Implementing Best Management Practices in Complex Agricultural Watersheds: Insights from High-Resolution Nitrogen Load Dynamics Analysis
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Study Area
2.2. SWAT Model Setup, Calibration, and Validation
2.3. Nitrogen Load Critical Source Areas Classification
2.4. Modeling BMP Scenario Design
2.5. Statistical Analysis
3. Results and Discussion
3.1. SWAT Calibration and Validation Results
3.2. Spatio-Temporal Distribution Characteristics of Flow and TN
3.2.1. Temporal Variability and Patterns
3.2.2. Characteristics of Spatial Distribution
3.2.3. Variations in Nitrogen Load Intensity Across Different Land Uses
3.3. Driving Factors of Spatio-Temporal Variation of Nitrogen Load
3.4. Effectiveness of BMP in Reducing Nitrogen Load
4. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
| FR | Fertilizer reduction |
| CF | Contour farming |
| RM | Residue management |
| FS | Filter strips |
| GW | Grassed waterways |
References
- Vörösmarty, C.J.; McIntyre, P.B.; Gessner, M.O.; Dudgeon, D.; Prusevich, A.; Green, P.; Glidden, S.; Bunn, S.E.; Sullivan, C.A.; Liermann, C.R.; et al. Global threats to human water security and river biodiversity. Nature 2010, 467, 555–561. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xia, Y.; Zhang, M.; Tsang, D.C.W.; Geng, N.; Lu, D.; Zhu, L.; Igalavithana, A.D.; Dissanayake, P.D.; Rinklebe, J.; Yang, X.; et al. Recent advances in control technologies for non-point source pollution with nitrogen and phosphorous from agricultural runoff: Current practices and future prospects. Appl. Biol. Chem. 2020, 63, 8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Grizzetti, B.; Vigiak, O.; Udias, A.; Aloe, A.; Zanni, M.; Bouraoui, F.; Pistocchi, A.; Dorati, C.; Friedland, R.; De Roo, A.; et al. How EU policies could reduce nutrient pollution in European inland and coastal waters. Glob. Environ. Change 2021, 69, 102281. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Volk, M.; Liersch, S.; Schmidt, G. Towards the implementation of the European Water Framework Directive?: Lessons learned from water quality simulations in an agricultural watershed. Land Use Policy 2009, 26, 580–588. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rankinen, K.; Keinänen, H.; Cano Bernal, J.E. Influence of climate and land use changes on nutrient fluxes from Finnish rivers to the Baltic Sea. Agric. Ecosyst. Environ. 2016, 216, 100–115. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ouyang, W.; Huang, H.; Hao, F.; Shan, Y.; Guo, B. Evaluating spatial interaction of soil property with non-point source pollution at watershed scale: The phosphorus indicator in Northeast China. Sci. Total Environ. 2012, 432, 412–421. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shrestha, S.; Bhatta, B.; Shrestha, M.; Shrestha, P.K. Integrated assessment of the climate and landuse change impact on hydrology and water quality in the Songkhram River Basin, Thailand. Sci. Total Environ. 2018, 643, 1610–1622. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kändler, M.; Blechinger, K.; Seidler, C.; Pavlů, V.; Šanda, M.; Dostál, T.; Krása, J.; Vitvar, T.; Štich, M. Impact of land use on water quality in the upper Nisa catchment in the Czech Republic and in Germany. Sci. Total Environ. 2017, 586, 1316–1325. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Arnold, J.G.; Moriasi, D.N.; Gassman, P.W.; Abbaspour, K.C.; White, M.J.; Srinivasan, R.; Santhi, C.; Harmel, R.D.; van Griensven, A.; Van Liew, M.W.; et al. SWAT: Model Use, Calibration, and Validation. Trans. ASABE 2012, 55, 1491–1508. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, W.; Li, H.; Hyndman, D.; Diao, Y.; Jianwei, G.; Pueppke, S. Water quality trends under rapid agricultural expansion and enhanced in-stream interception in a hilly watershed of Eastern China. Environ. Res. Lett. 2020, 15, 084030. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qi, D.; Wu, Q.; Zhu, J. Nitrogen and phosphorus losses from paddy fields and the yield of rice with different water and nitrogen management practices. Sci. Rep. 2020, 10, 9734. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, W.; Li, H.; Pueppke, S.G. Direct measurements of dissolved N2 and N2O highlight the strong nitrogen (N) removal potential of riverine wetlands in a headwater stream. Sci. Total Environ. 2022, 848, 157538. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, W.; Li, H.; Kendall, A.; Hyndman, D.; Diao, Y.; Jianwei, G.; Pang, J. Nitrogen transport and retention in a headwater catchment with dense distributions of lowland ponds. Sci. Total Environ. 2019, 683, 37–48. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pang, J.; Li, H.; Tang, X.; Geng, J. Carbon dynamics and environmental controls of a hilly tea plantation in Southeast China. Ecol. Evol. 2019, 9, 9723–9735. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pasha, S.V.; Dadhwal, V.K.; Kumari, K.; Ali, N. Historical expansion of tea plantations over 150 years (1876–2023) in North Bengal, India. Environ. Monit. Assess. 2024, 196, 1071. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Munasinghe, M.; Deraniyagala, Y.; Dassanayake, N.; Karunarathna, H. Economic, social and environmental impacts and overall sustainability of the tea sector in Sri Lanka. Sustain. Prod. Consum. 2017, 12, 155–169. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, X.; Lakshmanan, P.; Zhang, W.; Wang, X.; Liu, B.; Ni, K.; Ruan, J.; Shi, X.; Chen, X.; Zhang, F. Large loss of reactive nitrogen and the associated environmental damages from tea production in China. Agric. Ecosyst. Environ. 2025, 377, 109252. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lu, C.P.; Ji, K.Y.; Zhang, Y.; Fleckenstein, J.H.; Zheng, C.M.; Salsky, K. Event-Driven Hyporheic Exchange during Single and Seasonal Rainfall in a Gaining Stream. Water Resour. Manag. 2020, 34, 4617–4631. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, L.; Ouyang, W.; Wang, Y.; Lian, Z.; Pan, J.; Liu, H.; Chen, J.; Niu, S. Paddy water managements for diffuse nitrogen and phosphorus pollution control in China: A comprehensive review and emerging prospects. Agric. Water Manag. 2023, 277, 108102. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moriasi, D.; Arnold, J.; Van Liew, M.; Bingner, R.; Harmel, R.D.; Veith, T. Model Evaluation Guidelines for Systematic Quantification of Accuracy in Watershed Simulations. Trans. ASABE 2007, 50, 885–900. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Krause, P.; Boyle, D.; Bäse, F. Comparison of Different Efficiency Criteria for Hydrologic Models. Adv. Geosci. 2005, 5, 89–97. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Niraula, R.; Kalin, L.; Wang, R.; Srivastava, P.; Srivastava, P. Determining Nutrient and Sediment Critical Source Areas with SWAT: Effect of Lumped Calibration. Trans. ASABE 2011, 55, 137–147. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gupta, H.; Sorooshian, S.; Yapo, P. Status of Automatic Calibration for Hydrologic Models: Comparison With Multilevel Expert Calibration. J. Hydrol. Eng. 1999, 4, 135–143. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Giri, S.; Nejadhashemi, A.; Zhang, Z.; Woznicki, S. Integrating statistical and hydrological models to identify implementation sites for agricultural conservation practices. Environ. Model. Softw. 2015, 72, 327–340. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Arabi, M.; Frankenberger, J.R.; Engel, B.A.; Arnold, J.G. Representation of agricultural conservation practices with SWAT. Hydrol. Process. 2008, 22, 3042–3055. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, J.; Wang, D.; Zhang, G.; Wang, Y.; Wang, C.; Teng, Y.; Christie, P. Nitrogen and phosphorus leaching losses from intensively managed paddy fields with straw retention. Agric. Water Manag. 2014, 141, 66–73. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wei, X.; Bailey, R. Evaluating Nitrate and Phosphorus Remediation in Intensively Irrigated Stream-Aquifer Systems Using a Coupled Flow and Reactive Transport Model. J. Hydrol. 2021, 598, 126304. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, K.; Onodera, S.-i.; Saito, M.; Shimizu, Y. Assessment of nitrogen budget in detailed spatial pattern using high precision modeling approach with constructed accurate agricultural behavior. Sci. Total Environ. 2024, 912, 169631. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, R.; Peipei, Z.; Wang, X.; Chen, Y.; Shen, Z. Assessment of effects of best management practices on agricultural non-point source pollution in Xiangxi River watershed. Agric. Water Manag. 2013, 117, 9–18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tuppad, P.; Kannan, N.; Srinivasan, R.; Green, C.; Arnold, J. Simulation of Agricultural Management Alternatives for Watershed Protection. Water Resour. Manag. 2010, 24, 3115–3144. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Oduor, B.; Campo-Bescós, M.; Lana-Renault, N.; Kyllmar, K.; Mårtensson, K.; Casalí, J. Quantification of agricultural best management practices impacts on sediment and phosphorous export in a small catchment in southeastern Sweden. Agric. Water Manag. 2023, 290, 108595. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Evrard, O.; Persoons, E.; Vandaele, K.; van Wesemael, B. Effectiveness of erosion mitigation measures to prevent muddy floods: A case study in the Belgian loam belt. Agric. Ecosyst. Environ. 2007, 118, 149–158. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- López-Ballesteros, A.; Senent-Aparicio, J.; Srinivasan, R.; Pérez-Sánchez, J. Assessing the Impact of Best Management Practices in a Highly Anthropogenic and Ungauged Watershed Using the SWAT Model: A Case Study in the El Beal Watershed (Southeast Spain). Agron. J. 2019, 9, 576. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, S.; Tian, Y.; Li, L.; Zhuang, Y.; Zhou, X.; Zhang, H.; Zhan, W.; Zuo, W.; Luan, C.; Huang, K. Unraveling spatial patterns and source attribution of nutrient transport: Towards optimal best management practices in complex river basin. Sci. Total Environ. 2024, 906, 167686. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zeiger, S.; Hubbart, J. A SWAT Model Validation of Nested-Scale Contemporaneous Stream Flow, Suspended Sediment and Nutrients from a Multiple-Land-Use Watershed of the Central USA. Sci. Total Environ. 2016, 572, 232–243. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bryant, R.B.; Gburek, W.J.; Veith, T.L.; Hively, W.D. Perspectives on the potential for hydropedology to improve watershed modeling of phosphorus loss. Geoderma 2006, 131, 299–307. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, M.; Chen, X.; Yao, H.; Chen, Y. A coupled modeling approach to evaluate nitrogen retention within the Shanmei Reservoir watershed, China. Estuar. Coast. Shelf Sci. 2015, 166, 189–198. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jingyi, H.; Ouyang, W.; Yang, Z. Impacts of extreme climate on nitrogen loss in different forms and pollution risk with the copula model. J. Hydrol. 2023, 620, 129412. [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, Y.; Shi, P.; Li, F.; Wei, A.; Song, J.; Ma, J. Quantification of nitrate sources and fates in rivers in an irrigated agricultural area using environmental isotopes and a Bayesian isotope mixing model. Chemosphere 2018, 208, 493–501. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shi, P.; Zhang, Y.; Song, J.; Li, P.; Wang, Y.; Zhang, X.; Li, Z.; Bi, Z.; Zhang, X.; Qin, Y.; et al. Response of nitrogen pollution in surface water to land use and social-economic factors in the Weihe River watershed, northwest China. Sustain. Cities Soc. 2019, 50, 101658. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, W.; Li, H.; Pueppke, S.G.; Diao, Y.; Nie, X.; Geng, J.; Chen, D.; Pang, J. Nutrient loss is sensitive to land cover changes and slope gradients of agricultural hillsides: Evidence from four contrasting pond systems in a hilly catchment. Agric. Water Manag. 2020, 237, 106165. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, T.; Ma, F.; Wang, J.; Qiu, P.; Zhang, N.; Guo, W.; Xu, J.; Dai, T. Study on the Mechanism of Rainfall-Runoff Induced Nitrogen and Phosphorus Loss in Hilly Slopes of Black Soil Area, China. Water 2023, 15, 3148. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Haidary, A.; Amiri, B.J.; Adamowski, J.; Fohrer, N.; Nakane, K. Assessing the Impacts of Four Land Use Types on the Water Quality of Wetlands in Japan. Water Resour. Manag. 2013, 27, 2217–2229. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Peng, S.-Z.; Yang, S.-H.; Xu, J.-Z.; Luo, Y.-F.; Hou, H.-J. Nitrogen and phosphorus leaching losses from paddy fields with different water and nitrogen managements. Paddy Water Environ. 2011, 9, 333–342. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Giri, S.; Qiu, Z. Understanding the relationship of land uses and water quality in Twenty First Century: A review. J. Environ. Manag. 2016, 173, 41–48. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, Y.; Xu, J.F.; Yin, W.; Ai, L.; Fang, N.F.; Tan, W.F.; Yan, F.L.; Shi, Z.H. Hydrological and environmental controls of the stream nitrate concentration and flux in a small agricultural watershed. J. Hydrol. 2017, 545, 355–366. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Choi, W.-J.; Han, G.-H.; Lee, S.-M.; Lee, G.-T.; Yoon, K.-S.; Choi, S.-M.; Ro, H.-M. Impact of land-use types on nitrate concentration and δ15N in unconfined groundwater in rural areas of Korea. Agric. Ecosyst. Environ. 2007, 120, 259–268. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Z.; Liu, W.-z.; Zhang, X.-c.; Zheng, F.-l. Impacts of land use change and climate variability on hydrology in an agricultural catchment on the Loess Plateau of China. J. Hydrol. 2009, 377, 35–42. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, B.; Chang, S.X.; Lam, S.K.; Erisman, J.W.; Gu, B. Land use mediates riverine nitrogen export under the dominant influence of human activities. Environ. Res. Lett. 2017, 12, 094018. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chang, D.; Li, S.; Lai, Z. Effects of extreme precipitation intensity and duration on the runoff and nutrient yields. J. Hydrol. 2023, 626, 130281. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, K.; Onodera, S.-i.; Saito, M.; Ishida, T. Assessment of long-term phosphorus budget changes influenced by anthropogenic factors in a coastal catchment of Osaka Bay. Sci. Total Environ. 2022, 843, 156833. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, X.; Wang, H.-Y.; Zhou, J.; Hu, F.; Zhu, D.; Chen, Z.; Liu, Y. Effect of N Fertilization Pattern on Rice Yield, N Use Efficiency and Fertilizer–N Fate in the Yangtze River Basin, China. PLoS ONE 2016, 11, e0166002. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Woznicki, S.; Nejadhashemi, A.; Smith, C. Assessing Best Management Practice Implementation Strategies Under Climate Change Scenarios. Trans. ASABE 2011, 54, 171–190. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Akan, A.O.; Atabay, S. Grass filter strip residence time-trap efficiency relationship. Water Environ. J. 2017, 31, 277–283. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- López-Ballesteros, A.; Trolle, D.; Srinivasan, R.; Senent-Aparicio, J. Assessing the effectiveness of potential best management practices for science-informed decision support at the watershed scale: The case of the Mar Menor coastal lagoon, Spain. Sci. Total Environ. 2023, 859, 160144. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Y.; Guo, T.; Wang, R.; Engel, B.A.; Flanagan, D.C.; Li, S.; Pijanowski, B.C.; Collingsworth, P.D.; Lee, J.G.; Wallace, C.W. A SWAT-based optimization tool for obtaining cost-effective strategies for agricultural conservation practice implementation at watershed scales. Sci. Total Environ. 2019, 691, 685–696. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
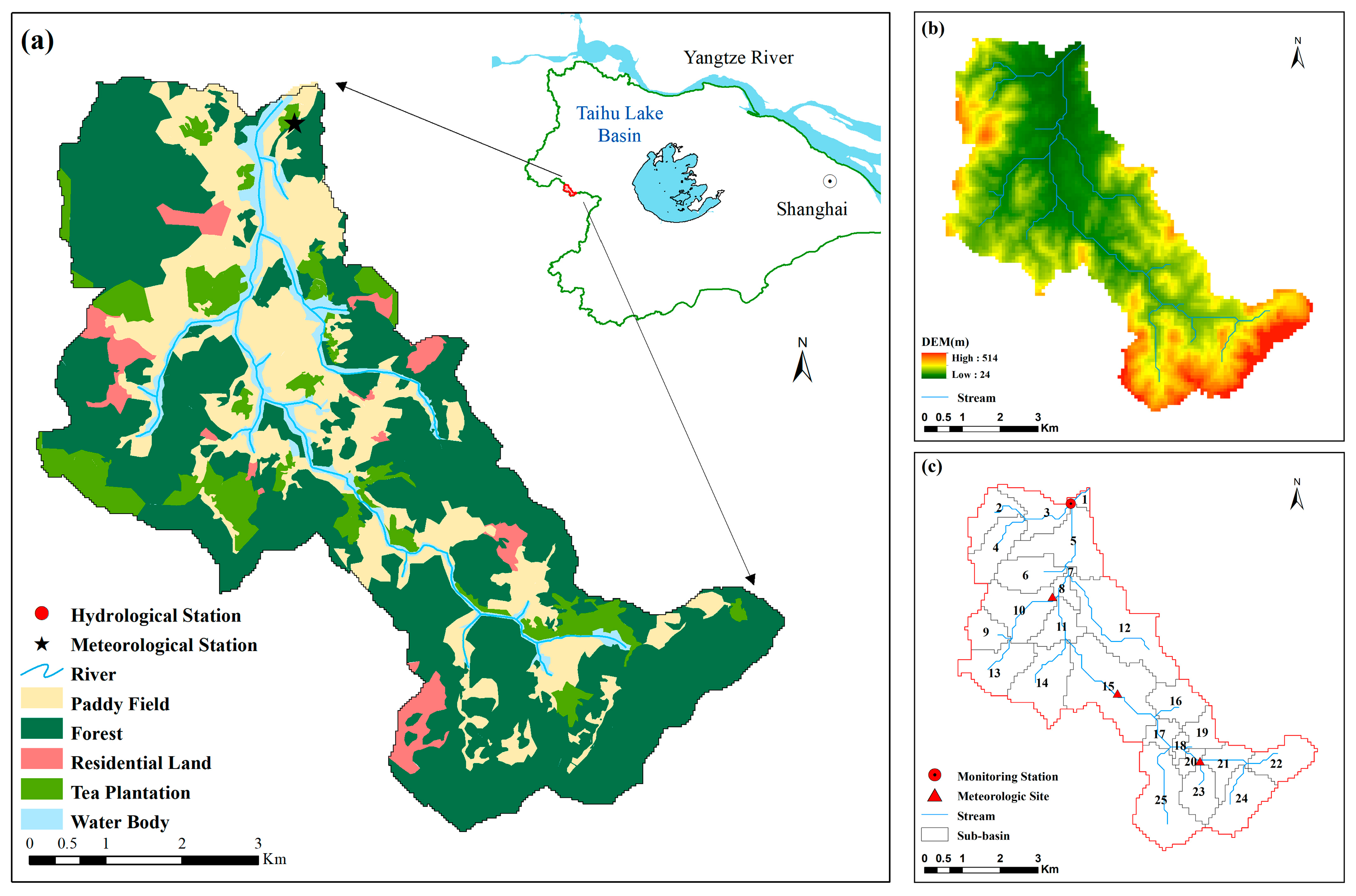
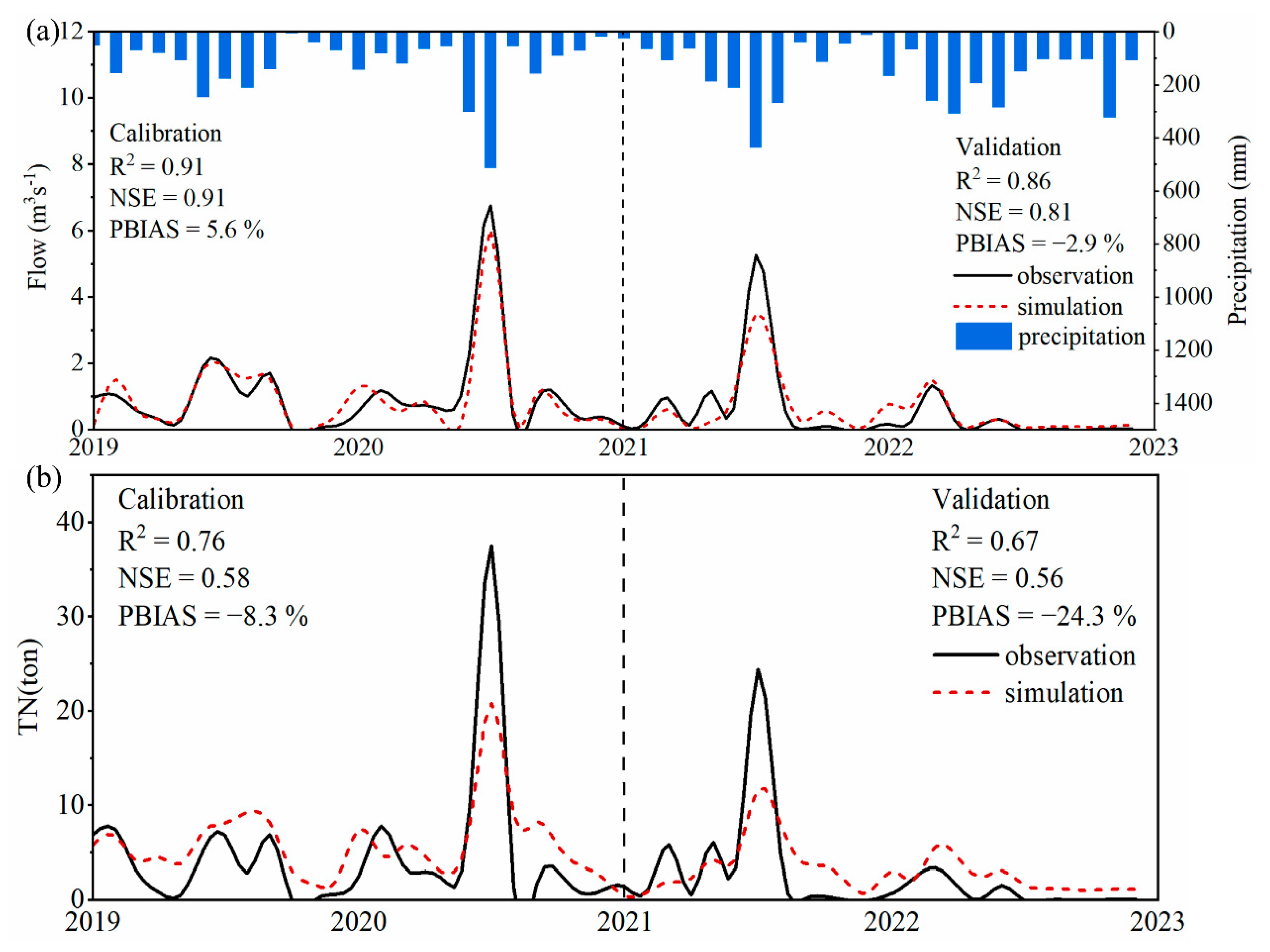


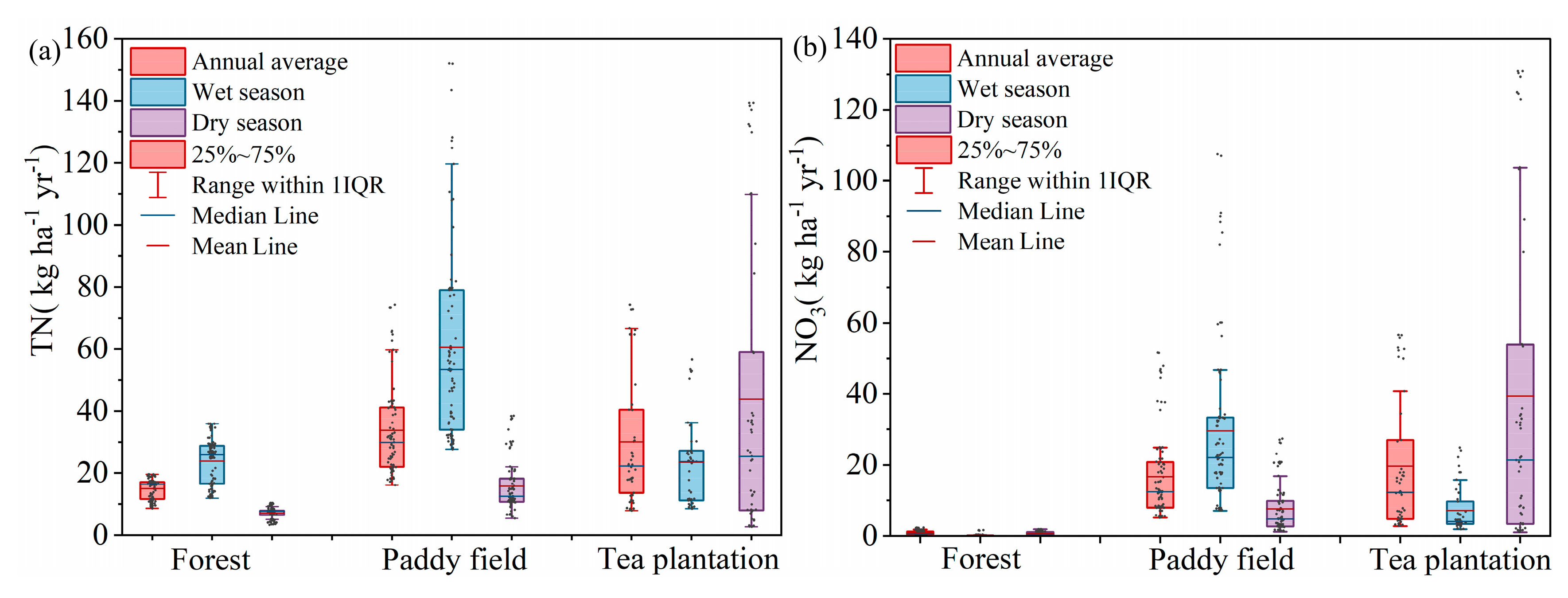

| Data Type | Source |
|---|---|
| DEM | NASA Aster G-DEM (https://www.earthdata.nasa.gov/news/new-aster-gdem, accessed on 15 March 2024) |
| Soil | The Soil Archives of Jiangsu Province and field survey |
| Land use | CNLUCC and field survey (http://www.resdc.cn, accessed on 15 March 2024) |
| Climate | The Jiangsu Provincial Meteorological Administration |
| Fertilization | Tianmuhu town, Changzhou City statistical yearbook, and field survey |
| BMP Type | Code | Scenario | Description | RTN | RNO3-N | RORGN |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Agricultural BMPs | FR | Fertilizer reduction | 30% reduction in fertilizer application | 6.44% | 21.26% | / |
| CF | Contour farming | Plowing along contour lines | 4.75% | / | 6.94% | |
| RM | Residue Management | Controlling the amount and distribution of crop/plant residue on the soil surface | 3.66% | / | 5.38% | |
| Engineered BMPs | FS | Filter strips | Set up filter strips with a 10 m width at the farmland periphery | 10.21% | 5.53% | 12.23% |
| GW | Grassed waterways | Set up grassed waterways with a 200 m length and a 0.6 m depth | 21.80% | 9.60% | 27.07% |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Shen, W.; Chen, R.; Zhao, X.; Lu, X.; Yan, H.; Wang, L. Implementing Best Management Practices in Complex Agricultural Watersheds: Insights from High-Resolution Nitrogen Load Dynamics Analysis. Water 2025, 17, 821. https://doi.org/10.3390/w17060821
Shen W, Chen R, Zhao X, Lu X, Yan H, Wang L. Implementing Best Management Practices in Complex Agricultural Watersheds: Insights from High-Resolution Nitrogen Load Dynamics Analysis. Water. 2025; 17(6):821. https://doi.org/10.3390/w17060821
Chicago/Turabian StyleShen, Wanqi, Ruidong Chen, Xingchen Zhao, Xiaoming Lu, Hao Yan, and Lachun Wang. 2025. "Implementing Best Management Practices in Complex Agricultural Watersheds: Insights from High-Resolution Nitrogen Load Dynamics Analysis" Water 17, no. 6: 821. https://doi.org/10.3390/w17060821
APA StyleShen, W., Chen, R., Zhao, X., Lu, X., Yan, H., & Wang, L. (2025). Implementing Best Management Practices in Complex Agricultural Watersheds: Insights from High-Resolution Nitrogen Load Dynamics Analysis. Water, 17(6), 821. https://doi.org/10.3390/w17060821





