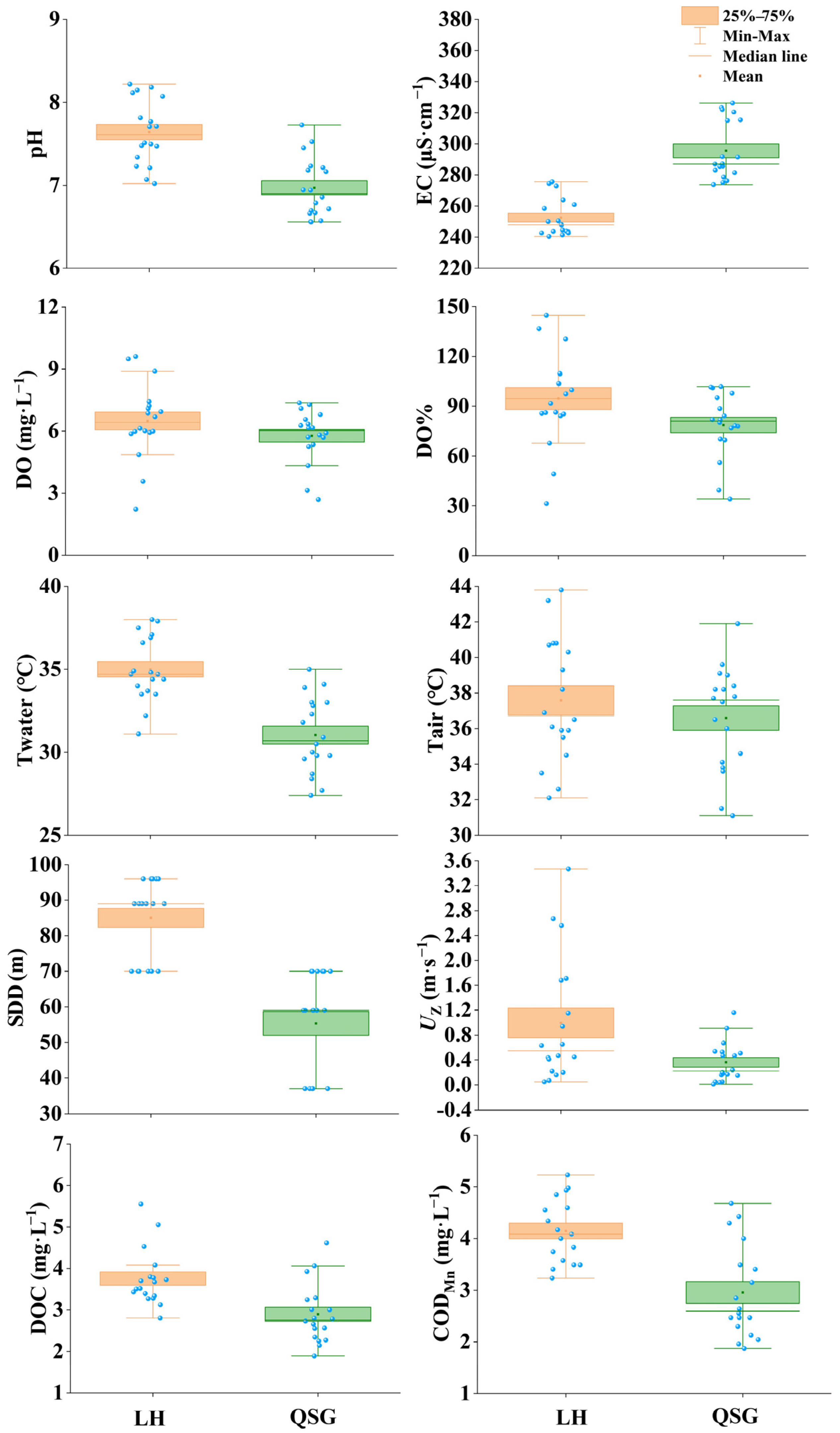
3.1. Physical and Chemical Parameters
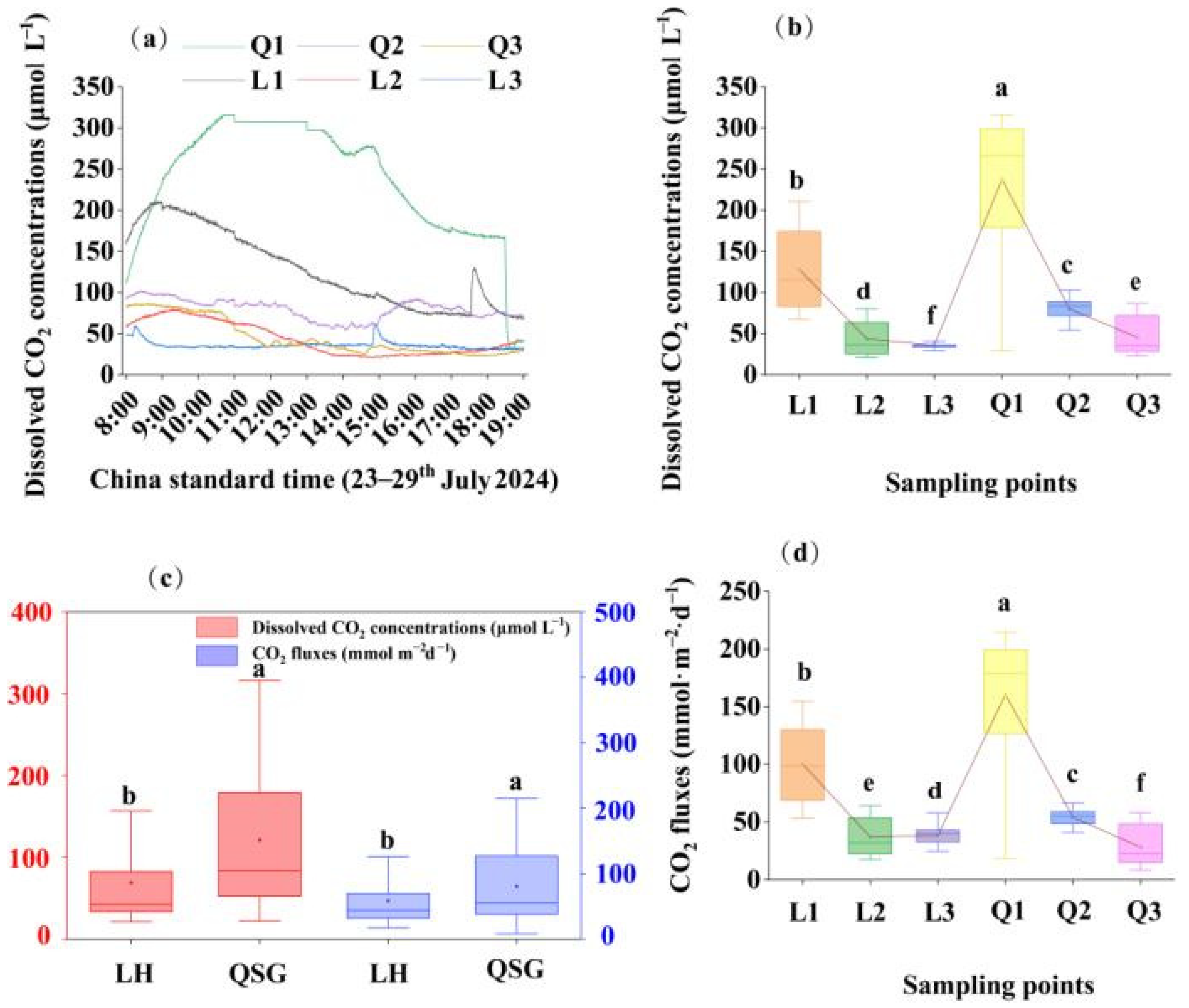
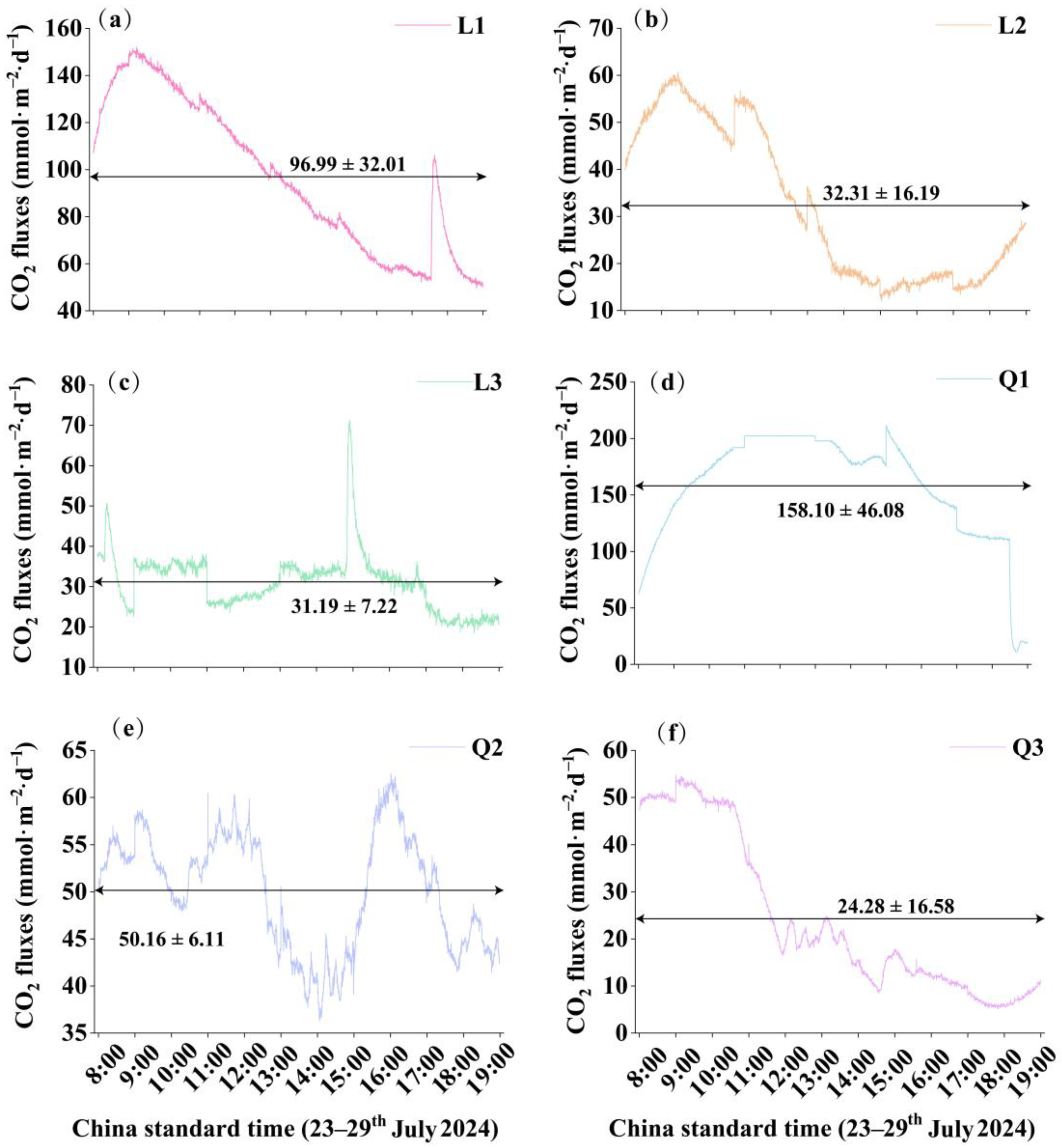
3.2. Diurnal Variation in CO2 Concentrations and Fluxes
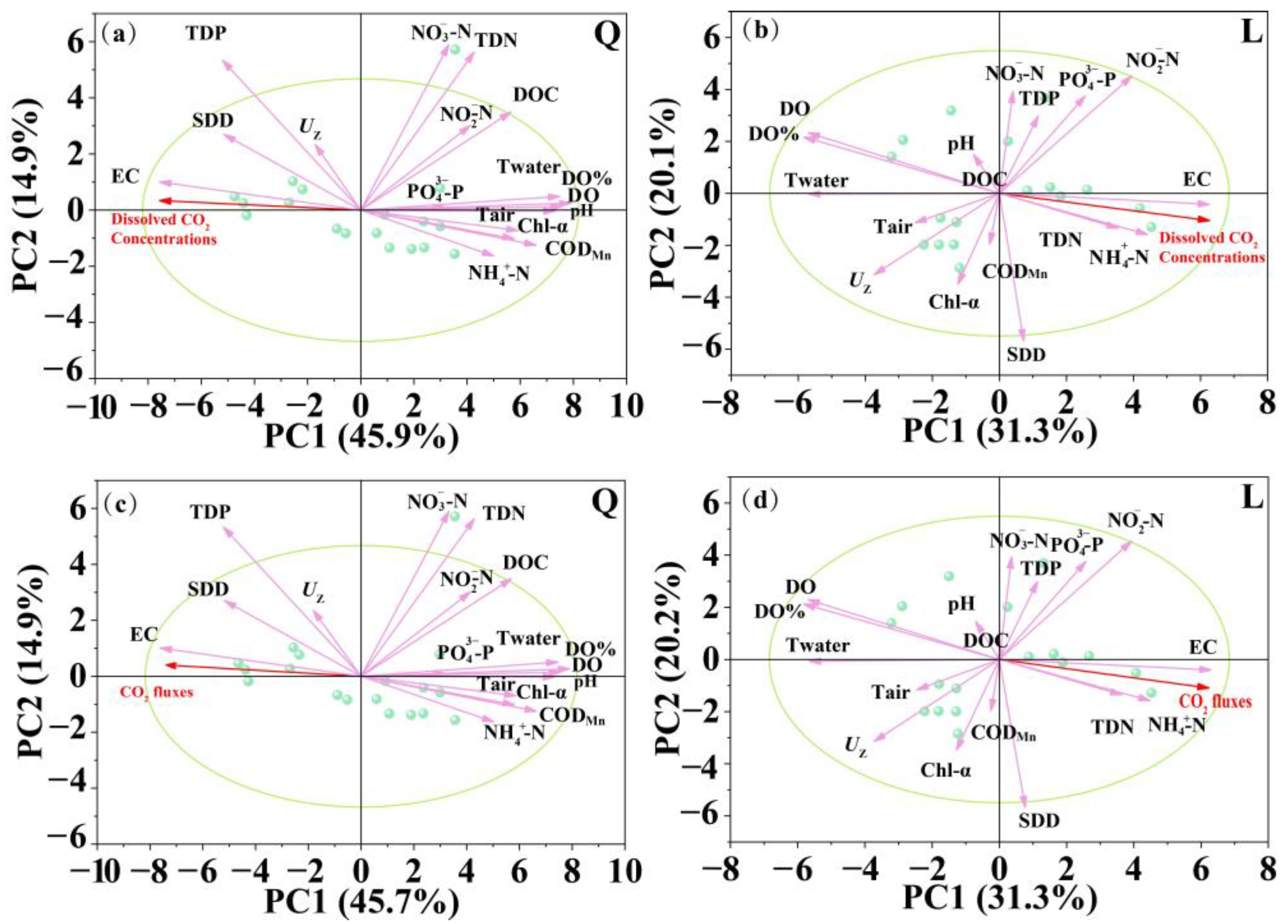
3.3. Relationships Between CO2 Concentrations and Fluxes with Environmental Variables
4. Discussion
4.1. Diurnal Variation of CO2 Concentrations and Fluxes
4.2. Influencing Factors of CO2 Concentration and Flux
4.3. CO2 Difference Between Landscape Lake and River
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Pilla, R.M.; Griffiths, N.A.; Gu, L.; Kao, S.C.; Mcmanamay, R.; Ricciuto, D.M.; Shi, X. Anthropogenically driven climate and landscape change effects on inland water carbon dynamics: What have we learned and where are we going? Glob. Change Biol. 2022, 28, 5601–5629. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vachon, D.; Sponseller, R.A.; Karlsson, J. Integrating carbon emission, accumulation and transport in inland waters to understand their role in the global carbon cycle. Glob. Change Biol. 2021, 27, 719–727. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Y.; Lyu, M.; Yang, P.; Lai, D.Y.F.; Tong, C.; Zhao, G.; Li, L.; Zhang, Y.; Yang, H. Spatial variations in CO2 fluxes in a subtropical coastal reservoir of Southeast China were related to urbanization and land-use types. J. Environ. Sci. 2021, 109, 206–218. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, L.; Li, H.; Xiao, Q.; Li, X. Urban rivers are hotspots of riverine greenhouse gas (N2O, CH4, CO2) emissions in the mixed-landscape chaohu lake basin. Water Res. 2021, 189, 116624. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Marescaux, A.; Thieu, V.; Garnier, J. Carbon dioxide, methane and nitrous oxide emissions from the human-impacted Seine watershed in France. Sci. Total Environ. 2018, 63, 247–259. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Johnson, M.S.; Billett, M.F.; Dinsmore, K.J.; Wallin, M.; Dyson, K.E.; Jassal, R.S. Direct and continuous measurement of dissolved carbon dioxide in freshwater aquatic systems—Method and applications. Ecohydrology 2009, 3, 68–78. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chang, N.; Zhang, Q.; Wang, Q.; Luo, L.; Wang, X.C.; Xiong, J.; Han, J. Corrigendum to “Current status and characteristics of urban landscape lakes in China”. Sci. Total Environ. 2021, 767, 145493. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Premke, K.; Attermeyer, K.; Augustin, J.; Cabezas, A.; Casper, P.; Deumlich, D.; Gelbrecht, J.; Gerke, H.H.; Gessler, A.; Grossart, H.P.; et al. The importance of landscape diversity for carbon fluxes at the landscape level: Small-scale heterogeneity matters. WIREs Water 2016, 3, 601–617. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Crawford, J.T.; Lottig, N.R.; Stanley, E.H.; Walker, J.F.; Hanson, P.C.; Finlay, J.C.; Striegl, R.G. CO2 and CH4 emissions from streams in a lake-rich landscape: Patterns, controls, and regional significance. Glob. Biogeochem. Cycles 2014, 28, 197–210. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Raymond, P.A.; Hartmann, J.; Lauerwald, R.; Sobek, S.; Mcdonald, C.; Hoover, M.; Butman, D.; Striegl, R.; Mayorga, E.; Humborg, C.; et al. Global carbon dioxide emissions from inland waters. Nature 2013, 503, 355–359. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ministry of Environmental Protection of the People’s Republic of China. Surface Water Environmental Quality Assessment Method (Trial Version); Ministry of Environmental Protection of the People’s Republic of China: Beijing, China, 2011.
- Ni, M.; Li, S. Dynamics and internal links of dissolved carbon in a karst river system: Implications for composition, origin and fate. Water Res. 2022, 226, 119289. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, B.; Wang, Y.; Jiang, P.; Li, S. The Influence of Seasonal Variability of Eutrophication Indicators on Carbon Dioxide and Methane Diffusive Emissions in the Largest Shallow Urban Lake in China. Water 2023, 16, 136. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cole, J.J.; Caraco, N.F. Atmospheric exchange of carbon dioxide in a low-wind oligotrophic lake measured by the addition of SF6. Limnol. Oceanogr. 2003, 43, 647–656. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, B.; Wang, D.; Zhou, J.; Meng, W.; Li, C.; Sun, Z.; Guo, X.; Wang, Z. Greenhouse gases emission from the sewage draining rivers. Sci. Total Environ. 2018, 612, 1454–1462. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nirmal Rajkumar, A.; Barnes, J.; Ramesh, R.; Purvaja, R.; Upstill-Goddard, R.C. Methane and nitrous oxide fluxes in the polluted Adyar River and estuary, SE India. Mar. Pollut. Bull. 2008, 56, 2043–2051. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lauerwald, R.; Allen, G.H.; Deemer, B.R.; Liu, S.; Maavara, T.; Raymond, P.; Alcott, L.; Bastviken, D.; Hastie, A.; Holgerson, M.A.; et al. Inland Water Greenhouse Gas Budgets for RECCAP2: 2. Regionalization and Homogenization of Estimates. Glob. Biogeochem. Cycles 2023, 37, e2022GB007658. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, L.; Wang, X.; Liu, T.; Chen, H.; He, Y.; Yuan, X. Ecological Restoration Effectively Mitigated pCO2 and CO2 Evasions From Severely Polluted Urban Rivers. J. Geophys. Res. Biogeosci. 2023, 128, e2023JG007531. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, L.; Xu, Y.J.; Li, S. Changes in CO2 concentration and degassing of eutrophic urban lakes associated with algal growth and decline. Environ. Res. 2023, 237 Pt 2, 117031. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, R.; Xu, Z.; Liu, S.; Xu, Y.J. Daily pCO2 and CO2 flux variations in a subtropical mesotrophic shallow lake. Water Res. 2019, 153, 29–38. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Heisler, J.; Glibert, P.; Burkholder, J.; Anderson, D.; Cochlan, W.; Dennison, W.; Gobler, C.; Dortch, Q.; Heil, C.; Humphries, E.; et al. Eutrophication and Harmful Algal Blooms: A Scientific Consensus. Harmful Algae 2008, 8, 3–13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tranvik, L.J.; Downing, J.A.; Cotner, J.B.; Loiselle, S.A.; Striegl, R.G.; Ballatore, T.J.; Dillon, P.; Finlay, K.; Fortino, K.; Knoll, L.B.; et al. Lakes and reservoirs as regulators of carbon cycling and climate. Limnol. Oceanogr. 2009, 54 Pt 2, 2298–2314. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hough, R. Photorespiration and productivity in submersed aquatic vascular plants1. Limnol. Oceanogr. 1974, 19, 912–927. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kragh, T.; Andersen, M.; Sand-Jensen, K. Profound afternoon depression of ecosystem production and nighttime decline of respiration in a macrophyte-rich, shallow lake. Oecologia 2017, 185, 157–170. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nydahl, A.; Wallin, M.; Tranvik, L.; Hiller, C.; Attermeyer, K.; Garrison, J.; Chaguaceda, F.; Scharnweber, K.; Weyhenmeyer, G. Colored organic matter increases CO2 in meso-eutrophic lake water through altered light climate and acidity. Limnol. Oceanogr. 2018, 64, 744–756. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Carter, M.; Cortés, P.; Rezende, E. Temperature variability and metabolic adaptation in terrestrial and aquatic ectotherms. J. Therm. Biol. 2021, 115, 103565. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hill, B.; Elonen, C.; Herlihy, A.; Jicha, T.; Mitchell, R. A synoptic survey of microbial respiration, organic matter decomposition, and carbon efflux in U.S. streams and rivers. Limnol. Oceanogr. 2017, 62, S147–S159. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, W.; Wang, W.; Zhong, J.; Chen, S.; Yi, Y.; Xu, X.; Chen, S.; Li, S.L. Carbon sequestration and decreased CO2 emission caused by biological carbon pump effect: Insights from diel hydrochemical variations in subtropical karst reservoirs. J. Hydrol. 2024, 632, 130909. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, Z.; Zhang, D.; Shi, W.; Ruan, X.; Sun, J. Understanding the Spatial Heterogeneity of CO2 and CH4 Fluxes from an Urban Shallow Lake: Correlations with Environmental Factors. J. Chem. 2017, 2017, 8175631. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Smyntek, P.M.; Maberly, S.C.; Grey, J. Dissolved carbon dioxide concentration controls baseline stable carbon isotope signatures of a lake food web. Limnol. Oceanogr.-Methods 2012, 57, 1292–1302. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Golub, M.; Desai, A.R.; Mckinley, G.A.; Remucal, C.K.; Stanley, E.H. Large Uncertainty in Estimating pCO2 From Carbonate Equilibria in Lakes. J. Geophys. Res.-Biogeosci. 2017, 122, 2909–2924. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Balmer, M.; Downing, J. Carbon dioxide concentrations in eutrophic lakes: Undersaturation implies atmospheric uptake. Inland Waters 2011, 1, 125–132. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, Y.; Gu, S.; Wu, K.; Tanentzap, A.J.; Yu, J.; Liu, X.; Li, Q.; He, P.; Qiu, D.; Deng, Y.; et al. Temperature-mediated microbial carbon utilization in China’s lakes. Glob. Change Biol. 2023, 29, 5044–5061. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, R.; Chen, Y.; Li, D.; Qiu, Y.; Lu, K.; Liu, S.; Song, H. Significant Daily CO2 Source–Sink Interchange in an Urbanizing Lake in Southwest China. Water 2023, 15, 3365. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tonetta, D.; Fontes, M.L.S.; Petrucio, M.M. Linking summer conditions to CO2 undersaturation and CO2 influx in a subtropical coastal lake. Limnology 2015, 16, 193–201. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, T.; Zhu, G.; Zhu, M.; Xu, H.; Zhang, Y.; Qin, B. Use of conductivity to indicate long-term changes in pollution processes in Lake Taihu, a large shallow lake. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. Int. 2020, 27, 21376–21385. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Almeida, F.V.; Guimaraes, J.R.; Jardim, W.F. Measuring the CO2 flux at the air/water interface in lakes using flow injection analysis. J. Environ. Monit. 2001, 3, 317–321. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Westberry, T.; Behrenfeld, M.J.; Siegel, D.A.; Boss, E. Carbon-based primary productivity modeling with vertically resolved photoacclimation. Glob. Biogeochem. Cycles 2008, 22. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pattanaik, S.; Mohapatra, P.K.; Mohapatra, D.; Swain, S.; Panda, C.R.; Dash, P.K. The Interaction of Seasons and Biogeochemical Properties of Water Regulate the Air-Water CO2 Exchanges in Two Major Tropical Estuaries, Bay of Bengal (India). Life 2022, 12, 1536. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pacheco, F.S.; Soares, M.C.S.; Assireu, A.T.; Curtarelli, M.P.; Roland, F.; Abril, G.; Stech, J.L.; Alvalá, P.C.; Ometto, J.P. The effects of river inflow and retention time on the spatial heterogeneity of chlorophyll and water–air CO2 fluxes in a tropical hydropower reservoir. Biogeosciences 2015, 12, 147–162. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, W.; Jiang, X.; Zhang, Q.; Li, F.; Liu, G. Has Submerged Vegetation Loss Altered Sediment Denitrification, N2O Production, and Denitrifying Microbial Communities in Subtropical Lakes? Glob. Biogeochem. Cycles 2018, 32, 1195–1207. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, S.; Zhang, Y.; Xu, Y.; Ye, C.; Li, S.Y. Greenhouse gas emissions from urban river waters of China’s major cities. Sustain. Horiz. 2025, 13, 100124. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, S.; Bush, R.T.; Santos, I.R.; Zhang, Q.; Song, K.; Mao, R.; Wen, Z.; Lu, X.X. Large greenhouse gases emissions from China’s lakes and reservoirs. Water Res. 2018, 147, 13–24. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shen, W.; Zhang, L.; Ury, E.A.; Li, S.; Xia, B.; Basu, N.B. Restoring small water bodies to improve lake and river water quality in China. Nat. Commun. 2025, 16, 294. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, B.; Zhang, R.; Zhu, L.; Wang, J.; Qin, B.; Shi, W. An Outsized Contribution of Rivers to Carbon Emissions From Interconnected Urban River-Lake Networks Within Plains. Geophys. Res. Lett. 2024, 51, e2023GL107250. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hutchins, R.; Aukes, P.; Schiff, S.; Dittmar, T.; Prairie, Y.; Giorgio, P. The Optical, Chemical, and Molecular Dissolved Organic Matter Succession Along a Boreal Soil-Stream-River Continuum. J. Geophys. Res.-Biogeosci. 2017, 122, 2892–2908. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ittekkot, V. Global trends in the nature of organic matter in river suspensions. Nature 1988, 332, 436–438. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Byzaakay, A.A.; Kolesnichenko, L.G.; Kolesnichenko, I.I.; Khovalyg, A.O.; Raudina, T.V.; Prokushkin, A.S.; Lushchaeva, I.V.; Kvasnikova, Z.N.; Vorobyev, S.N.; Pokrovsky, O.S.; et al. Dissolved Carbon Concentrations and Emission Fluxes in Rivers and Lakes of Central Asia (Sayan–Altai Mountain Region; Tyva). Water 2023, 15, 3411. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xiao, Q.; Duan, H.; Qi, T.; Hu, Z.; Liu, S.; Zhang, M.; Lee, X. Environmental investments decreased partial pressure of CO2 in a small eutrophic urban lake: Evidence from long-term measurements. Environ. Pollut. 2020, 263 Pt A, 114433. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]

| Parameter | CO2 Concentration | CO2 Flux |
|---|---|---|
| pH | −0.526 ** | −0.418 * |
| EC | 0.674 ** | 0.558 ** |
| DO | −0.858 ** | −0.853 ** |
| DO% | −0.909 ** | −0.857 ** |
| Twater | −0.730 ** | −0.590 ** |
| Tair | −0.380 | −0.272 |
| UZ | −0.310 | −0.212 |
| CODMn | −0.563 ** | −0.514 ** |
| DOC | −0.344 | −0.316 |
| Chl-a | −0.558 ** | −0.570 ** |
| TDN | 0.220 | −0.054 |
| NO3−-N | 0.242 | −0.083 |
| NO2−-N | 0.226 | −0.063 |
| NH4+-N | −0.027 | −0.068 |
| TDP | 0.429 * | 0.267 |
| Parameter | CO2 Concentration | CO2 Flux | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| State | L | Q | L | Q |
| pH | −0.057 | −0.789 ** | −0.078 | −0.740 ** |
| EC | 0.774 ** | 0.845 ** | 0.821 ** | 0.853 ** |
| DO | −0.831 ** | −0.849 ** | −0.844 ** | −0.866 ** |
| DO% | −0.862 ** | −0.907 ** | −0.854 ** | −0.909 ** |
| Twater | −0.835 ** | −0.728 ** | −0.756 ** | −0.660 * |
| Tair | −0.329 | −0.312 | −0.172 | −0.211 |
| UZ | −0.591 ** | 0.249 | −0.492 * | 0.238 |
| CODMn | −0.179 | −0.886 ** | −0.164 | −0. 882 ** |
| DOC | 0.210 | −0.626 ** | 0.036 | −0.624 ** |
| Chl-a | 0.039 | −0.893 ** | −0.019 | −0.878 ** |
| TDN | 0.376 | −0.593 ** | 0.305 | −0.591 * |
| NO3−-N | 0.191 | −0.329 | 0.139 | −0.366 |
| NO2−-N | 0.527 | −0.659 ** | 0.429 | −0.631 ** |
| NH4+-N | 0.472 * | −0.434 | 0.385 | −0.432 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Liu, M.; Tian, X.; Yan, Z.; Zhao, Y.; Li, S. Diurnal Variation of Carbon Dioxide Concentration and Flux in a River–Lake Continuum of a Mega City. Water 2025, 17, 306. https://doi.org/10.3390/w17030306
Liu M, Tian X, Yan Z, Zhao Y, Li S. Diurnal Variation of Carbon Dioxide Concentration and Flux in a River–Lake Continuum of a Mega City. Water. 2025; 17(3):306. https://doi.org/10.3390/w17030306
Chicago/Turabian StyleLiu, Menglin, Xiaokang Tian, Zilong Yan, Yuzhuo Zhao, and Siyue Li. 2025. "Diurnal Variation of Carbon Dioxide Concentration and Flux in a River–Lake Continuum of a Mega City" Water 17, no. 3: 306. https://doi.org/10.3390/w17030306
APA StyleLiu, M., Tian, X., Yan, Z., Zhao, Y., & Li, S. (2025). Diurnal Variation of Carbon Dioxide Concentration and Flux in a River–Lake Continuum of a Mega City. Water, 17(3), 306. https://doi.org/10.3390/w17030306







