Up-Flow Anaerobic Sludge Bed Reactors for Sustainable Wastewater Management: Challenges, Innovations, and Future Directions
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Working Principles of UASB Reactors
2.1. Process Principles
- Upward flow: Upward flow ensures maximum interaction between the biomass and substrate.
- Avoiding short circuits: Short circuits must be avoided to provide adequate retention time for higher removal efficiency.
- Efficient phase separation: A well-designed separator ensures the retention of solids and the exit of biogas and liquid.
- Better sludge properties: Sludge should have superior settling qualities and high methanogenic activity.
2.2. Microbial Ecology
2.2.1. Hydrolytic Bacteria
2.2.2. Fermentative Acidogenic Bacteria
2.2.3. Acetogenic Bacteria
2.2.4. Methanogenic Archaea and Their Taxonomy
2.3. Process Optimization
2.3.1. Organic Loading Rate (OLR)
2.3.2. Nutrients
2.3.3. Hydraulic Retention Time (HRT)
2.3.4. Volatile Fatty Acids (VFAs)
2.3.5. Operational Temperature
2.3.6. Operational pH
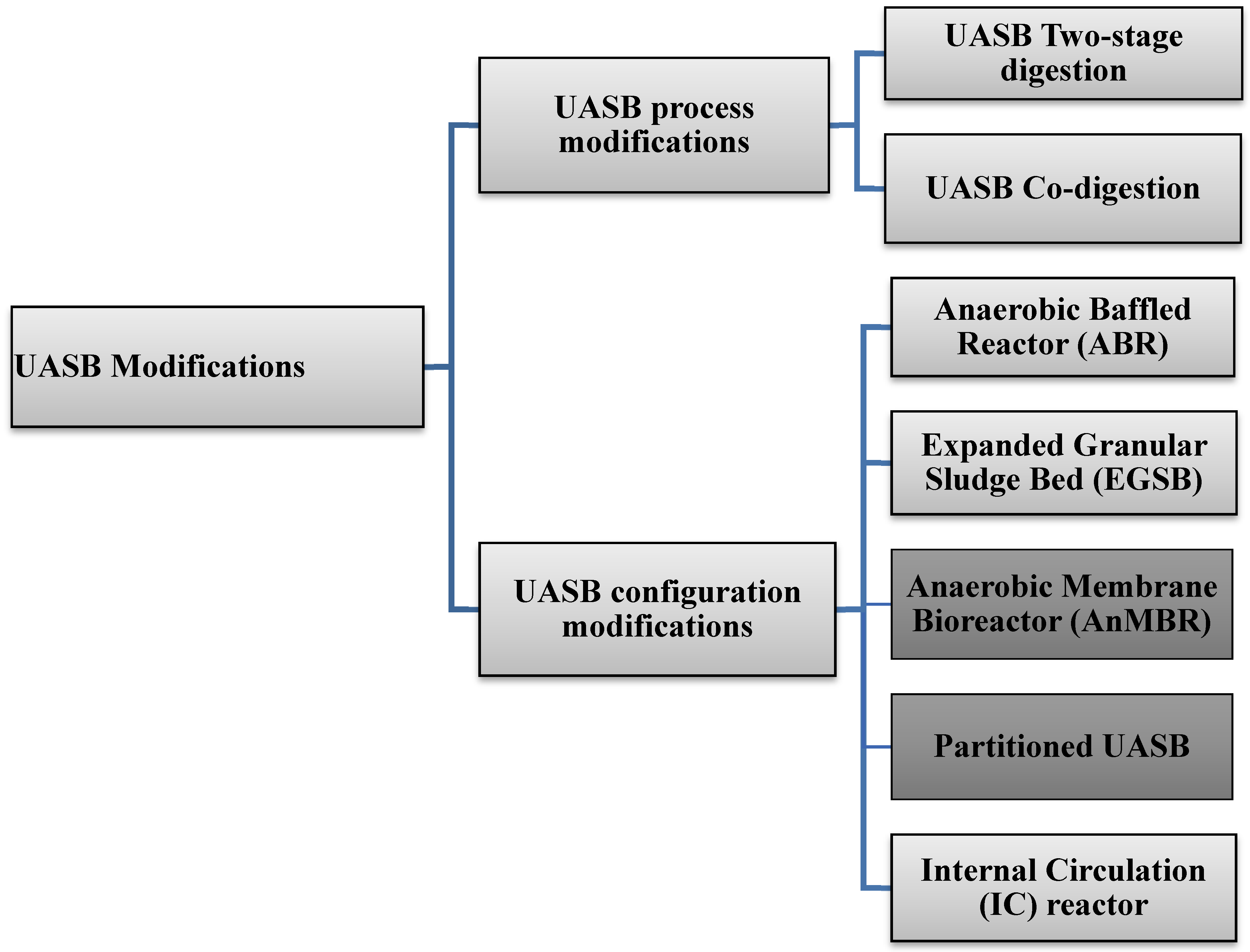
3. Technological Advances of UASB Reactors
3.1. Two-Stage UASB Anaerobic Digestion
3.2. UASB Co-Digestion
3.3. Anaerobic Baffled Reactors (ABRs)
3.4. Anaerobic Membrane Bioreactor (AnMBR)
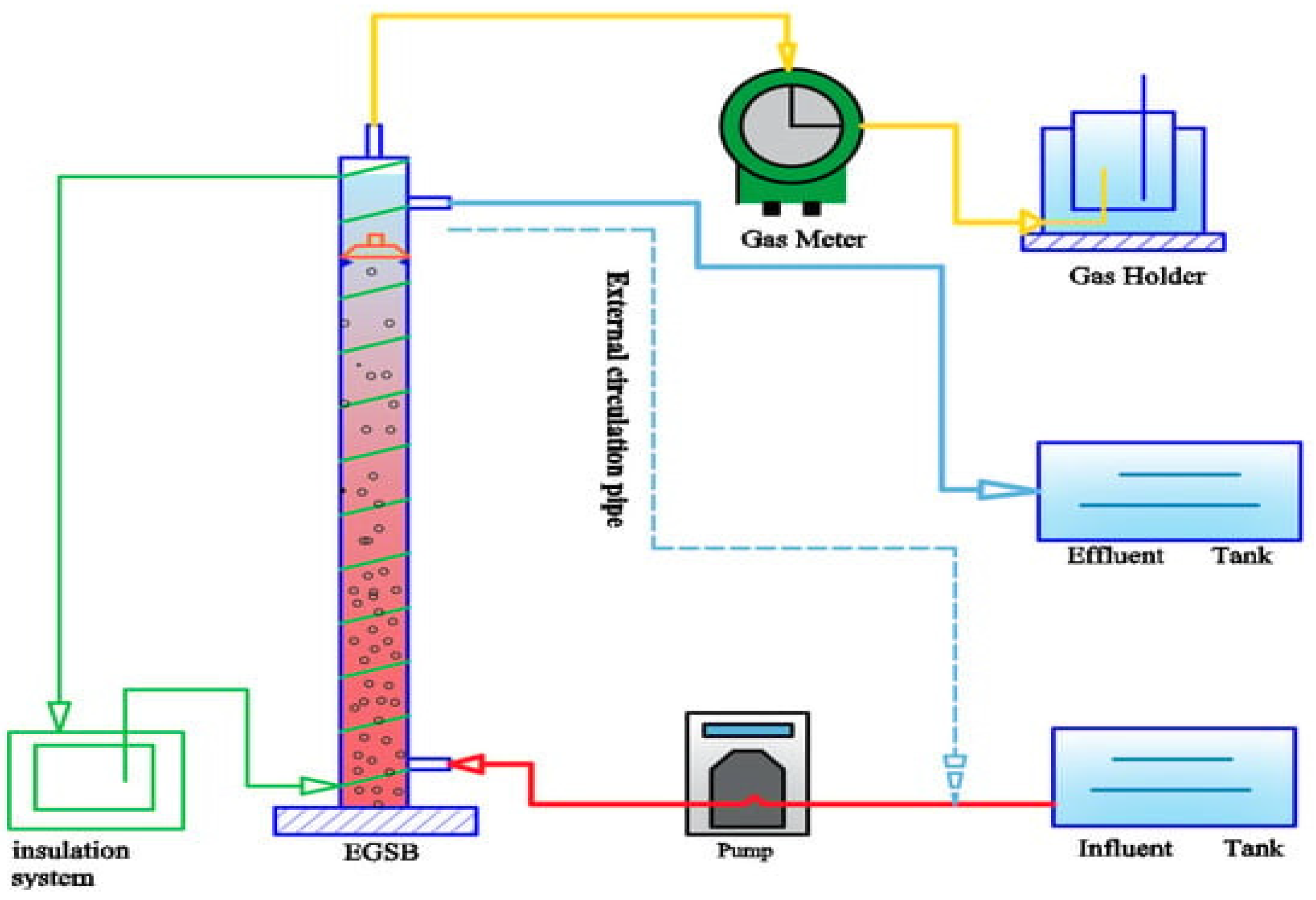
3.5. Expanded Granular Sludge Bed (EGSB)
3.6. Internal Circulation Reactor (IC)
3.7. Partitioned UASB Reactor
4. Application of UASB Reactor Technology for Treatment of Various Wastewater Types
5. Environmental and Economic Impact of UASB Reactors
5.1. Environmental Impact
5.2. Economic Impact
5.3. Dissolved CH4 Recovery from Effluent
5.4. Energy Recovery Calculations from UASB Reactors
6. Challenges and Limitations of UASB Reactor Technology
6.1. Temperature Constraints
6.2. Restrictions Imposed by Microbiological Indicators
6.3. Odor Emissions
6.4. Nutrition Recycling Restrictions
6.5. Restrictions Due to Micropollutants
6.6. Atmospheric CH4 Emission Control
6.7. Operational Obstructions
6.7.1. Low-Skilled Workforce
6.7.2. UASB Reactor Design Flaws
6.7.3. Sludge Withdrawal
6.7.4. Scum Removal
7. Future Directions and Opportunities
7.1. Optimization and Upgrades of UASB Reactors Against Emerging Pollutants
7.2. Microbial Dynamics of Granular Sludge
7.3. Ecological Footprint
8. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- El-Khateeb, M.; Hassan, G.K.; El-Liethy, M.A.; El-Khatib, K.M.; Abdel-Shafy, H.I.; Hu, A.; Gad, M. Sustainable municipal wastewater treatment using an innovative integrated compact unit: Microbial communities, parasite removal, and techno-economic analysis. Ann. Microbiol. 2023, 73, 35. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zeeman, G.; Kujawa, K.; De Mes, T.; Hernandez, L.; De Graaff, M.; Abu-Ghunmi, L.; Mels, A.; Meulman, B.; Temmink, H.; Buisman, C.; et al. Anaerobic treatment as a core technology for energy, nutrients and water recovery from source-separated domestic waste(water). Water Sci. Technol. 2008, 57, 1207–1212. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Morandi, C.G.; Wasielewski, S.; Mouarkech, K.; Minke, R.; Steinmetz, H. Impact of new sanitation technologies upon conventional wastewater infrastructures. Urban Water J. 2017, 15, 526–533. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bodík, I.; Herdová, B.; Drtil, M. Anaerobic treatment of the municipal wastewater under psychrophilic conditions. Bioprocess Biosyst. Eng. 2000, 22, 385–390. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lettinga, G.; Van Velsen, A.F.M.; Hobma, S.W.; De Zeeuw, W.; Klapwijk, A. Use of the upflow sludge blanket (USB) reactor concept for biological wastewater treatment, especially for anaerobic treatment. Biotechnol. Bioeng. 1980, 22, 699–734. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lettinga, G.; Pol, L.W.H. UASB-Process design for various types of wastewaters. Water Sci. Technol. 1991, 24, 87–107. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Capodaglio, A.G.; Callegari, A.; Cecconet, D.; Molognoni, D. Sustainability of decentralized wastewater treatment technologies. Water Pract. Technol. 2017, 12, 463–477. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pererva, Y.; Miller, C.D.; Sims, R.C. Approaches in design of Laboratory-Scale UASB reactors. Processes 2020, 8, 734. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gao, Y.; Heng, S.; Wang, J.; Liu, Z.; Liu, Y.; Chen, B.; Han, Y.; Li, W.; Lu, X.; Zhen, G. Bioelectrochemically altering microbial ecology in upflow anaerobic sludge blanket to enhance methanogenesis fed with high-sulfate methanolic wastewater. Bioresour. Technol. 2024, 406, 131026. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ouyang, E.; Lu, Y.; Ouyang, J.; Wang, L.; Wang, X. Performance and dynamic characteristics of microbial communities in multi-stage anaerobic reactors treating gibberellin wastewater. J. Biosci. Bioeng. 2018, 127, 318–325. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chernicharo, C.A.L. Anaerobic Reactors; IWA Publishing: London, UK, 2007. [Google Scholar]
- Van Lier, J.B.; Huibers, F.P. From unplanned to planned agricultural use: Making an asset out of wastewater. Irrig. Drain. Syst. 2009, 24, 143–152. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Enitan, A.M. Microbial Community Analysis of a UASB Reactor and Application of an Evolutionary Algorithm to Enhance Wastewater Treatment and Biogas Production. Ph.D. Thesis, Durban University of Technology, Durban, South Africa, 2015. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Daud, M.K.; Rizvi, H.; Akram, M.F.; Ali, S.; Rizwan, M.; Nafees, M.; Jin, Z.S. Review of Upflow Anaerobic Sludge Blanket Reactor Technology: Effect of different parameters and developments for domestic wastewater treatment. J. Chem. 2018, 2018, 1596319. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kuramae, E.E.; Dimitrov, M.R.; Da Silva, G.H.R.; Lucheta, A.R.; Mendes, L.W.; Luz, R.L.; Vet, L.E.M.; Fernandes, T.V. On-Site blackwater treatment fosters microbial groups and functions to efficiently and robustly recover carbon and nutrients. Microorganisms 2020, 9, 75. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Collivignarelli, M.C.; Abbà, A.; Caccamo, F.M.; Calatroni, S.; Torretta, V.; Katsoyiannis, I.A.; Miino, M.C.; Rada, E.C. Applications of Up-Flow Anaerobic Sludge Blanket (UASB) and characteristics of its microbial community: A review of bibliometric trend and recent findings. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2021, 18, 10326. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yangin-Gomec, C.; Engiz, G. Anaerobic treatment of propylene glycol-contaminated domestic wastewater and microbial community profile at threshold ratio. Heliyon 2021, 7, e06296. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Callejas, C.; López, I.; Bovio-Winkler, P.; Etchebehere, C.; Borzacconi, L. Temporal analysis of the microbiota involved in the anaerobic degradation of sugarcane vinasse in a full-scale methanogenic UASB reactor. Biomass Convers. Biorefin. 2021, 12, 3887–3897. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ziemiński, N.K. Methane fermentation process as anaerobic digestion of biomass: Transformations, stages and microorganisms. Afr. J. Biotechnol. 2012, 11, 4127–4139. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ribera-Pi, J.; Campitelli, A.; Badia-Fabregat, M.; Jubany, I.; Martínez-Lladó, X.; McAdam, E.; Jefferson, B.; Soares, A. Hydrolysis and methanogenesis in UASB-ANMBR Treating municipal wastewater under psychrophilic conditions: Importance of reactor configuration and inoculum. Front. Bioeng. Biotechnol. 2020, 8, 567695. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rajagopal, R.; Choudhury, M.R.; Anwar, N.; Goyette, B.; Rahaman, M.S. Influence of Pre-Hydrolysis on sewage treatment in an Up-Flow Anaerobic Sludge BLANKET (UASB) reactor: A review. Water 2019, 11, 372. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bhatti, Z.I.; Furukawa, K.; Fujita, M. Feasibility of methanolic waste treatment in UASB reactors. Water Res. 1996, 30, 2559–2568. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Garcia, J.-L.; Patel, B.K.C.; Ollivier, B. Taxonomic, phylogenetic, and ecological diversity of methanogenic archaea. Anaerobe 2000, 6, 205–226. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- De Vrieze, J.; Hennebel, T.; Boon, N.; Verstraete, W. Methanosarcina: The rediscovered methanogen for heavy duty biomethanation. Bioresour. Technol. 2012, 112, 1–9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mand, T.D.; Metcalf, W.W. Energy conservation and hydrogenase function in methanogenic archaea, in particular the GenusMethanosarcina. Microbiol. Mol. Biol. Rev. 2019, 83, e00020-19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guermazi-Toumi, S.; Chouari, R.; Sghir, A. Molecular analysis of methanogen populations and their interactions within anaerobic sludge digesters. Environ. Technol. 2018, 40, 2864–2879. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rastegar, S.O.; Mousavi, S.M.; Shojaosadati, S.A.; Sheibani, S. Optimization of petroleum refinery effluent treatment in a UASB reactor using response surface methodology. J. Hazard. Mater. 2011, 197, 26–32. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bhunia, P.; Ghangrekar, M.M. Analysis, evaluation, and optimization of kinetic parameters for performance appraisal and design of UASB reactors. Bioresour. Technol. 2007, 99, 2132–2140. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rincón, B.; Borja, R.; González, J.M.; Portillo, M.C.; Sáiz-Jiménez, C. Influence of organic loading rate and hydraulic retention time on the performance, stability and microbial communities of one-stage anaerobic digestion of two-phase olive mill solid residue. Biochem. Eng. J. 2008, 40, 253–261. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abbasi, T.; Abbasi, S.A. Formation and impact of granules in fostering clean energy production and wastewater treatment in upflow anaerobic sludge blanket (UASB) reactors. Renew. Sustain. Energy Rev. 2012, 16, 1696–1708. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Torkian, A.; Eqbali, A.; Hashemian, S.J. The effect of organic loading rate on the performance of UASB reactor treating slaughterhouse effluent. Resour. Conserv. Recycl. 2003, 40, 1–11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guillén, J.A.S.; Guardado, P.R.C.; Vazquez, C.M.L.; De Oliveira Cruz, L.M.; Brdjanovic, D.; Van Lier, J.B. Anammox cultivation in a closed sponge-bed trickling filter. Bioresour. Technol. 2015, 186, 252–260. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yu, H.Q.; Fang, H.H.P.; Tay, J.H. Enhanced sludge granulation in upflow anaerobic sludge blanket (UASB) reactors by aluminum chloride. Chemosphere 2001, 44, 31–36. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zandvoort, M.H.; Van Hullebusch, E.D.; Gieteling, J.; Lens, P.N.L. Granular sludge in full-scale anaerobic bioreactors: Trace element content and deficiencies. Enzyme Microb. Technol. 2006, 39, 337–346. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, J.; Zhang, Y.; Quan, X.; Chen, S. Effects of ferric iron on the anaerobic treatment and microbial biodiversity in a coupled microbial electrolysis cell (MEC)—Anaerobic reactor. Water Res. 2013, 47, 5719–5728. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yenigün, O.; Kizilgün, F.; Yilmazer, G. Inhibition effects of zinc and copper on volatile fatty acid production during anaerobic digestion. Environ. Technol. 1996, 17, 1269–1274. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Onodera, T.; Sase, S.; Choeisai, P.; Yoochatchaval, W.; Sumino, H.; Yamaguchi, T.; Ebie, Y.; Xu, K.; Tomioka, N.; Mizuochi, M.; et al. Development of a treatment system for molasses wastewater: The effects of cation inhibition on the anaerobic degradation process. Bioresour. Technol. 2013, 131, 295–302. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rajeshwari, K.V.; Balakrishnan, M.; Kansal, A.; Lata, K.; Kishore, V.V.N. State-of-the-art of anaerobic digestion technology for industrial wastewater treatment. Renew. Sustain. Energy Rev. 2000, 4, 135–156. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- You, J.H.; Guo, M.Z.; Zong, Y.C.; Wang, J.; Fu, C.H. Effect of hydraulic retention time on microbial community structure and nitrogen metabolism in anaerobic-anoxic-oxic process. Desalin. Water Treat. 2022, 259, 54–63. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, N.-P.; Tan, B.; Li, M.; Al-Dhabi, N.A.; Lin, B.; He, Q.; Shen, H.-N.; Cheng, J.-J.; Tang, W.; Zhang, Q. Deciphering the role of hydraulic retention time (HRT) in integrated fixed-film activated sludge (IFAS) system under aniline stress: Effects on microbial succession and communication. Chem. Eng. J. 2024, 482, 148834. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yea, N.K.; Abdullah, S.R.S.; Ismail, N.‘I.; Sharuddin, S.S.N. Effect of HRTs on COD and nutrient removal in sequencing batch reactor (SBR) process. J. Biochem. Microbiol. Biotechnol. 2022, 10, 29–39. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vítězová, M.; Kohoutová, A.; Vítěz, T.; Hanišáková, N.; Kushkevych, I. Methanogenic microorganisms in industrial wastewater anaerobic treatment. Processes 2020, 8, 1546. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Diamantis, V.I.; Aivasidis, A. Comparison of single- and two-stage UASB reactors used for anaerobic treatment of synthetic fruit wastewater. Enzyme Microb. Technol. 2007, 42, 6–10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Krakat, N.; Schmidt, S.; Scherer, P. Mesophilic fermentation of renewable biomass: Does hydraulic retention time regulate methanogen diversity? Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 2010, 76, 6322–6326. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- López-López, A.; León-Becerril, E.; Rosales-Contreras, M.E.; Villegas-García, E. Influence of alkalinity and VFAs on the performance of an UASB reactor with recirculation for the treatment of Tequila vinasses. Environ. Technol. 2015, 36, 2468–2476. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Palimeri, D.T.; Papadopoulou, K.; Vlyssides, A.G.; Vlysidis, A.A. Improving the Biogas Production and Methane Yield in a UASB Reactor with the Addition of Sulfate. Sustainability 2023, 15, 14896. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, Q.; Yang, Z.; Zhang, B.; Hua, M.; Liu, C.; Pan, B. Enhanced methane production during long-term UASB operation at high organic loads as enabled by the immobilized Fungi. Front. Environ. Sci. Eng. 2021, 16, 71. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ferrera, N.E.; Ruigómez, N.I.; Vera, N.L. Preliminary Study of Up-Flow Anaerobic Sludge Blanket (UASB) Technology for Energy Recovery from Domestic Wastewater. Renew. Energy Power Qual. J. 2022, 20, 542–547. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cecconet, D.; Callegari, A.; Capodaglio, A.G. UASB Performance and Perspectives in Urban Wastewater Treatment at Sub-Mesophilic Operating Temperature. Water 2022, 14, 115. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dohdoh, A.M.; Hendy, I.; Zelenakova, M.; Abdo, A. Domestic Wastewater Treatment: A Comparison between an Integrated Hybrid UASB-IFAS System and a Conventional UASB-AS System. Sustainability 2021, 13, 1853. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Donoso-Bravo, A.; Bandara, W.M.K.R.T.W.; Satoh, H.; Ruiz-Filippi, G. Explicit temperature-based model for anaerobic digestion: Application in domestic wastewater treatment in a UASB reactor. Bioresour. Technol. 2013, 133, 437–442. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mohan, S.M.; Swathi, T. A review on upflow anaerobic sludge blanket reactor: Factors affecting performance, modification of configuration and its derivatives. Water Environ. Res. 2021, 94, e1665. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, G.; Xu, F.; Yang, T.; Wang, X.; Lyu, T.; Huang, Z. Microbial Behavior and influencing factors in the anaerobic digestion of distiller: A Comprehensive review. Fermentation 2023, 9, 199. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sarker, S.; Lamb, J.J.; Hjelme, D.R.; Lien, K.M. A review of the role of critical parameters in the design and operation of biogas production plants. Appl. Sci. 2019, 9, 1915. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zieliński, M.; Kazimierowicz, J.; Dębowski, M. Advantages and Limitations of Anaerobic Wastewater Treatment—Technological Basics, development directions, and Technological Innovations. Energies 2022, 16, 83. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pellegrin, M.; Aguinaldo, J.; Arabi, S.; Sadler, M.E.; Min, K.; Liu, M.; Salamon, C.; Greiner, A.D.; Diamond, J.; McCandless, R.; et al. Membrane processes. Water Environ. Res. 2013, 85, 1092–1175. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ketheesan, B.; Stuckey, D.C. Effects of Hydraulic/Organic Shock/Transient loads in anaerobic wastewater Treatment: A review. Crit. Rev. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2015, 45, 2693–2727. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Akobi, C.; Yeo, H.; Hafez, H.; Nakhla, G. Single-stage and two-stage anaerobic digestion of extruded lignocellulosic biomass. Appl. Energy 2016, 184, 548–559. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gonçalves, R.F.; Assis, T.I.; Maciel, G.B.; Borges, R.M.; Cassini, S.T.A. Co-digestion of municipal wastewater and microalgae biomass in an upflow anaerobic sludge blanket reactor. Algal Res. 2020, 52, 102117. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barber, W.P.; Stuckey, D.C. The use of the anaerobic baffled reactor (ABR) for wastewater treatment: A review. Water Res. 1999, 33, 1559–1578. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Foxon, K.; Pillay, S.; Lalbahadur, T.; Rodda, N.; Holder, F.; Buckley, C. The anaerobic baffled reactor (ABR): An appropriate technology for on-site sanitation. Water SA 2007, 30, 44–50. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Y.; Zhang, K.; Bakke, R.; Li, C.; Liu, H. Membrane installation for enhanced up-flow anaerobic sludge blanket (UASB) performance. J. Biosci. Bioeng. 2013, 116, 357–361. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gouveia, J.; Plaza, F.; Garralon, G.; Fdz-Polanco, F.; Peña, M. Long-term operation of a pilot scale anaerobic membrane bioreactor (AnMBR) for the treatment of municipal wastewater under psychrophilic conditions. Bioresour. Technol. 2015, 185, 225–233. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sha, C.; Shen, S.; Zhang, J.; Zhou, C.; Lu, X.; Zhang, H. A review of Strategies and Technologies for sustainable Decentralized wastewater treatment. Water 2024, 16, 3003. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, H.; Liu, Y.; Gao, Y.; Li, F.; Yang, B.; Wang, M.; Ma, C.; Tian, Q.; Song, X.; Sand, W. Granulation process in an expanded granular sludge blanket (EGSB) reactor for domestic sewage treatment: Impact of extracellular polymeric substances compositions and evolution of microbial population. Bioresour. Technol. 2018, 269, 153–161. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xu, G.; Ji, J.; Zheng, Z.; Song, H.; Yang, H.; Liu, J.; Yin, F.; Zhang, W.; Hao, S. Performance and energy utilization Efficiency of an expanded granular sludge bed reactor in the treatment of cassava alcohol wastewater. Energies 2023, 16, 7496. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stazi, V.; Tomei, M.C. Enhancing anaerobic treatment of domestic wastewater: State of the art, innovative technologies and future perspectives. Sci. Total Environ. 2018, 635, 78–91. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, J.; Wang, C.; Wu, K.; Huang, L.; Tang, Z.; Zhang, C.; Wang, C.; Zhao, X.; Yin, F.; Yang, B.; et al. Novel start-up process for the efficient degradation of high COD wastewater with up-flow anaerobic sludge blanket technology and a modified internal circulation reactor. Bioresour. Technol. 2020, 308, 123300. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lu, Q.; Jeong, B.-G.; Lai, S.; Yan, Z.; Xiao, X.; Jiang, W. Performance comparison of EGSB and IC reactors for treating High-Salt Fatty Acid Organic Production wastewater. Processes 2022, 10, 1295. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Diamantis, V.; Aivasidis, A. Two-stage UASB design enables activated-sludge free treatment of easily biodegradable wastewater. Bioprocess Biosyst. Eng. 2009, 33, 287–292. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Espinosa, M.F.; Verbyla, M.E.; Vassalle, L.; Rosa-Machado, A.T.; Zhao, F.; Gaunin, A.; Mota, C.R. Reduction and partitioning of viral and bacterial indicators in a UASB reactor followed by high rate algal ponds treating domestic sewage. Sci. Total Environ. 2020, 760, 144309. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chernicharo, C.A.L.; Cardoso, M.D.R. Development and evaluation of a partitioned upflow anaerobic sludge blanket (UASB) reactor for the treatment of domestic sewage from small villages. Water Sci. Technol. 1999, 40, 107–113. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kamyab, B.; Zilouei, H. Investigating the efficiency of biogas production using modelling anaerobic digestion of baker’s yeast wastewater on two-stage mixed-UASB reactor. Fuel 2020, 285, 119198. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kumari, K.; Suresh, S.; Arisutha, S.; Sudhakar, K. Anaerobic co-digestion of different wastes in a UASB reactor. Waste Manag. 2018, 77, 545–554. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Saif, Y.; Ali, M.; Jones, I.M.; Ahmed, S. Performance evaluation of a Field-Scale anaerobic baffled reactor as an economic and sustainable solution for domestic wastewater treatment. Sustainability 2021, 13, 10461. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mainardis, M.; Buttazzoni, M.; Goi, D. Up-Flow Anaerobic Sludge Blanket (UASB) Technology for Energy Recovery: A Review on State-of-the-Art and Recent Technological Advances. Bioengineering 2020, 7, 43. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Smetana, G.; Grosser, A. The application of an upflow anaerobic sludge blanket reactor in the treatment of brewery and dairy wastewater: A Critical review. Energies 2024, 17, 1504. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Palenzuela-Rollon, A.; Zeeman, G.; Lubberding, H.J.; Lettinga, G.; Alaerts, G.J. Treatment of fish processing wastewater in a one- or two-step upflow anaerobic sludge blanket (UASB) reactor. Water Sci. Technol. 2002, 45, 207–212. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, Y.; Guo, B.; Zhang, L.; Zhang, H.; Liu, Y. Microbial community dynamics in granular activated carbon enhanced up-flow anaerobic sludge blanket (UASB) treating municipal sewage under sulfate reducing and psychrophilic conditions. Chem. Eng. J. 2020, 405, 126957. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, H.; Wei, Y.; Xie, C.; Wang, H.; Chang, S.; Xiong, Y.; Du, C.; Xiao, B.; Yu, G. Anaerobic treatment of glutamate-rich wastewater in a continuous UASB reactor: Effect of hydraulic retention time and methanogenic degradation pathway. Chemosphere 2019, 245, 125672. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, L.; Mou, A.; Sun, H.; Zhang, Y.; Zhou, Y.; Liu, Y. Calcium phosphate granules formation: Key to high rate of mesophilic UASB treatment of toilet wastewater. Sci. Total Environ. 2021, 773, 144972. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Esparza-Soto, M.; Jacobo-López, A.; Lucero-Chávez, M.; Fall, C. Anaerobic treatment of chocolate-processing industry wastewater at different organic loading rates and temperatures. Water Sci. Technol. 2019, 79, 2251–2259. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wu, J.; Jiang, B.; Kong, Z.; Yang, C.; Li, L.; Feng, B.; Luo, Z.; Xu, K.-Q.; Kobayashi, T.; Li, Y.-Y. Improved stability of up-flow anaerobic sludge blanket reactor treating starch wastewater by pre-acidification: Impact on microbial community and metabolic dynamics. Bioresour. Technol. 2021, 326, 124781. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Florencio, L.; Kato, M.T.; De Morais, J.C. Domestic sewage treatment in full-scale UASBB plant at Mangueira, Recife, Pernambuco. Water Sci. Technol. 2001, 44, 71–77. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, Y.; Wang, Q.; Li, M.; Yang, Y.; He, W.; Yan, G.; Guo, S. An alternative anaerobic treatment process for treatment of heavy oil refinery wastewater containing polar organics. Biochem. Eng. J. 2015, 105, 44–51. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Singh, K.S.; Viraraghavan, T. Impact of temperature on performance, microbiological, and hydrodynamic aspects of UASB reactors treating municipal wastewater. Water Sci. Technol. 2003, 48, 211–217. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sayed, S.; Van Campen, L.; Lettinga, G. Anaerobic treatment of slaughterhouse waste using a granular sludge UASB reactor. Biol. Wastes 1987, 21, 11–28. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lu, X.; Zhen, G.; Estrada, A.L.; Chen, M.; Ni, J.; Hojo, T.; Kubota, K.; Li, Y.-Y. Operation performance and granule characterization of upflow anaerobic sludge blanket (UASB) reactor treating wastewater with starch as the sole carbon source. Bioresour. Technol. 2015, 180, 264–273. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Younas, S.; Rizvi, H.; Ali, S.; Abbas, F. Irrigation of Zea mays with UASB-treated textile wastewater; effect on early irrigation of Zea mays with UASB-treated textile wastewater; effect on early growth and physiology. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 2020, 27, 15305–15324. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chávez, P.C.; Castillo, L.R.; Dendooven, L.; Escamilla-Silva, E.M. Poultry slaughter wastewater treatment with an up-flow anaerobic sludge blanket (UASB) reactor. Bioresour. Technol. 2005, 96, 1730–1736. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Agrawal, L.K.; Harada, H.; Okui, H. Treatment of dilute wastewater in a UASB reactor at a moderate temperature: Performance aspects. J. Ferment. Bioeng. 1997, 83, 179–184. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Verma, A.K.; Bhunia, P.; Dash, R.R.; Tyagi, R.D.; Surampalli, R.Y.; Zhang, T.C. Effects of physico-chemical pre-treatment on the performance of an upflow anaerobic sludge blanket (UASB) reactor treating textile wastewater: Application of full factorial central composite design. Can. J. Chem. Eng. 2015, 93, 808–818. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Álvarez, J.A.; Armstrong, E.; Presas, J.; Gómez, M.; Soto, N. Performance of a UASB-Digester system treating domestic wastewater. Environ. Technol. 2004, 25, 1189–1199. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yetilmezsoy, K.; Sapci-Zengin, Z. Stochastic modeling applications for the prediction of COD removal efficiency of UASB reactors treating diluted real cotton textile wastewater. Stoch. Environ. Res. Risk Assess. 2007, 23, 13–26. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, W.; Niu, Q.; Zhang, H.; Tian, Z.; Zhang, Y.; Gao, Y.; Li, Y.-Y.; Nishimura, O.; Yang, M. UASB treatment of chemical synthesis-based pharmaceutical wastewater containing rich organic sulfur compounds and sulfate and associated microbial characteristics. Chem. Eng. J. 2014, 260, 55–63. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bohdziewicz, J.; Kwarciak, A. The application of hybrid system UASB reactor-RO in landfill leachate treatment. Desalination 2008, 222, 128–134. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chamy, R.; Pizarro, C.; Vivanco, E.; Schiappacasse, M.C.; Jeison, D.; Poirrier, P.; Ruiz-Filippi, G. Selected experiences in Chile for the application of UASB technology for vinasse treatment. Water Sci. Technol. 2007, 56, 39–48. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mirsepasi, A.; Honary, H.R.; Mesdaghinia, A.R.; Mahvi, A.H.; Vahid, H.; Karyab, H. Performance Evaluation of Full Scale Uasb Reactor in Treating Stillage Wastewater. Iran. J. Environ. Health Sci. Eng. 2006, 3, 79–84. [Google Scholar]
- Amaral, K.G.C.D.; Rietow, J.C.; Aisse, M.M. Evaluation of the Environmental Life Cycle of an STP That Employs a Low-Rate Trickling Filter as Post-Treatment of a UASB Reactor and Different Sludge-Management Alternatives. Rev. Ambient. Água 2021, 16, e2648. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cañote, S.J.B.; Barros, R.M.; Lora, E.E.S.; Santos, I.F.S.D.; Silva, A.P.M.; Piñas, J.A.V.; Cañote, A.L.B.; De Castro E Silva, H.L. Life cycle assessment of upflow anaerobic sludge blanket sludge management and activated sludge systems aiming energy use in the municipality of Itajubá, Minas Gerais, Brazil. J. Mater. Cycles Waste Manag. 2021, 23, 1810–1830. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Foglia, A.; Andreola, C.; Cipolletta, G.; Radini, S.; Akyol, Ç.; Eusebi, A.L.; Stanchev, P.; Katsou, E.; Fatone, F. Comparative life cycle environmental and economic assessment of anaerobic membrane bioreactor and disinfection for reclaimed water reuse in agricultural irrigation: A case study in Italy. J. Clean. Prod. 2021, 293, 126201. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Freitas, F.F.; De Souza, S.S.; Ferreira, L.R.A.; Otto, R.B.; Alessio, F.J.; De Souza, S.N.M.; Venturini, O.J.; Ando Junior, O.H. The Brazilian market of distributed biogas generation: Overview, technological development and case study. Renew. Sustain. Energy Rev. 2018, 101, 146–157. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bressani-Ribeiro, T.; Chamhum-Silva, L.A.; Chernicharo, C.A.L. Constraints, performance and perspectives of anaerobic sewage treatment: Lessons from full-scale sewage treatment plants in Brazil. Water Sci. Technol. 2019, 80, 418–425. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rosa, A.P.; Conesa, J.A.; Fullana, A.; Melo, G.C.B.; Borges, J.M.; Chernicharo, C.A.L. Energy potential and alternative usages of biogas and sludge from UASB reactors: Case study of the Laboreaux wastewater treatment plant. Water Sci. Technol. 2015, 73, 1680–1690. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hartley, K.; Lant, P. Eliminating non-renewable CO2 emissions from sewage treatment: An anaerobic migrating bed reactor pilot plant study. Biotechnol. Bioeng. 2006, 95, 384–398. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cookney, J.; Cartmell, E.; Jefferson, B.; McAdam, E.J. Recovery of methane from anaerobic process effluent using poly-di-methyl-siloxane membrane contactors. Water Sci. Technol. 2012, 65, 604–610. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Luo, G.; Johansson, S.; Boe, K.; Xie, L.; Zhou, Q.; Angelidaki, I. Simultaneous hydrogen utilization and in situ biogas upgrading in an anaerobic reactor. Biotechnol. Bioeng. 2011, 109, 1088–1094. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Souza, C.L.; Chernicharo, C.A.L.; Melo, G.C.B. Methane and hydrogen sulfide emissions in UASB reactors treating domestic wastewater. Water Sci. Technol. 2012, 65, 1229–1237. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mora, E.C.; De Lemos Chernicharo, C.A. Simultaneous removal of dissolved sulphide and dissolved methane from anaerobic effluents with hollow fibre membrane contactors. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 2022, 29, 90549–90566. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Estrada-Arriaga, E.B.; Reynoso-Deloya, M.G.; Guillén-Garcés, R.A.; Falcón-Rojas, A.; García-Sánchez, L. Enhanced methane production and organic matter removal from tequila vinasses by anaerobic digestion assisted via bioelectrochemical power-to-gas. Bioresour. Technol. 2020, 320, 124344. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Call, D.; Logan, B.E. Hydrogen production in a single chamber microbial electrolysis cell lacking a membrane. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2008, 42, 3401–3406. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gajaraj, S.; Huang, Y.; Zheng, P.; Hu, Z. Methane production improvement and associated methanogenic assemblages in bioelectrochemically assisted anaerobic digestion. Biochem. Eng. J. 2016, 117, 105–112. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Elmitwalli, T.; Zeeman, G.; Lettinga, G. Anaerobic treatment of domestic sewage at low temperature. Water Sci. Technol. 2001, 44, 33–40. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fukuhara, S. A basis for the space of modular forms. Acta Arith. 2011, 151, 421–427. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mahmoud, N.; Amarneh, M.N.; Al-Sa’ed, R.; Zeeman, G.; Gijzen, H.; Lettinga, G. Sewage characterisation as a tool for the application of anaerobic treatment in Palestine. Environ. Pollut. 2003, 126, 115–122. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ho, J.; Sung, S. Methanogenic activities in anaerobic membrane bioreactors (AnMBR) treating synthetic municipal wastewater. Bioresour. Technol. 2009, 101, 2191–2196. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Martinez-Sosa, D.; Helmreich, B.; Netter, T.; Paris, S.; Bischof, F.; Horn, H. Anaerobic submerged membrane bioreactor (AnSMBR) for municipal wastewater treatment under mesophilic and psychrophilic temperature conditions. Bioresour. Technol. 2011, 102, 10377–10385. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Smith, A.L.; Skerlos, S.J.; Raskin, L. Psychrophilic anaerobic membrane bioreactor treatment of domestic wastewater. Water Res. 2012, 47, 1655–1665. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Özgün, H. Anaerobic Membrane Bioreactors For Cost-Effective Municipal Water Reuse. Ph.D. Thesis, Istanbul Technical University, Istanbul, Turkey, 2015. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pretel, R.; Durán, F.; Robles, A.; Ruano, M.V.; Ribes, J.; Serralta, J.; Ferrer, J. Designing an AnMBR-based WWTP for energy recovery from urban wastewater: The role of primary settling and anaerobic digestion. Sep. Purif. Technol. 2015, 156, 132–139. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dolejs, P.; Ozcan, O.; Bair, R.; Ariunbaatar, J.; Bartacek, J.; Lens, P.N.L.; Yeh, D.H. Effect of psychrophilic temperature shocks on a gas-lift anaerobic membrane bioreactor (Gl-AnMBR) treating synthetic domestic wastewater. J. Water Process Eng. 2017, 16, 108–114. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mahmoud, N.; Zeeman, G.; Gijzen, H.; Lettinga, G. Anaerobic sewage treatment in a one-stage UASB reactor and a combined UASB-Digester system. Water Res. 2004, 38, 2348–2358. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gao, D.-W.; Hu, Q.; Yao, C.; Ren, N.-Q. Treatment of domestic wastewater by an integrated anaerobic fluidized-bed membrane bioreactor under moderate to low temperature conditions. Bioresour. Technol. 2014, 159, 193–198. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Von Sperling, M.; Bastos, R.K.X.; Kato, M.T. Removal of E. coli and helminth eggs in UASB: Polishing pond systems in Brazil. Water Sci. Technol. 2005, 51, 91–97. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Valero, M.A.C.; Mara, D.D. Nitrogen removal in maturation ponds: Tracer experiments with 15N-labelled ammonia. Water Sci. Technol. 2007, 55, 81–85. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Uemura, S.; Harada, H. Application of UASB Technology for Sewage Treatment with a Novel Post-Treatment Process; Imperial College Press: London, UK, 2010; pp. 91–112. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ozgun, H.; Dereli, R.K.; Ersahin, M.E.; Kinaci, C.; Spanjers, H.; Van Lier, J.B. A review of anaerobic membrane bioreactors for municipal wastewater treatment: Integration options, limitations and expectations. Sep. Purif. Technol. 2013, 118, 89–104. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chernicharo, C.A.L.; de Araújo, A.L.C.; de Matos, M.P. Anaerobic sewage treatment: State of the art, constraints and challenges. Rev. Environ. Sci. Biotechnol. 2015, 14, 649–679. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Burgess, J.E.; Parsons, S.A.; Stuetz, R.M. Developments in odour control and waste gas treatment biotechnology: A review. Biotechnol. Adv. 2001, 19, 35–63. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- De Lemos Chernicharo, C.A.; Stuetz, R.M.; Souza, C.L.; De Melo, G.C.B. Alternativas para o controle de emissões odorantes em reatores anaeróbios tratando esgoto doméstico. Eng. Sanit. Ambient. 2010, 15, 229–236. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- De Oliveira, J.F.; Fia, R.; Nunes, B.S.B.; Siniscalchi, L.A.B.; De Matos, M.P.; Fia, F.R.L. Nitrogen and Phosphorus Removal Associated with Changes in Organic Loads from Biological Reactors Monitored by Multivariate Criteria. Water Air Soil Pollut. 2020, 231, 511. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kassab, G.; Halalsheh, M.; Klapwijk, A.; Fayyad, M.; Van Lier, J.B. Sequential anaerobic–aerobic treatment for domestic wastewater—A review. Bioresour. Technol. 2010, 101, 3299–3310. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Almeida, P.G.S.; Marcus, A.K.; Rittmann, B.E.; Chernicharo, C.A.L. Performance of plastic- and sponge-based trickling filters treating effluents from an UASB reactor. Water Sci. Technol. 2013, 67, 1034–1042. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Third, K.A.; Sliekers, A.O.; Kuenen, J.G.; Jetten, M.S.M. The CANON System (Completely Autotrophic Nitrogen-removal Over Nitrite) under Ammonium Limitation: Interaction and Competition between Three Groups of Bacteria. Syst. Appl. Microbiol. 2001, 24, 588–596. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wett, B.; Omari, A.; Podmirseg, S.M.; Han, M.; Akintayo, O.; Brandón, M.G.; Murthy, S.; Bott, C.; Hell, M.; Takács, I.; et al. Going for mainstream deammonification from bench to full scale for maximized resource efficiency. Water Sci. Technol. 2013, 68, 283–289. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Júnior, J.C.A.B.; De Almeida Silva, M.C.; Hoyos, N.L.M.; Monteggia, L.O. Evaluation of UASB effluent post-treatment in pilot-scale by microalgae HRP and macrophytes pond for nutrient recovery. J. Clean. Prod. 2022, 357, 131951. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stadtlander, T.; Förster, S.; Rosskothen, D.; Leiber, F. Slurry-grown duckweed (Spirodela polyrhiza) as a means to recycle nitrogen into feed for rainbow trout fry. J. Clean. Prod. 2019, 228, 86–93. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brandt, E.M.F.; De Queiroz, F.B.; Afonso, R.J.C.F.; Aquino, S.F.; Chernicharo, C.A.L. Behaviour of pharmaceuticals and endocrine disrupting chemicals in simplified sewage treatment systems. J. Environ. Manag. 2013, 128, 718–726. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Souza, C.L.; Chernicharo, C.a.L.; Aquino, S.F. Quantification of dissolved methane in UASB reactors treating domestic wastewater under different operating conditions. Water Sci. Technol. 2011, 64, 2259–2264. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Salomon, K.R.; Lora, E.E.S. Estimate of the electric energy generating potential for different sources of biogas in Brazil. Biomass Bioenergy 2009, 33, 1101–1107. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chernicharo, C.a.L.; Almeida, P.G.S. Feasibility of UASB/trickling filter systems without final clarifiers for the treatment of domestic wastewater in small communities in Brazil. Water Sci. Technol. 2011, 64, 1347–1354. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Souza, C.L.; Silva, S.Q.; Aquino, S.F.; Chernicharo, C.A.L. Production and characterization of scum and its role in odour control in UASB reactors treating domestic wastewater. Water Sci. Technol. 2006, 54, 201–208. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rodrigues, B.C.G.; De Mello, B.S.; Da Costa Araujo, M.L.G.; Da Silva, G.H.R.; Sarti, A. Soybean molasses as feedstock for sustainable generation of biomethane using high-rate anaerobic reactor. J. Environ. Chem. Eng. 2021, 9, 105226. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Koirala, N.; Odey, E.A.; Lu, Q.; Iu, H.I.; Lok, K.S.; Shim, H. Stimulatory effect of magnesium supplement on anaerobic co-digestion of food waste and domestic wastewater. J. Water Process Eng. 2020, 40, 101773. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Da Silva Do Nascimento, J.G.; De Araújo, M.H.P.; Santos, A.B.D.; Da Silva, M.E.R.; Firmino, P.I.M. Redox mediator, microaeration, and nitrate addition as engineering approaches to enhance the biotransformation of antibiotics in anaerobic reactors. J. Hazard. Mater. 2020, 403, 123932. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lopes, T.A.S.; Queiroz, L.M.; Torres, E.A.; Kiperstok, A. Low complexity wastewater treatment process in developing countries: A LCA approach to evaluate environmental gains. Sci. Total Environ. 2020, 720, 137593. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Maharjan, N.; Nomoto, N.; Tagawa, T.; Okubo, T.; Uemura, S.; Khalil, N.; Hatamoto, M.; Yamaguchi, T.; Harada, H. Assessment of UASB–DHS technology for sewage treatment: A comparative study from a sustainability perspective. Environ. Technol. 2018, 40, 2825–2832. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mainardis, M.; Goi, D. Pilot-UASB reactor tests for anaerobic valorisation of high-loaded liquid substrates in friulian mountain area. J. Environ. Chem. Eng. 2019, 7, 103348. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]



| Genus | Optimal pH Range |
|---|---|
| Methanothermus | 6.5 |
| Methanohalobium | 6.5–6.8 |
| Methanolacinia | 6.6–7.2 |
| Methanomicrobium | 7.0–7.5 |
| Methanosphaera | 6.8 |
| Methanogenium | 7.0 |
| Methanosprillum | 7.0–7.5 |
| Methanosaeta | 7.6 |
| Methanolobus | 6.5–6.8 |
| Methanothrix | 7.1–7.8 |
| Methanococcoides | 6.5–7.5 |
| UASB Advancement | Wastewater Type | HRT (h) | Organic Loading Rate (kg COD/m3d) | Methane (CH4) Yield (L) | COD Removal Efficiency (%) | NH3 Removal Efficiency (%) | References |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Two-stage UASB anaerobic digestion | Baker’s yeast wastewater | - | - | 113.4 | 35.98 | - | [71] |
| UASB co-digestion | Pre-treated municipal wastewater. | 8.1 | 1.0 | - | 63 | - | [59] |
| A mixture of sewage sludge (SS) and cow manure | 20/days | - | - | 86 | - | [72] | |
| Anaerobic baffled reactors (ABRs) | Domestic wastewater | 20 | - | - | 47.6 | 31.2/TKN (Total Khejhal Nitrogen) | [73] |
| Expanded granular sludge bed (EGSB) | Low-strength domestic sewage | 5 | 2.16 | - | 71.5 | - | [65] |
| Wastewater Type | Operational Temperature (°C) | HRT (h) | Organic Loading | Wastewater Type | References |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Fish processing wastewater | - | 7.2 ± 2.8 | 1–8 | 80–95 | [78] |
| Municipal sewage sludge | 16.5 ± 2 | 16, 24, 36 | - | 62–75 | [79] |
| Glutamate-rich wastewater | 35 | 2–48 | 16 | 90–95 | [80] |
| Toilet wastewater | 35 | 6 | 16 | 75.6 ± 6.0 | [81] |
| Chocolate wastewater | 15, 20, 25, and 30 | 6 | 2–6 | 39–94 | [82] |
| Synthetic starch wastewater | 35 ± 1 | 3, 6, 8, 12, 24 and 48 | 0.5–8 | 75–95 | [83] |
| Domestic sewage | 30 | 8.8, 9.4, 9.7 | 0.786, 1.376, 1.404 | 60–75 | [84] |
| Heavy oil refinery wastewater | - | - | 3.44 | 70–72 | [85] |
| Municipal wastewater | 20, 32, 20, 15, 11, and 6 | 48–3 | - | 70–90 | [86] |
| Slaughterhouse wastewater | 20, 30 | 1.7–9 | 2.5–19.5 | 40–67 | [87] |
| Starch wastewater | 35 | 24–3 | 1.0–8.0 | 81.1–98.7 | [88] |
| Textile effluents | 28 | 5, 10, 15 | - | 61.35 | [89] |
| Poultry slaughter wastewater | 25, 32.5, 40 | 2.30, 3.30, 4.30 | 95% removal of BOD5 | [90] | |
| Synthetic wastewater | 25 | 9 | 0.73 | 81 ± 5 | [91] |
| Textile wastewater | 22–27 | 18 | 2.60 | 70 | [92] |
| Domestic wastewater | 14–16 | 9.3–6.1 | - | 52 | [93] |
| Cotton textile wastewater | 36–37.5 | 4.5 and 9.0 | 0.072–0.602 | 60 and 80 | [94] |
| Pharmaceutical wastewater | 37 ± 1 | 1.3/day | 8 | 70 | [95] |
| Leachate | - | 7–2/days | 0.6–2.0 | 76 | [96] |
| Vinasse | - | 1.8/day | 5–11 | 93 | [97] |
| Stillage wastewater | 28–32 | >200 | 4–5.5 | 55 | [98] |
| 30 ± 2 | 20 | 10 | 80 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Senadheera, U.E.; Abeykoon, A.M.W.D.C.B.; Sewmini, P.M.N.; Weerasekara, W.M.R.B.; Darshani, N.P.; Jayasanka, J.; Weerasekara, N.A.; Hewawasam, C.; Sanjeewa, K.K.A.; Jayawardena, T.U. Up-Flow Anaerobic Sludge Bed Reactors for Sustainable Wastewater Management: Challenges, Innovations, and Future Directions. Water 2025, 17, 476. https://doi.org/10.3390/w17040476
Senadheera UE, Abeykoon AMWDCB, Sewmini PMN, Weerasekara WMRB, Darshani NP, Jayasanka J, Weerasekara NA, Hewawasam C, Sanjeewa KKA, Jayawardena TU. Up-Flow Anaerobic Sludge Bed Reactors for Sustainable Wastewater Management: Challenges, Innovations, and Future Directions. Water. 2025; 17(4):476. https://doi.org/10.3390/w17040476
Chicago/Turabian StyleSenadheera, Uvin Eksith, A. M. W. D. C. B. Abeykoon, P. M. N. Sewmini, W. M. R. B. Weerasekara, Nadeeka P. Darshani, Jasintha Jayasanka, Nuwan A. Weerasekara, Choolaka Hewawasam, K. K. Asanka Sanjeewa, and Thilina U. Jayawardena. 2025. "Up-Flow Anaerobic Sludge Bed Reactors for Sustainable Wastewater Management: Challenges, Innovations, and Future Directions" Water 17, no. 4: 476. https://doi.org/10.3390/w17040476
APA StyleSenadheera, U. E., Abeykoon, A. M. W. D. C. B., Sewmini, P. M. N., Weerasekara, W. M. R. B., Darshani, N. P., Jayasanka, J., Weerasekara, N. A., Hewawasam, C., Sanjeewa, K. K. A., & Jayawardena, T. U. (2025). Up-Flow Anaerobic Sludge Bed Reactors for Sustainable Wastewater Management: Challenges, Innovations, and Future Directions. Water, 17(4), 476. https://doi.org/10.3390/w17040476








