Enhancing the Operating Efficiency of Mixed-Flow Pumps Through Adjustable Guide Vanes
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Simulation Model
2.1. Model Before Renovation
2.2. Modified Model
2.3. Grid Division
3. CFD Settings
3.1. Computational Fluid Dynamics Equations
3.2. CFD Parameter Adjustment
3.3. Grid Independence Test
4. Performance and Verification
5. Orthogonal Experiments
5.1. Experimental Design
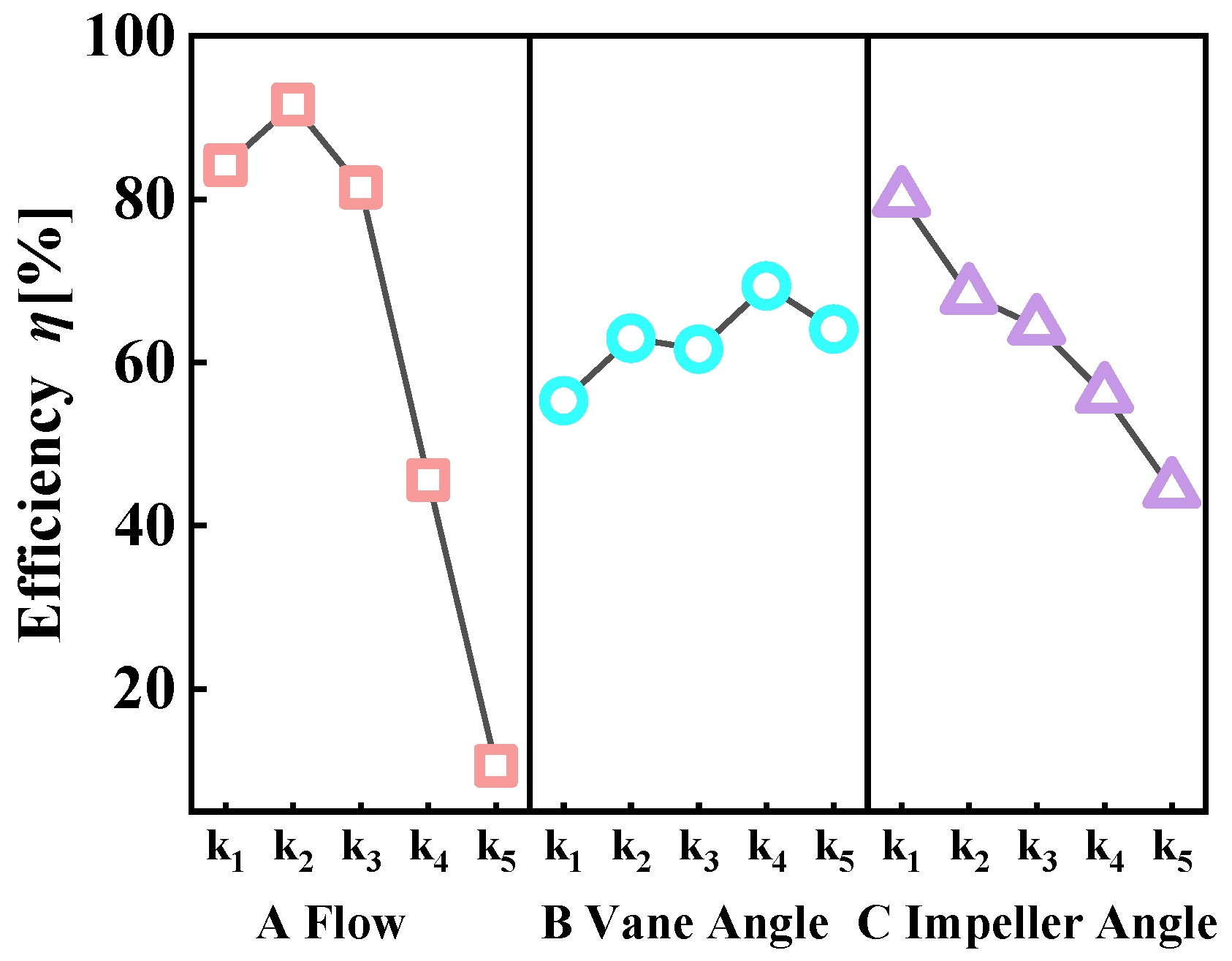
5.2. Analysis of Orthogonal Experimental Results
5.2.1. Analysis of Fixed Guide Vane Scheme
5.2.2. Analysis of Adjustable Guide Vane Scheme
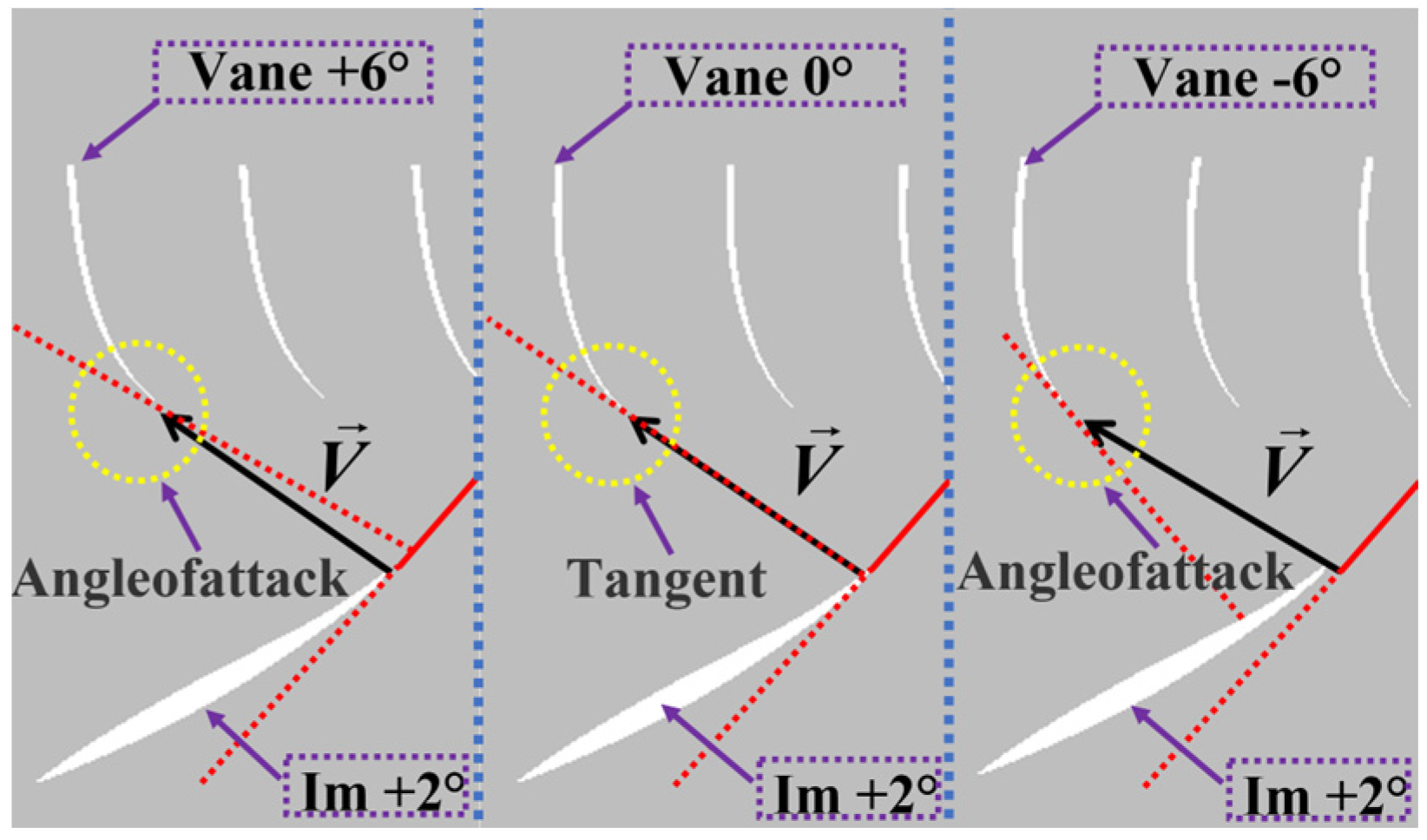
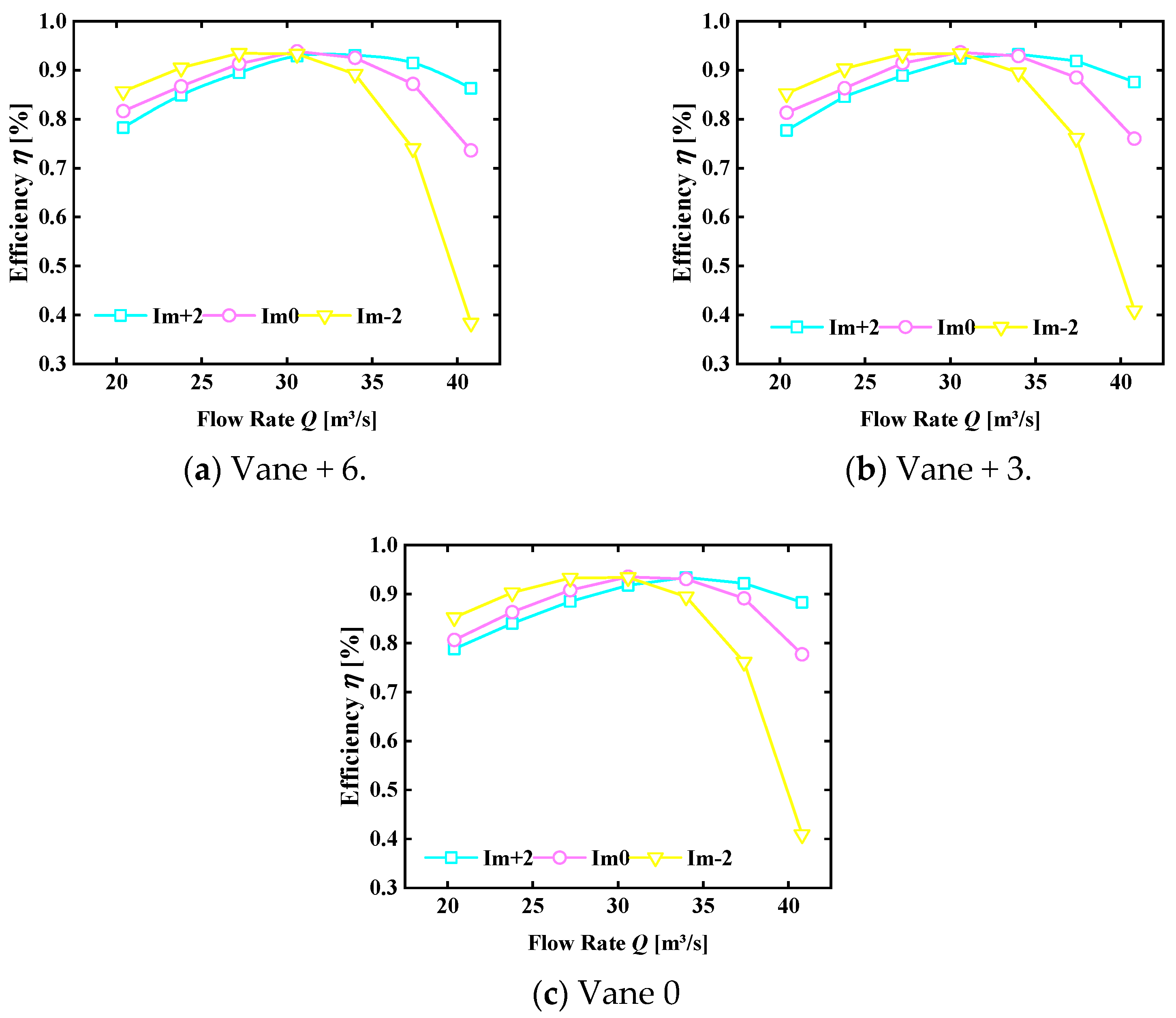
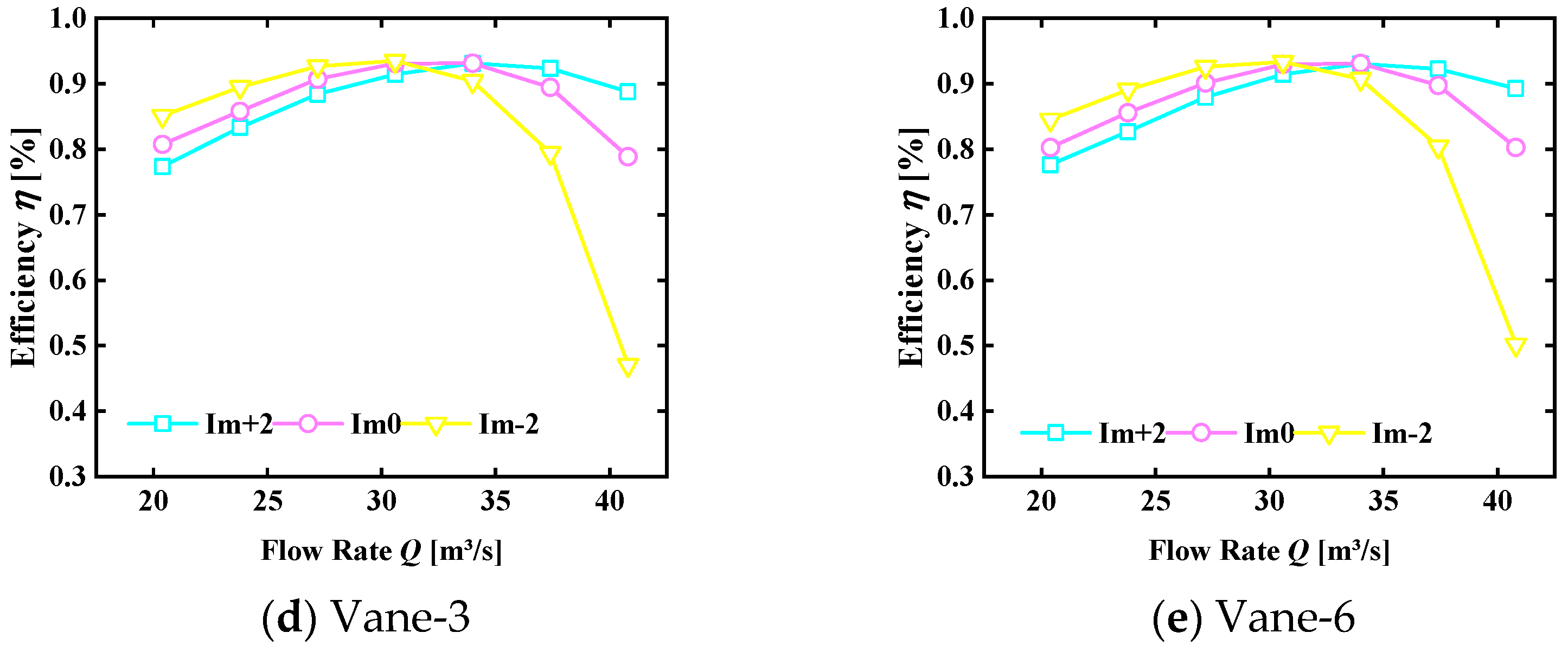
6. Matching Analysis of Moving and Stationary Blades
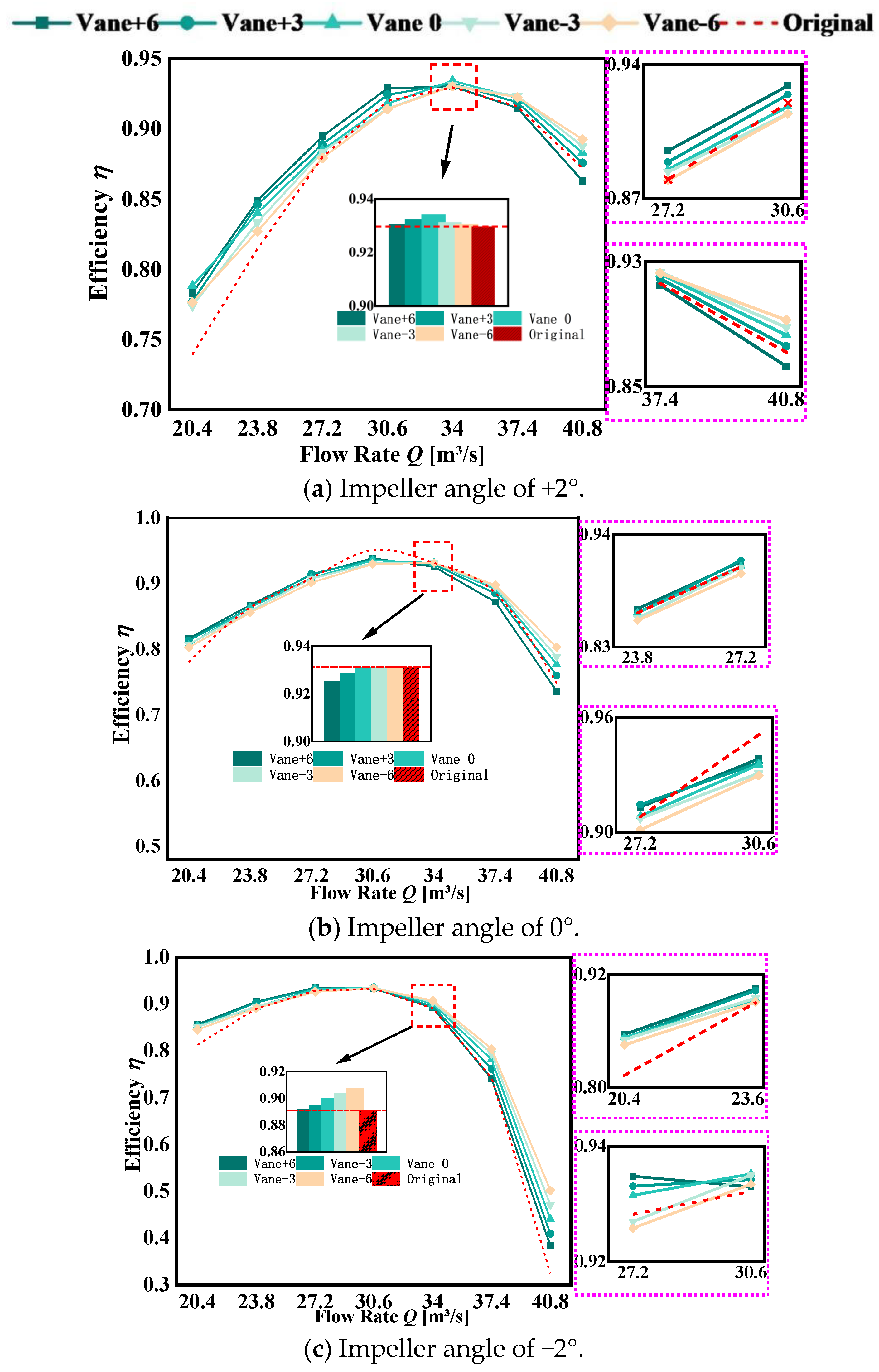
6.1. Analysis of Single Flow Efficiency Curve
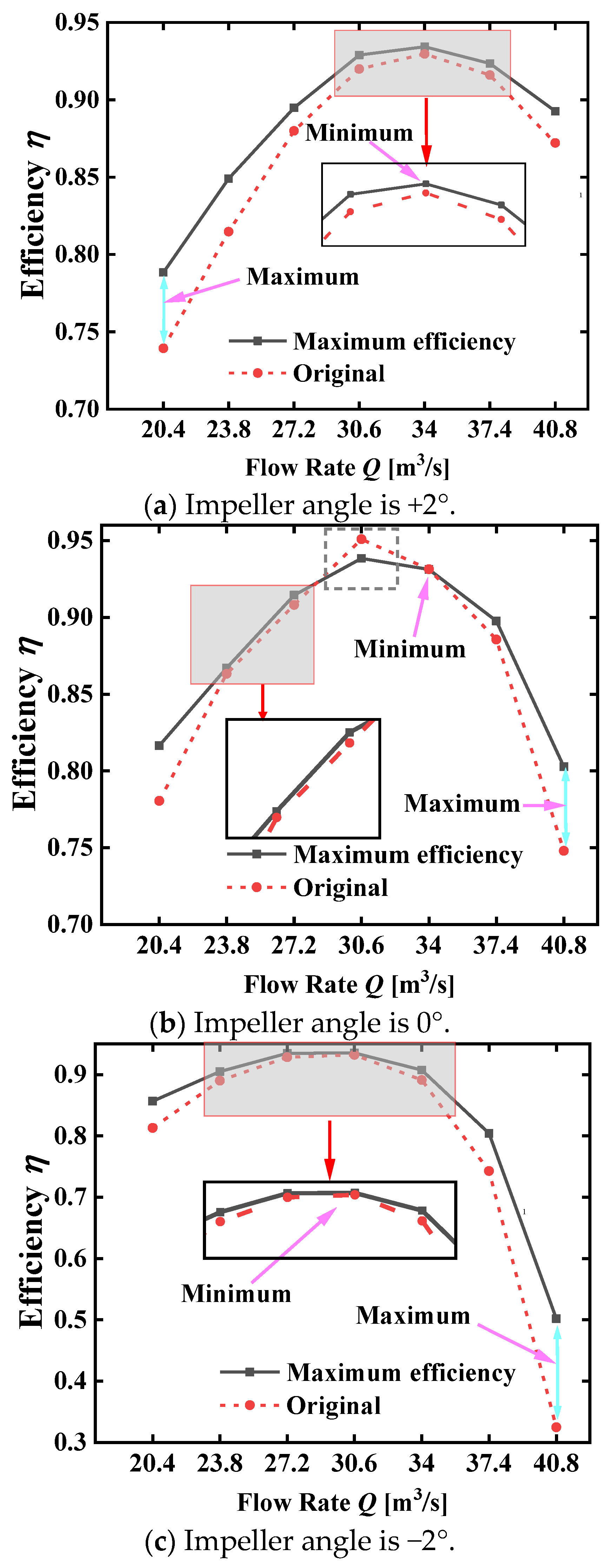
6.2. Analysis of Comprehensive Efficiency Curve
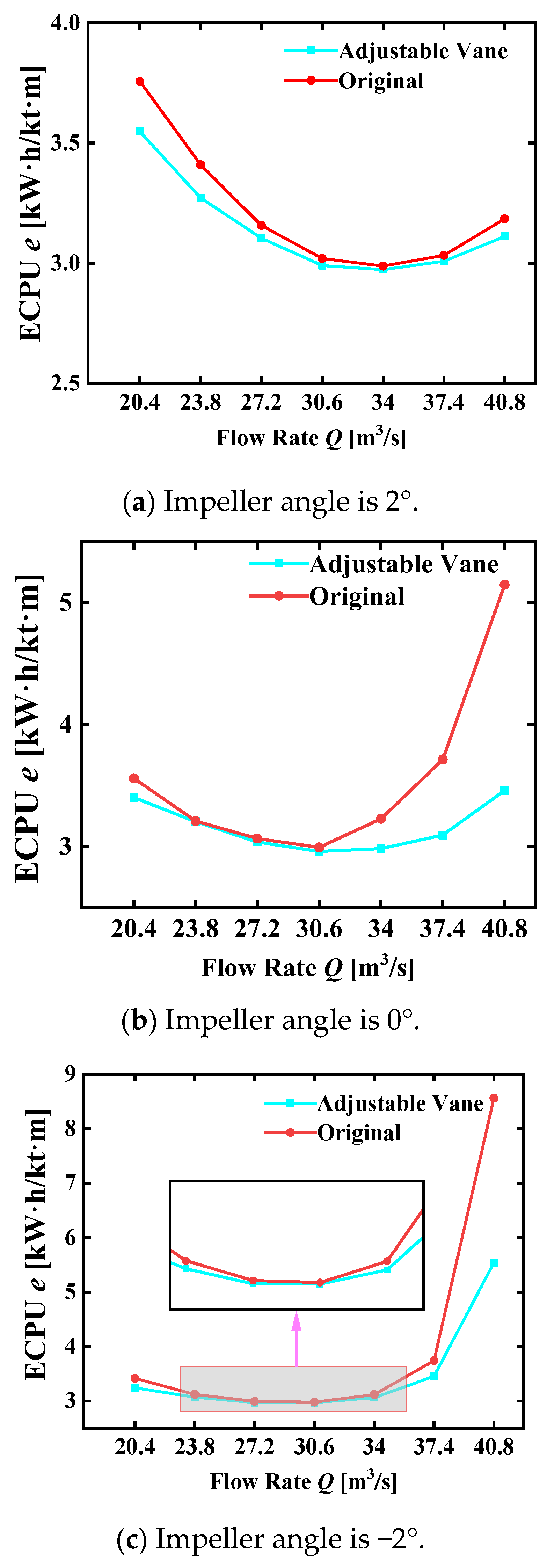
6.3. Energy Consumption Analysis
- —Energy consumption, kW·h/(kt·m);
- —Flow rate of water pump under different working conditions, m3/s;
- —Power of water pump under different working conditions, kW;
- —Head of water pump under different working conditions, m;
- —Motor efficiency, [%].
7. Flow Field Analysis of Moving and Stationary Blades
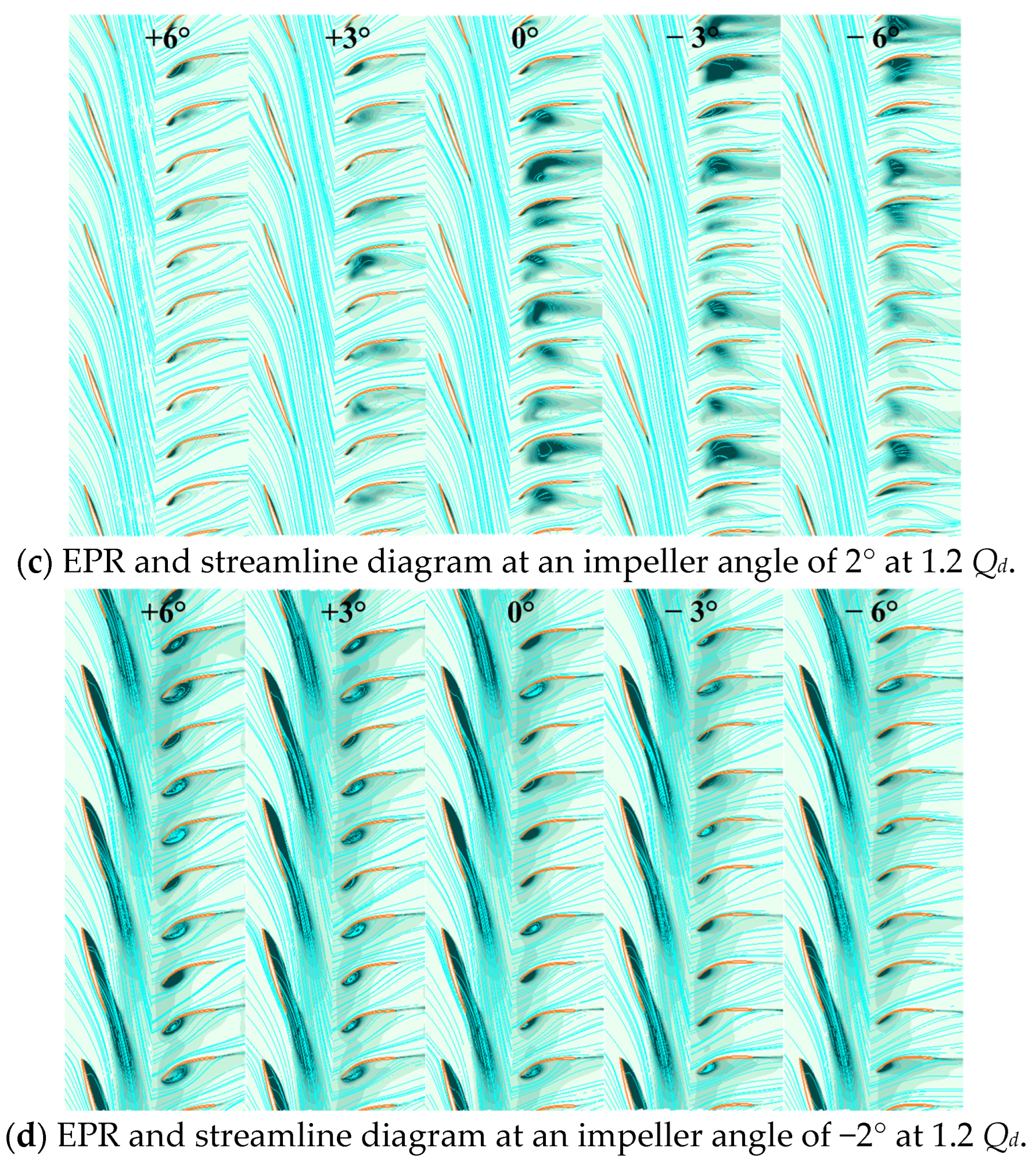
7.1. EPR Method
7.2. Flow Field Analysis
8. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Manivannan, A. Computational fluid dynamics analysis of a mixed flow pump impeller. Int. J. Eng. Sci. Technol. 2011, 30, 558–566. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, W.; Ping, Y.; Shi, W.; Ji, L.; Li, E.; Ma, L. Research progress in rotating stall in mixed-flow pumps with guide vane. J. Drain. Irrig. Mach. Eng. 2019, 37, 737–745. [Google Scholar]
- Kurokawa, J.; Jiang, J.; Kitahora, T. Inlet reverse-flow model and prediction of theoretical head and water power of mixed-flow pumps. JSME Int. J. Ser. B Fluids Therm. Eng. 1994, 37, 853–860. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kumar, A.; Hesheng, T.; Vashishtha, G.; Xiang, J. Noise subtraction and marginal enhanced square envelope spectrum (MESES) for the identification of bearing defects in centrifugal and axial pump. Mech. Syst. Signal Process. 2021, 165, 108366. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qian, Z.; Wang, Y.; Zheng, B.; Liu, D. Numerical simulation and analysis of performance of axial flow pump with adjustable guide vane. J. Hydroelectr. Eng. 2011, 30, 123. [Google Scholar]
- Yang, F.; Liu, C.; Tang, F.; Zhou, J.; Cheng, L. Numerical Simulation on Hydraulic Performance of Axial-flow Pumping System with Adjustable Inlet Guide vane. Trans. Chin. Soc. Agric. Mach. 2014, 45, 51–58. [Google Scholar]
- Al-Obaidi, A. Experimental Diagnostic of Cavitation Flow in the Centrifugal Pump Under Various Impeller Speeds Based on Acoustic Analysis Method. Arch. Acoust. 2023, 48, 159–170. [Google Scholar]
- Kim, S.; Lee, K.-Y.; Kim, J.-H.; Kim, J.-H.; Jung, U.-H.; Choi, Y.-S. High performance hydraulic design techniques of mixed-flow pump impeller and diffuser. J. Mech. Sci. Technol. 2015, 29, 227–240. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tanaka, H. Vibration Behavior and Dynamic Stress of Runners of Very High Head Reversible Pump-turbines. Int. J. Fluid Mach. Syst. 2011, 4, 289–306. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jin, F.Y.; Tao, R.; Zhu, D.; Li, P.X.; Xiao, R.F.; Liu, W.C. Transient simulation of the rapid guide vane adjustment under constant head of pump turbine in pump mode. J. Energy Storage 2022, 56, 105960. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, D.; Yan, W.; Guang, W.L.; Wang, Z.W.; Tao, R. Influence of Guide Vane Opening on the Runaway Stability of a Pump-Turbine Used for Hydropower and Ocean Power. J. Mar. Sci. Eng. 2023, 11, 1218. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tao, R.; Heng, Y.G.; Zhang, F.F.; Pan, J.L.; Zhu, D.; Liu, W.C.; Xiao, R.; Gui, Z. Analyzing the S-characteristic of pump-turbine under the same head condition from the perspective of flow energy dissipation. Proc. Inst. Mech. Eng. Part A: J. Power Energy 2023, 237, 1726–1742. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, W.; Yang, Q.; Yang, Y.; Ji, L.; Shi, W.; Agarwal, R. Optimization of pump transient energy characteristics based on response surface optimization model and computational fluid dynamics. Appl. Energy 2024, 362, 123038. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Belyaev, S.G.; Ishangaliev, T.S.; Kariev, D.A.; Kuklin, D.E. Energy investigations of a pumping station with an axial-flow pump and circular feed line. Hydrotech. Constr. 1991, 25, 683–685. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lu, J.; Chen, Q.; Liu, X.; Zhu, B.; Yuan, S. Investigation on pressure fluctuations induced by flow instabilities in a centrifugal pump. Ocean Eng. 2022, 258, 111805. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tao, R.; Wang, Z. Comparative numerical studies for the flow energy dissipation features in a pump-turbine in pump mode and turbine mode. J. Energy Storage 2021, 41, 102835. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qi, H.; Li, W.; Ji, L.; Liu, M.; Song, R.; Pan, Y.; Yang, Y. Performance optimization of centrifugal pump based on particle swarm optimization and entropy generation theory. Front. Energy Res. 2023, 10, 1094717. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Al-Obaidi, A.R. Effect of Different Guide Vane Configurations on Flow Field Investigation and Performances of an Axial Pump Based on CFD Analysis and Vibration Investigation. Exp. Tech. 2024, 48, 69–88. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Amiri, K.; Mulu, B.; Raisee Dehkordi, M.; Cervantes, M. Unsteady pressure measurements on the runner of a Kaplan turbine during load acceptance and load rejection. J. Hydraul. Res. 2015, 54, 56–73. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Favrel, A.; Müller, A.; Landry, C.; Yamamoto, K.; Avellan, F. LDV survey of cavitation and resonance effect on the precessing vortex rope dynamics in the draft tube of Francis turbines. Exp. Fluids 2016, 57, 168. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Olimstad, G.; Nielsen, T.; Børresen, B. Stability Limits of Reversible-Pump Turbines in Turbine Mode of Operation and Measurements of Unstable Characteristics. J. Fluids Eng. 2012, 134, 111202. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, C.; Wang, F.; An, D.; Yao, Z.; Xiao, R.; Lu, L.; He, C.; Zou, Z. A general alternate loading technique and its applications in the inverse designs of centrifugal and mixed-flow pump impeller. Sci. China Technol. Sci. 2021, 64, 898–918. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pope, S.B. The probability approach to the modelling of turbulent reacting flows. Combust. Flame 1976, 27, 299–312. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Celik, I.; Ghia, U.; Roache, P.J.; Freitas, C.J. Procedure for Estimation and Reporting of Uncertainty Due to Discretization in CFD Applications. J. Fluids Eng. 2008, 130, 078001. [Google Scholar]
- Guan, X. Morden Pumps Theory and Design; China Aerospace Publishing House: Beijing, China, 2011. [Google Scholar]

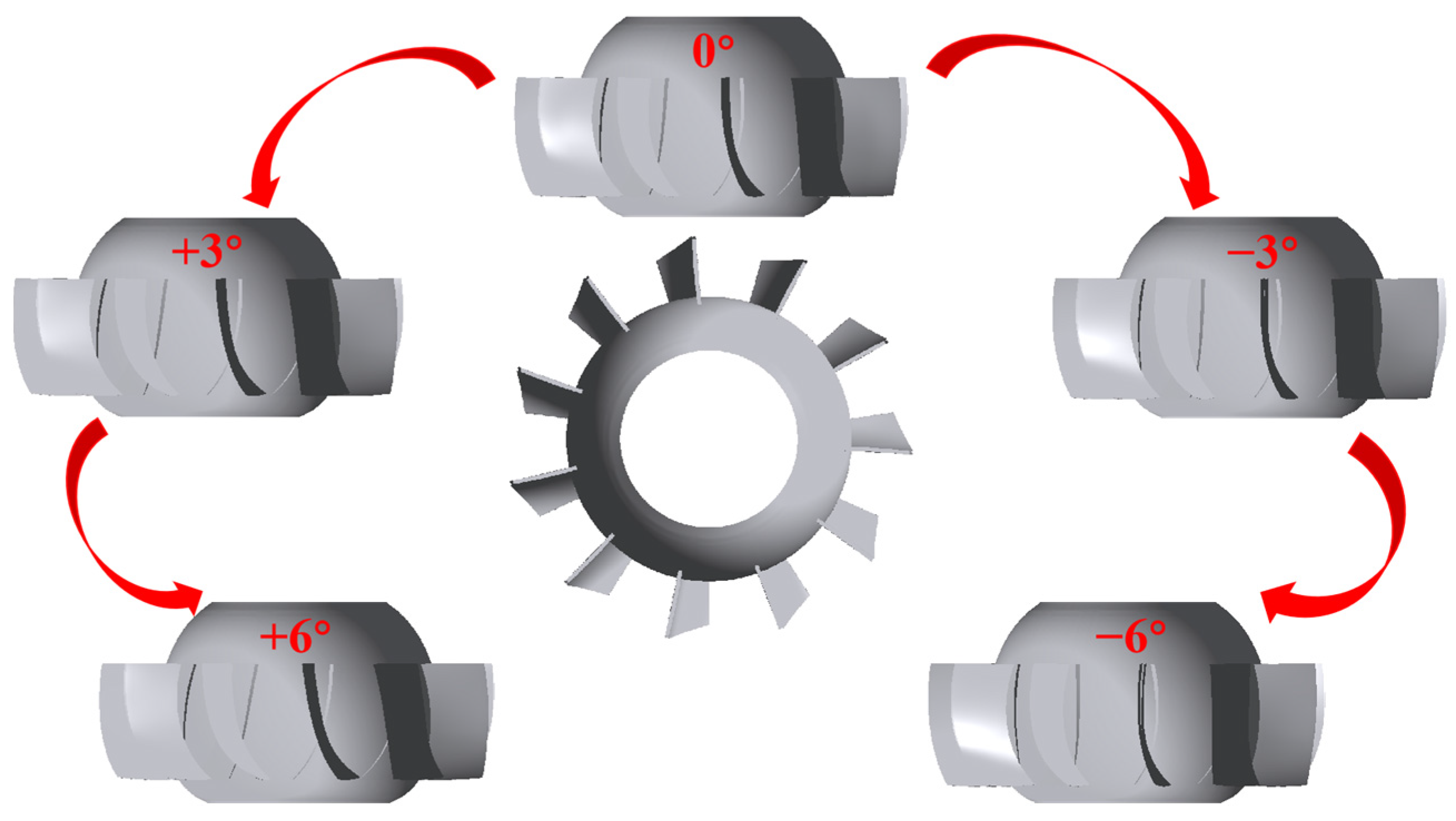

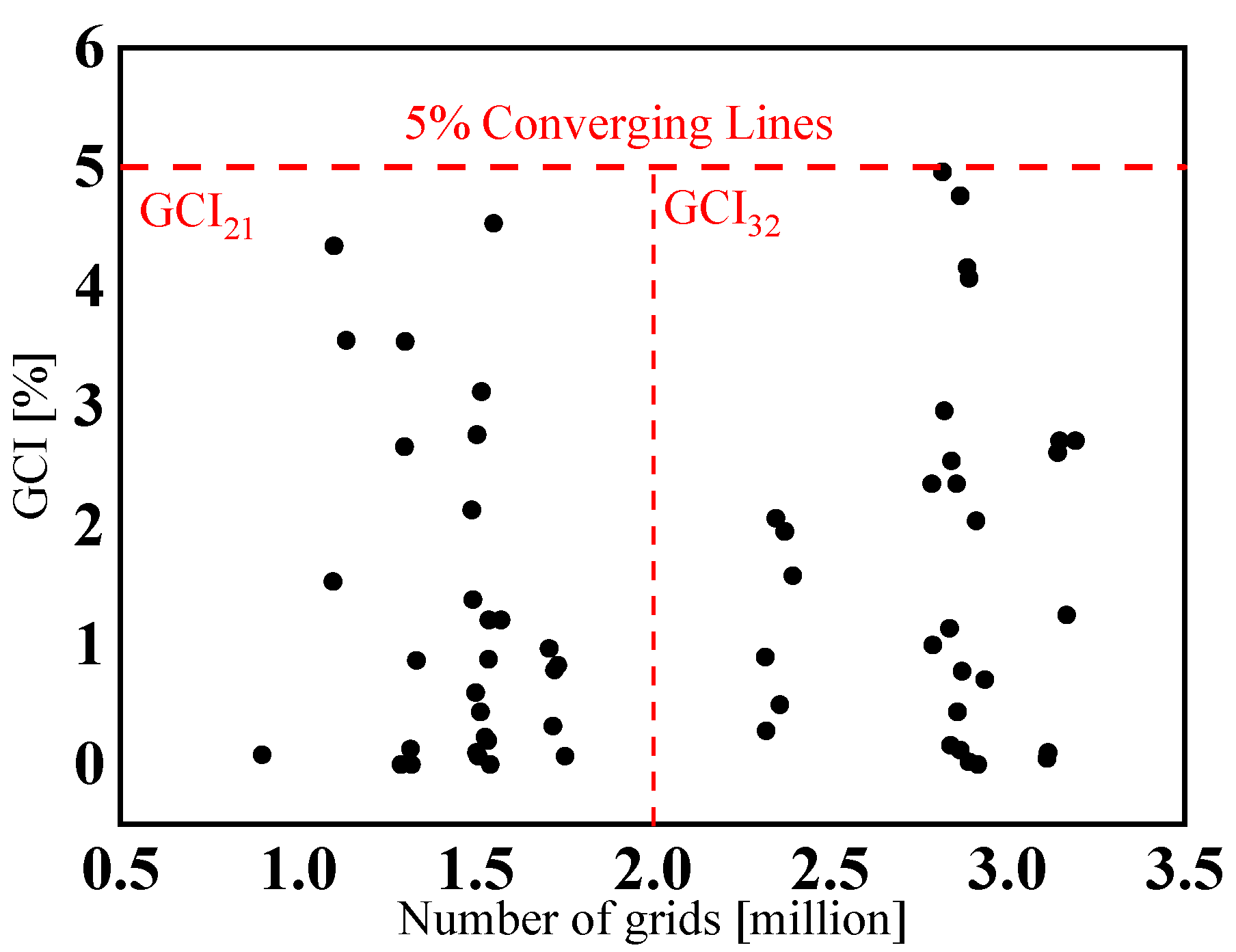
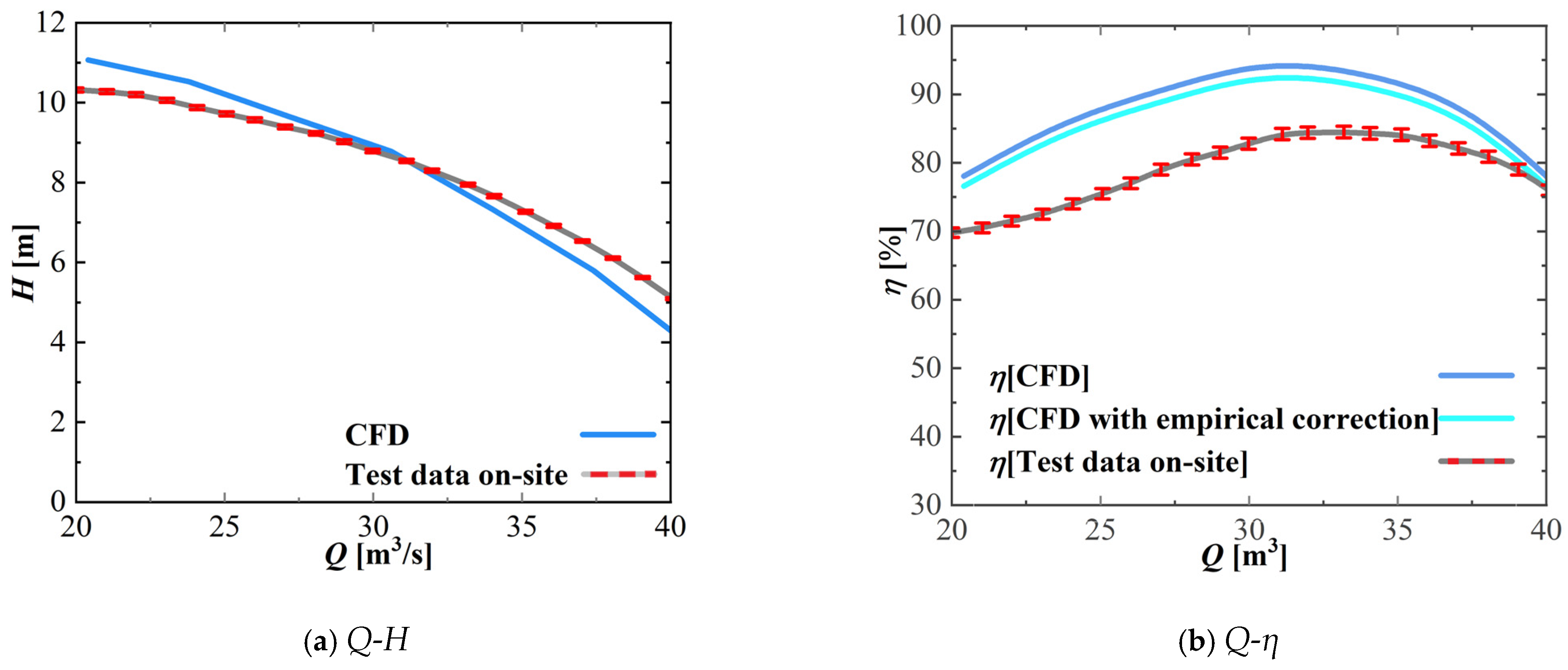
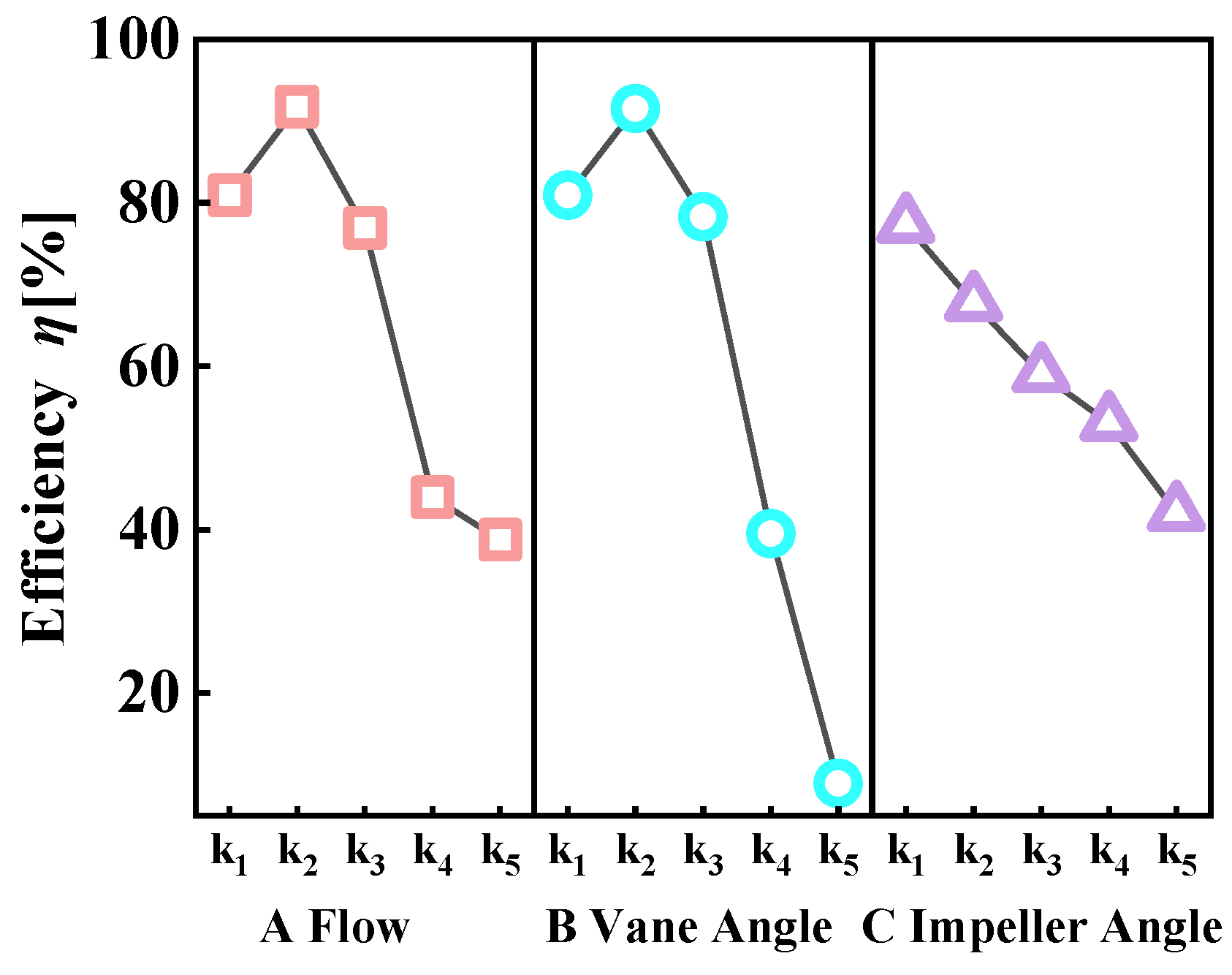



| Parameter | Value | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| Design Pump Head Hd | 7.6 | [m] |
| Design Flow Rate Qd | 34 | [m3/s] |
| Shaft Power P | 2157.22 | [kW] |
| Rated Rotational Speed nr | 125 | [r/min] |
| Total Efficiency η | 93.13 | [%] |
| Specific Speed ns | 581 | [-] |
| Impeller Blade Number zimp | 4 | [-] |
| Vane Blade Number zv | 12 | [-] |
| Orthogonal Design | A Flow Rate (m3/s) | B Guide Vane Angle (°) | C Impeller Angle (°) |
|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | 20.4 | +6 | +2 |
| 2 | 20.4 | +3 | 0 |
| 3 | 20.4 | 0 | −2 |
| 4 | 20.4 | −3 | −4 |
| 5 | 20.4 | −6 | −6 |
| 6 | 27.2 | +6 | 0 |
| 7 | 27.2 | +3 | −2 |
| 8 | 27.2 | 0 | −4 |
| 9 | 27.2 | −3 | −6 |
| 10 | 27.2 | −6 | +2 |
| 11 | 34 | +6 | −2 |
| 12 | 34 | +3 | −4 |
| 13 | 34 | 0 | −6 |
| 14 | 34 | −3 | +2 |
| 15 | 34 | −6 | 0 |
| 16 | 40.8 | +6 | −4 |
| 17 | 40.8 | +3 | −6 |
| 18 | 40.8 | 0 | +2 |
| 19 | 40.8 | −3 | 0 |
| 20 | 40.8 | −6 | −2 |
| 21 | 47.6 | +6 | −6 |
| 22 | 47.6 | +3 | +2 |
| 23 | 47.6 | 0 | 0 |
| 24 | 47.6 | −3 | −2 |
| 25 | 47.6 | −6 | −4 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Su, C.; Zhang, Z.; Zhu, D.; Tao, R. Enhancing the Operating Efficiency of Mixed-Flow Pumps Through Adjustable Guide Vanes. Water 2025, 17, 423. https://doi.org/10.3390/w17030423
Su C, Zhang Z, Zhu D, Tao R. Enhancing the Operating Efficiency of Mixed-Flow Pumps Through Adjustable Guide Vanes. Water. 2025; 17(3):423. https://doi.org/10.3390/w17030423
Chicago/Turabian StyleSu, Chenhan, Zhe Zhang, Di Zhu, and Ran Tao. 2025. "Enhancing the Operating Efficiency of Mixed-Flow Pumps Through Adjustable Guide Vanes" Water 17, no. 3: 423. https://doi.org/10.3390/w17030423
APA StyleSu, C., Zhang, Z., Zhu, D., & Tao, R. (2025). Enhancing the Operating Efficiency of Mixed-Flow Pumps Through Adjustable Guide Vanes. Water, 17(3), 423. https://doi.org/10.3390/w17030423







