Water-Quality Spatiotemporal Characteristics and Their Drivers for Two Urban Streams in Indianapolis
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
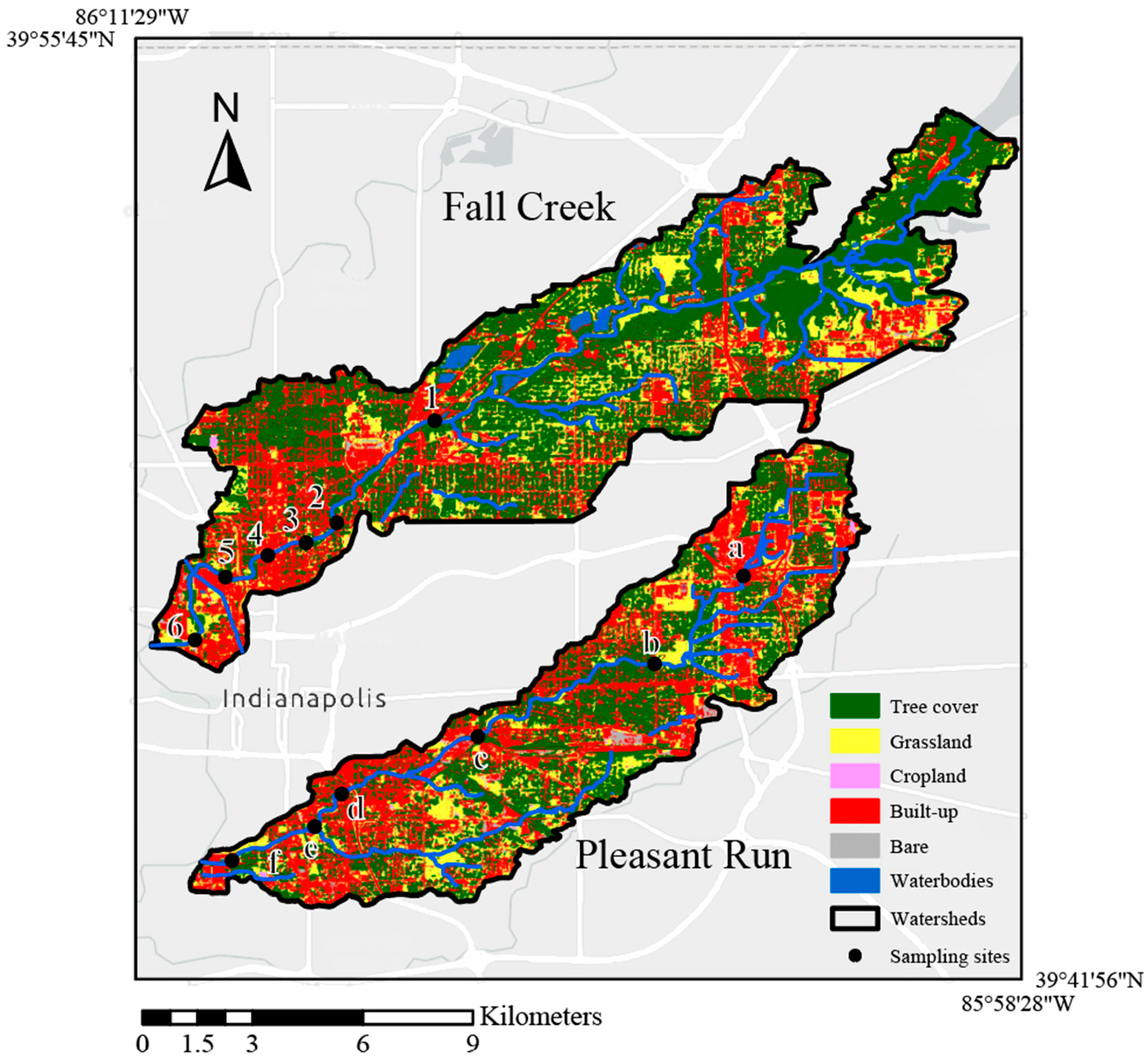
2.1. Study Area
2.2. Sampling and Measurement
2.3. Land-Cover Use and NDVI Data Preprocessing
2.4. Statistical Analyses
3. Results
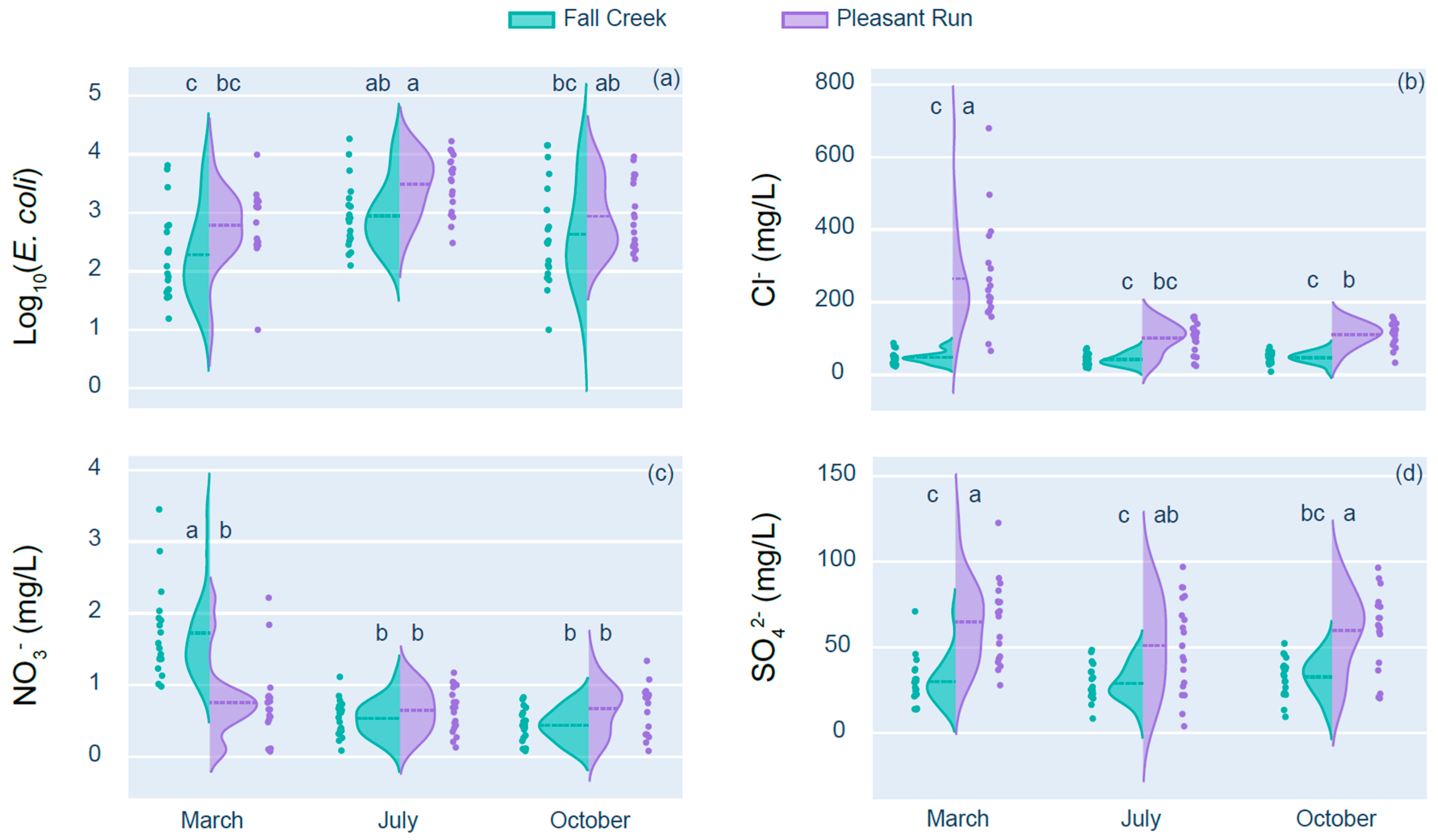
3.1. Long-Term and Seasonal Trends for log10(E. coli), Cl−, NO3−, and SO42− from 2003 to 2021
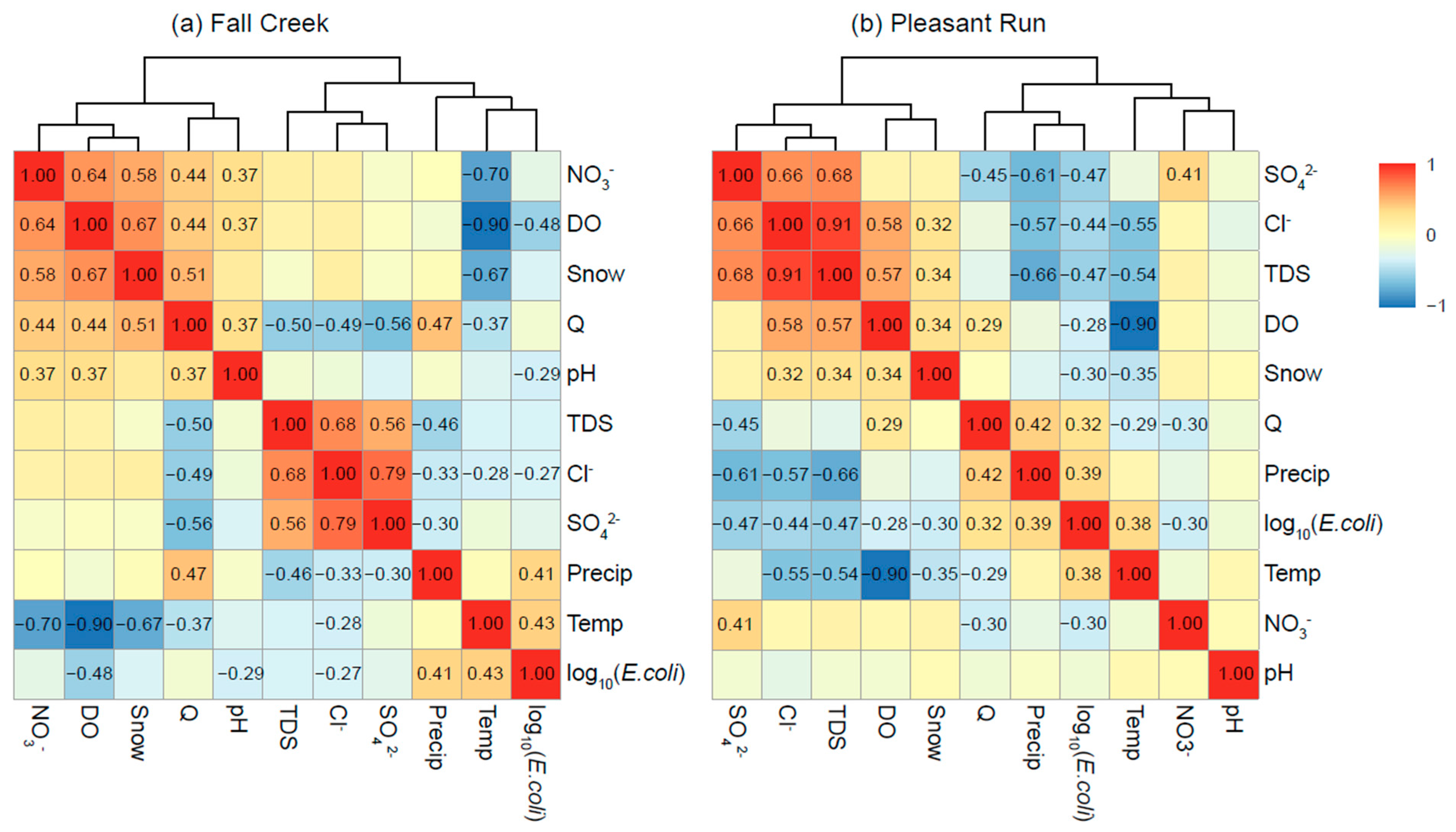
3.2. Relationships Between Water-Quality Variables and Potential Drivers over Time
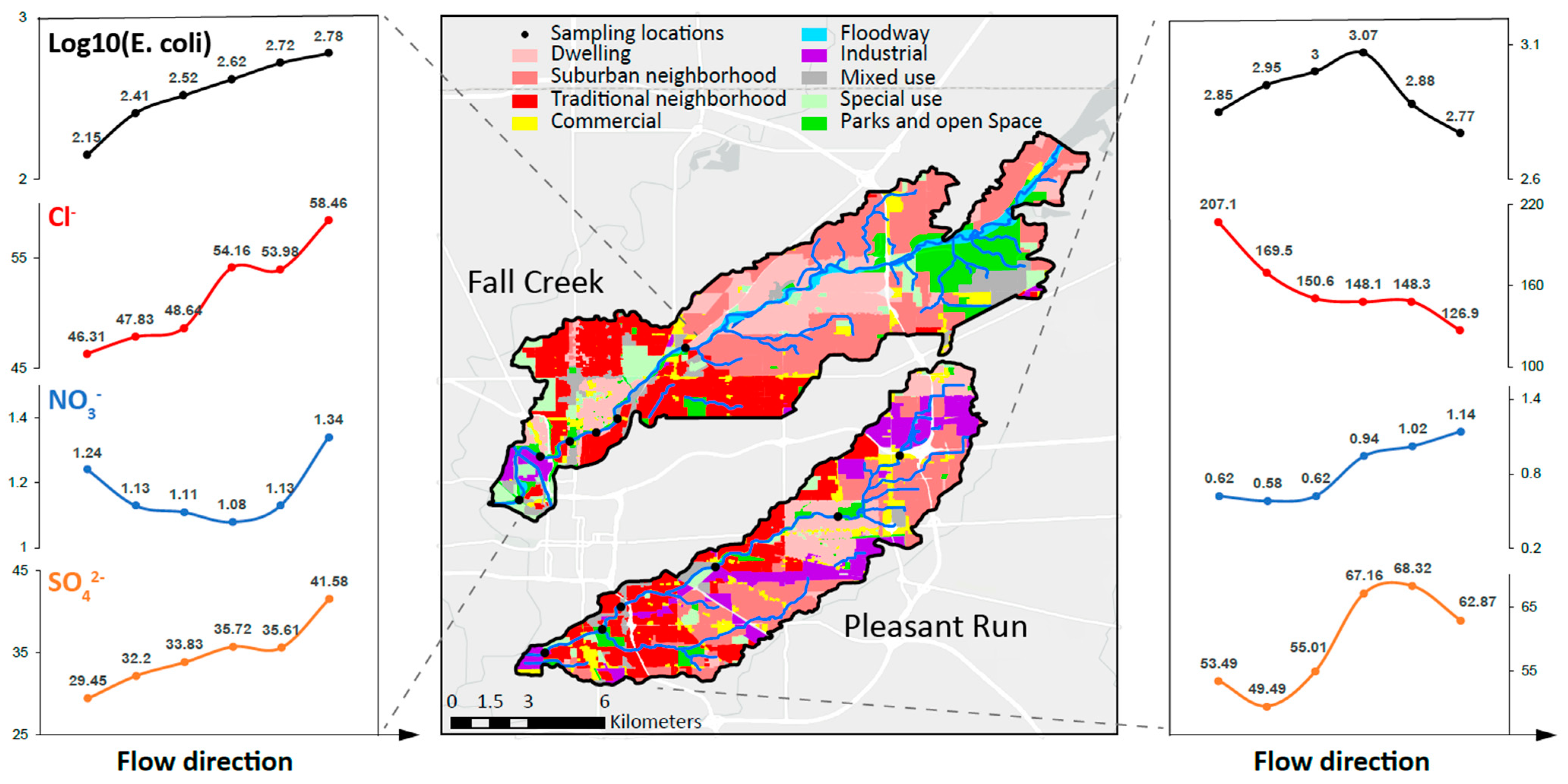
3.3. Spatial Patterns in Water-Quality Variables with Regards to Land-Use Factors
4. Discussion
4.1. Mechanisms of Changing Climate on Urban Stream Water Quality
4.2. Mechanisms of Land Use on Urban Stream Water Quality
4.3. Limitations and Management Implications
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Alamdari, N.; Sample, D.J.; Ross, A.C.; Easton, Z.M. Evaluating the Impact of Climate Change on Water Quality and Quantity in an Urban Watershed Using an Ensemble Approach. Estuaries Coasts 2020, 43, 56–72. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Adeola Fashae, O.; Abiola Ayorinde, H.; Oludapo Olusola, A.; Oluseyi Obateru, R. Landuse and surface water quality in an emerging urban city. Appl. Water Sci. 2019, 9, 1–12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ingram, W. Increases all round. Nat. Clim. Change 2016, 6, 443–444. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Whitehead, P.G.; Wilby, R.L.; Battarbee, R.W.; Kernan, M.; Wade, A.J. A review of the potential impacts of climate change on surface water quality. Hydrol. Sci. J. 2009, 54, 101–123. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Griffith, J.A.; Martinko, E.A.; Whistler, J.K.; Price, K.P. Interrelationships among landscapes, NDVI, and stream water quality in the U.S. Central Plains. Ecol. Appl. 2002, 12, 1702–1718. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, Y.Y.; Toor, G.S. Sources and mechanisms of nitrate and orthophosphate transport in urban stormwater runoff from residential catchments. Water Res. 2017, 112, 176–184. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Davis, B.; Birch, G. Comparison of heavy metal loads in stormwater runoff from major and minor urban roads using pollutant yield rating curves. Environ. Pollut. 2010, 158, 2541–2545. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brezonik, P.L.; Stadelmann, T.H. Analysis and predictive models of stormwater runoff volumes, loads, and pollutant concentrations from watersheds in the Twin Cities metropolitan area, Minnesota, USA. Water Res. 2002, 36, 1743–1757. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gilbert, J.K.; Clausen, J.C. Stormwater runoff quality and quantity from asphalt, paver, and crushed stone driveways in Connecticut. Water Res. 2006, 40, 826–832. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mora, A.; Mahlknecht, J.; Rosales-Lagarde, L.; Hernández-Antonio, A. Assessment of major ions and trace elements in groundwater supplied to the Monterrey metropolitan area, Nuevo León, Mexico. Environ. Monit. Assess. 2017, 189, 1–15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pfaff, J.D. Determination of Inorganic Anions by Ion Chromatography. EPA Method 300. 1993. Available online: https://www.epa.gov/sites/default/files/2015-08/documents/method_300-0_rev_2-1_1993.pdf (accessed on 1 June 2022).
- Zanaga, D.; Van De Kerchove, R.; Daems, D.; De Keersmaecker, W.; Brockmann, C.; Kirches, G.; Wevers, J.; Cartus, O.; Santoro, M.; Fritz, S.; et al. ESA WorldCover 10 m 2021 v200. 2022. Available online: https://pure.iiasa.ac.at/id/eprint/18478/ (accessed on 1 June 2022). [CrossRef]
- Corbin, T. Learning ArcGIS Pro; Packt Publishing Ltd.: Birmingham, UK, 2015. [Google Scholar]
- Qiao, N.; Wang, L. Satellite observed vegetation dynamics and drivers in the Namib sand sea over the recent 20 years. Ecohydrology 2022, 15, e2420. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Y.; Gentine, P.; Luo, X.; Lian, X.; Liu, Y.; Zhou, S.; Michalak, A.M.; Sun, W.; Fisher, J.B.; Piao, S.; et al. Increasing sensitivity of dryland vegetation greenness to precipitation due to rising atmospheric CO2. Nat. Commun. 2022, 13, 4875. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiao, W.; Wang, L.; Smith, W.K.; Chang, Q.; Wang, H.; D’Odorico, P. Observed increasing water constraint on vegetation growth over the last three decades. Nat. Commun. 2021, 12, 3777. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, X.; Zhao, W.; Wang, L.; Liu, Y.; Liu, Y.; Feng, Q. Relationship between soil water content and soil particle size on typical slopes of the Loess Plateau during a drought year. Sci. Total Environ. 2019, 648, 943–954. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kluyver, T.; Ragan-Kelley, B.; Pérez, F.; Granger, B.; Bussonnier, M.; Frederic, J.; Kelley, K.; Hamrick, J.; Grout, J.; Corlay, S.; et al. Jupyter Notebooks-a publishing format for reproducible computational workflows. In Positioning and Power in Academic Publishing: Players, Agents and Agendas; IOS Press: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 2016; Volume 2016, pp. 87–90. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Waskom, M.L. Seaborn: Statistical data visualization. J. Open Source Softw. 2021, 6, 3021. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bernal, S.; Butturini, A.; Sabater, F. Inferring nitrate sources through end member mixing analysis in an intermittent Mediterranean stream. Biogeochemistry 2006, 81, 269–289. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, H.J.; Chang, H. Response of discharge, TSS, and E. coli to rainfall events in urban, suburban, and rural watersheds. Environ. Sci. Process Impacts 2014, 16, 2313–2324. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gardner, K.M.; Royer, T.V. Effect of Road Salt Application on Seasonal Chloride Concentrations and Toxicity in South-Central Indiana Streams. J. Environ. Qual. 2010, 39, 1036–1042. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ledford, S.H.; Lautz, L.K. Floodplain connection buffers seasonal changes in urban stream water quality. Hydrol. Process 2015, 29, 1002–1016. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vermeulen, L.C.; Hofstra, N. Influence of climate variables on the concentration of Escherichia coli in the Rhine, Meuse, and Drentse Aa during 1985–2010. Reg. Environ. Change 2014, 14, 307–319. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, R.; Filippelli, G.; Wang, L. Annual Precipitation and Discharge Drive Increases in Escherichia Coli Concentrations in an Urban Stream. Sci. Total Environ. 2023, 886, 163892. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Graves, G.M.; Vogel, J.R. Spatiotemporal Variability Comparisons of Water Quality and Escherichia coli in an Oklahoma Stream. J. Contemp. Water Res. Educ. 2023, 177, 94–102. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kaushal, S.S.; Groffman, P.M.; Likens, G.E.; Belt, K.T.; Stack, W.P.; Kelly, V.R.; Band, L.E.; Fisher, G.T. Increased salinization of fresh water in the northeastern United States. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2005, 102, 13517–13520. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khatri, N.; Tyagi, S. Influences of natural and anthropogenic factors on surface and groundwater quality in rural and urban areas. Front. Life Sci. 2015, 8, 23–39. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shi, P.; Zhang, Y.; Li, Z.; Li, P.; Xu, G. Influence of land use and land cover patterns on seasonal water quality at multi-spatial scales. Catena 2017, 151, 182–190. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, J.; Lu, J. Effects of land use, topography and socio-economic factors on river water quality in a mountainous watershed with intensive agricultural production in East China. PLoS ONE 2014, 9, e102714. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, R.; Ma, Y.; Zhao, G.; Zhou, Y.; Shehab, I.; Burton, A. Investigating water quality sensitivity to climate variability and its influencing factors in four Lake Erie watersheds. J. Environ. Manag. 2023, 325, 116449. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, G.; Li, P.; Lu, K.; Tantai, Z.; Zhang, J.; Ren, Z.; Wang, X.; Yu, K.; Shi, P.; Cheng, Y. Seasonal changes in water quality and its main influencing factors in the Dan River basin. Catena 2019, 173, 131–140. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chang, H. Spatial analysis of water quality trends in the Han River basin, South Korea. Water Res. 2008, 42, 3285–3304. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Torres-Martínez, J.A.; Mora, A.; Knappett, P.S.K.; Ornelas-Soto, N.; Mahlknecht, J. Tracking nitrate and sulfate sources in groundwater of an urbanized valley using a multi-tracer approach combined with a Bayesian isotope mixing model. Water Res. 2020, 182, 115962. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Umwali, E.D.; Kurban, A.; Isabwe, A.; Mind’je, R.; Azadi, H.; Guo, Z.; Udahogora, M.; Nyirarwasa, A.; Umuhoza, J.; Nzabarinda, V.; et al. Spatio-seasonal variation of water quality influenced by land use and land cover in Lake Muhazi. Sci. Rep. 2021, 11, 17376. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dark, S.J.; Bram, D. The modifiable areal unit problem (MAUP) in physical geography. Prog. Phys. Geogr. 2007, 31, 471–479. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tang, W.; Lu, Z. Application of self-organizing map (SOM)-based approach to explore the relationship between land use and water quality in Deqing County, Taihu Lake Basin. Land Use Policy 2022, 119, 106205. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gu, Q.; Hu, H.; Ma, L.; Sheng, L.; Yang, S.; Zhang, X.; Zhang, M.; Zheng, K.; Chen, L. Characterizing the spatial variations of the relationship between land use and surface water quality using self-organizing map approach. Ecol. Indic. 2019, 102, 633–643. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]

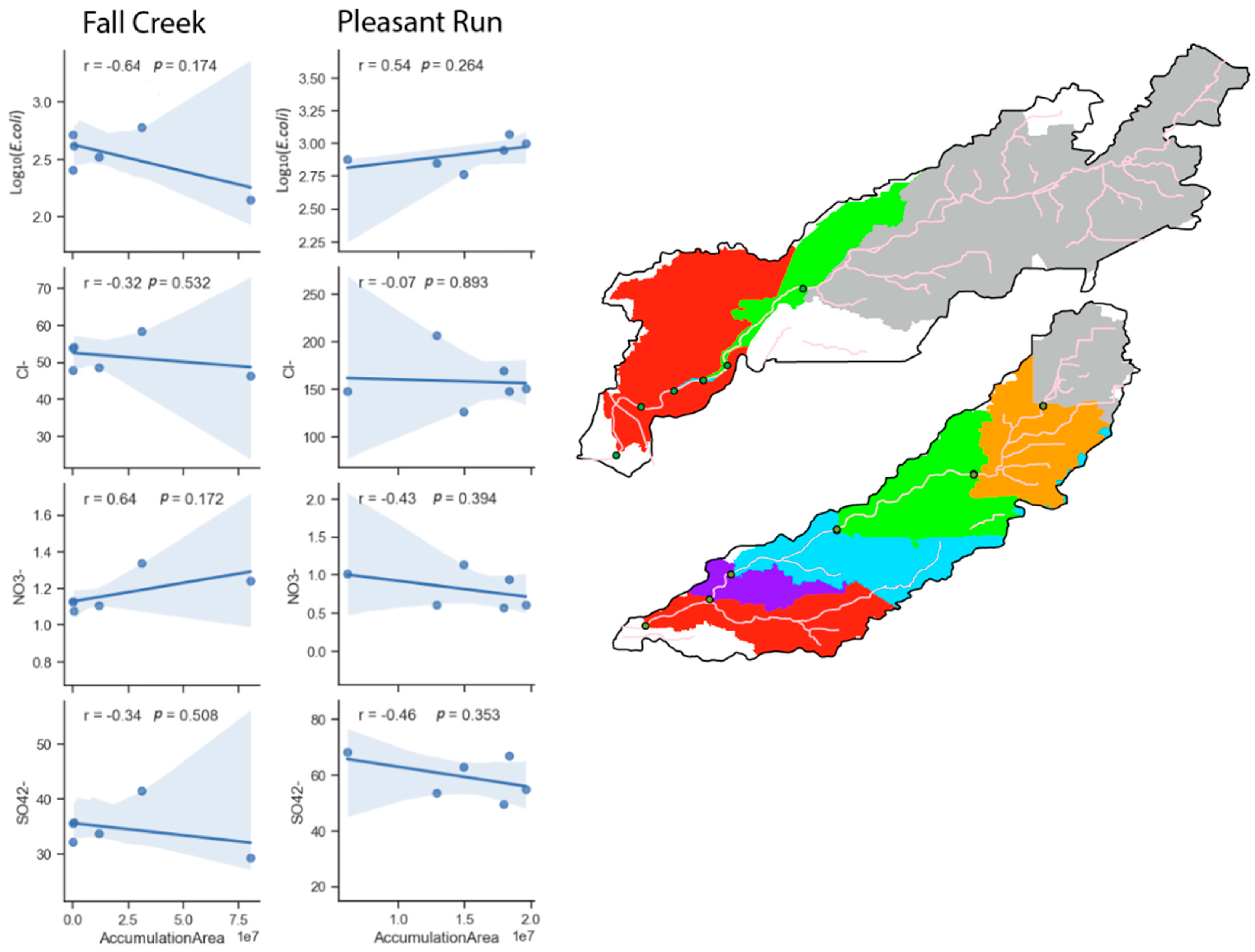
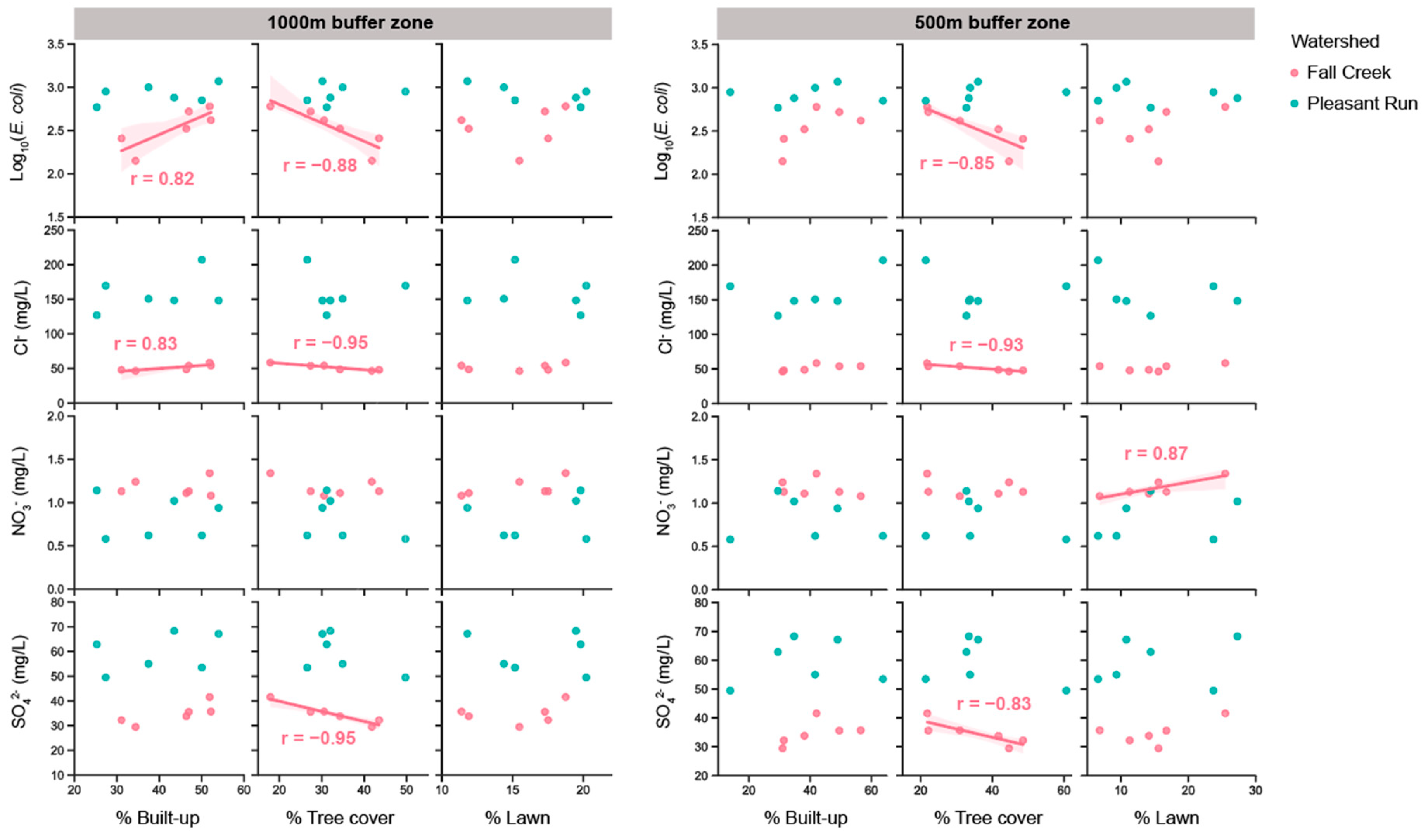
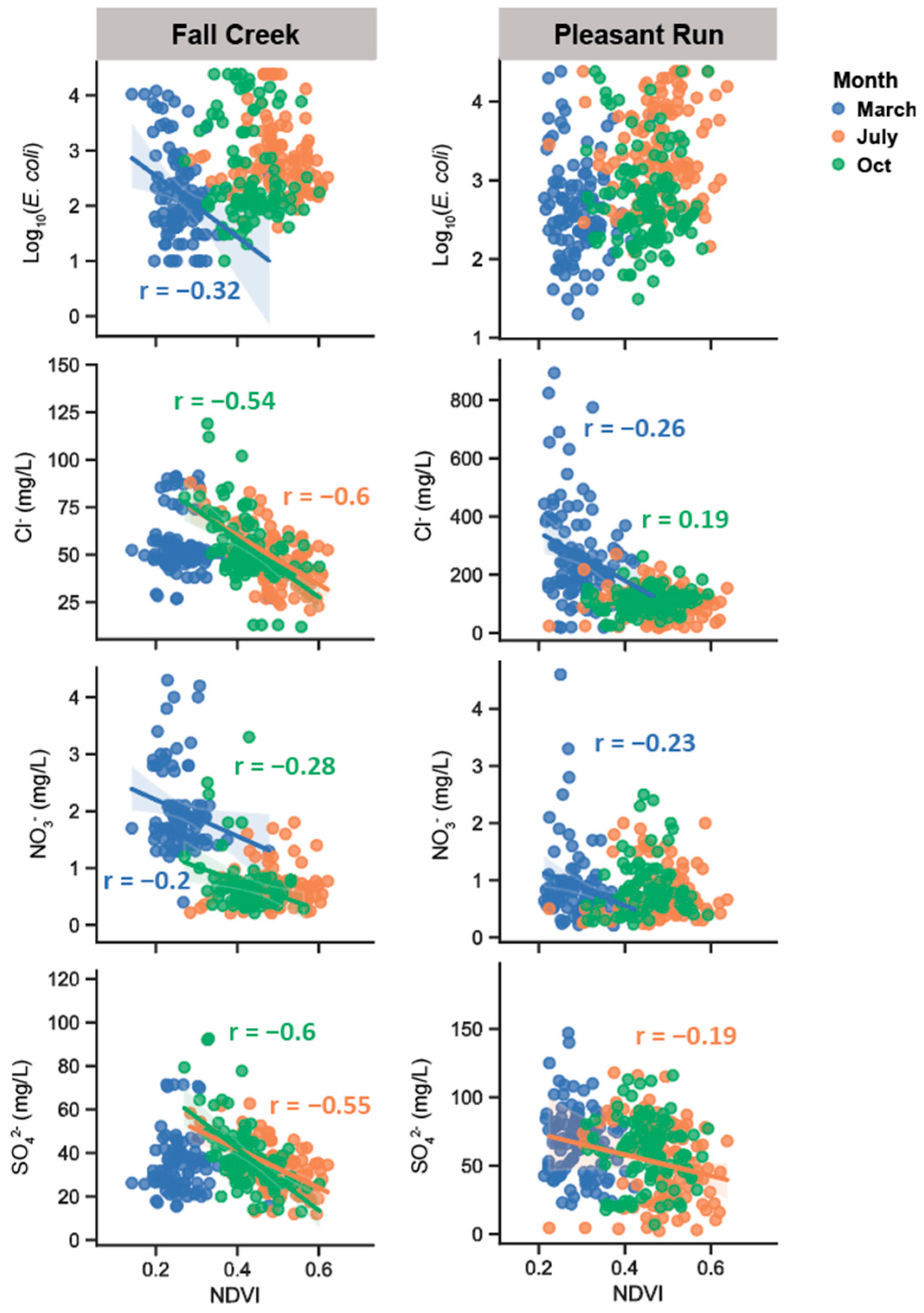
| Fall Creek | ||||||||||||
| log10(E.coli) | Cl− | NO3− | SO42− | |||||||||
| Order | Variable | R2 | Cumulated R2 | Variable | R2 | Cumulated R2 | Variable | R2 | Cumulated R2 | Variable | R2 | Cumulated R2 |
| 1 | DO | 0.182 ** | 0.182 | TDS | 0.478 ** | 0.478 | Temp | 0.537 ** | 0.537 | TDS | 0.276 ** | 0.276 |
| 2 | Precip | 0.133 ** | 0.315 | Snow | 0.055 * | 0.53 | Q | 0.049 * | 0.586 | pH | 0.031 | 0.307 |
| 3 | pH | 0.022 | 0.337 | Precip | 0.015 | 0.545 | TDS | 0.027 * | 0.613 | Precip | 0.021 | 0.328 |
| 4 | Q | 0.007 | 0.344 | DO | 0.012 | 0.557 | pH | 0.023 | 0.636 | DO | 0.018 | 0.346 |
| 5 | Temp | 0.002 | 0.346 | Temp | 0.007 | 0.564 | Precip | 0.006 | 0.642 | Snow | 0.017 | 0.363 |
| 6 | pH | 0.006 | 0.57 | Snow | 0.002 | 0.646 | Temp | 0.003 | 0.366 | |||
| 7 | Q | 0.002 | 0.368 | |||||||||
| Pleasant Run | ||||||||||||
| log10(E.coli) | Cl− | NO3− | SO42− | |||||||||
| Order | Variable | R2 | Cumulated R2 | Variable | R2 | Cumulated R2 | Variable | R2 | Cumulated R2 | Variable | R2 | Cumulated R2 |
| 1 | TDS | 0.235 ** | 0.235 | TDS | 0.651 ** | 0.651 | Snow | 0.254 ** | 0.254 | TDS | 0.400 ** | 0.400 |
| 2 | DO | 0.078 ** | 0.313 | Snow | 0.177 ** | 0.323 | DO | 0.007 | 0.261 | DO | 0.093 ** | 0.493 |
| 3 | Q | 0.068 * | 0.381 | pH | 0.023 ** | 0.851 | Q | 0.006 | 0.267 | Snow | 0.032 | 0.525 |
| 4 | Temp | 0.027 | 0.408 | Q | 0.013 | 0.864 | pH | 0.003 | 0.27 | Q | 0.03 | 0.555 |
| 5 | Precip | 0.013 | 0.421 | DO | 0.006 | 0.87 | TDS | 0.003 | 0.273 | Precip | 0.017 | 0.572 |
| 6 | pH | 0.011 | 0.432 | Temp | 0.001 | 0.274 | pH | 0.004 | 0.576 | |||
| 7 | Snow | 0.002 | 0.434 | Temp | 0.002 | 0.578 | ||||||
| Watershed | Site | Log10(E. coli) | Cl− (mg/L) | NO3− (mg/L) | SO42− (mg/L) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Fall Creek | Site 1 | 2.15 ± 0.54 b | 46.31 ± 13 b | 1.24 ± 0.95 a | 29.45 ± 9 b |
| Site 2 | 2.41 ± 0.85 ab | 47.83 ± 13 b | 1.13 ± 0.86 a | 32.2 ± 10 b | |
| Site 3 | 2.52 ± 0.81 ab | 48.64 ± 13 b | 1.11 ± 0.8 a | 33.83 ± 10 b | |
| Site 4 | 2.62 ± 0.87 ab | 54.16 ± 14 ab | 1.08 ± 0.85 a | 35.72 ± 10 ab | |
| Site 5 | 2.72 ± 0.89 a | 53.98 ± 15 ab | 1.13 ± 0.8 a | 35.61 ± 11 ab | |
| Site 6 | 2.78 ± 0.78 a | 58.46 ± 21 a | 1.34 ± 0.86 a | 41.58 ± 18 a | |
| Pleasant Run | Site a | 2.85 ± 0.6 a | 207.11 ± 170 a | 0.62 ± 0.68 b | 53.49 ± 25 bc |
| Site b | 2.95 ± 0.68 a | 169.51 ± 135 ab | 0.58 ± 0.27 b | 49.49 ± 21 c | |
| Site c | 3 ± 0.76 a | 150.59 ± 118 ab | 0.62 ± 0.4 b | 55.01 ± 23 abc | |
| Site d | 3.07 ± 0.64 a | 148.09 ± 112 ab | 0.94 ± 0.5 a | 67.16 ± 30 ab | |
| Site e | 2.88 ± 0.7 a | 148.28 ± 105 ab | 1.02 ± 0.55 a | 68.32 ± 29 a | |
| Site f | 2.77 ± 0.69 a | 126.93 ± 78 b | 1.14 ± 0.51 a | 62.87 ± 25 abc |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Li, R.; Filippelli, G.; Wilson, J.; Qiao, N.; Wang, L. Water-Quality Spatiotemporal Characteristics and Their Drivers for Two Urban Streams in Indianapolis. Water 2025, 17, 1225. https://doi.org/10.3390/w17081225
Li R, Filippelli G, Wilson J, Qiao N, Wang L. Water-Quality Spatiotemporal Characteristics and Their Drivers for Two Urban Streams in Indianapolis. Water. 2025; 17(8):1225. https://doi.org/10.3390/w17081225
Chicago/Turabian StyleLi, Rui, Gabriel Filippelli, Jeffrey Wilson, Na Qiao, and Lixin Wang. 2025. "Water-Quality Spatiotemporal Characteristics and Their Drivers for Two Urban Streams in Indianapolis" Water 17, no. 8: 1225. https://doi.org/10.3390/w17081225
APA StyleLi, R., Filippelli, G., Wilson, J., Qiao, N., & Wang, L. (2025). Water-Quality Spatiotemporal Characteristics and Their Drivers for Two Urban Streams in Indianapolis. Water, 17(8), 1225. https://doi.org/10.3390/w17081225







