A Mass Balance Model for Designing Green Roof Systems that Incorporate a Cistern for Re-Use
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Methodology for Estimating Retention of Water
3. Results and Discussion
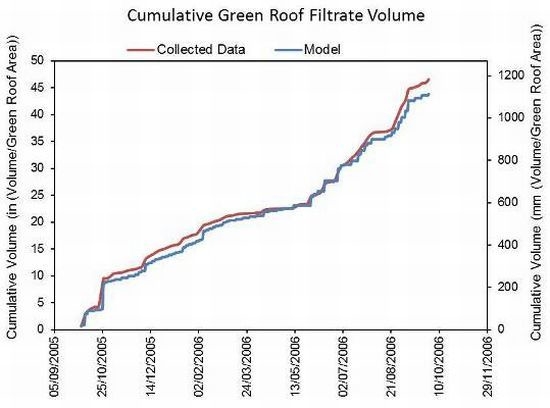
3.1. The Filtrate Factor and ET

| Month | C1 | C2 | EVR1 | EVR2 |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| July 2005 | 0.51 (0.02)^ | 0.00* | 4.32 (0.17) | 4.06 (0.16) |
| August 2005 | 0.00* | 0.51 (0.02)^ | 3.56 (0.14) | 3.56 (0.14) |
| September 2005 | 0.00* | 0.00* | 3.56 (0.14) | 3.30 (0.13) |
| October 2005 | 0.00* | 0.25 (0.01)^ | 2.54 (0.10) | 2.29 (0.09) |
| November 2005 | 0.00* | 0.00* | 2.29 (0.09) | 2.29 (0.09) |
| December 2005 | 0.00* | 0.00* | 2.03 (0.08) | 2.03 (0.08) |
| Jananuary 2006 | 0.00* | 0.25 (0.01)^ | 2.29 (0.09) | 2.54 (0.10) |
| Feberary 2006 | 0.00* | 0.00* | 2.54 (0.10) | 2.54 (0.10) |
| March 2006 | 0.00*+ | 0.00*+ | 3.05 (0.12) | 3.05 (0.12) |
| April 2006 | 0.00* | 0.00* | 3.81 (0.15) | 3.56 (0.14) |
| May 2006 | 0.00* | 0.51 (0.02)^ | 3.30 (0.13) | 3.30 (0.13) |
| June 2006 | 0.00* | 0.76 (0.03)^ | 4.32 (0.17) | 4.32 (0.17) |
| Month | C1 | C2 | EVR1 | EVR2 |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| July 2005 | 0.96 | 0.91 | 0.52 | 0.56 |
| August 2005 | 0.94 | 0.88 | 0.39 | 0.40 |
| September 2005 | 0.98 | 1.00 | 0.52 | 0.55 |
| October 2005 | 0.97 | 0.94 | 0.55 | 0.59 |
| November 2005 | 0.94 | 0.78 | 0.40 | 0.38 |
| December 2005 | 0.98 | 0.82 | 0.58 | 0.57 |
| Jananuary 2006 | 0.86 | 0.71 | 0.45 | 0.42 |
| Feberary 2006 | 0.98 | 0.87 | 0.45 | 0.44 |
| March 2006 | NA+ | NA+ | 0.19 | 0.17 |
| April 2006 | 0.97 | 0.83 | 0.14 | 0.16 |
| May 2006 | 0.99 | 0.81 | 0.27 | 0.30 |
| June 2006 | 0.99 | 0.84 | 0.44 | 0.47 |



3.2. Continuous Stormwater Treatment Outflow Reduction Model (CSTORM) Development
3.2.1. Mass Balance



















3.2.2. CSTORM Model Output
| Location | Cistern Storage Volume (mm (inch) over GR area) | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 0 | 25.4 (1) | 50.8 (2) | 76.2 (3) | 101.6 (4) | 127 (5) | |
| Austin, TX | 25% | 65% | 77% | 83% | 87% | 90% |
| Miami, FL | 42% | 63% | 69% | 73% | 76% | 78% |
| Orlando, FL | 43% | 69% | 78% | 82% | 85% | 87% |
| Tallahassee, FL | 35% | 58% | 66% | 70% | 72% | 74% |
4. Conclusions
5. Recommendations for Future Work
Acknowledgments
References
- Hoffman, L. The Earth Pledge Green Roof Stormwater Modeling System. In Proceedings of Greening Rooftops for Sustainable Communities Conference; Boston, MA, USA: 11–12 May 2006.
- Good, J.C. Roof stormwater runoff as a diffuse source of metals and aquatic toxicity in storm water. Water Sci. Technol. 1993, 28, 317–322. [Google Scholar]
- Vaze, J.; Chiew, F.H.S. Nutrient loads associated with different sediment sizes in urban stormwater and surface pollutants. J. Environ. Eng. 2004, 130, 391–396. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chopra, M.; Wanielista, M.; Kakuturu, S.; Hardin, M.; Stuart, E. Evaluation of Pollution Levels due to the Use of Consumer Fertilizers under Florida Conditions; Florida Department of Transportation: Tallahassee, FL, USA, 2010. [Google Scholar]
- Kelly, M.; Hardin, M.; Wanielista, M. A Stormwater Management Evaluation of the 2007 New American Home Stormwater Treatment System and the Stormwater Academy Green Roof; Florida Department of Environmental Protection: Tallahassee, FL, USA, 2007. [Google Scholar]
- Wanielista, M.; Hardin, M. A Comparative Analysis of Greenroof Depth as It Affects Retention of Rainfall; Florida Department of Environmental Protection: Tallahassee, FL, USA, 2011. [Google Scholar]
- Hunt, B.; Moran, A. Bioretention and Green Roof Field Research in North Carolina. In Proceedings of 1st Annual Stormwater Management Research Symposium, Orlando, FL, USA, 12–13 October 2004; pp. 89–102.
- Ellis, J.B. Infiltration systems: A sustainable source-control option for urban stormwater quality management? Water Environ. Manag. 2000, 14, 27–34. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Davis, A.P.; Shokouhian, M.; Sharma, H.; Minami, C.; Winogradoff, D. Water quality improvement through bioretention: Lead, copper, and zinc removal. Water Environ. Res. 2003, 75, 73–82. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hardin, M. The Effectiveness of a Specifically Designed Green Roof Stormwater treatment System Irrigated with Recycled Stormwater Runoff to Achieve Pollutant Removal and Stormwater Volume Reduction. Master’s Thesis, University of Central Florida, Orlando, FL, USA, 2006. [Google Scholar]
- Wanielista, M.; Kersten, R.; Eaglin, R. Hydrology: Water Quantity and Quality Control; John Wiley & Sons: New York, NY, USA, 1997. [Google Scholar]
- MacMillan, G. York University Rooftop Garden Stormwater Quantity and Quality Performance Monitoring Report. In Proceedings of Greening Rooftops for Sustainable Communities, Portland, OR, USA, 2–4 June 2004.
- Moran, A.; Hunt, B.; Jennings, G. A North Carolina Field Study to Evaluate Greenroof Runoff Quantity, Runoff Quality, and Plant Growth. In Proceedings of Greening Rooftops for Sustainable Communities Conference, Portland, OR, USA, 2–4 June 2004.
- Miller, C. Use of Vegetated Roof Covers in Runoff Management; RoofMeadow: Philadelphia, PA, USA, 2004. Available online: http://www.roofmeadow.com/wp-content/uploads/Runoff_Management_with_Green_Roofs.v2.pdf (accessed on 9 Novemeber 2012).
- Miller, C. Mathematical Simulation Methods: A Foundation for Developing General-Purpose Green Roof Simulation Models; RoofMeadow: Philadelphia, PA, USA, 2002. Available online: http://www.roofmeadow.com/wp-content/uploads/Mathematical-Simulation.pdf (accessed on 9 Novemeber 2012).
- Hilten, R.N.; Lawrence, T.M; Tollner, E.W. Modeling stormwater runoff from green roofs with HYDRUS-1D. J. Hydrol. 2008, 358, 288–293. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, Y.; Baetz, B.W. Sizing of rainwater storage units for green building applications. J. Hydrol. Eng. 2007, 12, 197–205. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liaw, C.-H.; Tsai, Y.-L. Optimum storage volume of rooftop rain water harvesting systems for domestic use. J. Am. Water Resour. Assoc. 2004, 40, 901–912. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jones, M.P.; Hunt, W.F. Performance of rainwater harvesting systems in the southeastern united states. Resour. Conserv. Recycl. 2010, 54, 623–629. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Douglas, E.M.; Jacobs, J.M.; Sumner, D.M.; Ray, R.L. A comparison of models for estimating potential evapotranspiration for florida land cover types. J. Hydrol. 2009, 373, 366–376. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wanielista, M.; Kelly, M.; Hardin, M. A Comparative Analysis of Greenroof Designs Including Depth of Media, Drainage Layer Materials, and Pollution Control Media; Florida Department of Environmental Protection: Tallahassee, FL, USA, 2008. [Google Scholar]
- Hagan, G. Personal communication. Tecta America, Sanford, FL, USA, 2012. [Google Scholar]
- Weather Underground Home Page. Available online: http://www.wunderground.com/history/ (accessed on 2 September 2012).
- Hardin, M.; Wanielista, M. Stormwater Effectiveness of an Operating Green Roof Stormwater Treatment System and Comparison to a Scaled Down Green Roof Stormwater Treatment System Chambers; Florida Department of Environmental Protection: Tallahassee, FL, USA, 2007. [Google Scholar]
- FLL, Guideline for the Planning, Execution and Upkeep of Green-roof Sites, January 2002 ed; Forschungsgesellschaft Landschaftsentwicklung Landschaftsbau E.V.: Bonn, Germany, 2002.
- Sonne, J. Evaluating green roof energy performance. ASHRAE J. 2006, 48, 59–61. [Google Scholar]
- Saiz, S.; Kennedy, C.; Bass, B.; Pressnail, K. Comparative life cycle assessment of standard and green roofs. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2006, 40, 4312–4316. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kosareo, L.; Ries, R. Comparative environmental life cycle assessment of green roofs. Build. Environ. 2007, 42, 2606–2613. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Teemusk, A.; Mander, U. Greenroof potential to reduce temperature fluctuations of a roof membrane: A case study from estonia. Build. Environ. 2009, 44, 643–650. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wanielista, M.; Hardin, M. A Stormwater Management Assessment of Green Roofs with Irrigation. In Proceedings of 2nd Biennal Stormwater Management Research Symposium, Orlando, FL, USA, 4–5 May 2006; pp. 153–164.
© 2012 by the authors; licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open-access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/3.0/).
Share and Cite
Hardin, M.; Wanielista, M.; Chopra, M. A Mass Balance Model for Designing Green Roof Systems that Incorporate a Cistern for Re-Use. Water 2012, 4, 914-931. https://doi.org/10.3390/w4040914
Hardin M, Wanielista M, Chopra M. A Mass Balance Model for Designing Green Roof Systems that Incorporate a Cistern for Re-Use. Water. 2012; 4(4):914-931. https://doi.org/10.3390/w4040914
Chicago/Turabian StyleHardin, Mike, Martin Wanielista, and Manoj Chopra. 2012. "A Mass Balance Model for Designing Green Roof Systems that Incorporate a Cistern for Re-Use" Water 4, no. 4: 914-931. https://doi.org/10.3390/w4040914
APA StyleHardin, M., Wanielista, M., & Chopra, M. (2012). A Mass Balance Model for Designing Green Roof Systems that Incorporate a Cistern for Re-Use. Water, 4(4), 914-931. https://doi.org/10.3390/w4040914