Remote Sensing Analysis of Lake Dynamics in Semi-Arid Regions: Implication for Water Resource Management. Lake Manyara, East African Rift, Northern Tanzania
Abstract
:1. Background
2. Study Area and Data
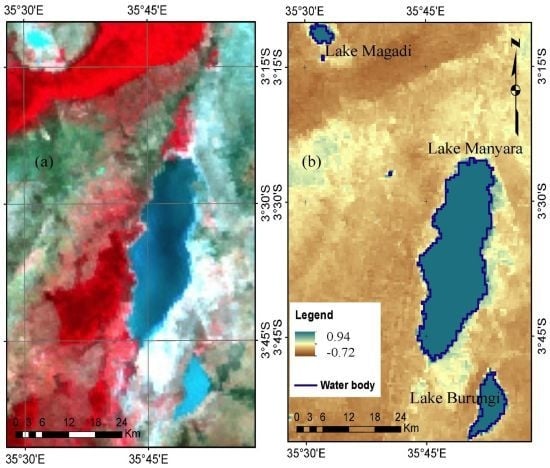
2.1. Study Area


2.2. Data
2.2.1. Satellite Data
(a) MODIS Land Surface Reflectance
(b) MODIS Land Surface Temperature
(c) MODIS Evapotranspiration

(d) Rainfall
2.2.2. Meteorological in situ Datasets
3. Methods
3.1. Indices


3.2. Lake Water Surface and Land Cover Mapping

3.3. Water Balance Modeling
3.4. Possible Sources of Errors
4. Results
4.1. Lake Manyara Surface Dynamic Mapping


| Year | Area (km2) | Duration | Change (km2) (%) | Duration | Change (km2) (%) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 2000 | 520.25 | – | – | – | – |
| 2001 | 497 | 2000–2001 | −23.25(4.46) | 2000–2001 | −23.25(4.46) |
| 2002 | 451.25 | 2001–2002 | −45.75(9.21) | 2000–2002 | −69(13.26) |
| 2003 | 373 | 2002–2003 | −78.25(17.34) | 2000–2003 | −147.25(28.30) |
| 2004 | 279 | 2003–2004 | −94(25.20) | 2000–2004 | −241.25(46.37) |
| 2005 | 13.25 | 2004–2005 | −265.75(95.25) | 2000–2005 | −507(97.45) |
| 2006 | 383.25 | 2005–2006 | 370(2792.45) | 2000–2006 | −137(26.33) |
| 2007 | 449.5 | 2006–2007 | 66.25(17.29) | 2000–2007 | −70.75(13.60) |
| 2008 | 398.25 | 2007–2008 | −51.25(11.40) | 2000–2008 | −122(23.45) |
| 2009 | 200.25 | 2008–2009 | −198(49.72) | 2000–2009 | −320(61.51) |
| 2010 | 433 | 2009–2010 | 232.75(38.05) | 2000–2010 | −87.25(16.77) |
| 2011 | 30.5 | 2010–2011 | −402.5(92.96) | 2000–2011 | −489.75(94.14) |


4.2. Water Surface Variations and Water Balance



4.3. Assessment of the Optimal Index for Water Extraction


4.4. Land Cover and Lake Surface Area Variation


5. Discussion

Implication to Water Resource Management
6. Conclusions
Acknowledgements
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Birol, E.; Karousakis, K.; Koundouri, P. Using economic valuation techniques to inform water resources management: A survey and critical appraisal of available techniques and an application. Sci. Total Environ. 2006, 365, 105–122. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chave, P. The EU Water Framework Directive: An Introduction; IWA Publishing: London, UK, 2001; p. 208. [Google Scholar]
- Gao, H.; Birkett, C.; Lettenmaier, D.P. Global monitoring of large reservoir storage from satellite remote sensing. Water Resour. Res. 2012, 48, W09504:1–W09504:12. [Google Scholar]
- Bai, J.; Chen, X.; Li, J.; Yang, L.; Fang, H. Changes in the area of inland lakes in arid regions of central Asia during the past 30 years. Environ. Monit. Assess. 2011, 178, 247–256. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mason, I.M.; Guzkowska, M.A.J.; Rapley, C.G. The response of lake levels and areas to climatic change. Clim. Change 1994, 27, 161–197. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mercier, F.; Cazenave, A.; Maheu, C. Interannual lake level fluctuations (1993–1999) in Africa from Topex/Poseidon: Connections with ocean-atmosphere interactions over the Indian Ocean. Glob. Planet. Change 2002, 32, 141–163. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Goerner, A.; Jolie, E.; Gloaguen, R. Non-climatic growth of the saline Lake Beseka, Main Ethiopian Rift. J. Arid Environ. 2009, 73, 287–295. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Verbesselt, J.; Hyndman, R.; Newnham, G.; Culvenor, D. Detecting trend and seasonal changes in satellite image time series. Remote Sens. Environ. 2010, 114, 106–115. [Google Scholar]
- Crétaux, J.; Jelinski, W.; Calmant, S.; Kouraev, A.; Vuglinski, V.; Bergé-Nguyen, M.; Gennero, M.-C.; Nino, F.; Abarca Del Rio, R.; Cazenave, A.; et al. SOLS: 2011. A lake database to monitor in the Near Real Time water level and storage variations from remote sensing data. Adv. Space Res. 2011, 47, 1497–1507. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Böhme, B.; Steinbruch, F.; Gloaguen, R.; Heilmeier, H.; Merkel, B. Geomorphology, hydrology, and ecology of Lake Urema, central Mozambique, with focus on lake extent changes. Phys. Chem. Earth 2006, 31, 745–752. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, H. Modification of normalised difference water index (NDWI) to enhance open water features in remotely sensed imagery. Int. J. Remote Sens. 2006, 27, 3025–3033. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, J.; Sheng, Y. An automated scheme for glacial lake dynamics mapping using Landsat imagery and digital elevation models: A case study in the Himalayas. Int. J. Remote Sens. 2012, 33, 5194–5213. [Google Scholar]
- Lu, S.; Wu, B.; Yan, N.; Wang, H. Water body mapping method with HJ-1A/B satellite imagery. Int. J. Appl. Earth Observ. Geoinf. 2011, 13, 428–434. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McFeeters, S.K. The use of normalized difference water index (NDWI) in the delineation of open water features. Int. J. Remote Sens. 1996, 17, 1425–1432. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Luo, J.; Sheng, Y.; Shen, Z.; Li, J. Automatic and high-precise extraction for water in- formation from multispectral images with the step-by-step iterative transformation mechanism. J. Remote Sens. 2009, 13, 604–609. [Google Scholar]
- Simonsson, L. Applied Landscape Assessment in a Holistic Perspective, A Case Study from Babati District, North-Central Tanzania; Department of Earth Science, Uppsala University: Uppsala, Sweden, 2001; pp. 1650X–1495X. [Google Scholar]
- Yanda, P.Z.; Madulu, N.F. Water resource management and biodiversity conservation in the Eastern Rift Valley Lakes, Northern Tanzania. Phys. Chem. Earth 2005, 30, 717–725. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kaspar, F.; Cubasch, U.; Offenbach, G. Simulation of East African precipitation patterns with the regional climate model CLM. Meteorol. Z. 2008, 17, 511–517. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khan, S.I.; Adhikari, P.; Hong, Y.; Vergara, H.; Adler, R.F.; Policelli, F.; Irwin, D.; Korme, T.; Okello, L. Hydroclimatology of Lake Victoria region using hydrologic model and satellite remote sensing data. Hydrol. Earth Syst. Sci. 2011, 15, 107–117. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Copeland, S.R. Potential hominin plant foods in northern Tanzania: Semi-arid savannas versus savanna chimpanzee sites. J. Hum. Evol. 2009, 57, 365–378. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Prins, H.T.; Loth, P.E. Rainfall patterns as background to plant phenology in northern Tanzania. J. Biogeogr. 1988, 15, 451–463. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vermote, E.F.; Kotchenova, S.Y.; Ray, J.P. MODIS Land Surface Reflectance User Guide V1.3. 2011. Available online: http://modis-sr.ltdri.org/products/MOD09_UserGuide_v1_3.pdf (accessed on 30 September 2012).
- Schaaf, C.B.; Gao, F.; Strahler, A.H.; Lucht, W.; Li, X.; Tsang, T.; Strugnell, N.; Zhang, X.Y.; Jin, Y.; Muller, J.P.; et al. First operational BRDF, albedo and nadir reflectance products from MODIS. Remote Sens. Environ. 2002, 83, 135–148. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wan, Z. New refinements and validation of the MODIS land-surface temperature/emissivity products. Remote Sens. Environ. 2008, 112, 59–74. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, Z.; Wang, Q.; Ouyang, Z.; Watanabe, M.; Matsushita, B.; Fukushima, T. Evaluation of MOD16 algorithm using MODIS and ground observational data in winter wheat field in North China Plain. Hydrol. Process. 2007, 21, 1196–1206. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mu, Q.; Heinsch, F.A.; Zhao, M.; Running, S.W. Development of a global evapotranspiration algorithm based on MODIS and global meteorology data. Remote Sens. Environ. 2007, 111, 519–536. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mu, Q.; Zhao, M.; Running, S.W. Improvements to a MODIS global terrestrial evapotranspiration algorithm. Remote Sens. Environ. 2011, 115, 1781–1800. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Oak Ridge National Laboratory Distributed Active Archive Center (ORNL DAAC), MODIS Subsetted Land Products, Collection 5. Oak Ridge, TN, USA, 2012. Available online: http://daac.ornl.gov/MODIS/modis.html (accessed on 31 August 2012).
- Bookhagen, B.; Burbank, D.W. Toward a complete Himalayan hydrological budget: Spatiotemporal distribution of snowmelt and rainfall and their impact on river discharge. J. Geophys. Res. 2010, 115, F03019:1–F03019:25. [Google Scholar]
- Kim, H.W.; Hwang, K.; Mu, Q.; Lee, O.S.; Choi, M. Validation of MODIS 16 global terrestrial evapotranspiration products in various climates and land cover types in Asia. KSCE J. Civil Eng. 2012, 16, 229–238. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tang, R.; Li, Z.; Chen, K. Validating MODIS–derived land surface evapotranspiration with in situ measurements at two AmeriFlux sites in a semiarid region. J. Geophys. Res. 2011, 116, D04106:1–D04106:14. [Google Scholar]
- Kummerow, C.; Barnes, W.; Kozu, T.; Shiue, J.; Simpson, J. The tropical rainfall measuring mission (TRMM) sensor package. J. Atmos. Ocean. Technol. 1998, 15, 809–817. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huffman, G.J.; Adler, R.F.; Bolvin, D.T.; Gu, G.J.; Nelkin, E.J.; Bowman, K.P.; Hong, Y.; Stocker, E.F.; Wolff, D.B. The TRMM multisatellite precipitation analysis (TMPA): Quasiglobal, multiyear, combined-sensor precipitation estimates at fine scales. J. Hydrometeorol. 2007, 8, 38–55. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rousel, J.W.; Haas, R.H.; Schell, J.A.; Deering, D.W. Monitoring vegetation systems in the great plains with ERTS. In Proceedings of the Third Earth Resources Technology Satellite—1 Symposium; NASA SP-351; NASA: Greenbelt, MD, USA, 1974; Volume 1, pp. 309–317. [Google Scholar]
- Soti, V.; Tran, A.; Bailly, J.; Puech, C.; Seen, D.L.; Bégué, A. Assessing optical earth observation systems for mapping and monitoring temporary ponds in arid areas. Int. J. Appl. Earth Observ. Geoinf. 2009, 11, 344–351. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Jensen, J.R. Introductory to Digital Image Processing: A Remote Sensing Perspective, 3rd ed.; Prentice Hall Press: Upper Saddle River, NJ, USA, 2005. [Google Scholar]
- Sobrino, J.A.; Raissouni, N. Toward remote sensing methods for land cover dynamic monitoring: Application to Morocco. Int. J. Remote Sens. 2000, 21, 353–366. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Glasbey, C.A. An analysis of histogram-based thresholding algorithms. Graph. Models Image Process. 1993, 55, 532–537. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cheriet, M.; Said, J.N.; Suen, C.Y. A recursive thresholding technique for image segmentation. IEEE Trans. Image Process. 1988, 7, 918–921. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jawahar, C.V.; Biswas, P.K.; Ray, A.K. Investigations on fuzzy thresholding based on fuzzy clustering. Pattern Recognit. 1997, 30, 1605–1613. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Otsu, N. A threshold selection method from grey-level histograms. IEEE Trans. Syst. Man Cybernet. 1979, 9, 62–66. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tizhoosh, H.R. Image thresholding using type II fuzzy sets. Pattern Recognit. 2005, 38, 2363–2372. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cheng, H.D.; Chen, Y.H.; Sun, Y. A novel fuzzy entropy approach to image enhancement and thresholding. Signal Process. 1999, 31, 745–752. [Google Scholar]
- Congalton, R.G.; Green, K. Assessing the Accuracy of Remotely Sensed Data: Principles and Practices; CRR/Lewis Publishers: Boca Raton, FL, USA, 1999; p. 137. [Google Scholar]
- Knight, J.F.; Lunetta, R.L.; Ediriwickrema, J.; Khorram, S. Regional scale land-cover characterization using MODIS-NDVI 250 m multi-temporal imagery: A phenology based approach. GISci. Remote Sens. 2006, 43, 1–23. [Google Scholar]
- Krause, P.; Hanisch, S. Simulation and analysis of the impact of projected climate change on the spatially distributed waterbalance in Thuringia, Germany. Adv. Geosci. 2009, 21, 33–48. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Deus, D.; Gloaguen, R.; Krause, P. Water balance modeling in a semi-arid environment with limited in situ data using remote sensing in Lake Manyara, East African Rift, Tanzania. Remote Sens. 2013, 5, 1651–1680. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nash, J.E.; Sutcliffe, J.V. River flow forecasting through conceptual models. Part I: A discussion of principles. J. Hydrol. 1970, 10, 282–290. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alesheikh, A.A.; Ghorbanali, A.; Nbouri, N. Coastline change detection using remote sensing. Int. J. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2007, 4, 61–66. [Google Scholar]
- Abram, N.J.; Gagan, M.K.; Liu, Z.; Hantoro, W.S.; McCulloch, M.T.; Suwargadi, B. Seasonal characteristics of the Indian Ocean Dipole during the Holocene epoch. Nature 2007, 445, 299–302. [Google Scholar]
- Paeth, H.; Hense, A. On the linear response of tropical African climate to SST changes deduced from regional climate model simulations. Theor. Appl. Climatol. 2006, 83, 1–19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schreck, C.J.; Semazzi, F.H. Variability of the recent climate of eastern Africa. Int. J. Climatol. 2004, 24, 681–701. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ummenhofer, C.C.; Gupta, A.S.; England, M.H.; Reason, C.J.C. Contributions of Indian Ocean sea surface temperatures to enhanced East African rainfall. J. Climatol. 2009, 22, 993–1013. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Donkor, S.M.K.; Wolde, Y.E. Intergrated Water Resource Management in Africa: Issues and Options. Available online: http://www.gdrc.org/uem/water/iwrm/iwrm-africa.pdf (accessed on 12 December 2012).
© 2013 by the authors; licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/3.0/).
Share and Cite
Deus, D.; Gloaguen, R. Remote Sensing Analysis of Lake Dynamics in Semi-Arid Regions: Implication for Water Resource Management. Lake Manyara, East African Rift, Northern Tanzania. Water 2013, 5, 698-727. https://doi.org/10.3390/w5020698
Deus D, Gloaguen R. Remote Sensing Analysis of Lake Dynamics in Semi-Arid Regions: Implication for Water Resource Management. Lake Manyara, East African Rift, Northern Tanzania. Water. 2013; 5(2):698-727. https://doi.org/10.3390/w5020698
Chicago/Turabian StyleDeus, Dorothea, and Richard Gloaguen. 2013. "Remote Sensing Analysis of Lake Dynamics in Semi-Arid Regions: Implication for Water Resource Management. Lake Manyara, East African Rift, Northern Tanzania" Water 5, no. 2: 698-727. https://doi.org/10.3390/w5020698
APA StyleDeus, D., & Gloaguen, R. (2013). Remote Sensing Analysis of Lake Dynamics in Semi-Arid Regions: Implication for Water Resource Management. Lake Manyara, East African Rift, Northern Tanzania. Water, 5(2), 698-727. https://doi.org/10.3390/w5020698