Abstract
The anticipated rise in extreme flood events in the Eastern Mediterranean region indicates an increase in significant societal impacts that have the potential to extend beyond the flooded areas and affect multiple sectors. Despite the criticality of understanding storm and flood risk and how they propagate in modern interconnected societies, the scope and complexity of storm- and flood-triggered cascading effects are still poorly comprehended. This study explores the effects created by the extreme Storm Daniel, occurring in Thessaly, Greece in 2023, aiming to gather new evidence on the types and scale of these cascading effects by analyzing its impacts in the region through fieldwork and official data collection. The results, as a contribution to existing knowledge on cascade effects, provide insights into the nature, the extent, the propagation mechanisms, and the consequences of these triggering events leading to diverse cascade effects. The study identifies the interactions between different phenomena following this extreme storm event to offer a better understanding of how impacts propagate, and therefore a better understanding of future challenges connected with this type of cascading hazards framework, ultimately contributing to predicting and mitigating associated risks.
1. Introduction
Despite recent advances in flood risk management technologies [1,2,3,4] and the numerous initiatives taken by governments, extreme storms and floods continue to pose an important threat in the Mediterranean region and across Europe [5,6,7].
Recent events have shown that their effects can be devastating for communities across the continent [8,9] and globally, in terms of societal, environmental, and economic impacts [10,11,12,13]. Under climate change, extreme storms and floods can become more frequent and more severe [14], leading potentially to more catastrophic impacts.
To deal with these impacts, it is important to gain a better understanding of the variety of effects and the mechanisms by which they propagate. Recently, a body of literature has been developed focusing on the typology and severity of effects of such extreme events, showing the different kinds of impacts that phenomena such as medicanes [15,16], storms [17,18], and flooding [19,20,21,22] can have on the built and natural environment as well as the population.
Modern societies depend heavily on complicated and interconnected systems like power, transport, and communication networks. These systems are very vulnerable to disruptions caused by extreme events like floods. When critical infrastructure fails, the results often spread, causing trouble through many interconnected systems, leading to wider and worse impacts beyond the nearby disaster area [23]. The idea of cascading disasters explains how sequential failures across different systems increase the effects of an initial disaster, complicating response and recovery efforts [24].
For instance, in times of extreme floods, power outages can cause the breakdown of transport systems, and contaminated water supplies can lead to public health issues like disease outbreaks. These cascading effects are especially challenging in urban areas where the need for linked critical infrastructure increases the flow of these troubles [25]. An outstanding case is the 2002 floods in the Czech Republic, where structure breakdowns greatly raised the full effect of the disaster, showing the complex nature of cascading disasters [23]. Similarly, the catastrophic Durunka flood in Egypt back in 1994, where lightning hit oil tanks, sparking fires that caused burning fuel to spread through floodwaters, showed the destructive power of extreme storms, as these cascading effects caused the loss of more than 400 lives [26]. Additionally, the 2024 floods in Valencia, Spain caused not only significant infrastructure damage but also cascading health crises. In Chiva, Valencia, 19 volunteers were poisoned from carbon monoxide while carrying out cleaning work in a flooded garage. The incident, worsened by a broken drainage pump, highlights the interconnections between infrastructure failures and health risks during flood events, further emphasizing the cascading effects of natural disasters [27,28].
Despite advancements in understanding cascading disasters, research specifically targeting cascading effects of floods remains limited [24,27,29,30]. The existing studies mostly highlight the direct consequences such as infrastructure damage and loss of life, while not adequately addressing how these failures spreads through interconnected networks [25]. This knowledge gap is especially evident in urban areas where critical infrastructure interdependence significantly heightens the risk of cascading disasters [23].
In fact, the current understanding of cascading disaster effects, particularly in the context of storms and floods, is hindered by certain research gaps. First, there is no universal framework for addressing cascading disasters, as most research emphasizes isolated events and crisis response rather than prevention [31]. Critical gaps include a limited understanding of physical cascading mechanisms, such as how different hazard events interact with each other [31]. Predicting the relationships and cascading effects of severe events like flooding remains a complex task. As technology dependence and interconnections spread across communities, the complexity of systemic interactions increases, which heightens the risks of unexpected cascading consequences. Existing risk models struggle to account for multidimensional, interdependent hazards, and do not have the necessary tools to accurately predict and manage these complex connections, making it challenging to quantify how an initial event influences subsequent risks or predict the timing of these events [24,31]. This limitation is compounded by an underestimation of the interdependencies among critical infrastructures, as well as inadequate data on infrastructure vulnerabilities [27,28,32]. Furthermore, assessments often overlook cross-scale impacts; for example, localized responses prescribed by directives like the European Floods Directive may not adequately address large-scale, cascading flood events [25]. Social impacts are similarly underexplored, with insufficient data on long-term effects or the pathways linking disasters to secondary crises [32,33,34].
Collectively, the above issues underscore a need for comprehensive, multidisciplinary approaches that integrate physical, social, and infrastructural dimensions to advance the understanding and management of cascading disaster effects, especially in urban environments [25], where the complexity and interdependence of infrastructure heighten risks.
In this context, the aim of this study is to provide a comprehensive analysis and provide insights into the cascade effects triggered by the extreme storm Daniel in Thessaly, Greece, in September 2023 as a contribution to the limited existing knowledge. By examining the various mechanisms that led to these cascading effects, this research seeks to improve our understanding of how extreme storms and floods can generate complex, interconnected consequences, given the lack of relevant evidence in the existing literature. In the context of climate change, where such events are expected to increase in frequency and intensity, this study aims to shed light on the nature, extent, and propagation of these cascading impacts by creating an inventory of the types of triggers and effects, exploiting evidence presented in the case of Storm Daniel. Through the collection of evidence from this recent event, the study explores the interplay between different types of impacts, such as infrastructure damage, environmental degradation, and societal disruption, that can be useful to enhance preparedness and response strategies for mitigating future risks.
2. The Case of Storm Daniel 2023
In early September 2023, Europe experienced a synoptic-scale weather pattern known as an Omega block, which led to severe weather conditions across multiple regions. An Omega block is characterized by a high-pressure system flanked by two low-pressure systems, forming a configuration reminiscent of the Greek letter omega. This atmospheric pattern exhibited high persistence over the course of a week.
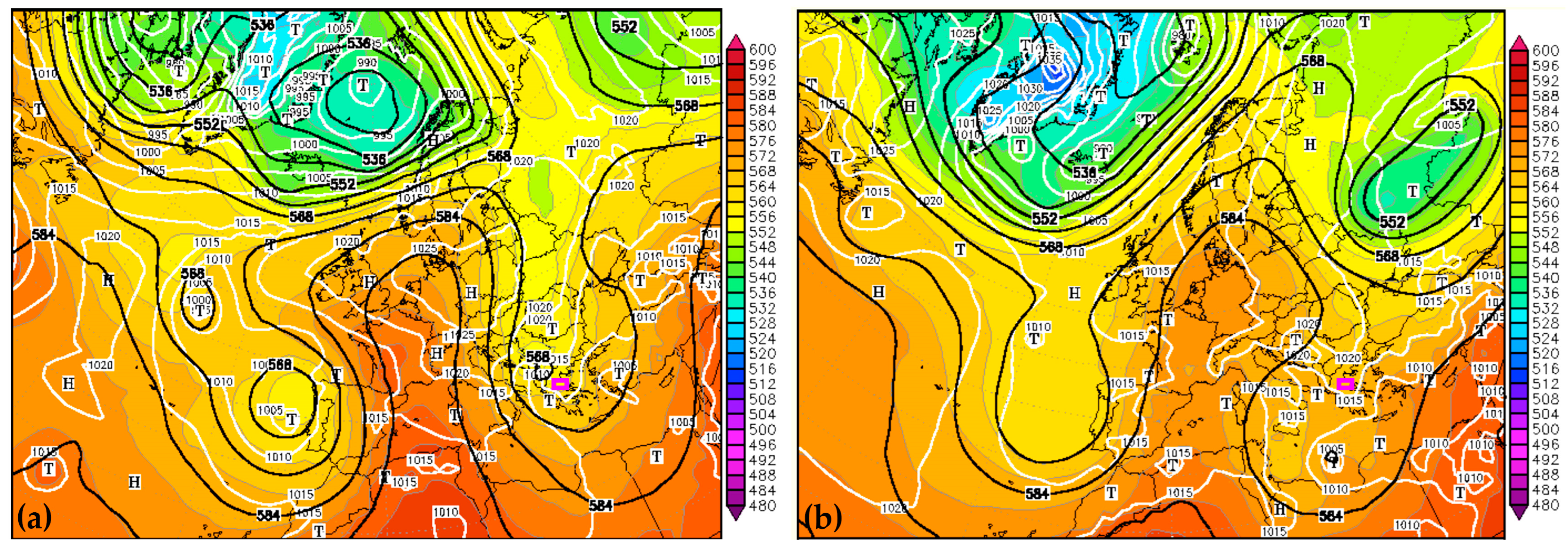
Figure 1a illustrates the synoptic setup at 500 hPa geopotential height alongside surface atmospheric pressure on 4 September 2023, at 12:00 UTC. A deep upper-level low-pressure trough developed along the western coast of the Iberian Peninsula, significantly altering the jet stream by causing it to bend and weaken. This disruption facilitated prolonged atmospheric instability over the Mediterranean region. Simultaneously, an upper-level ridge strengthened rapidly to the east, advecting warm, moist air from North Africa into Europe (Figure 2a), creating favorable conditions for cyclogenesis. The interaction of warm air masses from North Africa with cooler air masses to the north triggered the formation of a surface cyclone near Greece on 4 September 2023. This system was designated Cyclone Daniel under the EUMETNET storm naming initiative. As Cyclone Daniel tracked east-southeastward over the Mediterranean [35], it encountered anomalously warm sea surface temperatures (27–28 °C), which provided additional thermal energy [36]. By 9 September 2023, at 12:00 UTC, the system had intensified into a Mediterranean tropical-like cyclone, or medicane [37], characterized by a well-defined warm core and structural features resembling a tropical cyclone (Figure 1b and Figure 2b). The minimum mean sea-level pressure of the system ranged from 1002 hPa between 4 and 9 September 2023, and 997 hPa between 11 and 12 September, while the system moved from the Ionian Sea towards the Gulf of Sidra and eventually the northern coast of Africa, with an eastward direction [35].
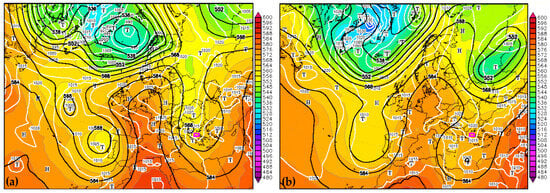
Figure 1.
The synoptic conditions with respect to 500 hPa geopotential height (gpdam; black lines), the surface atmospheric pressure (hPa; white lines), and the relative topography between 500 hPa and 1000 hPa (gpdam; color scale) at 12:00 UTC, on 4 September 2023 (a) and 9 September 2023 (b), based on the Global Forecast System (GFS) analysis. The pink box denotes the study area in Greece. Thin black lines denote the countries boundaries.
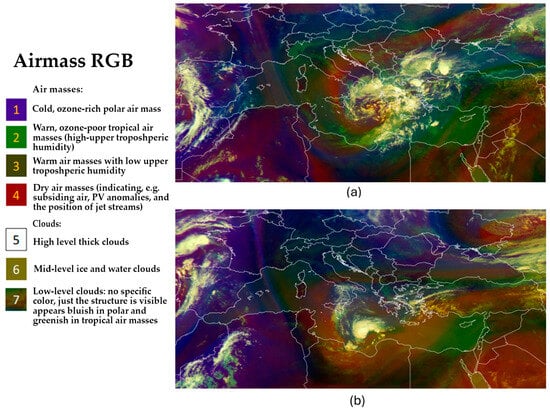
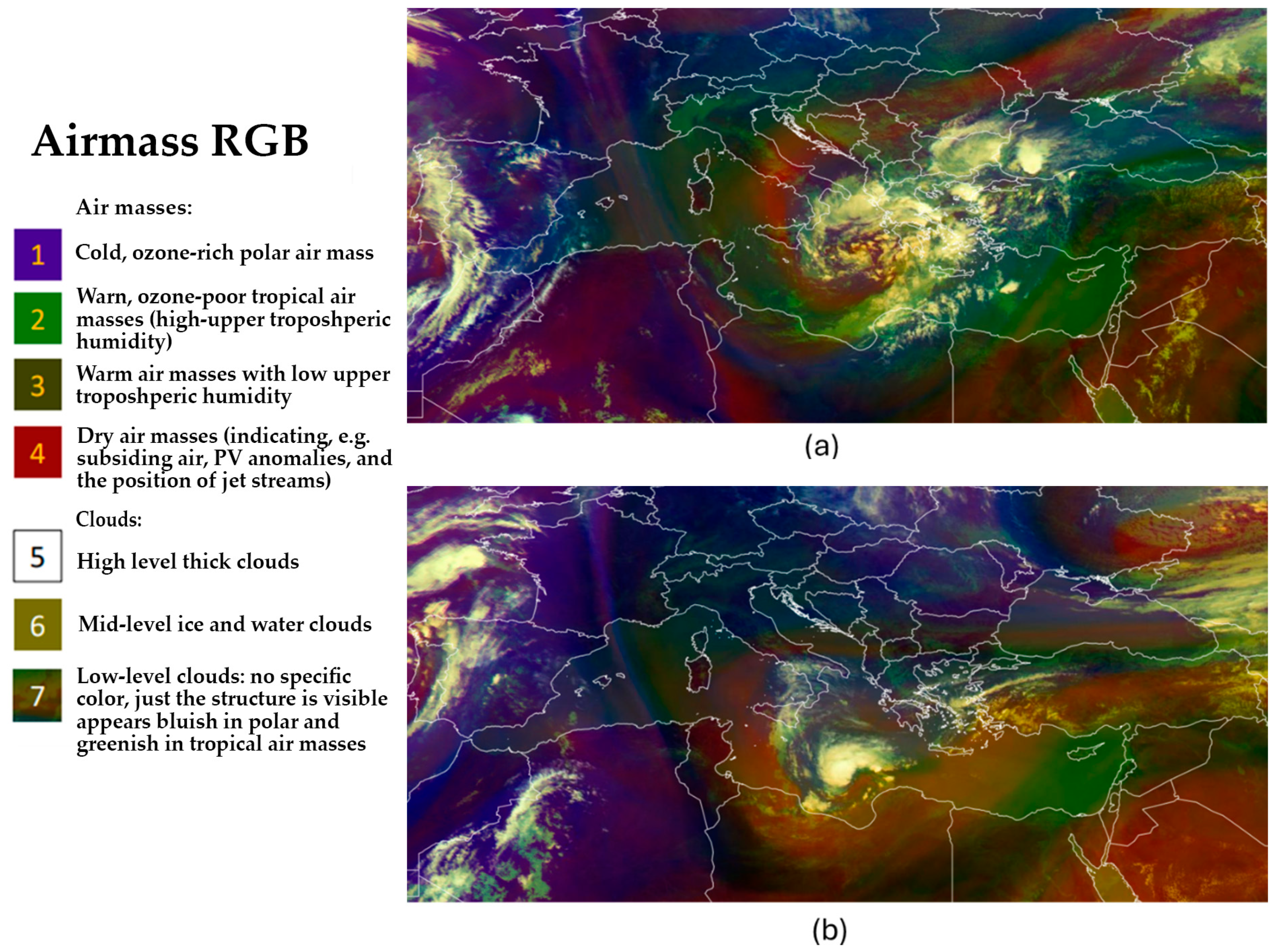
Figure 2.
MSG airmass RGB product derived by EUMETSAT at 12:00 UTC, on 4 September 2023 (a) and 9 September 2023 (b).
The combination of elevated sea surface temperatures, abundant atmospheric moisture, and the storm’s slow progression resulted in extreme precipitation events. Central Greece, including the region of Thessaly, experienced record-breaking rainfall, reaching over 600 mm in an extensive area, over the course of 5 days [38], leading to catastrophic flooding. During its medicane phase, Cyclone Daniel brought devastating floods to Derna, Libya, and surrounding areas, exacerbated by intense rainfall and the failure of critical dams.
Τhe ensuing deluge resulted in widespread flooding [39], landslides, and erosion, causing significant damage to agricultural land [38], infrastructure, and private property [40,41]. The flood claimed 17 lives in Greece, led to approximately 1900 rescues, and left hundreds of homes and businesses submerged in an inundated area of about 1150 km2 [38], with approximately 70% of it (roughly 730 km2) being Thessaly’s farmland. As the region is Greece’s primary agricultural production area, contributing 22% of the nation’s output, the flooding caused not only localized destruction but also economic and political disruption on a national scale [42], severely impacting the local population.
The extreme rainfall generated by Storm Daniel caused flooding and mudflows in the storm’s landfall area in Libya, while the collapse of two water retaining dams caused unprecedented flooding in the city of Derna, causing a total of at least 5923 casualties, and thousands more suspected deaths, 44,800 people displaced, and 18,838 houses damaged or destroyed in the whole coastal area encompassing Benghazi, Jabal Al Akhdar, Al Marj, and Derna [43,44].
While the Eastern Mediterranean region regularly encounters severe seasonal storms and medicanes, the unprecedented severity of Storm Daniel far surpassed expected impacts, as it was largely unforeseen in both its scale and impact. The overwhelming amount of rainfall over a short period exceeded the capacity of existing infrastructure and emergency response systems, with repercussions that extended beyond the actual flooded region.
3. Materials and Methods
For this study, data were collected from a variety of sources to comprehensively capture the cascade effects of Storm Daniel. The analysis focused on identifying and classifying specific sequences of events and various interdependencies between different elements reflecting either infrastructure, the environment, or socioeconomic activities that were impacted. Data was first collected through field research that was conducted in the affected areas to gather firsthand information on the extent and nature of the impacts, in the first days after the storm, but also in the months that followed. In total, 5 field trips were carried out in the year that followed the event. Communication with the official Operations Coordination Center and participation in some of their meetings provided valuable insights into the official response, as well as information on the unfolding of events and different crises after the storm. Additionally, several reports that followed the event were systematically reviewed to document the immediate and long-term consequences, while scientific publications focusing on specific effects (e.g., environmental pollution and others), were also analyzed. Data from the Bulletin of the Ministry of Health were also incorporated to assess public health impacts and related cascade effects, as well as information on water services availability. Regular announcements of the municipalities that were affected by water service outages were also taken into consideration. This multi-source approach was necessary since no official or unofficial source contained information on the diversity of elements impacted, and was used to ensure completeness of information and a thorough and nuanced understanding of the storm’s repercussions. The diverse sources of information are shown in Table 1.

Table 1.
Sources of information on storm’s impacts, along with the type of information.
For this study, we assumed the definition of Pescaroli and Alexander [55] for cascading effects, as follows: “Cascading effects are the dynamics present in disasters, in which the impact of a physical event or the development of an initial technological or human failure generates a sequence of events in human subsystems that result in physical, social or economic disruption”. We also assumed that cascading effects can be complex and multi-dimensional, having a non-linear progression, can involve escalation points and subsidiary disasters derived from failure of human systems, and can be defined by the vulnerability of the systems affected, even influencing areas not affected by the initial hazard.
4. Results
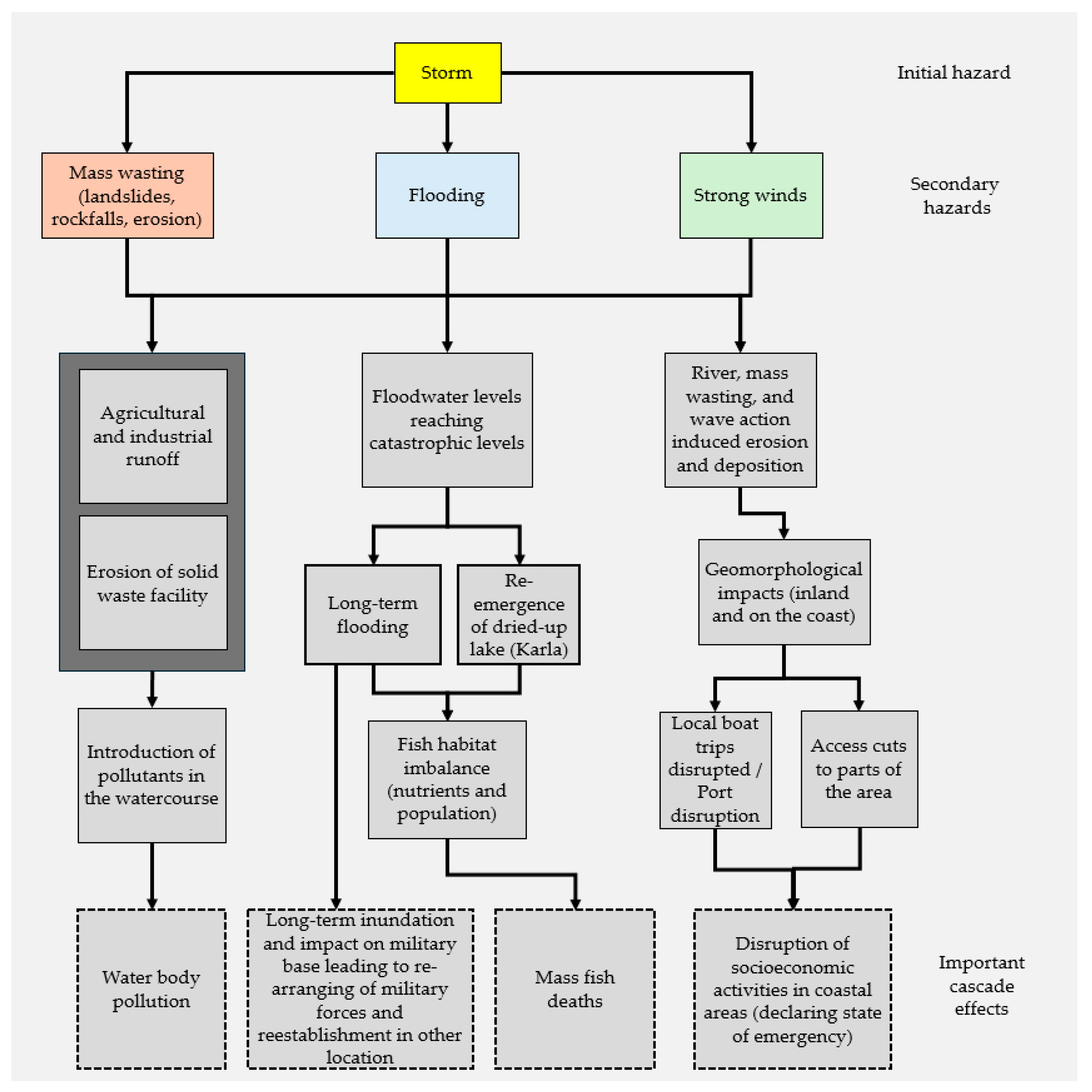
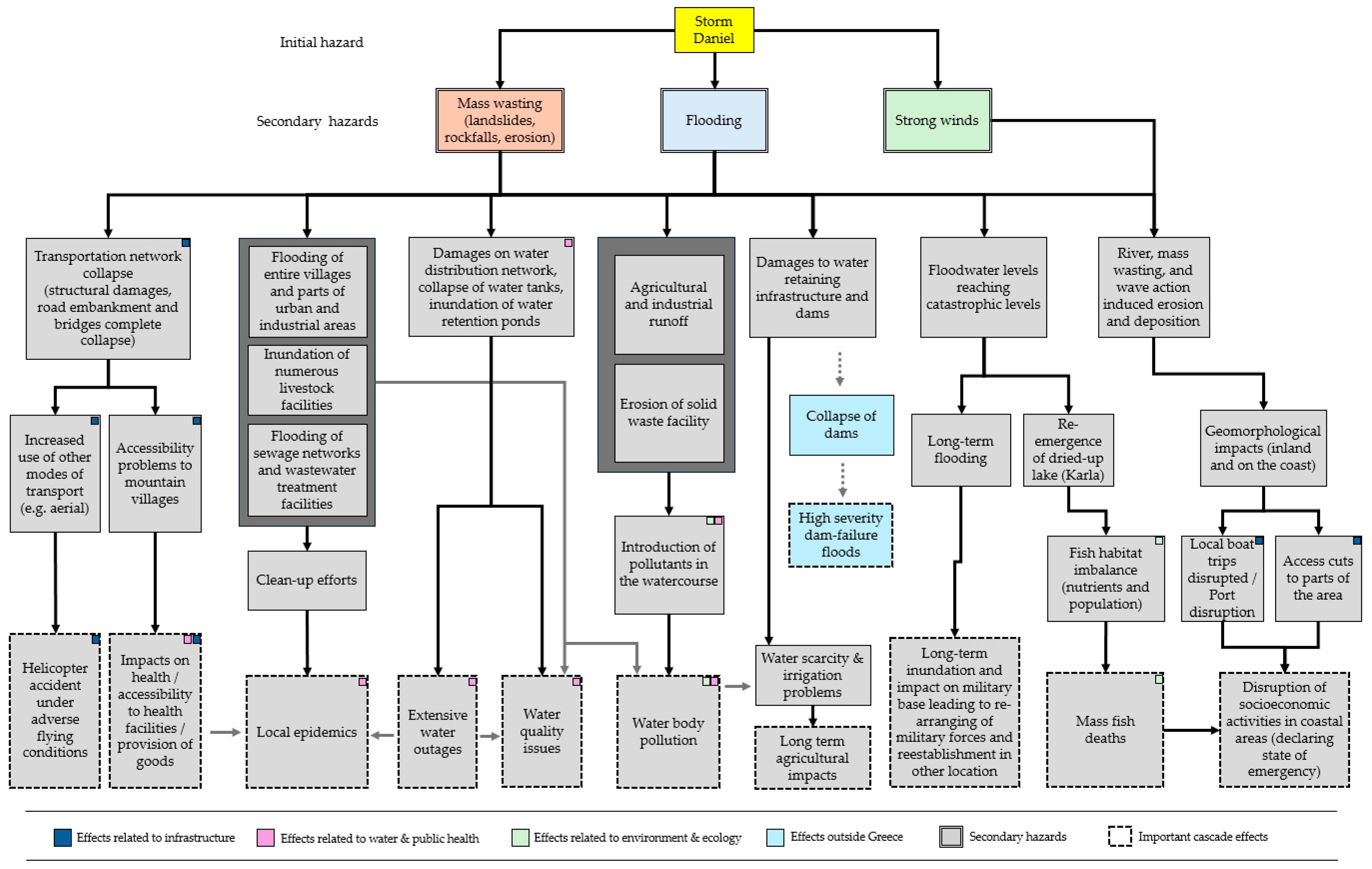
Based on the extensive field research conducted in the aftermath of the September 2023 catastrophic storm in Thessaly, along with the data detailed in the previous section, we identified a series of interconnected cascading effects. These effects illustrate the cascading consequences triggered by the storm event, affecting environmental, infrastructural, and socio-economic systems in the region. The mechanisms of these cascading effects, as mapped through our analysis, are depicted in the following sections and diagrams, which outline the key pathways through which the initial disaster propagated into secondary and tertiary impacts across multiple sectors.
4.1. Public Health
Flooding and the clean-up efforts that follow flooding events can greatly increase the risk of rodent-borne diseases [56]. Floodwaters often force rodents out of their natural habitats and into human areas, where they contaminate surfaces, food, and water with their urine. Additionally, floodwaters mix with sewage and other contaminants, increasing the risk of transmission when people come into contact with this water during cleanup efforts. Poor sanitation, limited access to clean drinking water, and delayed waste management further exacerbate this risk by attracting rodents. As people handle debris and stand in contaminated water without proper protection, they become more exposed to diseases like leptospirosis. Previous research has shown that flood disasters have led to such epidemics in the past [57,58,59]. Additionally, the inundation of livestock facilities has heightened water quality concerns, introducing biological contaminants into the water supply and compounding the challenges of restoring safe and reliable water access.
In the case of Storm Daniel, evidence from the Hellenic National Public Health Organization (NPHO) shows that the incidence of leptospirosis presented a statistically significant increase in the hit region after the disaster, from an average of 0.13 cases per 100,000 people (previous 10 years) to 6.5 cases per 100,000 people in 2023 (p < 0.001) [60], and a noteworthy uptick in cases also documented by Poulakida et al. [45]. The patients were infected with Leptospira kirscnheri and Leptospira interrogans, and two of them were reported to lose their lives from the infection [45,60].
Moreover, clusters of gastroenteritis cases and respiratory infections indicated an increase in the flood-hit region [61], although further research is needed to determine its statistical significance.
Based on data presented by Mavroulis et al. [46], no vector-borne or injury-related diseases (e.g., tetanus) presented significant increases in the study area. Minor problems deriving from issues related to the condition of inundated houses (e.g., encountering mold, etc.) or flood waste have been recorded in anecdotal form [46].
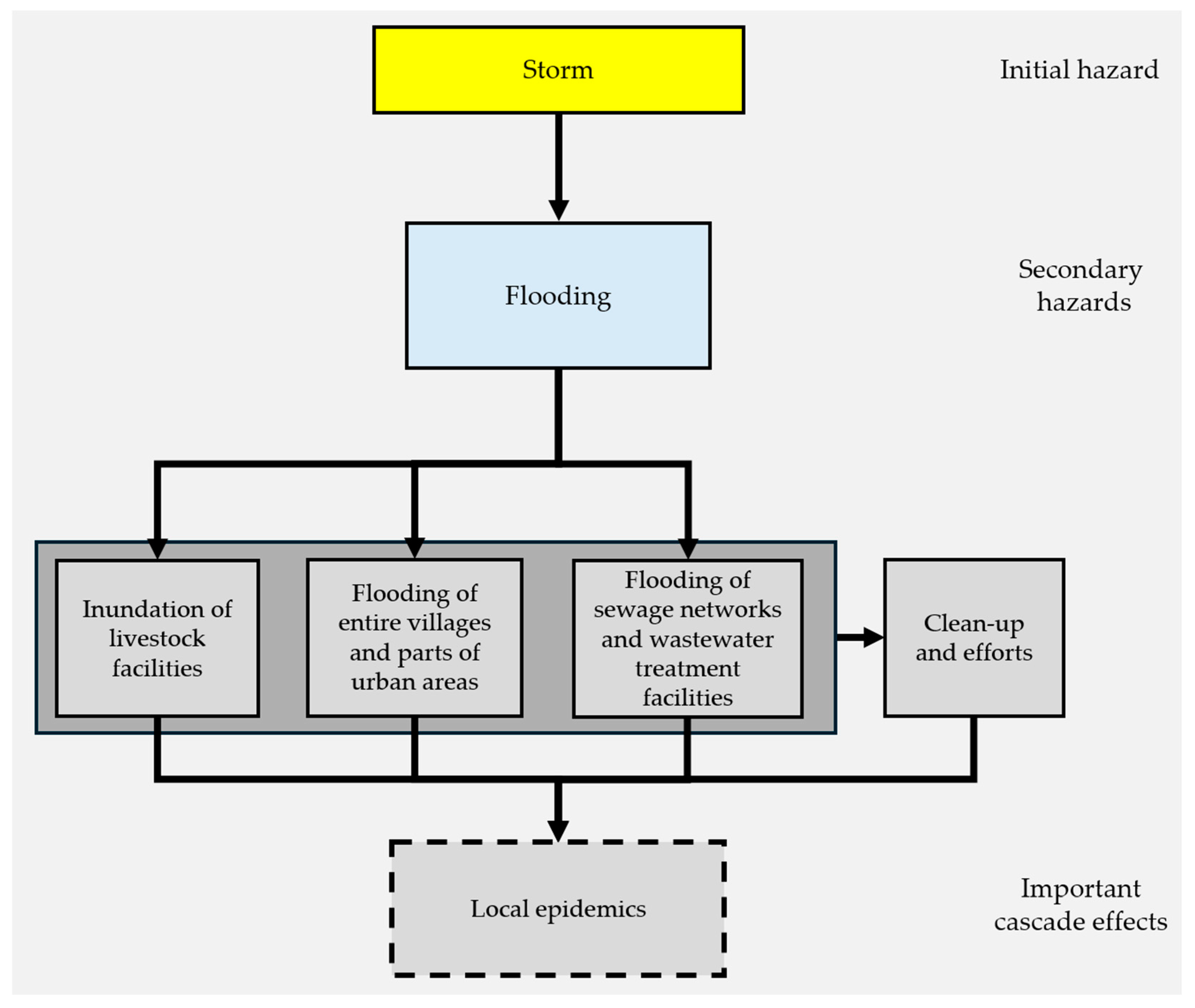
The figure below (Figure 3) describes the progression of effects influencing public health through local epidemics.
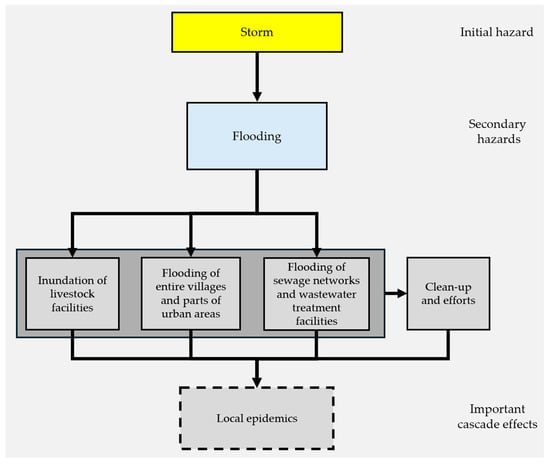
Figure 3.
Cascading effects through a progression of events affecting public health. Dashed rectangles denote important cascade effects.
4.2. Transportation Infrastructure Failure
The devastating floods and landslides caused by Storm Daniel in Thessaly, Greece, heavily damaged transportation infrastructure, affecting a total of 159 km of road networks and 110 bridges across multiple regions. Approximately EUR 900 million in emergency roadworks has been allocated for infrastructure restoration, with resource distribution prioritizing Magnesia (33%), Trikala (25%), Karditsa (21%), Larissa (9.5%), Euboea (9.5%), and Phthiotis (2%) [62]. The catastrophic events disrupted essential routes such as the Athens-Thessaloniki motorway and rail services, isolating communities and halting transportation. In the mountainous area of Pelion (Magnesia), restoration of the road network and its bridges cost EUR 278.2 million, while works for the restoration of the railway network were estimated at EUR 460 million [62,63].
Although no quantified data on vehicle circulation existed until the time of this writing, the extensive damage to Thessaly’s road network has disrupted the transport of goods and services, leading to shortages of essential supplies in isolated areas, which for some days were transported with helicopters [64].
Moreover, the loss of road access necessitated frequent helicopter flights, even under adverse weather conditions. One such instance involved a privately chartered A-109 civil aviation helicopter on a flight between Magnesia and the island of Euboea, which tragically crashed into the sea off northern Evia claiming one life [65].
In addition, although there is no quantified overview of the cascading effects related to accessibility, several incidents recorded the emergency evacuation and transport of individuals with various diseases (at least three persons with kidney disease), seeking emergency medical treatment in the hospital of the town of Volos [66]. In other cases, multiple patients, including a pregnant woman, were transported to a hospital using heavy machinery [67]. Due to this lack of accessibility to health services, according to reports [68,69], one patient with a snake bite, another in allergic shock from an insect sting, and several patients requiring oxygen support (such as those with chronic respiratory conditions) faced critical challenges in receiving timely medical care. Additionally, patients with chronic conditions did not have access to their necessary medications, further worsening their health risks in this crisis [68] (Figure 4).

Figure 4.
Scenes showing patients and other citizens being transported (a) using heavy machinery, (b) special boats that can approach the beach, and (c,d) using zipline-mounted stretchers across collapsed bridges and roads during the aftermath of Storm Daniel in September 2023.
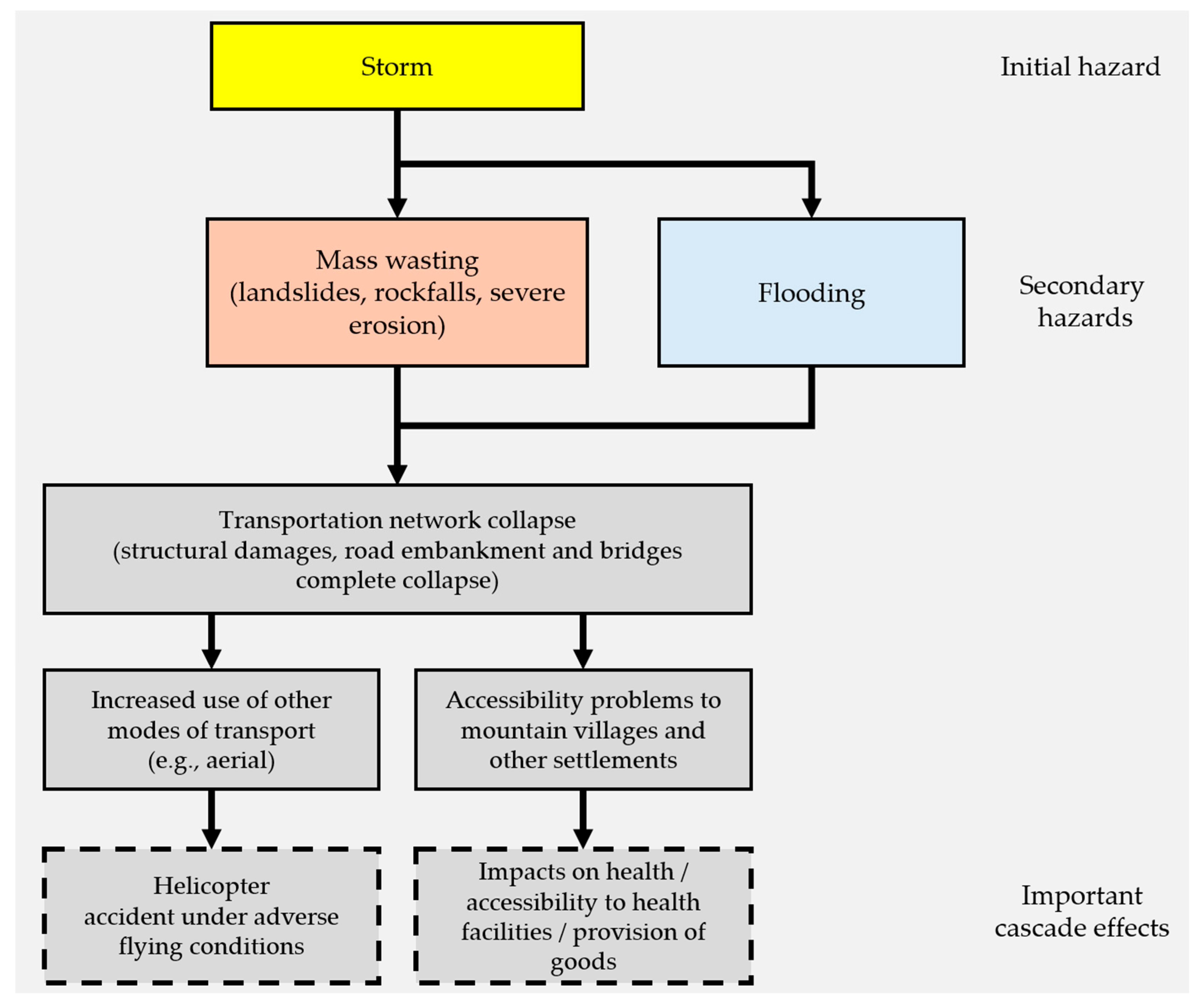
The figure below (Figure 5) describes the progression of effects influenced by transportation collapse.
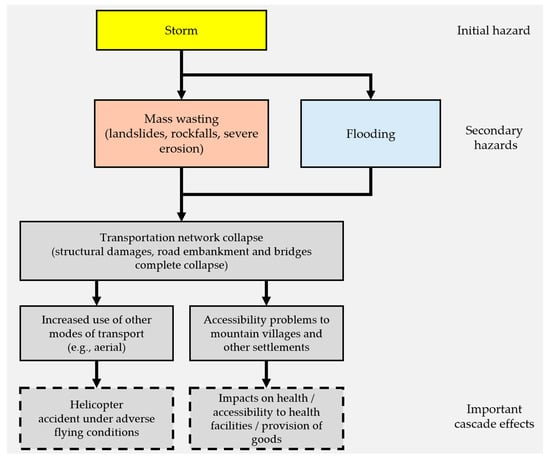
Figure 5.
Initial hazards and chain of events leading to cascading effects related to transportation infrastructure damages. Dashed rectangles denote important cascade effects.
4.3. Drinking Water Availability
Storms can cause water outages and supply problems by contaminating water sources, damaging water distribution pipes, damaging infrastructure that relies on electricity, and causing power outages [70,71,72]. Water treatment and distribution systems often depend on electricity, and during storms, severe winds or floodwaters can disable or damage this infrastructure [73]. Contamination of water sources due to sewage and debris can force water treatment plants to halt or limit operations. Additionally, the physical impact of floodwaters can damage water distribution networks, causing leaks and contamination [70]. Power outages, even without direct damage to water infrastructure, can disable critical systems, resulting in service disruptions.
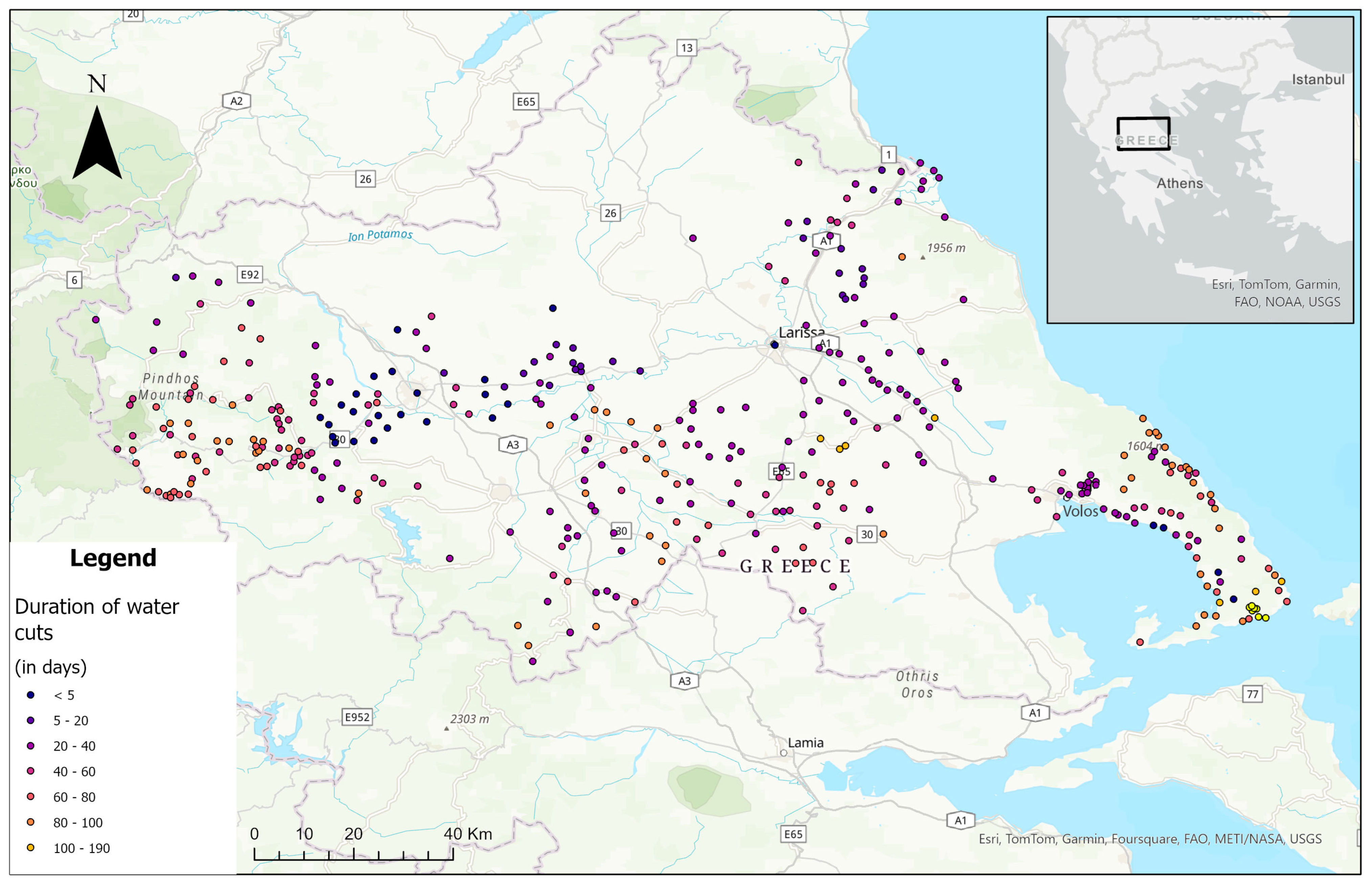
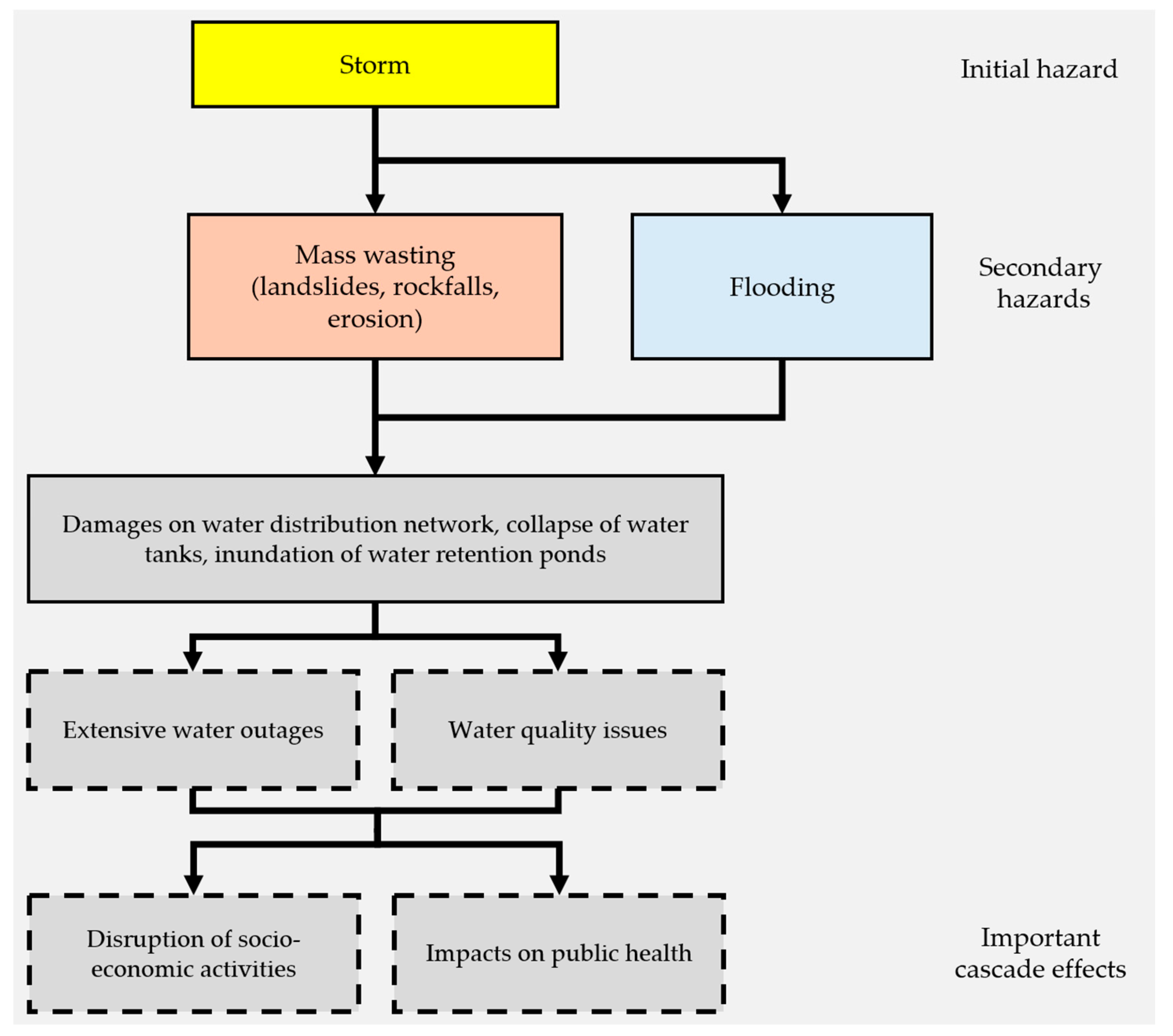
In the case of Storm Daniel, water treatment facilities were inundated, and the water distribution network was affected in multiple ways [41]. The physical force of floodwaters damaged water distribution pipes, while mass wasting events compromised water distribution tanks used for domestic water storage. The collapse of water-retaining tanks and artificial ponds, essential for agricultural use, further intensified the issue by causing leaks and increasing the risk of contamination. In one case, a shallow landslide led to the collapse of a water tank providing drinking water for a few villages on Pelion Mt [74]. This, in turn, led to months of water outage for the local community. Water supply outages were reported in affected areas, with some regions facing prolonged disruptions lasting for months. Based on official announcements from various authorities (see Table 1), the following map (Figure 6) shows the duration of these disruptions across the study area in 392 locations (cities and villages). The prolonged water outages and quality issues, apart from contributing to public health issues, also affected several other systems, leading to cascade effects. In the city of Volos, emergency operations were temporarily halted at the city’s main hospital [75]. In addition, hotels and other businesses were disrupted [76], due to lack of drinking water. Figure 7 describes the progression of effects influenced by damage on the water distribution network.
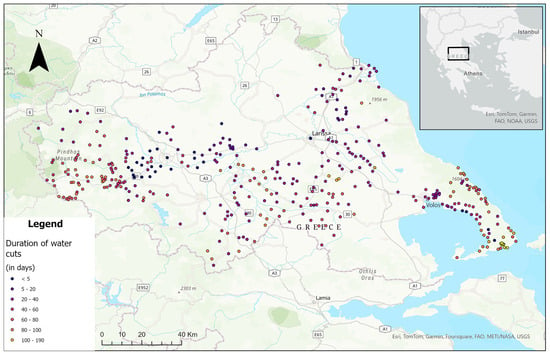
Figure 6.
Map of the study area illustrating the locations of 392 settlements and the respective duration of water outages (in days). The upper right corner of the map depicts a mini map of Greece and the neighboring countries, along with a black rectangle denoting the area hit by Storm Daniel. Location names, important road numbers and elevations points (grey triangles) can be seen in the background map.
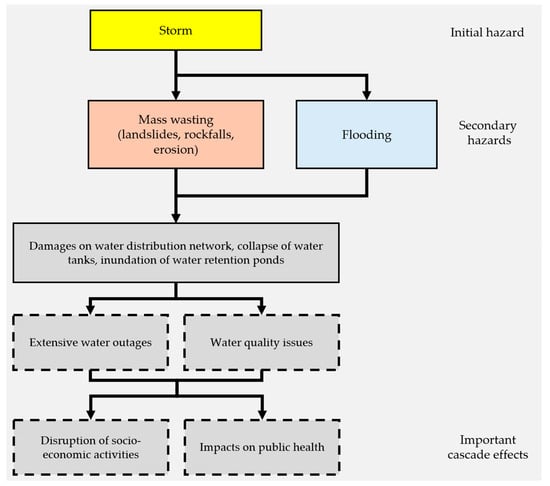
Figure 7.
Progression of effects influenced by damage to the drinking water distribution network. Dashed rectangles denote important cascade effects.
4.4. Dams and Water Retention Facilities
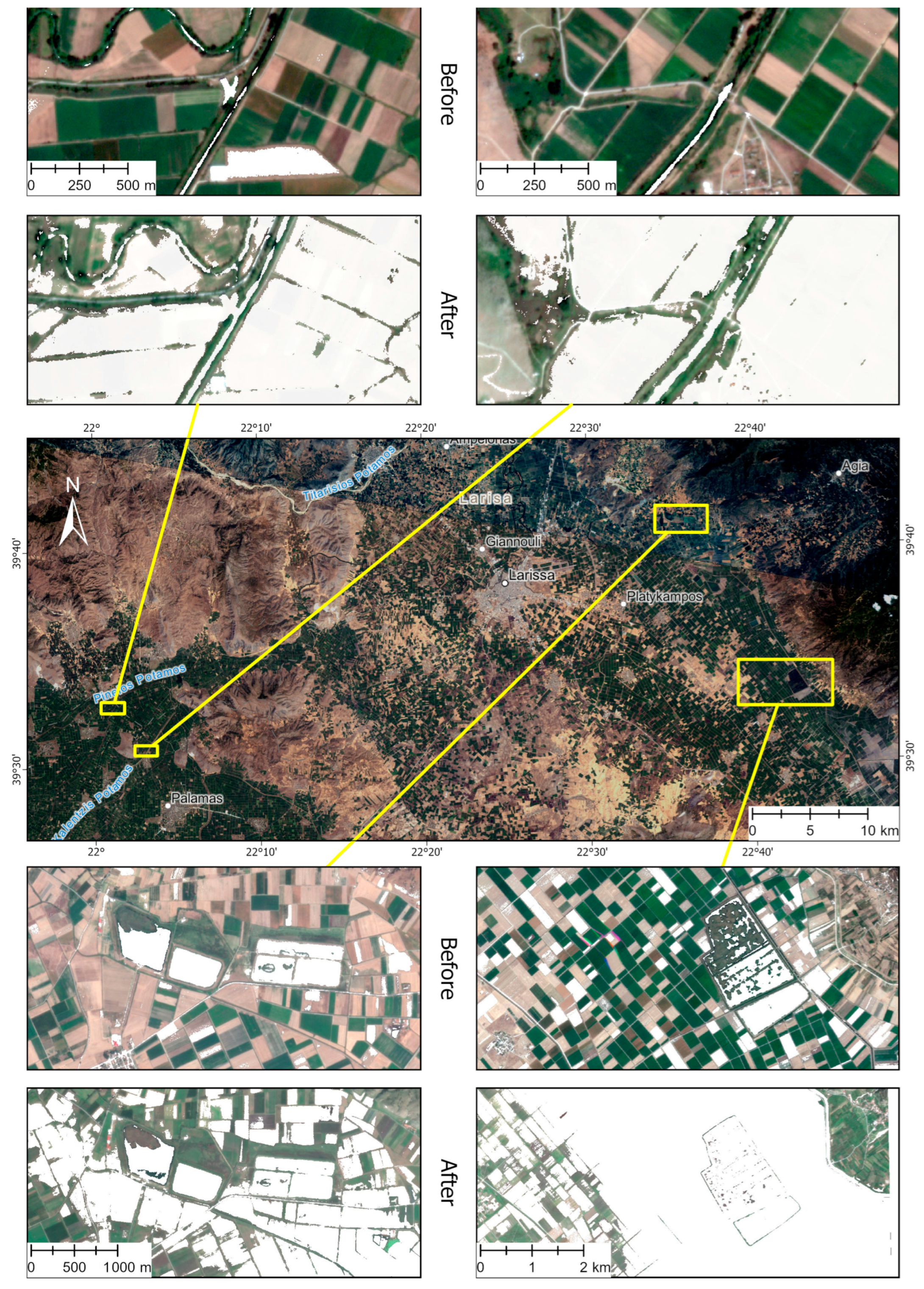
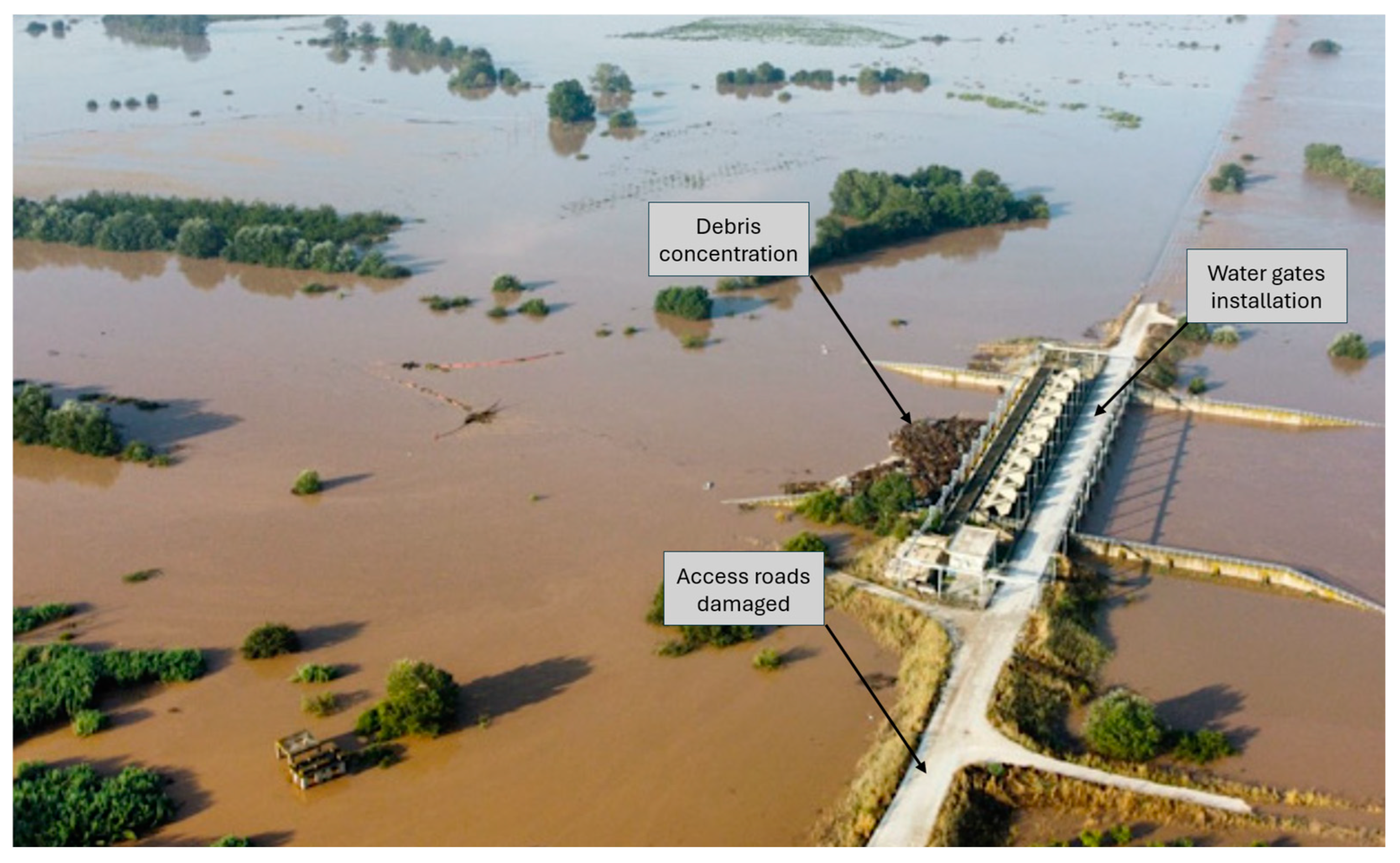
The Daniel flood caused significant damage to water retention facilities, dams, and related infrastructure: systems such as the water gates of Gyrtoni, Vlohos, and Marathea, compromising their ability to regulate irrigation and water storage effectively, as the installations suffered structural damages, with impacts on electrical infrastructure [41]. Moreover, the reservoirs received amounts of debris, reducing their storage capacity. The impaired functionality of these dams and water gates not only created immediate irrigation challenges but also threatened long-term agricultural productivity in the region (including water scarcity issues for parts of the area for the upcoming growing season). Figure 8 shows four examples of these installations inundated 23 days after the storm, while Figure 9 shows an aerial photo of the water gate of Gyrtoni damaged during the flood.
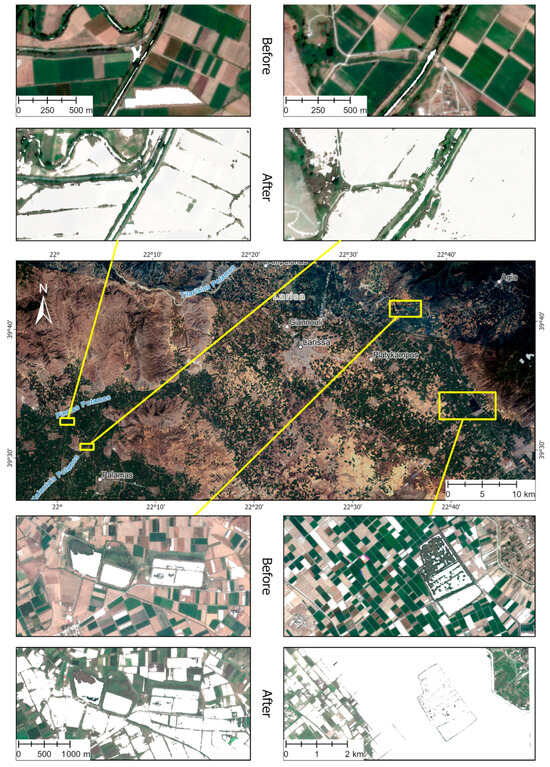
Figure 8.
Multitemporal interpretation of satellite images (PlanetScope) showing the impact of flooding in the Thessaly region (water in white color). At the processed enlarged insets, the Water Index (Green − Infrared/Green + Infrared) was applied, showing surface water presence (white areas), indicating water-retaining facilities (water gates and ponds) filled with water before (28 August 2023) and after (29 October 2023) the flooding events.
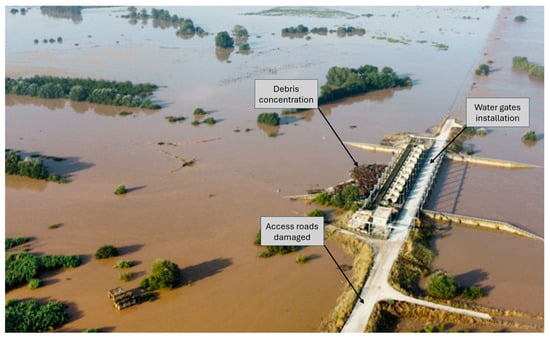
Figure 9.
Aerial view of the water gate of Gyrtoni during the ensuing flood, showing aggregation of the debris that damaged its installations and the overall inundation of the area that affected its function.
In terms of impacts on dams outside Greece, the catastrophic collapse of two dams in Derna, Libya, following the extreme rainfall induced by Storm Daniel in the area, represents probably the most severe cascade event of the storm. The collapse led to widespread flooding, the destruction of infrastructure, and significant loss of life [44,77], highlighting the interconnected vulnerabilities of hydrological and infrastructural systems to extreme weather events.
4.5. Impacts on the Environment and Ecology
Floods can significantly affect environmental and ecological processes [78,79,80,81], often causing widespread and long-lasting impacts. They can lead to soil erosion, nutrient depletion, and changes in land morphology, disrupting natural habitats and altering ecosystem dynamics [78]. Floodwaters may transport pollutants, such as chemicals and waste, into rivers, lakes, and coastal areas, degrading water quality and harming aquatic life [82].
Effects related to ecology were identified in the western part of Thessaly, as Storm Daniel, through the blocking of mountain streams due to numerous landslides across steep riverbanks caused by both high flows and high-intensity rainfall on slopes, induced a significant reduction (i.e., 99%) in particular species of fish (Salmo farioides) [48].
Flooding of Lake Karla, apart from the important landscape changes [54], created ideal conditions for fish breeding, especially for hardy species like Carassius gibelio and Cyprinus carpio. However, as the floodwaters receded, the dense fish population led to oxygen depletion, worsened by high summer temperatures and agricultural runoff. This resulted in many fish becoming exhausted or dying, with some drifting into Pagasitikos Bay [48].
This phenomenon resulted in a substantial accumulation of dead fish on the sea surface near the shoreline, generating strong odors for several days that significantly impacted daily life and activities in coastal areas of the city of Volos (Figure 10). These odors disrupted the operations of local businesses, including restaurants, hotels, and other establishments, leading to a significant decline in clientele and guests, and, therefore, income. This, in turn, led the Restaurants Association, the Hotel Owners’ Union of Volos, and the Professional Association of Anchialos to file a lawsuit with the Prosecutor’s Office against any party responsible [83]. The government announced financial support for these businesses (including tax and insurance suspension), while regional authorities enlisted fishing trawlers and earthmovers to collect the dead fish from the sea, load them onto trucks, and transport them to an incinerator for disposal. In addition, swimming was prohibited for several weeks in the Pagasetic Gulf [84].
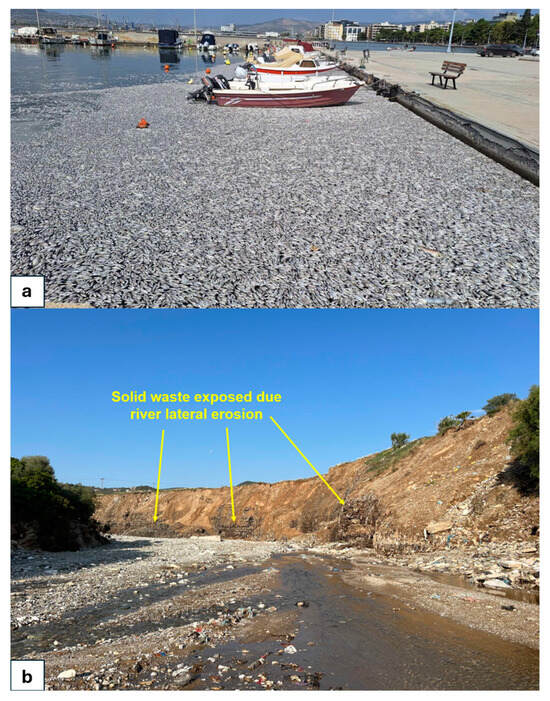

Figure 10.
Characteristic impacts of the storm on the natural environment, including (a) dead fish concentrated at the coast of the city of Volos in August 2024, almost one year after the storm and (b) riverbank erosion exposing parts of a solid waste facility upstream of Volos.
Previous works have shown that the effects of storms and subsequent flooding on marine environments often result in significant alterations to water quality, sediment dynamics, and the overall ecological balance of affected regions [80]. These impacts encompass elevated levels of suspended matter, shifts in bathymetry, contamination from anthropogenic sources, and disruptions to marine biogeochemical cycles [85]. Specifically, the case of Storm Daniel in September 2023 in Greece demonstrates the magnitude and complexity of such environmental disturbances. The Pineios River Delta, heavily affected by the storm, exhibited high concentrations of suspended matter, as detected through Copernicus Sentinel-2B Level 1C satellite imagery reported initially by Lekkas et al. [41]. Suspended matter values reached up to an estimated 300 gr/m3, extending over a range of 50 km from the river’s outlet. This elevated sediment load persisted for more than 15 days following the flooding, illustrating the enduring nature of the perturbation.
Further investigations revealed notable floating debris across impacted marine areas. Papageorgiou et al. [50] identified non-anthropogenic debris and a significant presence of plastic waste both in the Pagasetic Gulf and near the Pineios Delta, highlighting the role of urban and industrial runoff during flood events.
Additionally, preliminary analyses by Lougkovois et al. [52] identified a range of contaminants in increased concentration in the Pagasetic Gulf, including plant protection products like Azoxystrobin and Atrazine, which are commonly associated with agricultural activities. The overflow of wastewater treatment plants during the flooding was linked to the detection of pharmaceutical compounds such as Carbamazepine and per- and polyfluoroalkyl substances (PFAS) [52]. These findings underscore the compounded influence of agricultural runoff, industrial discharges, and compromised wastewater infrastructure, such as sewage treatment plants, etc., on marine pollution during extreme weather events.
Physical alterations to the marine environment were equally significant. Sediment deposition following the flooding led to changes in the bathymetry of the Pagasetic Gulf, as noted by the Greek Navy [86]. Sediment accumulation near the Volos port and the southern estuaries of Milina settlement reduced water depths to the extent that intervention was required to restore navigability and ensure the safety of maritime operations. Meanwhile, sediment composition analyses by Georgiou et al. [87] revealed an increase in potentially toxic elements (PTEs), such as cadmium (Cd) and arsenic (As), alongside higher silt content and diminished organic matter in the sediment. These findings indicate significant geochemical perturbations resulting from the influx of flood-borne material and can be probably partly attributed to the erosion of a solid waste facility and the introduction of solid waste and their byproducts in the watercourse and eventually into the sea (Figure 10).
From a biogeochemical perspective, the impacts of Storm Daniel extended to dissolved oxygen dynamics and nutrient concentrations. In situ sampling by Dimoudi et al. [49] recorded reduced oxygen levels in the deeper layers of the Pagasetic Gulf, particularly in its eastern regions. Coastal areas exhibited elevated concentrations of silicates and ammonium, further reflecting nutrient imbalances introduced by floodwaters. Similarly, Varkoulis et al. [51] reported increased concentrations of silicon dioxide (SiO2), nitrate (NO3−), and ammonium (NH4+) in the western sector of the gulf, indicating widespread changes to nutrient cycling and primary productivity.
Apart from the marine environment, previous research explored physicochemical changes in the waters of Lake Karla and Lake Plastira, indicating at least certain changes due to the flood [47,88]. Recent research [53] has shown also that soil was affected as well, with deposition derived from flooding affected the levels of CaCO3, phosphorus, and manganese around Thessaly, leading potentially to a decline in the yield of crops.
Overall, the impacts of Storm Daniel on the marine environment of Greece’s Thessaly region provide a clear example of how extreme weather events can trigger cascading ecological and geochemical disruptions, with evidence also showing the interplay of sediment transport, chemical contamination, bathymetric changes, and altered biogeochemical processes. Figure 11 shows the propagation of impacts on the natural environment and ecological balance.
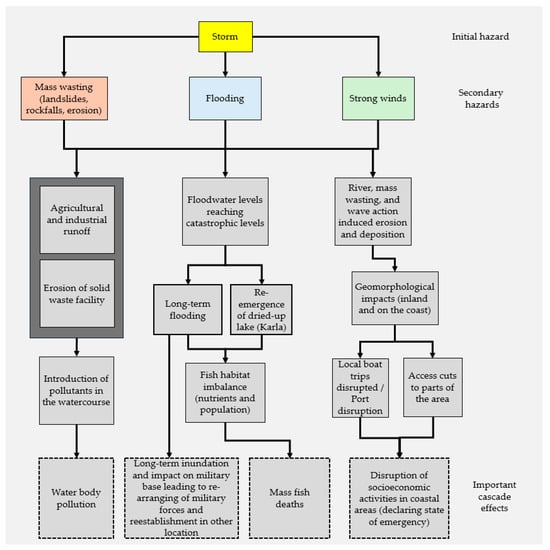
Figure 11.
Progression of effects of the storm on the environment and ecological balance. Dashed rectangles denote important cascade effects.
4.6. Other Disruptions
The long-term flooding, defined as prolonged inundation lasting for more several months in this study, affected Karla Lake, and caused inundation nearby military facilities, necessitating the gradual relocation of military operations and altering the placement of military forces in the area [89].
Additionally, certain mountain villages and remote beaches of Pelion, a popular tourism destination, suffered a sharp decline in visitors for some time. In detail, the region experienced significant declines across various sectors. Employment in restaurants and cafes dropped by 12%, while the hospitality industry saw a 13% reduction compared to 2022, in contrast to all other Greek regions that experienced growth. International arrivals at Achiallos Airport fell by 24%, while the number of cruise ship arrivals declined by 22%, with a 21% decrease in cruise ship passengers. Additionally, museum visits dropped by 31%, and heritage site attendance fell by 16% in 2023 compared to the previous year [90]. However, the full extent of the impact remains uncertain, as data from the winter season of 2024 has not yet been collected.
Tourism has been probably affected by the impacts on the cultural heritage of Thessaly that suffered damages due to Storm Daniel, particularly in Pelion and Volos. The architectural heritage of Pelion, including traditional mansions, churches, bridges, and cobblestone paths, was severely impacted, while the industrial heritage of Volos also suffered extensive destruction [91], potentially affecting tourism indirectly. Continuous media coverage of access restrictions, damaged infrastructure, inaccessible ports, prolonged electricity outages, and water shortages may have created a negative perception of the region, discouraging tourists and severely impacting the local economy dependent on seasonal tourism, leading local communities (like the city of Volos) to declare an emergency situation even one year after the event [92].
Overall, the identified cascade effects encompassed elements related to infrastructural failures, elements related to water quality and availability, and issues related to public health, as well as to the environment and ecological balance, as summarized in the figure below (Figure 12).
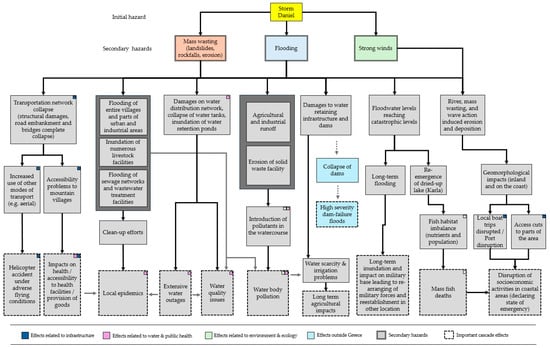
Figure 12.
Summary of the identified cascade effects in different sectors and diverse outcomes.
5. Discussion
The findings of this study examine a variety of effects and provide a comprehensive typology of the cascading effects triggered by Storm Daniel, encompassing a variety of impacts on the built and natural environment and indicating the complexity of impact propagation caused by extreme storms. As Storm Daniel caused severe flooding, numerous landslides, extensive infrastructure damage, and significant societal and environmental disruptions, the present study demonstrates how various cascading effects, such as water supply outages, public health crises, road cuts, and environmental degradation propagate through interconnected systems, amplifying the disaster’s impact. In addition, it provides one of the first detailed records in the literature demonstrating the propagation of impacts due to extreme storms, a field that is until today largely uncharted. Some of these effects have been increased due to the interconnectedness of modern societies and can potentially be challenging for existing risk management and emergency response frameworks, as they extend beyond the actual inundated area and the timeframe of the initial disaster.
In terms of added value, this study provides insights into the various cascading impacts by documenting the mechanisms through which the disaster propagated across sectors and offering an analysis of consequences spanning different fields such as public health, infrastructure, and the environment. In addition, it highlights the systemic vulnerabilities that intensify disaster impacts. By integrating field data, official reports, and the literature, the study establishes a framework for analyzing cascading effects that can be adapted to other regions and hazards.
As the findings are not exclusive to the Mediterranean context, their relevance may extend to other regions with similar infrastructure, governance, and climate conditions. However, notably, some of the identified effects pose a threat to coastal areas, an especially valuable part of the Mediterranean landscape, as these areas play a critical role in the blue economy, which serves as a key pillar of economic development in the region.
Overall, the findings show that the propagation of cascading effects observed in Storm Daniel can be attributed to mainly three mechanisms, including the following:
- (a)
- Infrastructure vulnerabilities: The storm’s physical force damaged critical infrastructure, such as water treatment facilities and distribution networks, leading to prolonged outages and contamination.
- (b)
- The interconnectedness of various systems: Dependence on electricity for water treatment and healthcare services meant that power outages had wide-ranging secondary impacts. In turn, water outages led to various effects related to health and socio-economic activity disruption.
- (c)
- Environmental and ecological interactions: Floodwaters caused both disruption to the natural environment and ecological balance, including fish population declines and water quality deterioration. These effects propagated due to runoff from agricultural and industrial areas but potentially due to more localized initial impacts (such as erosion of a solid waste facility).
In addition, from the findings of this study, it is evident that the interconnected nature of critical systems amplifies the impact of initial hazards. Secondly, the public health consequences, including disease outbreaks such as leptospirosis, demonstrate the urgent need for enhanced post-disaster medical infrastructure to prevent such epidemics from developing. Moreover, the environmental impacts acknowledged in this study underscore the vulnerability of ecosystems to compounding effects, which may persist long after the initial event, highlighting the need for a system or a group of protocols designed to monitor the environmental effects after a disaster in a systematic way. These processes can be included in an enhanced emergency response plan with the participation of both national and local authorities.
The practical implications of the present study are useful for disaster preparedness and resilience. Developing a typology for cascading extreme storm impacts enables planners to understand, compare, and learn from past events by mapping cause-and-effect chains to pinpoint where disaster impacts may propagate and what sectors they might affect. Identifying vulnerabilities and interdependencies between critical infrastructure systems like water, energy, and transportation is also very important, as storms (and secondary hazards such as floods and landslides) often cause network-wide failures that intensify cascading disruptions. Visualizing the sequence of cascading effects triggered by extreme storms and mapping interdependencies can inform enhanced emergency response strategies that aim to plan and respond beyond the direct effects of a disaster, to ensure smoother logistics and coordination for disaster relief.
This study aligns with prior research highlighting the cascading effects of storms, such as water contamination and disease outbreaks [70,71] and others presented in previous sections. However, it expands on existing knowledge by providing detailed pathways through which disasters propagate, such as the interaction between extreme rainfall, infrastructure vulnerabilities, agricultural and industrial runoff, service outages, and others. Through the mapping of these pathways, the findings contribute new evidence to the limited literature on the impact mechanisms of cascading effects, highlighting the broader socioeconomic and ecological consequences.
While this study offers valuable insights, several limitations must be acknowledged. In terms of temporal scope, the analysis focuses primarily on the immediate and short- and medium-term impacts by monitoring the study area for more than 1.5 years after the event. Longer-term consequences should be subject to continuous research investigating the prolonged effects. Limited availability of more systematic or instrumental data on certain impacts, such as transportation disruptions, constrained the depth of analysis to a more qualitative aspect. Future investigations using quantified data on effects, if available (e.g., floating car data for transportation impacts), could shed more light on the degree to which each field was affected in quantitative terms.
Further research efforts in the field of cascade effects of flood could benefit by expanding to multiple case studies and across different terrains and geographic areas to enrich the typology of impacts and the potential pathways of cascade disasters. To build on the findings of this study, apart from exploring long-term effects, we recommend collaborating across fields to better understand the complex interactions between storms and secondary hazards such as flooding and mass wasting, infrastructure, the natural and built environment, and the economy, as well as societal systems. In addition, research and development of predictive models that simulate these effects have the potential to provide an important basis of guiding potential pre-emptive or prevention measures. By addressing these areas, future research can further enhance our understanding of cascading hazards and improve resilience to extreme weather events in the Mediterranean and beyond.
This work underscores the critical need to understand cascading hazards in the context of extreme weather events, especially as such events become more frequent and severe due to climate change, and explore how insights from cascading impact studies can inform disaster risk reduction policies and climate adaptation strategies.
Integrating cascading risk concepts into disaster management policies and land-use planning can be very important, particularly for floodplain development and cross-sectoral coordination. Addressing gaps in legislation, such as improving standards to prevent hazardous-substance releases during storm-triggered industrial accidents, ensures more robust prevention of Natech risks. Enhancing community resilience by addressing the social, behavioral, and psychosocial impacts of floods and storms is equally important, as these events disrupt daily life and recovery processes. Lastly, investment in modeling, simulation, and database development regarding cascading effects has the potential to support future decision-makers in assessing cascading storm scenarios at local and regional scales. Such tools can help simulate infrastructure failures, evaluate risks, and design effective mitigation strategies, ultimately strengthening preparedness for the cascading effects of extreme weather events.
6. Conclusions
The analysis of the cascade effects triggered by Storm Daniel, which struck Thessaly, Greece, in September 2023, highlights the complex and interconnected nature of extreme flood impacts in modern societies. The findings of the study emphasize the urgent need for a deeper understanding and mapping of cascading hazards to effectively prevent impacts or mitigate risks in an overall effort to improve the resilience of communities, especially in the face of climate change.
Storm Daniel caused widespread and multifaceted impacts that propagated across environmental, infrastructural, and socio-economic systems, illustrating an intricate interplay of primary and secondary effects. The storm results revealed significant vulnerabilities in public health systems, sanitation, drinking water systems, and storage facilities, illustrating the critical need for improved post-disaster management of public health, including possible interventions to prevent impacts propagation (e.g., disease outbreaks).
Widespread damage to road networks, bridges, and railways are well-known and common impacts of such events, resulting in significant disruptions to mobility, emergency response, and the transportation of essential goods, leading to isolation of communities that, in turn, lead to life-threatening delays in accessing healthcare and emergency services. The cascading effects related to transportation failure and water infrastructure underscore the need for robust and climate-resilient infrastructure design to ensure the continuity of critical services during extreme events.
The storm’s environmental impacts were profound, ranging from soil erosion and sediment deposition to water contamination and disruptions in marine and freshwater ecosystems. The significant geochemical and ecological changes illustrate the long-lasting and far-reaching consequences of flood events on natural systems and highlight the importance of integrated environmental monitoring and ecosystem management to mitigate the long-term impacts of such disasters.
This study contributes to the growing body of knowledge on cascading hazards by providing new evidence and insights into the propagation mechanisms and consequences of extreme flood events. The cascading impacts of Storm Daniel demonstrate the interconnected vulnerabilities of modern societies to extreme weather events, in a way that it can be concluded that it is very important to adopt a holistic risk management approach that considers the interdependencies of critical systems and sectors, and plan ahead on possible impact-propagation scenarios in order to prevent such cascading effects. Ultimately, understanding and addressing the cascade effects of such events is essential to protect lives, livelihoods, and ecosystems and to build resilient communities capable of withstanding future challenges.
Author Contributions
Conceptualization, M.D., E.L. and C.F.; methodology, M.D., C.F. and A.S.; software, E.V. and A.K.; formal analysis, M.D.; investigation, M.D., C.F., I.K., E.V., A.K., M.G. and A.S.; resources, M.D., C.F. and A.S.; data curation, M.D., M.G., C.F. and A.S.; writing—original draft preparation, M.D., P.N., C.F. and I.K.; writing—review and editing, M.D., E.L., C.F. and I.K.; visualization, E.V., P.N. and A.K.; supervision, M.D. All authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript.
Funding
This research received no external funding.
Data Availability Statement
Data available upon request.
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare no conflicts of interest.
References
- Arduino, G.; Reggiani, P.; Todini, E. Recent Advances in Flood Forecasting and Flood Risk Assessment. Hydrol. Earth Syst. Sci. 2005, 9, 280–284. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Morrison, A.; Westbrook, C.j.; Noble, B.f. A Review of the Flood Risk Management Governance and Resilience Literature. J. Flood Risk Manag. 2018, 11, 291–304. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Merkuryeva, G.; Merkuryev, Y.; Sokolov, B.V.; Potryasaev, S.; Zelentsov, V.A.; Lektauers, A. Advanced River Flood Monitoring, Modelling and Forecasting. J. Comput. Sci. 2015, 10, 77–85. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dordi, T.; Henstra, D.; Thistlethwaite, J. Flood Risk Management and Governance: A Bibliometric Review of the Literature. J. Flood Risk Manag. 2022, 15, e12797. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kron, W.; Löw, P.; Kundzewicz, Z.W. Changes in Risk of Extreme Weather Events in Europe. Environ. Sci. Policy 2019, 100, 74–83. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hochman, A.; Marra, F.; Messori, G.; Pinto, J.G.; Raveh-Rubin, S.; Yosef, Y.; Zittis, G. Extreme Weather and Societal Impacts in the Eastern Mediterranean. Earth Syst. Dyn. 2022, 13, 749–777. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bevacqua, E.; Maraun, D.; Vousdoukas, M.I.; Voukouvalas, E.; Vrac, M.; Mentaschi, L.; Widmann, M. Higher Probability of Compound Flooding from Precipitation and Storm Surge in Europe under Anthropogenic Climate Change. Sci. Adv. 2019, 5, eaaw5531. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fekete, A.; Sandholz, S. Here Comes the Flood, but Not Failure? Lessons to Learn after the Heavy Rain and Pluvial Floods in Germany 2021. Water 2021, 13, 3016. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Grau-Bove, J.; Higha, R.; Orr, S.; Kumar, P. Short Note on the Mapping of Heritage Sites Impacted by the 2024 Floods in Valencia, Spain 2024. arXiv 2024, arXiv:2411.08717. [Google Scholar]
- Svetlana, D.; Radovan, D.; Ján, D. The Economic Impact of Floods and Their Importance in Different Regions of the World with Emphasis on Europe. Procedia Econ. Finance 2015, 34, 649–655. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alfieri, L.; Feyen, L.; Salamon, P.; Thielen, J.; Bianchi, A.; Dottori, F.; Burek, P. Modelling the Socio-Economic Impact of River Floods in Europe. Nat. Hazards Earth Syst. Sci. 2016, 16, 1401–1411. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brody, S.D.; Zahran, S.; Maghelal, P.; Grover, H.; Highfield, W.E. The Rising Costs of Floods: Examining the Impact of Planning and Development Decisions on Property Damage in Florida. J. Am. Plan. Assoc. 2007, 73, 330–345. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Erickson, T.B.; Brooks, J.; Nilles, E.J.; Pham, P.N.; Vinck, P. Environmental Health Effects Attributed to Toxic and Infectious Agents Following Hurricanes, Cyclones, Flash Floods and Major Hydrometeorological Events. J. Toxicol. Environ. Health B 2019, 22, 157–171. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- IPCC Climate Change 2023: Synthesis Report. In Contribution of Working Groups I, II and III to the Sixth Assessment Report of the Intergovernmental Panel on Climate Change; Intergovernmental Panel on Climate Change: Geneva, Switzerland, 2023; p. 115.
- Diakakis, M.; Mavroulis, S.; Filis, C.; Lozios, S.; Vassilakis, E.; Naoum, G.; Soukis, K.; Konsolaki, A.; Kotsi, E.; Theodorakatou, D.; et al. Impacts of Medicanes on Geomorphology and Infrastructure in the Eastern Mediterranean, the Case of Medicane Ianos and the Ionian Islands in Western Greece. Water 2023, 15, 1026. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nastos, P.T.; Karavana Papadimou, K.; Matsangouras, I.T. Mediterranean Tropical-like Cyclones: Impacts and Composite Daily Means and Anomalies of Synoptic Patterns. Atmos. Res. 2018, 208, 156–166. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Amores, A.; Marcos, M.; Carrió, D.S.; Gómez-Pujol, L. Coastal Impacts of Storm Gloria (January 2020) over the North-Western Mediterranean. Nat. Hazards Earth Syst. Sci. 2020, 20, 1955–1968. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Michaelides, S.; Karacostas, T.; Sánchez, J.L.; Retalis, A.; Pytharoulis, I.; Homar, V.; Romero, R.; Zanis, P.; Giannakopoulos, C.; Bühl, J.; et al. Reviews and Perspectives of High Impact Atmospheric Processes in the Mediterranean. Atmos. Res. 2018, 208, 4–44. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gaume, E.; Bain, V.; Bernardara, P.; Newinger, O.; Barbuc, M.; Bateman, A.; Blaškovičová, L.; Blöschl, G.; Borga, M.; Dumitrescu, A.; et al. A Compilation of Data on European Flash Floods. J. Hydrol. 2009, 367, 70–78. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hammond, M.J.; Chen, A.S.; Djordjević, S.; Butler, D.; Mark, O. Urban Flood Impact Assessment: A State-of-the-Art Review. Urban Water J. 2015, 12, 14–29. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Merz, B.; Blöschl, G.; Vorogushyn, S.; Dottori, F.; Aerts, J.C.J.H.; Bates, P.; Bertola, M.; Kemter, M.; Kreibich, H.; Lall, U.; et al. Causes, Impacts and Patterns of Disastrous River Floods. Nat. Rev. Earth Environ. 2021, 2, 592–609. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bubeck, P.; Otto, A.; Weichselgartner, J. Societal Impacts of Flood Hazards. In Oxford Research Encyclopedia of Natural Hazard Science; Oxford University Press: Oxford, UK, 2017; ISBN 978-0-19-938940-7. [Google Scholar]
- Pescaroli, G.; Kelman, I. How Critical Infrastructure Orients International Relief in Cascading Disasters. J. Contingencies Crisis Manag. 2017, 25, 56–67. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pescaroli, G.; Alexander, D. Understanding Compound, Interconnected, Interacting, and Cascading Risks: A Holistic Framework. Risk Anal. 2018, 38, 2245–2257. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nones, M.; Pescaroli, G. Implications of Cascading Effects for the EU Floods Directive. Int. J. River Basin Manag. 2016, 14, 195–204. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cerveny, R.S.; Bessemoulin, P.; Burt, C.C.; Cooper, M.A.; Cunjie, Z.; Dewan, A.; Finch, J.; Holle, R.L.; Kalkstein, L.; Kruger, A.; et al. WMO Assessment of Weather and Climate Mortality Extremes: Lightning, Tropical Cyclones, Tornadoes, and Hail. Weather Clim. Soc. 2017, 9, 487–497. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pescaroli, G.; Nones, M.; Galbusera, L.; Alexander, D. Understanding and Mitigating Cascading Crises in the Global Interconnected System. Int. J. Disaster Risk Reduct. 2018, 30, 159–163. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alexander, D. A Magnitude Scale for Cascading Disasters. Int. J. Disaster Risk Reduct. 2018, 30, 180–185. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zuccaro, G.; De Gregorio, D.; Leone, M.F. Theoretical Model for Cascading Effects Analyses. Int. J. Disaster Risk Reduct. 2018, 30, 199–215. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alexander, D. Cascading Disasters: Multiple Risk Reduction and Resilience. In Handbook of Disaster Risk Reduction for Resilience: New Frameworks for Building Resilience to Disasters; Eslamian, S., Eslamian, F., Eds.; Springer International Publishing: Cham, Switzerland, 2021; pp. 187–201. ISBN 978-3-030-61278-8. [Google Scholar]
- AghaKouchack, A.; Huning, L.S.; Chiang, F.; Sadegh, M.; Vahedifard, F.; Mazdiyasni, O.; Moftakhari, H.; Mallakpour, I. How do natural hazards cascade to cause disasters? Nature 2018, 561, 458–460. [Google Scholar]
- Cozzani, V.; Campedel, M.; Renni, E.; Krausmann, E. Industrial Accidents Triggered by Flood Events: Analysis of Past Accidents. J. Hazard. Mater. 2010, 175, 501–509. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Arrighi, C.; Pregnolato, M.; Castelli, F. Indirect Flood Impacts and Cascade Risk across Interdependent Linear Infrastructures. Nat. Hazards Earth Syst. Sci. 2021, 21, 1955–1969. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Suk, J.E.; Vaughan, E.C.; Cook, R.G.; Semenza, J.C. Natural Disasters and Infectious Disease in Europe: A Literature Review to Identify Cascading Risk Pathways. Eur. J. Public Health 2020, 30, 928–935. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- ECMWF Medicane Daniel: An Extraordinary Cyclone with Devastating Impacts. Available online: https://www.ecmwf.int/en/newsletter/179/earth-system-science/medicane-daniel-extraordinary-cyclone-devastating-impacts (accessed on 16 March 2025).
- Argüeso, D.; Marcos, M.; Amores, A. Storm Daniel Fueled by Anomalously High Sea Surface Temperatures in the Mediterranean. NPJ Clim. Atmos. Sci. 2024, 7, 307. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nastos, P.T.; Feloni, E.; Paraskevas, A.; Matsangouras, I.T. Meteorological and Remote Sensing Analysis of the Severe Storm Daniel over Greece. In Proceedings of the European Geosciences Union General Assembly 2024 (EGU24), Vienna, Austria, 14–19 April 2024. Copernicus Meetings. [Google Scholar]
- He, K.; Yang, Q.; Shen, X.; Dimitriou, E.; Mentzafou, A.; Papadaki, C.; Stoumboudi, M.; Anagnostou, E.N. Brief Communication: Storm Daniel Flood Impact in Greece in 2023: Mapping Crop and Livestock Exposure from Synthetic-Aperture Radar (SAR). Nat. Hazards Earth Syst. Sci. 2024, 24, 2375–2382. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dimitriou, E.; Efstratiadis, A.; Zotou, I.; Papadopoulos, A.; Iliopoulou, T.; Sakki, G.-K.; Mazi, K.; Rozos, E.; Koukouvinos, A.; Koussis, A.D.; et al. Post-Analysis of Daniel Extreme Flood Event in Thessaly, Central Greece: Practical Lessons and the Value of State-of-the-Art Water-Monitoring Networks. Water 2024, 16, 980. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Diakakis, M.; Mavroulis, S.; Filis, C.; Bantekas, Y.; Gogou, M.; Katsetsiadou, K.-N.; Mavrouli, M.; Giannopoulos, V.; Sarantopoulou, A.; Nastos, P.; et al. The Diverse Impacts of Extreme Storms in the European South. The Case of Storm Daniel (2023) in Greece. In Proceedings of the European Geosciences Union General Assembly 2024 (EGU24), Vienna, Austria, 14–19 April 2024. Copernicus Meetings. [Google Scholar]
- Lekkas, E.; Diakakis, M.; Mavroulis, S.; Filis, C.; Bantekas, Y.; Gogou, M.; Katsetsiadou, K.N.; Mavrouli, M.; Giannopoulos, M.; Sarantopoulou, A.; et al. The Early September 2023 Daniel Storm in Thessaly Region (Central Greece). In Newsletter of Environmental, Disaster and Crises Management Strategies; Post-graduate Studies Program “Environmental Disasters & Crises Management Strategies”; National and Kapodistrian University of Athens: Athens, Greece, 2024; p. 212. [Google Scholar]
- Karakatsani, E. Greece Economy Briefing: The Economic Impact of the Recent Devastating Floods in Greece. China-CEE Inst. 2023, 65, 1–6. [Google Scholar]
- USAID. Libya Assistance Overview, April 2024—Libya|ReliefWeb; USAID Bureau for Humanitarian Assistance: Washington, DC, USA, 2024; p. 2.
- Normand, J.C.L.; Heggy, E. Assessing Flash Flood Erosion Following Storm Daniel in Libya. Nat. Commun. 2024, 15, 6493. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Poulakida, I.; Kotsiou, O.S.; Boutlas, S.; Stergioula, D.; Papadamou, G.; Gourgoulianis, K.I.; Papagiannis, D. Leptospirosis Incidence Post-Flooding Following Storm Daniel: The First Case Series in Greece. Infect. Dis. Rep. 2024, 16, 880–887. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mavroulis, S.; Mavrouli, M.; Lekkas, E.; Tsakris, A. Impact of the September 2023 Storm Daniel and Subsequent Flooding in Thessaly (Greece) on the Natural and Built Environment and on Infectious Disease Emergence. Environments 2024, 11, 163. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Perivolioti, T.-M.; Zachopoulos, K.; Zioga, M.; Tompoulidou, M.; Katsavouni, S.; Kemitzoglou, D.; Terzopoulos, D.; Mouratidis, A.; Tsiaoussi, V. Monitoring the Impact of Floods on Water Quality Using Optical Remote Sensing Imagery: The Case of Lake Karla (Greece). Water 2024, 16, 3502. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vardakas, L.; Koutsikos, N.; Dimitriou, E.; Vavalidis, T.; Kouraklis, P.; Kalogianni, E. Short-Term Effects of Storm Daniel on Salmo Farioides (Karaman, 1938) in a High-Gradient Stream. River Res. Appl. 2024, 40, 647–654. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dimoudi, A.; Voulgaris, K.; Varkoulis, A.; Georgiou, K.; Klaoudatos, D.; Skordas, K.; Vafidis, D.; Neofitou, N. The Impacts of Daniel and Elias Storms on Water Quality of Pagasitikos Gulf—A First Record. In Proceedings of the HydroMediT, Mytilene, Greece, 30 May–2 June 2024; University of the Aegean: Mytilene, Greece, 2024. [Google Scholar]
- Papageorgiou, D.; Spondylidis, S.; Topouzelis, K. Post-Extreme Event Monitoring of Runoff-Carried Natural and Anthropogenic Floating Marine Debris with Sentinel-2 Data. The Case of Storm Daniel in North-Eastern Mediterranean. In Proceedings of the IGARSS 2024—2024 IEEE International Geoscience and Remote Sensing Symposium, Athena, Greece, 7–12 July 2024; pp. 1896–1899. [Google Scholar]
- Varkoulis, A.; Voulgaris, K.; Dimoudi, A.; Georgiou, K.; Skordas, K.; Neofitou, N.; Vafidis, D. Upper Sublittoral Meiofaunal Communities of Pagasitikos Gulf after Two Extreme Storms. In Proceedings of the HydroMediT, Mytilene, Greece, 30 May–2 June 2024; University of the Aegean: Mytilene, Greece, 2024. [Google Scholar]
- Lougkovois, R.; Parinos, K.; Gkotsis, G.; Nika, M.-C.; Thomaidis, N.; Pavlidou, A.; Hatzianestis, I. Monitoring the Presence of Priority Pollutants and Emerging Contaminants at Pagasitikos Gulf, Greece, Following Daniel and Elias Storm Events, Utilizing the Technique of LC-VIP-HESI-TIMS-HRMS. In Proceedings of the EGU General Assembly 2024, Vienna, Austria, 14–19 April 2024. Copernicus Meetings. [Google Scholar]
- Iatrou, M.; Tziouvalekas, M.; Tsitouras, A.; Evangelou, E.; Noulas, C.; Vlachostergios, D.; Aschonitis, V.; Arampatzis, G.; Metaxa, I.; Karydas, C.; et al. Analyzing the Impact of Storm ‘Daniel’ and Subsequent Flooding on Thessaly’s Soil Chemistry through Causal Inference. Agriculture 2024, 14, 549. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pavlis, E. Landscape Loss and Restoration: The Case of Lake Karla in Greece. Landsc. Res. 2024, 1–15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pescaroli, G.; Alexander, D. A Definition of Cascading Disasters and Cascading Effects: Going beyond the “Toppling Dominos” Metaphor. In GRF Davos Planet@Risk, Volume 3, Number 1, Special Issue on the 5th IDRC Davos 2014, March 2015; GRF Davos Global Risk Forum: Davos, Switzerland, 2015; pp. 58–67. [Google Scholar]
- Diaz, J.H. Rodent-Borne Infectious Disease Outbreaks after Flooding Disasters: Epidemiology, Management, and Prevention. J. Emerg. Manag. West. Mass 2015, 13, 459–467. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ahern, M.; Kovats, R.S.; Wilkinson, P.; Few, R.; Matthies, F. Global Health Impacts of Floods: Epidemiologic Evidence. Epidemiol. Rev. 2005, 27, 36–46. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alderman, K.; Turner, L.R.; Tong, S. Floods and Human Health: A Systematic Review. Environ. Int. 2012, 47, 37–47. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Paterson, D.L.; Wright, H.; Harris, P.N.A. Health Risks of Flood Disasters. Clin. Infect. Dis. 2018, 67, 1450–1454. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- National Public Health Organization. National Public Health Organization’s Newsletter—May 2024; National Public Health Organization: Athens, Greece, 2024; p. 1.
- National Public Health Organization. Epidemiological Data on Leptospirosis in Greece (2004–2023) Mandatory Disease Notification System; National Public Health Organization Directorate of Epidemiological Surveillance and Intervention for Infectious Diseases Department of Zoonoses: Athens, Greece, 2024; pp. 1–5.
- Hellenic Government. The Restoration Plan for Damages Caused by the Extreme Weather Events “Daniel” and “Elias,” in School, Railway, and Road Infrastructure in Thessaly and Central Greece 2024; Hellenic Government: Athens, Greece, 2024.
- Ministry of Infrastructure and Transport Ministerial Decision. Inclusion of the Project “SUB-PROJECT 2: Restoration of Accessibility after the Devastating Impacts of Storms ‘DANIEL’ and ‘ELIAS’—Restoration of the Railway Network” (OPS Code TA 5225196) 2024; Ministry of Infrastructure and Transport: Athens, Greece, 2024.
- Imerisia Newspaper. Storm Daniel: Food Delivery by Helicopters to East Pelion—The Situation in Volos and Larissa. Imerisia Newspaper, 10 September 2023; p. 1.
- Stamos Prousalis; Lefteris Papadimas Flooded Homes, Streets as Another Storm Hits Battered Central Greece. Reuters, 28 September 2023.
- SKAI Operation to transport kidney patients with ropes in Pelion. SKAI News, 6 September 2023.
- LIFO Severe Weather: Pregnant Woman Trapped in Palamas—Taken to the Hospital after Rescue. LIFO Newsroom, 8 September 2023.
- Iatropedia Storm Daniel: Dozens of People in Hospitals across Thessaly—Trapped Patients at Risk. Iatropedia Website, 9 September 2023.
- Magnesia News Forty Residents of Farkadona, Trikala Found Shelter at the Health Center—Among Them Were Six Patients and One Person Who Was Bitten by a Snake. Magnesia News, 10 September 2023.
- Arrighi, C.; Tarani, F.; Vicario, E.; Castelli, F. Flood Impacts on a Water Distribution Network. Nat. Hazards Earth Syst. Sci. 2017, 17, 2109–2123. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Budiyono; Ginandjar, P.; Saraswati, L.D.; Pangestuti, D.R.; Martini; Jati, S.P.; Rahfiludin, Z. Risk Assessment of Drinking Water Supply System in the Tidal Inundation Area of Semarang—Indonesia. Procedia Environ. Sci. 2015, 23, 93–98. [CrossRef]
- Sänger, N.; Heinzel, C.; Sandholz, S. Advancing Resilience of Critical Health Infrastructures to Cascading Impacts of Water Supply Outages—Insights from a Systematic Literature Review. Infrastructures 2021, 6, 177. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gannon, K.E.; Conway, D.; Pardoe, J.; Ndiyoi, M.; Batisani, N.; Odada, E.; Olago, D.; Opere, A.; Kgosietsile, S.; Nyambe, M.; et al. Business Experience of Floods and Drought-Related Water and Electricity Supply Disruption in Three Cities in Sub-Saharan Africa during the 2015/2016 El Niño. Glob. Sustain. 2018, 1, e14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kyriakopoulos, K. Severe Weather Daniel: Two Girls from Drakeia, Pelion, Describe the Nightmare Their Village Experienced. Manifesto News, 8 September 2023. [Google Scholar]
- Documento News Visit of the President of POEDHN to the Hospital of Volos. Documento News, 9 September 2023.
- Vicky Karantzavellou Association of Hoteliers of Magnesia: The Issue of Survival Is Now Imminent. Travel Daily News, 20 September 2023.
- Ashoor, A.; Eladawy, A. Navigating Catastrophe: Lessons from Derna amid Intensified Flash Floods in the Anthropocene. Euro-Mediterr. J. Environ. Integr. 2024, 9, 1125–1140. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kozlowski, T.T. Physiological-Ecological Impacts of Flooding on Riparian Forest Ecosystems. Wetlands 2002, 22, 550–561. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Poff, N.L. Ecological Response to and Management of Increased Flooding Caused by Climate Change. Philos. Trans. R. Soc. Lond. Ser. Math. Phys. Eng. Sci. 2002, 360, 1497–1510. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Peters, D.L.; Caissie, D.; Monk, W.A.; Rood, S.B.; St-Hilaire, A. An Ecological Perspective on Floods in Canada. Can. Water Resour. J. Rev. Can. Ressour. Hydr. 2016, 41, 288–306. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Markantonis, V.; Meyer, V.; Lienhoop, N. Evaluation of the Environmental Impacts of Extreme Floods in the Evros River Basin Using Contingent Valuation Method. Nat. Hazards 2013, 69, 1535–1549. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Talbot, C.J.; Bennett, E.M.; Cassell, K.; Hanes, D.M.; Minor, E.C.; Paerl, H.; Raymond, P.A.; Vargas, R.; Vidon, P.G.; Wollheim, W.; et al. The Impact of Flooding on Aquatic Ecosystem Services. Biogeochemistry 2018, 141, 439–461. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- SKAI Business Owners in Magnesia Have Filed a Lawsuit against All Responsible Parties for the Damages. SKAI News, 8 September 2024.
- Decentralized Administration of Thessaly—Central Greece. Public and Stakeholder Notification Regarding the Lifting of the Swimming Ban in Areas along the Coastal Front of the Pagasitikos Gulf; Decentralized Administration of Thessaly—Central Greece: Larissa, Greece, 2024. [Google Scholar]
- Vieira, R.; Marques, S.M.; Neto, J.M.; Barría, P.; Marques, J.C.; Gonçalves, F.J.M.; Gonçalves, A.M.M. Brain as a Target Organ of Climate Events: Environmental Induced Biochemical Changes in Three Marine Fish Species. Ecol. Indic. 2018, 95, 815–824. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hellenic Navy Hydrographic Service. Pagasitikos Gulf Volos Port, Reported Existence of Decreased Depths; Hellenic Navy Hydrographic Service: Attica, Greece, 2023. [Google Scholar]
- Georgiou, K.; Kelepertzis, E.; Vafidis, D.; Skordas, K. Assessing the Environmental Impacts of Two Intensive Storms on Pagasitikos Gulf Surficial Sediments. In Proceedings of the HydroMediT, Mytilene, Greece, 30 May–2 June 2024; University of the Aegean: Mytilene, Greece, 2024; pp. 33–35. [Google Scholar]
- Katsoulis, K.; Papadopoulou, A. Case Study: Nutrients Distribution and Assessment of the Current Trophic Status of Plastiras Lake in Thessaly (Central Greece) after Tropical Storm Daniel. GSC Adv. Res. Rev. 2024, 20, 477–483. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ioannidis, S. Stefanovikeio: Time for Decisions for the Army Aviation. Kathimerini, 14 March 2024. [Google Scholar]
- SETE Institute. Region of Thessaly: Annual Report on Competitiveness and Structural Adaptation in the Tourism Sector for the Year 2023 December 2024; SETE Institute: Athens, Greece, 2024; p. 263. [Google Scholar]
- Cheirchanteri, G. Climate Change and the Effect of Natural Disasters on the Tourism of Architectural, Cultural Heritage Sites: The Case of Broader Area of Thessaly, Greece. In Proceedings of the World Summit: Civil Engineering-Architecture-Urban Planning Congress—CAUSummit 2024, Antalya, Turkiye, 2–6 September 2024; CAUSummit: Antalya, Turkiye, 2024. [Google Scholar]
- Raftopoulou, E. Volos in a State of Emergency for One Month—Collection of Dead Fish Continues. Hell. Broadcast. Corp. 2024. [Google Scholar]
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).