Enhanced Adsorption of Aqueous Ciprofloxacin Hydrochloride by a Manganese-Modified Magnetic Dual-Sludge Biochar
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Chemicals and Materials
2.2. Mn@MDSBC Synthesis
2.3. Artificial CIP-Bearing Solution
2.4. Static CIP Adsorption Test
2.5. Regeneration and Reuse of Adsorbent
2.6. Characterization of Adsorbent
3. Results and Discussion
3.1. Exploration of Mn@MDSBCs Preparation
3.1.1. Effect of MnCl2 to (IBWS+PMS) Mass Ratio on CIP Adsorption
3.1.2. Influence of Pyrolysis Temperature on CIP Adsorption
3.2. Adsorbent Characterization
3.2.1. Specific Surface Area and Pore Analysis
3.2.2. SEM Images and SEM-EDS Results
3.2.3. XRD Analysis
3.3. Static Adsorption
3.3.1. Influence of Starting Solution pH
3.3.2. Adsorption Kinetics
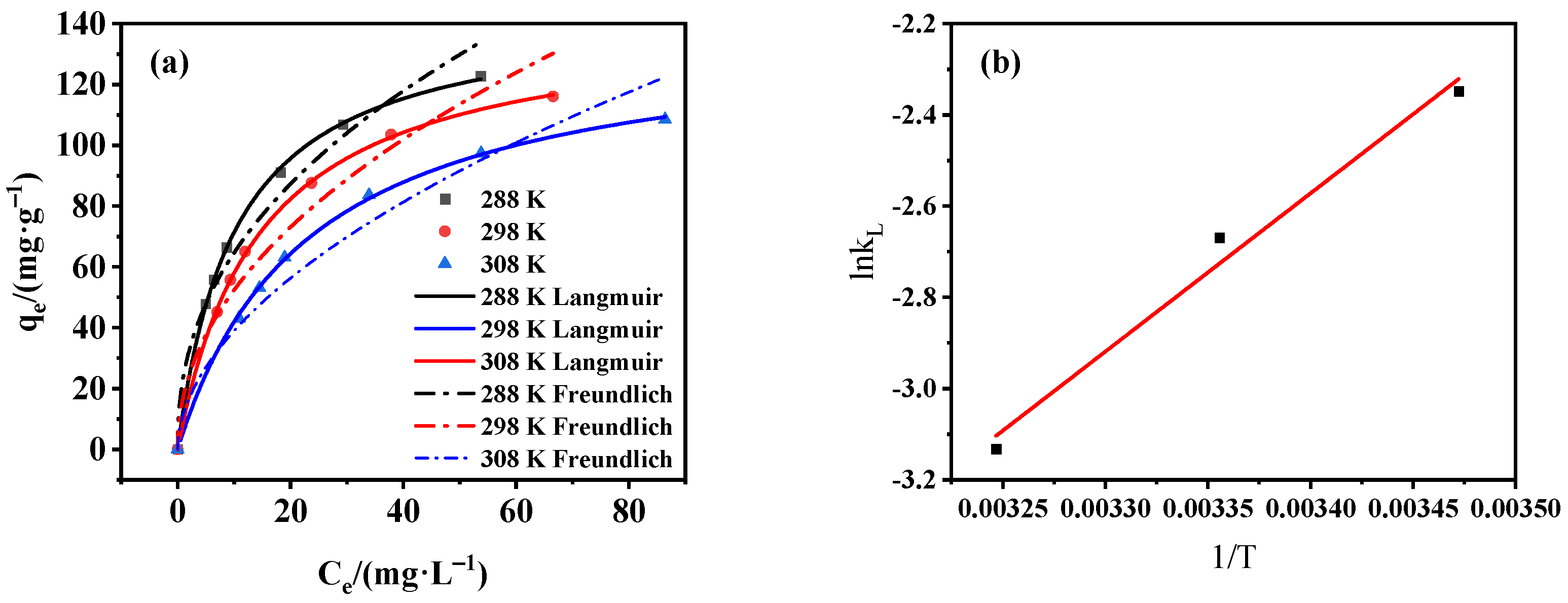
3.3.3. Adsorption Isotherm and Thermodynamics Analysis
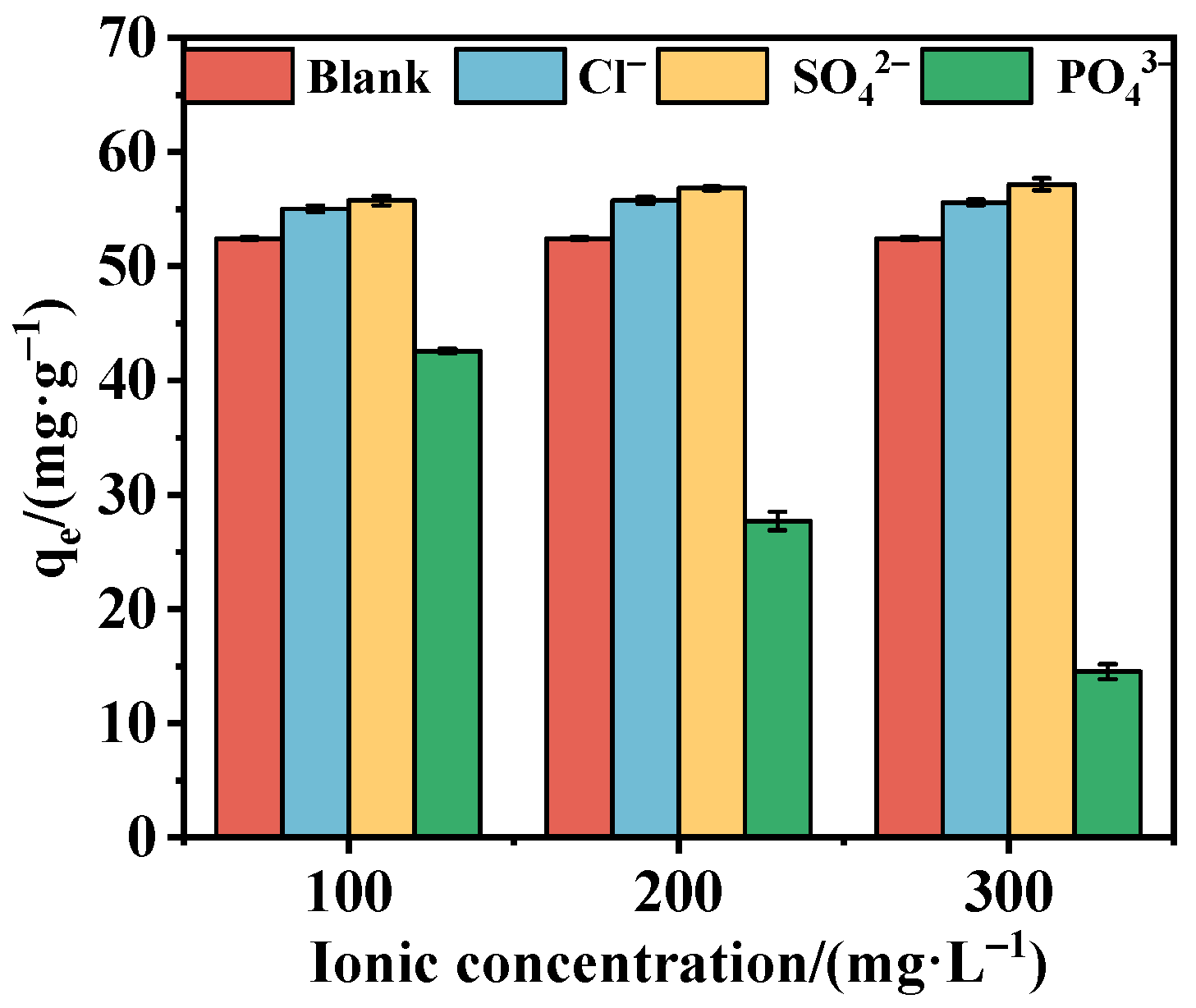
3.3.4. Effect of Coexisting Anions
3.3.5. Reusability of the Adsorbent
4. CIP Removal Mechanism
4.1. FTIR
4.2. XPS
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Hu, H.; Yan, Z.Y.; Li, S.Y.; Zhu, Z.T.; Li, W.Z.; Tai, J.J.; Zhang, H. Multiresidue analysis and health risk assessment of sulfonamides and quinolones from edible Batrachia and other aquatic products. Int. Food Res. J. 2023, 30, 1461–1470. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tian, C.Y.; Li, J.Y.; Zhao, L.; Wang, Y.Z.; Li, S.T.; Zhao, Z.B.; Liang, N. Activation of peroxymonosulfate by N, S co-doped magnetic FeCoS for the degradation of ciprofloxacin hydrochloride: Catalytic performance and mechanism. J. Environ. Chem. Eng. 2023, 11, 110362. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Q.Q.; Ying, G.G.; Pan, C.G.; Liu, Y.S.; Zhao, J.L. Comprehensive evaluation of antibiotics emission and fate in the river basins of China: Source analysis, multimedia modeling, and linkage to bacterial resistance. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2015, 49, 6772–6782. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Carmosini, N.; Lee, L.S. Ciprofloxacin sorption by dissolved organic carbon from reference and bio-waste materials. Chemosphere 2009, 77, 813–820. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ghosh, S.; Pourebrahimi, S.; Malloum, A.; Ajala, O.J.; AlKafaas, S.S.; Onyeaka, H.; Nnaji, N.D.; Oroke, A.; Bornman, C.; Christian, O.; et al. A review on ciprofloxacin removal from wastewater as a pharmaceutical contaminant: Covering adsorption to advanced oxidation processes to computational studies. Mater. Today Commun. 2023, 37, 107500. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guellati, A.; Maachi, R.; Chaabane, T.; Darchen, A.; Danish, M. Aluminum dispersed bamboo activated carbon production for effective removal of Ciprofloxacin hydrochloride antibiotics: Optimization and mechanism study. J. Environ. Manage. 2022, 301, 113765. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hua, W.J.; Kang, Y.; Liu, S. Synergistic removal of aqueous ciprofloxacin hydrochloride by water surface plasma coupled with peroxymonosulfate activation. Sep. Purif. Technol. 2022, 303, 122301. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nan, F.; Xi, Y.H.; Zhang, J.; Wu, J.; Cheng, H.C.; He, Q. Insight into adsorption kinetics, equilibrium, thermodynamics, and modeling of ciprofloxacin onto iron ore tailings. Water 2025, 17, 760. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gao, M.; Sun, M.M.; Bi, J.T.; Wang, S.Z.; Guo, X.F.; Li, F.; Liu, J.; Zhao, Y.Y. Removal of ciprofloxacin by PAA-PAM hydrogel: Adsorption performance and mechanism studies. J. Water Process. Eng. 2025, 71, 107361. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bodawar, N.; Shetty, R.; Kamble, S.; Kulkarni, P. Enhanced degradation of ciprofloxacin hydrochloride using hybrid advanced oxidation process of hydrodynamic cavitation and ozonation. Chem. Eng. Technol. 2024, 47, e202300469. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, K.Q.; Xu, D.F.; Li, Z.F.; Zhang, S.M.; Tong, L.C.; Peng, J.H.; Zhang, S.Y.; Shen, J.; Chen, X.H. Enhanced visible-light photocatalytic degradation of ciprofloxacin hydrochloride by bulk iodine doped BiOCl with rich oxygen vacancy. Appl. Surf. Sci. 2022, 578, 152083. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Al-Buriahi, A.K.; Al-shaibani, M.M.; Mohamed, R.M.S.R.; Al-Gheethi, A.A.; Sharma, A.; Ismail, N. Ciprofloxacin removal from non-clinical environment: A critical review of current methods and future trend prospects. J. Water Process Eng. 2022, 47, 102725. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tang, Y.H.; Hao, J.J.; He, S.X.; Luo, T.T.; Wu, L.S.; Wang, X.T.; Guo, J.Q. Characterization of edible fungus substrate modified biochar and its adsorption capacity for ciprofloxacin hydrochloride. Bull. Environ. Contam. Toxicol. 2022, 108, 1153–1158. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gao, R.Q.; Huang, Y.R.; He, J.L.; Shi, W.J.; Huang, S.Y.; Pan, L.; Pan, Z.Y.; Li, G.T. Preparation of MgAl layered double oxides and its adsorption kinetics for ciprofloxacin hydrochloride in water. Environ. Prog. Sustain. 2022, 41, e13899. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gu, J.H.; Liu, Z.; Jia, A.Y.; Wang, Y.Q.; Li, N.N.; Liu, Z.S.; Li, Y.X.; Zhang, H.X. New insight into adsorption and co-adsorption of chlortetracycline hydrochloride and ciprofloxacin hydrochloride by Ga-based metal-organic gel/sodium alginate composite beads. Sep. Purif. Technol. 2023, 312, 123408. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Peng, S.W.; Wei, Y.F.; Huang, Y.M.; Wei, L.M.; Chen, P.C. Highly efficient adsorption of antibiotic ciprofloxacin hydrochloride from aqueous solution by diatomite-basic zinc chloride composites. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 2023, 30, 98490–98501. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Badiger, S.; Nidheesh, P.V. Coconut Shell Biochar for the Removal of Acetaminophen and Ciprofloxacin in Low Concentrations: Single and Competitive Adsorption Studies. Ind. Eng. Chem. Res. 2024, 63, 19120–19134. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cong, Q.; Zhang, T.T.; Wang, J.H.; Yuan, X. The adsorption performance of ciprofloxacin hydrochloride (CPX) on polyurethane and carbon nanotubes foams. Fresenius Environ. Bull. 2022, 31, 1127–1137. [Google Scholar]
- Pham, T.D.; Nguyen, D.T.; Nguyen, H.L.; Nguyen, M.Q.; Tran, T.M.; Nguyen, M.V.; Nguyen, T.L.; Ngo, T.M.V.; Namakamura, K.; Tsubota, T. Adsorption characteristics of ciprofloxacin and naproxen from aqueous solution using bamboo biochar. Biomass Convers. Biorefin. 2023, 15, 3071–3082. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, M.; Wu, J.S.; Wang, J.S.; Zhou, W.Y.; Li, Y.L.; Li, H.Y. Bamboo leaf-derived biochar/iron silicate composite for an adsorption-degradation synergistic removal of ciprofloxacin. Process. Saf. Environ. 2024, 186, 1183–1196. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, X.R.; Tian, X.; Xue, Y.N.; Wang, C.P. Application of iron-modified biochar in the fields of adsorption and degradation of antibiotics. J. Environ. Manage. 2025, 380, 124875. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, M.; Lin, K.; Li, X.D.; Wu, L.J.; Yu, J.; Cao, S.; Zhang, D.; Xu, L.H.; Parikh, S.J.; Ok, Y.S. Removal of phosphate from water by paper mill sludge biochar. Environ. Pollut. 2022, 293, 118521. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chakhtouna, H.; Benzeid, H.; Zari, N.; Bouhfid, R. Functional CoFe2O4-modified biochar derived from banana pseudostem as an efficient adsorbent for the removal of amoxicillin from water. Sep. Purif. Technol. 2021, 266, 118592. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yin, K.Y.; Wang, J.Y.; Tian, X.F.; Yu, N.; Zhang, X.X.; Zhao, Y.Y.; Liu, Y.H.; Sui, S.C.; Wang, C.P.; Lian, F.J.C.E.J. Effect of biochar-derived dissolved organic matter on tetracycline sorption by KMnO4-modified biochar. Chem. Eng. J. 2023, 474, 145872. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, P.; Li, Y.X.; Cai, Z.Y.; Liu, H.; Wang, Z.G.; Huang, W.; Wang, Q.C.; Zhang, C. Simultaneous removal of Cd and ciprofloxacin hydrochloride by ZVI/biochar composite in water: Compound effects and removal mechanism. Sep. Purif. Technol. 2023, 327, 124821. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, X.M.; Wang, Y.Q.; Zhou, S.Q.; Cui, P.; Wang, W.W.; Huang, W.F.; Yu, Z.; Zhou, S.G. Differentiated strategies of animal-derived and plant-derived biochar to reduce nitrogen loss during paper mill sludge composting. Bioresour. Technol. 2022, 360, 127583. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, S.L.; Wen, Y.M.; Hammarström, H.; Jönsson, P.G.; Yang, W.H. Pyrolysis behaviour, kinetics and thermodynamic data of hydrothermal carbonization–Treated pulp and paper mill sludge. Renew. Energy 2021, 177, 1282–1292. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, Z.Y.; Lin, Y.Q.; Lin, Y.J.; Yang, D.; Zheng, H.M. Adsorption behaviors of paper mill sludge biochar to remove Cu, Zn and As in wastewater. Environ. Technol. Innov. 2021, 23, 101616. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, J.; Li, X.D.; Wu, M.; Lin, K.; Xu, L.H.; Zeng, T.; Shi, H.; Zhang, M. Synergistic role of inherent calcium and iron minerals in paper mill sludge biochar for phosphate adsorption. Sci. Total Environ. 2022, 834, 155193. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cao, Y.W.; Xu, D.Y. Enhanced adsorption of quinoline from aqueous solution by NaOH-treated biochar derived from orange peel: Preparation, performance, mechanism, and density functional theory study. Desalin. Water Treat. 2023, 316, 306–316. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Han, Y.L.; Chen, M.F.; Wang, J.W.; Sun, C.T.; Zang, S.Y.; Shao, X.Y. Selective and efficient removal of As(III) from water by Ce-Mn oxide-modified biochar: Synergetic role of rapid oxidation and enhanced adsorption. Process. Saf. Environ. 2024, 186, 1543–1554. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, D.Y.; He, Y.; Zeng, S.Q.; Tian, H.L.; Ji, Z.H. A novel magnetic S/N co-doped tea residue biochar applied to tetracycline adsorption in water environment. Colloids Surf. A 2024, 703, 135400. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zheng, W.X.; Zhang, Y.J.; Xu, Y.; Guo, Y.R.; Pan, Q.J. Fabrication of magnetic ferroferric oxide-based composite for efficiently removing and recycling ciprofloxacin. Colloids Surf. A 2024, 702, 135067. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shao, S.; Zhang, M.; Lv, Z.A.; Sun, Y.K.; Li, P.H.; Zhou, R.J. Research on efficient removal of ciprofloxacin through sequential rice straw biochar modification via alkali activation and manganese oxides. Environ. Technol. Innov. 2024, 34, 103611. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tran, T.M.H.; Tran, T.D.; Dinh, T.D.; Nguyen, M.K.; Anh, N.T.N.; Nga, N.K.; Doan, T.H.Y.; Pham, T.D. Adsorption characteristics of individual and binary mixtures of ciprofloxacin and Cr(VI) in water using MnO2 colloidal particles. Colloid Polym. Sci. 2024, 302, 1395–1405. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alsulais, H.M.; Alqaisum, A.K.; Aldoulah, A.A.; Mohsin, A.A.; Ghonaim, H.M. Comparative study of brand and generics ciprofloxacin tablets available in the Saudi Market. Dissolut. Technol. 2023, 30, GC12–GC18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ahmed, W.; Mehmood, S.; Mahmood, M.; Ali, S.; Shakoor, A.; Núñez-Delgado, A.; Asghar, R.M.A.; Zhao, H.W.; Liu, W.J.; Li, W.D.J.E.P. Adsorption of Pb (II) from wastewater using a red mud modified rice-straw biochar: Influencing factors and reusability. Environ. Pollut. 2023, 326, 121405. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, Y.; Li, S.X.; Chen, J.H.; Zhang, X.L.; Chen, Y.P. Adsorption of Pb(II) on mesoporous activated carbons fabricated from water hyacinth using H3PO4 activation: Adsorption capacity, kinetic and isotherm studies. Appl. Surf. Sci. 2014, 293, 160–168. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Samson, T.; Aminah, U.; Rika, T.Y.; Ridla, B.; Budi, R.P.; Wulan, T.W.; Arifutzzaman, A.; Mohamed, K.A.; Munawar, K. Mesoporous metal oxide via nanocasting: Recent advances on types of templates, properties, and catalytic activities. Mater. Today Commun. 2024, 40, 110152. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Z.J.; Miao, R.R.; Ning, P.; He, L.; Guan, Q.Q. From wastes to functions: A paper mill sludge-based calcium-containing porous biochar adsorbent for phosphorus removal. J. Colloid Interface Sci. 2021, 593, 434–446. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tie, J.X.; Li, W.P.; Duan, X.H.; Wang, H.W.; Liu, S.L.; Zhao, W.G. Magnetic iron-based waterworks sludge modified by chitosan and FeS for aqueous Cr(vi) adsorption and reduction. RSC Adv. 2024, 14, 28915–28926. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, S.B.; Huang, B.Y.; Chai, L.Y.; Liu, Y.G.; Zeng, G.M.; Wang, X.; Zeng, W.; Shang, M.R.; Deng, J.Q.; Zhou, Z. Enhancement of As(v) adsorption from aqueous solution by a magnetic chitosan/biochar composite. RSC Adv. 2017, 7, 10891–10900. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yan, H.; Hu, W.H.; Cheng, S.; Xia, H.Y.; Chen, Q.; Zhang, L.B.; Zhang, Q. Microwave-assisted preparation of manganese dioxide modified activated carbon for adsorption of lead ions. Water Sci. Technol. 2020, 82, 170–184. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tran, Q.T.; Do, T.H.; Ha, X.L.; Nguyen, H.P.; Nguyen, A.T.; Ngo, T.C.Q.; Chau, H.D. Study of the ciprofloxacin adsorption of activated carbon prepared from mangosteen peel. Appl. Sci. 2022, 12, 8770. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lu, X.Y.; Deng, X.Y.; Li, Y.J.; Shen, H.Y.; Chen, C.J.; Tong, Z.F. Adsorption properties of ciprofloxacin hydrochloride on magnetic activated carbon based on eucalyptus sawdust and oil sludge. Fine Chem. 2024, 42, 1–16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Raheem, A.; Rahman, N.; Khan, S. Monolayer Adsorption of Ciprofloxacin on Magnetic Inulin/Mg–Zn–Al Layered Double Hydroxide: Advanced Interpretation of the Adsorption Process. Langmuir. 2024, 40, 12939–12953. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xiang, Y.J.; Yang, X.; Xu, Z.Y.; Hu, W.Y.; Zhou, Y.Y.; Wan, Z.H.; Yang, Y.H.; Wei, Y.Y.; Yang, J.; Tsang, D.C.W. Fabrication of sustainable manganese ferrite modified biochar from vinasse for enhanced adsorption of fluoroquinolone antibiotics: Effects and mechanisms. Sci. Total Environ. 2020, 709, 136079. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Al-Musawi, T.J.; Mahvi, A.H.; Khatibi, A.D.; Balarak, D. Effective adsorption of ciprofloxacin antibiotic using powdered activated carbon magnetized by iron(III) oxide magnetic nanoparticles. J. Porous Mater. 2021, 28, 835–852. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yoon, K.; Kwon, G.; Kim, E.; Rinklebe, J.; Song, H. Production of Fe-biochar from paper-mill sludge and its application to Se(VI) and Se(IV) removal. Chem. Eng. J. 2024, 484, 149470. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zheng, Z.H.; Zhao, B.L.; Guo, Y.P.; Guo, Y.J.; Pak, T.; Li, G.T. Preparation of mesoporous batatas biochar via soft-template method for high efficiency removal of tetracycline. Sci. Total Environ. 2021, 787, 147397. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lei, W.Z.; Qi, M.D.; Song, J.L.; Li, H.C.; Wang, X.N.; Ma, Y.; Gao, Z.P. Adsorption of polyphenolic compounds by sodium alginate-modified starch nanoparticles in a multiphase system: Kinetic, thermodynamic and release characteristics studies. Food Hydrocoll. 2025, 162, 110900. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gulen, B.; Demircivi, P. Adsorption properties of flouroquinolone type antibiotic ciprofloxacin into 2:1 dioctahedral clay structure: Box-Behnken experimental design. J. Mol. Struct. 2020, 1206, 127659. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, Y.F.; Li, M.; Li, P.; Yang, L.; Wu, L.; Gao, F.; Qi, X.B.; Zhang, Z.L. Hydrothermal synthesis of magnetic sludge biochar for tetracycline and ciprofloxacin adsorptive removal. Bioresour. Technol. 2021, 319, 124199. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Malik, R.; Goyal, A.; Yadav, S.; Gupta, N.; Goel, N.; Kaushik, A.; Kumar, V.; Tikoo, K.B.; Singhal, S. Functionalized magnetic nanomaterials for rapid and effective adsorptive removal of fluoroquinolones: Comprehensive experimental cum computational investigations. J. Hazard. Mater. 2019, 364, 621–634. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zheng, D.Y.; Wu, M.; Zheng, E.Y.; Wang, Y.; Feng, C.; Zou, J.L.; Juan, M.L.; Bai, X.x.; Wang, T.; Shi, Y.X. Parallel adsorption of low concentrated ciprofloxacin by a CoFe-LDH modified sludge biochar. J. Environ. Chem. Eng. 2022, 10, 108381. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Damiyine, B.; Guenbour, A.; Boussen, R. Adsorption of rhodamine b dye onto expanded perlite from aqueous solution: Kinetics, equilibrium and thermodynamics. JMES 2017, 8, 345–355. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dong, Y.; Gao, M.; Song, Z.; Qiu, W. Adsorption mechanism of As(III) on polytetrafluoroethylene particles of different size. Environ. Pollut. 2019, 254, 112950. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sahmoune, M.N. Evaluation of thermodynamic parameters for adsorption of heavy metals by green adsorbents. Environ. Chem. Lett. 2019, 17, 697–704. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lu, Y.P.; Jiang, M.; Wang, C.W.; Wang, Y.P.; Yang, W.B. Impact of molecular size on two antibiotics adsorption by porous resins. J. Taiwan Inst. Chem. Eng. 2014, 45, 955–961. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Seibert, D.; Felgueiras, H.P.; Módenes, A.N.; Borba, F.H.; Bergamasco, R.; Homem, N.C. Application of cork as adsorbent for water and wastewater treatment using ciprofloxacin as pharmaceutical model. Int. J. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2024, 22, 3021–3038. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Afzal, M.Z.; Sun, X.F.; Liu, J.; Song, C.; Wang, S.G.; Javed, A. Enhancement of ciprofloxacin sorption on chitosan/biochar hydrogel beads. Sci. Total Environ. 2018, 639, 560–569. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Soares, S.F.; Nogueira, J.; Trindade, T.; Daniel-da-Silva, A.L. Towards efficient ciprofloxacin adsorption using magnetic hybrid nanoparticles prepared with κ-, ι-, and λ-carrageenan. J. Nanostruct. Chem. 2022, 13, 283–302. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alameri, A.A.; Alfilh, R.H.C.; Awad, S.A.; Zaman, G.S.; Al-Musawi, T.J.; Joybari, M.M.; Balarak, D.; McKay, G. Ciprofloxacin adsorption using magnetic and ZnO nanoparticles supported activated carbon derived from Azolla filiculoides biomass. Biomass Convers. Biorefin. 2022, 14, 27001–27014. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zou, C.L.; Wu, Q.; Nie, F.H.; Xu, Z.W.; Xiang, S.L. Application of magnetic porous graphite bochar prepared through one-step modification in the adsorption of tetracycline and ciprofloxacin from aqueous solutions. Waste Biomass Valorization 2023, 15, 1477–1494. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tang, Y.; Chen, Q.M.; Li, W.Q.; Xie, X.Y.; Zhang, W.X.; Zhang, X.D.; Chai, H.X.; Huang, Y.M. Engineering magnetic N-doped porous carbon with super-high ciprofloxacin adsorption capacity and wide pH adaptability. J. Hazard. Mater. 2020, 388, 122059. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moradi-Choghamarani, F.; Moosavi, A.A.; Baghernejad, M. Determining organo-chemical composition of sugarcane bagasse-derived biochar as a function of pyrolysis temperature using proximate and Fourier transform infrared analyses. J. Therm. Anal. Calorim. 2019, 138, 331–342. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Elzayat, N.A.; Abbas, H.; Helmy, M.W.; Habib, D.A. Phyto-therapeutic and nanomedicinal approaches: A new hope for management of Alzheimer’s disease. Int. J. Pharm. 2022, 627, 122213. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lal, C.; Garg, R.; Gupta, G. Pharmacokinetic and Pharmacodynamic Studies of Nifedipine Loaded Microspheres for the Treatment of Hypertension. Curr. Drug Deliv. 2020, 17, 65–70. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sahoo, S.; Chakraborti, C.; Mishra, S.; Naik, S.; Nanda, U.; Sahoo, M. FTIR and Raman spectroscopy as a tool for analyzing sustained release hydrogel of ciprofloxacin/carbopol polymer. Int. J. Pharm. Sci. Res. 2011, 2, 268–277. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Unnimaya, S.; Mithun, N.; Lukose, J.; Nair, M.P.; Gopinath, A.; Chidangil, S. Identification of Microplastics Using a Custom Built Micro-Raman Spectrometer. J. Phys. Conf. Ser. 2023, 2426, 012007. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, X.N.; Wang, X.H.; Fang, D. A review on C1s XPS-spectra for some kinds of carbon materials. Fuller. Nanotub. Carbon Nanostruct. 2020, 28, 1048–1058. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hasabeldaim, E.H.H.; Swart, H.C.; Coetsee, E.; Kumar, P.; Kroon, R.E. Degradation and chemical stability of graphitic carbon nitride during ultraviolet light irradiation. Mater. Chem. Phys. 2023, 308, 128252. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, C.X.; Wang, B.; Du, H.M.; Zhao, J.S.; Dong, Y.Y.; Xie, Y. Conjugated microporous polymer derived N, O and S co-doped sheet-like carbon materials as anode materials for high-performance lithium-ion batteries. J. Taiwan Inst. Chem. Eng. 2022, 134, 104293. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Okpalugo, T.I.T.; Papakonstantinou, P.; Murphy, H.; McLaughlin, J.; Brown, N.M.D. High resolution XPS characterization of chemical functionalised MWCNTs and SWCNTs. Carbon 2005, 43, 153–161. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Puerto, M.A.; Costa, T.M.H.; Jornada, J.A.H.; Balzaretti, N.M. Pyrolisys of α-aminoacids under high-pressure investigated by XPS, Raman and infrared spectroscopy. Mater. Chem. Phys. 2018, 211, 107–116. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liang, L.F.; Song, L.Z.; Yang, Y.L.; Li, F.; Ma, Y.L. Tribological properties of polytetrafluoroethylene improved by incorporation of fluorinated graphene with various fluorine/carbon ratios under dry sliding condition. Mater. Chem. Phys. 2021, 69, 122049. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, J.N.; Cao, Y.H.; Wen, H.J.; Zhang, J.; Wang, H.J.; Yu, H.; Peng, F. Unraveling the intrinsic enhancement of fluorine doping in the dual-doped magnetic carbon adsorbent for the environmental remediation. J. Colloid Interface Sci. 2019, 538, 327–339. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, J.L.; Zhang, L.Z. Achieving F-doped porous hollow carbon nanospheres with ultrahigh pore volume via a gas–solid interface reaction. J. Mater. Chem. A 2021, 9, 27560–27567. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sahin, H.T. RF-CF4 plasma treatment of tetrafluoroethane pre-deposited paper, part 1: Hypotheses on surface reactions. J. Wood Chem. Technol. 2020, 40, 91–104. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tian, C.H.; Tao, X.; Luo, S.; Qing, Y.; Lu, X.H.; She, J.H.; Wu, Y.Q. Cellulose nanofibrils anchored Ag on graphitic carbon nitride for efficient photocatalysis under visible light. Environ. Sci.-Nano. 2018, 5, 2129–2143. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, H.C.; Ye, D.Q.; Huang, B.C. Nitrogen plasma modification of viscose-based activated carbon fibers. Surf. Coat. Tech. 2007, 201, 9533–9540. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dupin, J.-C.; Gonbeau, D.; Vinatier, P.; Levasseur, A. Systematic XPS studies of metal oxides, hydroxides and peroxides. PCCP 2000, 2, 1319–1324. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, Y.; Fan, W.H.; Zhang, K.; Xiang, H.D.; Wang, X.R. Nano-manganese oxides-modified biochar for efficient chelated copper citrate removal from water by oxidation-assisted adsorption process. Sci. Total Environ. 2020, 709, 136154. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, S.M.; Wang, X.H.; Li, Y.; Zhang, Y.X.; Hu, Q.; Hua, X.H.; Liu, G.; Xie, E.Q.; Zhang, Z.X. Moderate oxygen-deficient Fe(III) oxide nanoplates for high performance symmetric supercapacitors. J. Colloid Interface Sci. 2020, 565, 458–464. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fanlo, I.; Gervilla, F.; Mateo, E.; Irusta, S. X-ray photoelectron spectroscopy characterization of natural chromite from Mercedita Mine (Eastern Cuba): Quantification of the Fe3+/Fe2+ ratio. Eur. J. Mineral. 2008, 20, 125–129. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, G.H.; Kim, Y.S.; Kim, D.W. Redox effect of Fe2+/Fe3+ in iron phosphates for enhanced electrocatalytic activity in Li-O2 batteries. Chem. Eng. J. 2020, 388, 124294. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pathan, S.; Pandita, N.; Kishore, N. Acid functionalized-Nanoporous carbon/MnO2 composite for removal of arsenic from aqueous medium. Arab. J. Chem. 2016, 12, 5200–5211. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cheng, Y.; Zhang, Y.Z.; Xiong, W.Y.; Huang, T.L.; Tang, H. Effects of iron doping on catalytic oxidation activity of Mn-based co-oxide filter media for removal of ammonium and manganese from groundwater. J. Clean. Prod. 2022, 332, 130091. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Neelapala, S.D.; Patnaik, H.; Dasari, H. Enhancement of soot oxidation activity of manganese oxide (Mn2O3) through doping by the formation of Mn1. 9M0. 1O3–δ (M= Co, Cu, and Ni). Asia-Pac. J. Chem. Eng. 2018, 13, e2234. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rana, S.; Usmani, A.B.S.; Devi, S.; Wadhwa, R.; Yadav, K.K.; Mehta, S.K.; Jha, M. Tailoring crystalline Mn5O8 nanostructures: Kinetic control and stabilization for enhanced electrocatalytic O2 evolution. Fuel 2024, 367, 131485. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, J.L.; Wang, S.Z. Preparation, modification and environmental application of biochar: A review. J. Clean. Prod. 2019, 227, 1002–1022. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]




| Kinetics | Parameters | Initial Concentration (C0) (mg/L) | |
|---|---|---|---|
| 100 | 200 | ||
| Pseudo-first order | q e,exp(mg/g) | 36.572 | 76.233 |
| q e,cal(mg/g) | 35.112 | 72.779 | |
| k1 (min−1) | 0.02337 | 0.02669 | |
| R2 | 0.989 | 0.983 | |
| Pseudo-second order | k2 [g/(mg·min)] | 38.368 | 79.026 |
| q e,cal(mg/g) | 0.000912 | 0.000517 | |
| R2 | 0.999 | 0.999 | |
| Intra-particle diffusion | ki1 [mg/(g·min0.5)] | 2.126 | 3.753 |
| C1 | 8.339 | 24.726 | |
| R12 | 0.955 | 0.875 | |
| ki2 [mg/(g·min0.5)] | 0.821 | 1.716 | |
| C2 | 22.318 | 45.807 | |
| R22 | 0.980 | 0.999 | |
| ki3 [mg/(g·min0.5)] | 0.149 | 0.334 | |
| C3 | 32.550 | 67.657 | |
| R32 | 0.990 | 0.867 | |
| T/(K) | Langmuir Parameters | Freundlich Parameters | Thermodynamic Parameters | ||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Qm (mg/g) | kL (L/mg) | R2 | Kf (Ln·mg1–n/g) | n | R2 | ∆G0 (kJ/mol) | ∆H0 (kJ/mol) | ∆S0 (kJ/mol·K) | |
| 288 | 145.985 | 0.0955 | 0.999 | 26.941 | 2.513 | 0.972 | 5.558 | −28.842 | −0.119 |
| 298 | 141.643 | 0.0693 | 0.999 | 21.946 | 2.404 | 0.958 | 6.753 | ||
| 308 | 137.931 | 0.0436 | 0.999 | 16.253 | 2.258 | 0.959 | 7.947 | ||
| No. | Adsorbents | qm (mg/g) | Reaction Conditions | Reference |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | MMT | 416.66 | -, - | [52] |
| 2 | FMB | 357 | 298 K, pH 5 | [47] |
| 3 | Mn@MDSBC | 145.985 | 288 K, pH 5 | This work |
| 141.643 | 298 K, pH 5 | |||
| 137.931 | 308 K, pH 5 | |||
| 4 | SBC | 13.5 | -, - | [53] |
| Zn-SBC | 77.3 | -, - | ||
| Fe/Zn-SBC | 74.2 | -, - | ||
| 5 | Dopa-CoF NPs | 16.5 | 298 K, pH 7 | [54] |
| Gluta-CoFN | 14.0 | 298 K, pH 7 | ||
| PsMela-CoF NPs | 7.18 | 298 K, pH 7 | ||
| 6 | CoFe-LDH-modified sludge biochar | 19 | 298 K, - | [55] |
| 16 | 303 K, - | |||
| 12 | 308 K, - |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Tie, J.; Yan, M.; Shao, S.; Duan, X. Enhanced Adsorption of Aqueous Ciprofloxacin Hydrochloride by a Manganese-Modified Magnetic Dual-Sludge Biochar. Water 2025, 17, 1229. https://doi.org/10.3390/w17081229
Tie J, Yan M, Shao S, Duan X. Enhanced Adsorption of Aqueous Ciprofloxacin Hydrochloride by a Manganese-Modified Magnetic Dual-Sludge Biochar. Water. 2025; 17(8):1229. https://doi.org/10.3390/w17081229
Chicago/Turabian StyleTie, Jingxi, Mengjia Yan, Sihao Shao, and Xiaohan Duan. 2025. "Enhanced Adsorption of Aqueous Ciprofloxacin Hydrochloride by a Manganese-Modified Magnetic Dual-Sludge Biochar" Water 17, no. 8: 1229. https://doi.org/10.3390/w17081229
APA StyleTie, J., Yan, M., Shao, S., & Duan, X. (2025). Enhanced Adsorption of Aqueous Ciprofloxacin Hydrochloride by a Manganese-Modified Magnetic Dual-Sludge Biochar. Water, 17(8), 1229. https://doi.org/10.3390/w17081229






