Irrigation Promotes Arsenic Mobilization via Goethite: Insight from the Perspective of the Solid–Liquid Interface Interaction Process
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Materials
2.2. Batch Experiments
2.2.1. Saline–Alkali Environment and PO43− and FA Input
2.2.2. Oxic and Anoxic Experiments
2.3. Column Experiments
2.3.1. Synthesis of Goethite-Coated Quartz Sand
2.3.2. Method of Column Experiments
2.4. Analytical Methods
2.4.1. Aqueous Phase Analysis
2.4.2. XPS and FTIR Analyses
2.5. Statistical Analysis
3. Results and Discussion
3.1. Adsorption of As(III) on Goethite Surface
3.1.1. Effects of the Saline–Alkali Environment
3.1.2. Effects of PO43− and FA
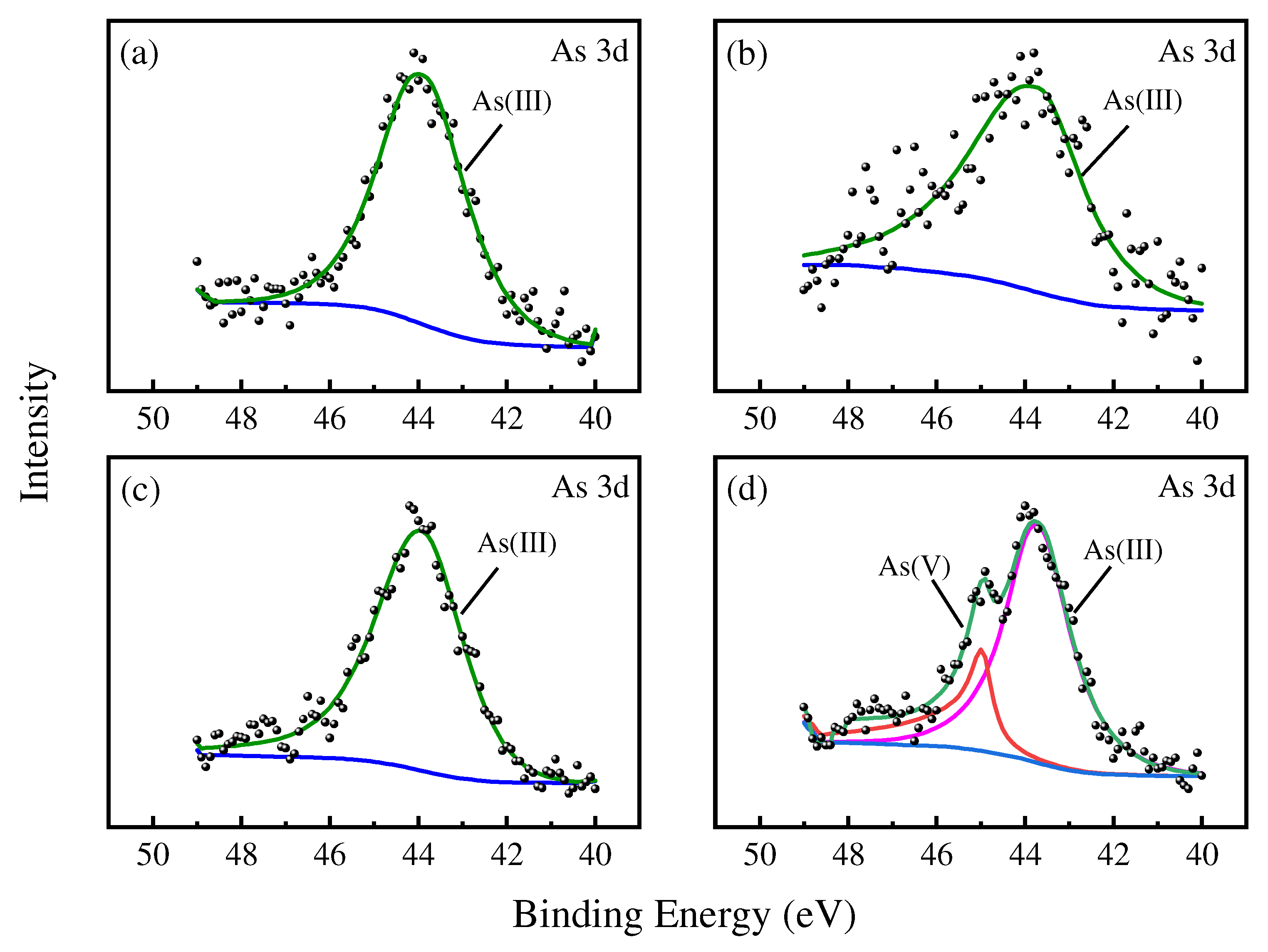
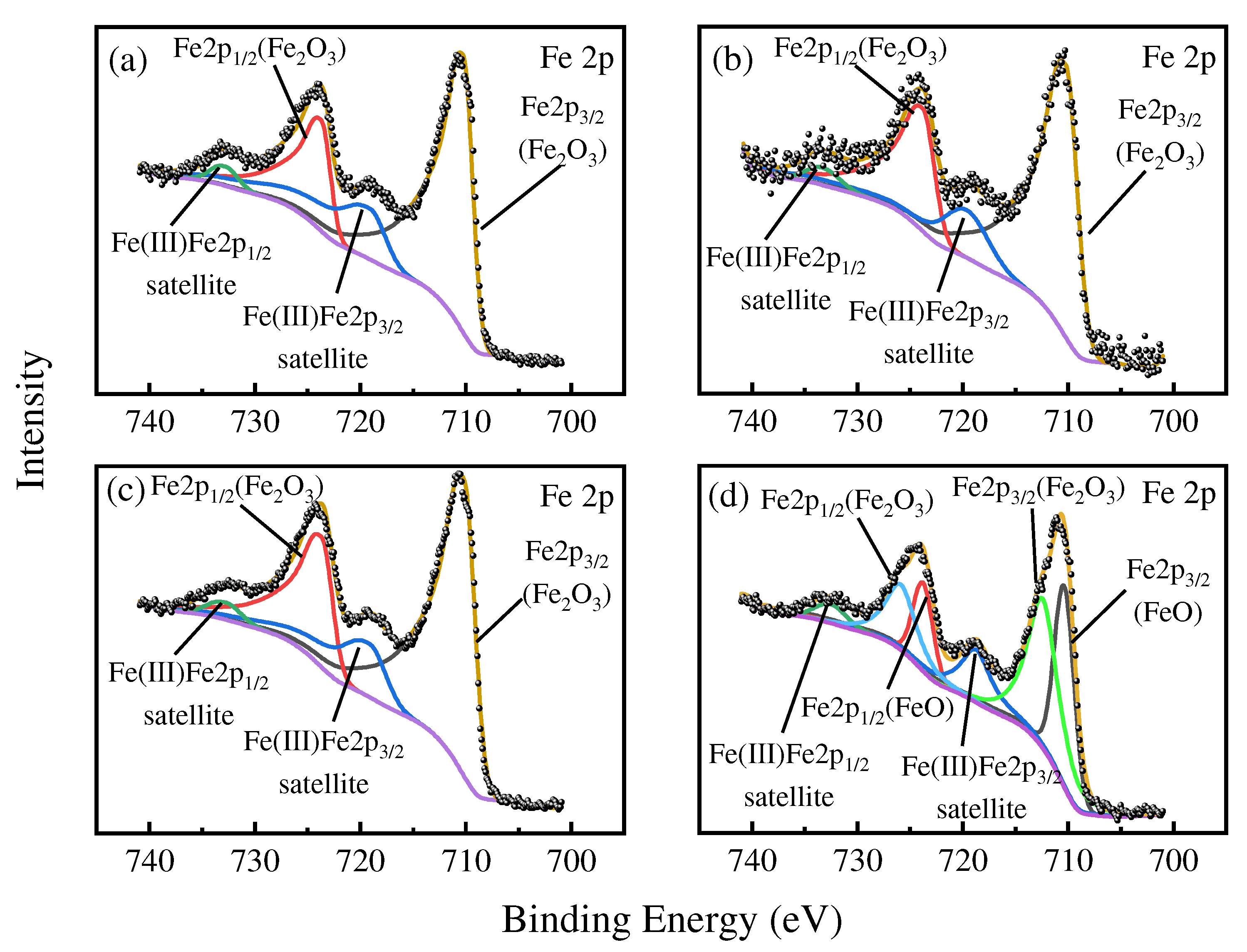
3.1.3. XPS and FTIR Analyses
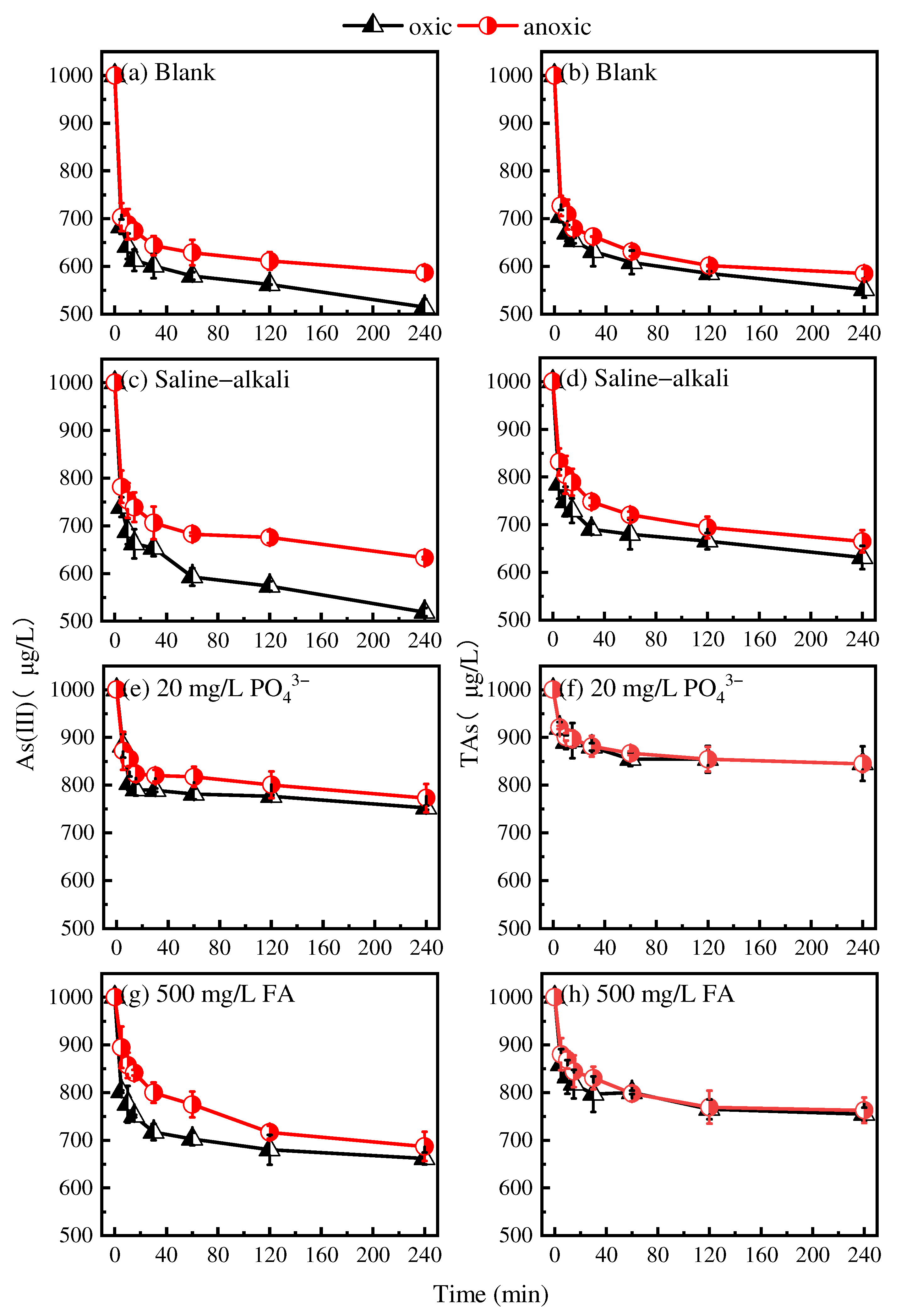
3.2. Adsorption of As(III) Under Oxic and Anoxic Conditions
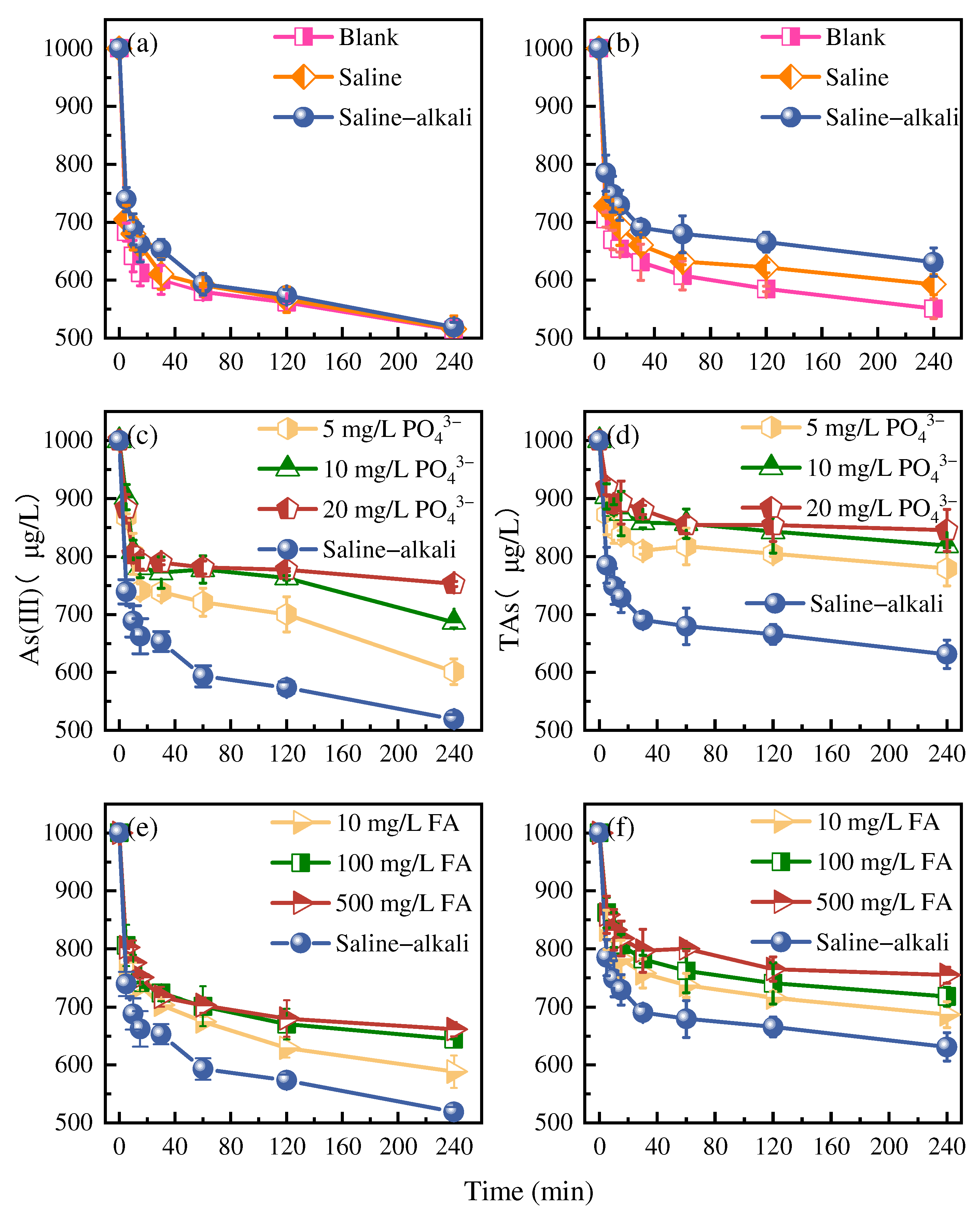
3.3. As Mobilization During Irrigation
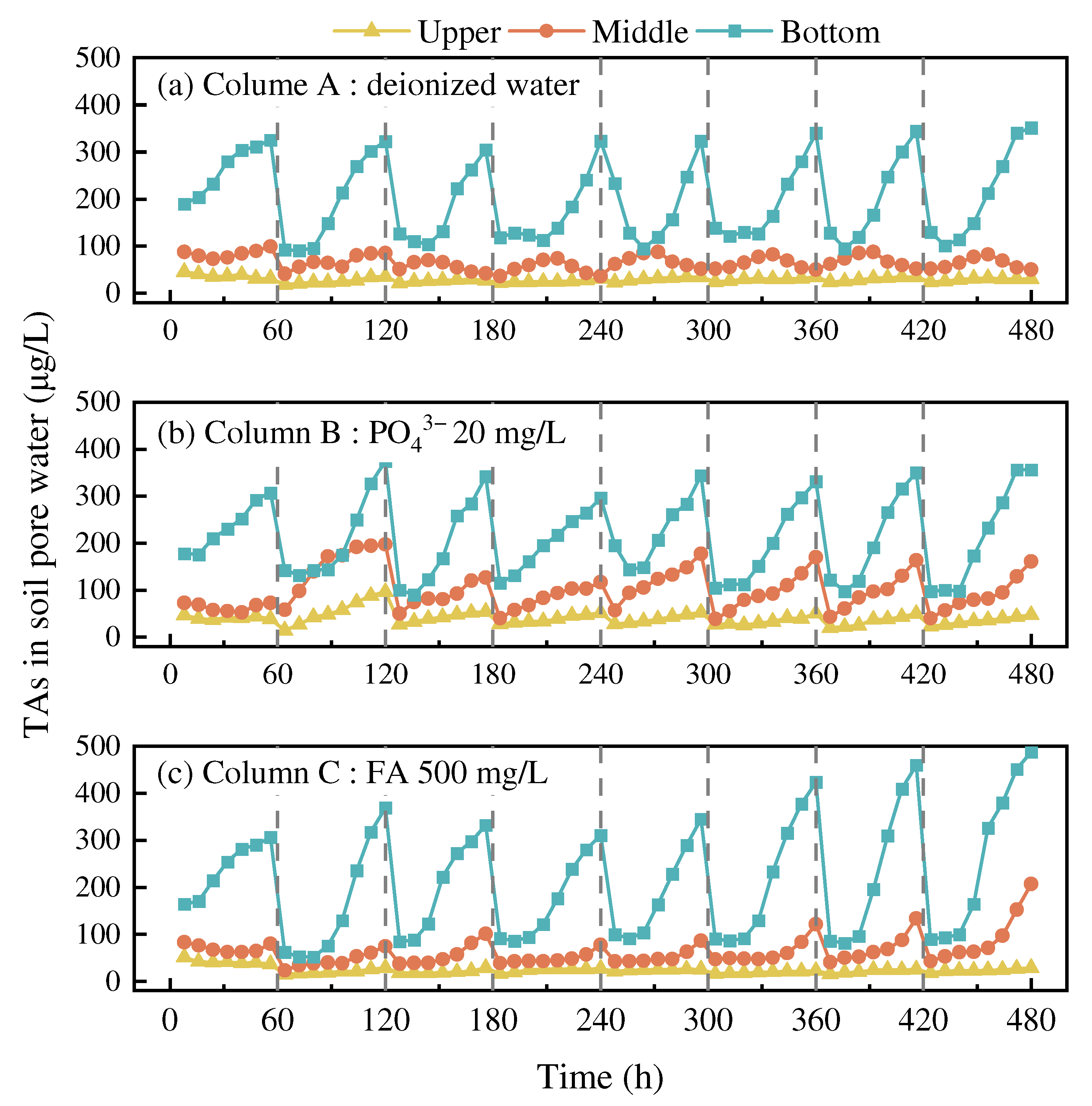
3.3.1. Variations in As Content in Pore Water
3.3.2. Influence of Irrigation Water Composition
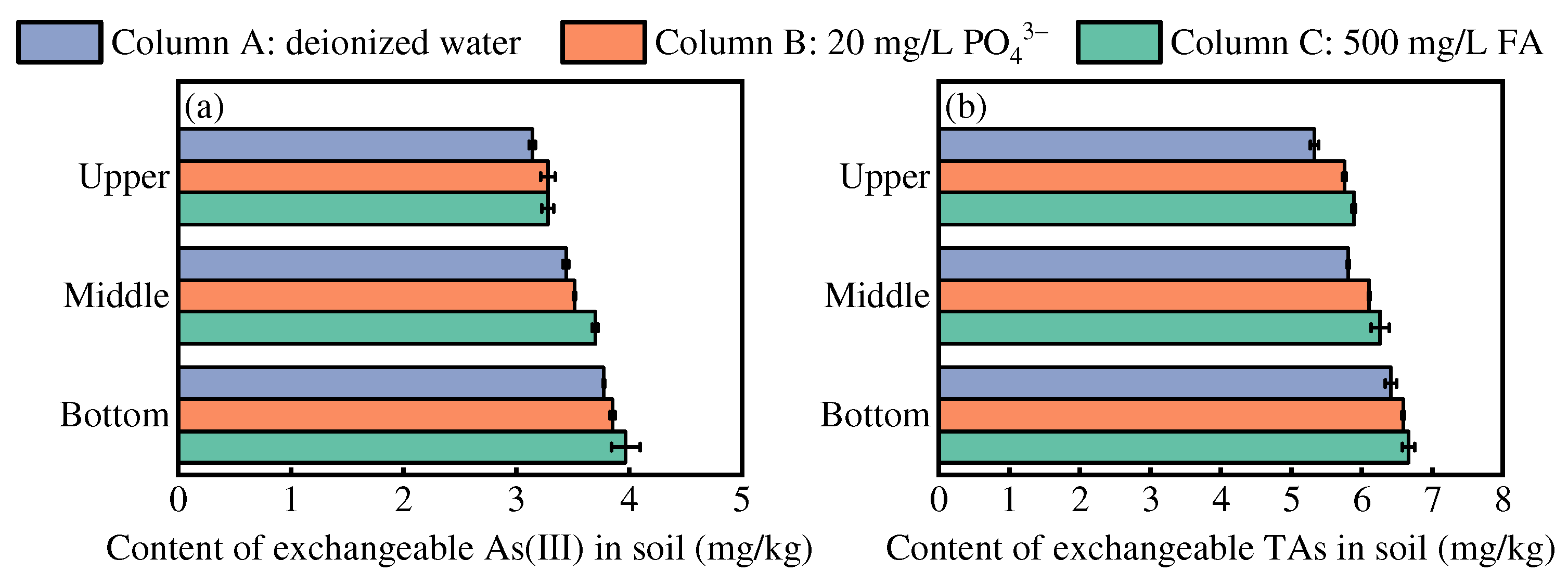
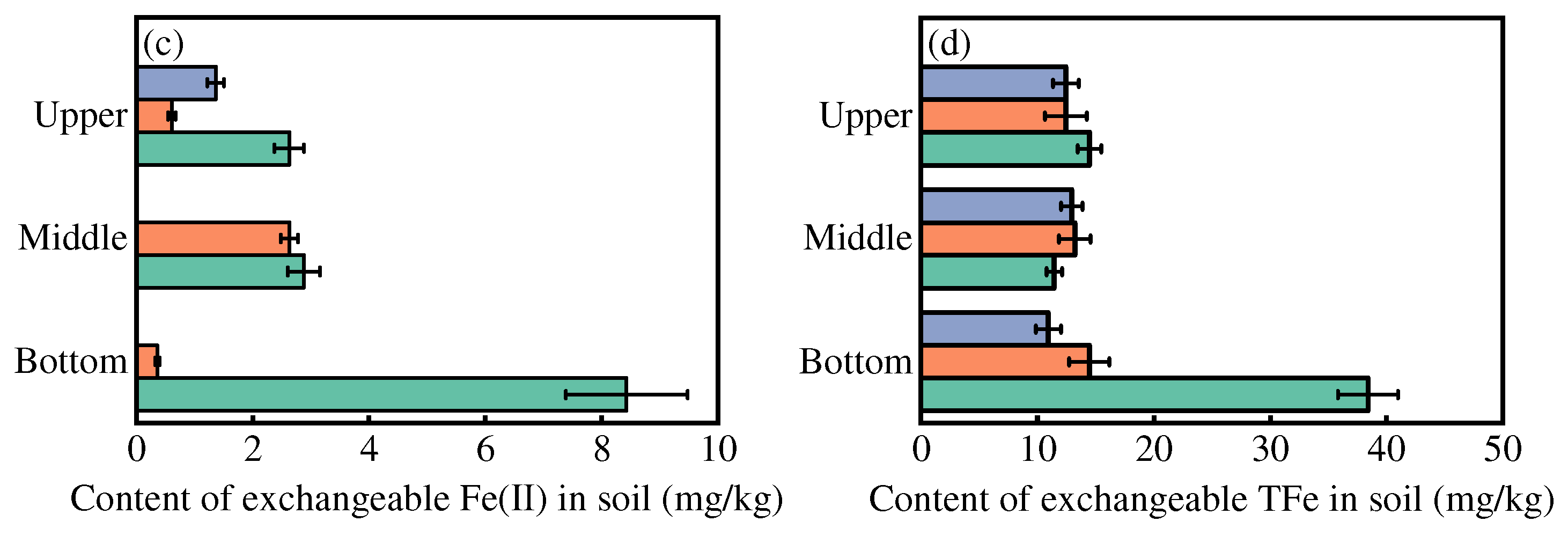
3.4. Mechanism of As Mobilization During Irrigation
4. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Srivastava, A.K.; Pandey, M.; Ghate, T.; Kumar, V.; Upadhyay, M.K.; Majumdar, A.; Sanjukta, A.K.; Agrawal, A.K.; Bose, S.; Srivastava, S.; et al. Chemical intervention for enhancing growth and reducing grain arsenic accumulation in rice. Environ. Pollut. 2021, 276, 116719. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, Y.; Pi, K.; Fendorf, S.; Deng, Y.; Xie, X. Sedimentogenesis and hydrobiogeochemistry of high arsenic Late Pleistocene-Holocene aquifer systems. Earth-Sci. Rev. 2019, 189, 79–98. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xiao, Z.; Xie, X.; Pi, K.; Gong, J.; Wang, Y. Impact of organic matter on arsenic mobilization induced by irrigation in the unsaturated and saturated zones. J. Hydrol. 2021, 602, 126821. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mishra, R.K.; Tiwari, S.; Patel, A.; Prasad, S.M. Arsenic contamination, speciation, toxicity and defense strategies in plants. Braz. J. Bot. 2021, 44, 1–10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schiavo, M. The role of different sources of uncertainty on the stochastic quantification of subsurface discharges in heterogeneous aquifers. J. Hydrol. 2023, 617, 128930. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schiavo, M. Entropy, fractality, and thermodynamics of groundwater pathways. J. Hydrol. 2023, 623, 129824. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, J.; Wang, Y.; Xie, X. Cl/Br ratios and chlorine isotope evidences for groundwater salinization and its impact on groundwater arsenic, fluoride and iodine enrichment in the Datong basin, China. Sci. Total Environ. 2016, 544, 158–167. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ayers, J.C.; Goodbred, S.; George, G.; Fry, D.; Benneyworth, L.; Hornberger, G.; Roy, K.; Karim, M.R.; Akter, F. Sources of salinity and arsenic in groundwater in southwest Bangladesh. Geochem. Trans. 2016, 17, 4. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Eiche, E.; Neumann, T.; Berg, M.; Weinman, B.; van Geen, A.; Norra, S.; Berner, Z.; Trang, P.T.K.; Viet, P.H.; Stüben, D. Geochemical processes underlying a sharp contrast in groundwater arsenic concentrations in a village on the Red River delta, Vietnam. Appl. Geochem. 2008, 23, 3143–3154. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rowland, H.A.L.; Omoregie, E.O.; Millot, R.; Jimenez, C.; Mertens, J.; Baciu, C.; Hug, S.J.; Berg, M. Geochemistry and arsenic behaviour in groundwater resources of the Pannonian Basin (Hungary and Romania). Appl. Geochem. 2011, 26, 1–17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, H.; Liu, C.; Lu, H.; Wanty, R.B.; Wang, J.; Zhou, Y. Pathways of coupled arsenic and iron cycling in high arsenic groundwater of the Hetao basin, Inner Mongolia, China: An iron isotope approach. Geochim. Cosmochim. Acta 2013, 112, 130–145. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jia, Y.; Guo, H.; Xi, B.; Jiang, Y.; Zhang, Z.; Yuan, R.; Yi, W.; Xue, X. Sources of groundwater salinity and potential impact on arsenic mobility in the western Hetao Basin, Inner Mongolia. Sci. Total Environ. 2017, 601–602, 691–702. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gao, Z.; Guo, H.; Li, S.; Wang, J.; Ye, H.; Han, S.; Cao, W. Remote sensing of wetland evolution in predicting shallow groundwater arsenic distribution in two typical inland basins. Sci. Total Environ. 2022, 806, 150496. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gao, Z.P.; Jia, Y.F.; Guo, H.M.; Zhang, D.; Zhao, B. Quantifying Geochemical Processes of Arsenic Mobility in Groundwater From an Inland Basin Using a Reactive Transport Model. Water Resour. Res. 2020, 56, 22. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, H.; Zhou, Y.; Jia, Y.; Tang, X.; Li, X.; Shen, M.; Lu, H.; Han, S.; Wei, C.; Norra, S.; et al. Sulfur Cycling-Related Biogeochemical Processes of Arsenic Mobilization in the Western Hetao Basin, China: Evidence from Multiple Isotope Approaches. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2016, 50, 12650–12659. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, C.; Bundschuh, J.; Gao, X.; Li, Y.; Zhang, X.; Luo, W.; Pan, Z. Occurrence and behavior of arsenic in groundwater-aquifer system of irrigated areas. Sci. Total Environ. 2022, 838, 155991. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xie, X.J.; Wang, Y.X.; Su, C.L.; Li, J.X.; Li, M.D. Influence of irrigation practices on arsenic mobilization: Evidence from isotope composition and Cl/Br ratios in groundwater from Datong Basin, northern China. J. Hydrol. 2012, 424, 37–47. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, J.; Xie, X.; Wang, Y. Effects of the groundwater flowing and redox conditions on arsenic mobilization in aquifers of the Datong Basin, Northern China. J. Hydrol. 2024, 636, 131256. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, S.; Mulligan, C.N. Effect of natural organic matter on arsenic release from soilsand sediments into groundwater. Environ. Geochem. Health 2006, 28, 197–214. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, H.; Zhang, D.; Ni, P.; Cao, Y.; Li, F.; Jia, Y.; Li, H.; Wan, L.; Wang, G. On the scalability of hydrogeochemical factors controlling arsenic mobility in three major inland basins of P.R. China. Appl. Geochem. 2017, 77, 15–23. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Amstaetter, K.; Borch, T.; Larese-Casanova, P.; Kappler, A. Redox Transformation of Arsenic by Fe(II)-Activated Goethite (α-FeOOH). Environ. Sci. Technol. 2010, 44, 102–108. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cheng, H.; Hu, Y.; Luo, J.; Xu, B.; Zhao, J. Geochemical processes controlling fate and transport of arsenic in acid mine drainage (AMD) and natural systems. J. Hazard. Mater. 2009, 165, 13–26. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tang, W.-W.; Zeng, G.-M.; Gong, J.-L.; Liang, J.; Xu, P.; Zhang, C.; Huang, B.-B. Impact of humic/fulvic acid on the removal of heavy metals from aqueous solutions using nanomaterials: A review. Sci. Total Environ. 2014, 468–469, 1014–1027. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Guo, H.; Li, X.; Xiu, W.; He, W.; Cao, Y.; Zhang, D.; Wang, A. Controls of organic matter bioreactivity on arsenic mobility in shallow aquifers of the Hetao Basin, P.R. China. J. Hydrol. 2019, 571, 448–459. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Deng, W.; Luo, Y.; Wang, X.; Liu, K. Distribution characteristics and cause analysis of arsenic and salt in groundwater in Kuitun area of Xinjiang (in Chinese). Environ. Pollut. Control. 2021, 43, 1404–1409. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Scheidegger, A.; Borkovec, M.; Sticher, H. Coating of silica sand with goethite: Preparation and analytical identification. Geoderma 1993, 58, 43–65. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, D.; Guo, H.; Xiu, W.; Ni, P.; Zheng, H.; Wei, C. In-situ mobilization and transformation of iron oxides-adsorbed arsenate in natural groundwater. J. Hazard. Mater. 2017, 321, 228–237. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hua, J.; Fei, Y.-h.; Feng, C.; Liu, C.; Liang, S.; Wang, S.-L.; Wu, F. Anoxic oxidation of As(III) during Fe(II)-induced goethite recrystallization: Evidence and importance of Fe(IV) intermediate. J. Hazard. Mater. 2022, 421, 126806. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Frierdich, A.J.; Helgeson, M.; Liu, C.; Wang, C.; Rosso, K.M.; Scherer, M.M. Iron Atom Exchange between Hematite and Aqueous Fe(II). Environ. Sci. Technol. 2015, 49, 8479–8486. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bianchi Janetti, E.; Dror, I.; Riva, M.; Guadagnini, A.; Sanchez-Vila, X.; Berkowitz, B. Mobility and Interaction of Heavy Metals in a Natural Soil. Transp. Porous Media 2013, 97, 295–315. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yin, S.H.; Tian, Y.; Yang, L.S.; Wen, Q.Q.; Wei, B.G. Dynamics of Spatiotemporal Variation of Groundwater Arsenic Due to Salt-Leaching Irrigation and Saline-Alkali Land. Remote Sens. 2022, 14, 18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Saalfield, S.L.; Bostick, B.C. Synergistic effect of calcium and bicarbonate in enhancing arsenate release from ferrihydrite. Geochim. Cosmochim. Acta 2010, 74, 5171–5186. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bissen, M.; Frimmel, F.H. Arsenic-a review. Part II: Oxidation of arsenic and its removal in water treatment. Acta Hydroch. Hydrob. 2003, 31, 97–107. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, X.; Doner, H.E. Adsorption and oxidation of arsenite on goethite. Soil Sci. 1998, 163, 278–287. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, M.-J.; Nriagu, J. Oxidation of arsenite in groundwater using ozone and oxygen. Sci. Total Environ. 2000, 247, 71–79. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yuan, C.; Li, Q.; Sun, Z.; Zhang, W.; Chen, J.; Chen, Z.; Na, S.; Sun, H. Chemical oxidation of arsenic in the environment and its application in remediation: A mini review. Pedosphere 2023, 33, 185–193. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lou, Z.; Cao, Z.; Xu, J.; Zhou, X.; Zhu, J.; Liu, X.; Ali Baig, S.; Zhou, J.; Xu, X. Enhanced removal of As(III)/(V) from water by simultaneously supported and stabilized Fe-Mn binary oxide nanohybrids. Chem. Eng. J. 2017, 322, 710–721. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, F.; Guo, H.; Zhou, X.; Zhao, K.; Shen, J.; Liu, F.; Wei, C. Impact of natural organic matter on arsenic removal by modified granular natural siderite: Evidence of ternary complex formation by HPSEC-UV-ICP-MS. Chemosphere 2017, 168, 777–785. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Otero-Fariña, A.; Fiol, S.; Arce, F.; Antelo, J. Effects of natural organic matter on the binding of arsenate and copper onto goethite. Chem. Geol. 2017, 459, 119–128. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fakour, H.; Lin, T.-F. Experimental determination and modeling of arsenic complexation with humic and fulvic acids. J. Hazard. Mater. 2014, 279, 569–578. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sharma, P.; Ofner, J.; Kappler, A. Formation of Binary and Ternary Colloids and Dissolved Complexes of Organic Matter, Fe and As. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2010, 44, 4479–4485. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- An, X.-L.; Huang, F.-G.; Ren, H.-T.; Wang, Y.-F.; Chen, Y.; Liu, Z.-M.; Zhang, H.-W.; Han, X. Oxidative dissolution of amorphous FeS and speciation of secondary Fe minerals: Effects of pH and As(III) concentration. Chem. Geol. 2017, 462, 44–54. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moghaddam, A.Z.; Esmaeilkhanian, E.; Shakourian-Fard, M. Immobilizing magnetic glutaraldehyde cross-linked chitosan on graphene oxide and nitrogen-doped graphene oxide as well-dispersible adsorbents for chromate removal from aqueous solutions. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2019, 128, 61–73. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shan, H.; Peng, S.; Zhao, C.; Zhan, H.; Zeng, C. Highly efficient removal of As(III) from aqueous solutions using goethite/graphene oxide/chitosan nanocomposite. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2020, 164, 13–26. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mei, L.; Liao, L.; Wang, Z.; Xu, C. Interactions between phosphoric/tannic acid and different forms of FeOOH. Adv. Mater. Sci. Eng. 2015, 2015, 250836. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, M.; Li, Y.; Long, X.; Chong, Y.; Yu, G.; He, Z. An alternative approach for nitrate and arsenic removal from wastewater via a nitrate-dependent ferrous oxidation process. J. Environ. Manag. 2018, 220, 246–252. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cai, D.W.; Kong, S.Q.; Shao, Y.X.; Liu, J.J.; Liu, R.Q.; Wei, X.U.; Bai, B.; Werner, D.; Gao, X.B.; Li, C.C. Mobilization of arsenic from As-containing iron minerals under irrigation: Effects of exogenous substances, redox condition, and intermittent flow. J. Hazard. Mater. 2022, 440, 11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brechbühl, Y.; Christl, I.; Elzinga, E.J.; Kretzschmar, R. Competitive sorption of carbonate and arsenic to hematite: Combined ATR-FTIR and batch experiments. J. Colloid Interface Sci. 2012, 377, 313–321. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, X.; Liu, T.; Li, F.; Zhang, W.; Zhou, S.; Li, Y. Reduction of structural Fe(III) in oxyhydroxides by Shewanella decolorationis S12 and characterization of the surface properties of iron minerals. J. Soils Sediments 2012, 12, 217–227. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, X.; Li, W.; Harrington, R.; Liu, F.; Parise, J.B.; Feng, X.; Sparks, D.L. Effect of Ferrihydrite Crystallite Size on Phosphate Adsorption Reactivity. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2013, 47, 10322–10331. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, X.; Wang, J.; He, Y.; Li, J.; Tian, Q.; Xu, H. The redistribution process of As(III) and Fe(II) caused by As/Fe ratio, organic matter, and co-existing ions: Co-precipitation and co-oxidation. Ecotoxicol. Environ. Saf. 2024, 281, 116631. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ololade, I.A.; Zhou, Q.; Pan, G. Influence of oxic/anoxic condition on sorption behavior of PFOS in sediment. Chemosphere 2016, 150, 798–803. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Busbee, M.W.; Kocar, B.D.; Benner, S.G. Irrigation produces elevated arsenic in the underlying groundwater of a semi-arid basin in Southwestern Idaho. Appl. Geochem. 2009, 24, 843–859. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huling, J.R.; Huling, S.G.; Ludwig, R. Enhanced adsorption of arsenic through the oxidative treatment of reduced aquifer solids. Water Res. 2017, 123, 183–191. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cao, H.; He, J.; Xie, X.; Wang, Y.; Li, J.; Qian, K.; Deng, Y.; Gan, Y. The effect of groundwater velocities on sulfidation of arsenic-bearing ferrihydrite: Insight from column experiments. J. Hydrol. 2020, 586, 124827. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Melnikova, A.; Faggiano, A.; Visconti, M.; Cucciniello, R.; Iannece, P.; Kostryukova, N.; Proto, A.; Fiorentino, A.; Rizzo, L. Photo driven homogeneous advanced oxidation coupled to adsorption process for an effective arsenic removal from drinking water. J. Environ. Manag. 2024, 349, 9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chi, Z.Y.; Xie, X.J.; Wang, Y.X. Understanding spatial heterogeneity of groundwater arsenic concentrations at a field scale: Taking the Datong Basin as an example to explore the significance of hydrogeological factors. J. Environ. Manag. 2024, 352, 11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, M.; Wang, X.M.; Wei, C.Y.; Wang, M.L.; Han, W.; Yuan, Z.; Ji, H.B. Effects of exogenous phosphates on speciation and bioavailability of arsenic and cadmium in farmland soils. J. Soils Sediments 2023, 23, 1832–1843. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Paikaray, S.; Peiffer, S. Arsenic fractionation and mobilization in agricultural soils of NE Punjab, India. Appl. Geochem. 2022, 139, 105255. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.; Zhang, L.; Guo, C.; Gao, Y.; Pan, S.; Liu, Y.; Li, X.; Wang, Y. Arsenic removal performance and mechanism from water on iron hydroxide nanopetalines. Sci. Rep. 2022, 12, 17264. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
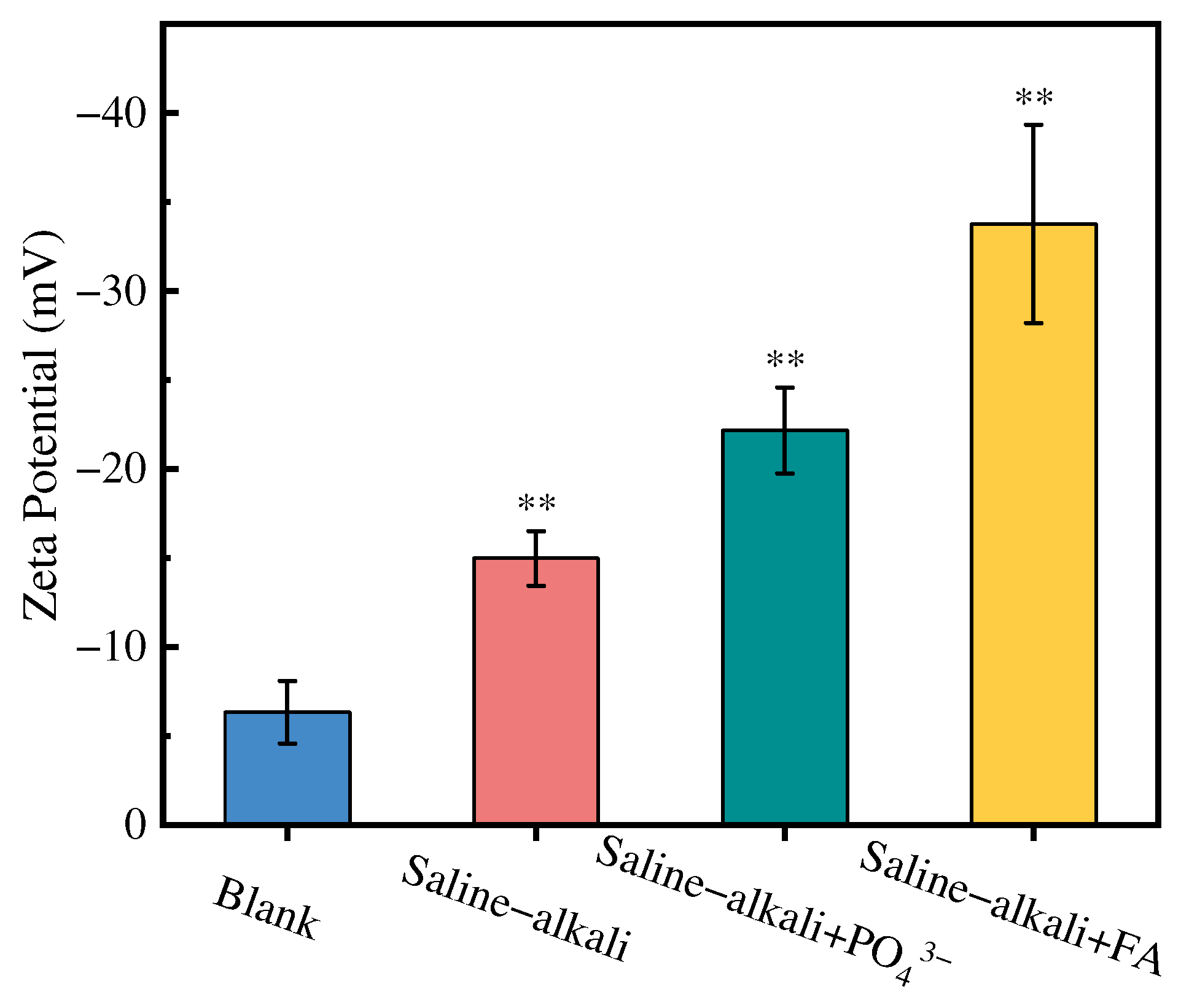


Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Xu, H.; Wang, Y.; Wang, J.; Liu, X.; Chen, C.; Zhou, C.; Tian, Q. Irrigation Promotes Arsenic Mobilization via Goethite: Insight from the Perspective of the Solid–Liquid Interface Interaction Process. Water 2025, 17, 1058. https://doi.org/10.3390/w17071058
Xu H, Wang Y, Wang J, Liu X, Chen C, Zhou C, Tian Q. Irrigation Promotes Arsenic Mobilization via Goethite: Insight from the Perspective of the Solid–Liquid Interface Interaction Process. Water. 2025; 17(7):1058. https://doi.org/10.3390/w17071058
Chicago/Turabian StyleXu, Hong, Yaru Wang, Jiankang Wang, Xin Liu, Cuizhong Chen, Chang Zhou, and Qingyuan Tian. 2025. "Irrigation Promotes Arsenic Mobilization via Goethite: Insight from the Perspective of the Solid–Liquid Interface Interaction Process" Water 17, no. 7: 1058. https://doi.org/10.3390/w17071058
APA StyleXu, H., Wang, Y., Wang, J., Liu, X., Chen, C., Zhou, C., & Tian, Q. (2025). Irrigation Promotes Arsenic Mobilization via Goethite: Insight from the Perspective of the Solid–Liquid Interface Interaction Process. Water, 17(7), 1058. https://doi.org/10.3390/w17071058





