Influence of Precipitation on the Estimation of Karstic Water Storage Variation
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Construction of the Combined Discrete-Continuum Model
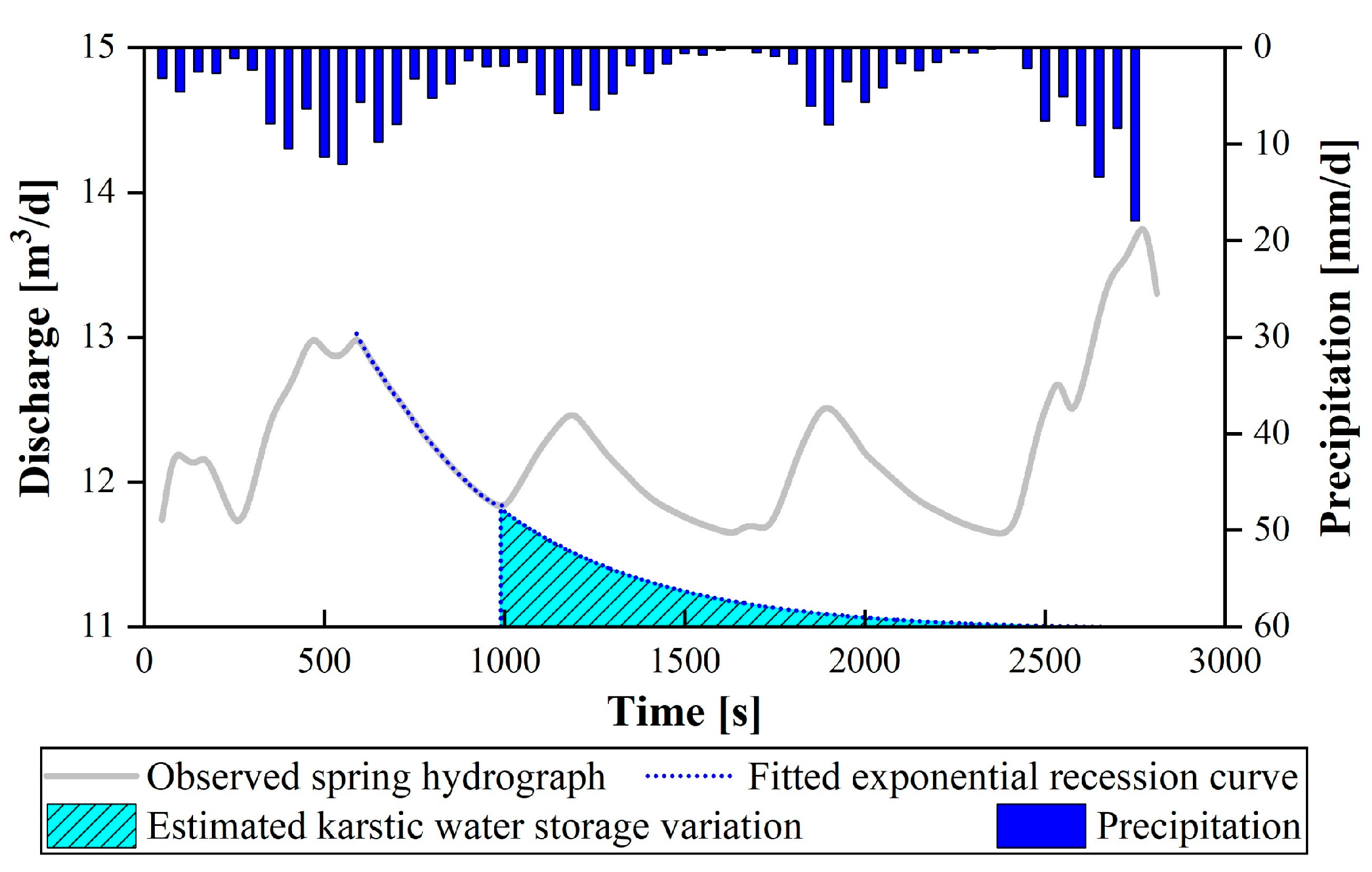
2.2. Analysis Methods
2.3. Numerical Simulation Scheme
3. Results and Discussion
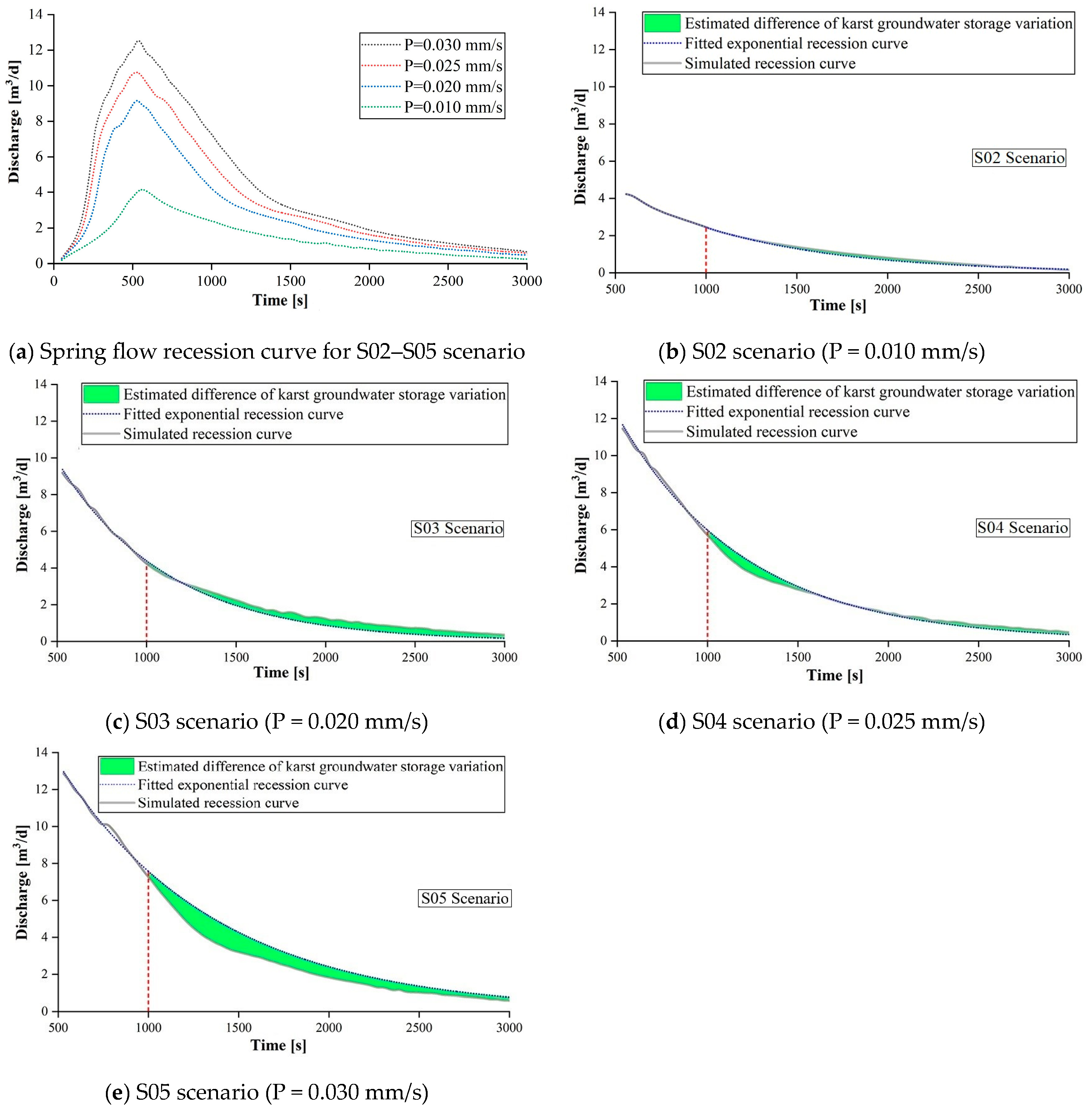
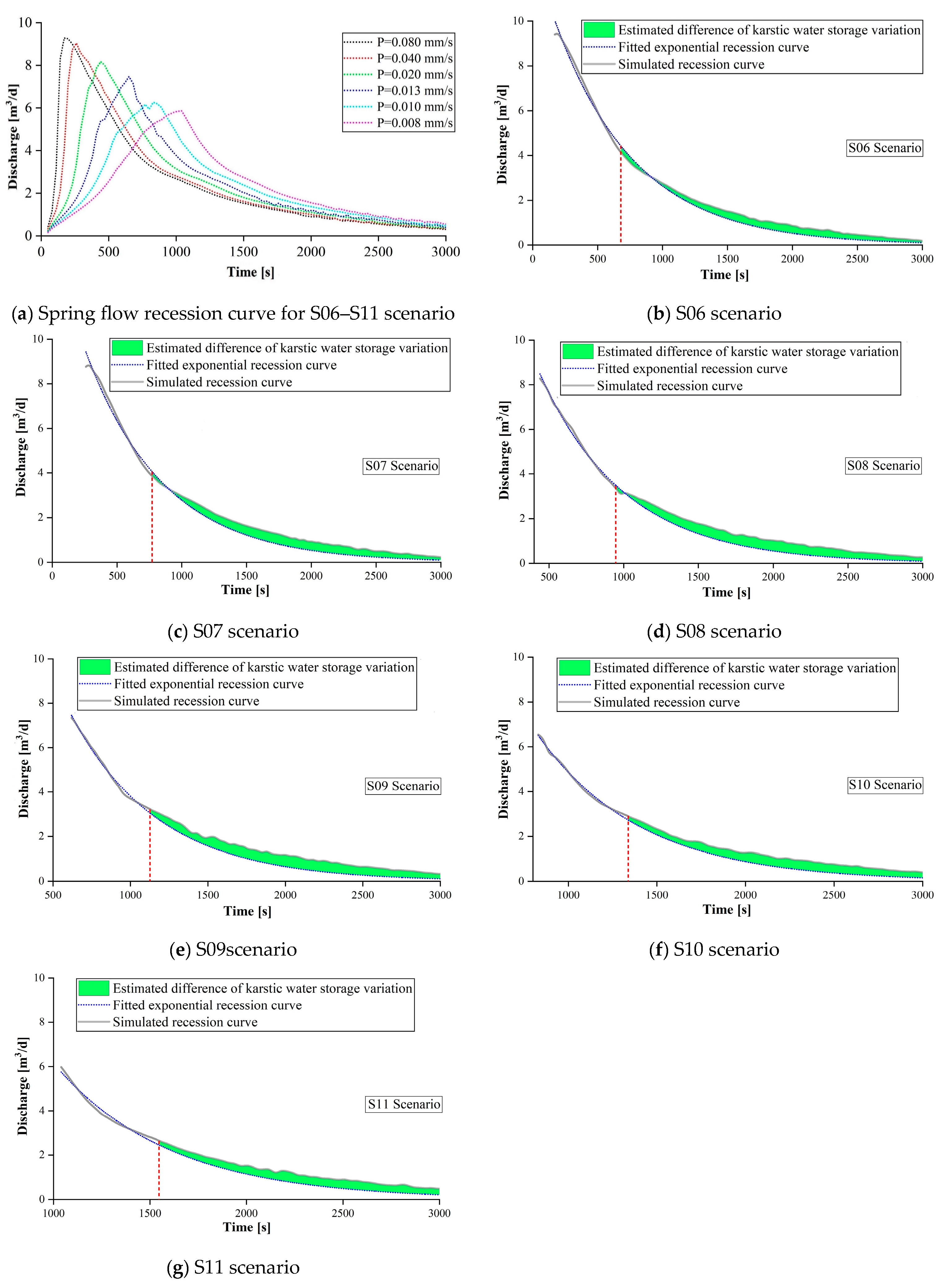
3.1. Precipitation Events with the Same Duration but Different Intensities
3.2. Precipitation Events with the Same Total Volume but Different Intensities
3.3. Limitations
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Bakalowicz, M. Karst groundwater: A challenge for new resources. Hydrogeol. J. 2005, 13, 148–160. [Google Scholar]
- Koit, O.; Mayaud, C.; Kogovšek, B.; Vainu, M.; Terasmaa, J.; Marandi, A. Surface water and groundwater hydraulics of lowland karst aquifers of Estonia. J. Hydrol. 2022, 610, 127908. [Google Scholar]
- Goldscheider, N.; Chen, Z.; Auler, A.; Bakalowicz, M.; Broda, S.; Drew, D.; Hartmann, J.; Jiang, G.; Moosdorf, N.; Stevanovic, Z.; et al. Global distribution of carbonate rocks and karst water resources. Hydrogeol. J. 2020, 28, 1661–1677. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dagès, C.; Voltz, M.; Bsaibes, A.; Prévot, L.; Huttel, O.; Louchart, X.; Garnier, F.; Negro, S. Estimating the role of a ditch network in groundwater recharge in a Mediterranean catchment using a water balance approach. J. Hydrol. 2009, 375, 498–512. [Google Scholar]
- Weatherl, R.K.; Salgado, M.J.H.; Ramgraber, M.; Moeck, C.; Schirmer, M. Estimating surface runoff and groundwater recharge in an urban catchment using a water balance approach. Hydrogeol. J. 2021, 29, 2411–2428. [Google Scholar]
- Yi, Y.; Brock, B.E.; Falcone, M.D.; Wolfe, B.B.; Edwards, T.W. A coupled isotope tracer method to characterize input water to lakes. J. Hydrol. 2008, 350, 1–13. [Google Scholar]
- Borghi, A.; Renard, P.; Cornaton, F. Can one identify karst conduit networks geometry and properties from hydraulic and tracer test data? Adv. Water Resour. 2016, 90, 99–115. [Google Scholar]
- Chen, X.; Zhang, Y.; Zhou, Y.; Zhang, Z. Analysis of hydrogeological parameters and numerical modeling groundwater in a karst watershed, southwest China. Carbonates Evaporites 2013, 28, 89–94. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dafny, E.; Burg, A.; Gvirtzman, H. Effects of Karst and geological structure on groundwater flow: The case of Yarqon-Taninim Aquifer, Israel. J. Hydrol. 2010, 389, 260–275. [Google Scholar]
- Basha, H.A. Flow recession equations for karst systems. Water Resour. Res. 2020, 56, e2020WR027384. [Google Scholar]
- Fiorillo, F. The recession of spring hydrographs, focused on karst aquifers. Water Resour. Manag. 2014, 28, 1781–1805. [Google Scholar]
- Felton, G.K.; Currens, J.C. Peak flow rate and recession-curve characteristics of a karst spring in the Inner Bluegrass, central Kentucky. J. Hydrol. 1994, 162, 99–118. [Google Scholar]
- Ding, H.; Zhang, X.; Chu, X.; Wu, Q. Simulation of groundwater dynamic response to hydrological factors in karst aquifer system. J. Hydrol. 2020, 587, 124995. [Google Scholar]
- Martin, J.M.; Screaton, E.J.; Martin, J.B. Monitoring well response to karst conduit head fluctuations: Implications for fluid exchange and matrix transmissivity in the Floridan aquifer. Geol. Soc. America Spec. 2006, 404, 209–217. [Google Scholar]
- Guo, X.; Huang, K.; Li, J.; Kuang, Y.; Chen, Y.; Jiang, C.; Luo, M.; Zhou, H. Rainfall–Runoff Process Simulation in the Karst Spring Basins Using a SAC–Tank Model. J. Hydrol. Eng. 2023, 28, 04023024. [Google Scholar]
- Kovács, A.; Perrochet, P.; Király, L.; Jeannin, P.-Y. A quantitative method for the characterisation of karst aquifers based on spring hydrograph analysis. J. Hydrol. 2005, 303, 152–164. [Google Scholar]
- Zimmerman, R.W.; Bodvarsson, G.S. Hydraulic conductivity of rock fractures. Transp. Porous Media 1996, 23, 1–30. [Google Scholar]
- Neuman, S.P. On methods of determining specific yield. Groundwater 1987, 25, 679–684. [Google Scholar]
- Abirifard, M.; Birk, S.; Raeisi, E.; Sauter, M. Dynamic volume in karst aquifers: Parameters affecting the accuracy of estimates from recession analysis. J. Hydrol. 2022, 612, 128286. [Google Scholar]
- Shu, L.; Zou, Z.; Li, F.; Wu, P.; Chen, H.; Xu, Z. Laboratory and numerical simulations of spatio-temporal variability of water exchange between the fissures and conduits in a karstic aquifer. J. Hydrol. 2020, 590, 125219. [Google Scholar]
- Chang, Y.; Wu, J.; Liu, L. Effects of the conduit network on the spring hydrograph of the karst aquifer. J. Hydrol. 2015, 527, 517–530. [Google Scholar]
- Peterson, E.W.; Wicks, C.M. Assessing the importance of conduit geometry and physical parameters in karst systems using the storm water management model (SWMM). J. Hydrol. 2006, 329, 294–305. [Google Scholar]
- Huang, F.; Gao, Y.; Hu, X.; Wang, X.; Pu, S. Interaction mechanism between the karst aquifer and stream under precipitation infiltration recharge. EGUsphere 2025, 2025, 1–56. [Google Scholar]
- Mohammadi, Z.; Shoja, A. Effect of annual rainfall amount on characteristics of karst spring hydrograph. Carbonates Evaporites 2014, 29, 279–289. [Google Scholar]
- Chang, W.; Wan, J.; Tan, J.; Wang, Z.; Jiang, C.; Huang, K. Responses of spring discharge to different rainfall events for single-conduit karst aquifers in Western Hunan province, China. Int. J. Environ. Res. Pub. Health 2021, 18, 5775. [Google Scholar]
- Li, Y.; Shu, L.; Wu, P.; Zou, Z.; Zhou, T.; Huang, L. Rainfall events-spring flow relationship and karst flow component analysis in a conduit-matrix coupled system. Hydrol. Process 2023, 37, e14990. [Google Scholar]
- Solórzano-Rivas, S.C.; Werner, A.D.; Robinson, N.I. Assessing the reliability of exponential recession in the water table fluctuation method. Adv. Water Resour. 2024, 193, 104821. [Google Scholar]
- Li, G.; Goldscheider, N.; Field, M.S. Modeling karst spring hydrograph recession based on head drop at sinkholes. J. Hydrol. 2016, 542, 820–827. [Google Scholar]
- Boussinesq, J. Sur un mode simple d’écoulement des nappes d’eau d’infiltration à lit horizontal, avec rebord vertical tout autour lorsqu’une partie de ce rebord est enlevée depuis la surface jusqu’au fond. CR Acad. Sci. 1903, 137, 11–23. [Google Scholar]
- Maillet, E.T. Essais D’hydraulique Souterraine & Fluviale; A. Hermann: Paris, France, 1905. [Google Scholar]
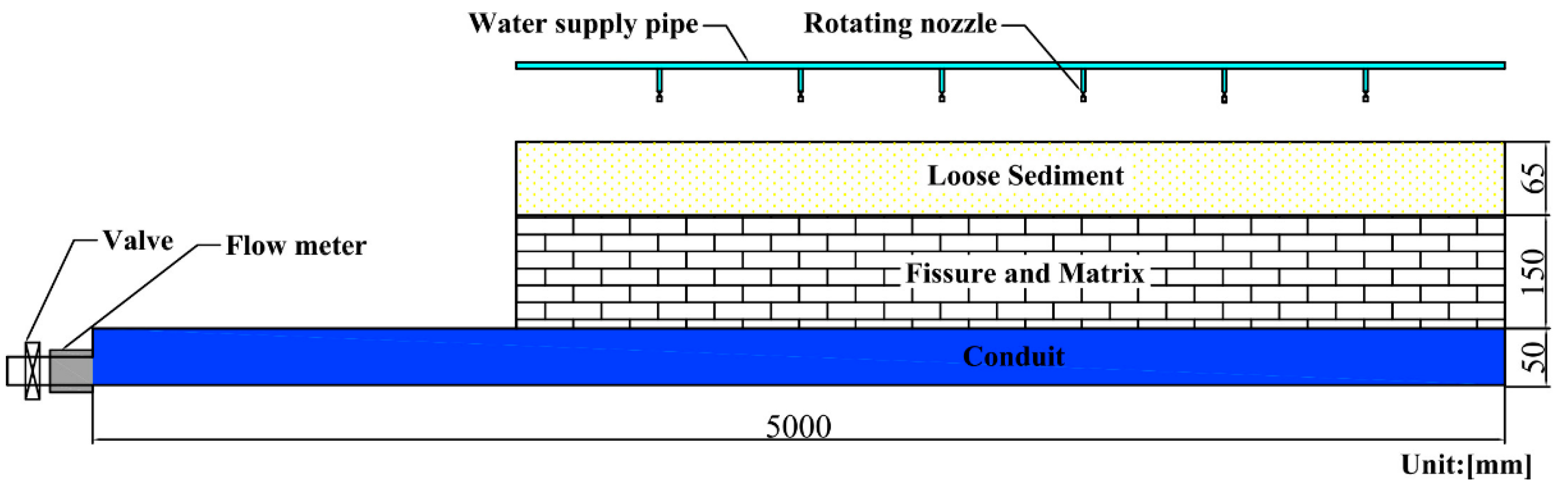
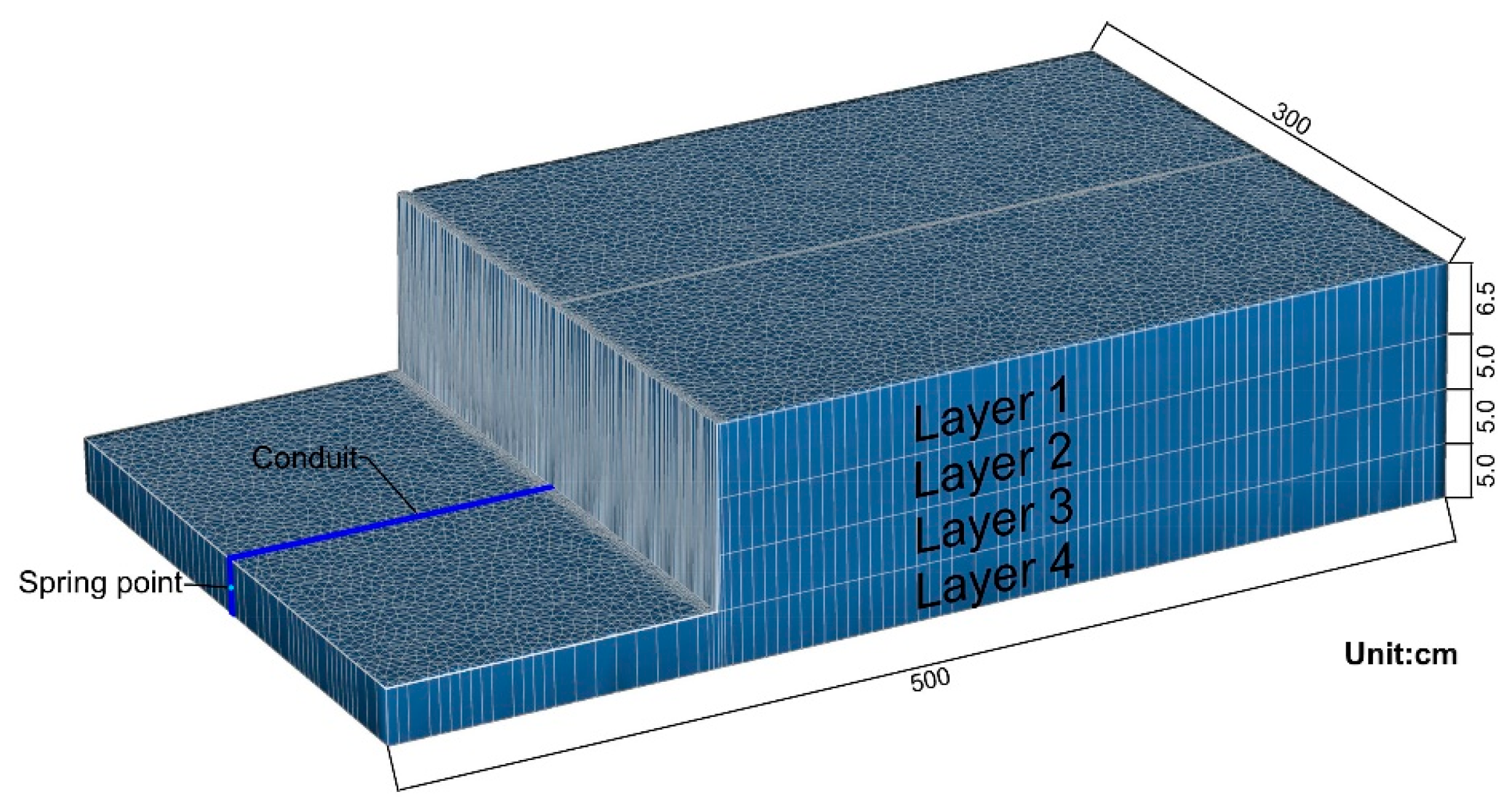
| Hydrogeological Parameters | Matrix | Conduit | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Hydraulic Conductivity (m/s) | Specific Yield | ) | Length (cm) | |
| First layer | 0.001 | 0.10 | -- | -- |
| Second layer | 0.015 | 0.06 | -- | -- |
| Third layer | 0.015 | 0.06 | -- | -- |
| Fourth layer | 0.015 | 0.06 | 1.0 | 500 |
| Number | Scenario | Parameter Settings |
|---|---|---|
| S01 | Basic model | Hydraulic conductivity: layers 2–4; K = 0.015 m/s; μ = 0.06; ; |
| S02 | Precipitation events with the same duration but different intensities | Intensity: 0.010 mm/s; Duration: 540 s |
| S03 | Intensity: 0.020 mm/s; Duration: 540 s | |
| S04 | Intensity: 0.025 mm/s; Duration: 540 s | |
| S05 | Intensity: 0.030 mm/s; Duration: 540 s |
| Number | Scenario | Parameter Settings |
|---|---|---|
| S06 | Precipitation events with the same total volume but different intensity | Duration: 100 s; Total volume: 84 L; Intensity: 0.08 mm/s; |
| S07 | Duration: 200 s; Total volume: 84 L; Intensity: 0.04 mm/s; | |
| S08 | Duration: 400 s; Total volume: 84 L; Intensity: 0.02 mm/s; | |
| S09 | Duration: 600 s; Total volume: 84 L; Intensity: 0.0133 mm/s; | |
| S10 | Duration: 800 s; Total volume: 84 L; Intensity: 0.01 mm/s; | |
| S11 | Duration: 1000 s; Total volume: 84 L; Intensity: 0.008 mm/s; |
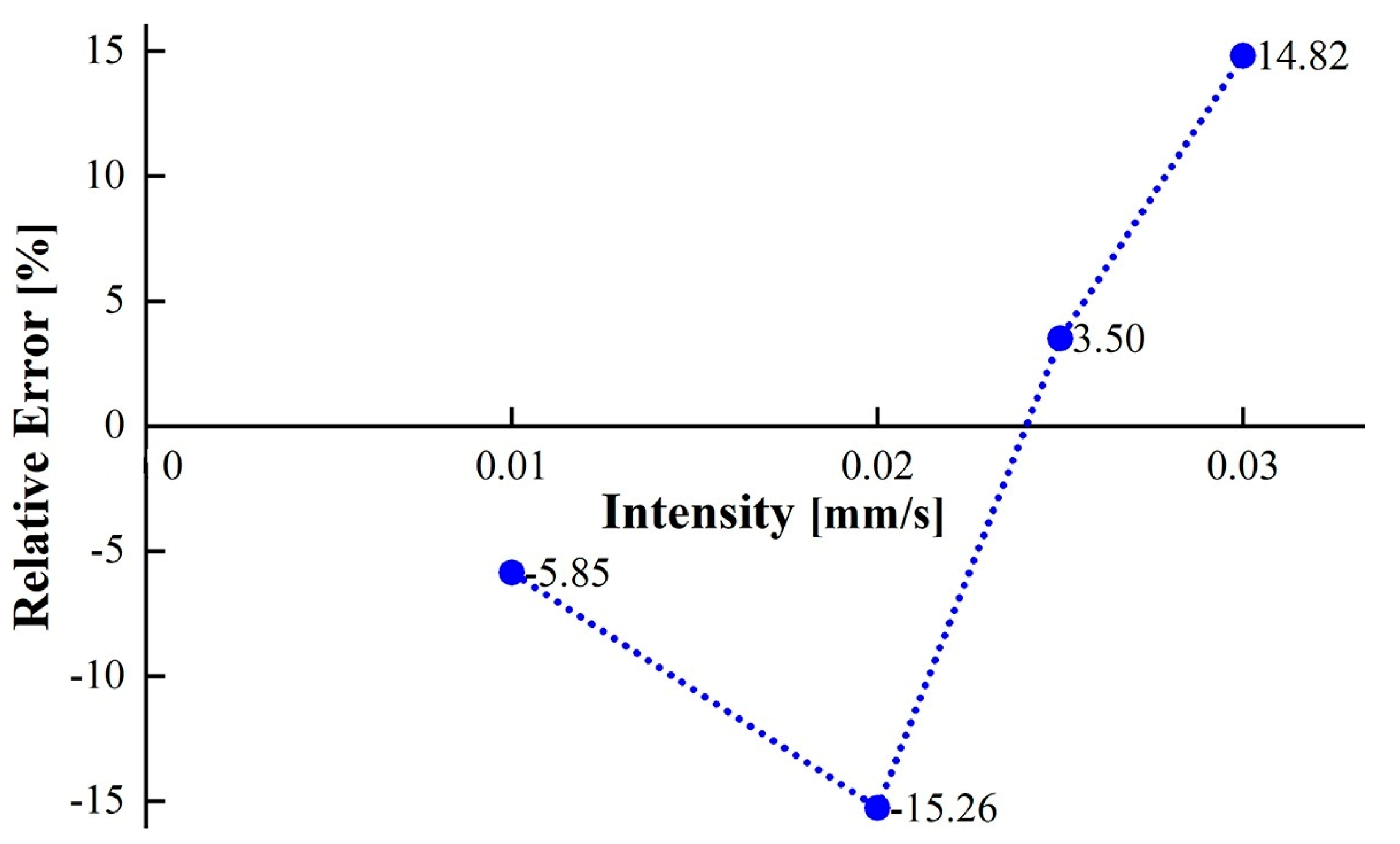
| Scenarios | Exponential Recession Equation | Recession Coefficient | Estimated Value (L) | Simulated Value (L) | Relative Error (%) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| S02 | y = 8.65e−0.00127x | 0.00127 | 20.53 | 21.80 | −5.85 |
| S03 | y = 22.04e−0.00161x | 0.00161 | 30.24 | 35.69 | −15.26 |
| S04 | y = 24.76e−0.00142x | 0.00142 | 45.86 | 44.32 | 3.50 |
| S05 | y = 23.75e−0.00114x | 0.00114 | 68.81 | 59.93 | 14.82 |
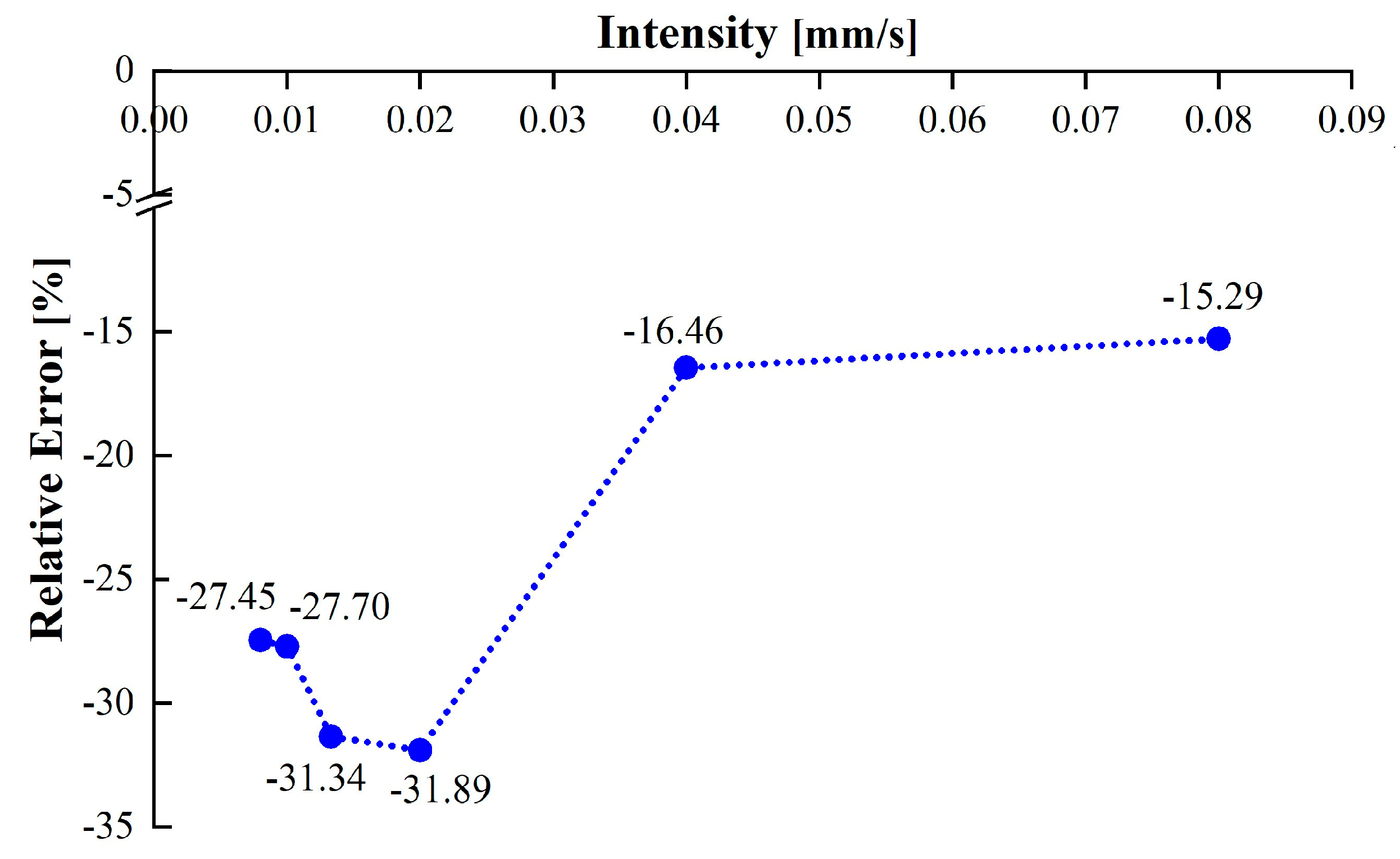
| Scenarios | Exponential Recession Equation | Recession Coefficient | Estimated Value (L) | Simulated Value (L) | Relative Error (%) | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| S06 | t = 100 s, P = 0.08 mm/s | y = 13.21e−0.00161x | 0.00161 | 31.03 | 36.63 | −15.29 |
| S07 | t = 200 s, P = 0.04 mm/s | y = 14.46e−0.00165x | 0.00165 | 27.80 | 33.28 | −16.46 |
| S08 | t = 400 s, P = 0.02 mm/s | y = 18.99e−0.00180x | 0.00180 | 20.25 | 29.74 | −31.89 |
| S09 | t = 600 s, P = 0.0133 mm/s | y = 22.25e−0.00177x | 0.00177 | 19.11 | 27.84 | −31.34 |
| S10 | t = 800 s, P = 0.010 mm/s | y = 26.86e−0.00171x | 0.00171 | 17.34 | 23.98 | −27.70 |
| S11 | t = 1000 s, P = 0.008 mm/s | y = 33.05e−0.00168x | 0.00168 | 15.35 | 21.16 | −27.45 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Dong, Y.; Li, Y.; Fu, Y.; Shu, L.; Zheng, C.; Hu, X. Influence of Precipitation on the Estimation of Karstic Water Storage Variation. Water 2025, 17, 986. https://doi.org/10.3390/w17070986
Dong Y, Li Y, Fu Y, Shu L, Zheng C, Hu X. Influence of Precipitation on the Estimation of Karstic Water Storage Variation. Water. 2025; 17(7):986. https://doi.org/10.3390/w17070986
Chicago/Turabian StyleDong, Yanan, Yuxi Li, Yang Fu, Longcang Shu, Canzheng Zheng, and Xiaonong Hu. 2025. "Influence of Precipitation on the Estimation of Karstic Water Storage Variation" Water 17, no. 7: 986. https://doi.org/10.3390/w17070986
APA StyleDong, Y., Li, Y., Fu, Y., Shu, L., Zheng, C., & Hu, X. (2025). Influence of Precipitation on the Estimation of Karstic Water Storage Variation. Water, 17(7), 986. https://doi.org/10.3390/w17070986






