Regional Drought Monitoring Using Satellite-Based Precipitation and Standardized Palmer Drought Index: A Case Study in Henan Province, China
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Study Area and Dataset
2.1. Study Area Description
2.2. Dataset
3. Research Methods
3.1. Evaluation of Satellite-Based Precipitation
3.1.1. Pearson Correlation Coefficient ()
3.1.2. Mean Absolute Error () and Root Mean Square Error ()
3.1.3. Nash–Sutcliffe Efficiency ()
3.2. Traditional Palmer Drought Indicators
3.3. Construction of Standardized Palmer Drought Index
4. Results and Analyses
4.1. Accuracy of Satellite-Based Precipitation Product
4.2. Time Series of Drought Indices
4.3. Statistical Characteristics of Drought Index
4.4. Validation with Historical Drought Records
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Jun, Z.; Guiya, C.; Wenfa, Y. Overview of drought research in and outside China. People’s Yangtze 2011, 42, 65–69. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guiqin, J. Research on Drought Driving Mechanism and Evaluation Method. Ph.D. Thesis, China Institute of Water Resources and Hydropower Research, Beijing, China, 2013. [Google Scholar]
- Yunyun, L. Drought Assessment—Propagation-Drive—Prediction of River basins under climate and land use change. Ph.D. Thesis, Xi’an University of Technology, Xi’an, China, 2018. [Google Scholar]
- Jinsong, W.; Jiangyong, G.; Yuewu, Z.; Lanfang, Y. Progress and prospect of drought index research. Arid. Land Geogr. 2007, 30, 60–65. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mingwei, M. Multivariate Drought Monitoring and Evaluation Methods and Applications, 1st ed.; China Water Resources and Hydropower Press: Beijing, China, 2019; p. 148. [Google Scholar]
- Bozhen, L.; Guangsheng, Z. Research progress of drought indicators. Acta Ecol. Sin. 2014, 34, 1043–1052. [Google Scholar]
- Yiping, L.; Yaohui, L. Research progress on adaptability of meteorological drought index in China. J. Arid. Meteorol. 2017, 35, 709–723. [Google Scholar]
- Rashid, M.M.; Beecham, S. Development of a non-stationary Standardized Precipitation Index and its application to a South Australian climate. Sci. Total Environ. 2019, 657, 882–892. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lorenzo, M.N.; Pereira, H.; Alvarez, I.; Dias, J.M. Standardized Precipitation Index (SPI) evolution over the Iberian Peninsula during the 21st century. Atmos. Res. 2024, 297, 107132. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mupepi, O.; Matsa, M.M. A combination of vegetation condition index, standardized precipitation index and human observation in monitoring spatio-temporal dynamics of drought. A case of Zvishavane District in Zimbabwe. Environ. Dev. 2023, 45, 100802. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- He, Q.; Wang, M.; Liu, K.; Wang, B. High-resolution Standardized Precipitation Evapotranspiration Index (SPEI) reveals trends in drought and vegetation water availability in China. Geogr. Sustain. 2024, 6, 100228. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dai, A. Characteristics and trends in various forms of the Palmer Drought Severity Index during 1900–2008. J. Geophys. Res. Atmos. 2011, 116. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mingwei, M. Improvement and Application of Palmer Drought Indices for Drought Characterization. Ph.D. Thesis, Hohai University, Nanjing, China, 2015. [Google Scholar]
- Ma, M.; Wang, W.; Yuan, F.; Ren, L.; Tu, X.; Zang, H. Application of a hybrid multiscalar indicator in drought identification in Beijing and Guangzhou, China. Water Sci. Eng. 2018, 11, 177–186. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, M.; Ren, L.; Yuan, F.; Jiang, S.; Liu, Y.; Kong, H.; Gong, L. A new standardized Palmer drought index for hydro-meteorological use. Hydrol. Process. 2014, 28, 5645–5661. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Z.; Yang, Y.; Zhang, C.; Guo, H.; Hou, Y. Historical and future Palmer Drought Severity Index with improved hydrological modeling. J. Hydrol. 2022, 610, 127941. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, H.; Zhang, Q.; Xu, C.-Y.; Du, J.; Sun, P.; Hu, P. Modified Palmer Drought Severity Index: Model improvement and application. Environ. Int. 2019, 130, 104951. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ma, M.; Ren, L.; Singh, V.P.; Yang, X.; Yuan, F.; Jiang, S. New variants of the Palmer drought scheme capable of integrated utility. J. Hydrol. 2014, 519, 1108–1119. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xiao, S.; Zou, L.; Xia, J.; Yang, Z.; Yao, T. Bias correction framework for satellite precipitation products using a rain/no rain discriminative model. Sci. Total Environ. 2022, 818, 151679. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mishra, A.K. Improving precipitation estimates over orographic regions by integrating multi-spectral satellite observations with rain gauge in India. Remote Sens. Appl. Soc. Environ. 2019, 15, 100252. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, C.; Hu, D.; Shao, H.; Dai, X.; Liu, G.; Wu, S. Runoff simulation driven by multi-source satellite data based on hydrological mechanism algorithm and deep learning network. J. Hydrol. Reg. Stud. 2024, 52, 101720. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bandara, K.M.P.S. Monitoring irrigation performance in Sri Lanka with high-frequency satellite measurements during the dry season. Agric. Water Manag. 2003, 58, 159–170. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Atiah, W.A.; Johnson, R.; Muthoni, F.K.; Mengistu, G.T.; Amekudzi, L.K.; Kwabena, O.; Kizito, F. Bias correction and spatial disaggregation of satellite-based data for the detection of rainfall seasonality indices. Heliyon 2023, 9, e17604. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Suh, J.W.; Zhu, Z.; Zhao, Y. Monitoring construction changes using dense satellite time series and deep learning. Remote Sens. Environ. 2024, 309, 114207. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Granero-Belinchon, C.; Adeline, K.; Briottet, X. Impact of the number of dates and their sampling on a NDVI time series reconstruction methodology to monitor urban trees with Venμs satellite. Int. J. Appl. Earth Obs. Geoinf. 2021, 95, 102257. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, W.; Ma, C.; Wang, X.; Feng, J.; Dong, L.; Kang, J.; Jin, R.; Li, X. A soil moisture experiment for validating high-resolution satellite products and monitoring irrigation at agricultural field scale. Agric. Water Manag. 2024, 304, 109071. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zheng, C.; Jia, L.; Hu, G. Global land surface evapotranspiration monitoring by ETMonitor model driven by multi-source satellite earth observations. J. Hydrol. 2022, 613, 128444. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Christian, J.I.; Basara, J.B.; Lowman, L.E.L.; Xiao, X.; Mesheske, D.; Zhou, Y. Flash drought identification from satellite-based land surface water index. Remote Sens. Appl. Soc. Environ. 2022, 26, 100770. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, J.Y.a.X. The 30m annual land cover dataset and its dynamics in China from 1990 to 2019. Earth Syst. Sci. Data 2021, 13, 3907–3925. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, Y.; Shunqing, A.; Weiwei, L.; Sheng, X.; Guoliang, Z.; Jianguo, Q.; Lin, W.; Wen, Z. Application of Palmer drought index method in national real-time drought monitoring. Adv. Water Sci. 2007, 18, 52–57. [Google Scholar]
- An Shunqing, X.J. Correction of Palmer drought model. J. Acad. Meteorol. Sci. 1986, 1, 79–82. [Google Scholar]
- Liu Weiwei, A.S.; Gengshan, L. Further modification of the Palmer drought model. J. Appl. Meteorol. 2004, 2, 207–216. [Google Scholar]
- Chen, D.; Gao, G.; Xu, C.Y.; Guo, J.; Ren, G. Comparison of the Thornthwaite method and pan data with the standard Penman-Monteith estimates of reference evapotranspiration in China. Clim. Res. 2005, 28, 123–132. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Van der Schrier, G.; Jones, P.D.; Briffa, K.R. The sensitivity of the PDSI to the Thornthwaite and Penman-Monteith parameterizations for potential evapotranspiration. J. Geophys. Res. Atmos. 2011, 116. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, W.; Kang, Y.; Li, L.; Gao, R.; Shu, Z.; Song, S. Comprehensive assessment of five near-real-time satellite precipitation products in the Lower Yangtze River Basin and the Lixiahe region, China: Dual perspectives from time series and extreme events. Atmos. Res. 2024, 308, 107520. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Suliman, A.H.A.; Awchi, T.A.; Shahid, S. Drought deciles index for spatial and temporal assessment of satellite-based precipitation datasets. Phys. Chem. Earth Parts A/B/C 2024, 135, 103624. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shi, J.; Zhang, J.; Bao, Z.; Parajka, J.; Wang, G.; Liu, C.; Jin, J.; Tang, Z.; Ning, Z.; Fang, J. A novel error decomposition and fusion framework for daily precipitation estimation based on near-real-time satellite precipitation product and gauge observations. J. Hydrol. 2024, 640, 131715. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dos Santos, V.; Oliveira, R.A.J.; Datok, P.; Sauvage, S.; Paris, A.; Gosset, M.; Sánchez-Pérez, J.M. Evaluating the performance of multiple satellite-based precipitation products in the Congo River Basin using the SWAT model. J. Hydrol. Reg. Stud. 2022, 42, 101168. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shen, Z.; Yong, B.; Gourley, J.J.; Qi, W. Real-time bias adjustment for satellite-based precipitation estimates over Mainland China. J. Hydrol. 2021, 596, 126133. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McCuen, R.H.; Knight, Z.; Cutter, A.G. Evaluation of the Nash–Sutcliffe Efficiency Index. J. Hydrol. Eng. 2006, 11, 597–602. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Makra, L.; Horváth, S.; Pongrácz, R.; Mika, J. Long term climate deviations: An alternative approach and application on the Palmer drought severity index in Hungary. Phys. Chem. Earth Parts A/B/C 2002, 27, 1063–1071. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tatli, H.; Türkeş, M. Empirical Orthogonal Function analysis of the palmer drought indices. Agric. For. Meteorol. 2011, 151, 981–991. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Altunkaynak, A.; Jalilzadnezamabad, A. Extended lead time accurate forecasting of palmer drought severity index using hybrid wavelet-fuzzy and machine learning techniques. J. Hydrol. 2021, 601, 126619. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Palmer, W.C. Meteorological Drough; US Weather Bureau: Washington, DC, USA, 1965. [Google Scholar]
- Wells, N.; Goddard, S.; Hayes, M.J. A self-calibrating Palmer drought severity index. J. Clim. 2004, 17, 2335–2351. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abramowitz, M.; Stegun, I.A.; Romer, R.H. Handbook of mathematical functions: With formulas, graphs, and mathematical tables. Dover Books Adv. Math. 1965, 56, 136–144. [Google Scholar]
- McKee, T.B.; Doesken, N.J.; Kleist, J. The Relationship of Drought Frequency and Duration to Time Scales. In Proceedings of the 8th Conference on Applied Climatology, Anaheim, CA, USA, 17–22 January 1993; pp. 179–183. [Google Scholar]
- Mika, J.; Horváth, S.; Makra, L.; Dunkel, Z. The Palmer Drought Severity Index (PDSI) as an indicator of soil moisture. Phys. Chem. Earth Parts A/B/C 2005, 30, 223–230. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cai, S.; Zuo, D.; Wang, H.; Xu, Z.; Wang, G.; Yang, H. Assessment of agricultural drought based on multi-source remote sensing data in a major grain producing area of Northwest China. Agric. Water Manag. 2023, 278, 108142. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shahfahad; Talukdar, S.; Ali, R.; Nguyen, K.-A.; Naikoo, M.W.; Liou, Y.-A.; Islam, A.R.M.T.; Mallick, J.; Rahman, A. Monitoring drought pattern for pre- and post-monsoon seasons in a semi-arid region of western part of India. Environ. Monit. Assess. 2022, 194, 396. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vitkovskaya, I.; Batyrbayeva, M.; Berdigulov, N.; Mombekova, D. Prospects for Drought Detection and Monitoring Using Long-Term Vegetation Indices Series from Satellite Data in Kazakhstan. Land 2024, 13, 2225. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shahfahad, S.; Talukdar, S.; Ghose, B.; Islam, A.R.M.T.; Hasanuzzaman, M.; Ahmed, I.A.; Praveen, B.; Asif, A.; Paarcha, A.; Rahman, A.; et al. Predicting long term regional drought pattern in Northeast India using advanced statistical technique and wavelet-machine learning approach. Model. Earth Syst. Environ. 2024, 10, 1005–1026. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Behifar, M.; Kakroodi, A.A.; Kiavarz, M.; Azizi, G. Satellite-based drought monitoring using optimal indices for diverse climates and land types. Ecol. Inform. 2023, 76, 102143. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]


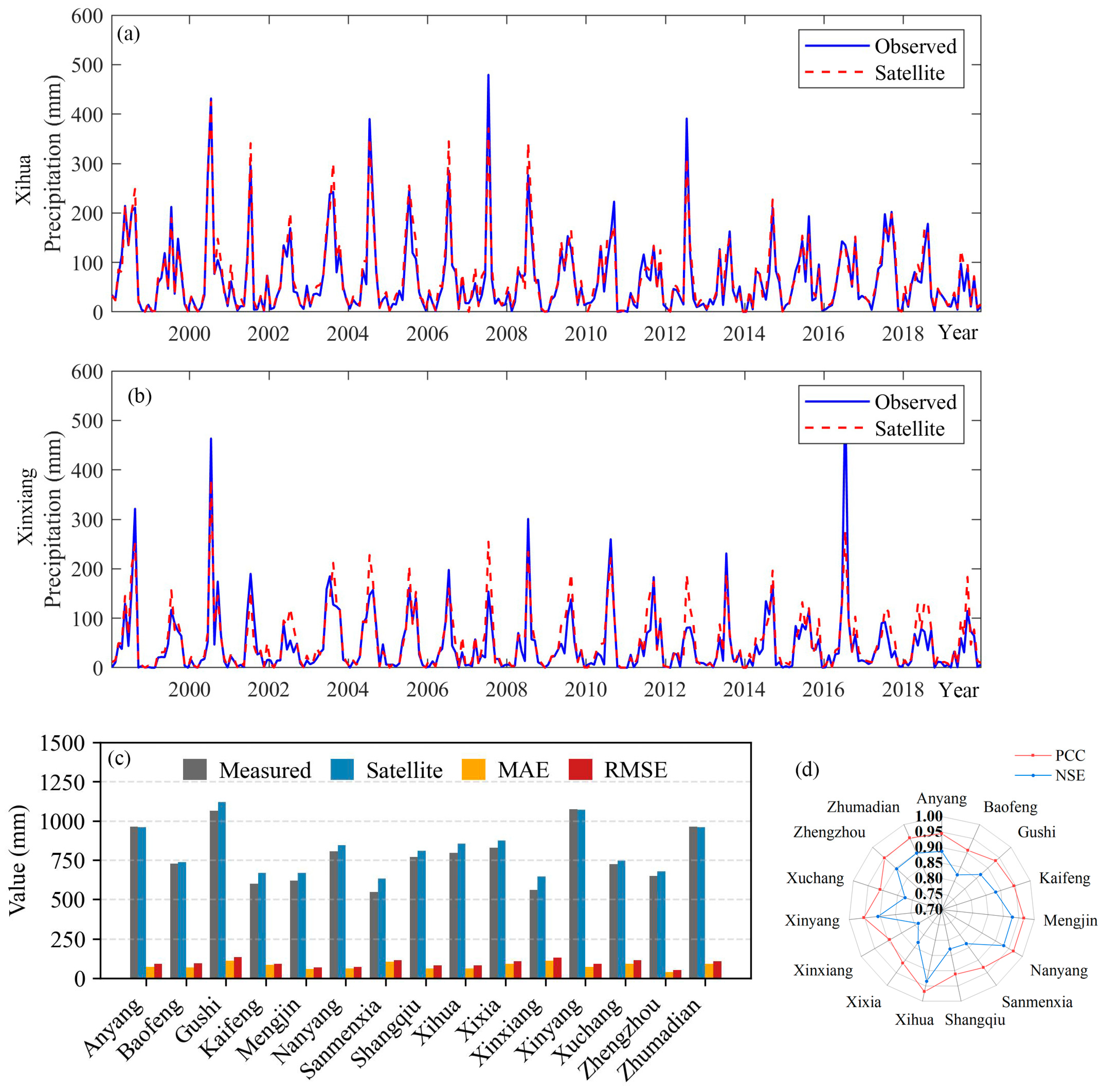

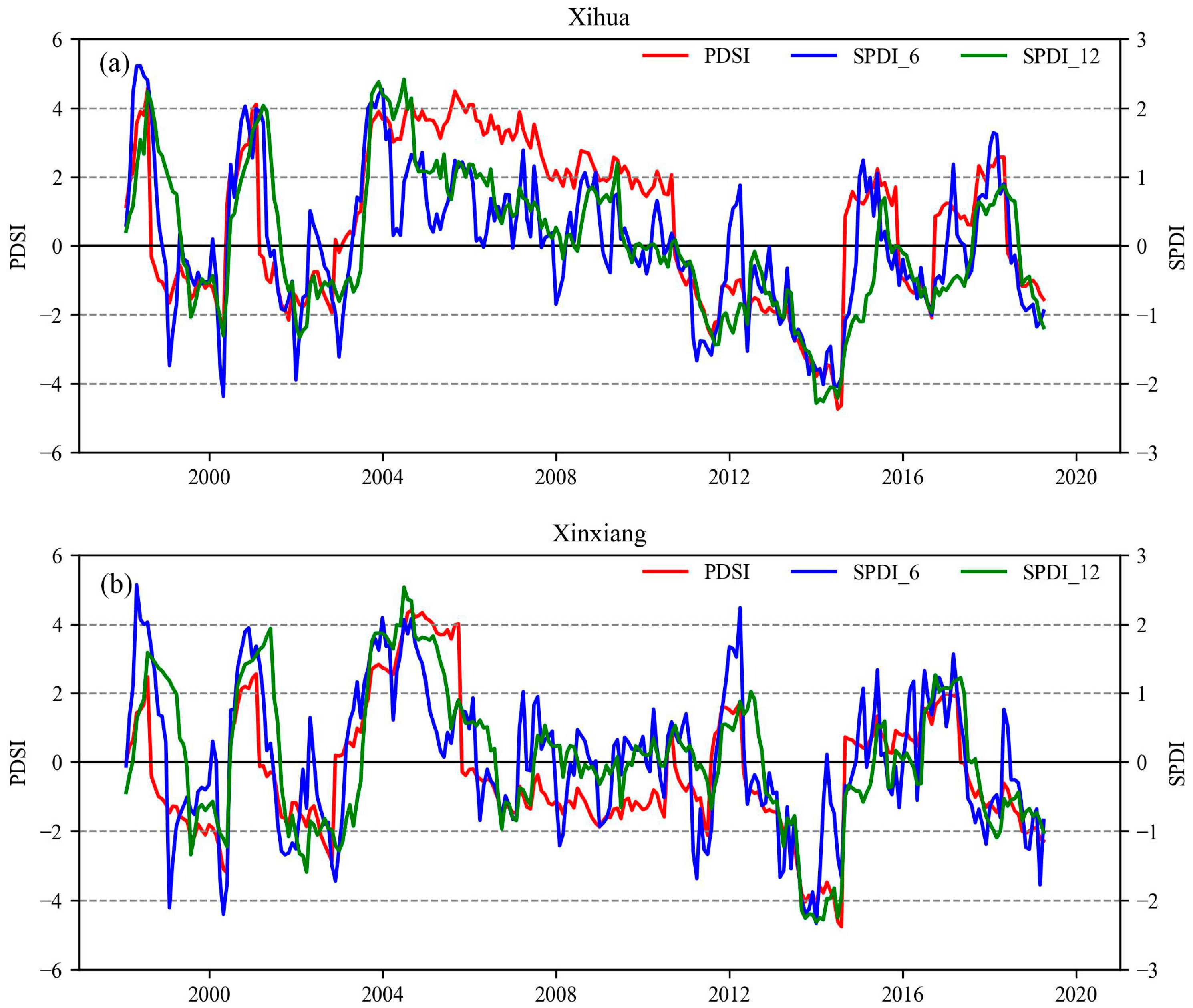
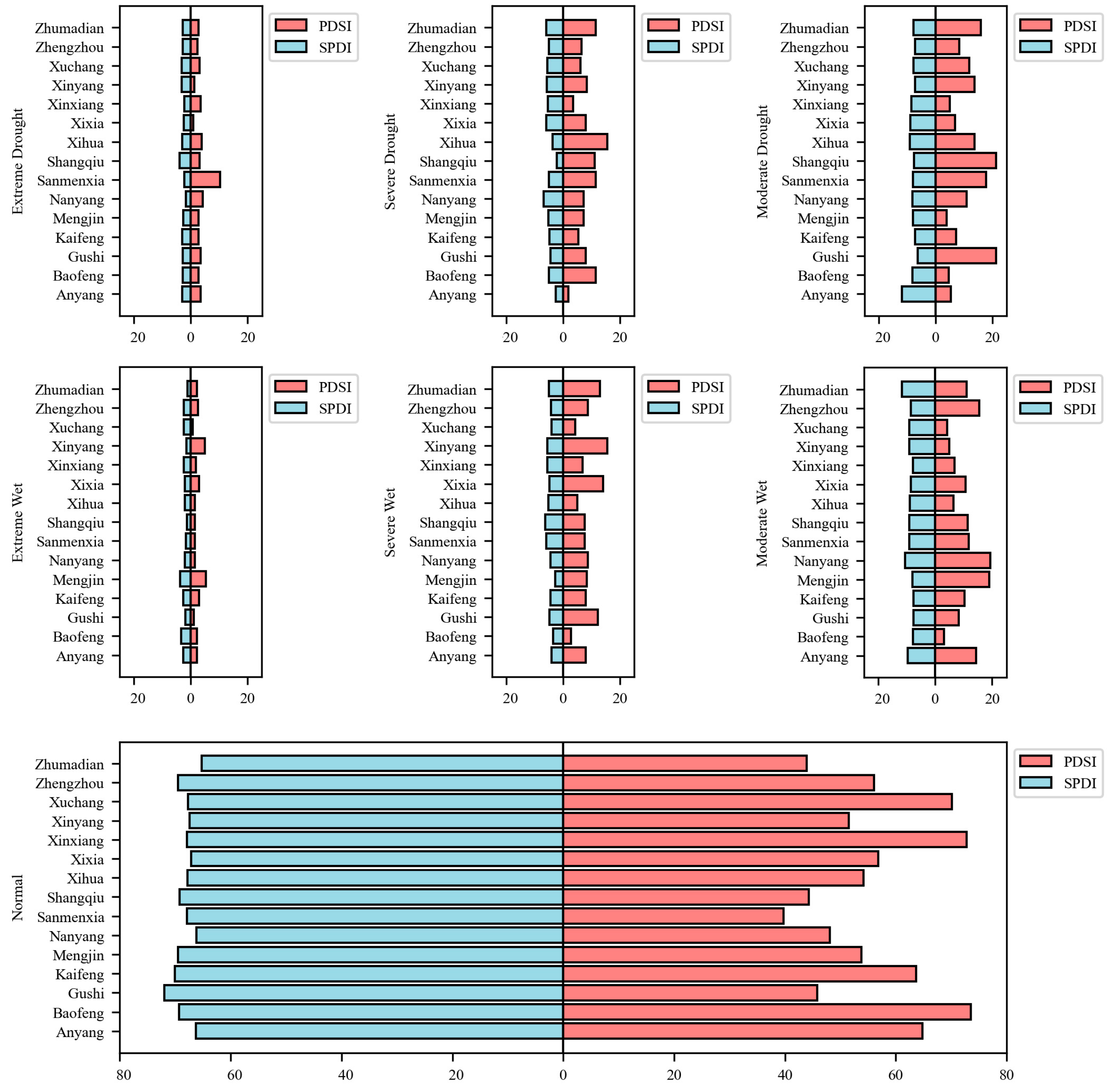
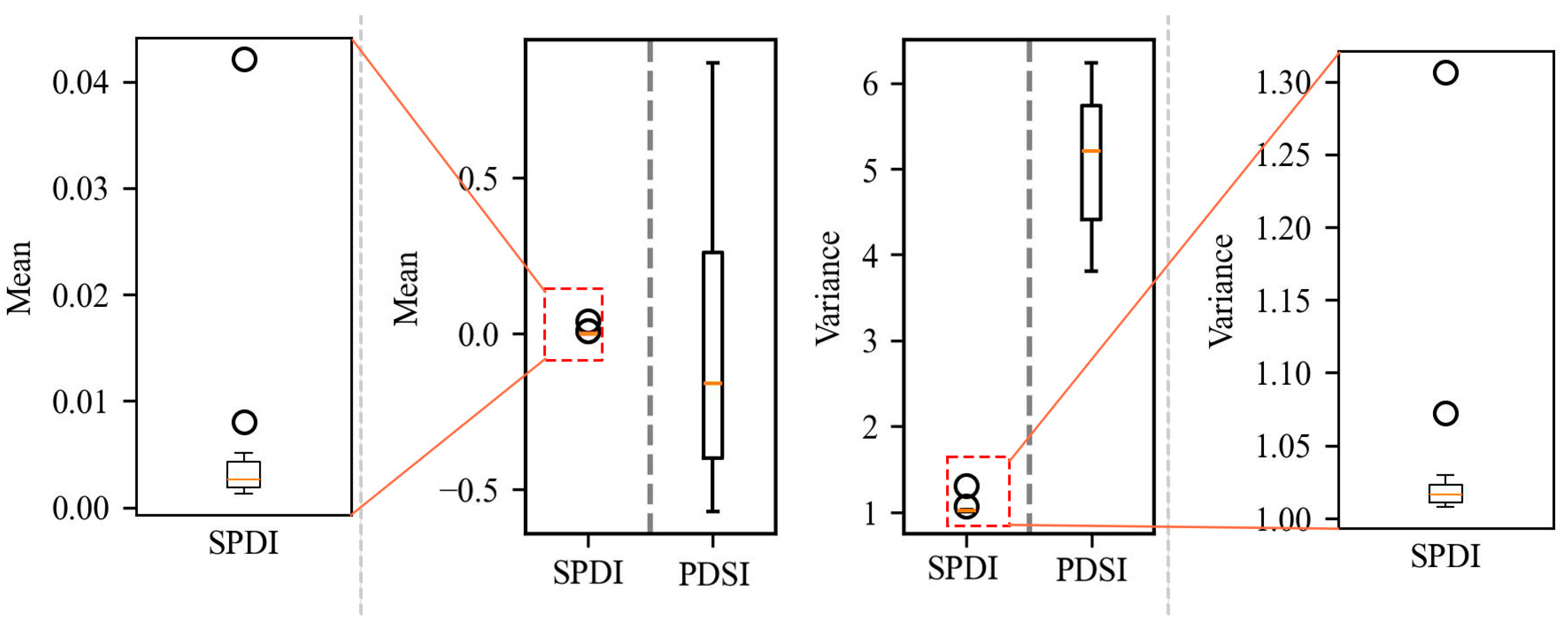

| Name | Date | Temporal Resolution | Spatial Resolution | Reference |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Precipitation (Measured) | 1998–2019 | Monthly | - | http://data.cma.cn/ (accessed on 1 August 2024) |
| Temperature (Measured) | 1998–2019 | Monthly | - | http://data.cma.cn/ (accessed on 1 August 2024) |
| Precipitation (Satellite) | 1998–2019 | Monthly | 0.25° | https://disc.gsfc.nasa.gov/datasets/TRMM_3B43_7/summary?keywords=TRMM (accessed on 1 August 2024) |
| Historical drought event | 2006–2019 | - | - | http://www.mwr.gov.cn/sj/#tjgb (accessed on 1 August 2024) |
| SPDI | PDSI | Dry and Wet Condition |
|---|---|---|
| ≥2 | ≥4 | Extreme Wet |
| [1.5, 2) | [3, 4) | Severe Wet |
| [1, 1.5) | [2, 3) | Middling Wet |
| [0.5, 1) | [1, 2) | Mild Wet |
| (−0.5, 0.5) | (−1, 1) | Basically Normal |
| (−1, −0.5] | (−2, −1] | Minor Drought |
| (−1.5, −1] | (−3, −2] | Middling Drought |
| (−2, −1.5] | (−4, −3] | Severe Drought |
| ≤−2 | ≤−4 | Extreme Drought |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Ma, M.; Xiong, F.; Zang, H.; Zhao, C.; Wang, Y.; He, Y. Regional Drought Monitoring Using Satellite-Based Precipitation and Standardized Palmer Drought Index: A Case Study in Henan Province, China. Water 2025, 17, 1123. https://doi.org/10.3390/w17081123
Ma M, Xiong F, Zang H, Zhao C, Wang Y, He Y. Regional Drought Monitoring Using Satellite-Based Precipitation and Standardized Palmer Drought Index: A Case Study in Henan Province, China. Water. 2025; 17(8):1123. https://doi.org/10.3390/w17081123
Chicago/Turabian StyleMa, Mingwei, Fandi Xiong, Hongfei Zang, Chongxu Zhao, Yaquan Wang, and Yuhuai He. 2025. "Regional Drought Monitoring Using Satellite-Based Precipitation and Standardized Palmer Drought Index: A Case Study in Henan Province, China" Water 17, no. 8: 1123. https://doi.org/10.3390/w17081123
APA StyleMa, M., Xiong, F., Zang, H., Zhao, C., Wang, Y., & He, Y. (2025). Regional Drought Monitoring Using Satellite-Based Precipitation and Standardized Palmer Drought Index: A Case Study in Henan Province, China. Water, 17(8), 1123. https://doi.org/10.3390/w17081123






