Decline in Performance of Biochemical Reactors for Sulphate Removal from Mine-Influenced Water is Accompanied by Changes in Organic Matter Characteristics and Microbial Population Composition
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Selection of Organic Materials and Preparation
2.2. Bioreactor Set-Up, Operation and Sampling
2.3. Chemical Analyses
2.4. Microbial Population Characterization
2.5. Statistical Methods
3. Results and Discussion
3.1. Sulphate-Reduction Rate within the BCRs
3.2. Sulphide Concentrations within the BCRs
3.3. Supply of Dissolved Organic Carbon
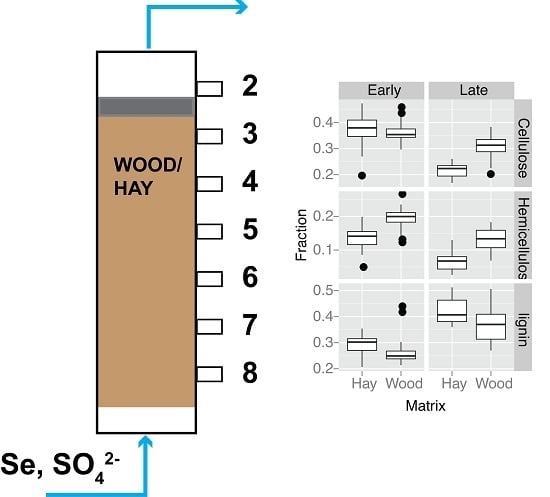
3.4. Organic Matter Degradation
3.5. Microbial Communities Supported by the Hay- and Wood-Rich BCRs and Their Evolution over Time
4. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Acknowledgments
Author Contributions
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
| BCR | Biochemical reactor |
| CDB | Cellulose degrading bacteria |
| DCA | Detrended corresponsence analysis |
| DO | Dissolved oxygen |
| DOC | Dissolved organic carbon |
| DNA | Deoxyribonucleic acid |
| H | Hay |
| HRT | Hydraulic retention time |
| MIW | Mine influenced water |
| NDF | Neutral detergent fibre |
| NDS | Neutral detergent soluble |
| OM | Organic matter |
| PCR | Polymerase chain reaction |
| ORP | Oxidation-reduction potential |
| OUT | Operational taxonomic unit |
| SRB | Sulphate-reducing bacteria |
| TOC | Total organic carbon |
| W | Wood |
References
- Outridge, P.M.; Scheuhammer, A.M.; Fox, G.A.; Braune, B.M.; White, L.M.; Gregorich, L.J.; Keddy, C. An Assessment of the Potential Hazards of Environmental Selenium for Canadian Water Birds. Environ. Rev. 1999, 7, 81–96. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lemly, A.D. Teratogenic effects of selenium in natural populations of freshwater fish. Ecotoxicol. Environ. Saf. 1993, 26, 181–204. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Elphick, J.R.; Davies, M.; Gilron, G.; Canaria, E.C.; Lo, B.; Bailey, H.C. An aquatic toxicological evaluation of sulfate: the case for considering hardness as a modifying factor in setting water quality guidelines. Environ. Toxicol. Chem. 2011, 30, 247–253. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Johnson, D. Recent Developments in Microbiological Approaches for Securing Mine Wastes and for Recovering Metals from Mine Waters. Minerals 2014, 4, 279–292. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Blumenstein, E.P.; Gusek, J.J. Designing a biochemical reactor for selenium and thallium removal, from bench scale testing through pilot construction. In Hydrometallurgy 2008—Proceedings of the Sixth International Symposium, Phoenix, AZ, USA, 17–20 August 2008; Young, C.A., Taylor, P.R., Anderson, C.G., Choi, Y.C.A., Eds.; Society for Mining, Metallurgy, Exploration Inc.: Phoenix, AZ, USA, 2008; pp. 117–129. [Google Scholar]
- Baldwin, S.A.; Hodaly, A.H. Selenium Uptake by a Coal Mine Wetland Sediment. Water Qual. Res. J. Can. 2003, 38, 483–497. [Google Scholar]
- Zinck, J.; Griffith, W. Review of Mine Drainage Treatment and Sludge Management Operations; Report CANMET-MMSL 10-058(CR); CANMET Mining and Mineral Sciences Laboratory, Natural Resources Canada: Ottawa, ON, Canada, 2013. [Google Scholar]
- Mattes, A.; Evans, L.J.; Gould, D.W.; Duncan, W.F.A.; Glasauer, S. The long term operation of a biologically based treatment system that removes As, S and Zn from industrial (smelter operation) landfill seepage. Appl. Geochem. Sources Transp. Fate Trace Toxic Elem. Environ. 2011, 26, 1886–1896. [Google Scholar]
- Schmidtova, J.; Baldwin, S.A. Correlation of bacterial communities supported by different organic materials with sulfate reduction in metal-rich landfill leachate. Water Res. 2011, 45, 1115–1128. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Logan, M.V.; Reardon, K.F.; Figueroa, L.A.; McLain, J.E.; Ahmann, D.M. Microbial community activities during establishment, performance, and decline of bench-scale passive treatment systems for mine drainage. Water Res. 2005, 39, 4537–4551. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pereyra, L.; Hiibel, S. Detection and quantification of functional genes of cellulose-degrading, fermentative, and sulfate-reducing bacteria and methanogenic archaea. Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 2010, 76, 2192–2202. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Roman, H.; Madikane, M.; Pletschke, B.I.; Rose, P.D. The Degradation of Lignocellulose in a Chemically and Biologically Generated Sulphidic. Environ. Bioresour. Technol. 2008, 99, 2333–2339. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Costa, M.C.; Martins, M.; Jesus, C.; Duarte, J.C. Treatment of Acid Mine Drainage by Sulphate-reducing Bacteria Using Low Cost Matrices. Water Air Soil Pollut. 2007, 189, 149–162. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lindsay, M.B.J.; Blowes, D.W.; Condon, P.D.; Ptacek, C.J. Organic Carbon Amendments for Passive in situ Treatment of Mine Drainage: Field Experiments. Appl. Geochem. 2011, 26, 1169–1183. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zagury, G.J.; Kulnieks, V.I.; Neculita, C.M. Characterization and reactivity assessment of organic substrates for sulphate-reducing bacteria in acid mine drainage treatment. Chemosphere 2006, 64, 944–954. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sjöström, E. Wood Chemistry: Fundamentals and Applications, 2nd ed.; Academic Press: San Diego, CA, USA, 2013. [Google Scholar]
- Hall, M.B.; Pell, A.N.; Chase, L.E. Characteristics of neutral detergent-soluble fiber fermentation by mixed ruminal microbes. Anim. Feed Sci. Technol. 1998, 70, 23–39. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schofield, P.; Pell, A.N. Measurement and kinetic analysis of the neutral detergent-soluble carbohydrate fraction of legumes and grasses. J. Anim. Sci. 2014, 73, 3455–3463. [Google Scholar]
- Van der Weijde, T.; Alvim Kamei, C.L.; Torres, A.F.; Vermerris, W.; Dolstra, O.; Visser, R.G.; Trindade, L.M. The potential of C4 grasses for cellulosic biofuel production. Front. Plant Sci. 2013, 4, 107. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Waybrant, K.R.; Blowes, D.W.; Ptacek, C.J. Selection of Reactive Mixtures for Use in Permeable Reactive Walls for Treatment of Mine Drainage. Environ. Sci. Technol. 1998, 32, 1972–1979. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pereyra, L.P.; Hiibel, S.R.; Perrault, E.M.; Reardon, K.F.; Pruden, A. Effect of bioaugmentation and biostimulation on sulfate-reducing column startup captured by functional gene profiling. FEMS Microbiol. Ecol. 2012, 82, 135–147. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pruden, A.; Messner, N.; Pereyra, L.; Hanson, R.E.; Hiibel, S.R.; Reardon, K.F. The Effect of Inoculum on the Performance of Sulfate-Reducing Columns Treating Heavy Metal Contaminated Water. Water Res. 2007, 41, 904–914. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lefèvre, E.; Pereyra, L.P.; Hiibel, S.R.; Perrault, E.M.; De Long, S.K.; Reardon, K.F.; Pruden, A. Molecular assessment of the sensitivity of sulfate-reducing microbial communities remediating mine drainage to aerobic stress. Water Res. 2013, 47, 5316–5325. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mirjafari, P.; Baldwin, S.A. Performance of sulphate- and selenium-reducing biochemical reactors using different ratios of labile to recalcitrant organic materials. Water Sci. Technol. 2015, 72, 875. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Eaton, A.D.; Clesceri, L.S.; Rice, E.W.; Greenberg, A.E. Standard Methods for the Examination of Water and Wastewater; American Public Health Association: Washington, DC, USA, 2005. [Google Scholar]
- Vansoest, P.J.; Robertson, J.B.; Lewis, B.A. Methods for Dietary Fiber, Neutral Detergent Fiber, and Nonstarch Polysaccharides in Relation to Animal Nutrition. J. Dairy Sci. 1991, 74, 3583–3597. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hall, M.B. Neutral-Detergent Soluble Carbohydrates-Nutritional Relevance And Analysis; Laboratory Manual; Institute of Food and Agricultural Sciences, University of Florida: Gainesville, FL, USA, 2000; Bulletin 339. [Google Scholar]
- Wieder, R.K.; Starr, S.T. Quantitative Determination of Organic Fractions in Highly Organic, Sphagnum Peat Soils. Commun. Soil Sci. Plant Anal. 1998, 29, 847–857. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Edgar, R.C. Search and clustering orders of magnitude faster than BLAST. Bioinformatics 2010, 26, 2460–2461. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Caporaso, J.G.; Kuczynski, J.; Stombaugh, J.; Bittinger, K.; Bushman, F.D.; Costello, E.K.; Fierer, N.; Pena, A.G.; Goodrich, J.K.; Gordon, J.I.; et al. QIIME allows analysis of high-throughput community sequencing data. Nat. Methods 2010, 7, 335–336. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Quast, C.; Pruesse, E.; Yilmaz, P.; Gerken, J.; Schweer, T.; Yarza, P.; Peplies, J.; Glöckner, F.O. The SILVA ribosomal RNA gene database project: Improved data processing and web-based tools. Nucleic Acids Res. 2013, 41, D590–D596. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lozupone, C.; Knight, R. UniFrac: A new phylogenetic method for comparing microbial communities. Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 2005, 71, 8228–8235. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Washington, H.G. Diversity, biotic and similarity indices. Water Res. 1984, 18, 653–694. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hill, M.O.; Gauch, H.G. Detrended Correspondence Analysis: An Improved Ordination Technique. Vegetatio 1980, 42, 47–58. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Oksanen, J.; Guillaume Blanchet, F.; Kindt, R.; Legendre, P.; Minchin, P.R.; O’Hara, R.B.; Simpson, G.L.; Solymos, P.; Stevens, M.H.H.; Wagner, H. Vegan: Community Ecology Package. R package version 2.3-3, 2016. Available online: https://CRAN.R-project.org/package=vegan (accessed on 29 March 2016).
- Bratkova, S.; Koumanova, B.; Beschkov, V. Biological treatment of mining wastewaters by fixed-bed bioreactors at high organic loading. Bioresour. Technol. 2013, 137, 409–413. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- O’Flaherty, V.; Mahony, T.; O’Kennedy, R.; Colleran, E. Effect of pH on growth kinetics and sulphide toxicity thresholds of a range of methanogenic, syntrophic and sulphate-reducing bacteria. Process Biochem. 1998, 33, 555–569. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Reis, M.A.; Almeida, J.S.; Lemos, P.C.; Carrondo, M.J. Effect of hydrogen sulfide on growth of sulfate reducing bacteria. Biotechnol. Bioeng. 1992, 40, 593–600. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Elferink, S.; Luppens, S.; Marcelis, C.; Stams, A. Kinetics of acetate oxidation by two sulfate reducers isolated from anaerobic granular sludge. Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 1998, 64, 2301–2303. [Google Scholar]
- Muyzer, G.; Stams, A.J.M. The ecology and biotechnology of sulphate-reducing bacteria. Nat. Rev. Microbiol. 2008, 6, 441–454. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mösche, M.; Jördening, H.-J. Comparison of different models of substrate and product inhibition in anaerobic digestion. Water Res. 1999, 33, 2545–2554. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fengel, D.; Wegener, G. Wood: Chemistry, Ultrastructure, Reactions; Walter de Gruyter: New York, NY, USA, 1989. [Google Scholar]
- Pereyra, L.P.; Hiibel, S.R.; Pruden, A.; Reardon, K.F. Comparison of microbial community composition and activity in sulfate-reducing batch systems remediating mine drainage. Biotechnol. Bioeng. 2008, 101, 702–713. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shannon, C.E. A Mathematical Theory of Communication. Bell. Syst. Tech. J. 1948, 27, 379–423. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Legendre, P.; Legendre, L. Numerical Ecology, 3rd ed.; Elsevier: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 2012. [Google Scholar]
- Cotruvo, J.A.; Dufour, A.; Rees, G.; Bartram, J.; Carr, R.; Cliver, D.O.; Craun, G.F.; Fayer, R.; Gannon, V.P.J. Waterborne Zoonoses: Identification, Causes, and Control; World Heath Organization (WHO), IWA Publishing: London, UK, 2004. [Google Scholar]
- Flint, H.J.; Bayer, E.A.; Rincon, M.T.; Lamed, R.; White, B.A. Polysaccharide utilization by gut bacteria: Potential for new insights from genomic analysis. Nat. Rev. Microbiol. 2008, 6, 121–131. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Giuliano, C.; Khan, A.W. Cellulase and Sugar Formation by Bacteroides cellulosolvens, a Newly Isolated Cellulolytic Anaerobe. Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 1984, 48, 446–448. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Mewis, K.; Armstrong, Z.; Song, Y.C.; Baldwin, S.A.; Withers, S.G.; Hallam, S.J. Biomining active cellulases from a mining bioremediation system. J. Biotechnol. 2013, 167, 462–471. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wexler, H.M. Bacteroides: The good, the bad, and the nitty-gritty. Clin. Microbiol. Rev. 2007, 20, 593–621. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ueki, A.; Akasaka, H.; Suzuki, D.; Ueki, K. Paludibacter Propionicigenes gen. nov., sp nov., A Novel Strictly Anaerobic, Gram-Negative, Propionate-Producing Bacterium Isolated from Plant Residue in Irrigated Rice-Field Soil in Japan. Int. J. Syst. Evol. Microbiol. 2006, 56, 39–44. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dillon, J.G.; Fishbain, S.; Miller, S.R.; Bebout, B.M.; Habicht, K.S.; Webb, S.M.; Stahl, D.A. High rates of sulfate reduction in a low-sulfate hot spring microbial mat are driven by a low level of diversity of sulfate-respiring microorganisms. Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 2007, 73, 5218–5226. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pester, M.; Bittner, N.; Deevong, P.; Wagner, M.; Loy, A. A “rare biosphere” microorganism contributes to sulfate reduction in a peatland. ISME J. 2010, 4, 1591–1602. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]











| BCR | Contents (%dw) | Length of Operation (Days) | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Wood | Hay | Manure | Early | Late | |
| BCR_H1 | 20 | 50 | 30 | 159 | |
| BCR_H2 | 20 | 50 | 30 | 159 | |
| BCR_H3 | 20 | 50 | 30 | 430 | |
| BCR_W1 | 40 | 30 | 30 | 159 | |
| BCR_W2 | 40 | 30 | 30 | 455 | |
| BCR_W2 | 40 | 30 | 30 | 455 | |
© 2016 by the authors; licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons by Attribution (CC-BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Mirjafari, P.; Baldwin, S.A. Decline in Performance of Biochemical Reactors for Sulphate Removal from Mine-Influenced Water is Accompanied by Changes in Organic Matter Characteristics and Microbial Population Composition. Water 2016, 8, 124. https://doi.org/10.3390/w8040124
Mirjafari P, Baldwin SA. Decline in Performance of Biochemical Reactors for Sulphate Removal from Mine-Influenced Water is Accompanied by Changes in Organic Matter Characteristics and Microbial Population Composition. Water. 2016; 8(4):124. https://doi.org/10.3390/w8040124
Chicago/Turabian StyleMirjafari, Parissa, and Susan A. Baldwin. 2016. "Decline in Performance of Biochemical Reactors for Sulphate Removal from Mine-Influenced Water is Accompanied by Changes in Organic Matter Characteristics and Microbial Population Composition" Water 8, no. 4: 124. https://doi.org/10.3390/w8040124
APA StyleMirjafari, P., & Baldwin, S. A. (2016). Decline in Performance of Biochemical Reactors for Sulphate Removal from Mine-Influenced Water is Accompanied by Changes in Organic Matter Characteristics and Microbial Population Composition. Water, 8(4), 124. https://doi.org/10.3390/w8040124