Nitrate Pollution and Preliminary Source Identification of Surface Water in a Semi-Arid River Basin, Using Isotopic and Hydrochemical Approaches
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Study Area
2.2. Water Sampling Sites and Measurements
3. Results and Discussion
3.1. Hydrochemistry
3.2. Concentrations of NO2−-N, NO3−-N and NH4+-N
3.3. Spatial Distribution of Nitrate and Its Controlling Factors
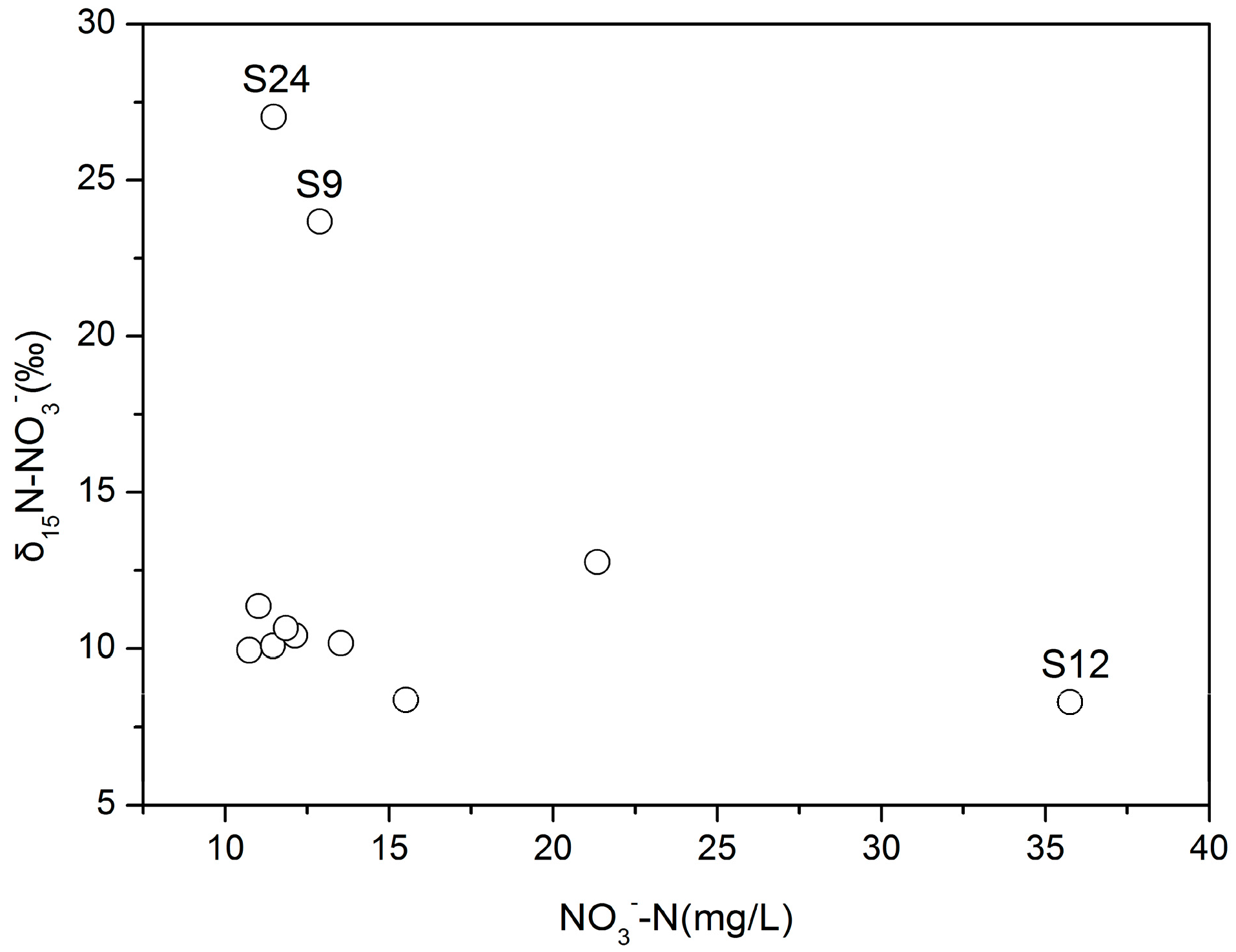
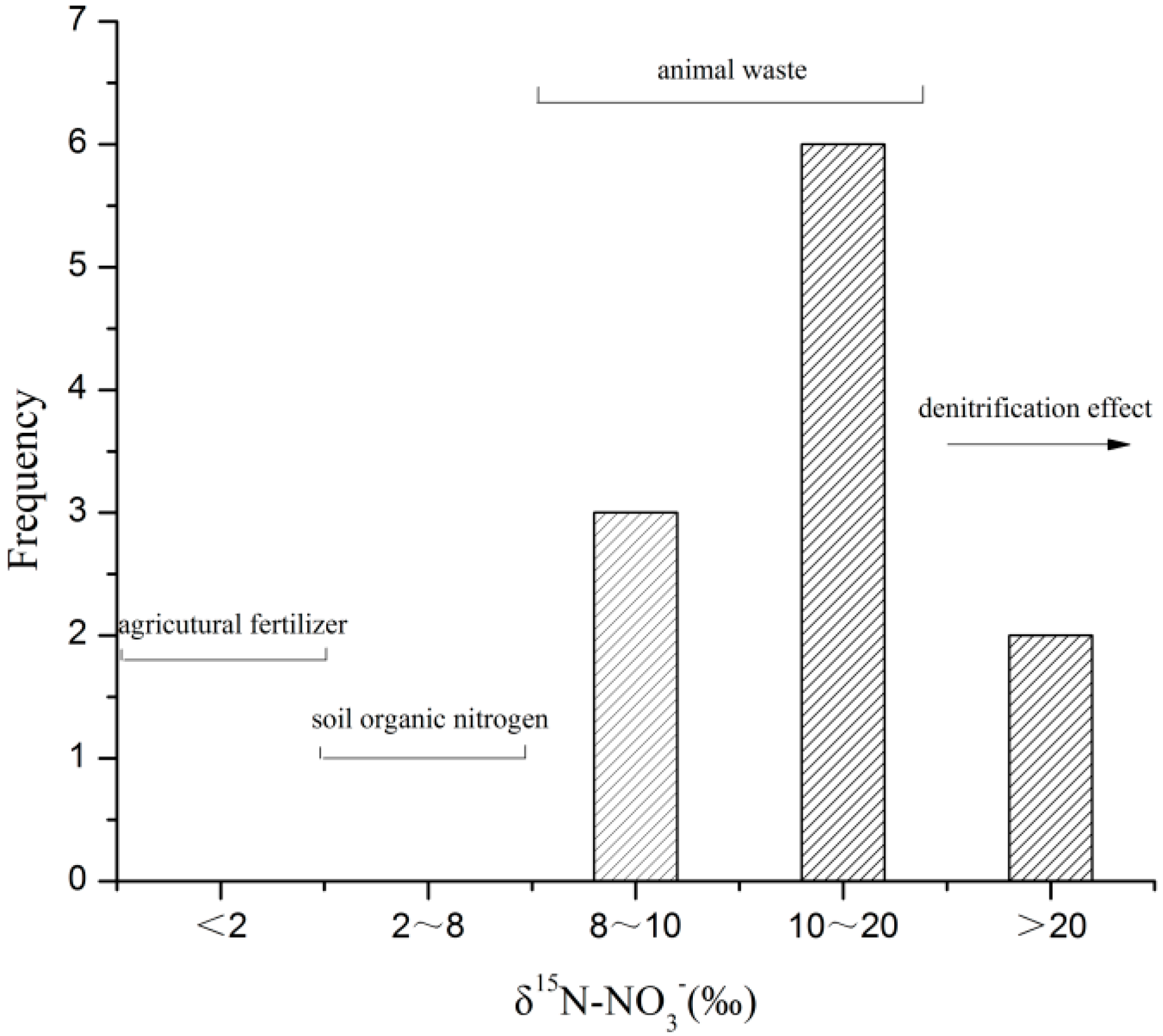
3.4. Sources and Transformations of Nitrate
4. Conclusions
Acknowledgments
Author Contributions
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Erisman, J.W.; Galloway, J.N.; Seitzinger, S.; Bleeker, A.; Dise, N.B.; Petrescu, A.R.; Leach, A.M.; de Vries, W. Consequences of human modification of the global nitrogen cycle. Philos. Trans. R. Soc. B Biol. Sci. 2013, 368, 91–97. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lu, L.; Cheng, H.G.; Pu, X.; Liu, X.L.; Cheng, Q.D. Nitrate behaviors and source apportionment in an aquatic system from a watershed with intensive agricultural activities. Environ. Sci. Process. Impacts 2015, 17, 131–144. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, Y.; Li, F.D.; Zhang, Q.Y.; Li, J.; Liu, Q. Tracing nitrate pollution sources and transformation in surface- and ground-waters using environmental isotopes. Sci. Total Environ. 2014, 490, 213–222. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, S.L.; Liu, C.Q.; Li, J.; Liu, X.L.; Chetelat, B.; Wang, B.L.; Wang, F.S. Assessment of the sources of nitrate in the Changjiang River, China using a nitrogen and oxygen isotopic approach. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2010, 44, 1573–1578. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cook, P.L.M.; Aldridge, K.T.; Lamontagne, S.; Brookes, J.D. Retention of nitrogen, phosphorus and silicon in a large semi-arid riverine lake system. Biogeochemistry 2009, 99, 49–63. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dise, N.B.; Wright, R.F. Nitrogen leaching from European forests in relation to nitrogen deposition. For. Ecol. Manag. 1995, 71, 153–161. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Smith, V.H.; Tilman, G.D.; Nekola, J.C. Eutrophication: Impacts of excess nutrient inputs on freshwater, marine, and terrestrial ecosystems. Environ. Pollut. 1999, 100, 179–196. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vitousek, P.M.; Aber, J.D.; Howarth, R.W.; Likens, G.E.; Matson, P.A.; Schindler, D.W.; Schlesinger, W.H.; Tilman, D.G. Human alteration of the global nitrogen cycle: Sources and consequences. Ecol. Appl. 1997, 7, 737–750. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- He, B.; Kanae, S.; Oki, T.; Hirabayashi, Y.; Yamashiki, Y.; Takara, K. Assessment of global nitrogen pollution in rivers using an integrated biogeochemical modeling framework. Water Res. 2011, 45, 2573–2586. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, S.L.; Liu, C.Q.; Li, J.; Xue, Z.C.; Guan, J.; Lang, Y.C.; Ding, H.; Li, L.B. Evaluation of nitrate source in surface water of southwestern China based on stable isotopes. Environ. Earth. Sci. 2013, 68, 219–228. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gautam, S.; Iqbal, M. Using stable isotopes of nitrogen to study its source and transformation in a heavily farmed watershed. Environ. Earth. Sci. 2010, 60, 11–20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, J.; Li, F.D.; Liu, Q.; Suzuki, Y. Nitrate pollution and its transfer in surface water and groundwater in irrigated areas: A case study of the Piedmont of South Taihang Mountains, China. Environ. Sci. Process. Impacts 2014, 16, 2764–2773. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Carpenter, S.R.; Caraco, N.F.; Correll, D.L.; Howarth, R.W.; Sharpley, A.N.; Smith, V.H. Nonpoint pollution of surface waters with phosphorus and nitrogen. Ecol. Appl. 1998, 8, 559–568. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, T.; Wang, F.; Michalski, G.; Xia, X.H.; Liu, S.D. Using 15N, 17O, and 18O to determine nitrate sources in the Yellow River, China. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2013, 47, 13412–13421. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yang, L.; Song, X.; Zhang, Y.; Han, D.; Zhang, B.; Long, D. Characterizing interactions between surface water and groundwater in the Jialu River basin using major ion chemistry and stable isotopes. Hydrol. Earth Syst. Sci. Discuss. 2012, 9, 5955–5981. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Itoh, M.; Takemon, Y.; Makabe, A.; Yoshimizu, C.; Kohzu, A.; Ohte, N.; Tumurskh, D.; Tayasu, I.; Yoshida, N.; Nagata, T. Evaluation of wastewater nitrogen transformation in a natural wetland (Ulaanbaatar, Mongolia) using dual-isotope analysis of nitrate. Sci. Total Environ. 2011, 409, 1530–1538. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Huang, G.X.; Fallowfield, H.; Guan, H.D.; Liu, F. Remediation of nitrate-nitrogen contaminated groundwater by a heterotrophic-autotrophic denitrification approach in an aerobic environment. Water Air Soil Pollut. 2012, 223, 4029–4038. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fogg, G.E.; Rolston, D.E.; Decker, D.L.; Louie, D.T.; Grismer, M.E. Spatial variation in nitrogen isotope values beneath nitrate contamination sources. Gound Water 1998, 36, 418–426. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stevenson, F.J. Origin and distribution of nitrogen in soil. Agron. Monogr. 1982, 22, 1–42. [Google Scholar]
- Hübner, H. Isotope effects of nitrogen in the soil and biosphere. In Handbook of Environmental Isotope Geochemistry; Fritz, P., Fontes, J.C., Eds.; Elsevier: New York, NY, USA, 1986; pp. 361–425. [Google Scholar]
- Mayer, B.; Boyer, E.W.; Goodale, C.; Jaworski, N.A.; Van Breemen, N.; Howarth, R.W.; Seitzinger, S.; Billen, G.; Lajtha, K.; Nadelhoffer, K.; et al. Sources of nitrate in rivers draining sixteen watersheds in the northeastern U.S.: Isotopic constraints. Biogeochemistry 2002, 57, 171–197. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Macko, S. Pollution studies using stable isotopes. In Stable Isotopes in Ecology and Environmental Science; Lajtha, K., Michener, R.M., Eds.; Blackwell Sci.: Malden, MA, USA, 1994; pp. 45–62. [Google Scholar]
- Böhlke, J.K.; Denver, J.M. Combined use of groundwater dating, chemical, and isotopic analyses to resolve the history and fate of nitrate contamination in two agricultural watersheds, Atlantic coastal plain, Maryland. Water Resour. Res. 1995, 31, 2319–2339. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- BryantMason, A.; Xu, Y.J.; Altabet, M. Isotopic signature of nitrate in river waters of the lower Mississippi and its distributary, the Atchafalaya. Hydrol. Process. 2013, 27, 2840–2850. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Heaton, T. Isotopic studies of nitrogen pollution in the hydrosphere and atmosphere: A review. Chem. Geol. Isot. Geosci. Sect. 1986, 59, 87–102. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kendall, C. Tracing nitrogen sources and cycling in catchments. Isot. Tracers Catchment Hydrol. 1998, 1, 519–576. [Google Scholar]
- Liu, C.Q.; Li, S.L.; Lang, Y.C.; Xiao, H.Y. Using δ15N- and δ18O-values to identify nitrate sources in karst ground water, Guiyang, Southwest China. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2006, 40, 6928–6933. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fang, C.L.; Xie, Y. Sustainable urban development in water-constrained Northwest China: A case study along the mid-section of Silk-Road—He-Xi corridor. J. Arid Environ. 2010, 74, 140–148. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zuo, D.P.; Xu, Z.X.; Wu, W.; Zhao, J.; Zhao, F.F. Identification of streamflow response to climate change and human activities in the Wei River Basin, China. Water Resour. Manag. 2014, 28, 833–851. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Song, J.X.; Xu, Z.X.; Liu, C.M.; Li, H.E. Ecological and environmental instream flow requirements for the Wei River—The largest tributary of the Yellow River. Hydrol. Process. 2007, 21, 1066–1073. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, J.K.; Li, H.E.; Shen, B.; Li, Y.J. Effect of non-point source pollution on water quality of the Weihe River. Int. J. Sediment Res. 2011, 26, 50–61. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Q.; Li, F.D.; Guo, J.Q.; Wu, X.D.; Song, S.; Zhao, G.S. Source and variation of nitrogen along middle and down stream of Weihe River and its main tributaries. J. Water Resour. Water Eng. 2011, 22, 128–132. [Google Scholar]
- Xing, M.; Liu, W.G.; Hu, J. Using nitrate isotope to trace the nitrogen pollution in Chanhe and Laohe River. Environ. Sci. 2010, 10, 2305–2310. [Google Scholar]
- Water Quality-Technical Regulation on the Design of Sampling Programmes. HJ 495-2009.
- Silva, S.; Kendall, C.; Wilkison, D.; Ziegler, A.; Chang, C.; Avanzino, R. A new method for collection of nitrate from fresh water and the analysis of nitrogen and oxygen isotope ratios. J. Hydrol. 2000, 228, 22–36. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, S.Q.; Tang, C.Y.; Song, X.F.; Yuan, R.Q.; Wang, Q.X.; Zhang, Y.H. Using major ions and delta 15N-NO3− to identify nitrate sources and fate in an alluvial aquifer of the baiyangdian lake watershed, north China plain. Environ. Sci. Process. Impacts 2013, 15, 1430–1443. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Di Lorenzo, T.; Brilli, M.; Del Tosto, D.; Galassi, D.M.P.; Petitta, M. Nitrate source and fate at the catchment scale of the Vibrata River and aquifer (central Italy): An analysis by integrating component approaches and nitrogen isotopes. Environ. Earth. Sci. 2012, 67, 2383–2398. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yue, F.J.; Liu, X.L.; Li, J.; Zhu, Z.Z.; Wang, Z.L. Using nitrogen isotopic approach to identify nitrate sources in waters of Tianjin, China. Bull. Environ. Contam. Toxicol. 2010, 85, 562–567. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jolly, I.D.; McEwan, K.L.; Holland, K.L. A review of groundwater-surface water interactions in arid/semi-arid wetlands and the consequences of salinity for wetland ecology. Ecohydrology 2008, 1, 43–58. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, J.M.; Liu, J.H.; Yu, X.B.; Yang, W.B.; Zhou, M.P. Variation of nitrogen resource in groundwater and river water in Changchun Region. J. Soil Water Conserv. 2010, 24, 255–257. [Google Scholar]
- Tabayashi, Y.; Koba, K. Heterogeneous atmospheric nitrogen deposition effects upon the nitrate concentration of stream waters in a forested mountain area. Water Air Soil Pollut. 2011, 216, 105–115. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Koszelnik, P.; Gruca-Rokosz, R. Determination of nitrate isotopic signature in waters of different sources by analysing the nitrogen and oxygen isotopic ratio. Environ. Sci. Process. Impacts 2013, 15, 751–759. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gu, B.J.; Ge, Y.; Chang, S.X.; Luo, W.D.; Chang, J. Nitrate in groundwater of China: Sources and driving forces. Glob. Environ. Chang. 2013, 23, 1112–1121. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ju, X.T.; Xing, G.X.; Chen, X.P.; Zhang, S.L.; Zhang, L.J.; Liu, X.J.; Cui, Z.L.; Yin, B.; Christie, P.; Zhu, Z.L.; et al. Reducing environmental risk by improving N management in intensive Chinese agricultural systems. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2009, 106, 3041–3046. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Bakhsh, A.; Kanwar, R.S.; Baker, J.L. N-application methods and precipitation pattern effects on subsurface drainage nitrate losses and crop yields. Water Air Soil Pollut. 2010, 212, 65–76. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jin, Z.F.; Pan, Z.Y.; Jin, M.T.; Li, F.L.; Wan, Y.; Gu, B. Determination of nitrate contamination sources using isotopic and chemical indicators in an agricultural region in China. Agric. Ecosyst. Environ. 2012, 155, 78–86. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, W.G.; Xing, M. Isotopic indicators of carbon and nitrogen cycles in river catchments during soil erosion in the arid Loess Plateau of China. Chem. Geol. 2012, 296–297, 66–72. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, D.; Yang, W.; Zhao, J.L. Tracing nitrate sources of the Yellow River and its tributaries with nitrogen isotope. J. Ecol. Rural Environ. 2012, 28, 622–627. [Google Scholar]
- Urresti-Estala, B.; Vadillo-Pérez, I.; Jiménez-Gavilán, P.; Soler, A.; Sánchez-Garcia, D.; Carrasco-Cantos, F. Application of stable isotopes (δ34S-SO4, δ18O-SO4, δ15N-NO3, δ18O-NO3) to determine natural background and contamination sources in the Guadalhorce River Basin (southern Spain). Sci. Total Environ. 2015, 506–507, 46–57. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Urresti-Estala, B.; Jiménez-Gavilán, P.; Vadillo-Pérez, I.; Carrasco-Cantos, F. Assessment of hydrochemical trends in the highly anthropised Guadalhorce River Basin (southern Spain) in terms of compliance with the European groundwater directive for 2015. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. Int. 2016. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yu, H.Y.; Yu, Z.M.; Song, X.X.; Cao, X.H.; Yuan, Y.Q.; Lu, G.Y. Seasonal variations in the nitrogen isotopic composition of dissolved nitrate in the Changjiang River estuary, China. Estuar. Coast. Shelf Sci. 2015, 155, 148–155. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]




| Mean (mg/L) | Maximum (mg/L) | Minimum (mg/L) | Median (mg/L) | MCL 1 (mg/L) | Exceeded Rate (%) | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| NO2−-N | 0.009 | 0.015 | BDL 2 | 0.01 | 0.2 | 0 |
| NO3−-N | 8.6 | 35.7 | 1.3 | 7.4 | 10 | 32.4 |
| NH4+-N | 0.3 | 8.0 | 0.008 | 0.05 | 1.0 | 2.9 |
© 2016 by the authors; licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC-BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Xue, Y.; Song, J.; Zhang, Y.; Kong, F.; Wen, M.; Zhang, G. Nitrate Pollution and Preliminary Source Identification of Surface Water in a Semi-Arid River Basin, Using Isotopic and Hydrochemical Approaches. Water 2016, 8, 328. https://doi.org/10.3390/w8080328
Xue Y, Song J, Zhang Y, Kong F, Wen M, Zhang G. Nitrate Pollution and Preliminary Source Identification of Surface Water in a Semi-Arid River Basin, Using Isotopic and Hydrochemical Approaches. Water. 2016; 8(8):328. https://doi.org/10.3390/w8080328
Chicago/Turabian StyleXue, Ying, Jinxi Song, Yan Zhang, Feihe Kong, Ming Wen, and Guotao Zhang. 2016. "Nitrate Pollution and Preliminary Source Identification of Surface Water in a Semi-Arid River Basin, Using Isotopic and Hydrochemical Approaches" Water 8, no. 8: 328. https://doi.org/10.3390/w8080328
APA StyleXue, Y., Song, J., Zhang, Y., Kong, F., Wen, M., & Zhang, G. (2016). Nitrate Pollution and Preliminary Source Identification of Surface Water in a Semi-Arid River Basin, Using Isotopic and Hydrochemical Approaches. Water, 8(8), 328. https://doi.org/10.3390/w8080328






