Abstract
The effect of low-molecular-weight dissolved organic matter (LDOM) on antimony enrichment in groundwater remains unclear. In this study, the spectroscopic and molecular characteristics of high- and low-Sb groundwater are compared using optical spectrophotometry, ultrafiltration, and Fourier transform ion cyclotron resonance mass spectrometry. The results demonstrated that although the mean DOM concentration in LDOM groundwater (3.98 mg/L) accounted for only 69.22% of the mean DOM concentration, the proportion of Sb(V) within the total Sb varied between 80.29% and 99.56%. LDOM was characterized by higher biological and fluorescence index values, a greater H/C ratio, and reduced double-bond equivalent values compared with high-molecular-weight dissolved organic matter. High abundances of LDOM can enhance the primary enrichment of Sb(V) within the total Sb concentration via competitive adsorption and, as energy and electron acceptors for microbial communities facilitate Sb(III), oxidation within groundwater systems. This study provides new perspectives on understanding how DOM influences the migration and speciation transformation of Sb in groundwater environments.
1. Introduction
As a priority heavy metal, products containing Sb are widely used in flame retardants, batteries, and the automotive tire and alloy industries, consequently leading to significant Sb contamination [1]. Increasing evidence has shown that the Sb content in soils, sediments, and water has increased significantly in recent decades globally, particularly near mining, smelting, fossil-fuel combustion, and ammunition sites [2,3]. Recent surveys have revealed that the maximum detected concentration of Sb in the groundwater of the Xikuangshan Sb mine is 18.402 mg/L [4,5], which exceeds the Chinese standards for drinking water quality (0.005 mg/L) [6] and unpolluted water body limits (0.001 mg/L) by 3680 and 18,402 times, respectively [7]. Oxidation of Sb2S3 is a major natural source of Sb pollution in groundwater [8,9,10]. During this process, Sb(III) and Sb(V) are the main species detected, with Sb(V) and Sb(III) dominating in oxic and anoxic environments, respectively [11,12]. The toxicity of Sb species is comparable to that of arsenic, with Sb(III) posing a greater risk than Sb(V). However, owing to its weaker adsorption affinity for Fe/Mn hydroxides and higher solubility, Sb(V) generally exhibits greater mobility than Sb(III) in the environment [13,14,15]. Arsenic generally occurs as As(III) and As(V) compounds in groundwater. Therefore, analyzing the processes by which Sb(III) is oxidized to Sb(V) is essential for a comparison of the biogeochemical behaviors of As and Sb in groundwater environments.
Dissolved organic matter (DOM), which contains an abundance of functional groups, such as carboxyl, hydroxyl, carbonyl, and amide groups, is crucial for Sb mobilization and transformation [5,11,16]. Moreover, DOM can bind Sb to form Sb-Fe-DOM or Sb-DOM complexes [17,18,19], compete for adsorption with Sb on mineral surfaces [20,21], act as an electron acceptor [14,22], and induce Sb(III) oxidation under sunlight [14,23,24,25], thereby increasing Sb content in groundwater. The molecular weight of DOM serves as a fundamental characteristic, with a substantial impact on its bioavailability [11,26,27]. Previous studies have shown that DOM with different molecular weights exhibit distinct fluorescence properties and molecular structures, which have an impact on Sb migration in groundwater [11,14]. DOM with a high molecular weight (HDOM, >100 kDa) show a greater adsorption capacity for Fe minerals, which promote the formation of Sb-Fe-DOM or Sb-DOM complexes by binding with Sb species [25,26]. Furthermore, microorganisms can typically degrade low-molecular-weight DOM (LDOM, <1 kDa), which is considered bioactive and easily utilized [28,29]. Consequently, the degradation process of microorganisms can accelerate the oxidation of Sb(III) to Sb(V) [24,30], and the competitive adsorption of Sb(V) in an alkaline oxic environment with high concentrations of HCO3− [5,24,31]. Therefore, understanding the functions and effects of LDOM is essential to manage environmental Sb contamination.
Although the effects of the spectroscopic and molecular signatures of DOM on Sb migration in Xikuangshan Sb mining groundwater have been confirmed in our previous research [5,25], the effect of LDOM on Sb(V) enrichment and Sb(III) oxidation is not extensively understood. Therefore, considering the North Mine of the Xikuangshan Sb mining area, China, as the study site, this study aims to (1) compare the spectroscopic properties and molecular characteristics of LDOM between high- and low-Sb groundwater and (2) identify the roles of LDOM in the migration of Sb in shallow groundwater systems through ultrafiltration. The findings of this study provide new perspectives on Sb enrichment in groundwater.
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Study Area
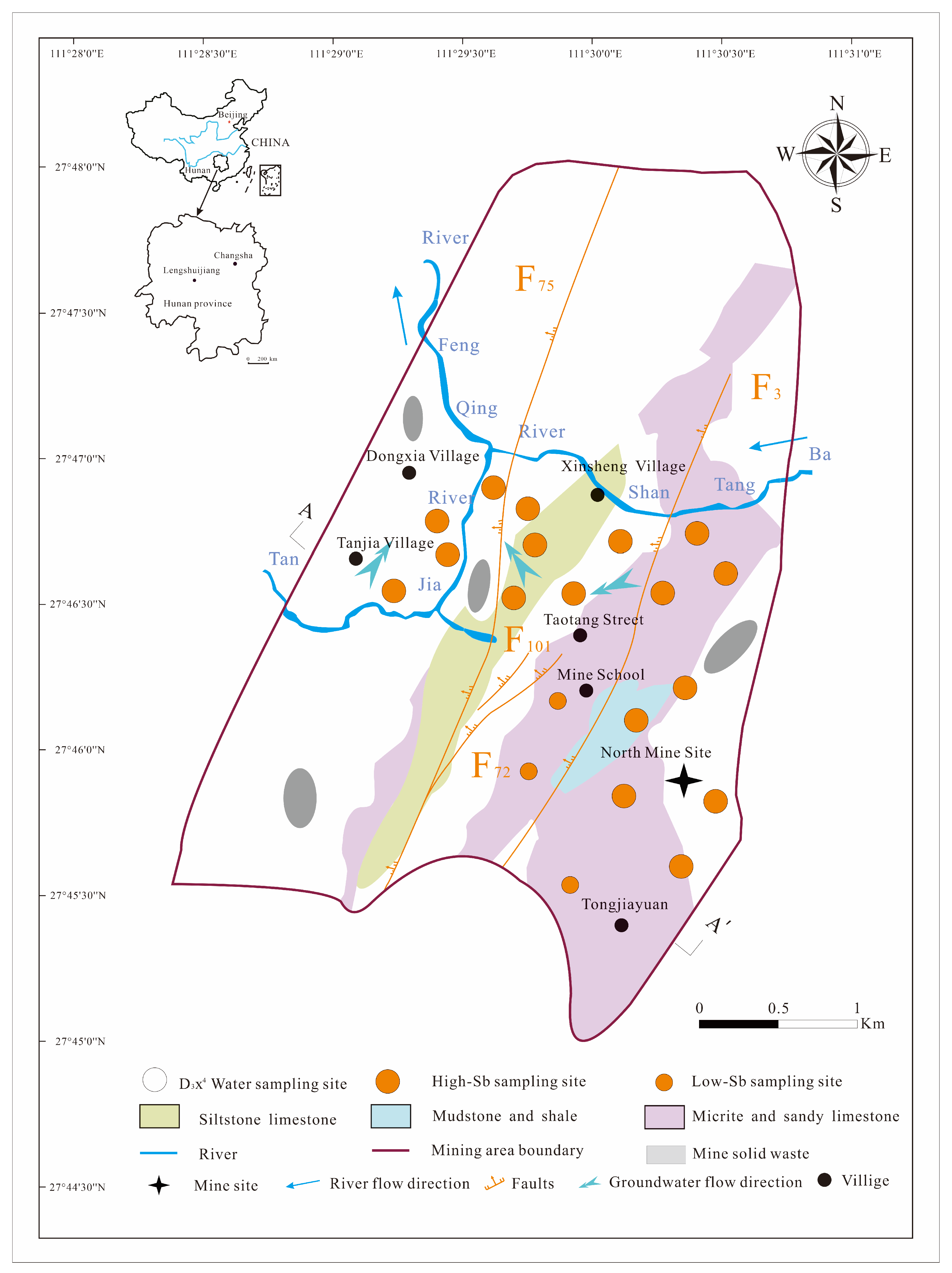
The North Mine of Xikuangshan Sb mining area is located 13 km north of the city of Lengshuijiang in Hunan province, China, between 111°30′00″–111°31′22″ E and 27°46′00″–27°48′00″ N. It covers approximately 0.50 km2 in a mountainous region with a mean annual precipitation of approximately 1382 mm and mean annual evaporation of approximately 903 mm [4,5,9]. The study area is impacted by an F75 fault to the west and a lamprophyre vein to the east (Figure 1). The Magunao Aquifer (D3s2 groundwater) and Shetianqiao Aquifer (D3x4 groundwater) constitute the two primary aquifers under investigation, exhibiting limited hydraulic connectivity with each other. Large residential areas, grasslands, vegetable plantations, and abandoned mining residual slags cover the weathered D3x4 water layer.
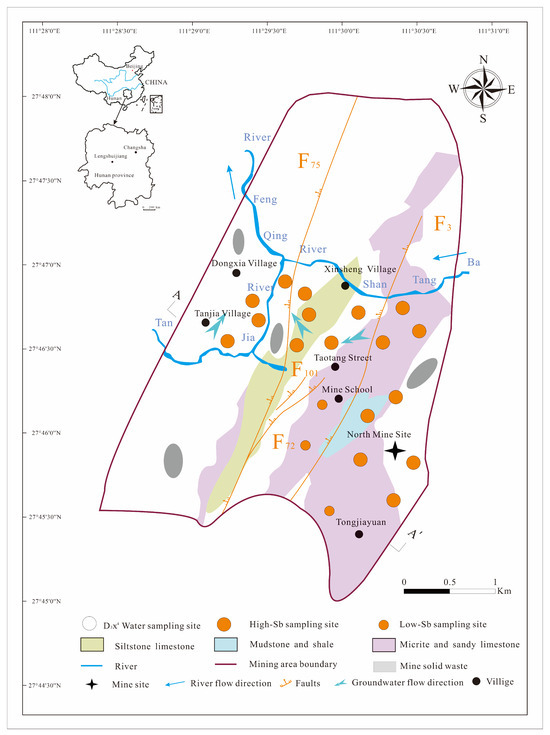
Figure 1.
Location of the study area and sampling sites.
The D3x4 groundwater, an extensively distributed and exposed groundwater system, is 258 m thick and serves as the main source of drinking water for residents in the study area. Moreover, the D3x4 groundwater mainly consists of micrite, sandy limestone, mudstone, and shale, exhibiting an average hydraulic conductivity of 0.0092 m/d. The main water supply for the D3x4 groundwater originates from precipitation, whereas discharge generally occurs through seasonal springs and mine drainage. Despite the general groundwater flow moving from northeast to southwest, the flow direction of the D3x4 groundwater in the North Mine of the Xikuangshan Sb mining area is from southeast to northwest [32,33]. Additional details regarding the study area have been presented by Hao et al. [4,5,9,25].
2.2. Groundwater Sampling and Analyses
A total of 80 groundwater samples were systematically collected from the D3x4 groundwater between September and October 2024, as shown in Figure 1. Twenty groundwater samples were used to analyze the Sb concentration, species, and HCO3− concentration; twenty groundwater samples were used to assess DOM concentration and conduct Fourier transform ion cyclotron resonance mass spectrometry (FT-ICR MS, Billerica, MA, USA) analyses; and 40 groundwater samples were used to perform fluorescence spectroscopy on DOM with varying molecular weights. Before collecting the samples, each of the 500 mL sampling bottles were rinsed 2–3 times sequentially with distilled water and D3x4 groundwater samples. To determine the levels and species of Sb, the D3x4 groundwater samples were initially passed through a 0.45 μm glass fiber membrane and subsequently treated with equal parts dilution of nitric acid with a 1:1 (v/v) dilution, along with 5% (v/v) 0.25 M ethylenediaminetetraacetic acid. They were then covered with aluminum foil to ensure a pH below 2.0 and avoid photochemical reactions [11,12]. Samples for DOM and FT-ICR MS detection were acidified with H2SO4 to a pH below 2 through 0.22 μm membrane filters in the field [25,29,34]. LDOM D3x4 groundwater (LDOM groundwater) samples and high-molecular-weight DOM D3x4 groundwater (HDOM groundwater) samples were processed using a polymer-enhanced ultrafiltration system (CFUS, Sartorius Vivaflow® 200, Gottingen, Germany) equipped with 1 kDa and 0.45 μm millipore filters by applying pressure with N2 gas to facilitate the filtration. The pH, oxidation redox potential (ORP), and total-dissolved-solids content of all D3x4 groundwater samples were measured in the field using a portable pH/ORP meter (HANNA H18424, Padua, Italy) and portable conductivity meter (HANNA H1833, Padua, Italy), respectively.
Sb concentrations and species were determined using HPLC-HG-AFS instrumentation (Qingdao), achieving a relative standard deviation within ±5% and analysis precision of 0.001 mg/L. Sb species concentration in HDOM and LDOM groundwater were listed in Table S1. The levels of bicarbonate ions (HCO3−) were measured using acid-base titration, achieving a measurement accuracy of 1.0 mg/L. The LDOM and HDOM samples were examined using a total organic carbon analyzer (TOC-5000, Kyoto, Japan) to determine the DOC concentrations with an analytical precision of 0.01 mg/L. The UV-visible absorbance, as well as fluorescence-spectroscopy measurements and molecular signatures of LDOM and HDOM, were obtained using a UV-visible spectrophotometer (Dayton, NJ, USA) and SolariX XR-15T FTMS (Billerica, MA, USA), respectively.
2.3. EEM-PARAFAC and FT-ICR MS Analysis
The EEM data were obtained at an excitation range of 250–450 nm with increments of 5 nm and an emission range of 220–520 nm with increments of 2 nm. Scanning was performed at a speed of 500 nm/min. The PARAFAC model can be utilized to examine extensive datasets containing hundreds or thousands of EEMs, thereby facilitating the identification of LDOM and HDOM components. The average fluorescence intensities were obtained from three repeated measurements, in which the PARAFAC-modeled EEM was subtracted from the measured EEM. This process ensured that the maximum deviation did not exceed 10% when compared with the original measured EEM intensities [29,35,36]. The appropriate number of components for the models was determined and verified through independent residual analysis and split-half analysis after outlier identification was performed. The fluorescence intensities and relative abundances of six distinct organic components (C1, C2, C3, C4, C5, and C6) within the LDOM and HDOM were satisfactorily modeled in Table 1.

Table 1.
Six distinct organic components (C1, C2, C3, C4, C5, and C6) within the LDOM and HDOM groundwater.
Finally, the humification index (HIX), which indicates the extent of DOM humification and its sources; the biological index (BIX), serving as a marker for autochthonous biological origins; the specific UV absorbance at 254 nm (SUVA254), reflecting the aromatic character of DOM; and the fluorescence index (FI), used to differentiate between terrestrial and microbial DOM origins, were calculated in detail based on previous descriptions by Hao et al. [5], Liu et al. [37], and Jia et al. [11].
Molecular formulas were primarily determined based on the elemental compositions of 1H(1–120), 16O(1–50), 12C(1–60),14N(0–5), and 32S(0–3). These calculations were conducted for mass peaks exhibiting a signal-to-noise ratio (S/N) of 5 or higher, and the “nitrogen rule” was simultaneously applied in the process [38,39]. The double-bond equivalent (DBE), indicating the degree of unsaturation in DOM molecules, modified aromaticity index (AImod), reflecting the aromaticity of DOM molecules and nominal oxidation state of carbon were determined as described by Zark et al., Zhang et al., and Xu et al. [40,41,42].
Using the H/C and O/C ratios, the LDOM and HDOM constituents were classified into seven distinct groups within a van Krevelen diagram [25,29,34], as shown in Table 2. Among these compounds, those with a higher H/C ratio (H/C > 0.50) have previously been classified as bioreactive DOM [25,27], whereas those with a higher O/C ratio (O/C > 0.50) exhibit greater humic DOM characteristics [39,43].

Table 2.
Seven distinct groups in DOM constituents were categorized into the van Krevelen diagram.
3. Results
3.1. Geochemical Characterization of HDOM and LDOM Groundwater
The geochemical data of the HDOM and LDOM groundwater samples are listed in Table S1. The Sb concentrations in the HDOM and LDOM groundwater samples varied between 0.001 and 20.800 mg/L (average of 3.641 mg/L) and 0.001 and 20.600 mg/L (average of 3.519 mg/L), respectively. Moreover, Sb(V) accounted for 82.74–99.58% of the total Sb in HDOM groundwater samples (mean value of 3.203 mg/L), whereas in LDOM groundwater samples, the percentage of Sb(V) in the total Sb ranged from 80.29% to 99.56% (average of 3.095 mg/L). These minor differences between HDOM and LDOM groundwater suggest that Sb primarily exists in a dissolved form in LDOM groundwater, with Sb(V) being the predominant species [11]. Based on the natural background values and statistical criteria [4,5,9], the D3x4 groundwater samples were categorized into two groups: those with low antimony concentrations (<0.015 mg/L, namely low-Sb groundwater) and those with high antimony concentrations (≥0.015 mg/L, namely high-Sb groundwater).
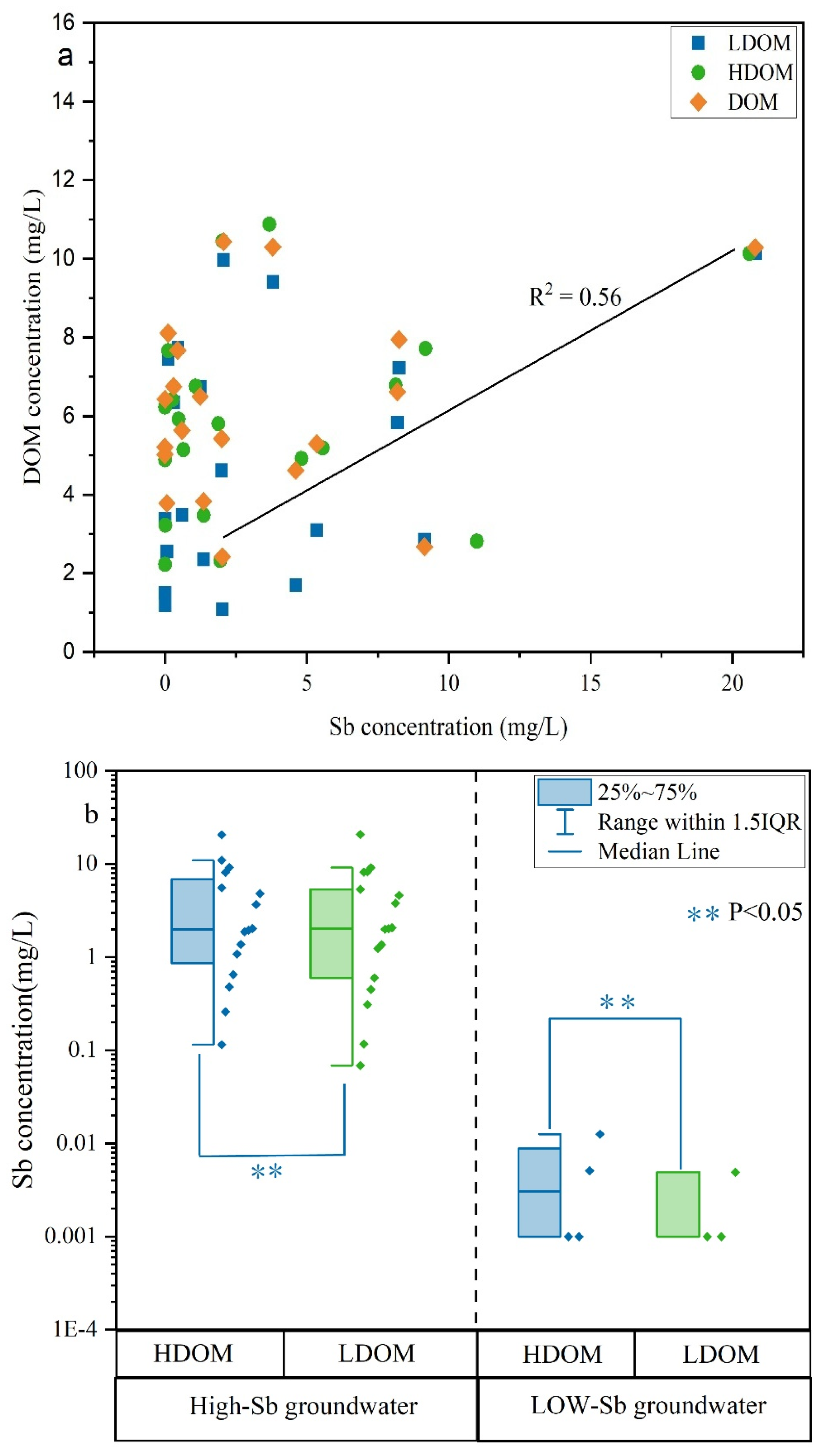
The average DOM concentration in LDOM groundwater (3.98 mg/L) was noticeably lower than that of the HDOM groundwater (5.75 mg/L) (Table S1), indicating that the LDOM groundwater contained a lower amount of DOM. However, the concentrations of Sb and DOM exhibited a positive correlation (R2 = 0.56) in the original DOM groundwater (Figure 2a), suggesting that DOM significantly influenced the mobilization and transport of Sb in these groundwater types. The concentration of Sb exhibited a comparable range in both the high- and low-Sb groundwater samples in both HDOM and LDOW (Figure 2b), further confirming that the presence of LDOM may enhance the Sb concentration in D3X4 groundwater [5,11].
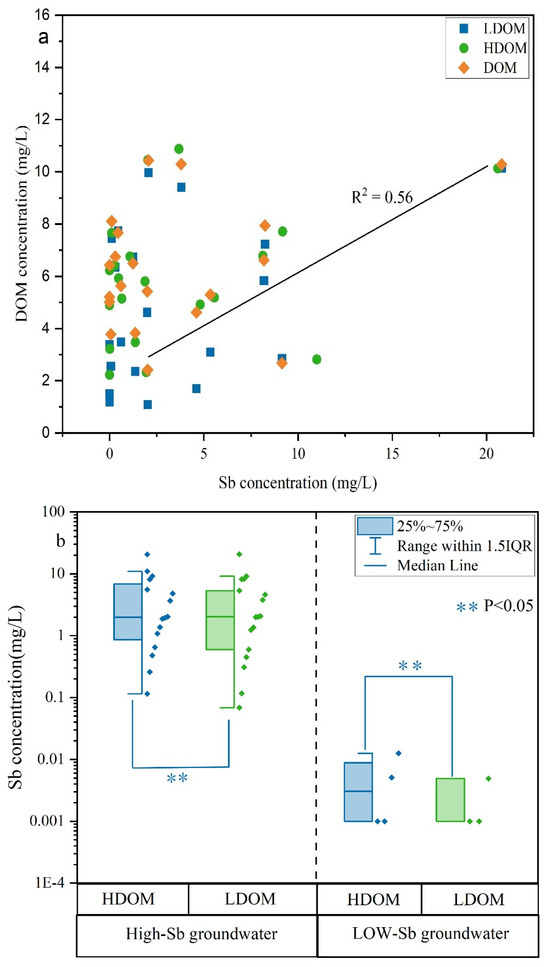
Figure 2.
Plots of (a) the association between DOM and Sb concentration and (b) boxplots illustrating the Sb concentration differences in groundwater with high and low Sb levels, categorized by HDOM and LDOM.
3.2. Fluorescent Characteristics of DOM in HDOM and LDOM Groundwater
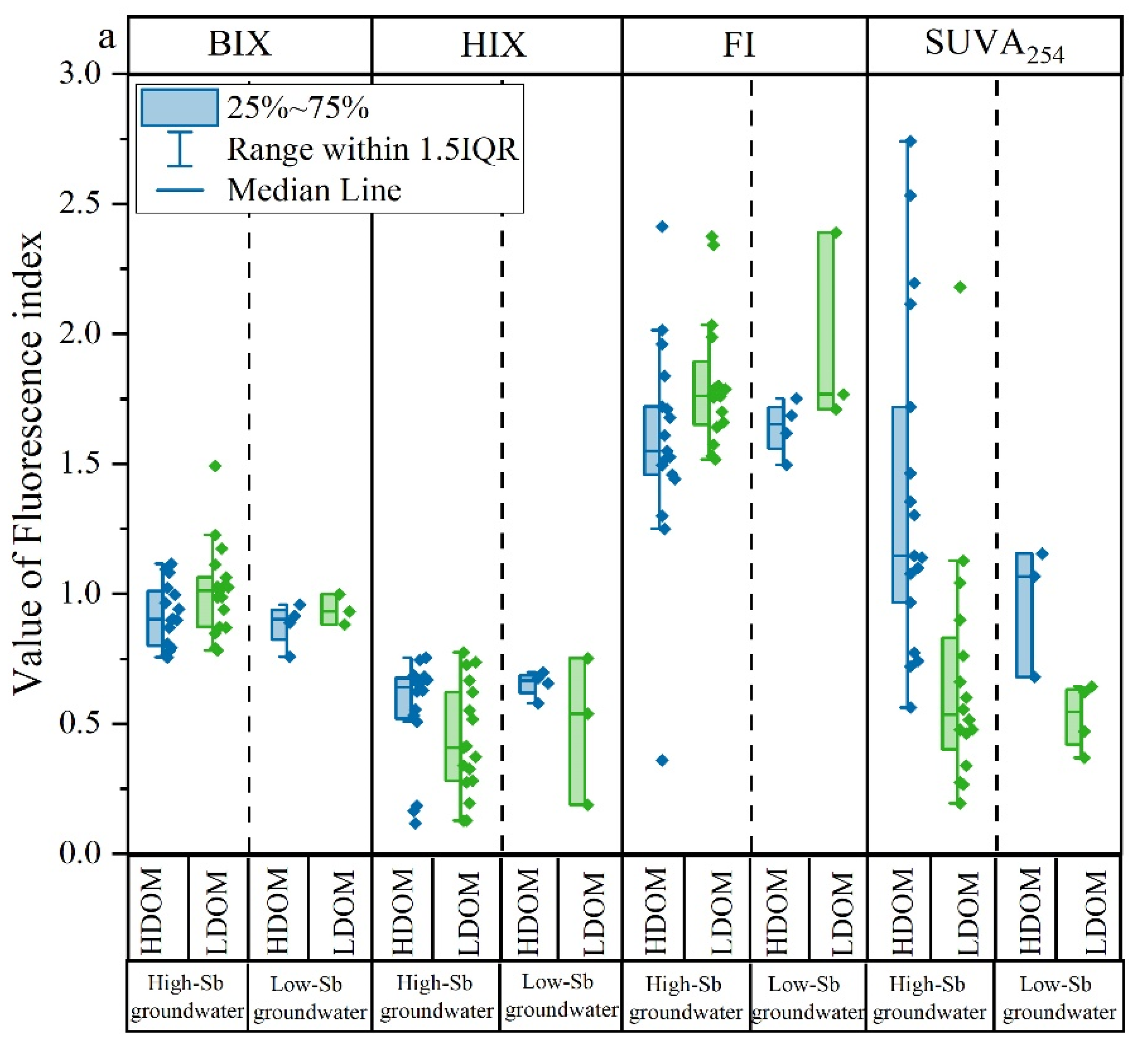
Fluorescent characteristic indicators such as BIX, HIX, FI, and SUVA254 of the HDOM and LDOM groundwater are shown in Figure 3a and Table S1. Compared with the HDOM groundwater samples, BIX slightly increased, whereas HIX and SUVA254 obviously decreased in the LDOM groundwater samples, indicating a stronger biological source and less humic character in the LDOM [27,29]. Moreover, the FI value slightly increased from a mean value of 1.64 (terrestrially and microbially derived zones) in HDOM groundwater to a mean value of 1.78 (microbially derived zones) in LDOM groundwater [44,45,46,47,48], further demonstrating a larger contribution from microbial sources in LDOM [44,49,50]. Notably, low-Sb groundwater had similar HIX, SUVA254, FI, and BIX values to those of high-Sb groundwater, suggesting that the fluorescence characteristics of LDOM were dominant in both high- and low-Sb groundwater.
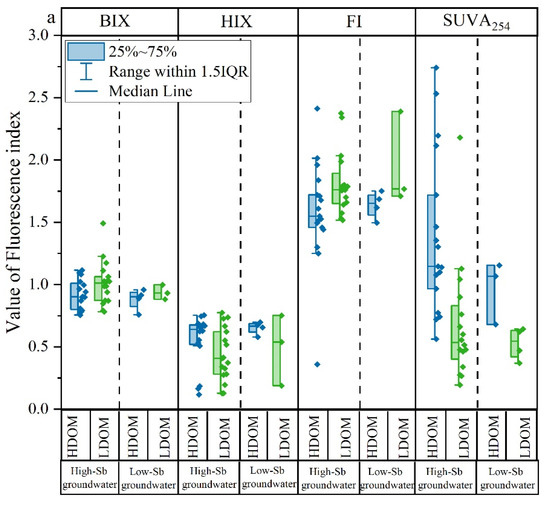
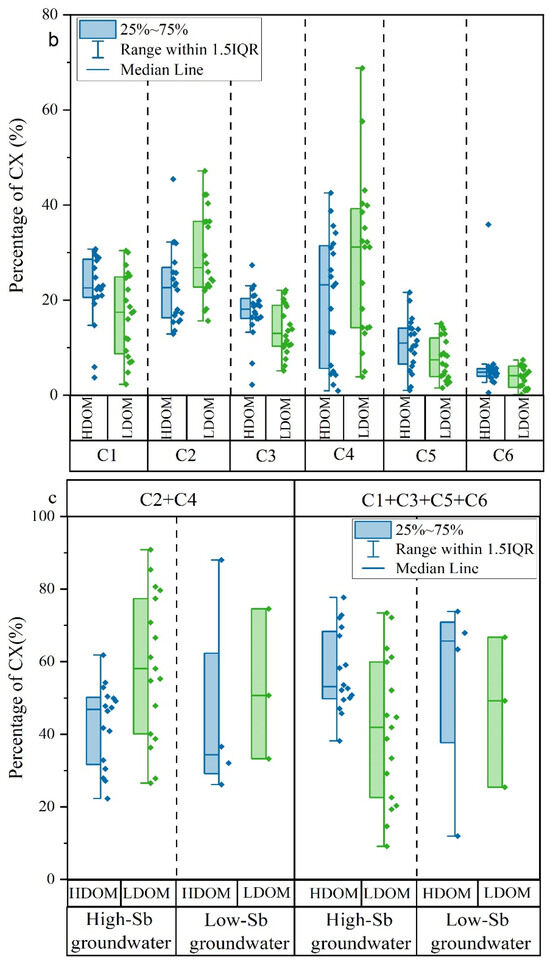
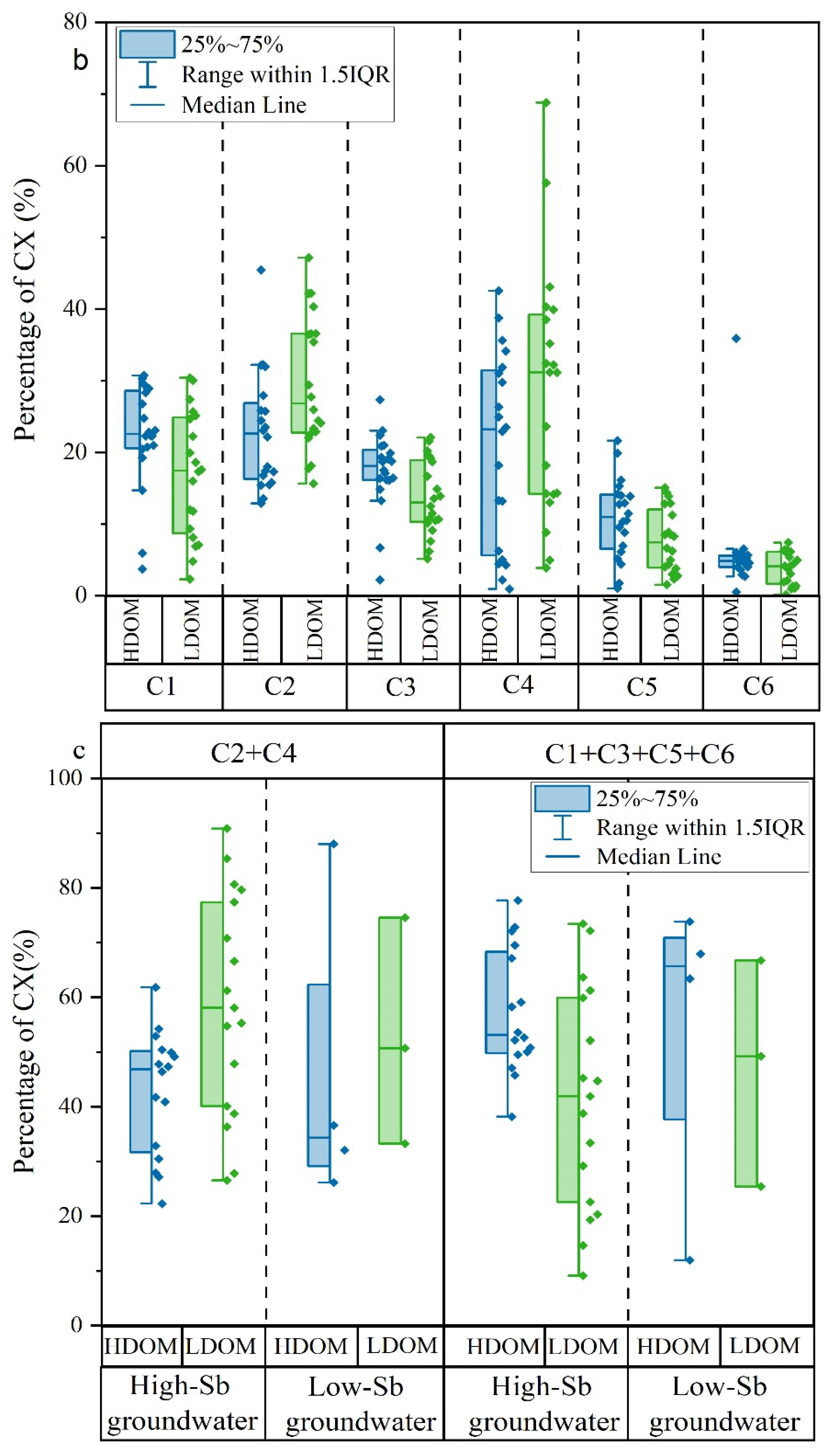
Figure 3.
Box and whisker plots of (a) fluorescent characteristics index; (b) percentages of C1, C2, C3, C4, C5, and C6; (c) percentages of the combined proportions of C1, C3, C5, and C6 and the combined proportions of C2 and C4 in HDOM and LDOM groundwater.
Six different fluorescent components (C1, C2, C3, C4, C5, and C6) were successfully identified in all high- and low-Sb groundwater samples using the PARAFAC models. C1, C3, C5, and C6 had similar excitation and emission wavelengths and were aligned with humic-like substances. In contrast, C2 and C4 were categorized as protein-like components [5,51,52]. In contrast to HDOM, the relative proportions of C1, C3, C5, and C6 in LDOM groundwater samples decreased noticeably, whereas a significant increase was observed in the relative proportions of C2 and C4 (Figure 3b). These findings suggest that protein-like compounds from microbial sources were predominantly observed in the LDOM groundwater samples.
This observation provides further evidence that protein-like components were dominant in high-Sb groundwater DOM, whereas humic-like components were predominantly present in low-Sb groundwater DOM (Figure 3c). This indicates that protein-like components were more favorable for Sb concentration enrichment in groundwater [5,29].
3.3. Molecular Characteristics of DOM in HDOM and LDOM Groundwater
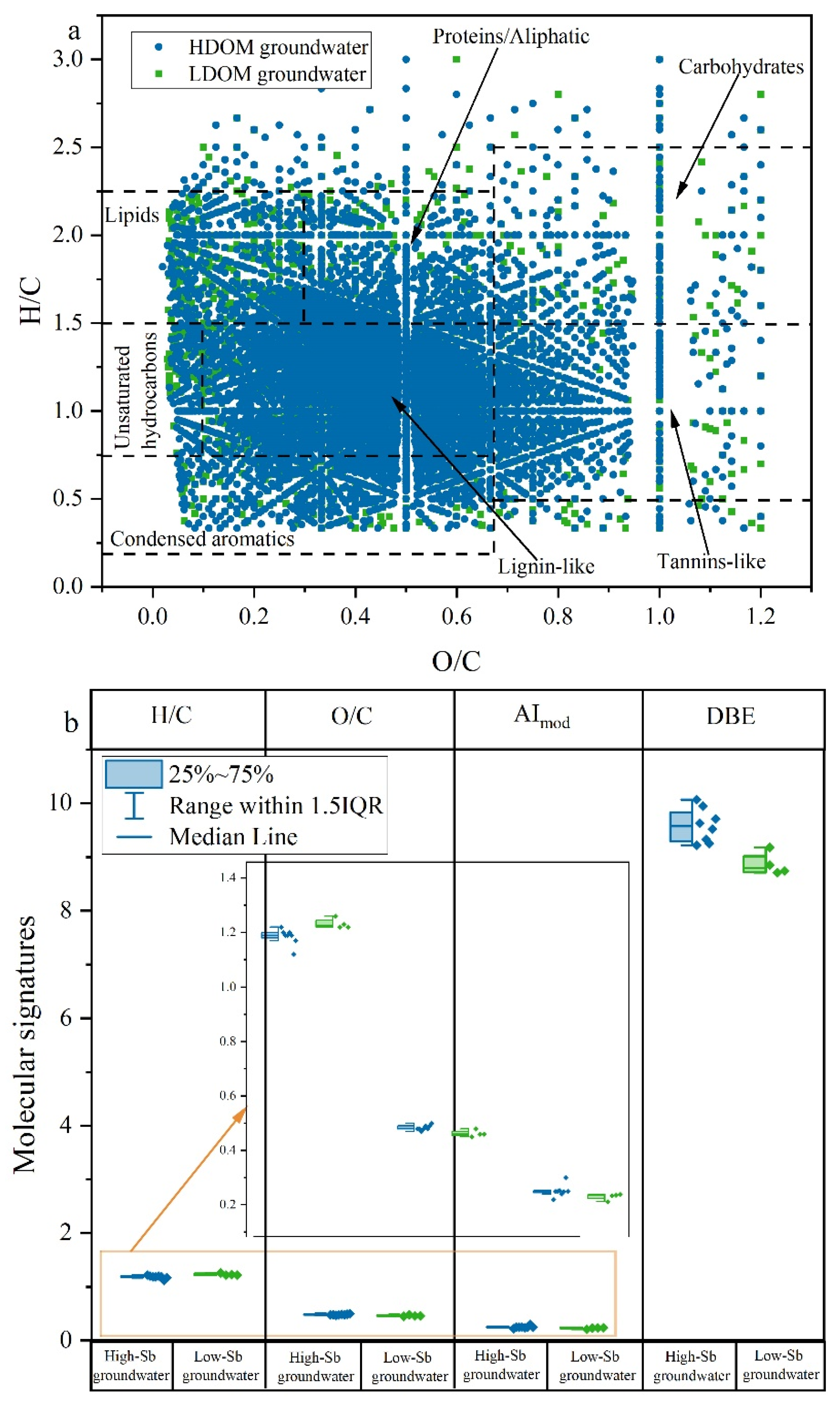
A total of 3632–6278 molecular formulas were detected in groundwater LDOM, whereas 3041–5338 formulas were observed in the groundwater HDOM (Table S2). The groundwater LDOM, characterized by relatively higher molecular abundances, exhibited greater complexity than HDOM. This increased complexity may be attributed to a wider variety of DOM molecules resulting from microbial decomposition processes [29,34,35,43]. In general, the H/C ratios were comparatively elevated, and DBE and AImod values were reduced compared to HDOM (Figure 4b). This suggests that the groundwater LDOM contains a greater abundance of newly saturated and less aromatic compounds [25,53,54], which aligns with the higher BIX and lower HIX and SUVA254 values observed. Compared to HDOM, groundwater LDOM had similar levels of abundance for lipids, proteins/aliphatics, unsaturated hydrocarbons, carbohydrates, lignin-like compounds, tannin-like compounds, and condensed aromatics in the van Krevelen diagram (Figure 4a), indicating that groundwater LDOM can reflect the predominant molecular signatures of the initial DOM in groundwater [38,55].
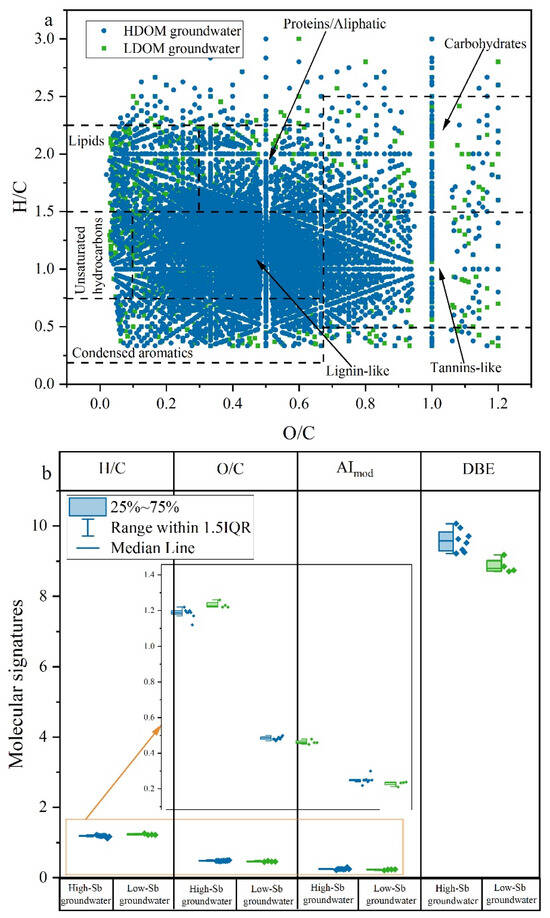
Figure 4.
Graph of (a) van Krevelen diagram of DOM compositions for 20 groundwater samples. HDOM groundwater samples were assigned a blue color, while LDOM groundwater samples were designated with a green color. The uncovered points indicate the differences in molecular signatures between HDOM and LDOM groundwater. Graph of (b) molecular signatures indices in HDOM and LDOM groundwater.
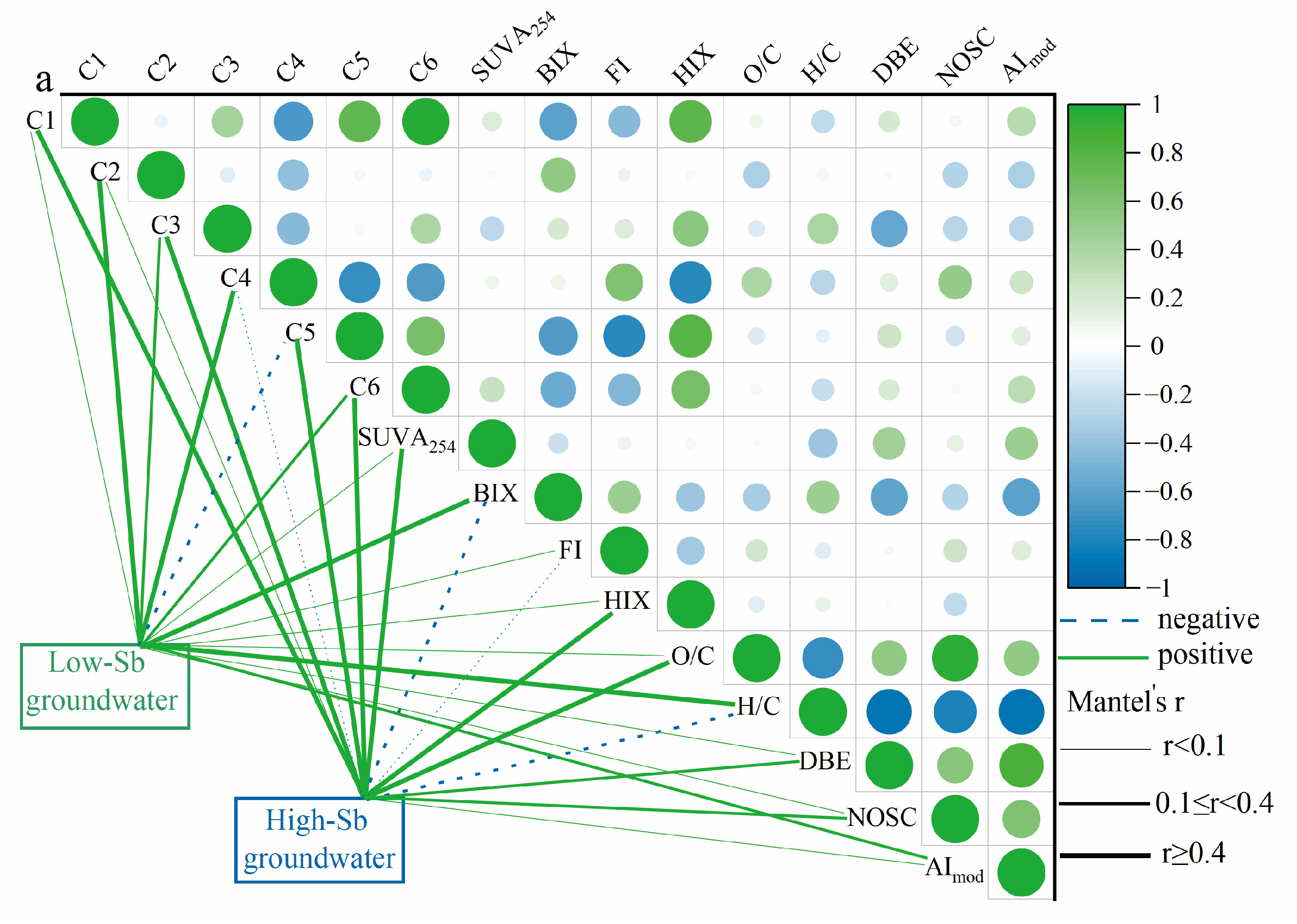
Based on the correlations with Sb concentrations in the LDOM groundwater, the optical properties, PARAFAC components, and molecular characteristics of the DOM were divided into two categories, as shown in Figure 5a. The HIX, SUVA254, C1, C3, C5, C6, and O/C ratios were positively correlated, indicating the presence of more stable and aromatic DOM components. In contrast, the second group, which included BIX, FI, C2, C4, H/C ratio, DBE, and AImod, exhibited negative correlations, reflecting more reactive DOM components. Generally, the high-Sb groundwater DOM exhibited higher HIX, SUVA254 values, and O/C ratios in Figure 5a, while exhibiting lower BIX values and H/C ratios compared to low-Sb groundwater DOM. This suggests that the high-Sb groundwater DOM was more unsaturated, richer in humic substances, and less susceptible to biodegradation. These findings are consistent with those of earlier studies by Hao et al. (2022) and Jia et al. (2023) [5,11], further confirming that the increased prevalence of recalcitrant organic compounds in high-Sb groundwater likely contributes to Sb enrichment.
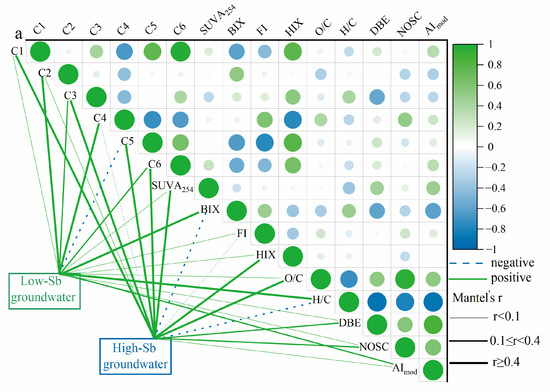
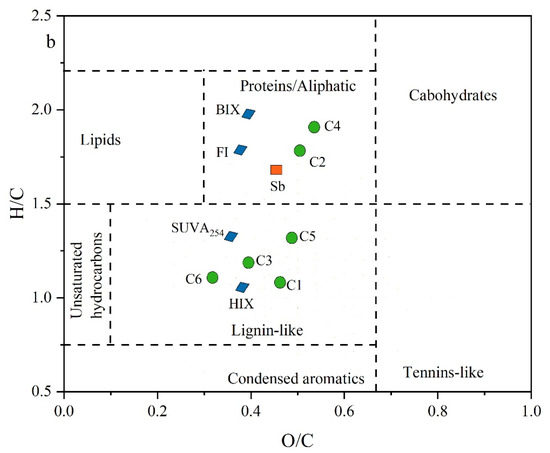
Figure 5.
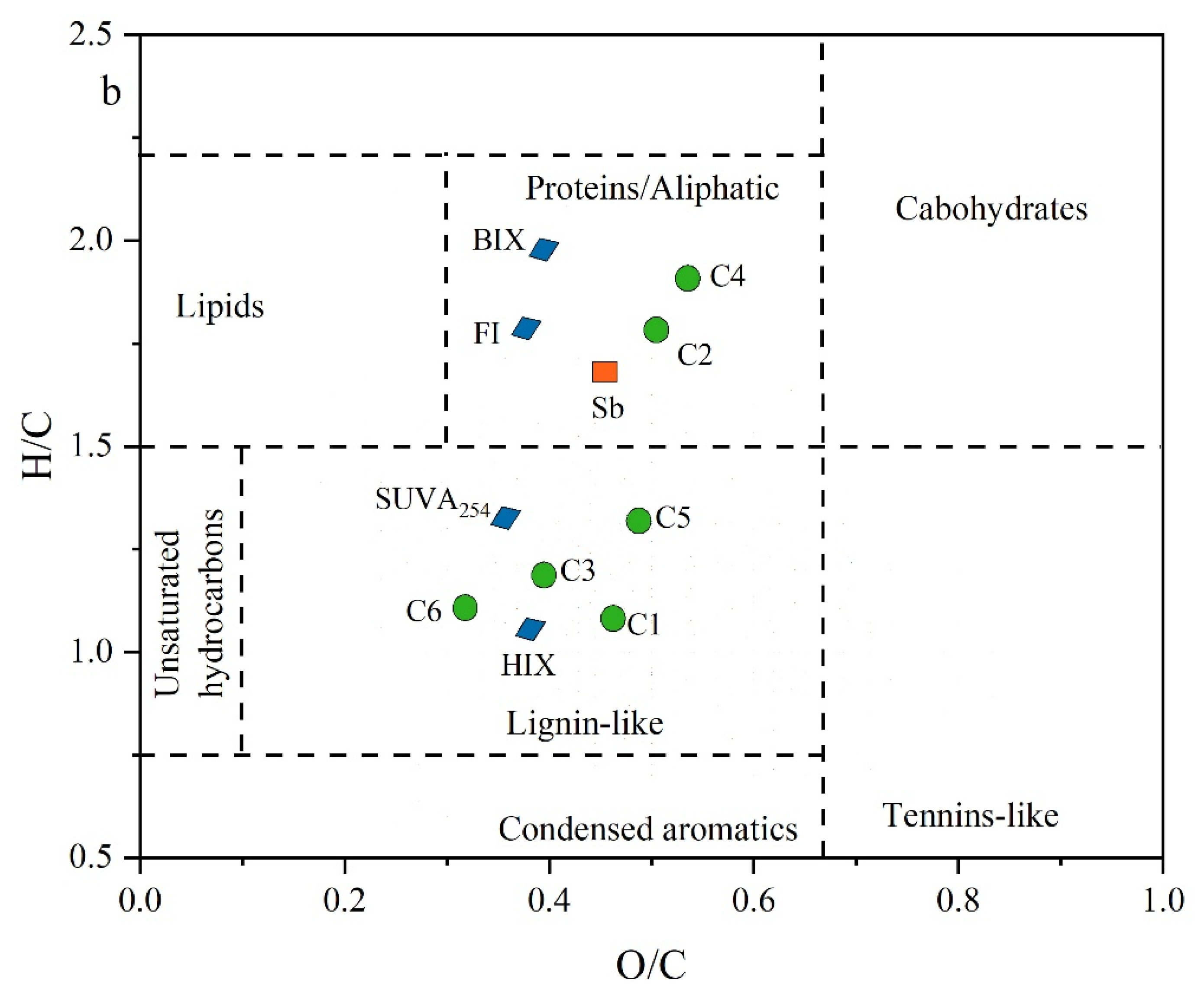
Plots of (a) correlation analysis of molecular compositions indices, optical parameters, and Sb concentrations in groundwater and (b) average characteristics of organic molecules associated with BIX, HIX, FI, and SUVA254, (C1, C2, C3, C4, C5, and C6), and Sb concentrations in van Krevelen diagram.
In the van Krevelen diagram (Figure 5b), the Sb mean concentration, BIX, FI, and protein-like components (C2 and C4) clustered within the range characterized by protein/aliphatic (highly unsaturated) compounds, exhibiting H/C ratios greater than 1.2. Conversely, parameters such as HIX and SUVA254 aligned with the intervals of lignin- and tannin-like (humic and less biodegradable) compounds, marked by O/C ratios exceeding 1.2, as illustrated in Figure 5b. The strong correlation between Sb concentration and optical indices, PARAFAC components, and molecular signatures in groundwater LDOM highlights that biodegradable protein-like components play a crucial role in Sb mobility, which cannot be ignored in high-Sb groundwater.
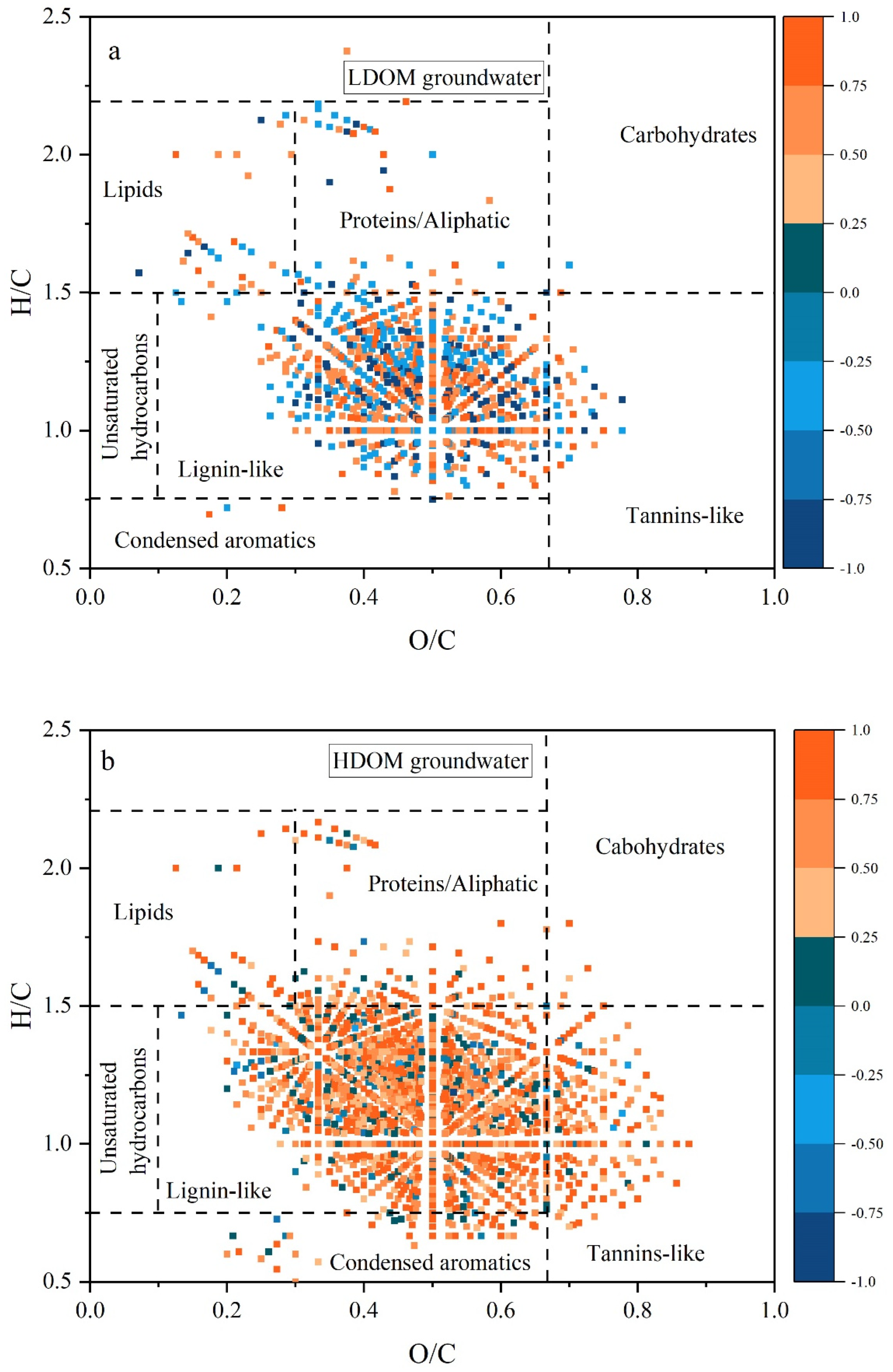
As shown in Figure 6, for both HDOM and LDOM groundwater, the lignin- and tannin-like molecules exhibited strong positive correlations with Sb concentrations. These molecules were typically characterized by their aromatic properties and resistance to degradation [38,39,56]. These findings suggest a positive association between Sb levels and the presence of aromatic and recalcitrant DOM compounds in both HDOM and LDOM groundwater. The number of lignin- and tannin-like substances positively correlated with the Sb concentration and was lower in LDOM groundwater than in HDOM groundwater, further suggesting that groundwater LDOM exhibits fewer aromatic structures and higher bioreactivity [25,34,35]. Previous research has shown that humic-like components with a higher HIX are linked to DOM molecules characterized by lower H/C ratios, higher DBE values, and elevated AImod indices. In contrast, protein-like components with higher BIX values are associated with higher H/C ratios and lower DBE and AImod values [25,27,29,43].
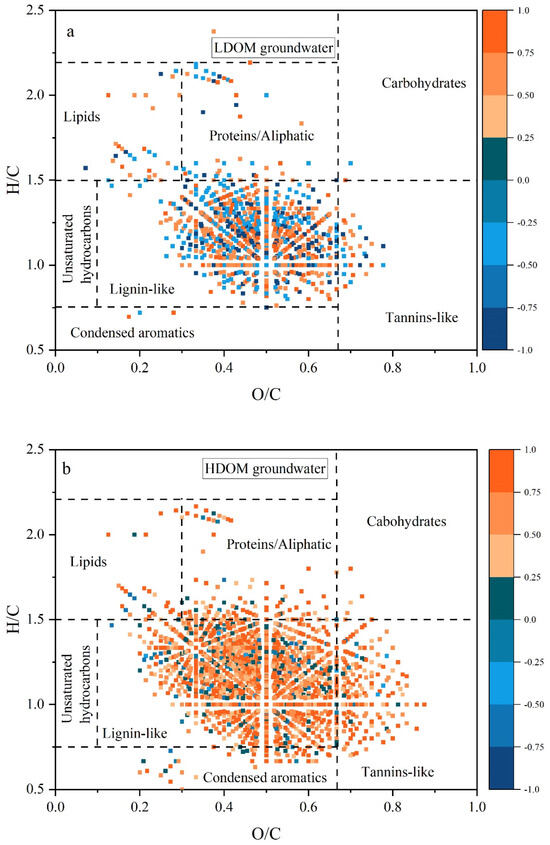
Figure 6.
Notable relationships between molecular characteristics and Sb from Spearman’s analysis (r ≥ 0.5, p < 0.01) for HDOM (b) and LDOM (a) groundwater samples. The blue to orange colors in the color bar denote the correlation coefficients (r), increasing from −1.0 to 1.0. The number of molecules correlated with Sb concentration is obviously more in HDOM groundwater than in LDOM groundwater.
4. Discussion
Based on the aforementioned findings, LDOM groundwater exhibited higher BIX and FI values, along with lower HIX and SUVA254 values in its fluorescent characteristics. Additionally, it demonstrated an elevated H/C ratio and comparatively reduced DBE and AImod values in its molecular signature. LDOM is considered to be easily degraded by microorganisms, whereas HDOM is considered a resistant substance that hinders microbial degradation [25,39,57]. Moreover, Sb existed mainly as total Sb, and 82.74% of the samples exceeded the natural background value (0.015 mg/L) and belonged to high-Sb groundwater in the LDOM groundwater. This indicates that bioreactive LDOM with a higher BIX value and H/C ratio can facilitate Sb enrichment in groundwater.
4.1. Competitive Adsorption Effect
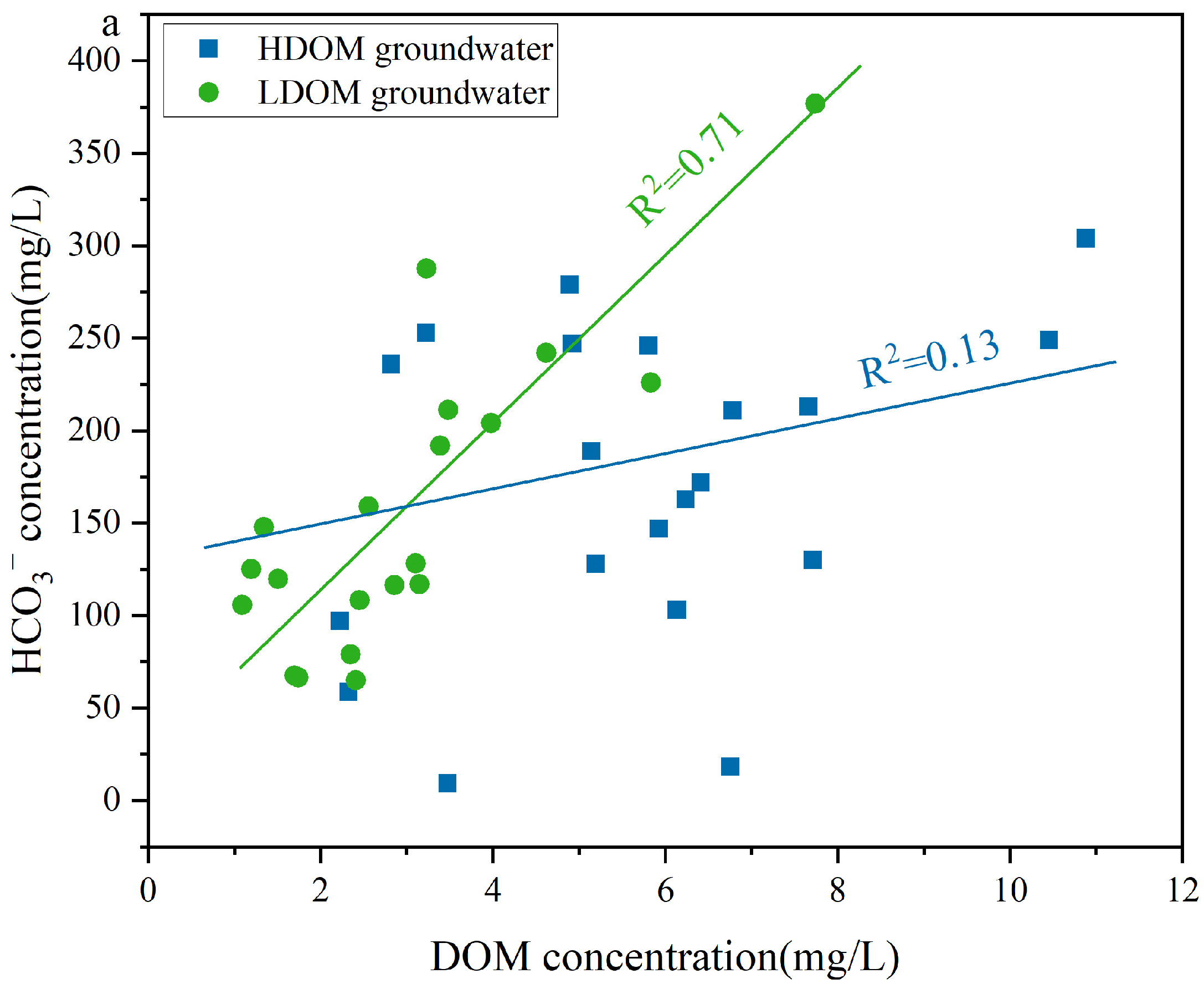
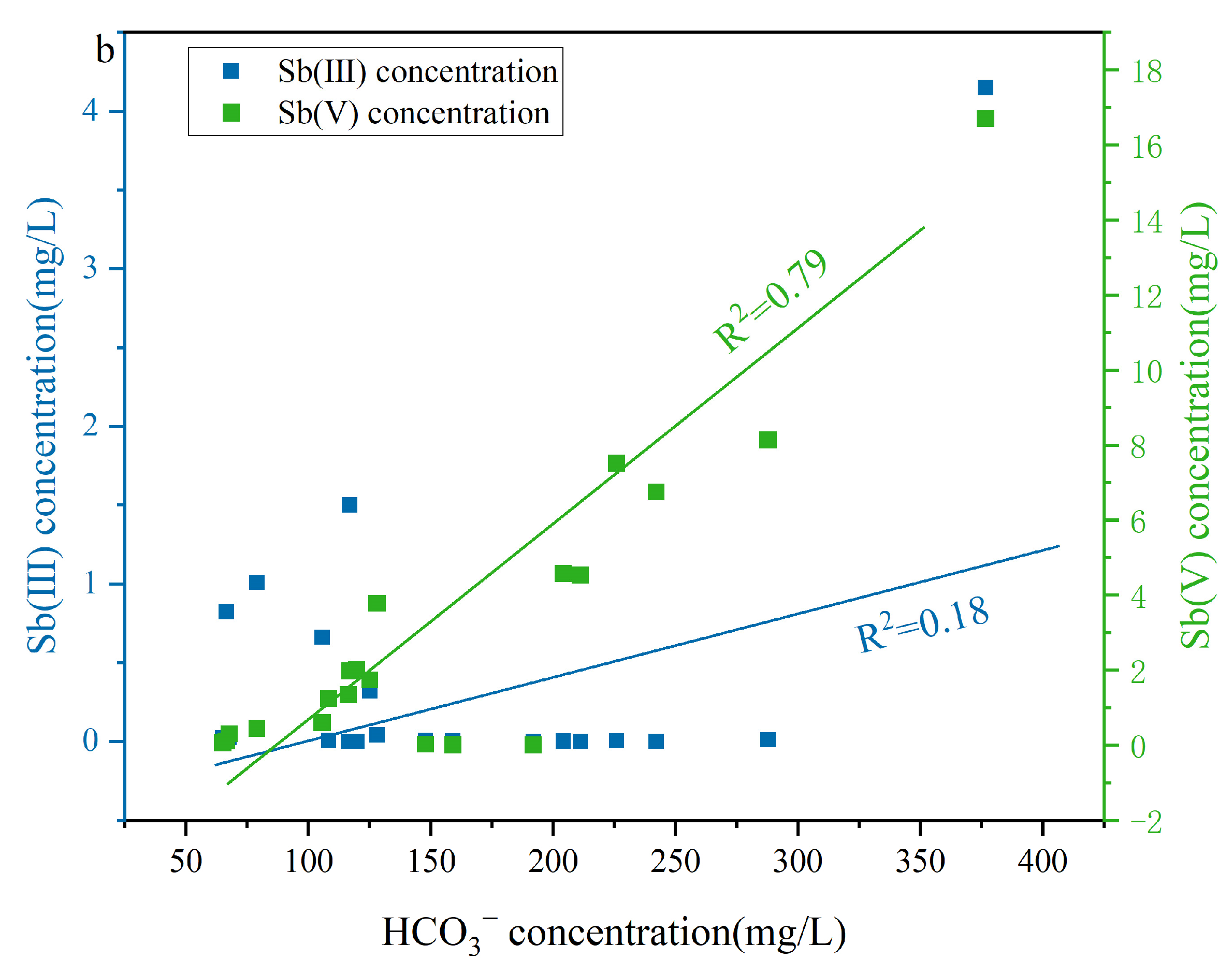
A moderate positive correlation existed between DOM and HCO3− in the LDOM groundwater (R2 = 0.71), whereas a weak positive correlation was observed in the HDOM groundwater (R2 = 0.13) (Figure 7a), indicating that the presence of HCO3− in the LDOM groundwater was mainly due to the microbial degradation of LDOM [51,58]. Under anaerobic conditions, microorganisms can biodegrade DOM to obtain electrons or energy, thereby supporting microbial respiration and leading to CO2 production [59]. This process subsequently enhances the dissolution of carbonate minerals, thereby increasing the HCO3− concentration in the LDOM groundwater [51,60,61]. The concentration of Sb(V) increased with increasing HCO3− levels (R2 = 0.79), whereas Sb(III) enrichment in the LDOM groundwater samples was negligible (R2 = 0.18) (Figure 7b). This suggests that competitive adsorption effects reduce Sb(V) removal from Fe/Mn hydroxide surfaces, whereas Sb(III) removal is minimally influenced by HCO3− [28,31,51]. Sb(III) and Sb(V) can form complexes with goethite, which are observed as monodentate or bidentate inner-sphere configurations via infrared spectroscopy or X-ray absorption fine-structure analysis [28,31]. Previous research has demonstrated that the surfaces of Fe/Mn hydroxides have a greater binding preference for Sb(III) than for Sb(V), attributed to the larger atomic radius of Sb(III) (0.076 nm) compared to Fe(III) (0.064 nm) [2,8,62,63]. Therefore, the increase in HCO3− led to Sb(V) being readily displaced from the surfaces of Fe/Mn hydroxides into groundwater enrichment, owing to intense competition for adsorption sites [8,64].
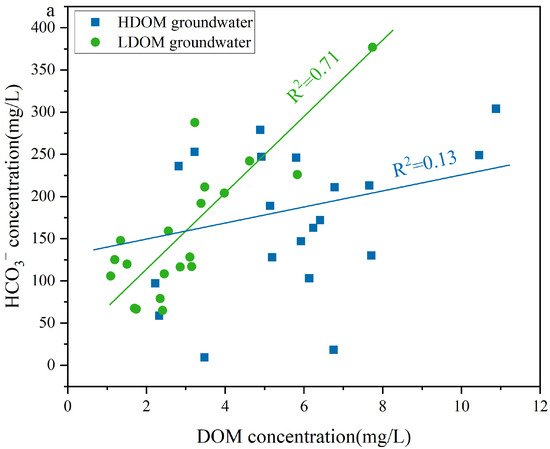
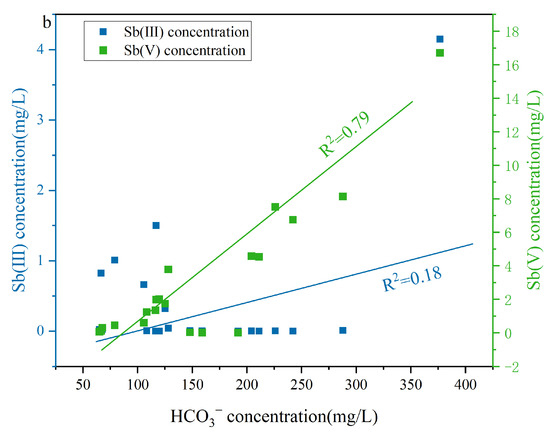
Figure 7.
Correlation analysis of (a) DOM concentration and (b) Sb(V) and Sb(III) concentration versus Sb concentration versus HCO3− concentration in LDOM groundwater.
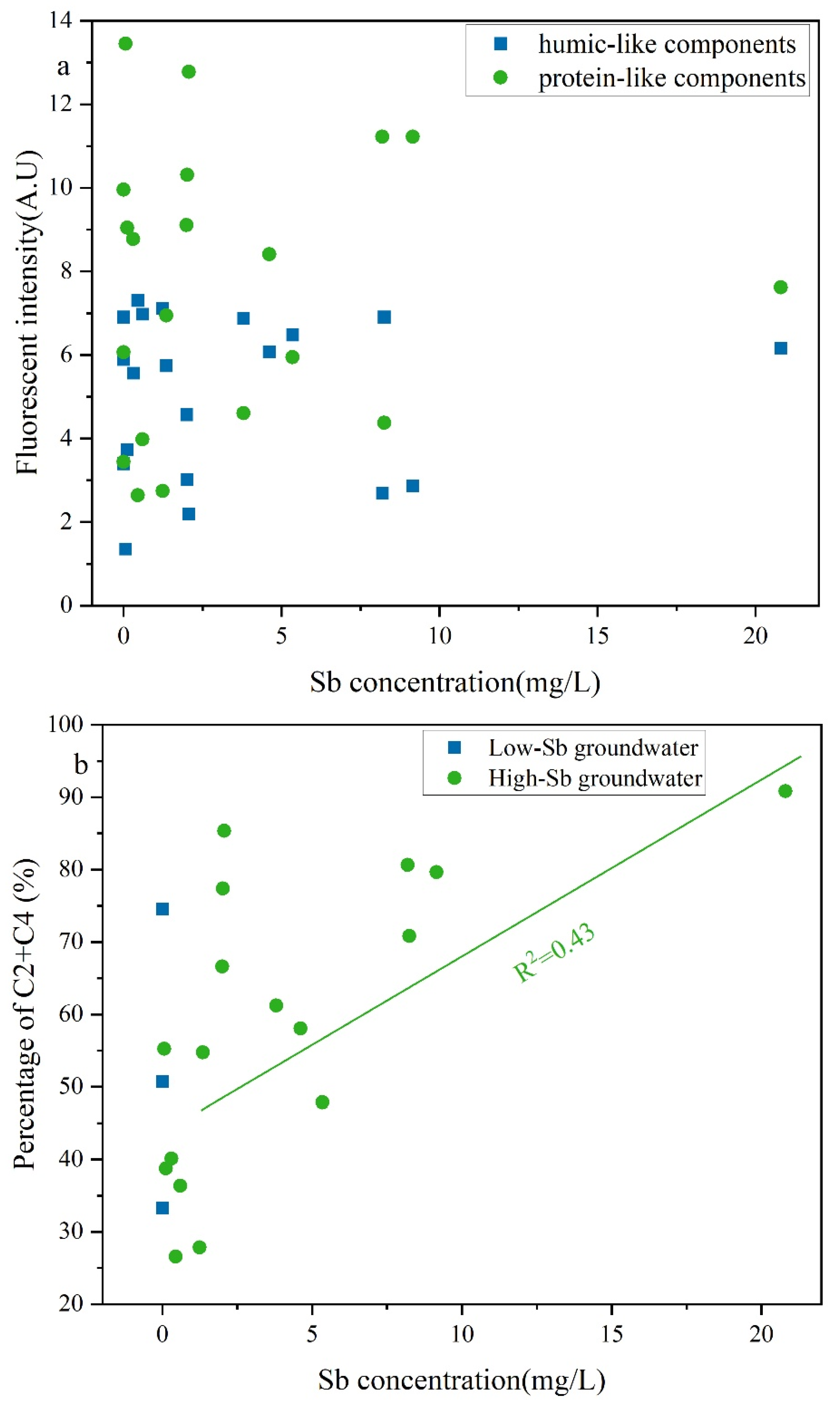
LDOM can also compete with Sb(V) for binding sites on Fe/Mn hydroxides [13,65,66], resulting in LDOM groundwater primarily existing as Sb(V) species. Owing to the greater number of functional groups in oxygen-rich DOM, LDOM was preferentially adsorbed onto Fe/Mn hydroxides and experienced stronger competition with Sb(V) for binding site [67,68,69,70]. The elevated protein-like components in LDOM intensified competition with Sb(V) [68]. The protein-like components in LDOM exhibited a moderate (R2 = 0.43) positive correlation with the Sb concentration in LDOM groundwater (Figure 8b), whereas no obvious correlations were observed between humic-like components and Sb concentration. This indicates that these easily degradable compounds in LDOM, characterized by higher BIX values, lower HIX and SUVA254 values, and greater proportions of C2 and C4, may contribute to increasing Sb concentrations in the LDOM groundwater through competitive adsorption. The fluorescence intensities of the protein-like components initially decreased and then decreased more gradually as the Sb concentration increased. In contrast, only slight quenching effects were observed for the humic-like components (Figure 8a). These findings further indicate that protein-like components served as more effective complexing agents for Sb than humic-like components in the LDOM groundwater [52,71,72,73].
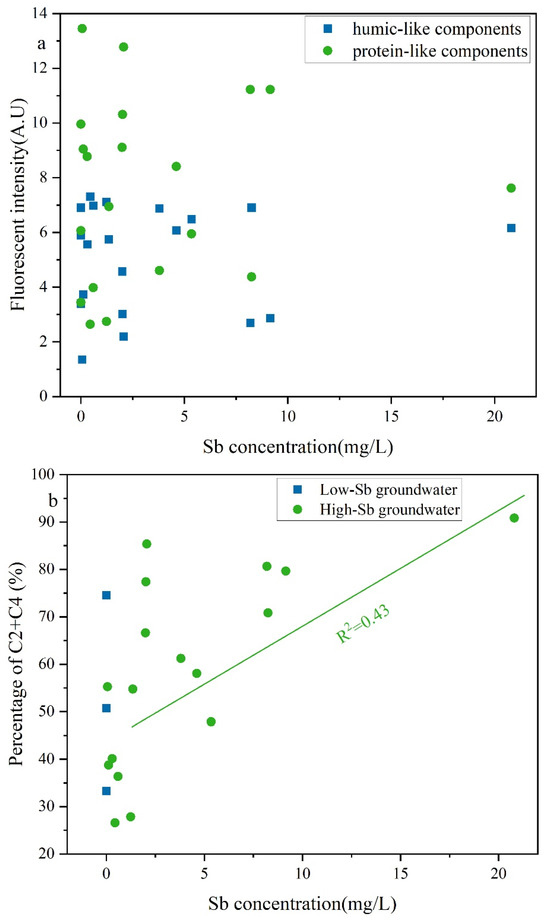
Figure 8.
Correlation analyses of (a) fluorescent intensity and (b) percentage of the combined proportions of C2 and C4 compared to Sb concentration in LDOM groundwater.
The pH level may have a substantial impact on the development of O-, OH, and OH2+ surface functional groups within the LDOM [74]. In an acidic environment, Sb may attach to LDOM through electrostatic forces or by creating inner-sphere complexes. Conversely, in alkaline settings, LDOM promotes Sb mobility by generating soluble aqueous complexes [73,74]. Furthermore, under near-neutral conditions, the complexing of Sb(V) with LDOM was less pronounced than that of Sb(III), facilitating the mobilization of Sb(V). Hence, the weakly alkaline environment in D3x4 water (Table S1) can cause competitive adsorption between LDOM and Sb(V) on Fe/Mn hydroxide sites, promoting Sb(V) enrichment in high-Sb groundwater [72,75].
4.2. Microorganisms Sb(III) Oxidative Dissolution
Previous research demonstrated that HDOM contains a greater amount of humic substances with quinone functional groups than LDOM, facilitating higher levels of microbial Fe reduction in natural settings. According to Li (2022), the addition of HDOM notably enhanced Fe(III) reduction during incubation compared to samples in which HDOM was not included. Typically, HDOM consists of a higher proportion of aromatic and hydrophobic structures, whereas the LDOM remaining in the solution is more biologically accessible to microorganisms [76]. Humic-like components in HDOM, which have high molecular weights, aromaticity, HIX, and O/C ratios, exhibited higher electron-acceptor capacities than protein-like components [48,77]; however, lower concentrations of protein-like LDOM substances similarly revealed a significant influence of microbially derived DOM on Sb(III) oxidation. For example, 1,4-benzoquinone, which had a low DBE value, could efficiently oxidize Sb(III) under alkaline groundwater conditions, leading to the creation of hydroquinone by transferring electrons between O2 and labile DOM [28]. Furthermore, the co-oxidation of Sb(III) and Fe(II) facilitates the generation of Fe(IV) and Sb(V) through an outer-sphere electron-acceptor mechanism involving bioreactive LDOM (such as EDTA and oxalate) [22,23,30].
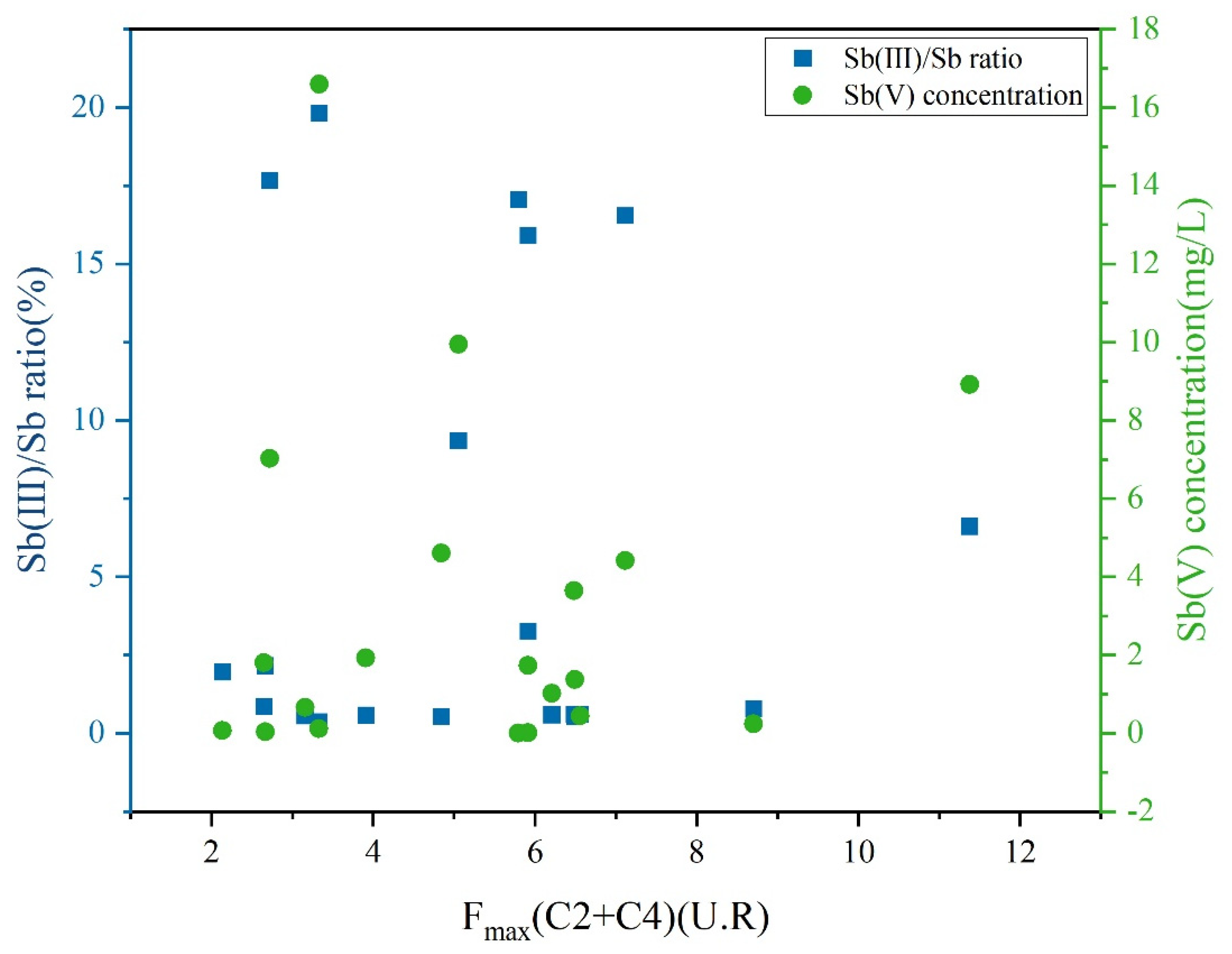
The Sb(III) oxidative reactions were highly dependent on pH and ORP, affecting the generation of reactive oxygen species in LDOM groundwater. As shown in Table S1, LDOM may facilitate Sb(III) oxidation by affecting the generation of semiquinone radicals and other reactive species in higher pH value and alkaline conditions [68,78,79]. The transformation of Sb(III) in LDOM groundwater is influenced by both biological and non-biological oxidation processes, leading to a progressive reduction in Sb(III) levels and corresponding increase in Sb(V) [68,70,80]. The concentration of Sb(V) was positively correlated with the combined fluorescence intensity of C2 and C4, whereas the oxidation ratio of Sb(III)/Sb progressively decreased, as illustrated in Figure 9. This phenomenon proved that Sb(III) oxidation was stronger in the presence of protein-like DOM substances. At the same time, as shown in Table S1, the positive ORP value indicated an oxidizing environment, which facilitated Sb(III) oxidation in LDOM groundwater. Previous studies had proved that Sb(III) can be rapidly oxidized to Sb(V) in oxic groundwater conditions in the absence of high concentrations of LDOM [8,24].
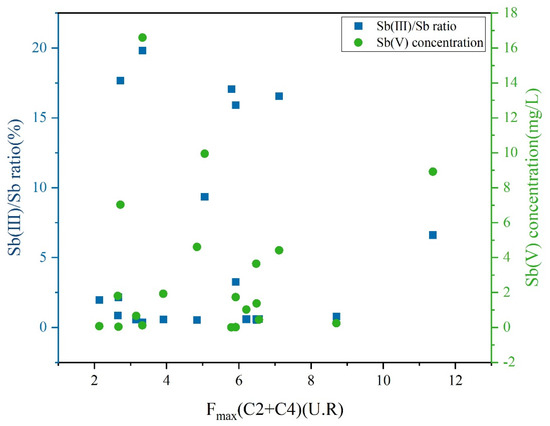
Figure 9.
Plots depicting the Sb(V) concentration and the oxidation ratio of Sb(III)/Sb versus fluorescence intensity of the combined proportions of C2 and C4 in LDOM groundwater.
Furthermore, bioreactive LDOM can provide increased energy and electron yields for microbial respiration, thereby enhancing the microbially driven release of Sb [10,12]. Although different metabolic pathways are involved in Sb(III) oxidation, two bacterial strains, Ensifer sp. NLS4 and Shewanella sp. NLS1, which are capable of oxidizing Sb(III) to generate Sb(V), have been identified in previous studies under conditions of limited nutrients [81]. In addition, Thiobacillus and Rhizobium spp. within the tailing microbiomes have been recognized as key populations capable of oxidizing both As(III) and Sb(III). However, the oxidation rate of Sb(III) is significantly higher than that of As(III) [12]. At mining locations, Sb-sulfide minerals, LDOM (ligand-like protein components of DOM), and tailings serve as attachment surfaces and energy sources for aerobic microorganisms under increasing-pH conditions, ultimately leading to complete Sb(III) oxidation [16,82]. Microorganisms may play a role in the oxidation of Sb(III) through a metabolic pathway similar to that of As(III) (e.g., arsenite oxidase Aio, comprising aioA and anoA) during the degradation of LDOM [12]. Notably, the initial bacterial community structure and diversity in Sb-polluted soil were weakened and diminished by Sb(III) and Sb(V), whereas Sb(III) decreased the variety of bacteria and abundance of particular bacterial species more strongly than Sb(V) [10].
5. Conclusions
Insights derived from the analysis of the spectral and molecular characteristics of DOM with varying molecular weights revealed that LDOM exerts a significant influence on antimony mobility. Sb exists mainly as dissolved Sb in LDOM groundwater, with Sb(V) being the dominant species. Moreover, LDOM, which is characterized by higher BIX and FI values in its fluorescent properties, a higher H/C ratio, and relatively lower DBE and AImod values in its molecular structure, demonstrated greater bioreactive activity than HDOM.
The presence of HCO3−, resulting from the biodegradation of LDOM, enhanced Sb(V) enrichment in LDOM groundwater, which was attributed to the stronger competitive adsorption of Sb(V) compared with Sb(III) at Fe/Mn hydroxide sites. In addition, protein-like DOM substances, which function as energy and electron acceptors, can enhance Sb(III) oxidation during the co-oxidation of Sb(III) and Fe(II), Sb(III) photooxidation, and microbially driven processes.
Therefore, our findings provide a novel perspective on how the molecular weights of DOM influence Sb(V) enrichment and Sb(III) oxidation in high-Sb groundwater and solve issues (e.g., tailing and rebound) related to the future remediation of Sb-polluted groundwater.
Supplementary Materials
The following supporting information can be downloaded at: https://www.mdpi.com/article/10.3390/w17081206/s1, Table S1: Descriptive statistics of geochemistry data, DOM, HIX, SUVA254, BIX, and FI in HDOM and LDOM groundwater; Table S2: Statistics of molecular signatures of DOM in HDOM and LDOM groundwater.
Author Contributions
Methodology, Q.S.; Investigation, Z.L.; Writing—original draft, T.Q.; Project administration, C.H. All authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript.
Funding
This work was funded by the Natural Science Foundation of Hebei Province (D2024508003; D2021508004), the Fundamental Research Funds for the Nantong Institute of Technology (Grant No. 2023XK(B)05), and the projects from “Jiangsu Marine Structure Service Performance Improvement Engineering Research Center” and “Nantong Building Structure Key Laboratory (CP12015005)”.
Data Availability Statement
Data is contained within the article.
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
References
- Qi, P.; Pichler, T. Sequential and simultaneous adsorption of Sb (III) and Sb (V) on ferrihydrite: Implications for oxidation and competition. Chemosphere 2016, 145, 55–60. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Leuz, A.K.; Johnson, C.A.R. Oxidation of Sb (III) to Sb (V) by O2 and H2O2 in aqueous solutions. Geochim. Cosmochim. Acta 2005, 69, 1165–1172. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shan, J.; He, M.; Lin, C.; Ouyang, W.; Liu, X. Simultaneous electrochemical determination of Sb (III) and Sb (V) in Water samples: Deposition potential differences and Sb (III) photooxidation characteristics. Sens. Actuators B-Chem. 2020, 305, 127454. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hao, C.; Zhang, W.; Gui, H. Hydrogeochemistry characteristic contrasts between low-and high-antimony in shallow drinkable groundwater at the largest antimony mine in hunan province, China. Appl. Geochem. 2020, 117, 1693545. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hao, C.; Liu, M.; Peng, Y.; Wei, Z. Comparison of Antimony Sources and Hydrogeochemical Processes in Shallow and Deep Groundwater Near the Xikuangshan Mine, Hunan Province, China. Mine Water Environ. 2022, 41, 194–209. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- GB 5749-2022; Standards for Drinking Water Quality. State Administration for Market Regulation and Standardization Administration of China: Beijing, China, 2022.
- Filella, M.; Belzile, N.; Chen, Y.-W. Antimony in the environment: A review focused on natural waters: II. Relevant solution chemistry. Earth-Sci. Rev. 2002, 59, 265–285. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, Z.; He, M.; Guo, X.; Zhou, R. Removal of antimony (III) and antimony (V) from drinking water by ferric chloride coagulation: Competing ion effect and the mechanism analysis. Sep. Purif. Technol. 2010, 76, 184–190. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hao, C.; Gui, H.; Sheng, L.; Miao, J.; Lian, H. Contrasting water-rock interaction behaviors of antimony and arsenic in contaminated rivers around an antimony mine, Hunan Province, China. Geochemistry 2021, 81, 125748. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, A.; He, M.; Ouyang, W.; Lin, C.; Liu, X. Effects of antimony (III/V) on microbial activities and bacterial community structure in soil. Sci. Total Environ. 2021, 789, 148073. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jia, X.; Majzlan, J.; Ma, L.; Liu, P.; Fan, P.; Li, W.; Zhou, J.; Wen, B. Novel insights into the mechanisms for Sb mobilization in groundwater in a mining area: A colloid field study. J. Hazard. Mater. 2023, 459, 132212. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kong, T.; Sun, X.; Gu, Z.; Yang, N.; Huang, Y.; Lan, L.; Gao, P.; Liu, H.; Wang, Y.; Jiang, F.; et al. Differential Mechanisms of Microbial As (III) and Sb (III) Oxidation and Their Contribution to Tailings Reclamation. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2024, 58, 11447–11458. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, X.; Wu, Z.; He, M.; Meng, X.; Jin, X.; Qiu, N.; Zhang, J. Adsorption of antimony onto iron oxyhydroxides: Adsorption behavior and surface structure. J. Hazard. Mater. 2014, 276, 339–345. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kong, L.; Hu, X.; He, M. Mechanisms of Sb (III) Oxidation by Pyrite-Induced Hydroxyl Radicals and Hydrogen Peroxide. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2015, 49, 3499–3505. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, J.; Bao, H.; Xiong, X.; Sun, Y.; Guan, X. Effective Sb (V) immobilization from water by zero-valent iron with weak magnetic field. Sep. Purif. Technol. 2015, 151, 276–283. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Q.; Huang, M.; Shu, S.; Chen, X.; Gao, N.; Zhu, Y. Quinone-mediated Sb removal from sulfate-rich wastewater by anaerobic granular sludge: Performance and mechanisms. Sci. Total Environ. 2022, 838, 156217. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fan, Y.; Zheng, C.; Huo, A.; Wang, Q.; Shen, Z.; Xue, Z.; He, C. Investigating the binding properties between antimony (V) and dissolved organic matter (DOM) under different pH conditions during the soil sorption process using fluorescence and FTIR spectroscopy. Ecotoxicol. Environ. Saf. 2019, 181, 34–42. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dündar, O.A.; Mehenktaş, C.; Arar, Ö. Removal of Antimony (III) and Antimony (V) from water samples through water-soluble polymer-enhanced ultrafiltration. Environ. Res. 2022, 215, 114324. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bagherifam, S.; Brown, T.C.; Bagherifam, S.; Baglieri, A. Sequential extraction of labile and recalcitrant fractions of soil organic matter: A case study focusing on antimony (Sb) in humic acids, fulvic acids and humin fractions of long-term aged contaminated soils. Environ. Pollut. 2023, 327, 121610. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xi, J.; He, M.; Kong, L. Adsorption of antimony on kaolinite as a function of time, pH, HA and competitive anions. Environ. Earth Sci. 2016, 75, 136. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Karimian, N.; Johnston, S.G.; Tavakkoli, E.; Frierdich, A.J.; Burton, E.D. Mechanisms of Arsenic and Antimony Co-sorption onto Jarosite: An X-ray Absorption Spectroscopic Study. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2023, 57, 4813–4820. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.; Kong, L.; He, M.; Lin, C.; Ouyang, W.; Liu, X.; Peng, X. Mechanistic insights into Sb (III) and Fe (II) co-oxidation by oxygen and hydrogen peroxide: Dominant reactive oxygen species and roles of organic ligands. Water Res. 2023, 242, 120296. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kong, L.; He, M. Mechanisms of Sb (III) Photooxidation by the Excitation of Organic Fe (III) Complexes. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2016, 50, 6974–6982. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, T.-l.; Qin, W.-x.; Alves, M.E.; Fang, G.-D.; Sun, Q.; Cui, P.-x.; Liu, C.; Zhou, D.-m.; Wang, Y.-j. Mechanisms of Sb (III) oxidation mediated by low molecular weight phenolic acids. Chem. Eng. J. 2019, 356, 190–198. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hao, C.; Sun, Q.; Sun, X.; Li, Q. Novel insights into antimony mobilization in different high- antimony aquifers from the molecular signatures of dissolved organic matter. Ecotoxicol. Environ. Saf. 2024, 277, 116377. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, X.; Guo, H.; Zheng, H.; Xiu, W.; He, W.; Ding, Q. Roles of different molecular weights of dissolved organic matter in arsenic enrichment in groundwater: Evidences from ultrafiltration and EEM-PARAFAC. Appl. Geochem. 2019, 104, 124–134. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gao, Z.; Guo, H.; Qiao, W.; He, C.; Shi, Q.; Ke, T.; Cao, Y. Dissolved Organic Matter Sources in High Arsenic Groundwater from a Sand-Gravel Confined Aquifer. J. Geophys. Res.-Biogeosci. 2023, 128, e2022JG007178. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, T.-l.; Sun, Q.; Fang, G.-d.; Cui, P.-x.; Liu, C.; Alves, M.E.; Qin, W.-x.; Zhou, D.-m.; Shi, Z.-q.; Wang, Y.-j. Unraveling the effects of gallic acid on Sb (III) adsorption and oxidation on goethite. Chem. Eng. J. 2019, 369, 414–421. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qiao, W.; Guo, H.; He, C.; Shi, Q.; Zhao, B. Unraveling roles of dissolved organic matter in high arsenic groundwater based on molecular and optical signatures. J. Hazard. Mater. 2021, 406, 124702. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.; Kong, L.; He, M.; Ouyang, W.; Lin, C.; Liu, X. Influences of Particles and Aquatic Colloids on the Oxidation of Sb (III) in Natural Water. Acs Earth Space Chem. 2020, 4, 661–671. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, X.; He, M.; Lin, C.; Gao, Y.; Zheng, L. Antimony (III) oxidation and antimony (V) adsorption reactions on synthetic manganite. Chem. Der Erde-Geochem. 2012, 72, 41–47. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wen, B.; Zhou, J.; Zhou, A.; Liu, C.; Xie, L. Sources, migration and transformation of antimony contamination in the water environment of Xikuangshan, China: Evidence from geochemical and stable isotope (S, Sr) signatures. Sci. Total Environ. 2016, 569, 114–122. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wen, B.; Zhou, A.; Zhou, J.; Liu, C.; Huang, Y.; Li, L. Coupled S and Sr isotope evidences for elevated arsenic concentrations in groundwater from the world’s largest antimony mine, Central China. J. Hydrol. 2018, 557, 211–221. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maqbool, T.; Sun, M.; Chen, L.; Zhang, Z. Exploring the fate of dissolved organic matter at the molecular level in the reactive electrochemical ceramic membrane system using fluorescence spectroscopy and FT-ICR MS. Water Res. 2022, 210, 117979. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ohno, T.; Parr, T.B.; Gruselle, M.-C.I.; Fernandez, I.J.; Sleighter, R.L.; Hatcher, P.G. Molecular Composition and Biodegradability of Soil Organic Matter: A Case Study Comparing Two New England Forest Types. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2014, 48, 7229–7236. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Phungsai, P.; Kurisu, F.; Kasuga, I.; Furumai, H. Changes in Dissolved Organic Matter Composition and Disinfection Byproduct Precursors in Advanced Drinking Water Treatment Processes. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2018, 52, 3392–3401. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, S.; Hou, J.; Suo, C.; Chen, J.; Liu, X.; Fu, R.; Wu, F. Molecular-level composition of dissolved organic matter in distinct trophic states in Chinese lakes: Implications for eutrophic lake management and the global carbon cycle. Water Res. 2022, 217, 118438. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maqbool, T.; Sun, M.; Chen, L.; Zhang, Z. Molecular-level characterization of natural organic matter in the reactive electrochemical ceramic membrane system for drinking water treatment using FT-ICR MS. Sci. Total Environ. 2022, 846, 157531. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ning, C.; Gao, Y.; Zhang, H.; Wang, L.; Yu, H.; Zou, L.; Cao, R.; Chen, J. Molecular chemodiversity of water-soluble organic matter in atmospheric particulate matter and their associations with atmospheric conditions. Sci. Total Environ. 2022, 809, 151171. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zark, M.; Christoffers, J.; Dittmar, T. Molecular properties of deep-sea dissolved organic matter are predictable by the central limit theorem: Evidence from tandem FT-ICR-MS. Mar. Chem. 2017, 191, 9–15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, B.; Shan, C.; Wang, S.; Fang, Z.; Pan, B. Unveiling the transformation of dissolved organic matter during ozonation of municipal secondary effluent based on FT-ICR-MS and spectral analysis. Water Res. 2021, 188, 116484. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, H.; Li, X.; Guo, M.; Li, F.; Yang, K.; Liu, X. Dissolved organic matters with low molecular weight fractions exhibit high photochemical potential for reactive oxygen formation. Chemosphere 2022, 305, 135542. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Du, L.; Liu, Y.; Hao, Z.; Chen, M.; Li, L.; Ren, D.; Wang, J. Fertilization regime shifts the molecular diversity and chlorine reactivity of soil dissolved organic matter from tropical croplands. Water Res. 2022, 225, 119106. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Guo, X.-J.; He, X.-S.; Li, C.-W.; Li, N.-X. The binding properties of copper and lead onto compost-derived DOM using Fourier-transform infrared, UV-vis and fluorescence spectra combined with two-dimensional correlation analysis. J. Hazard. Mater. 2019, 365, 457–466. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kulkarni, H.; Mladenov, N.; Datta, S. Effects of acidification on the optical properties of dissolved organic matter from high and low arsenic groundwater and surface water. Sci. Total Environ. 2019, 653, 1326–1332. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Richards, L.A.; Lapworth, D.J.; Magnone, D.; Gooddy, D.C.; Chambers, L.; Williams, P.J.; van Dongen, B.E.; Polya, D.A. Dissolved organic matter tracers reveal contrasting characteristics across high arsenic aquifers in Cambodia: A fluorescence spectroscopy study. Geosci. Front. 2019, 10, 1653–1667. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, Y.; Lan, J.; Chen, X.; Ye, H.; Du, D.; Li, J.; Hou, H. High arsenic levels in sediments, Jianghan Plain, central China: Vertical distribution and characteristics of arsenic species, dissolved organic matter, and microbial community. J. Geochem. Explor. 2021, 228, 106822. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aftabtalab, A.; Rinklebe, J.; Shaheen, S.M.; Niazi, N.K.; Moreno-Jiménez, E.; Schaller, J.; Knorr, K.-H. Review on the interactions of arsenic, iron (oxy)(hydr)oxides, and dissolved organic matter in soils, sediments, and groundwater in a ternary system. Chemosphere 2022, 286, 131790. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Malik, A.; Parvaiz, A.; Mushtaq, N.; Hussain, I.; Javed, T.; Rehman, H.U.; Farooqi, A. Characterization and role of derived dissolved organic matter on arsenic mobilization in alluvial aquifers of Punjab, Pakistan. Chemosphere 2020, 251, 126374. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.; Zhang, G.; Wang, H.; Cheng, Y.; Liu, H.; Jiang, Z.; Li, P.; Wang, Y. Effects of different dissolved organic matter on microbial communities and arsenic mobilization in aquifers. J. Hazard. Mater. 2021, 411, 125146. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pi, K.; Wang, Y.; Xie, X.; Huang, S.; Yu, Q.; Yu, M. Geochemical effects of dissolved organic matter biodegradation on arsenic transport in groundwater systems. J. Geochem. Explor. 2015, 149, 8–21. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, H.; Li, X.; Xiu, W.; He, W.; Cao, Y.; Zhang, D.; Wang, A. Controls of organic matter bioreactivity on arsenic mobility in shallow aquifers of the Hetao Basin, PR China. J. Hydrol. 2019, 571, 448–459. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gao, S.-X.; Zhang, X.; Fan, W.-Y.; Sheng, G.-P. Molecular insight into the variation of dissolved organic phosphorus in a wastewater treatment plant. Water Res. 2021, 203, 117529. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ge, J.; Qi, Y.; Li, C.; Ma, J.; Yi, Y.; Hu, Q.; Mostofa, K.M.G.; Volmer, D.A.; Li, S.-L. Fluorescence and molecular signatures of dissolved organic matter to monitor and assess its multiple sources from a polluted river in the farming-pastoral ecotone of northern China. Sci. Total Environ. 2022, 837, 154575. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Huang, Z.; Lv, J.; Cao, D.; Zhang, S. Iron plays an important role in molecular fractionation of dissolved organic matter at soil-water interface. Sci. Total Environ. 2019, 670, 300–307. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yang, P.; Jiang, T.; Cao, D.; Sun, T.; Liu, G.; Guo, Y.; Liu, Y.; Yin, Y.; Cai, Y.; Jiang, G. Unraveling Multiple Pathways of Electron Donation from Phenolic Moieties in Natural Organic Matter. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2023, 57, 16895–16905. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Z.; Shakiba, S.; Deng, N.; Chen, J.; Louie, S.M.; Hu, Y. Natural Organic Matter (NOM) Imparts Molecular-Weight-Dependent Steric Stabilization or Electrostatic Destabilization to Ferrihydrite Nanoparticles. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2020, 54, 6761–6770. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Saalfield, S.L.; Bostick, B.C. Synergistic effect of calcium and bicarbonate in enhancing arsenate release from ferrihydrite. Geochim. Cosmochim. Acta 2010, 74, 5171–5186. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, S.; Chen, M.; Diao, Y.; Feng, Q.; Zeng, R.J.; Zhou, S. Dissolved Organic Matter Acting as a Microbial Photosensitizer Drives Photoelectrotrophic Denitrification. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2022, 56, 4632–4641. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kulkarni, H.V.; Mladenov, N.; Johannesson, K.H.; Datta, S. Contrasting dissolved organic matter quality in groundwater in Holocene and Pleistocene aquifers and implications for influencing arsenic mobility. Appl. Geochem. 2017, 77, 194–205. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qiu, J.; Li, T.; Lu, F.; Huang, Y.; Li, C.; Zhang, H.; Shao, L.; He, P. Molecular behavior and interactions with microbes during anaerobic degradation of bio-derived DOM in waste leachate. J. Environ. Sci. 2023, 126, 174–183. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xi, J.; He, M.; Lin, C. Adsorption of antimony (III) and antimony (V) on bentonite: Kinetics, thermodynamics and anion competition. Microchem. J. 2011, 97, 85–91. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xi, J.; He, M.; Wang, K.; Zhang, G. Adsorption of antimony(III) on goethite in the presence of competitive anions. J. Geochem. Explor. 2013, 132, 201–208. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xi, J.; He, M.; Lin, C. Adsorption of antimony (V) on kaolinite as a function of pH, ionic strength and humic acid. Environ. Earth Sci. 2010, 60, 715–722. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Saada, A.; Breeze, D.; Crouzet, C.; Cornu, S.; Baranger, P. Adsorption of arsenic (V) on kaolinite and on kaolinite-humic acid complexes-Role of humic acid nitrogen groups. Chemosphere 2003, 51, 757–763. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Groeneveld, M.; Catalan, N.; Attermeyer, K.; Hawkes, J.; Einarsdottir, K.; Kothawala, D.; Bergquist, J.; Tranvik, L. Selective Adsorption of Terrestrial Dissolved Organic Matter to Inorganic Surfaces Along a Boreal Inland Water Continuum. J. Geophys. Res. Biogeosci. 2020, 125, e2019JG005236. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Z.; Song, L.; Yan, W.; Chen, M.; Zhong, Z.; Li, C. Mechanisms of antimony release from lacustrine sediments with increasing temperature*. Environ. Pollut. 2023, 323, 121301. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, J.; Liu, M.; Tong, L.; Zhou, Y.; Kong, L. Decomposition of waterside plants greatly affects the transformation and mobility of sedimentary antimony in water-sediment-sediment systems after emergency treatment: A microcosm study. J. Hazard. Mater. 2024, 478, 135598. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qiu, X.; Chen, M.; Wu, P.; Li, Y.; Sun, L.; Shang, Z.; Wang, T.; Dang, Z.; Zhu, N. Influence of dissolved organic matter with different molecular weight from chicken manure on ferrihydrite adsorption and re-release of antimony (V). J. Environ. Manag. 2024, 358, 120883. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, E.; Wu, S.; Liu, J.; Li, H.; Liu, X.; Lu, Y.; Ge, C.; Zhou, D. Activated carbon as a strong DOM adsorbent mitigates antimony and arsenic release in flooded mining-impacted soils. J. Hazard. Mater. 2024, 473, 134663. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, B.; Zhao, M.; Liu, C.; Feng, M.; Ma, S.; Liu, R.; Chen, K. Comparison of copper binding properties of DOM derived from fresh and pyrolyzed biomaterials: Insights from multi-spectroscopic investigation. Sci. Total Environ. 2020, 721, 137827. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, X.; Xie, X.; Liu, Y.; Wang, C.; Yang, M.; Huang, Y. Effects of digestate DOM on chemical behavior of soil heavy metals in an abandoned copper mining areas. J. Hazard. Mater. 2020, 393, 122436. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wu, Y.; Xi, B.; Fang, F.; Kou, B.; Gang, C.; Tang, J.; Tan, W.; Yuan, Y.; Yu, T. Insights into relationships between polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbon concentration, bacterial communities and organic matter composition in coal gangue site. Environ. Res. 2023, 236, 116502. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yang, H.; Lu, X.; He, M. Effect of organic matter on mobilization of antimony from nanocrystalline titanium dioxide. Environ. Technol. 2018, 39, 1515–1521. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hao, C.; Sun, X.; Peng, Y.; Xie, B.; He, K.; Wang, Y.; Liu, M.; Fan, X. Geochemical impact of dissolved organic matter on antimony mobilization in shallow groundwater of the Xikuangshan antimony mine, Hunan Province, China. Sci. Total Environ. 2023, 860, 160292. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Y.; Gong, X.; Sun, Y.; Shu, Y.; Niu, D.; Ye, H. High molecular weight fractions of dissolved organic matter (DOM) determined the adsorption and electron transfer capacity of DOM on iron minerals. Chem. Geol. 2022, 604, 120907. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abdelrady, A.; Sharma, S.; Sefelnasr, A.; Kennedy, M. Characterisation of the impact of dissolved organic matter on iron, manganese, and arsenic mobilisation during bank filtration. J. Environ. Manag. 2020, 258, 110003. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, K.-L.; Min, D.; Chen, G.-L.; Liu, D.-F.; Yu, H.-Q. Oxidation of Sb (III) by Shewanella species with the assistance of extracellular organic matter. Environ. Res. 2023, 236, 116834. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, X.; Feng, Y.; Yang, A.; Hu, X.; Li, Q.; Song, X.; He, Y. Humic Substances-Induced Changes in the Properties of Sb-Contaminated Soil and Effects on Sb Forms. Water Air Soil Pollut. 2024, 235, 144. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Su, L.; Wang, S.; Ji, R.; Zhuo, G.; Liu, C.; Chen, M.; Li, H.; Zhang, L. New insight into the role of FDOM in heavy metal leaching behavior from MSWI bottom ash during accelerated weathering using fluorescence EEM-PARAFAC. Waste Manag. 2022, 144, 153–162. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nguyen, V.K.; Choi, W.; Yu, J.; Lee, T. Microbial oxidation of antimonite and arsenite by bacteria isolated from antimony-contaminated soils. Int. J. Hydrogen Energy 2017, 42, 27832–27842. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Loni, P.C.; Wu, M.; Wang, W.; Wang, H.; Ma, L.; Liu, C.; Song, Y.; Tuovinen, O.H. Mechanism of microbial dissolution and oxidation of antimony in stibnite under ambient conditions. J. Hazard. Mater. 2020, 385, 121561. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).