Study on Large-Scale Geomechanical Experiments on Tunnel External Water Pressure
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Background
3. Geomechanical Model
3.1. Experimental Design
3.2. Loading System
3.3. Model Materials
4. Analysis of Model Experimental Results
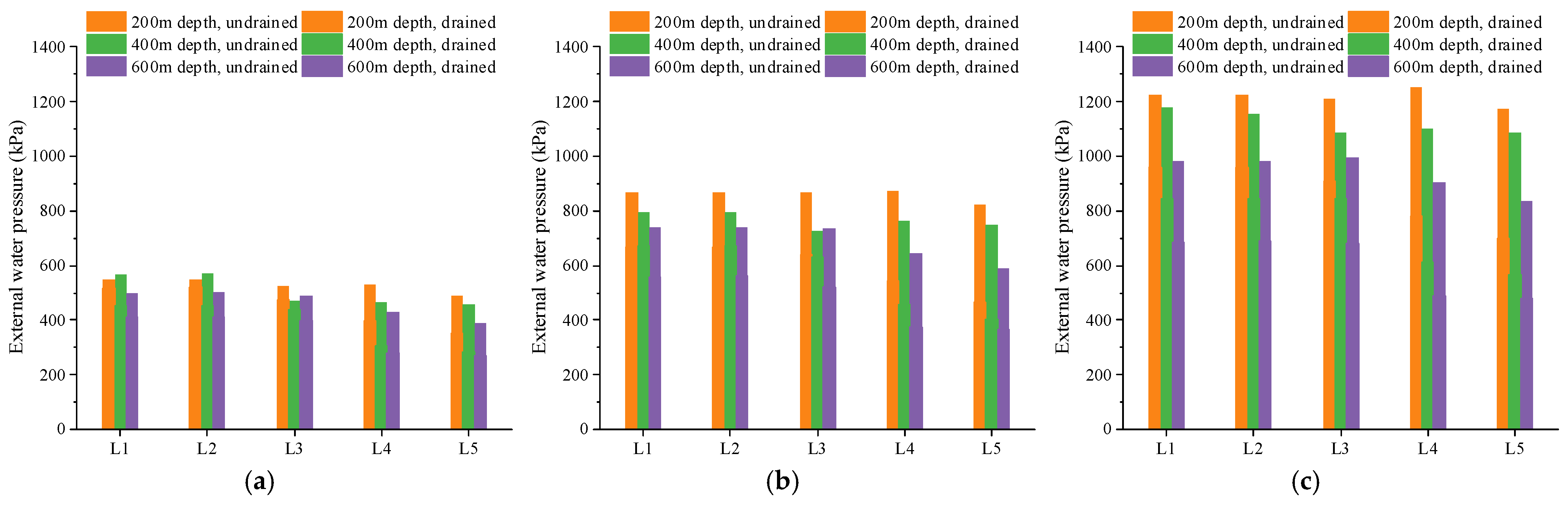
4.1. Influence of Tunnel Depth
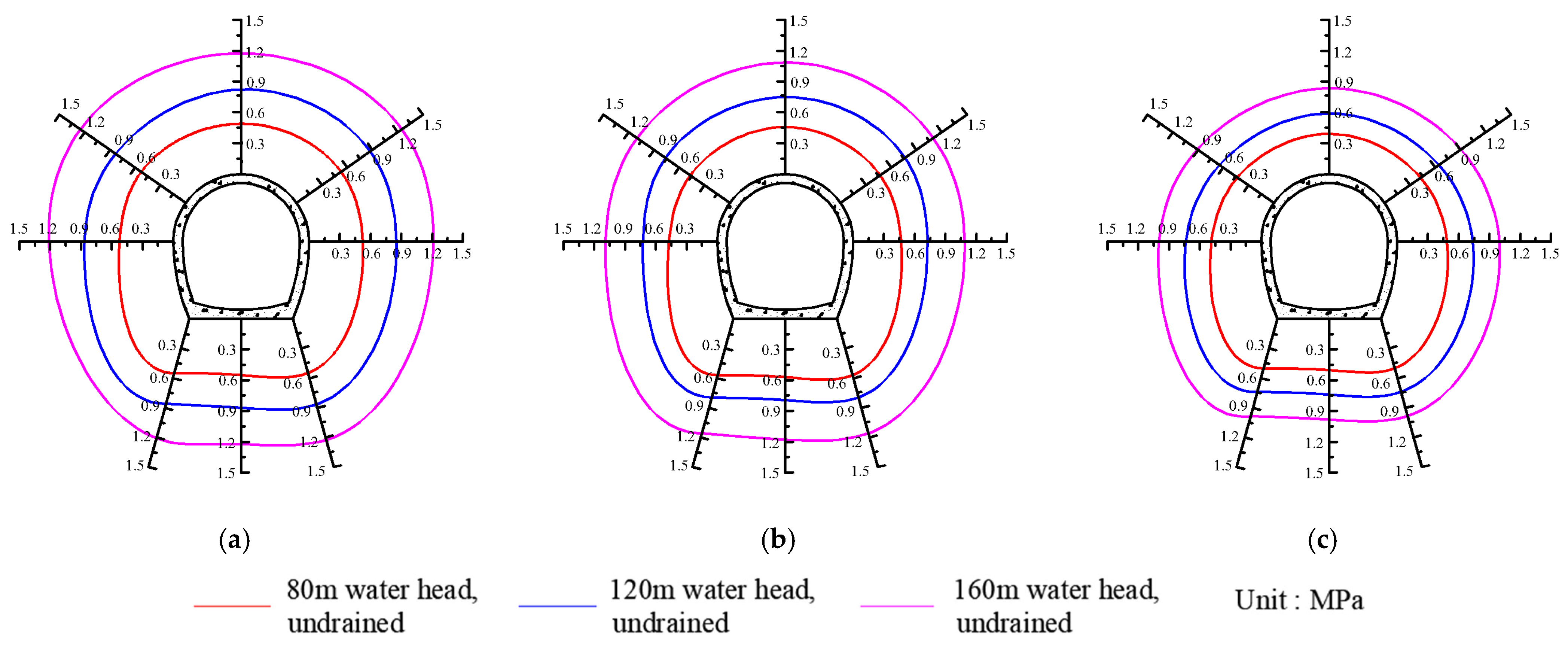
4.2. Influence of Water Head
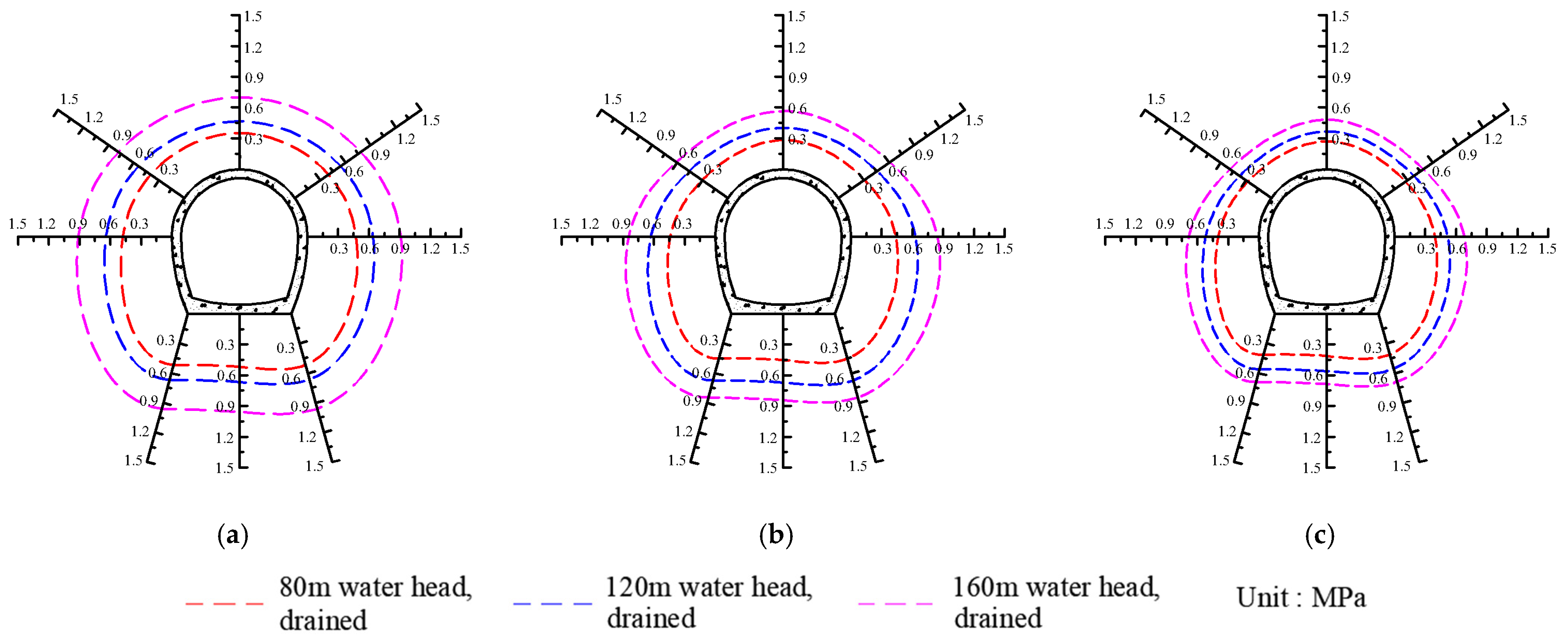
4.3. Influence of Drainage Conditions
4.4. Discussion on Reduction Coefficient Values
5. Conclusions
- 1.
- The geomechanical model system was developed to investigate high external water pressure under complex geological conditions. This system includes a waterproof model framework, a stress loading system, a seepage pressure loading system, and a monitoring and data acquisition system. The system meets the waterproofing requirements and provides constant pressure.
- 2.
- The model experiments revealed the distribution pattern of external water pressure in the Songlin Tunnel. Under undrained conditions, the external water pressure is mainly controlled by the water head and tunnel depth. At low water heads, the tunnel depth has little effect on the external water pressure. At a water head of 160 m, the external water pressure significantly decreases with an increasing tunnel depth.
- 3.
- For undrained conditions, the reduction coefficients decrease with increasing tunnel depth and slightly increase with higher water heads. The suggested coefficients are 0.65–0.80 for shallowly buried tunnels with high water heads and 0.50–0.65 for deeply buried tunnels with low water heads. For drained conditions, the recommended reduction coefficients are 0.30–0.55 for the arch vault and spandrels. For the haunch, arch springing, and arch bottom, the suggested coefficients are 0.50 to 0.60 under the low water head and 0.40 to 0.60 under the high water head.
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Peng, Y.; Cao, C.; Ji, F.; Chen, X. Water inrush-induced failure during deep excavation for a metro station in karst regions in Shenzhen, China: Cause diagnosis and post-accident restoration. Eng. Fail. Anal. 2024, 162, 108346. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, W.; Sun, W.; Zhang, J.; Wang, Y.; Zhang, Y.; Xu, W. Research review on high external water pressure of deep-buried tunnels. J. China Three Gorges Univ. Nat. Sci. 2023, 45, 1–11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, D.M.; Xie, X.C.; Zhou, M.L.; Huang, Z.K.; Zhang, D.M. An incident of water and soil gushing in a metro tunnel due to high water pressure in sandy silt. Eng. Fail. Anal. 2021, 121, 105196. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, Y.; Che, Y.; Gong, J. Behavior of corrosion damaged circular reinforced concrete columns under cyclic loading. Constr. Build. Mater. 2012, 29, 548–556. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, J.; Fu, W.; Hu, X.; Liu, C.; Yang, Q.; Ju, J.W. Experimental study on the long-term behaviors of spray-applied acrylate waterproofing membrane for tunnels exposed to aggressive ions. Constr. Build. Mater. 2020, 258, 119603. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bobet, A. Analytical solutions for shallow tunnels in saturated ground. J. Eng. Mech. 2001, 127, 1258–1266. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bobet, A. Effect of pore water pressure on tunnel support during static and seismic loading. Tunn. Undergr. Space Technol. 2003, 18, 377–393. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nam, S.W.; Bobet, A. Liner stresses in deep tunnels below the water table. Tunn. Undergr. Space Technol. 2006, 21, 626–635. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Duan, S.; Jiang, X.; Jiang, Q.; Xiong, J.; Li, C. Theoretical solution and failure analysis of water pressure on lining of deep-buried non-circular hydraulic tunnel based on the equivalent hydraulic radius method. Eng. Fail. Anal. 2023, 148, 107163. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shin, J.; Shin, Y.; Kim, S.; Shin, H. Evaluation of residual pore water pressures on linings for undersea tunnels. Chin. J. Rock Mech. Eng. 2007, 26, 3682–3685. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, X.Y.; Wang, M.S.; Zhang, M. A simple method to calculate tunnel discharge and external water pressure on lining. J. Beijing Jiaotong Univ. 2004, 28, 8–10. [Google Scholar]
- Kolymbas, D.; Wagner, P. Groundwater ingress to tunnels: The exact analytical solution. Tunn. Undergr. Space Technol. 2007, 22, 23–27. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shen, J.; Ma, H.; Du, H.; Xin, Y.; Liu, H.; Ma, W. Numerical Simulation of the External Water Pressure in Seepage Anisotropy Under Heterogeneous Conditions. Water 2024, 16, 3173. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schwartz, F.W.; Sudicky, E.A.; McLaren, R.G.; Park, Y.J.; Huber, M.; Apted, M. Ambiguous hydraulic heads and 14C activities in transient regional flow. Groundwater 2010, 48, 366–379. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xie, X.; Xie, X.; Wang, X.; Lu, B.; Chen, H. Influences of aquiclude on external water pressures on linings of deep-buried tunnels. Chin. J. Geotech. Eng. 2020, 42, 146–150. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Long, C.S.; Wilson, C.R.; Witherspoon, P. Porous media equivalents for networks of discontinuous fractures. Water Resour. Res. 1982, 18, 645–658. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cacas, M.C.; Ledoux, E.; Marsily, G.; Tillie, B.; Barbreau, A.; Durand, E.; Feuga, P.; Peaudecerf, P. Modeling fracture flow with a stochastic discrete fracture network: Calibration and validation: 1. the flow model. Water Resour. Res. 1990, 26, 479–489. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, Y.; Fu, Z.; Chen, J.; Liu, X. The external water pressure on a deep buried tunnel in fractured rock. Tunn. Undergr. Space Technol. 2015, 48, 58–66. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xiong, F.; Zhu, C.; Feng, G.; Zheng, J.; Sun, H. A three-dimensional coupled thermo-hydro model for geothermal development in discrete fracture networks of hot dry rock reservoirs. Gondwana Res. 2023, 122, 331–347. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shin, J.; Potts, D.; Zdravkovic, L. The effect of pore-water pressure on NATM tunnel linings in decomposed granite soil. Can. Geotech. J. 2005, 42, 1585–1599. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Arjnoi, P.; Jeong, J.H.; Kim, C.Y.; Lee, J.Y. Effect of drained conditions on porewater pressure distributions and lining stresses in drained tunnels. Tunn. Undergr. Space Technol. 2009, 24, 376–389. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, L.; Yang, J.; Fu, J.; Wang, S.; Zhang, C.; Xiang, M. Experimental investigation on the invert stability of operating railway tunnels with different drainage systems using 3D printing technology. J. Rock Mech. Geotech. Eng. 2022, 14, 1470–1485. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fang, Y.; Guo, J.; Grasmick, J.; Zhang, H. The effect of external water pressure on the liner behavior of large cross-section tunnels. Tunn. Undergr. Space Technol. 2016, 60, 80–95. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fan, H.; Zhu, Z.; Song, Y.; Li, B. Water pressure evolution and structural failure characteristics of tunnel lining under hydrodynamic pressure. Eng. Fail. Anal. 2021, 130, 105747. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, P.; Feng, C.; Liu, H.; Zhao, Z.; Li, Y.; Xiong, H. Development and assessment of a water pressure reduction system for lining invert of underwater tunnels. Mar. Georesour. Geotechnol. 2021, 39, 365–371. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, X.; Tan, Z.; Wang, M.; Huangfu, M.; Zhang, Z. Theoretical and experimental study of external water pressure on tunnel lining in controlled drainage under high water level. Tunn. Undergr. Space Technol. 2008, 23, 552–560. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qian, W.P.; Wang, B.; Luo, D.W.; Xu, A.; Li, S.C. Experimental investigation and application on mechanical properties of tunnel linings under different blockage rates of drainage system in a karst tunnel. Tunn. Undergr. Space Technol. 2025, 157, 106359. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, G.; Yang, X.; Zhang, J.; He, M.; Hao, Z.; Yang, F.; Shao, J. Effect of Roof Cutting Technology on Broken Roof Rock Bulking and Abutment Stress Distribution: A Physical Model Test. Rock Mech. Rock Eng. 2024, 57, 3767–3785. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- He, B.; Xue, R.; Zhang, Z.; Feng, X.; Wu, C. A novel method of imposing external water pressure to explore the failure behavior of railway tunnel linings. Tunn. Undergr. Space Technol. 2023, 133, 104942. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiang, Y.; Zhou, F.; Lin, J.; Li, J.; Qi, Y.; Wang, X.; Zhou, Z. Evolution mechanism of tunnel water and sand inrush considering water-rich sandy dolomite hazard-causing structures. Eng. Fail. Anal. 2023, 153, 107554. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- He, B.; Zhang, Z.; Xue, B.; He, X.; Feng, Z.; Sun, C. Model test on the behavior of tunnel linings under earth pressure conditions and external water pressure. Transp. Geotech. 2021, 26, 100457. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, R.; Wang, X.; Zhang, W.; Xu, W.; Lu, J.; Xiang, T. Physical model experiment of external water pressure in lining surrounding rock of a deep tunnel with cross faults. J. Tsinghua Univ. Sci. Technol. 2024, 64, 1179–1192. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]

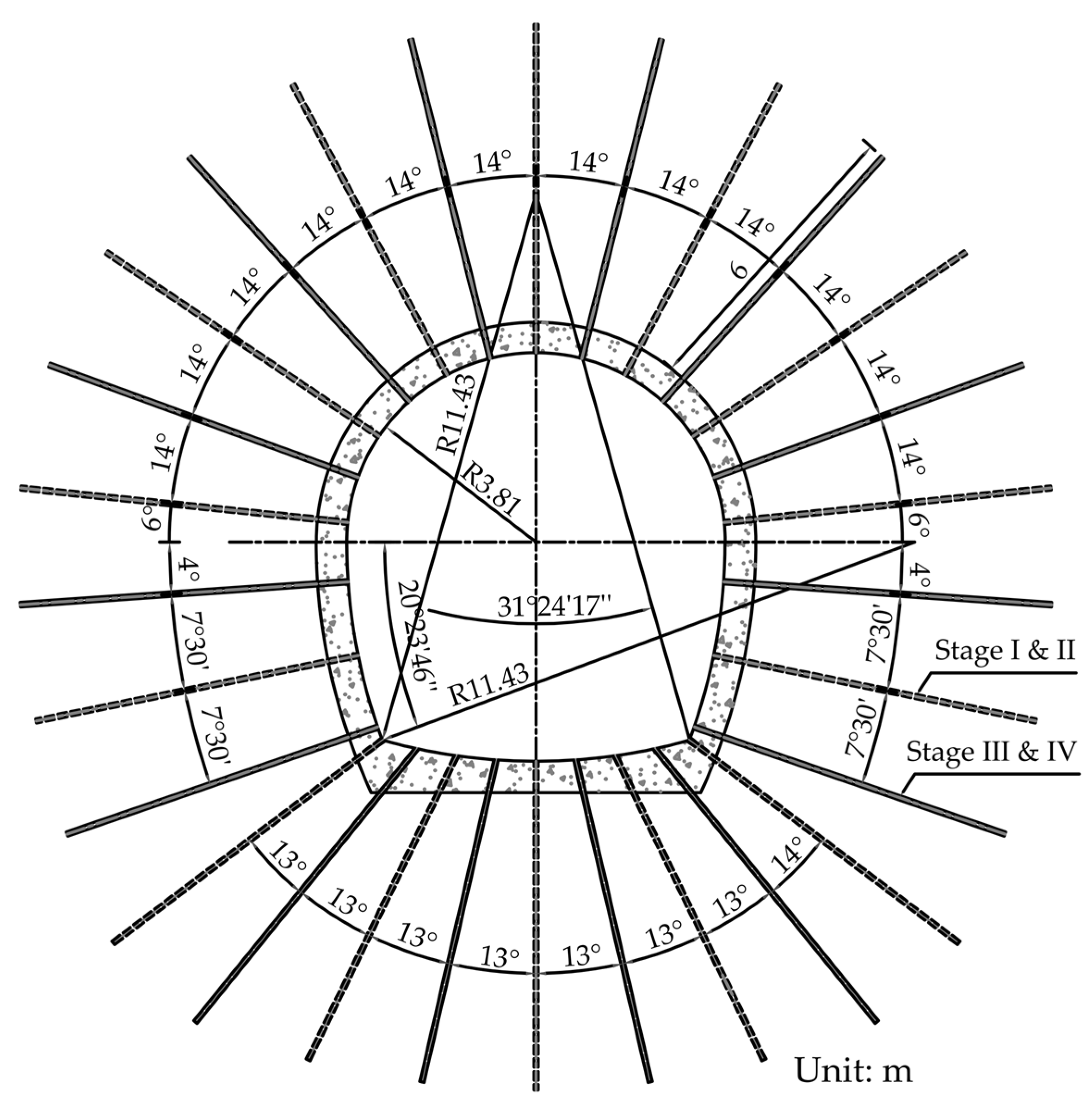
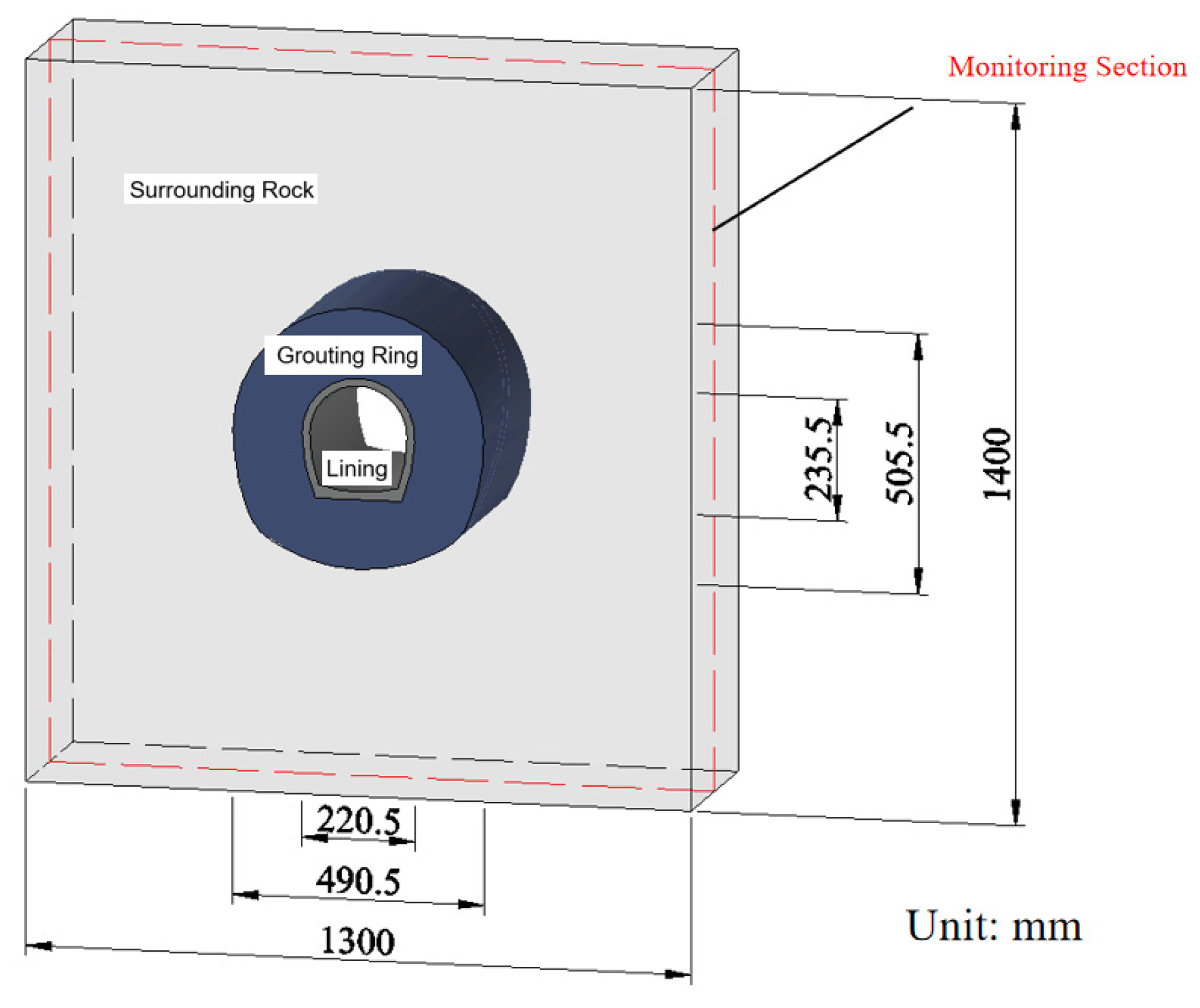
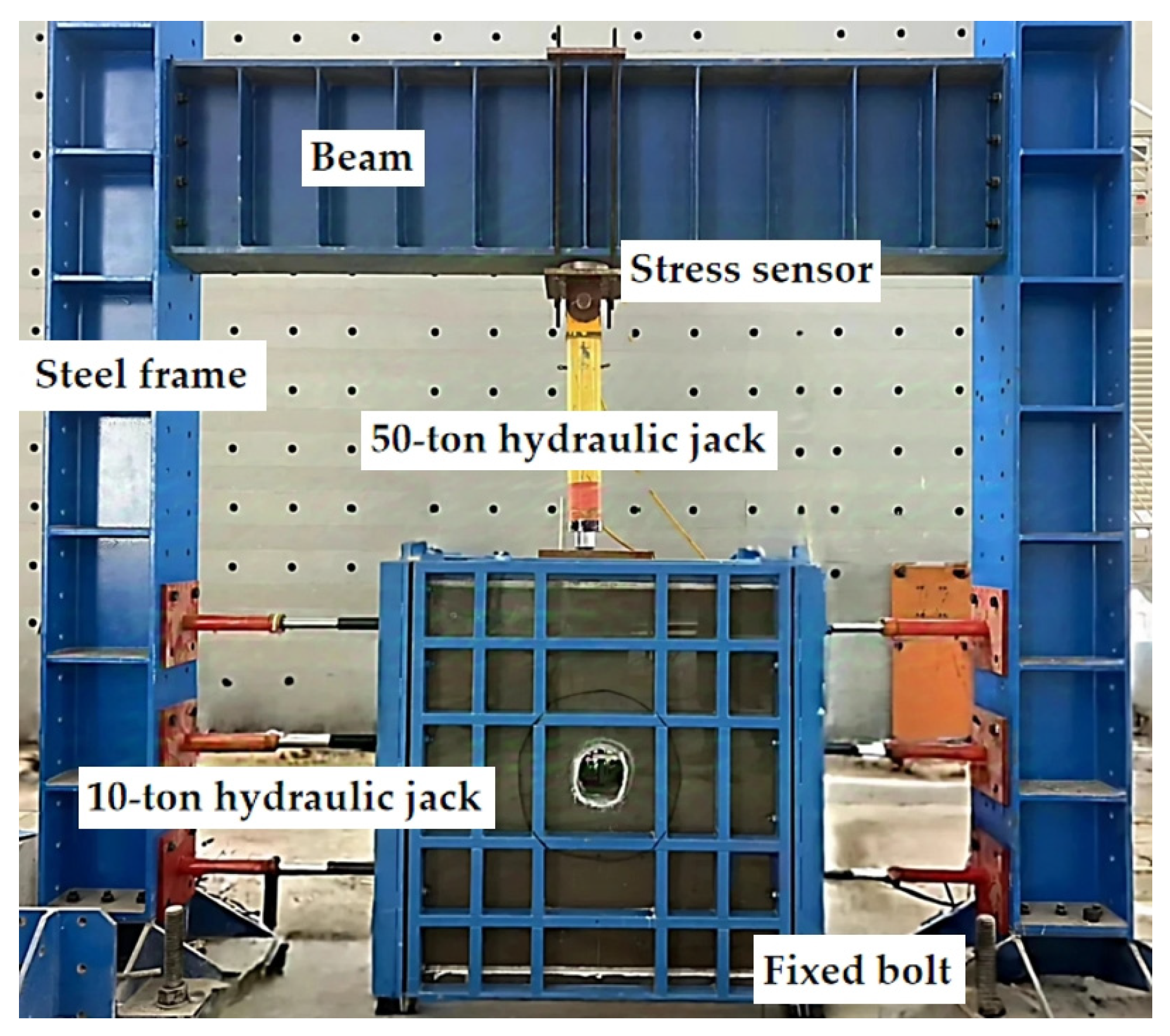
| Scheme | Drainage Condition | Tunnel Depth (m) | Water Head (m) |
|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | Undrained | 200 | 80 |
| 2 | 120 | ||
| 3 | 160 | ||
| 4 | 400 | 80 | |
| 5 | 120 | ||
| 6 | 160 | ||
| 7 | 600 | 80 | |
| 8 | 120 | ||
| 9 | 160 | ||
| 10 | Drained * | 200 | 80 |
| 11 | 120 | ||
| 12 | 160 | ||
| 13 | 400 | 80 | |
| 14 | 120 | ||
| 15 | 160 | ||
| 16 | 600 | 80 | |
| 17 | 120 | ||
| 18 | 160 |
| Material | Iron Powder | Quartz Sand (%) | Barite Powder (%) | White Cement (%) | Silicone Oil (%) | Water (%) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Surrounding Rock | 25.09 | 22.99 | 36.26 | 8.66 | 1.21 | 5.78 |
| Grouting Ring | 31.34 | 26.59 | 23.07 | 11.25 | 0.26 | 7.49 |
| Model Component | Density (g·cm−3) | Elastic Modulus (GPa) | Permeability Coefficient (10−5 cm·s−1) |
|---|---|---|---|
| Surrounding Rock | 2.68 | 2.31 | 5.70 |
| Grouting Ring | 2.83 | 3.40 | 1.70 |
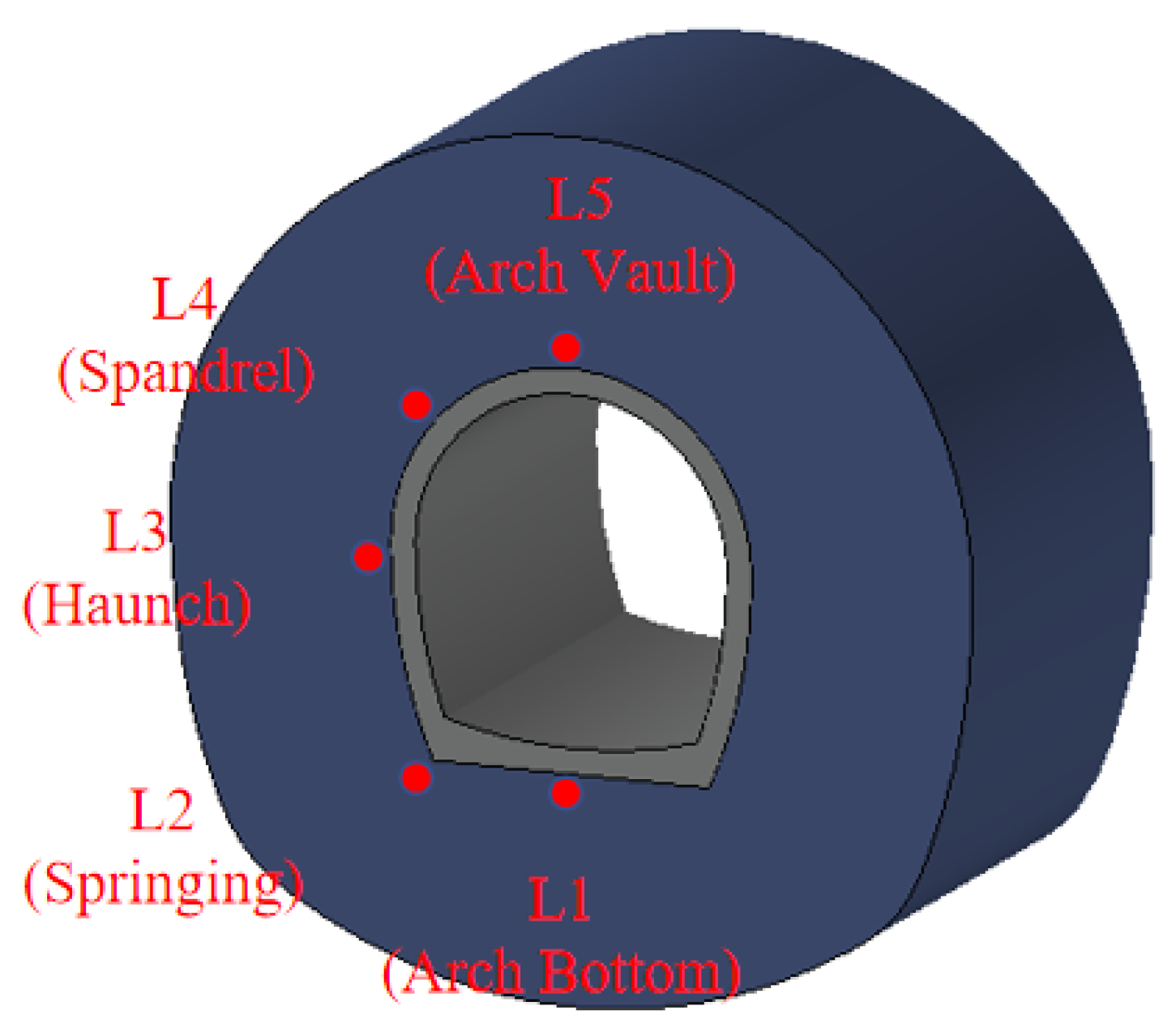
| Water Head (m) | Tunnel Depth (m) | Arch Bottom (L1)/kPa | Springing (L2)/kPa | Haunch (L3)/kPa | Spandrels (L4)/kPa | Arch Vault (L5)/kPa | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Undrained | Drained | Undrained | Drained | Undrained | Drained | Undrained | Drained | Undrained | Drained | ||
| 80 | 200 | 549 | 518 | 549 | 519 | 524 | 475 | 528 | 397 | 489 | 351 |
| 400 | 866 | 667 | 867 | 668 | 866 | 641 | 873 | 542 | 822 | 466 | |
| 600 | 1223 | 958 | 1224 | 960 | 1212 | 911 | 1251 | 781 | 1174 | 699 | |
| 120 | 200 | 569 | 452 | 570 | 453 | 470 | 438 | 468 | 308 | 456 | 282 |
| 400 | 794 | 671 | 795 | 673 | 725 | 629 | 764 | 458 | 749 | 402 | |
| 600 | 1177 | 843 | 1158 | 845 | 1089 | 845 | 1101 | 610 | 1086 | 565 | |
| 160 | 200 | 500 | 411 | 501 | 412 | 487 | 396 | 430 | 277 | 390 | 269 |
| 400 | 739 | 560 | 740 | 561 | 735 | 519 | 643 | 375 | 590 | 367 | |
| 600 | 983 | 687 | 983 | 688 | 996 | 682 | 907 | 490 | 834 | 481 | |
| Water Head (m) | Tunnel Depth (m) | Arch Bottom (L1)/% | Springing (L2)/% | Haunch (L3)/% | Spandrels (L4)/% | Arch Vault (L5)/% |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 80 | 200 | 5.7 | 5.5 | 9.4 | 24.7 | 28.3 |
| 400 | 20.6 | 20.5 | 6.9 | 34.1 | 38.2 | |
| 600 | 17.7 | 17.6 | 18.7 | 35.6 | 31.0 | |
| 120 | 200 | 23.1 | 22.9 | 25.9 | 37.9 | 43.3 |
| 400 | 15.5 | 15.4 | 13.3 | 40.1 | 46.4 | |
| 600 | 24.3 | 24.1 | 29.4 | 41.6 | 37.7 | |
| 160 | 200 | 21.7 | 21.6 | 24.8 | 37.5 | 40.5 |
| 400 | 28.4 | 27.0 | 22.4 | 44.6 | 48.0 | |
| 600 | 30.1 | 30.0 | 31.5 | 46.0 | 42.3 |
| Water Head (m) | Tunnel Depth (m) | Arch Bottom (L1) | Springing (L2) | Haunch (L3) | Spandrels (L4) | Arch Vault (L5) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 80 | 200 | 0.65 | 0.65 | 0.66 | 0.69 | 0.66 |
| 400 | 0.67 | 0.67 | 0.59 | 0.61 | 0.61 | |
| 600 | 0.59 | 0.59 | 0.61 | 0.56 | 0.52 | |
| 120 | 200 | 0.69 | 0.69 | 0.72 | 0.75 | 0.72 |
| 400 | 0.64 | 0.64 | 0.61 | 0.66 | 0.65 | |
| 600 | 0.59 | 0.59 | 0.61 | 0.55 | 0.52 | |
| 160 | 200 | 0.74 | 0.74 | 0.76 | 0.80 | 0.76 |
| 400 | 0.71 | 0.70 | 0.68 | 0.70 | 0.70 | |
| 600 | 0.60 | 0.60 | 0.62 | 0.58 | 0.54 |
| Water Head (m) | Tunnel Depth (m) | Arch Bottom (L1) | Springing (L2) | Haunch (L3) | Spandrels (L4) | Arch Vault (L5) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 80 | 200 | 0.61 | 0.61 | 0.60 | 0.52 | 0.47 |
| 400 | 0.53 | 0.53 | 0.55 | 0.40 | 0.38 | |
| 600 | 0.48 | 0.49 | 0.50 | 0.36 | 0.36 | |
| 120 | 200 | 0.53 | 0.53 | 0.54 | 0.47 | 0.41 |
| 400 | 0.54 | 0.54 | 0.53 | 0.39 | 0.35 | |
| 600 | 0.45 | 0.45 | 0.43 | 0.32 | 0.32 | |
| 160 | 200 | 0.58 | 0.58 | 0.57 | 0.50 | 0.45 |
| 400 | 0.51 | 0.51 | 0.53 | 0.39 | 0.37 | |
| 600 | 0.42 | 0.42 | 0.43 | 0.31 | 0.31 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Huang, W.; Hu, M.; Wang, R.; Zhang, J.; Xu, W. Study on Large-Scale Geomechanical Experiments on Tunnel External Water Pressure. Water 2025, 17, 913. https://doi.org/10.3390/w17070913
Huang W, Hu M, Wang R, Zhang J, Xu W. Study on Large-Scale Geomechanical Experiments on Tunnel External Water Pressure. Water. 2025; 17(7):913. https://doi.org/10.3390/w17070913
Chicago/Turabian StyleHuang, Wei, Mingtao Hu, Rubin Wang, Jianping Zhang, and Weiya Xu. 2025. "Study on Large-Scale Geomechanical Experiments on Tunnel External Water Pressure" Water 17, no. 7: 913. https://doi.org/10.3390/w17070913
APA StyleHuang, W., Hu, M., Wang, R., Zhang, J., & Xu, W. (2025). Study on Large-Scale Geomechanical Experiments on Tunnel External Water Pressure. Water, 17(7), 913. https://doi.org/10.3390/w17070913






