Abstract
Harmful algal blooms (HABs), harmful microorganisms (pathogens) and toxic metals represent three major agents of water quality deterioration. Water quality of three northern lakes (Sardis, Enid, and Grenada) and a central lake (Ross Barnett Reservoir) of Mississippi, USA were examined in this study. While all these lakes are heavily used for recreational purposes, the Ross Barnett Reservoir serves additionally as the primary water supply for the City of Jackson, the capital city of Mississippi. The main goal of this study was to comprehensively assess the water quality of these lakes employing field and satellite data, and evaluate the potential human and aquatic health impacts. A time-series of true color images derived from satellite data indicated that algal blooms have been a recurring phenomenon in these lakes. Cyanobacteria, the algal group that predominantly occur in freshwater and form toxic blooms, were always present in these lakes and were most abundant on many occasions. The most toxic cyanotoxin, microcystin-LR, was found in all lakes, and its concentrations exceeded federal drinking water guidelines for children under six years of age many times. Potential bioaccumulation and biomagnification of microcystin-LR may pose serious risk to the aquatic ecosystem and human health including adults. Nutrient measurements indicated that all four lakes were eutrophic. Among bacterial populations, total coliforms and enterococci exceeded guideline values on several occasions. Arsenic, cadmium, chromium, and lead were found in the water of all the lakes, with arsenic exceeding the guideline values at two sites in Ross Barnett Reservoir. While it is apparent from this study that these lakes face many water quality issues, data across all seasons will be required to document potential trends and to devise management strategies. Use of remote sensing technology is recommended to monitor some of the water quality parameters such as suspended particulate matter and algal blooms, especially cyanobacterial blooms.
1. Introduction
Water bodies are increasingly affected by undesirable harmful algal blooms (HABs), harmful microorganisms (pathogens) and toxic metals as a result of non-point source pollutant runoff from upstream agricultural production and introduction of nutrients and sediments by local rivers and streams [1,2,3]. HABs are caused by species of photosynthetic microorganisms, phytoplankton. Among the HABs, cyanobacteria, also known as blue-green algae, represent the major harmful algal group in freshwater systems. Cyanobacterial blooms are aesthetically undesirable since they discolor the water, cause turbidity in recreational facilities, and synthesize a large number of low molecular weight compounds, which cause taste and odor problems [4,5]. Of particular concern are a diverse range of toxins produced by cyanobacteria, termed cyanotoxins, which are hazardous to human, animal, and aquatic ecosystem health [6,7,8]. Due to potential human health threats and their negative impact on aquatic life, recreation and tourism, cyanobacterial blooms have been associated with significant economic and sociocultural impacts worldwide [9]. Additionally, the water bodies are affected by pollution leading to undesirable increases in harmful microorganisms (pathogens) and toxic metals. An array of microorganisms such as Escherichia coli (E. coli), enterococci, vibrios and mycobacteria are responsible for severe infections in people exposed to water and also pathogenic to many aquatic organisms [10,11]. Toxic metals such as arsenic, cadmium, lead, mercury, selenium, and lithium are introduced to the aquatic ecosystems through both point and non-point source pollution that are hazardous to fish, shrimps, and bivalves, as well as to humans, as some of the metal toxicity (e.g., mercury) has the potential to propagate through the food chain [12].
Sixty-six percent of drinking water supply systems in the United States obtain water from surface water sources [13]. Compared to groundwater, which is naturally filtered over time, surface water sources are more vulnerable to the risks of contamination of nutrients, pathogens and heavy metals because they are directly exposed to the atmosphere and surface runoff. Water treatment facilities select the appropriate treatment methods based on the contaminants found in the source water. Emergency situations can arise if contaminants are accidentally discharged into the watershed from industrial sources, old sewer systems or in situations that are recurrent around Lake Erie, in which the municipal water suppliers had to shut down the drinking water treatment facilities for numerous days. In September 2013 and August 2014, municipal water supplies of the city of Toledo had to issue a “do not drink” advisory for two days because cyanotoxin concentrations were greater than the World Health Organization (WHO) guideline [14,15,16]. Currently, U.S. Environmental Protection Agency (EPA) does not require water-treatment facilities to test for cyanotoxins and leaves the decision to perform the tests up to individual facilities on a voluntary basis. Hence, continuous monitoring of all the important water quality parameters including cyanotoxins is crucial for lake management. Furthermore, sampling at one site or a few sites may be sufficient to assess general water quality of a lake, however, if the objective is to diagnose the lake for ensuring the safety of drinking water and recreation or to determine how the lake functions, sampling sites encompassing the entire lake would be necessary for assessing the lake’s overall water quality [17,18]. Thus a comprehensive examination of an array of water quality parameters in a high spatial and temporal scale is necessary to ensure the most appropriate water treatment for drinking water supplies, to determine the suitability for water-based recreation or to devise lake management strategies.
Remote sensing provides a valuable tool for rapidly assessing the spatial variability of water quality parameters, such as concentrations of HABs, suspended sediments and dissolved organic matter over the entire aerial extent of lakes [19,20]. Remote sensing is being increasingly utilized in lake management over the past fifteen years [16,21,22,23], but is still far behind land remote sensing and ocean remote sensing in adoption and overall public awareness [24]. Limited use of remote sensing for studying lake water quality mainly stems from unavailability of appropriate sensor platforms. Hence, operative monitoring of inland waters is currently limited to larger lakes or using airborne and hand-held remote sensing instruments as there are no satellite sensors with sufficient spatial resolution to provide daily coverage [25]. Additionally, the water quality parameters that can be quantified using remotely sensed data is mainly limited to parameters that are optically active, e.g., HABs, suspended sediments, dissolved organic matter, etc. Additionally, optical complexity of inland lakes requires somewhat sophisticated algorithms to retrieve the aforementioned water quality parameters from remotely sensed data. Nevertheless, true color images that are analogous to photographs taken from up above the lake, can be generated from the data collected by a satellite sensor that can show how the lake would appear to a human observer in the sky. The “greenness” in true color images corroborates to the presence of algal blooms in a water body, whereas a “brown” appearance can depict the presence of inorganic suspended sediments for a qualitative examination if not quantitative. Furthermore, a time-series of historical satellite data can also allow for a qualitative comparison of the bloom intensity and suspended sediment levels from true color images, while they will be deemed suitable for the quantitative analysis of the occurrence of phytoplankton blooms or suspended sediment concentrations when remote sensing algorithms are applied [16,23,24,26]. A comprehensive examination of the water quality parameters collected from the field or satellite data with an appropriate spatial and temporal scale will provide useful information on the human and aquatic health impacts of water quality for lakes [27,28,29,30].
The Ross Barnett Reservoir, located adjacent to the City of Jackson, the capital city of Mississippi, USA, and the three northern Mississippi lakes (Sardis, Enid, and Grenada) represent four major lakes of the state of Mississippi, USA. The Ross Barnett Reservoir is used as a source of drinking water for the City of Jackson and all four lakes have traditionally been used for recreational activities such as swimming, boating and sport fishing. These lakes produce commercial quantities of anglers, bass, and crappie fish [31,32]. Therefore, a comprehensive knowledge of their water quality is imperative. Previous water quality studies of the Ross Barnett Reservoir have included bacterial [33,34] and macrophyte surveys [35] at a few near-shore sites. Additionally, Sobolev et al. [36] examined the effects of nutrient and sediment dynamics on phytoplankton abundance in Ross Barnett Reservoir, and found that despite the presence of abundant nutrients, inorganic turbidity limited algal growth at five near-shore sites. These results indicate the water quality of a few near-shore sites, hence they are not representative of the entire Ross Barnett Reservoir. As opposed to above approaches, we followed a systematic sampling design and collected an array of water quality parameters at regularly spaced intervals over the entire surface area of all the four lakes.
A number of studies have examined the sedimentation patterns [37,38], physical and chemical characteristics of sediments [39], texture, spatial distribution and rate of sedimentation in Grenada Lake [40,41]. Hugget et al. [41] investigated the concentration of mercury in the sediments and fish tissues from Sardis, Enid, and Grenada Lakes and found that fish from Enid Lake are accumulating levels of mercury that may be hazardous to those consuming fish, whereas the level of mercury in Sardis and Grenada Lakes did not pose a human health hazard. Lim and Surbeck [42] statistically analyzed a time-series of nutrient and turbidity data from Lake Sardis and found that the lake as a whole changed temporally by season, rather than spatially and storm events caused the greatest shifts in nutrient and turbidity levels. Ochs and Rhew [43] and Sthapit et al. [44] studied the phytoplankton community structure along the longitudinal axis of Lake Sardis from April 1994 to September 1995 and March 2004 to April 2005, respectively, and found that the population dynamics varied spatially and temporally in response to physiochemical properties, hydraulic residence time, nutrients, temperature, and light conditions. Few other notable studies on these lakes include the report of Largemouth Bass Virus in all four lakes [45], mussel community structure and conservation of freshwater mussels in Lake Sardis [46], and evaluation of the regulations for crappie and angler fishing in Lake Sardis [47].
Despite the importance of these lakes, to our knowledge, there has been no study dealing with a comprehensive examination of the water quality of these lakes. To date, there are no prior reports of measurements of the HABs or phycotoxins in these lakes. Thus, the overall goal of this study was to report a comprehensive assessment of the water quality of these lakes, so that specific issues could be identified for further investigation. After the issues are identified, the reasons for those could be established. Understanding of the causal mechanisms for the spatial and temporal variation of specific water quality issues would be essential for lake managers concerned with drinking water quality, fisheries or recreation. The specific aims of the study were to: (1) examine historical evidence of algal blooms in these four large Mississippi lakes using satellite data from multiple sensors; (2) determine concentrations of algal groups and cyanotoxins, sediments, nutrients, bacteria, trace elements and heavy metals in water samples collected from several sites on multiple trips to all four lakes; and (3) evaluate potential human and aquatic health hazards because of these pollutants in each of these lakes.
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Site Description
The Ross Barnett reservoir and the three northern Mississippi lakes, Sardis, Enid, Grenada, were considered for this study (Figure 1). Ross Barnett Reservoir (32°23′52″ N 90°03′52″ W), a 52 square mile (~134 km2) freshwater body, provides drinking water to the City of Jackson and the surrounding areas and provides recreational opportunities that include 48 recreational facilities (5 campgrounds, 16 parks, 22 boat launches, and 5 trails) for an estimated 2.5 million annual visitors. The Pearl River Valley Water Supply District manages the Ross Barnett Reservoir and carries out its multi-purpose mission without any state or local tax dollars [32]. Lake Sardis (34°24′32″ N 89°47′45″ W), the largest lake in Mississippi, is located in North Mississippi on the Little Tallahatchie River 50 miles south of Memphis, TN. The surface area of this lake is approximately 154 square miles (~400 km2). Lake Sardis is an important recreation destination for several reasons. The lake is popular with anglers and has a reputation for its abundant bass and crappie. Other recreation activities include hunting, camping, boating, skiing, swimming and picnicking. Annual visitation to Lake Sardis exceeds 5 million people. Together with Lake Sardis, Lake Enid (34°08′59″ N 89°54′18″ W) is part of the Yazoo Headwater Project, which was designed to help protect the Mississippi Delta from flooding. Lake Enid is located 72 miles south of Memphis, TN and 140 miles north of Jackson, MS. Enid Lake not only provides premier camping opportunities, but offers many other recreational opportunities including hiking, boating, swimming, picnicking, fishing, hunting, horseback riding, and wildlife viewing. Lake Enid has been recognized as one of America’s Top 10 Fishing Spots [33]. It is also home of the world record white crappie, which weighed an impressive 5 pounds 3 ounces. Lake Enid encompasses over 44 square miles (~114 km2) and is visited each year by more than 1.7 million visitors. Lakes Sardis, Enid and Grenada are managed by the US Army Corps of Engineers. Lake Grenada (33°49′48″ N 89°46′22″ W) has a surface area of approximately 142 square miles (~366 km2) and is the second largest lake in Mississippi. Although the primary purpose of Grenada Lake is flood risk management, many other benefits have been derived from the lake including hiking, boating, fishing, hunting, skiing, and bird watching, to camping, picnicking, golfing, swimming, and much more.
2.2. Satellite Data
Quantitative mapping and monitoring of the spatial and temporal variation of near surface phytoplankton during bloom conditions is possible using satellite data [48]. To investigate the occurrence of phytoplankton blooms in the Lakes Sardis, Enid, Grenada, and Ross Barnett Reservoir in a historical perspective, a time-series of satellite data collected by an array of satellite sensors—SeaWiFS (Sea-viewing Wide Field-of-view Sensor), MODIS (Moderate-resolution Imaging Spectroradiometer), and MERIS (Medium Resolution Imaging Spectrometer) were downloaded from the National Aeronautics and Space Administration (NASA) Ocean Color portal from January 2010 to July 2014. All the downloaded clear-sky images from this time-series of satellite data were processed and true color images were generated using NASA’s SeaWiFS Data Analysis System (SeaDAS) 6.4 software.
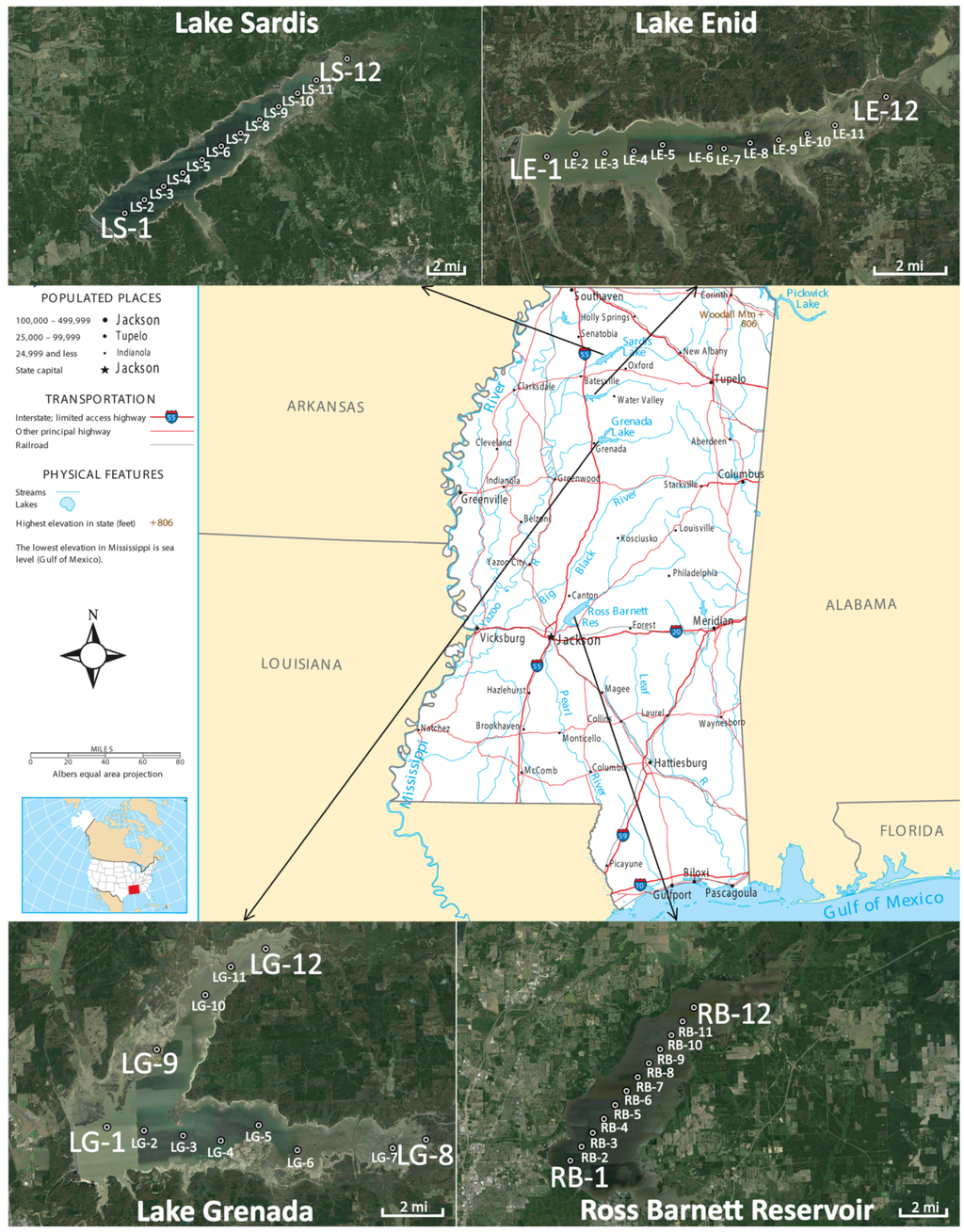
Figure 1.
Location map of Lakes Sardis, Enid, Grenada, and Ross Barnett Reservoir in Mississippi, USA with twelve sampling sites in each of the water bodies indicated.
Figure 1.
Location map of Lakes Sardis, Enid, Grenada, and Ross Barnett Reservoir in Mississippi, USA with twelve sampling sites in each of the water bodies indicated.
2.3. Field Data
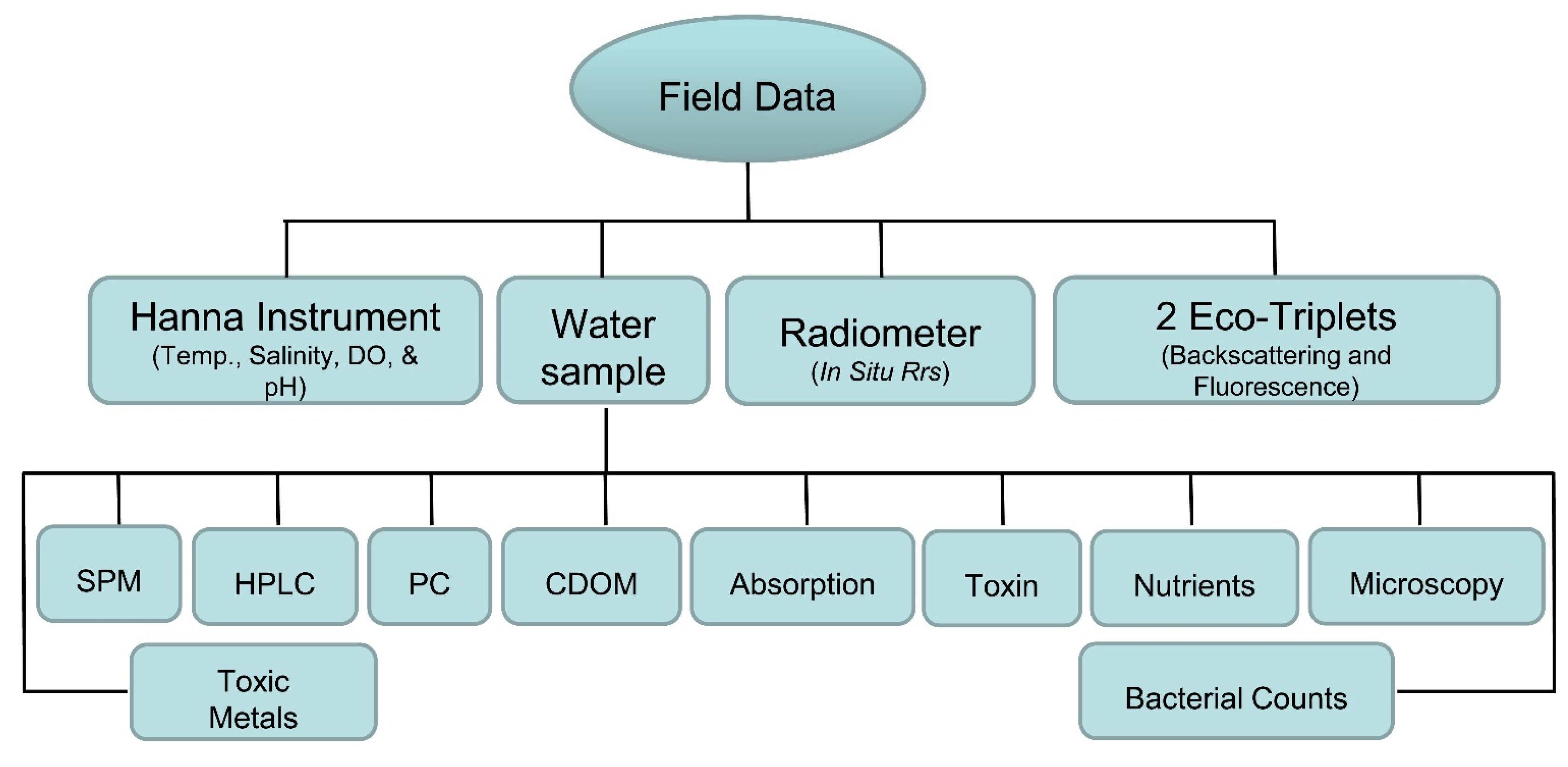
A total of eleven sampling trips, five to the Ross Barnett Reservoir, two in summer 2012, two in summer 2013, and one in summer 2014, and a total of two sampling trips to each of the lakes, Grenada, Enid and Sardis, one each in the summers of 2012 and 2013, were undertaken to sample twelve sites in each of the lakes (Figure 1). The field data collection included water samples in clean Nalgene bottles, in situ remote sensing reflectance measurements using a GER 1500 spectro-radiometer (Spectravista Inc., Poughkeepsie, NY, USA), backscattering and fluorescence measurements using two Eco-Triplets (Wetlabs Inc., Philomath, OR, USA), and physical parameter measurements using a calibrated Hanna multiparameter probe (HI9828, Hanna Instruments, Woonsocket, RI, USA). The water samples were collected for Suspended Particulate Matter (SPM), high performance liquid chromatography (HPLC) photopigments, the cyanobacterial specific pigment phycocyanin (PC), Colored Dissolved Organic Matter (CDOM), absorption, cyanotoxins, nutrients, microscopy, bacterial counts, and toxic metal analyses (Figure 2).
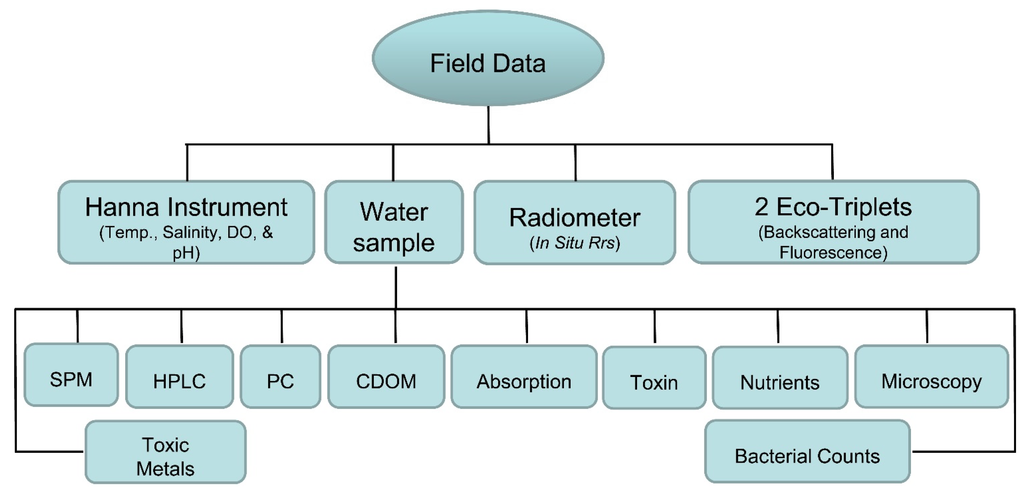
Figure 2.
Flow chart showing the field data collected and the laboratory analyses performed.
Figure 2.
Flow chart showing the field data collected and the laboratory analyses performed.
SPM concentrations were determined by following the glass fiber filter method with each sample run in duplicate [49]. Two hundred-milliliter aliquots of water were filtered onto pre-weighed GF/F filter papers and SPM was calculated as the increase in mass of the filter paper after drying at 105 °C. Ashing the residue at 500 °C provided the inorganic sediment fraction or suspended particulate inorganic matter (SPIM). Subsequently, the organic fraction or the suspended particulate organic matter (SPOM) was determined by subtracting SPIM from SPM. For HPLC analysis of photopigments, 100 mL aliquots of surface water were filtered onto 4.7 cm diameter glass fiber filters (Whatman GF/F), immediately frozen, and stored at −80 °C. The filter papers were shipped overnight on dry ice to Dr. James L. Pinckney at the Department of Biological Sciences, University of South Carolina, Columbia, SC, USA. HPLC analysis provided concentrations of 40 algal pigments including chlorophyll a [50,51]. ChemTax, a matrix factorization program, was used to calculate the relative abundances of major algal groups in the water samples from the HPLC photopigment data [52,53]. For ChemTax, an iterative scheme [54] was followed using the initial pigment ratios from published ratios [55,56]. The ChemTax analysis revealed the relative abundance of seven major algal groups including cyanobacteria, euglenophytes, chlorophytes, dinoflagellates, cryptophytes, diatoms and chrysophytes. The algal groups were expressed as relative values of chlorophyll a. The absolute chlorophyll a contribution of each algal group is particularly useful because it partitions the total chlorophyll a into major phytoplankton groups. Full discussions, validation, and sensitivity analyses of ChemTax are provided in Mackey et al. [52,57], Wright et al. [58] and Higgins et al. [53].
For determination of phycocyanin (PC) concentrations, subsamples (replicate 50 mL aliquots of water) were filtered and kept frozen at −80 °C until analysis. PC was extracted from the filtered water samples according to Downes et al. [59] with Tris-buffer and the concentration was measured fluorometrically using a Horiba Jovin Yvon Fluoromax-4 fluorometer (Horiba Scientific, Edision, NJ, USA). Spectral absorption coefficients of CDOM were determined by filtering the water samples through 0.2 µm Nuclepore membrane filters followed by absorption measurements of the filtrates using a PerkinElmer Lambda 850 spectrophotometer (PerkinElmer, Waltham, MA, USA). Subsamples (50 mL aliquots) of water samples were filtered onto 2.5 cm diameter glass fiber filters (Whatman GF/F) to determine the absorption coefficients of total particulate matter, non-algal particulate (NAP) matter and phytoplankton following Mitchell et al. [60] and Cleveland and Weidemann [61]. For determination of particulate microcystin concentrations, subsamples (50 mL aliquots of surface water) were filtered onto 2.5 cm diameter glass fiber filters (Whatman GF/F), and kept frozen at −80 °C. On the day of the analysis, 5 mL of extraction solvent (methanol:water:acetic acid::50:49:1) [4,62] was added to the filter papers, vortexed (1 min), sonicated (2 min, 30–40 W) on ice, centrifuged (10 min, 3000 rpm) and the supernatant was pooled for the determination of cellular microcystin concentrations using a commercially available enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay (ELISA) kit (Abraxis LLC, Warminster, PA, USA) [4].
Whole water samples were sent on ice to Dr. Richard Lizotte at the USDA ARS National Sedimentation Laboratory, Oxford, MS for nutrient analysis including NH4-N, NOX-N, NO2-N, NO3-N, total Kjeldahl N (TKN) unfiltered, TKN filtered, particulate TKN, PO4-P, total P unfiltered, total P filtered, and total P particulate using standard methods [63,64]. Analysis of total nitrogen (TN) included total Kjeldahl N (TKN), NO3-N and NO2-N, where TKN included NH4-N and organically bonded nitrogen. Particulate TKN (TKN (P)) was computed by subtracting filtered TKN (TKN (F)) from unfiltered TKN (TKN (UF)). Similarly, Particulate total phosphorus (TP (F)) was computed by subtracting filtered total phosphorus (TP (F)) from unfiltered total phosphorus (TP (UF)). For determining the algal community structure and the species composition, subsamples (100 mL) were preserved with 1% glutaraldehyde and refrigerated until analysis. Currently, all the genera are being enumerated using an imaging microscope, FlowCAM (Fluid Imaging Technologies, Scarborough, ME, USA) [65], and particle properties are being analyzed in order to classify the phytoplankton communities at a genus or species level.
For bacterial counts, dehydrated media of m-Endo agar LES, m-HPC agar, m-Enterococcus agar, and Difco m-FC agar were rehydrated following manufacturer’s directions for enumerating total coliform, heterotrophic, enterococcus and fecal coliform (E. coli) bacteria, respectively (BD Diagnostics, Sparks, MD, USA). Replicate water samples were filtered onto 0.45 µm, 47 mm membrane filters and were transferred to petri dishes with agar media. For total coliforms, the filter papers were placed onto pads containing Lauryl Tryptose Broth and incubated at 35 °C for 2 h before transferring the membrane to the petri dishes containing m Endo Agar LES medium. The petri dishes were then incubated for 24 h at 35 °C for total coliform, 48 h at 35 °C for enterococci and heterotrophic bacteria, and 24 h at 44.5 °C for fecal coliform bacteria. After incubation, colonies with a red color with a metallic sheen were enumerated as total coliforms, white color colonies were enumerated as heterotrophic bacteria, light or dark red colonies were enumerated as enterococci and various shades of blue colonies were enumerated as fecal coliforms.
For trace elements and heavy metals analyses, subsamples (100 mL aliquots of surface water) were acidified with 1% (v/v) HNO3 and sent to Dr. Zikri Arslan at the Department of Chemistry and Biochemistry, Jackson State University, Jackson, MS. First, standard curves were constructed using five point standard calibration sets for 23 trace elements and heavy metals, and then the samples were analyzed using a Varian 820-MS ICP Mass Spectrometer (Varian, Inc., Palo Alto, CA, USA). Subsequently, concentrations of the trace elements and heavy metals were computed using the standard curve equations. For quality control of the elemental ICP-MS measurements, fresh water certified reference material (SRM 1640a Trace Elements in Natural Water) from National Institute of Standards and Technology, Gaithersburg, MD was used. The values measured from SRM 1640a were within 95% confidence level of the certified values. Similar to the field water samples, subsamples of the SRM 1640a (n = 4) were acidified to 1% (v/v) HNO3, which is the recommended matrix for trace element measurements by ICP-MS. No significant interferences were observed on any determinations in SRM 1640a including that for arsenic. Thus, possible interferences that could have arisen in field samples were deemed insignificant.
3. Results and Discussions
A time-series of satellite data from 2010–2014 were processed and true color images were generated. Some of the representative true color images are presented in Figure 3. The greenness in this sequence of true color images signifies the presence of algal blooms in the lakes. The greenness increases with increasing concentration of algal blooms. In the true color images, greenness was observed throughout the year in all the lakes, however, only images from the months of January and September–December were chosen to be displayed in Figure 3 as they provided a greater contrast of the greenness in the lakes compared to the senescent land vegetation during the winter and the fall. The true color MERIS images as shown in the 29 September and 21 October, 2011 insets for Lake Grenada and 8 January 2011 inset for Lake Sardis were able to resolve the algal blooms in these small lakes more efficiently than other satellite sensors because of higher spatial resolution (260 m across track × 300 m along track) of MERIS. However, MERIS lacked frequent revisit cycles, whereas both SeaWiFS and MODIS provided daily coverage at 1000 m spatial resolution. Furthermore, MODIS sensor has two high resolution bands that were used to produce high 250 m resolution MODIS images [66], which resolved the algal blooms in the lakes effectively. The true color MERIS and high resolution MODIS images clearly showed the presence of algal blooms in the lakes whereas the spatial resolution of SeaWiFS was not adequate to resolve the algal blooms in the lake (not shown) at the same time in 2010 when phytoplankton blooms were observed in the MERIS and MODIS images. The true color images indicated that algal blooms have been occurring in these lakes historically.
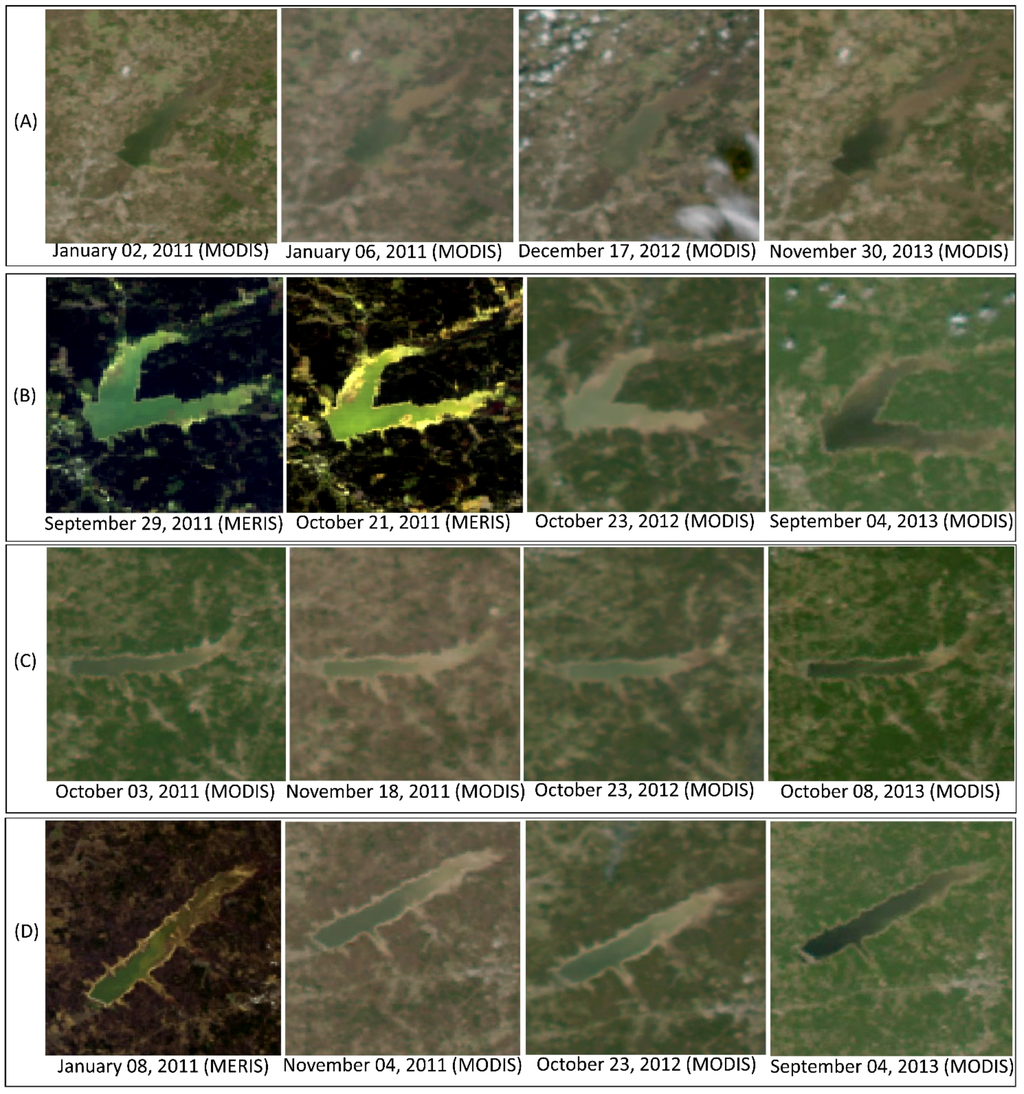
Figure 3.
True color satellite images showing (A) Ross Barnett Reservoir and Lakes; (B) Grenada; (C) Enid; and (D) Sardis. Greenness in these images indicates algal blooms. Images are not to scale.
Figure 3.
True color satellite images showing (A) Ross Barnett Reservoir and Lakes; (B) Grenada; (C) Enid; and (D) Sardis. Greenness in these images indicates algal blooms. Images are not to scale.
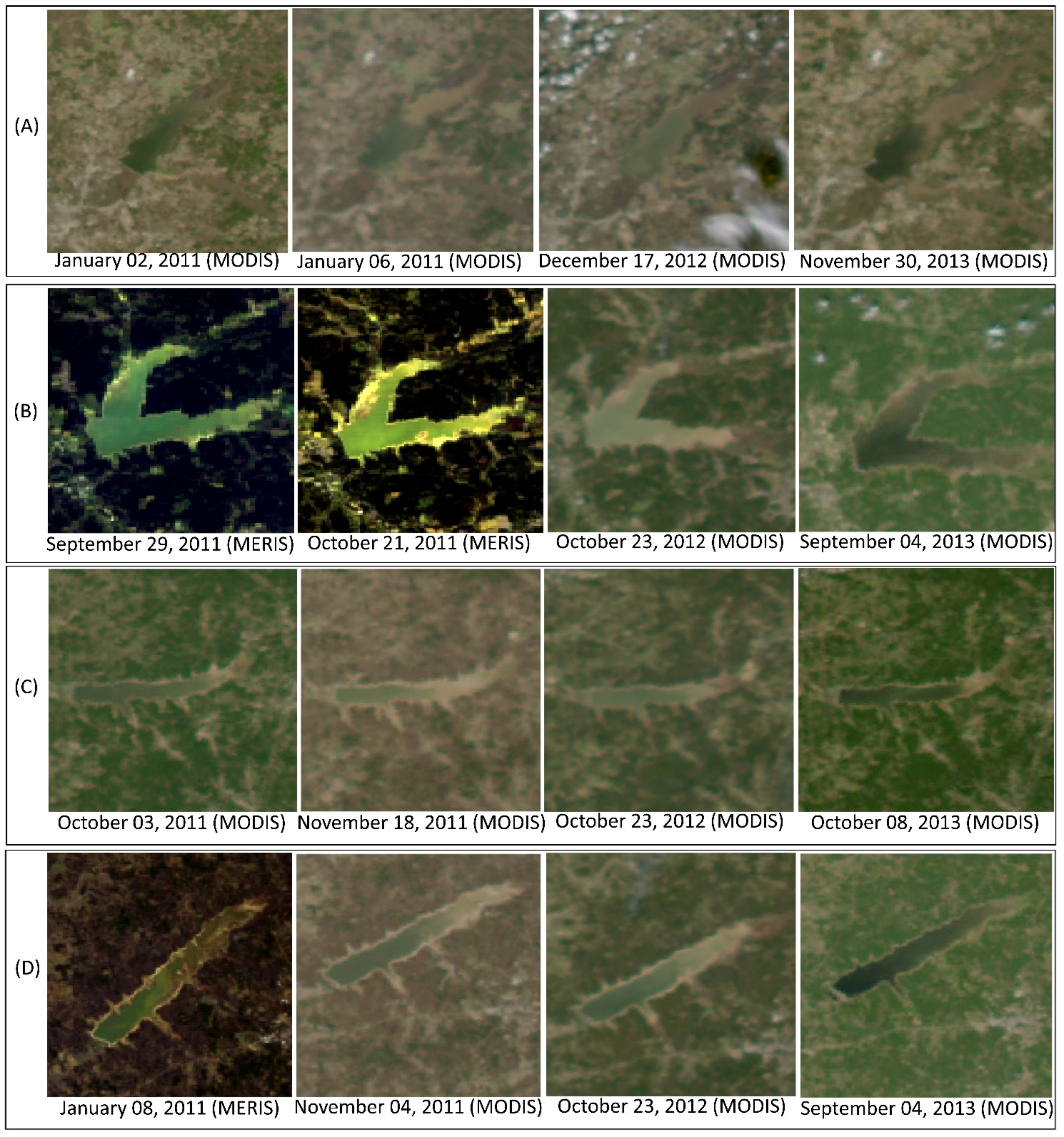
Figure 4 shows the total suspended particulate matter (SPM) concentrations along with organic and inorganic SPM concentrations. SPM, which is synonymous to suspended sediments, is the most widely measured water quality parameter since it relates directly to water quality as well as clarity. SPM concentrations can indicate the trophic conditions and also considered as carriers of pathogens, nutrients, trace elements and heavy metals [67,68]. SPM concentrations exceeded the advisory limit for turbidity of 5 NTU (~20 mg/L) in drinking water by WHO [69] on three sampling days, on 19 June 2012 in Lake Grenada at seven sampling sites, on 20 June 2012 in Lake Enid at four sampling sites, and on 22 May 2013 in Ross Barnett Reservoir at two sampling sites. A comparison of organic and inorganic SPM concentrations indicates the relative contribution of particulates from biotic (e.g., algae and bacteria) and abiotic (e.g., silt and sediment) sources in the absence of confounding factors such as high winds causing resuspension of bottom sediments. Of all the sampling days, a higher organic SPM than the inorganic counterpart was observed on 22 May 2013 in Ross Barnett Reservoir, on 20 June 2012 in Lake Enid, and on 19 June 2012 in Lake Grenada, indicating the possible presence of algal blooms in these lakes on these days. On other sampling dates, the concentration of organic SPM was higher at a few sites, which can be attributed to higher biological activity at those sites, whereas a higher concentration of inorganic SPM at other sites suggested a lower contribution of particulate matter from the algal blooms at these sites to the total suspended particulate matter. Although organic SPM concentrations do not provide conclusive information on algal sources, they provide a preliminary idea on the proportions of organic and inorganic sources of the total SPM concentrations. The ChemTax, microscopic and bacterial analyses conducted in this study provide further insights into the biotic populations in these lakes.
Figure 5 shows the chlorophyll a concentrations in comparison with cyanobacterial-specific pigment phycocyanin concentrations. Overall, higher concentration of chlorophyll a was observed in 2012 than 2013. Chlorophyll a is one of the most-often used estimators of total algal biomass in water bodies. In addition to the “bottom-up” (e.g., nutrients, light, etc.) and “top-down” controls (e.g., grazing), physical forcings such as decreased residence time or increased rate of flushing due to increased rainfall probably resulted in less phytoplankton production during summer 2013 as compared to summer 2012. As chlorophyll a is common to all taxonomic groups, its use in showing phytoplankton distributions does not permit taxonomic differentiation [70]. In addition to chlorophyll a, phytoplankton contain a range of accessory pigments as part of their photosynthetic systems [71]. Phycocyanin is such an accessory pigment, which is unique to cyanobacteria [72]. The presence of phycocyanin in all the lakes demonstrates the relative presence of cyanobacteria in all the lakes. The phycocyanin concentrations corresponded well with the chlorophyll a concentrations for the sites where cyanobacteria was the dominant algal group. The ChemTax analyses conducted in this study provide further insights into the phytoplankton community structure of these lakes.
Phytoplankton photopigment concentrations were analyzed using ChemTax to determine the relative abundances of seven major algal groups in units of µg chlorophyll a per liter. Qualitative microscopic examination of samples confirmed the presence of all seven algal groups. ChemTax analysis exhibited that cyanobacteria were always present in all the four lakes (Figure 6). In 2012, Ross Barnett Reservoir was sampled twice, on 13 June and on 19 June. Cyanobacteria were not the dominant algal group on 13 June while diatoms and euglenophytes dominated, however cyanobacteria achieved highest abundance among all the algal groups on 29 June. In 2013, Ross Barnett Reservoir was sampled twice as well, on 22 May and on 10 July. The cyanobacterial concentration was low in comparison to euglenophytes on 22 May, however on 10 July cyanobacterial concentrations were relatively higher, although euglenophytes and chlorophytes were dominant. In Lake Grenada, cyanobacteria were not the dominant algal group on the sampling days, neither in 2012 nor in 2013. In Lake Enid, cyanobacteria were the dominant algal group on the sampling days both in 2012 and 2013. On 26 July 2012, the sites closer towards the dam in Lake Sardis showed higher concentrations of cyanobacteria, while upstream sites showed higher concentrations of euglenophytes. Site 12, which is the farthest site from the dam in the upstream direction, showed the highest cyanobacterial concentrations. On 18 June 2013 cyanobacterial concentrations were lower than 2012 concentrations in Lake Sardis. In summary, cyanobacteria dominated in Lake Enid on both 2012 and 2013 sampling days, on one of the sampling days in Ross Barnett Reservoir in 2012, and in half of Lake Sardis on 26 July 2012. Although the relative abundances of algal groups were quite variable between 2012 and 2013 on other dates, cyanobacteria were always present in these lakes. To characterize detailed species composition, FlowCAM is currently being used in tandem with quantitative PCR (qPCR) and additional microscopic examinations.
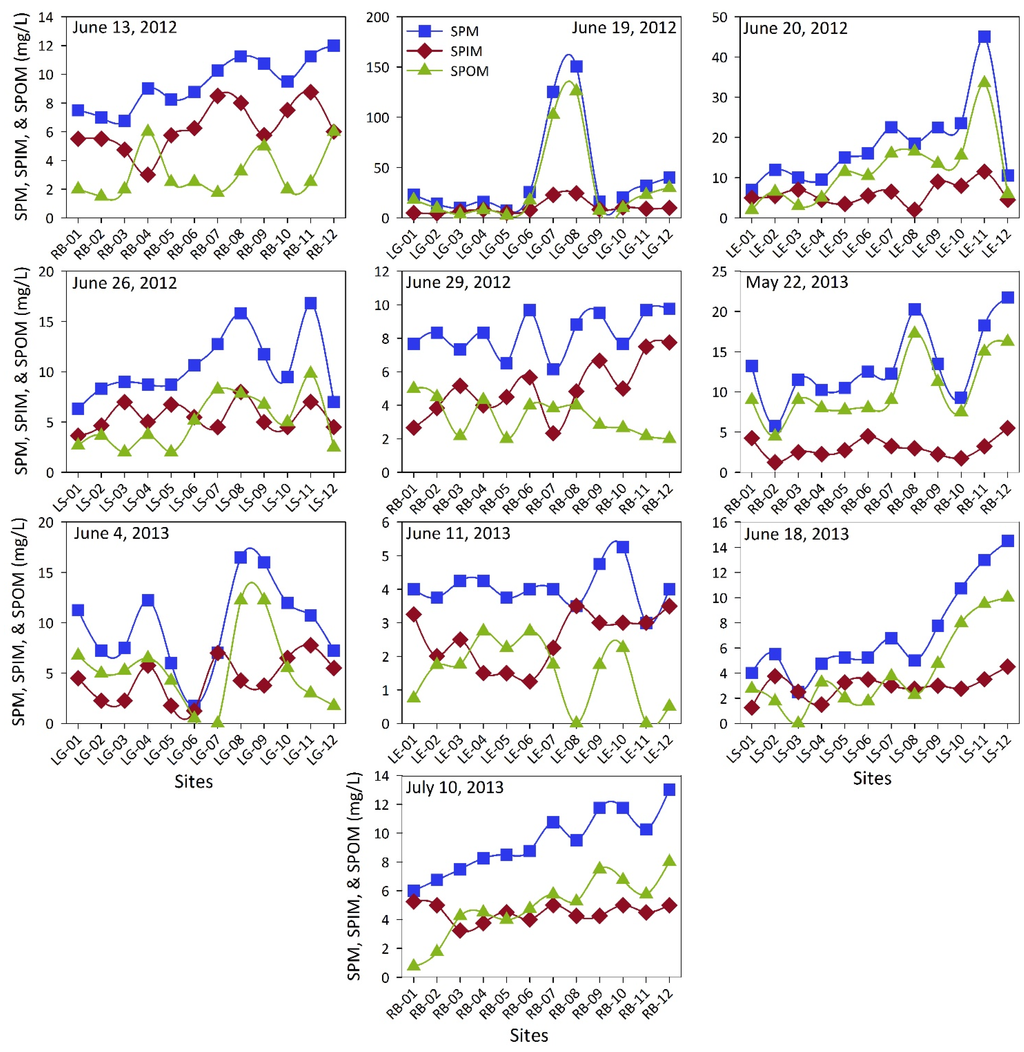
Figure 4.
Suspended particulate matter (SPM), suspended inorganic particulate matter (SPIM), and suspended organic particulate matter (SPOM) concentrations at twelve sampling sites in each of the lakes (RB = Ross Barnett Reservoir, LG = Lake Grenada, LE = Lake Enid, and LS = Lake Sardis) with sampling dates indicated.
Figure 4.
Suspended particulate matter (SPM), suspended inorganic particulate matter (SPIM), and suspended organic particulate matter (SPOM) concentrations at twelve sampling sites in each of the lakes (RB = Ross Barnett Reservoir, LG = Lake Grenada, LE = Lake Enid, and LS = Lake Sardis) with sampling dates indicated.


Figure 5.
Chlorophyll a concentrations shown with cyanobacterial unique pigment phycocyanin concentrations at twelve sampling sites in each of the lakes (RB = Ross Barnett Reservoir, LG = Lake Grenada, LE = Lake Enid, and LS = Lake Sardis) with sampling dates indicated.
Figure 5.
Chlorophyll a concentrations shown with cyanobacterial unique pigment phycocyanin concentrations at twelve sampling sites in each of the lakes (RB = Ross Barnett Reservoir, LG = Lake Grenada, LE = Lake Enid, and LS = Lake Sardis) with sampling dates indicated.
Members of the cyanobacterial genera, Microcystis, Anabaena, and Oscillatoria produce cyclic peptides, termed microcystins, which are potent liver toxins [73]. Adverse effects of these toxins on human health has been widely recognized [74]. These phycotoxins are also responsible for deaths of fish, birds, wild animals, and agricultural livestock in many countries where freshwaters contain toxic cyanobacterial blooms [73,75,76]. Among more than 80 microcystins identified to date, Microcystin-LR is among the most frequent and most toxic microcystin congeners, hence WHO has released guidelines suggesting a microcystin-LR concentration of <1 µg/L for drinking water and <20 µg/L for recreational waters [77]. U.S. EPA recommended health advisory levels for drinking water are <0.3 µg/L for children under six years of age and <1.6 µg/L for adults [78,79]. While several U.S. states including Minnesota, Ohio, and Oregon have adopted WHO’s and EPA’s drinking water guidance for microcystin-LR concentrations [80], and several other states have implemented standards for microctsin-LR levels in recreational waters [74,80], the state of Mississippi has no guidelines, water quality criteria and standards, or regulations concerning the management of harmful algal blooms in drinking water under the Safe Drinking Water ACT (SDWA) or in the ambient waters under the Clean Water Act (CWA).
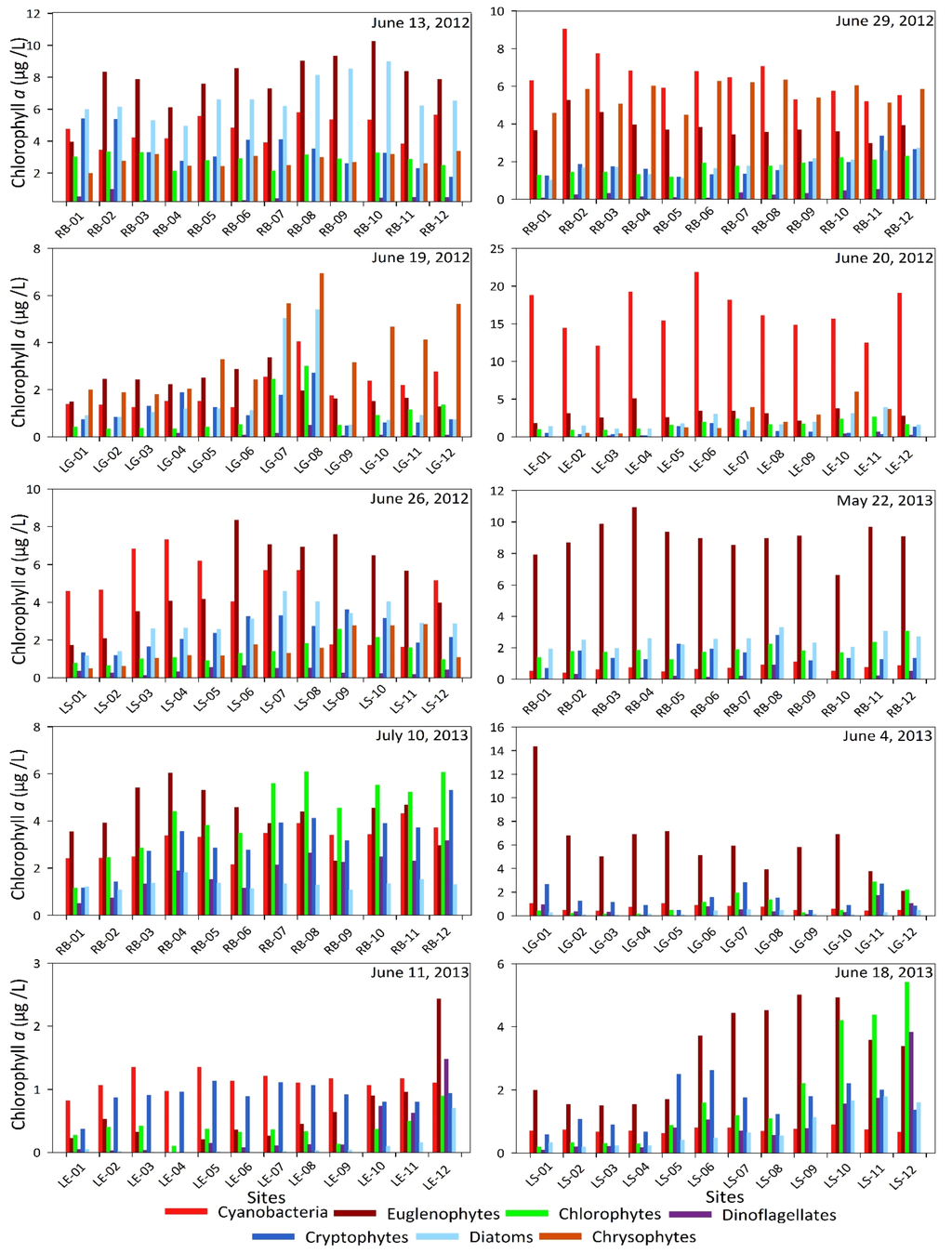
Figure 6.
Relative abundance of major algal groups determined by ChemTax program using HPLC photo-pigment data at twelve sampling sites in each of the lakes (RB = Ross Barnett Reservoir, LG = Lake Grenada, LE = Lake Enid, and LS = Lake Sardis) with sampling dates indicated.
Figure 6.
Relative abundance of major algal groups determined by ChemTax program using HPLC photo-pigment data at twelve sampling sites in each of the lakes (RB = Ross Barnett Reservoir, LG = Lake Grenada, LE = Lake Enid, and LS = Lake Sardis) with sampling dates indicated.
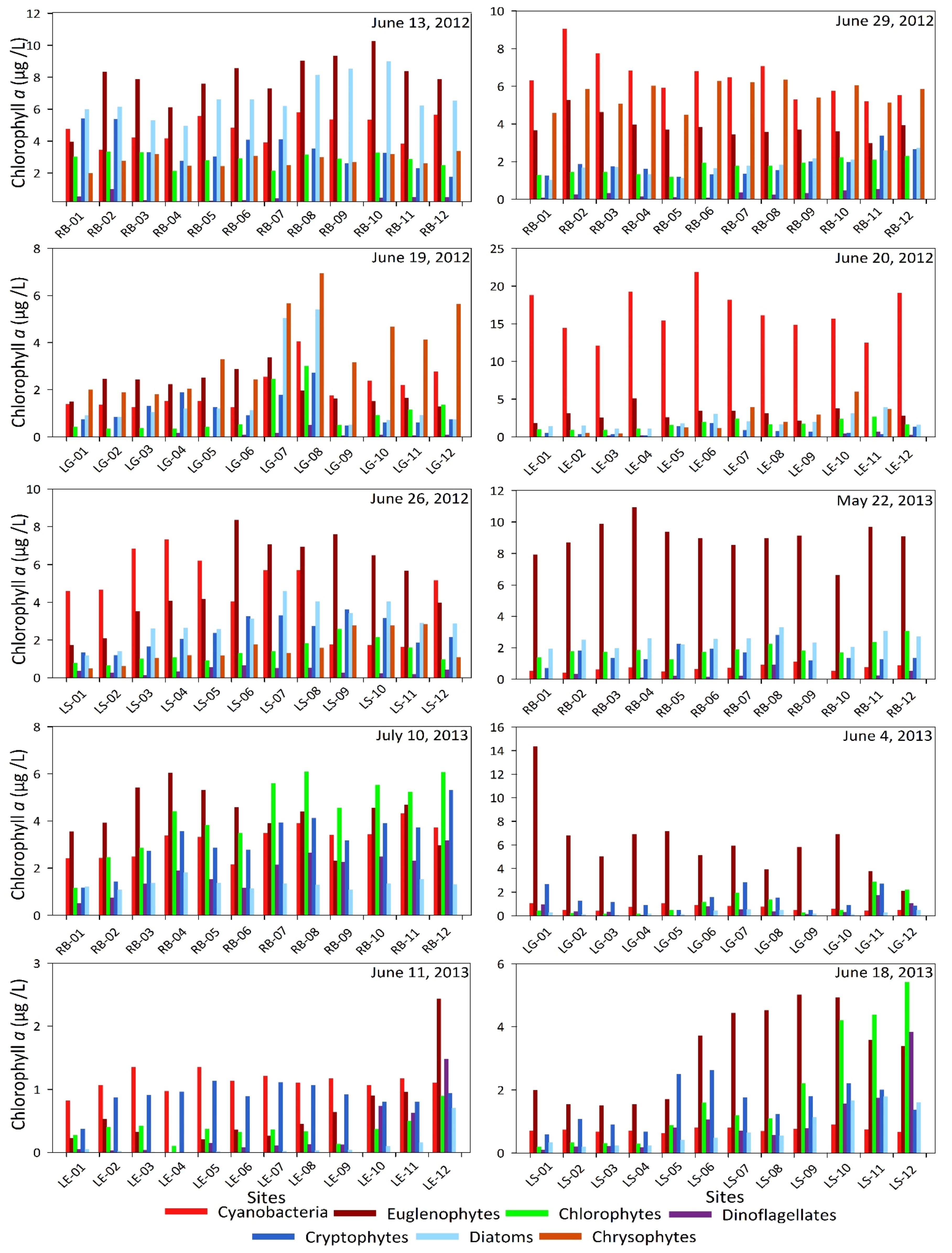
Figure 7 shows the cellular microcystin-LR concentrations in comparison with chlorophyll a in Lakes Sardis, Enid, and Grenada and Ross Barnett Reservoir. The microcystin-LR concentrations mostly followed the pattern of chlorophyll a concentrations. Although the concentrations never exceeded 1 µg/L, which is WHO’s guideline value for drinking water, they exceeded U.S. EPA’s advisory level of 0.3 µg/L for children under six years of age many times (at one site in Ross Barnett Reservoir on 29 June 2013, at nine sites in Ross Barnett Reservoir on 22 May 2013, at three sites in Lake Grenada on 4 June 2013, at three sites in Lake Enid on 11 June 2013, at three sites in Lake Sardis on 18 June 2013 and at eight sites in Ross Barnett Reservoir on 10 July 2013). At all other sampling sites in all the four lakes, although the concentrations were less than 0.3 µg/L, the toxin was always present. Because Ross Barnett Reservoir is used as a source for drinking water, the occurrence of microcystin-LR greater than 0.3 µg/L can be a major concern for children under six years of age. When the concentrations were less than 0.3 µg/L, although drinking the water from these four lakes may not present any imminent danger to human health from microcystin-LR toxicity, consuming fish from these lakes could pose a danger due to potential bioaccumulation and biomagnification of microcystin-LR in fish tissues. One of our previous studies reported that the blue crabs contained high concentration of microcystin through bioaccumulation which exceeded the total daily intake guidelines of WHO for human consumption [4]. Hence, these cyanotoxin concentrations pose a danger to human health, especially since these lakes are very popular for fishing. In addition to human health impacts, these concentrations also pose a serious danger to the aquatic life and the whole aquatic ecosystems as the toxin propagates through the food web.
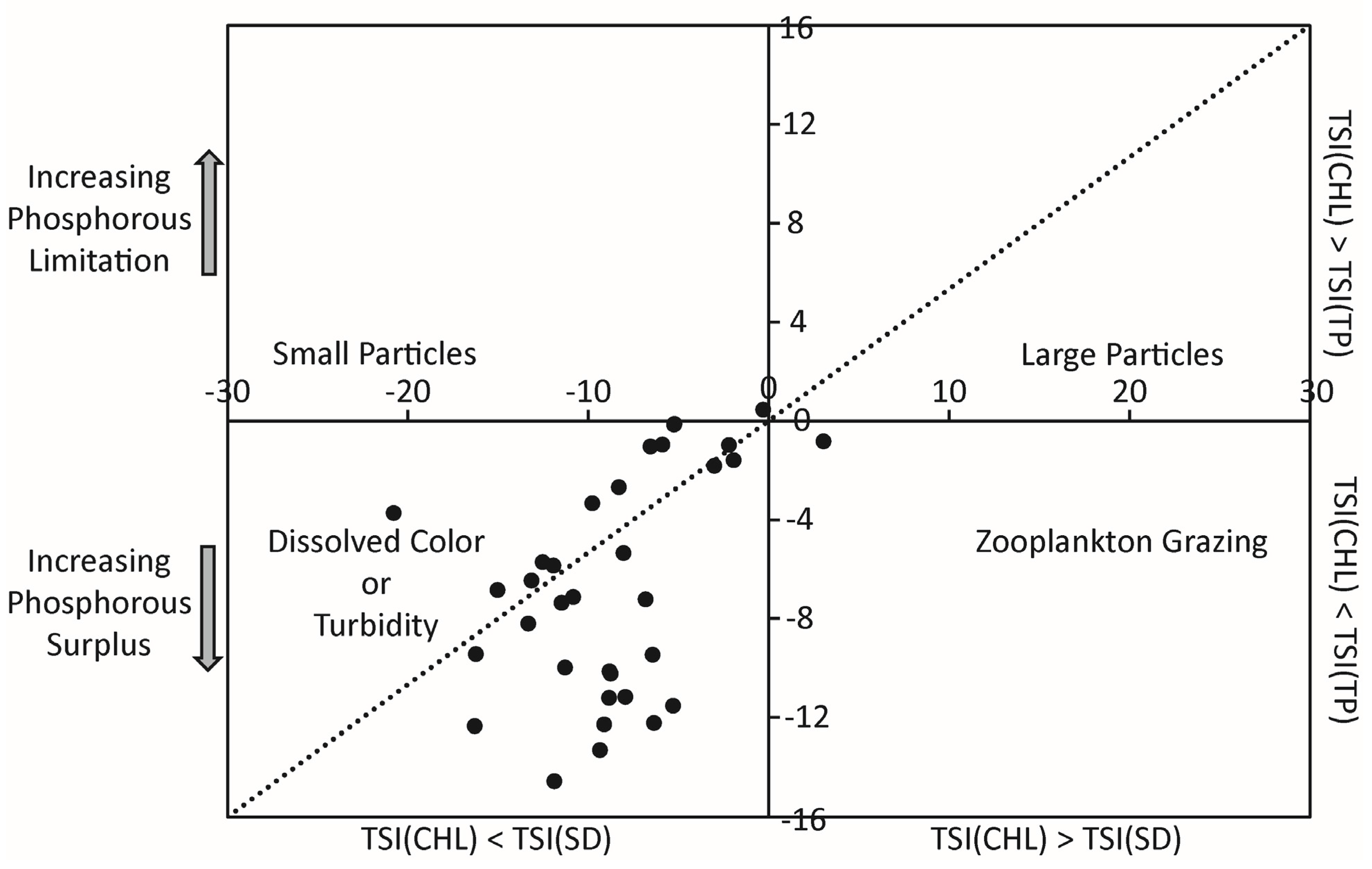
Water samples from five sampling trips in 2013 were analyzed for eleven nutrients that are shown in Figure 8. The total nitrogen concentrations ranged from 1.38–1.69 mg/L (mean = 1.5 mg/L) in Ross Barnett Reservoir on 22 May 2013, from 1.23–1.51 mg/L (mean = 1.37 mg/L) in Lake Grenada on 4 June 2013, from 1.07–2.27 mg/L (mean = 1.37 mg/L) in Lake Enid on 11 June 2013, from 0.97–1.23 mg/L (mean = 1.11 mg/L) in Lake Sardis on 18 June 2013, and from 0.53–1.59 mg/L (mean = 0.75 mg/L) in Ross Barnett Reservoir on 10 July 2013. The total phosphorus concentrations ranged from 0.08–0.1 mg/L (mean = 0.09 mg/L) in Ross Barnett Reservoir, from 0.04–0.06 mg/L (mean = 0.05 mg/L) in Lake Grenada, from 0.036–0.042 mg/L (mean = 0.039 mg/L) in Lake Enid, and from 0.032–0.045 mg/L (mean = 0.038 mg/L) in Lake Sardis, and from 0.041–0.54 mg/L (mean = 0.049 mg/L) in Ross Barnett Reservoir on the corresponding sampling days. Overall, the total nitrogen concentrations were slightly over 1 mg/L (1000 µg/L) in all lakes and total phosphorous concentrations ranged from 0.04–0.1 mg/L (40–100 µg/L). Trophic State Indices (TSI) were calculated using the chlorophyll a concentrations, total phosphorus concentrations, total nitrogen concentrations and Secchi depth following Carlson [81]. TSI derived from chlorophyll a concentrations (TSI (CHL)) indicated that all the lakes were eutrophic, except for 11 June 2013 when Lake Enid was mostly mesotrophic. TSI computed using total phosphorous concentrations (TSI (TP)), total nitrogen concentrations (TSI (TN)) and the available Sechhi depth (TSI (SD)) for the five sampling days in 2013 also indicated that the lakes were eutrophic. When TSI (CHL)–TSI (TP) was plotted on the vertical axis against TSI (CHL)–TSI (SD) on the horizontal axis following Carlson [82], the indices fell mostly in the southwest quadrant, suggesting a situation where transparency was dominated by dissolved color (Figure 9) corroborating water turbidity that was visually observed on sampling days. Thus, parallel factor analysis of the dissolved organic matter is underway for examining the source and fate of the dissolved matter.
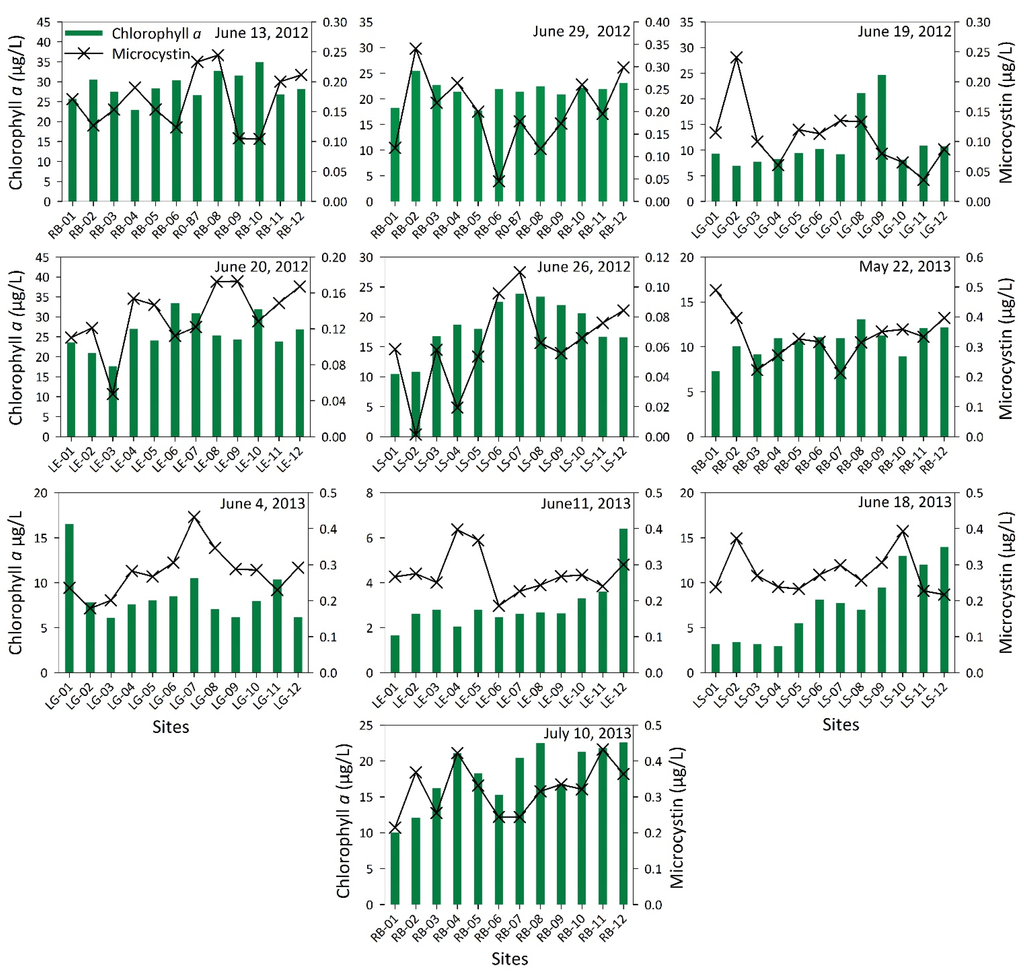
Figure 7.
Cellular microcystin concentrations shown with chlorophyll a concentrations at twelve sampling sites in each of the lakes (RB = Ross Barnett Reservoir, LG = Lake Grenada, LE = Lake Enid, and LS = Lake Sardis) with sampling dates indicated.
Figure 7.
Cellular microcystin concentrations shown with chlorophyll a concentrations at twelve sampling sites in each of the lakes (RB = Ross Barnett Reservoir, LG = Lake Grenada, LE = Lake Enid, and LS = Lake Sardis) with sampling dates indicated.

Total nitrogen to total phosphorus ratio (TN:TP) ranged from 14.82–20.30 (mean = 17.18) in Ross Barnett Reservoir, from 22.01–33.34 (mean = 28.71) in Lake Grenada, from 29.51–55.60 (mean = 34.71) in Lake Enid, and from 24.86–31.20 (mean = 29.20) in lake Sardis. A TN:TP ratio of 10:1 differentiates between lakes with cyanobacterial dominance (TN:TP < 10:1) and lakes without such dominance (TN:TP > 10:1) [83,84]. When the ratio is less than 10:1, then nitrogen becomes the limiting nutrient. In nitrogen limiting conditions (TN:TP < 10:1), nitrogen-fixing cyanobacterial genera (e.g., Anabaena, Aphanizomenon, Cylindrospermopsis, Gloeotrichia, and Nodularia) have a competitive advantage over other algal groups. When nitrogen is not limited (TN:TP > 10:1), proliferation of non-N2-fixing genera (Microcystis, Oscillatoria, Lyngbya) and other algal groups is observed [84]. The nutrients measured for four sampling days in 2013 indicated that the TN:TP mass ratio was greater than 10:1 in all lakes, which is why cyanobacteria did not achieve highest abundance in Lake Sardis, Lake Grenada and Ross Barnett Reservoir. However, Lake Enid was dominated by cyanobacteria despite having a TN:TP ratio greater than 10:1. Therefore, it was our expectation that the cyanobacterial genera that was present in Lake Enid would be mostly non-N2-fixing genera. Our expectation was proved correct by an examination of the phytoplankton community structure in Lake Enid on the same date using FlowCAM that showed the dominance of Microcystis cf. firma, Microcystis wesenbergii, Chlamydomonas, and Euglenophytes, all of which are non-N2-fixing.
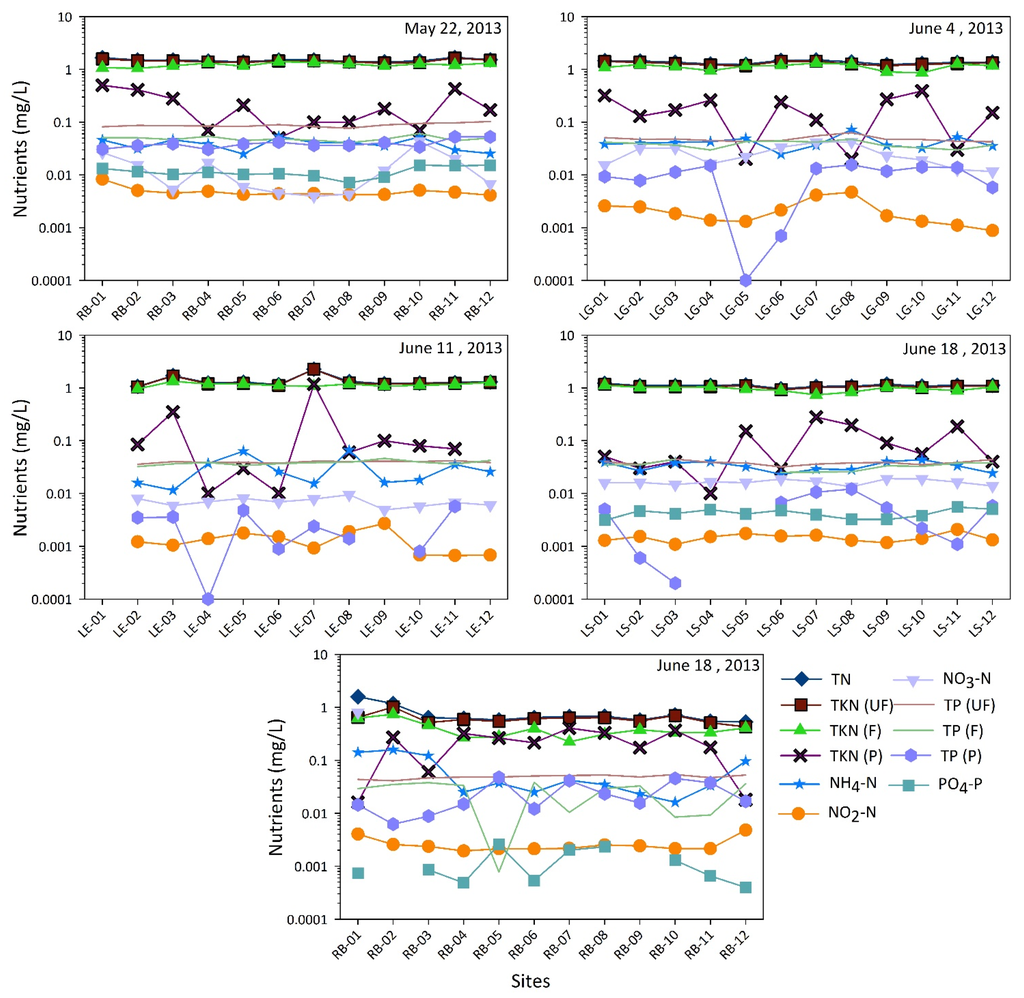
Figure 8.
Nutrients at twelve sampling sites in each of the lakes (RB = Ross Barnett Reservoir, LG = Lake Grenada, LE = Lake Enid, and LS = Lake Sardis) with sampling dates indicated.
Figure 8.
Nutrients at twelve sampling sites in each of the lakes (RB = Ross Barnett Reservoir, LG = Lake Grenada, LE = Lake Enid, and LS = Lake Sardis) with sampling dates indicated.
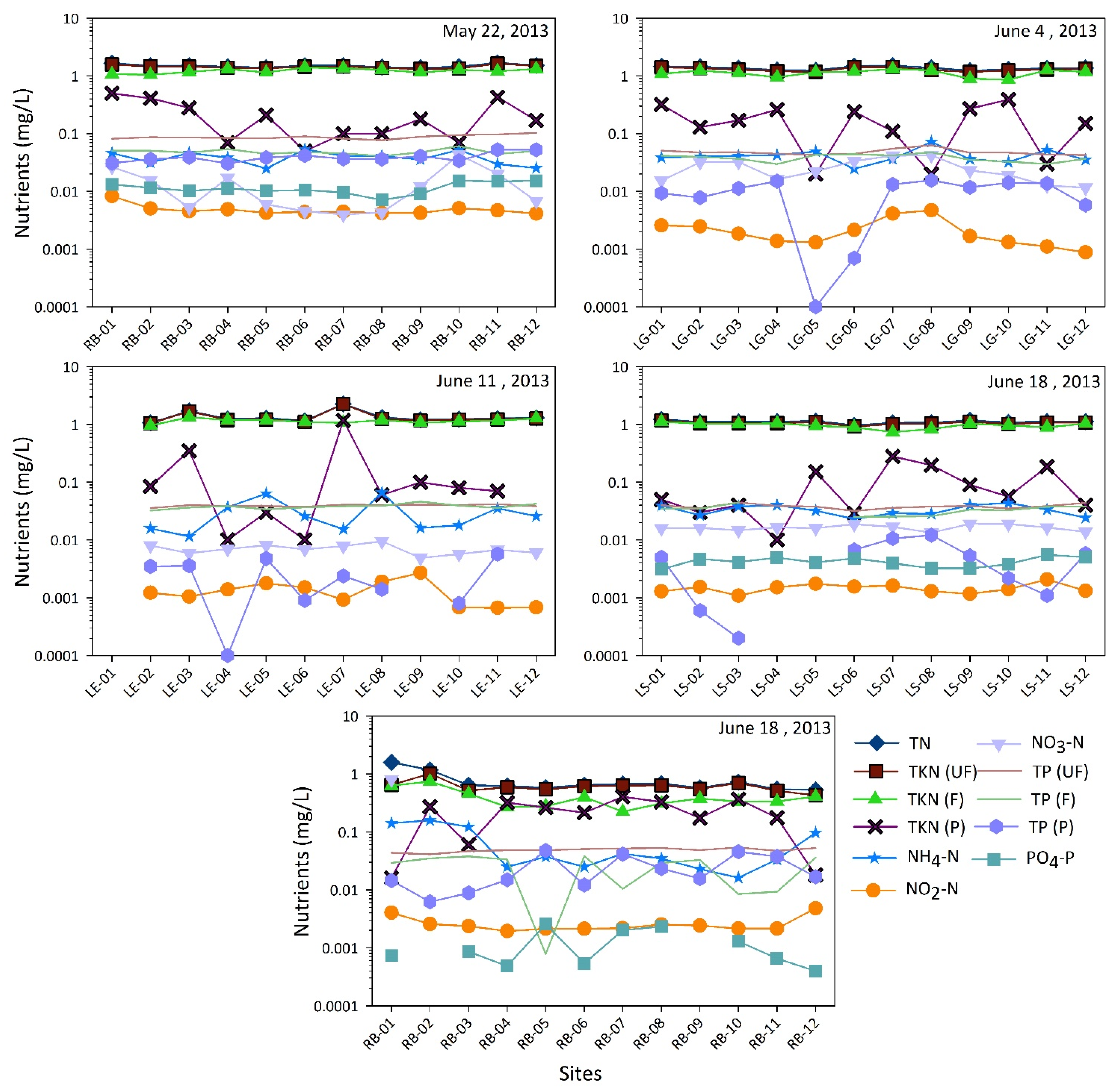
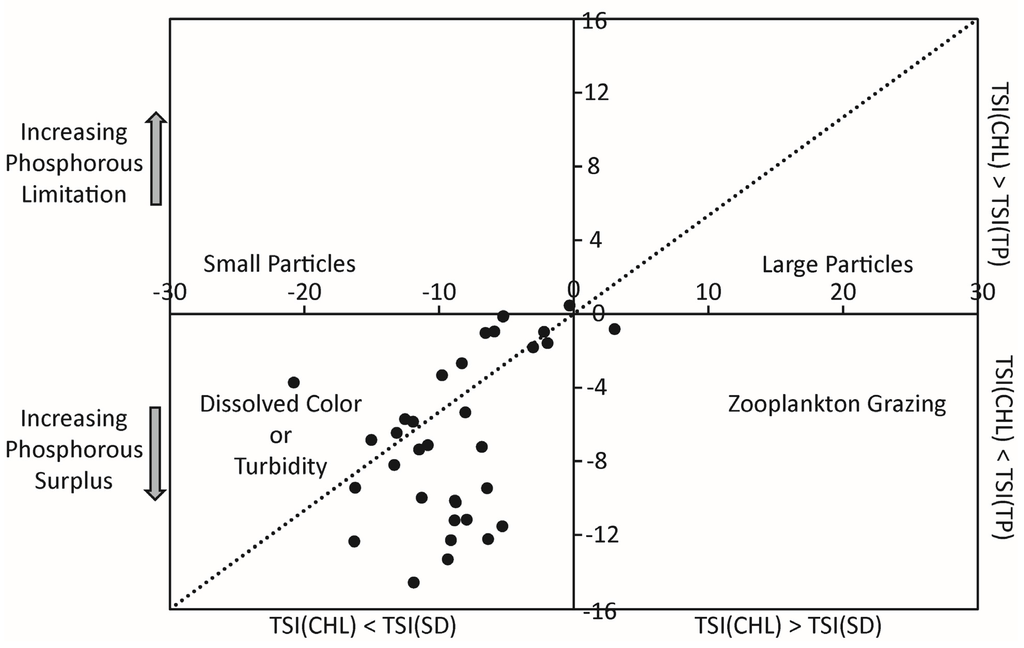
Figure 9.
Illustration of possible causes of deviations between the trophic state indices (TSI) derived from chlorophyll a concentrations, Secchi depth and total phosphorous concentrations.
Figure 9.
Illustration of possible causes of deviations between the trophic state indices (TSI) derived from chlorophyll a concentrations, Secchi depth and total phosphorous concentrations.
From the two sampling dates during summer 2012 in Ross Barnett Reservoir, it was found that cyanobacteria was not the dominant algal group on 13 June while diatoms and euglenophytes dominated, however cyanobacteria achieved highest abundance among all the algal groups on 29 June. There were several rainfall events in the upper Pearl River watershed before the 13 June 2012 sampling trip that possibly increased the nitrogen concentration in the Ross Barnett Reservoir through runoff of nitrogen from soil. Thus, a higher TN:TP ratio (>10:1) facilitated proliferation of numerous algal groups. However, there was no rainfall for two weeks before 29 June 2012 in the upper Pearl River watershed. Within these two weeks, it is possible that nitrogen was used up resulting in nitrogen limiting conditions. Consequently, a lower TN:TP ratio (<10:1) on 29 June 2012 supported a proliferation of nitrogen-fixing cyanobacterial genera. In addition, an increased residence time of water resulted in greater phytoplankton production. Hence, cyanobacteria was the dominant algal group on 29 June 2012. Indeed, nitrogen-fixing cyanobacteria including Anabaenopsis circularis, Aphanizomenon flos aque, Gloeocapsa sp. were abundant on 29 June 2012, whereas non-N2-fixing cyanobacteria including Microcystis wesenbergii and Microcystis flos aquae were abundant on 13 June 2012 in Ross Barnett Reservoir as indicated by the detailed phytoplankton community structure obtained using the imaging microscope, FlowCAM.
Bacterial analysis included counts for total coliforms only in 2012, however, in 2013 and 2014, water samples were analyzed for heterotrophic, enterococcus and fecal coliform (E. coli) bacteria in addition to total coliforms (Figure 10). In drinking water, EPA Federal Maximum Contaminant Level Goal (MCLG) for total coliform bacteria is no more than five percent of samples should test positive during one month, for water systems that collect at least 40 routine samples per month [83]. The pathogens found in the water bodies are not indicative of the conditions of tap water; however knowing their concentrations in source waters helps water treatment facilities decide the required treatment, as it is difficult to measure pathogens in the treated water because of the very low levels. EPA’s Maximum Residual Disinfectant Level (MRDL; the highest level of a disinfectant allowed in drinking water) recommends no more than 500 heterotrophic bacterial colonies per milliliter. Presence of E. coli and enterococci indicates that the water may be contaminated with human or animal wastes, which may cause short-term effects, such as diarrhea, cramps, nausea, headaches, or other symptoms that could pose severe health risk for infants, young children, and people with compromised immune systems. Hence, EPA guideline value for E. coli and enterococci in drinking water is zero. For recreational waters, EPA’s recommended total coliforms density used to be 2300 colonies per 100 mL of water [85]. While total coliforms are no longer recommended by EPA as a pathogen indicator in recreational waters, total coliforms are still the standard test for pathogens in drinking water because their presence indicates contamination by an outside source. EPA recommends E. coli and enterococci as the best indicator of health risk from water contact in recreational waters. As per the EPA recommendations, presence of >30 colonies/100 mL of enterococci or >100 colonies/100 mL of E. coli can be a concern for recreational waters [86].
In 2012, total coliform colonies per 100 mL ranged from 540–1120 (mean = 788) for Lake Grenada, 160–760 (mean = 440) for Lake Enid, 40–800 (mean = 334) for Lake Sardis, and 20–600 (mean = 140) for Ross Barnett Reservoir. In 2013, they ranged from 0–7850 (mean = 4630) for Lake Grenada, 0–1960 (mean = 602) for Lake Enid, 20–1900 (mean = 624) for Lake Sardis, 610 to >10,000 (mean >10,000) for Ross Barnett Reservoir on 22 May, and 50–4480 (mean = 1464) for Ross Barnett Reservoir on 29 June. In 2014, the mean total coliform colonies in Ross Barnett Reservoir ranged from 0–7400 (mean = 3200) per 100 mL water. Thus, the total coliform density exceeded the EPA recommended old recreational standards at least twice in Ross Barnett Reservoir and once in Lake Grenada. Among all these lakes, Ross Barnett Reservoir is used as a source for drinking water. Although total coliform was not sampled as many times as required by EPA for monitoring drinking water, such high concentration of total coliform bacteria at most of the sites on all the sampling days indicates the necessity for proper treatment of the water before it reaches the taps. In addition, pathogen control measures need to be implemented in the reservoir to minimize the usage of disinfectants during water treatment.
In 2013, heterotrophic bacterial concentrations per 1 mL of water ranged from 4–83 (mean = 44) for Lake Grenada, 4–46 (mean = 15) for Lake Enid, 13–66 (mean = 35) for Lake Sardis, 21–63 (mean = 41) for Ross Barnett Reservoir on 22 May, and 50–180 (mean = 121) for Ross Barnett Reservoir on 29 June. In 2014, heterotrophic bacterial colonies in Ross Barnett Reservoir ranged from 98–181 (mean = 141) per 1 mL of water. Since the concentrations of heterotrophic bacterial colonies found did not exceed the EPA guideline value of 500 colonies per milliliter of water, we report that they did not pose a water quality problem for any of the lakes. Enterococci and E. coli colonies per 100 mL of water in 2013 ranged from 0–27 (mean = 5) and 0–65 (mean = 9) for Lake Grenada, 0–550 (mean = 85) and 0–35 (mean = 12) for Lake Enid, 0–21 (mean = 8) and 0–20 (mean = 5) for Lake Sardis, 0–10 (mean = 3) and 0–30 (mean = 6) for Ross Barnett Reservoir on 22 May, and 0–18 (mean = 4) and 0–30 (mean = 4) for Ross Barnett Reservoir on 29 June, respectively. In 2014, E. coli and enterococci colonies in Ross Barnett Reservoir ranged from 2–128 (mean = 32) and 4–88 (mean = 30) per 100 mL water, respectively. While E. coli counts were less than the EPA recommended levels for recreational waters, enterococci counts exceeded EPA recommended levels in two instances, once in Lake Enid on the sampling day in 2013 and another time in Ross Barnett Reservoir on the sampling day in 2014. Since these lakes are heavily used for recreational activities, and especially since Ross Barnett Reservoir is used as a drinking water source, we recommend continuous monitoring of these lakes for microbial pathogens.
Water samples from all five sampling trips in 2012 and four sampling trips in 2013 were analyzed for 23 trace elements and heavy metals that included beryllium, aluminum, vanadium, chromium, manganese, iron, cobalt, nickel, copper, zinc, arsenic, selenium, strontium, molybdenum, silver, cadmium, antimony, barium, mercury, thallium, lead, thorium, and uranium (Figure 11). EPA’s national primary drinking water regulations include recommendations for the maximum contaminant level (MCL) of beryllium, chromium, arsenic, selenium, cadmium, antimony, barium, mercury, thallium, lead, and uranium, and the national secondary drinking water regulations include recommendations for the MCL of aluminum, copper, iron, manganese, silver, and zinc [83]. The mean, minimum and maximum concentrations of these EPA recommended trace elements and heavy metals are presented in Table 1 with the EPA recommended MCLs, instrumental detection limits and highlighted values of the elements that exceeded the EPA recommended MCLs. The lakes exceeded the EPA recommended MCL for aluminum, iron and manganese on many occasions. These elements include EPA’s national secondary drinking water regulations that are non-enforceable guidelines but may cause cosmetic effects (such as skin or tooth discoloration) or aesthetic effects (such as taste, odor, or color) in drinking water. Among the heavy metals, arsenic was found at all sites in all lakes exceeding EPA recommended MCL at two sites in Ross Barnett Reservoir on 10 July 2013 (Figure 11; Table 1). Although mercury and thallium were below the detection limits in the waters of all the lakes, cadmium was found at one site in Lake Enid on 20 June 2012, at two sites in Ross Barnett Reservoir on 29 June 2012, at all sites in Lake Grenada on 4 June 2013, at four sites in Lake Enid on 11 June 2013, at seven sites in Lake Sardis on 18 June 2013, and at all sites in Ross Barnett Reservoir on 10 July 2013. Chromium was found at all sites in all lakes except for Ross Barnett Reservoir on 29 June 2012, Lake Sardis on 26 June 2012, and at eleven sites in Lake Enid on 20 June 2012, when it was below the detection limit. Lead was found at almost all the sites in all the four lakes (Figure 11). The presence of these trace elements and heavy metals warrants continuous monitoring, investigation of fate and transport of pollutants, and implementation of best management practices for all these lakes.
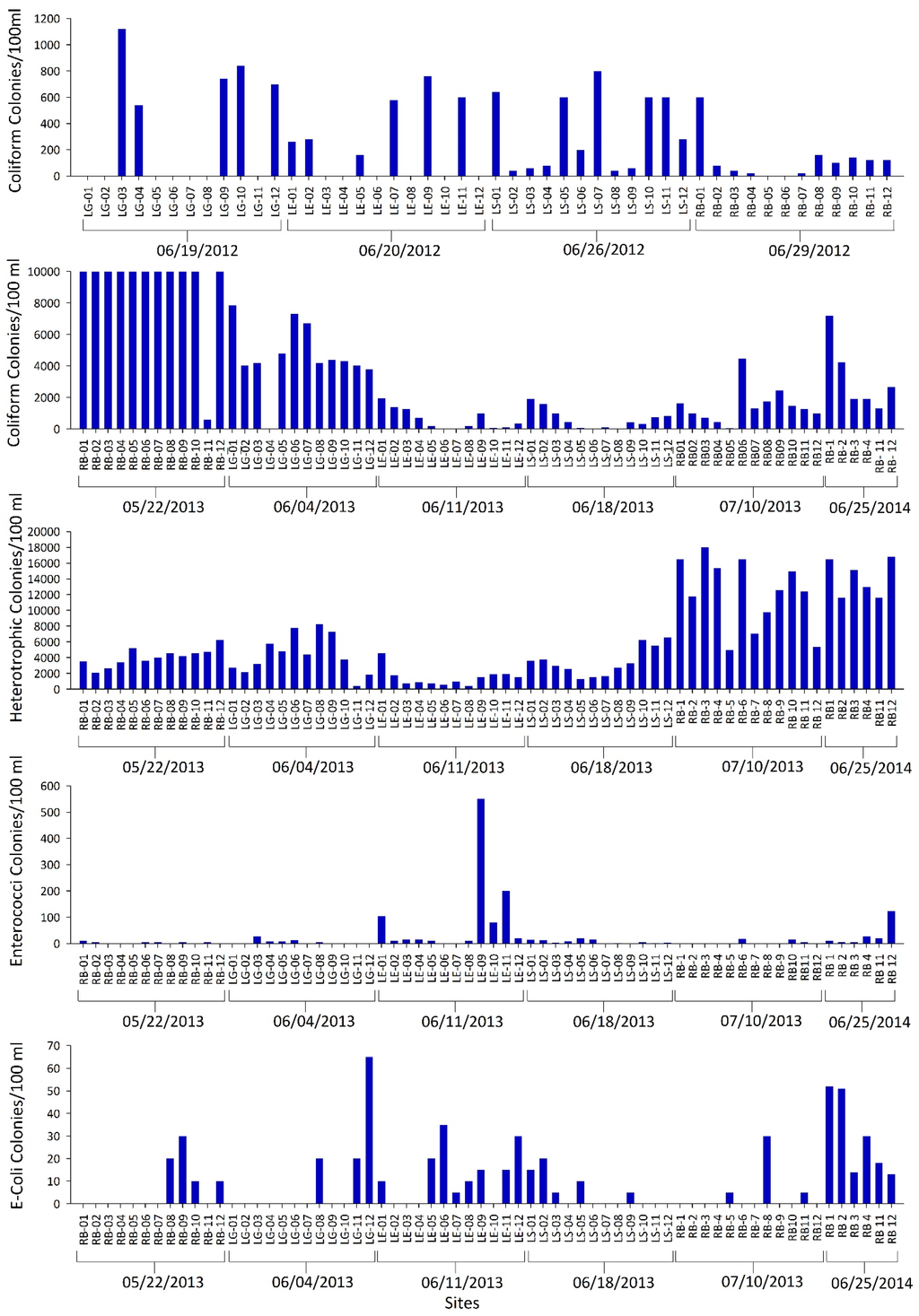
Figure 10.
Bacterial colony counts at twelve sampling sites in each of the lakes (RB = Ross Barnett Reservoir, LG = Lake Grenada, LE = Lake Enid, and LS = Lake Sardis) with sampling dates indicated.
Figure 10.
Bacterial colony counts at twelve sampling sites in each of the lakes (RB = Ross Barnett Reservoir, LG = Lake Grenada, LE = Lake Enid, and LS = Lake Sardis) with sampling dates indicated.

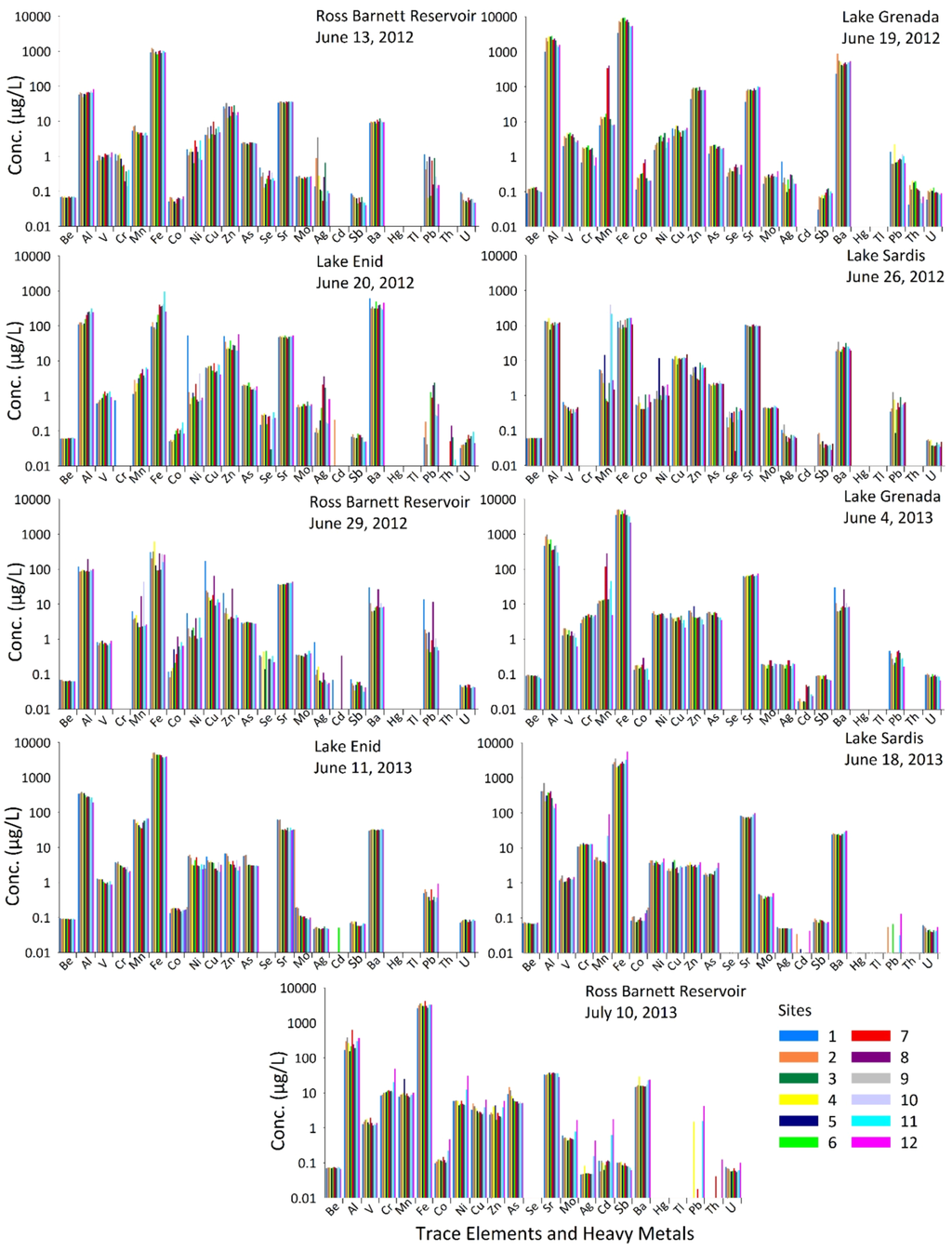
Figure 11.
Trace elements and heavy metals at twelve sampling sites in each of the lakes (RB = Ross Barnett Reservoir, LG = Lake Grenada, LE = Lake Enid, and LS = Lake Sardis) with sampling dates indicated.
Figure 11.
Trace elements and heavy metals at twelve sampling sites in each of the lakes (RB = Ross Barnett Reservoir, LG = Lake Grenada, LE = Lake Enid, and LS = Lake Sardis) with sampling dates indicated.
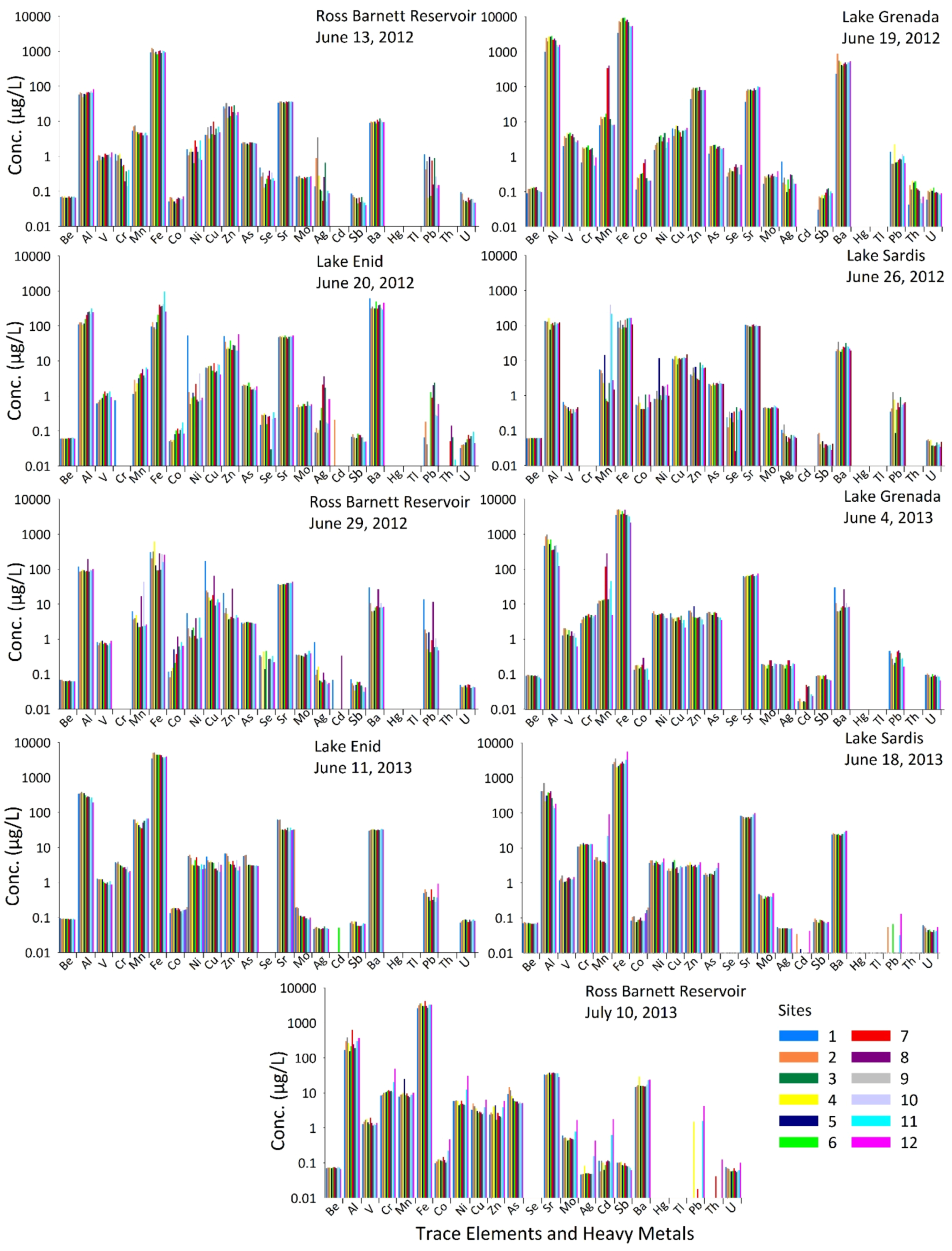

Table 1.
Mean, minimum, and maximum concentration of selected trace elements and heavy metals measured at 12 sites in each of the lakes (RB = Ross Barnett Reservoir, LG = Lake Grenada, LE = Lake Enid, and LS = Lake Sardis) given in µg/L with EPA recommended maximum contaminant level (MCL) in µg/L, detection limits (DL) in µg/L, and values highlighted for the elements that exceeded the MCLs indicated (BD—below detection limit).
| Elements and Metals | Be | Cr | As | Se | Cd | Sb | Ba | Hg | Tl | Pb | U | Al | Cu | Fe | Mn | Ag | Zn | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| MCL (µg/L) | 4 | 100 | 10 | 50 | 5 | 6 | 2000 | 2 | 2 | 15 | 30 | 200 | 1000 | 300 | 50 | 100 | 5000 | ||
| DL (µg/L) | 0.008 | 0.023 | 0.026 | 0.018 | 0.012 | 0.015 | 0.008 | 0.005 | 0.003 | 0.013 | 0.004 | 0.035 | 0.018 | 0.042 | 0.012 | 0.008 | 0.024 | ||
| RB | 13 June 2012 | Mean | 0.069 | 0.657 | 2.39 | 0.272 | BD | 0.061 | 9.94 | BD | BD | 0.476 | 0.061 | 65.0 | 5.54 | 991 | 5.10 | 0.521 | 21.7 |
| Minimum | 0.066 | 0.142 | 2.16 | 0.129 | BD | 0.040 | 8.59 | BD | BD | 0.065 | 0.047 | 48.5 | 3.20 | 809 | 3.99 | 0.052 | 12.3 | ||
| Maximum | 0.073 | 1.20 | 2.54 | 0.478 | BD | 0.086 | 12.3 | BD | BD | 1.14 | 0.095 | 82.5 | 9.72 | 1217 | 7.52 | 3.52 | 33.3 | ||
| LG | 19 June 2012 | Mean | 0.117 | 1.47 | 1.87 | 0.444 | BD | 0.084 | 492 | BD | BD | 0.977 | 0.098 | 2066 | 5.81 | 7012 | 70.6 | 0.246 | 83.2 |
| Minimum | 0.090 | 0.551 | 1.22 | 0.270 | BD | 0.031 | 233 | BD | BD | 0.619 | 0.059 | 992 | 3.72 | 3494 | 7.80 | 0.097 | 44.2 | ||
| Maximum | 0.135 | 2.11 | 2.17 | 0.618 | BD | 0.124 | 875 | BD | BD | 2.28 | 0.131 | 2849 | 7.74 | 9415 | 398 | 0.726 | 98.8 | ||
| LE | 20 June 2012 | Mean | 0.062 | 0.740 | 1.87 | 0.237 | 0.205 | 0.067 | 384 | BD | BD | 0.804 | 0.057 | 185 | 6.48 | 291 | 3.71 | 0.809 | 30.5 |
| Minimum | 0.060 | 0.740 | 1.45 | 0.030 | 0.205 | 0.048 | 296 | BD | BD | 0.042 | 0.033 | 107 | 4.09 | 80.2 | 1.12 | 0.089 | 19.8 | ||
| Maximum | 0.066 | 0.740 | 2.39 | 0.344 | 0.205 | 0.083 | 614 | BD | BD | 2.39 | 0.097 | 316 | 8.53 | 947 | 6.39 | 3.63 | 56.7 | ||
| LS | 26 June 2012 | Mean | 0.060 | BD | 2.19 | 0.272 | BD | 0.046 | 23.7 | BD | BD | 0.571 | 0.043 | 118 | 11.5 | 126 | 54.4 | 0.077 | 5.22 |
| Minimum | 0.060 | BD | 1.92 | 0.026 | BD | 0.028 | 17.7 | BD | BD | 0.085 | 0.035 | 76.3 | 7.75 | 77.7 | 0.658 | 0.048 | 2.70 | ||
| Maximum | 0.061 | BD | 2.62 | 0.469 | BD | 0.085 | 34.1 | BD | BD | 1.25 | 0.057 | 161 | 13.5 | 166 | 399 | 0.149 | 8.90 | ||
| RB | 29 June 2012 | Mean | 0.064 | BD | 2.94 | 0.308 | 0.204 | 0.050 | 11.6 | BD | BD | 2.92 | 0.045 | 102 | 32.7 | 237 | 7.94 | 0.146 | 8.06 |
| Minimum | 0.062 | BD | 2.75 | 0.139 | 0.069 | 0.032 | 6.12 | BD | BD | 0.430 | 0.041 | 84.8 | 9.30 | 91.9 | 2.18 | 0.052 | 3.74 | ||
| Maximum | 0.070 | BD | 3.16 | 0.466 | 0.338 | 0.071 | 30.2 | BD | BD | 13.7 | 0.051 | 192 | 174 | 629 | 44.6 | 0.817 | 28.3 | ||
| LG | 2 June 2013 | Mean | 0.090 | 4.37 | 5.11 | BD | 0.024 | 0.083 | 29.1 | BD | BD | 0.322 | 0.089 | 529 | 3.83 | 4012 | 47.4 | 0.067 | 4.96 |
| Minimum | 0.075 | 2.90 | 3.55 | BD | 0.003 | 0.067 | 26.0 | BD | BD | 0.164 | 0.066 | 125 | 2.15 | 2137 | 5.00 | 0.047 | 2.63 | ||
| Maximum | 0.097 | 5.21 | 6.08 | BD | 0.050 | 0.094 | 31.4 | BD | BD | 0.473 | 0.104 | 983 | 5.46 | 5127 | 283 | 0.184 | 8.88 | ||
| LE | 11 June 2013 | Mean | 0.090 | 2.93 | 3.07 | BD | 0.014 | 0.066 | 31.9 | BD | BD | 0.471 | 0.081 | 301 | 2.89 | 4120 | 54.0 | 0.049 | 3.34 |
| Minimum | 0.086 | 1.97 | 2.94 | BD | 0.000 | 0.057 | 30.4 | BD | BD | 0.278 | 0.071 | 195 | 1.94 | 3461 | 35.5 | 0.046 | 2.24 | ||
| Maximum | 0.096 | 3.91 | 3.19 | BD | 0.052 | 0.078 | 34.3 | BD | BD | 0.927 | 0.088 | 388 | 4.09 | 4544 | 67.1 | 0.056 | 4.94 | ||
| LS | 18 June 2013 | Mean | 0.070 | 12.4 | 2.07 | BD | 0.017 | 0.080 | 25.2 | BD | BD | 0.057 | 0.047 | 330 | 2.80 | 2898 | 13.1 | 0.051 | 3.21 |
| Minimum | 0.067 | 10.9 | 1.52 | BD | 0.005 | 0.070 | 22.5 | BD | BD | 0.004 | 0.039 | 136 | 1.91 | 1983 | 3.37 | 0.049 | 2.76 | ||
| Maximum | 0.075 | 13.7 | 3.72 | BD | 0.043 | 0.096 | 30.7 | BD | BD | 0.129 | 0.062 | 708 | 4.51 | 5552 | 92.4 | 0.055 | 3.83 | ||
| RB | 10 July 2014 | Mean | 0.072 | 14.4 | 7.36 | BD | 0.281 | 0.088 | 18.1 | BD | BD | 1.84 | 0.066 | 292 | 3.57 | 3226 | 10.2 | 0.093 | 3.03 |
| Minimum | 0.066 | 8.39 | 4.94 | BD | 0.056 | 0.061 | 14.7 | BD | BD | 0.018 | 0.055 | 153 | 2.46 | 2629 | 7.60 | 0.046 | 1.68 | ||
| Maximum | 0.078 | 49.2 | 14.5 | BD | 1.77 | 0.105 | 29.1 | BD | BD | 4.22 | 0.101 | 620 | 6.39 | 4163 | 25.1 | 0.440 | 5.84 | ||
4. Conclusions
An array of water quality deteriorating agents were measured in four major Mississippi lakes. Suspended particulate matter (SPM) exceeded the WHO advisory limits at multiple sites in Lakes Grenada and Enid on 19 and 20 June 2012, respectively, and in Ross Barnett Reservoir on 22 May 2013. Improved water quality is of utmost importance to water bodies that provide recreational opportunities, and even better quality is expected in the water bodies that serve as drinking water sources. Hence, high SPM concentrations can be of greatest concern for Ross Barnett Reservoir as it serves as a drinking water source for the city of Jackson. Additionally, high SPM negatively impacts aesthetics, recreation, phytoplankton production, fisheries, and water storage capacity, thus can be problematic for all the four lakes. Historical algal blooms, as attested by a time-series of satellite data, and further measured by chlorophyll a during this study indicate continuous monitoring of these lakes is necessary for the management of these lakes, since algal blooms negatively impact water bodies by blocking the sunlight for other organisms, causing hypoxia within the hypolimnion and most importantly, by production of potent toxins that can propagate through the food web and harm the whole ecosystem, including humans. Of particular concern is the presence of cyanobacteria (as noted by the presence of pigment phycocyanin and the ChemTax analysis) that could potentially produce a diverse range of toxins. Although measured values of the most frequent and most toxic cyanotoxin, microcystin-LR, did not exceed the WHO guideline value for drinking water, its concentrations exceeded U.S. EPA advisory levels for children under six years of age. Potential bioaccumulation and biomagnification of microcystin-LR poses human health risks as well as danger to the aquatic ecosystem health.
Nutrient measurements indicated that all the lakes are eutrophic with occasional nitrogen limitation that can potentially provide a competitive advantage to toxin producing cyanobacteria. Among four bacterial populations measured, heterotrophic bacteria and E. coli did not exceed EPA’s guideline values, however, total coliforms and enterococci bacteria exceeded EPA’s guideline values on several occasions. Because these lakes are heavily used for recreational purposes and one of the lakes is used as a drinking water source, the potential for pathogen contamination pose a significant concern. Thus, a comprehensive pathogen source assessment and management plan is necessary for all these lakes. Trace element and heavy metal analyses indicated the presence of arsenic, cadmium, chromium, and lead in the water of all the four lakes, while levels of arsenic, a carcinogen, exceeded EPA’s national primary drinking water regulations at two sites in the Ross Barnett Reservoir. Aluminum, iron and manganese exceeded MCLs set by EPA’s national secondary drinking water regulations, which may cause skin or tooth discoloration or change the taste, odor, or color of drinking water. While mercury was largely absent or below detection level in the surface water in all of the lakes during this study period, a previous study by Hugget et al. [41] had found presence of mercury in fish tissues and sediments at Lake Sardis, Lake Enid and Lake Grenada. Hence, continuous monitoring of the sediments and fish tissues in addition to surface water samples will help to document potential trends.
This study represents a comprehensive examination of water quality employing field and satellite data. The approaches described in this study can be adopted by water managers to obtain a broad understanding of the water quality based on the designated use of any water body. From this study, it is apparent that the four important lakes in Mississippi are facing many water quality issues including high SPM, occurrence of cyanobacterial blooms, potent microcystin toxicity, eutrophication, presence of pathogens, presence of several trace elements and heavy metals. More data, covering all seasons, will be required to further validate our findings and to devise management strategies. For example, by the use of remote sensing technologies, suspended particulate matter and the algal blooms can be precisely measured and a time-series of products could be generated. The cyanobacterial concentrations can also be precisely measured using remotely sensed data and phycocyanin measurements, as has been done in our previous studies [19,26]. Long time-series datasets can help to develop total maximum daily load (TMDL) for sediments, nutrients and pathogens that are negatively impacting the lakes.
Acknowledgments
The authors are indebted to the outstanding contributions of undergraduate student interns Rayford Parnell, LaTia Peavy, Michael Collins, Tasha Norwood, Grant Ikenga, Daniel Kibet, Winny Tanui, Joyce Chumo, and Marlon Flowers in Padmanava Dash’s laboratory with summer internship support from Mississippi INBRE, funded by an Institutional Development Award (IDeA) from the National Institute of General Medical Sciences of the National Institutes of Health under grant number P20GM103476. Field sampling costs were supported by the Faculty Start-up grant to Padmanava Dash and a Faculty Development Research grant to Julius O. Ikenga. The authors would like to thank the four anonymous reviewers for their timely review and helpful comments.
Author Contributions
Padmanava Dash conducted the study, prepared, and revised the manuscript. Saurav Silwal participated in field data collection and laboratory analysis of water samples. Julius Ikenga participated in field data collection. James Pinckney analyzed the samples for HPLC photopigments and determined the relative abundance of major algal groups using ChemTax program. Zikri Arslan analyzed the samples for toxic elements and heavy metal concentrations and Richard Lizotte analyzed the samples for nutrient concentrations. All authors edited the manuscript prior to submission and during revision.
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
References
- Diaz, R.J.; Rosenberg, R. Spreading dead zones and consequences for marine ecosystems. Science 2008, 321, 926–929. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lotze, H.K.; Lenihan, H.S.; Bourque, B.J.; Bradbury, R.H.; Cooke, R.G.; Kay, M.C.; Kidwell, S.M.; Kirby, M.X.; Peterson, C.H.; Jackson, J.B.C. Depletion, degradation, and recovery potential of estuaries and coastal seas. Science 2006, 312, 1806–1809. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rabalais, N.N.; Turner, R.E.; Sen Gupta, B.K.; Boesch, D.F.; Chapman, P.; Murrell, M.C. Hypoxia in the northern gulf of mexico: Does the science support the plan to reduce, mitigate, and control hypoxia? Estuaries Coasts 2007, 30, 753–772. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Garcia, A.C.; Bargu, S.; Dash, P.; Rabalais, N.N.; Sutor, M.; Morrison, W.; Walker, N.D. Evaluating the potential risk of microcystins to blue crab (callinectes sapidus) fisheries and human health in a eutrophic estuary. Harmful Algae 2010, 9, 134–143. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Metcalf, J.S.; Codd, G.A. Cyanobacterial Toxins in the Water Environment: A Review of Current Knowledge. Foundation for Water Research. Available online: http://www.fwr.org/cyanotox.pdf (accessed on 24 May 2015).
- Carmichael, W. The cyanotoxins. Adv. Bot. Res. 1997, 27, 211–257. [Google Scholar]
- Codd, G.A.; BELL, S.G.; Kaya, K.; WARD, C.J.; BEATTIE, K.A.; METCALF, J.S. Cyanobacterial toxins, exposure routes and human health. Eur. J. Phycol. 1999, 34, 405–415. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Falconer, I.R. Cyanobacteria—Toxins in Drinking Water. In Encyclopedia of Environmental Microbiology; John Wiley & Sons, Inc.: Hoboken, NJ, USA, 2003. [Google Scholar]
- Anderson, D.M.; Burkholder, J.M.; Cochlan, W.P.; Glibert, P.M.; Gobler, C.J.; Heil, C.A.; Kudela, R.M.; Parsons, M.L.; Rensel, J.J.; Townsend, D.W. Harmful algal blooms and eutrophication: Examining linkages from selected coastal regions of the united states. Harmful Algae 2008, 8, 39–53. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cousins, F. Deadly Bacteria Found in Gulf Coast Tar Balls. Available online: http://www.desmogblog.com/deadly-bacteria-found-gulf-coast-tar-balls (assessed on 24 May 2015).
- Roig, F.J.; Sanjuán, E.; Llorens, A.; Amaro, C. Pilf polymorphism-based pcr to distinguish vibrio vulnificus strains potentially dangerous to public health. Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 2010, 76, 1328–1333. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Langmuir, D.; Chrostowski, P.; Vigneault, B.; Chaney, R. Issue Paper on the Environmental Chemistry of Metals. Available online: http://ofmpub.epa.gov/eims/eimscomm.getfile?p_download_id=437514 (assessed on 15 May 2015).
- US Environmental Protection Agency. Water on Tap: What You Need to Know. Available online: http://www.epa.gov/safewater/wot/pdfs/book_waterontap_full.pdf (assessed on 1 August 2015).
- Fitzsimmons, E.G. Tap Water Ban for Toledo Residents. New York Times, 3 August 2014; A12. [Google Scholar]
- Henry, T. Carrol Township’s Scare with Toxin a “Wake-up Call”. Toledo Blade, 2013. Available online: http://www.toledoblade.com/local/2013/09/15/Carroll-Township-s-scare-with-toxin-a-wake-up-call.html (accessed on 24 May 2015).
- Wynne, T.T.; Stumpf, R.P. Spatial and temporal patterns in the seasonal distribution of toxic cyanobacteria in western lake erie from 2002–2014. Toxins 2015, 7, 1649–1663. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- US Environmental Protection Agency. Monitoring Lake Quality. Available online: http://www.epa.state.il.us/water/conservation/lake-notes/monitoring-lake-quality/monitoring-lake-quality.pdf (assessed on 15 July 2015).
- Niu, X.; Williams, J.; Miller, D.; Lehnert, K.; Bills, B.; Brantley, S. An ontology driven relational geochemical database for the earth’s critical zone: Czchemdb. J. Environ. Inf. 2014, 23, 10–23. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dash, P.; Walker, N.; Mishra, D.; D’Sa, E.; Ladner, S. Atmospheric correction and vicarious calibration of oceansat-1 ocean color monitor (ocm) data in coastal case 2 waters. Remote Sens. 2012, 4, 1716–1740. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gould, R.W.; Arnone, R.A. Remote sensing estimates of inherent optical properties in a coastal environment. Remote Sens. Environ. 1997, 61, 290–301. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Olmanson, L.G.; Brezonik, P.L.; Bauer, M.E. Airborne hyperspectral remote sensing to assess spatial distribution of water quality characteristics in large rivers: The mississippi river and its tributaries in minnesota. Remote Sens. Environ. 2013, 130, 254–265. [Google Scholar]
- Song, K.; Li, L.; Tedesco, L.; Duan, H.; Li, L.; Du, J. Remote quantification of total suspended matter through empirical approaches for inland waters. J. Environ. Inf. 2014, 23, 23–36. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stumpf, R.P.; Wynne, T.T.; Baker, D.B.; Fahnenstiel, G.L. Interannual variability of cyanobacterial blooms in lake erie. PLoS One 2012, 7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bradt, S. Applications of remote sensing for lake basin management. Available online: http://wldb.ilec.or.jp/ILBMTrainingMaterials/resources/Remote_Sensing.pdf (assessed on 31 July 2015).
- Kutser, T. Passive optical remote sensing of cyanobacteria and other intense phytoplankton blooms in coastal and inland waters. Int. J. Remote Sens. 2009, 30, 4401–4425. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dash, P.; Walker, N.D.; Mishra, D.R.; Hu, C.; Pinckney, J.L.; D’Sa, E.J. Estimation of cyanobacterial pigments in a freshwater lake using OCM satellite data. Remote Sen. Environ. 2011, 115, 3409–3423. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- David, M.B.; Flint, C.G.; McIsaac, G.F.; Gentry, L.E.; Dolan, M.K.; Czapar, G.F. Biophysical and social barriers restrict water quality improvements in the mississippi river basin. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2013, 47, 11928–11929. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lerch, R.; Baffaut, C.; Sadler, E.; Kremer, R. Long-term agroecosystem research in the central mississippi river basin: Goodwater creek experimental watershed and regional herbicide water quality data. J. Environ. Qual. 2015, 44, 28–36. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ling, J.; Wu, M.; Chen, Y.; Zhang, Y.; Dong, J. Identification of spatial and temporal patterns of coastal waters in sanya bay, south China sea by chemometrics. J. Environ. Inf. 2014, 23, 37–43. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shiller, A.M.; Shim, M.-J.; Guo, L.; Bianchi, T.S.; Smith, R.W.; Duan, S. Hurricane katrina impact on water quality in the east pearl river, mississippi. J. Hydrol. 2012, 414, 388–392. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- MSDEQ. Comprehensive protection and restoration plan for the ross barnett reservoir watershed, Mississippi. Available online: http://rezonate-ms.org/wp-content/uploads/2013/09/FINAL-Executive-Summary.pdf (assessed on 24 May 2015).
- US Army Corps of Engineers. Welcome to the Vicksburg District’s Corps Lakes. Available online: http://www.mvk.usace.army.mil/Missions/Recreation.aspx (assessed on 24 May 2015).
- Kishinhi, S.; Tchounwou, P.B.; Farah, I.O.; Chigbu, P. Recreational water quality control in Mississippi, USA: Bacteriological assessment in the pearl river and ross barnett reservoir. Rev. Environ. Health 2006, 21, 295–307. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tchounwou, P.B.; Warren, M. Physicochemical and bacteriological assessment of water quality at the ross barnett reservoir in central Mississippi, USA. Rev. Environ. Health 2001, 16, 203–212. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wersal, R.M.; Madsen, J.D.; Tagert, M.L. Aquatic plant survey of ross barnett reservoir for 2005. GeoResour. Inst. Rep. 2006, 5003, 1–11. [Google Scholar]
- Sobolev, D.; Moore, K.; Morris, A.L. Nutrients and light limitation of phytoplankton biomass in a turbid southeastern reservoir: Implications for water quality. Southeast. Nat. 2009, 8, 255–266. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Downer, C.W.; DeLaune, R.; Nyman, J.A. Characteristics and Long-Term Sedimentation Patterns of Wetlands Constructed in the Fluctuation Zone of Grenada Lake, Mississippi; US Army Engineer Waterways Experiment Station: Vicksburg, MS, USA, 1995. [Google Scholar]
- Dunbar, J.A.; Bennett, S.J.; Higley, P.D.; Rhoton, F.E. Sedimentation patterns within a flood control reservoir: Grenada lake, MS. Res. Rep. 2003, 38, 44. [Google Scholar]
- Bennett, S.J.; Rhoton, F.E. Physical and chemical characteristics of sediment impounded within Grenada lake, MS. 2003. Available online: http://www.ars.usda.gov/SP2UserFiles/Place/60600505/TechnicalReports/NSLTechnicalReport36.pdf (assessed on 7 September 2015). [Google Scholar]
- Bennett, S.J.; Rhoton, F.E.; Dunbar, J.A. Texture, spatial distribution, and rate of reservoir sedimentation within a highly erosive, cultivated watershed: Grenada lake, Mississippi. Water Resour. Res. 2005, 41. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huggett, D.; Steevens, J.; Allgood, J.; Lutken, C.; Grace, C.; Benson, W. Mercury in sediment and fish from north Mississippi lakes. Chemosphere 2001, 42, 923–929. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lim, K.-Y.; Surbeck, C.Q. A multi-variate methodology for analyzing pre-existing lake water quality data. J. Environ. Monit. 2011, 13, 2477–2487. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ochs, C.A.; Rhew, K. Population dynamics of autotrophic picoplankton in a southeastern us reservoir. Int. Rev. Gesamten Hydrobiol. Hydrogr. 1997, 82, 293–313. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sthapit, E.; Ochs, C.A.; Zimba, P.V. Spatial and temporal variation in phytoplankton community structure in a southeastern us reservoir determined by HPLC and light microscopy. Hydrobiologia 2008, 600, 215–228. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hanson, L.A.; Hubbard, W.D.; Petrie-Hanson, L. Distribution of Largemouth Bass Virus may be expanding in Mississippi. Fish health newsletter: Bethesda, MD, USA, 2003. Available online: http://www.afs-fhs.org/communications/newsletter/V29-4_2001.PDF (assessed on 7 September 2015).
- Haag, W.R.; Warren, M.L. Freshwater mussel assemblage structure in a regulated river in the lower Mississippi river alluvial basin, USA. Aquat. Conserv.: Mar. Freshw. Ecosyst. 2007, 17, 25–36. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dorr, B.; Munn, I.A.; Meals, K.O. A socioeconomic and biological evaluation of current and hypothetical crappie regulations in Sardis lake, Mississippi: An integrated approach. North Am. J. Fish. Manag. 2002, 22, 1376–1384. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McClain, C.R. Science quality seawifs data for global biosphere research. Sea Technol. 1998, 39, 10–16. [Google Scholar]
- Britton, L.J.; Greeson, P.E. Methods for Collection and Analysis of Aquatic Biological and Microbiological Samples; U.S. Geological Survey: Lakewood, CO, USA, 1989.
- Pinckney, J.; Millie, D.; Howe, K.; Paerl, H.; Hurley, J. Flow scintillation counting of 14c-labeled microalgal photosynthetic pigments. J. Plankton Res. 1996, 18, 1867–1880. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Roy, S.; Llewellyn, C.A.; Egeland, E.S.; Johnsen, G. Phytoplankton Pigments: Characterization, Chemotaxonomy and Applications in Oceanography; Cambridge University Press: Cambridge, UK, 2011. [Google Scholar]
- Mackey, M.; Mackey, D.; Higgins, H.; Wright, S. Chemtax-a program for estimating class abundances from chemical markers: Application to HPLC measurements of phytoplankton. Mar. Ecol. Prog. Ser. 1996, 144, 265–283. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Higgins, H.W.; Wright, S.W.; Schluter, L. Quantitative Interpretation of Chemotaxonomic Pigment Data; Cambridge University Press: Cambridge, UK, 2011. [Google Scholar]
- Latasa, M. Improving estimations of phytoplankton class abundances using chemtax. Mar. Ecol. Prog. Ser. 2007, 329, 13–21. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pinckney, J.L.; Wee, J.L.; Hou, A.; Walker, N.D. Phytoplankton community structure responses to urban effluent inputs following hurricanes katrina and rita. Mar. Ecol. Prog. Ser. 2009, 387, 137–146. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schlüter, L.; Lauridsen, T.; Krogh, G.; Jørgensen, T. Identification and quantification of phytoplankton groups in lakes using new pigment ratios—A comparison between pigment analysis by HPLC and microscopy. Freshw. Biol. 2006, 51, 1474–1485. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mackey, M.D.; Higgins, H.W.; Mackey, D.J.; Wright, S.W. Chemtax User’s Manual: A Program for Estimating Class Abundances from Chemical Markers—Application to HPLC Measurements of Phytoplankton Pigments; CSIRO Marine Laboratories: Hobart, Australia, 1997. [Google Scholar]
- Wright, S.; Thomas, D.; Marchant, H.; Higgins, H.; Mackey, M.; Mackey, D. Analysis of phytoplankton of the australian sector of the southern ocean: Comparisons of microscopy and size frequency data with interpretations of pigment HPLC data using the ‘CHEMTAX’ matrix factorisation program. Mar. Ecol. Prog. Ser. 1996, 14, 285–298. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Downes, M.T.; Hall, J.A. A sensitive fluorometric technique for the measurement of phycobilin pigments and its application to the study of marine and freshwater picophytoplankton in oligotrophic environments. J. Appl. Phycol. 1998, 10, 357–363. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mitchell, B.G.; Kahru, M.; Wieland, J.; Stramska, M. Determination of spectral absorption coefficients of particles, dissolved material and phytoplankton for discrete water samples. In Ocean Optics Protocols For Satellite Ocean Color Sensor Validation, Revision 2; National Aeronautics and Space Administration, Goddard Space Flight Center: Greenbelt, MD, USA, 2002; Volume 3, pp. 231–257. [Google Scholar]
- Cleveland, J.; Weidemann, A.D. Quantifying absorption by aquatic particles: A multiple scattering correction for glass-fiber filters. Limnol. Oceanogr. 1993, 38, 1321–1327. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Boyer, G.L. Cyanobacterial toxins in new york and the lower great lakes ecosystems. In Cyanobacterial Harmful Algal Blooms: State of the Science and Research Needs; Springer: Berlin, Germany, 2008; pp. 153–165. [Google Scholar]
- American Public Health Association; American Water Works Association; Water Environment Federation. Standard Methods for the Examination of Water and Wastewater; American Public Health Association (APHA): Washington, DC, USA, 2005. [Google Scholar]
- Shields, F.D.; Lizotte, R.E.; Knight, S.S.; Cooper, C.M.; Wilcox, D. The stream channel incision syndrome and water quality. Ecol. Eng. 2010, 36, 78–90. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sieracki, C.K.; Sieracki, M.E.; Yentsch, C.S. An imaging-in-flow system for automated analysis of marine microplankton. Mar. Ecol. Prog. Ser. 1998, 168, 285–296. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Franz, B.A.; Werdell, P.J.; Meister, G.; Kwiatkowska, E.J.; Bailey, S.W.; Ahmad, Z.; McClain, C.R. Modis Land Bands for Ocean Remote Sensing Applications. In Proceedings of the Ocean Optics XVIII, Montreal, Canada, 9–13 October 2006.
- Miller, J.R.; Sinclair, J.T.; Walsh, D. Controls on suspended sediment concentrations and turbidity within a reforested, southern appalachian headwater basin. Water 2015, 7, 3123–3148. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cullum, R.; Knight, S.; Cooper, C.; Smith, S. Combined effects of best management practices on water quality in oxbow lakes from agricultural watersheds. Soil Tillage Res. 2006, 90, 212–221. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- WHO. Turbidity Measurement. Available online: http://www.who.int/water_sanitation_health/hygiene/emergencies/fs2_33.pdf (assessed on 24 May 2015).
- Hunter, P.; Tyler, A.; Willby, N.; Gilvear, D. The spatial dynamics of vertical migration by microcystis aeruginosa in a eutrophic shallow lake: A case study using high spatial resolution time-series airborne remote sensing. Limnol. Oceanogr. 2008, 53, 2391–2406. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schalles, J.F.; Yacobi, Y.Z. Remote detection and seasonal patterns of phycocyanin, carotenoid and chlorophyll pigments in eutrophic waters. Ergeb. Limnol. 2000, 55, 153–168. [Google Scholar]
- Hunter, P.D.; Tyler, A.N.; Gilvear, D.J.; Willby, N.J. Using remote sensing to aid the assessment of human health risks from blooms of potentially toxic cyanobacteria. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2009, 43, 2627–2633. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- MacKintosh, C.; Beattie, K.A.; Klumpp, S.; Cohen, P.; Codd, G.A. Cyanobacterial microcystin-lr is a potent and specific inhibitor of protein phosphatases 1 and 2a from both mammals and higher plants. FEBS Lett. 1990, 264, 187–192. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Graham, J.L.; Loftin, K.A.; Kamman, N. Monitoring recreational freshwaters. Lakelines 2009, 29, 18–24. [Google Scholar]
- Codd, G.A.; Bell, S.G.; Brooks, W.P. Cyanobacterial toxins in water. Water Sci. Technol. 1989, 21, 1–13. [Google Scholar]
- Falconer, D.S.; Mackay, T.F.C. Introduction to Quantitative Genetics; Ronald Press: New York, NY, USA, 1960. [Google Scholar]
- WHO Geneva. Guidelines for Drinking-Water Quality; World Health Organization: Geneva, Switzerland, 2011. [Google Scholar]
- US Environmental Protection Agency. 2015 Drinking Water Health Advisories for Two Cyanobacterial Toxins. Available online: http://www2.epa.gov/sites/production/files/2015-06/documents/cyanotoxins-fact_sheet-2015.pdf (assessed on 31 July 2015).
- Messina, I. Microcystin Detected in Raw Lake Erie Water, Toledo Water Deemed Safe to Drink. The Blade, 2015. Available online: http://www.toledoblade.com/local/2015/07/27/Microcystin-detected-in-raw-Lake-Erie-water-Toledo-water-deemed-safe-to-drink.html (accessed on 24 May 2015).
- US Environmental Protection Agency. What is the Regulatory Status of Habs Cyanobacteria and Cyanotoxins in the U.S.? Available online: http://www2.epa.gov/nutrient-policy-data/policies-and-guidelines (assessed on 24 May 2015).
- Carlson, R.E. A trophic state index for lakes1. Limnol. Oceanogr. 1977, 22, 361–369. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Carlson, R.E. Expanding the trophic state concept to identify non-nutrient limited lakes and reservoirs; Enhancing the States’s Lake Management Programs; North American Lake management Society: Madison, WI, USA, 1991; pp. 59–71. [Google Scholar]
- US Environmental Protection Agency. Drinking Water Contaminants. Available online: http://water.epa.gov/drink/contaminants/#Microorganisms (assessed on 15 May 2015).
- Paerl, H.W.; Fulton, R.S.; Moisander, P.H.; Dyble, J. Harmful freshwater algal blooms, with an emphasis on cyanobacteria. Sci. World J. 2001, 1, 76–113. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Stevenson, A.H. Studies of bathing water quality and health*. Am. J. Public Health Nations Health 1953, 43, 529–538. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- US Environmental Protection Agency. 2012 Recreational Water Quality Criteria. Available online: http://water.epa.gov/scitech/swguidance/standards/criteria/health/recreation/Upload/factsheet2012.pdf (assessed on 15 May 2015).
© 2015 by the authors; licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
