Effect of the Resolution of Tipping-Bucket Rain Gauge and Calculation Method on Rainfall Intensities in an Andean Mountain Gradient
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Study Area
2.1. Zhurucay Observatory
2.2. Quinuas Observatory
2.3. Sensors
- Davis Rain Collector II (Davis): The collecting diameter is 16.5 cm, and the rain gauge resolution 0.254 mm. The time (hh:mm:ss) of each tip was recorded.
- Hobo Data Logging Rain Gauge—RG3-M (Onset): The collecting diameter is 15.39 cm, and the rain gauge resolution 0.2 mm. The time (hh:mm:ss) of each tip was recorded.
- Rain Gauge Tipping Bucket TE525MM Rainfall sensor (Texas): The collecting diameter is 24.5 cm, and the rain gauge resolution 0.1 mm. The number of tips per minute was recorded.
- Disdrometer-Thies Clima Laser Precipitation Monitor 5.4110.00.000 V2.4× STD (LPM): Rainfall amounts are generated using the measurement of the size and falling velocity of the raindrops. The resolution of the LPM is 0.01 mm and the laser measuring area is 45.6 cm2. Full information on the features and operation of the disdrometer is available in the LPM manual [27,29].
3. Methods
3.1. Methods for Rainfall Intensity Calculation
3.2. Intensity Magnitudes and Timescales of Data Aggregation
3.3. Methodology to Calculate the Error
3.4. Analyzing the Effect of the Andean Altitudinal Gradient on Cumulative Rainfall and Intensities
4. Results and Discussion
4.1. Effect of the Calculation Method for Rainfall Intensity, Rainfall Intensity Class, and Timescale on the Percent Absolute Bias
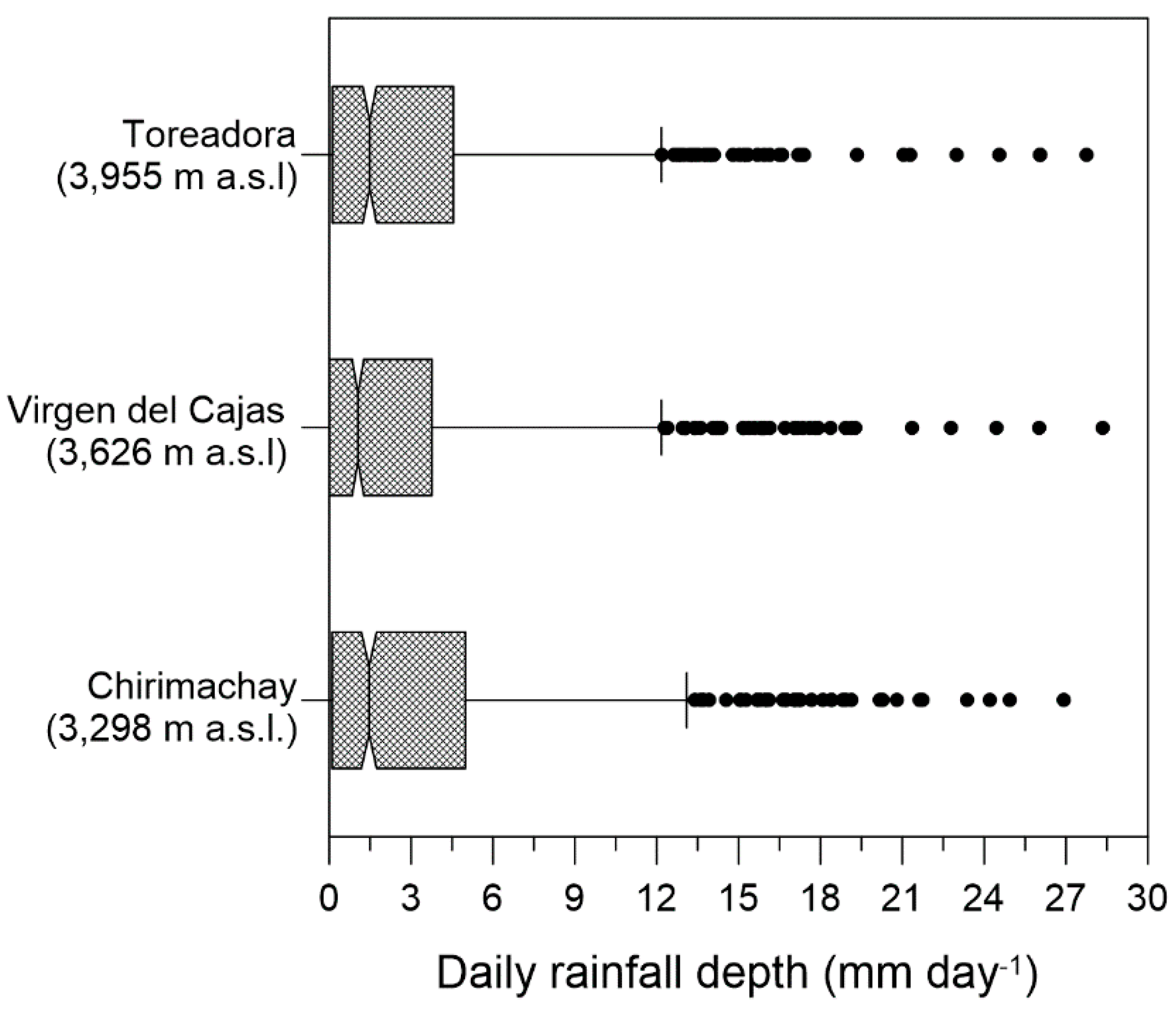
4.2. Effect of the Altitudinal Gradient
5. Conclusions
Acknowledgments
Author Contributions
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
| TB | Tipping Bucket |
| DRTB | Different Resolution Tipping Buckets |
| TC | Tip Counting |
| CS | Cubic Spline. |
References
- González, J.; Lajara, J.; Díaz, S. Errors Analysis in extreme rainfall recording due to tipping bucket rain gauge performance. In Proceedings of the 36th IAHR World Congress, The Hague, The Netherlands, 28 June–3 July 2015.
- Buytaert, W.; Célleri, R.; De Bièvre, B.; Cisneros, F.; Wyseure, G.; Deckers, J.; Hofstede, R. Human impact on the hydrology of the Andean páramos. Earth-Sci. Rev. 2006, 79, 53–72. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Dinerstein, E.; Graham, D.J.; Olsen, D.M.; Webster, A.; Primm, S.; Bookbinder, M.; Ledec, G. Una Evaluación del Estado de Conservación de las Eco-Regiones Terrestres de América Latina y el Caribe; Banco Internacional de Reconstrucción y Fomento/Banco Mundial: Washington, DC, USA; World Wildlife Fund: Washington, DC, USA, 1995. [Google Scholar]
- Sarmiento, L.; Lambí, L.D.; Escalona, A.; Márquez, N. Vegetation patterns, regeneration rates and divergence in an old field-succession of the high tropical Andes. Plant Ecol. 2003, 166, 63–74. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Célleri, R.; Feyen, J. The Hydrology of Tropical Andean Ecosystems: Importance, Knowledge Status, and Perspectives. Mt. Res. Dev. 2009, 29, 350–355. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Buytaert, W.; Cuesta-Camacho, F.; Tobón, C. Potential impacts of climate change on the environmental services of humid tropical alpine regions. Glob. Ecol. Biogeogr. 2011, 20, 19–33. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Messerli, B.; Viviroli, D.; Weingartner, R. Mountains of the world: Vulnerable water towers for the 21st century. Ambio 2004, 13, 29–34. [Google Scholar]
- Kumar, S.; Gill, G.S.; Santosh, S. Spatial Distribution of Rainfall with Elevation in Satluj River Basin: 1986–2010, Himachal Pradesh, India. Int. Lett. Chem. Phys. Astron. 2015, 57, 163. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alijani, B. Effect of the Zagros Mountains on the spatial distribution of precipitation. J. Mt. Sci. 2008, 5, 218–231. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Buytaert, W.; Celleri, R.; Willems, P.; De Bièvre, B.; Wyseure, G. Spatial and temporal rainfall variability in mountainous areas: A case study from the south Ecuadorian Andes. J. Hydrol. 2006, 329, 413–421. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Celleri, R.; Willems, P.; Buytaert, W.; Feyen, J. Space-time rainfall variability in the Paute Basin, Ecuadorian Andes. Hydrol. Process. 2007, 21, 3316–3327. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Espinoza Villar, J.C.; Ronchail, J.; Guyot, J.L.; Cochonneau, G.; Naziano, F.; Lavado, W.; De Oliveira, E.; Pombosa, R.; Vauchel, P. Spatio-temporal rainfall variability in the Amazon basin countries (Brazil, Peru, Bolivia, Colombia, and Ecuador). Int. J. Climatol. 2009, 29, 1574–1594. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- De Biévre, B.; Iñiguez, V.; Buytaert, W. Hidrología del Páramo. Importancia, propiedades y vulnerabilidad. In Investigaciones Biofísicas en el Páramo, No. 21; GTP/Abya Yala: Quito, Ecuador, 2006. [Google Scholar]
- Rollenbeck, R.; Bendix, J. Rainfall distribution in the Andes of southern Ecuador derived from blending weather radar data and meteorological field observations. Atmos. Res. 2011, 99, 277–289. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ochoa-Tocachi, B.F.; Buytaert, W.; De Bièvre, B.; Célleri, R.; Crespo, P.; Villacís, M.; Llerena, C.A.; Acosta, L.; Villazón, M.; Guallpa, M.; et al. Impacts of land use on the hydrological response of tropical Andean catchments. Hydrol. Process. 2016, 30, 4074–4089. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rossenaar, A.J.G.A.; Hofstede, R.G.M. Effects of burning and grazing on root biomass in the páramo ecosystem. In Páramo: An Andean Ecosystem Under Human Influence; Balslev, H., Luteyn, J.L., Eds.; Academic Press: London, UK, 1992; pp. 211–213. [Google Scholar]
- World Meteorological Organisation. World Hydrological Cycle Observing System Guidelines; World Meteorological Organisation: Geneva, Switzerland, 2015; p. 87. [Google Scholar]
- Lanza, L.G.; Vuerich, E. The WMO field intercomparison of rain intensity gauges. Atmos. Res. 2009, 94, 534–543. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Organización Meteorológica Mundial. Guía de Prácticas Hidrológicas; Organización Meteorológica Mundial: Geneva, Switzerland, 2008; OMM-NO. 168; p. 324. [Google Scholar]
- Ciach, G.J. Local random errors in tipping-bucket rain gauge measurements. J. Atmos. Ocean. Technol. 2003, 20, 752–759. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Habib, E.; Krajewski, W.F.; Kruger, A. Sampling Errors of Tipping-Bucket Rain Gauge Measurements. J. Hydrol. Eng. 2001, 6, 159–166. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, J.; Fisher, B.L.; Wolff, D.B. Estimating rain rates from tipping-bucket rain gauge measurements. J. Atmos. Ocean. Technol. 2008, 25, 43–56. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Michaelides, S.C. Precipitation: Advances in Measurement, Estimation and Prediction; Springer Science & Business Media: Berlin, Germany, 2008. [Google Scholar]
- Nystuen, J.A.; Proni, J.R.; Black, P.G.; Wilkerson, J.C. A comparison of automatic rain gauges. J. Atmos. Ocean. Technol. 1996, 13, 62–73. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Padrón, R.S.; Wilcox, B.P.; Crespo, P.; Célleri, R. Rainfall in the Andean Páramo: New Insights from High-Resolution Monitoring in Southern Ecuador. J. Hydrometeorol. 2015, 16, 985–996. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, X.C.; Gao, T.C.; Liu, L. A comparison of rainfall measurements from multiple instruments. Atmos. Meas. Tech. 2013, 6, 1585–1595. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Upton, G.; Brawn, D. An investigation of factors affecting the accuracy of Thies disdrometers. In Proceedings of WMO Technical Conference on Instruments and Methods of Observation (TECO-2008), St. Petersburg, Russia, 27–29 November 2008; pp. 1–9.
- Nešpor, V.; Sevruk, B. Estimation of wind-induced error of rainfall gauge measurements using a numerical simulation. J. Atmos. Ocean. Technol. 1999, 16, 450–464. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lanzinger, E. Rainfall amount and intensity measured by the Thies laser precipitation monitor. In Proceedings of the WMO Technical Conference on Instruments and Methods of Observation (TECO-2006), Geneva, Switzerland, 7–14 December 2006; pp. 1–9.
- Williams, R.G.; Erdman, M.D. Low-cost computer interfaced rain gauge. Comput. Electron. Agric. 1987, 2, 67–73. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sadler, E.J.; Busscher, W.J. High-intensity rainfall rate determination from tipping-bucket rain gauge data. Agron. J. 1989, 81, 930–934. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Peleg, N.; Ben-Asher, M.; Morin, E. Radar subpixel-scale rainfall variability and uncertainty: Lessons learned from observations of a dense rain-gauge network. Hydrol. Earth Syst. Sci. 2013, 17, 2195–2208. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Colli, M.; Lanza, L.G.; Chan, P.W. Co-located tipping-bucket and optical drop counter RI measurements and a simulated correction algorithm. Atmos. Res. 2013, 119, 3–12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Costello, T.A.; Williams, H.J. Short duration rainfall intensity measured using calibrated time-of-tip data from a tipping bucket raingage. Agric. For. Meteorol. 1991, 57, 147–155. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Al-Wagdany, A.S. Evaluation of Dual Tipping-Bucket Rain Gauges Measurement in Arid Region Western Saudi Arabia. Arab. J. Sci. Eng. 2014, 40, 171–179. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- World Meteorological Organisation. Guide to Meteorological Instruments and Methods of Observation; World Meteorological Organisation: Geneva, Switzerland, 2010. [Google Scholar]
- Tokay, A.; Wolff, D.B.; Wolff, K.R.; Bashor, P. Rain gauge and disdrometer measurements during the Keys Area Microphysics Project (KAMP). J. Atmos. Ocean. Technol. 2003, 20, 1460–1477. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mosquera, G.M.; Lazo, P.X.; Célleri, R.; Wilcox, B.P.; Crespo, P. Runoff from tropical alpine grasslands increases with areal extent of wetlands. Catena 2015, 125, 120–128. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shedekar, V.S.; King, K.W.; Fausey, N.R.; Soboyejo, A.B.O.; Harmel, R.D.; Brown, L.C. Assessment of measurement errors and dynamic calibration methods for three different tipping bucket rain gauges. Atmos. Res. 2016, 178–179, 445–458. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vasvári, V. Calibration of tipping bucket rain gauges in the Graz urban research area. Atmos. Res. 2005, 77, 18–28. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nystuen, J.A. Relative performance of automatic rain gauges under different rainfall conditions. J. Atmos. Ocean. Technol. 1999, 16, 1025–1043. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shi, H.; Li, T.; Wei, J.; Fu, W.; Wang, G. Spatial and temporal characteristics of precipitation over the Three-River Headwaters region during 1961–2014. J. Hydrol. Reg. Stud. 2016, 6, 52–65. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]



| Study Area | Sensor | Available Data | Number of Events | % Missing Data | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Since | To | ||||
| Zhurucay observatory | Davis_Zhu | 21/02/2011 | 14/02/2014 | 953 | 4 |
| Onset_Zhu | 21/02/2011 | 04/01/2014 | 1133 | 7 | |
| Texas_Zhu | 21/02/2011 | 19/03/2014 | 1658 | 4 | |
| LPM | 21/02/2011 | 01/10/2012 | 4 | ||
| 09/11/2012 | 19/03/2014 | ||||
| Quinuas observatory | Davis_Chi | 22/01/2014 | 05/02/2016 | 681 | 5 |
| Texas_Chi | 22/01/2014 | 05/02/2016 | 1115 | 0 | |
| Davis_Tor | 16/01/2014 | 06/04/2015 | 573 | 11 | |
| 09/05/2015 | 29/06/2015 | ||||
| 29/07/2015 | 05/02/2016 | ||||
| Texas_Tor | 16/01/2014 | 05/02/2016 | 1205 | 0 | |
| Davis_Vir | 20/01/2014 | 19/08/2015 | 503 | 5 | |
| Texas_Vir | 20/01/2014 | 05/02/2016 | 1044 | 0 | |
© 2016 by the authors; licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC-BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Muñoz, P.; Célleri, R.; Feyen, J. Effect of the Resolution of Tipping-Bucket Rain Gauge and Calculation Method on Rainfall Intensities in an Andean Mountain Gradient. Water 2016, 8, 534. https://doi.org/10.3390/w8110534
Muñoz P, Célleri R, Feyen J. Effect of the Resolution of Tipping-Bucket Rain Gauge and Calculation Method on Rainfall Intensities in an Andean Mountain Gradient. Water. 2016; 8(11):534. https://doi.org/10.3390/w8110534
Chicago/Turabian StyleMuñoz, Paul, Rolando Célleri, and Jan Feyen. 2016. "Effect of the Resolution of Tipping-Bucket Rain Gauge and Calculation Method on Rainfall Intensities in an Andean Mountain Gradient" Water 8, no. 11: 534. https://doi.org/10.3390/w8110534
APA StyleMuñoz, P., Célleri, R., & Feyen, J. (2016). Effect of the Resolution of Tipping-Bucket Rain Gauge and Calculation Method on Rainfall Intensities in an Andean Mountain Gradient. Water, 8(11), 534. https://doi.org/10.3390/w8110534







