Hydrogeochemical Characteristics of Groundwater Highly Polluted with Nitrate in an Agricultural Area of Hongseong, Korea
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
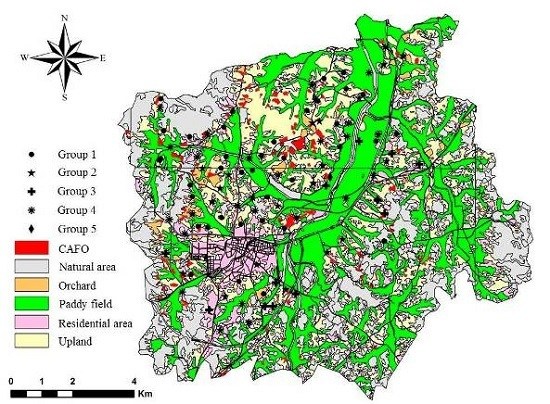
2.1. Study Area
2.2. Hydrogeochemical Investigation
2.3. Statistical Analysis
3. Results
3.1. Hydrogeochemical Characteristics of Groundwater
3.2. Correlations of Hydrochemical Factors
3.3. Principal Component Analysis
3.4. Hierarchical Cluster Analysis
4. Discussion
4.1. Hydrogeochemical Processes Affecting Groundwater Chemistry
4.2. Nitrate Contamination Source
4.3. Natural Attenuation of Nitrate
5. Conclusions
Acknowledgments
Author Contributions
Conflicts of Interest
References
- World Meteorological Organization (WMO). Comprehensive Assessment of the Freshwater Resources of the World; World Meteorological Organization: Geneva, Switzerland, 1997. [Google Scholar]
- Arnell, N.W. Climate change and blobal water resources. Glob. Environ. Chang. 1999, 9 (Suppl. S1), S31–S49. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alley, W.M.; Healy, R.W.; LaBaugh, J.W.; Reilly, T.E. Flow and storage in groundwater systems. Science 2002, 296, 1985–1990. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Davis, M.L.; Cornwell, D.A. Introduction to Environmental Engineering, 4th ed.; McGraw-Hill: New York, NY, USA, 2008; pp. 226–229. [Google Scholar]
- Shindo, J.; Okamoto, K.; Kawashima, H. Prediction of the environmental effects of excess nitrogen caused by increasing food demand with rapid economic growth in eastern Asian countries, 1961–2020. Ecol. Model. 2006, 193, 703–720. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Korea Department Agriculture. Report of the Study on Measure to Reduce the Application of Agricultural Pesticide; Division of Food Policy, Korea Department of Agriculture: Seoul, Korea, 2006. (In Korean)
- Min, J.H.; Yun, S.T.; Kim, K.; Kim, H.S.; Hahn, J.; Lee, S.M. Nitrate contamination of alluvial groundwaters in the Nakdong river basin Korea. Geosci. J. 2002, 6, 35–46. (In Korean) [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, K.; Rajmohan, N.; Kim, H.J.; Hwang, G.; Cho, M.J. Assessment of groundwater chemistry in a coastal region (Kunsan, Korea) having complex contaminant sources: A stoichiometric approach. Environ. Geol. 2004, 46, 763–774. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kaown, D.I.; Hyun, Y.J.; Bae, G.O.; Lee, K.K. Factors affecting the spatial pattern of nitrate concentration in shallow groundwater. J. Environ. Qual. 2007, 36, 1479–1487. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jeon, S.R.; Park, S.J.; Kim, H.S.; Jeong, S.K.; Lee, Y.; Jeong, J. Hydeogeochemical characteristics of groundwater in an agricultural area of Sunchang, South Korea. J. Geol. Soc. Korea 2011, 47, 185–197. (In Korean) [Google Scholar]
- Williams, A.; Johnson, J.; Lund, L.; Kabala, Z. Spatial and temporal variations in nitrate contamination of a rural aquifer, California. J. Environ. Qual. 1998, 27, 1147–1157. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Spalding, R.F.; Exner, M.E. Occurrence of nitrate in groundwater—A review. J. Environ. Qual. 1993, 22, 392–402. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Green, C.T.; Böhlke, J.K.; Bekins, B.A.; Phillips, S.P. Mixing effects on apparent reaction rates and isotope fractionation during denitrification in a heterogeneous aquifer. Water Resour. Res. 2010, 46. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Koh, D.C.; Kim, E.Y.; Ryu, J.S.; Ko, K.S. Factors controlling groundwater chemistry in an agricultural area with complex topographic and land use patterns in mid-western South Korea. Hydrol. Process. 2009, 23, 2915–2928. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mohapatra, P.K.; Vijay, R.; Pujari, P.R.; Sundaray, S.K.; Mohanty, B.P. Determination of processes affecting groundwater quality in the coastal aquifer beneath Puri city, India: A multivariate statistical approach. Water Sci. Technol. 2011, 64, 809–817. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nolan, B.T. Nitrate behavior in ground waters of the Southeastern USA. J. Environ. Qual. 1999, 28, 1518–1527. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tang, C.; Chen, J.; Shindo, S.; Sakura, Y.; Zhang, W.; Shen, Y. Assessment of groundwater contamination by nitrates associated with wastewater irrigation: A case study in Shijiazhuang region, China. Hydrol. Process. 2004, 18, 2303–2312. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thivya, C.S.; Thilagavathi, R.; Prasanna, M.V.; Singaraja, C.; Adithya, V.S.; Nepolian, M. A multivariate statistical approach to identify the spatio-temporal variation of geochemical process in a hard rock auifer. Environ. Monit. Assess. 2015, 187. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Farnham, I.M.; Johannesson, K.H.; Sing, A.K.; Hodge, V.F.; Stetzenbach, K.J. Factor analytical approaches for evaluating groundwater trace element chemistry data. Anal. Chim. Acta 2003, 490, 123–138. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ministry for Food Agriculture Forestry and Fisheries. Food Agriculture Forestry and Fisheries Statistical Yearbook; Ministry for Food Agriculture Forestry and Fisheries: Seoul, Korea, 2011.
- Ki, M.G.; Koh, D.C.; Yoon, H.; Kim, H.S. Temporal variability of nitrate concentration in groundwater affected by intensive agricultural activities in a rural area of Hongseong, South Korea. Environ. Earth Sci. 2015, 74, 6147–6161. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Statistics Korea. Statistical Yearbook of Hongseong; Statistics Korea: Hongseong, Korea, 2013. (In Korean)
- Lee, J.H.; Kim, S.S. Geologic Map of Hongseong (1:50000); Geological Society of Korea: Seoul, Korea, 1963; p. 33.
- Thyne, G.; Guler, C.; Poeter, E. Sequential analysis of hydrochemical data for watershed characterization. Ground Water 2004, 42, 711–723. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Helena, B.; Pardo, R.; Vega, M.; Barrado, E.; Fernadez, J.M.; Fernandez, L. Temporal evolution of ground water composition in an alluvial aquifer (Pisuerga River, Spain) by principal component analysis. Water Res. 2000, 34, 807–816. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Suk, H.; Lee, K.K. Characterization of a ground water hydrochemical system through multivariate analysis: Clustering into ground water zones. Ground Water 1999, 37, 358–366. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, K.; Jeong, G. Factors influencing natural occurrence of fluoride-rich groundwater: A case study in the southeastern part of the Korean Peninsula. Chemosphere 2005, 58, 1399–1408. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Madison, R.J.; Brunett, J.O. Overview of the Occurrences of Nitrate in Groundwater of the United States; U.S. Geological Survery Water Supply Paper: Washington, DC, USA, 1985; Volume 2275, pp. 93–105.
- Nolan, B.T.; Hitt, K.J. Vulnerability of shallow groundwater and drinking-water wells to nitrate in the United States. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2006, 40, 7834–7840. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Koh, D.C.; Ko, K.S.; Kim, Y.; Lee, S.G.; Chang, H.W. Effect of agricultural land use on the chemistry of groundwater from basaltic aquifer, Jeju Islnad, South Korea. Hydrogeol. J. 2007, 5, 727–743. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hill, A.R. Nitrate distribution in the groundwater of the Alliston region of Ontaniro, Canada. Ground Water 1982, 20, 696–702. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Poinke, H.B.; Urban, J.B. Effect of agricultural land use on groundwater quality in a small Pennsylvania watershed. Ground Water 1984, 23, 68–80. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rock, L.; Mayer, B. Isotopic assessment of sources and processes affecting sulfate and nitrte in surface water and groundwater of Luxembourg. Isotopes Environ. Health Stud. 2002, 38, 191–206. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Negrel, P.; Pauwels, H. Interaction between different groundwaters in Brittany catchments (France): Characterizing multiple sources through strontium- and Sulphur isotope trancing. Water Air Soil Pollut. 2004, 151, 261–285. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Choi, D. Formation of Jeju island and the characteristics of groundwater. J. Cheju Stud. 1988, 5, 59–78. (In Korean) [Google Scholar]
- Lee, J.; Jeon, H.; Jeon, Y. Geochemical characteristics of groundwater in relation to aquifer geology and temperature—A comparison with groundwater in granitic aquifer. J. Soil Groundw. Environ. 1997, 4, 212–222. [Google Scholar]
- Kumar, M.; Ramanathan, A.L.; Rao, M.S.; Kumar, B. Identification and evaluation of hydrogeochemical processes in the groundwater environment of Delhi, India. Environ. Geol. 2006, 50, 1025–1039. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, E.Y.; Koh, D.C.; Ko, K.S.; Yoe, I.W. Prediction of nitrate contamination of groundwater in the northern Nonsan area using multiple regression analysis. J. Soil Groundw. Environ. 2008, 13, 57–73. [Google Scholar]
- Böhlke, J.K. Groundwater recharge and agricultural contamination. Hydrogeol. J. 2002, 10, 153–179. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liang, X.Q.; Harter, T.; Porta, L.; van Kessel, C.; Linquist, B.A. Nitrate leaching in Californian rice fields: A field- and regional-scale assessment. Sci. Total Environ. 2014, 43, 881–894. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kao, Y.H.; Liu, C.W.; Jang, C.S.; Zanh, S.W.; Lin, K.H. Assessment of nitrogen contamination of groundwater in paddy and upland fields. Paddy Water Environ. 2011, 9, 301–307. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rivett, M.O.; Buss, S.R.; Morgan, P.; Smith, J.W.N.; Bemment, C.D. Nitrate attenuation in groundwater: A review of biogeochemical controlling processes. Water Res. 2008, 42, 4215–4232. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Böhlke, J.K.; Denver, J.M. Combined use of groundwater dating, chemical, and isotopic analyses to resolve the history and fate of nitrte contamination in two agricultural watersheds, Atlantic coastal plain, Maryland. Water Resour. Res. 1995, 31, 2319–2339. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tang, C.; Sakura, Y. The characteristics of geochemistry in a headwater wetland, Chiba, Japan. In Dynamics and Biogeochemistry of River Corridors and Wetlands; Heathwaite, A.L., Ed.; IAHS Publication: Wallingford, UK, 2005; Volume 294, pp. 167–175. [Google Scholar]
- Rust, C.M.; Aelion, C.M.; Flora, J.R.V. Control of pH during denitrification in subsurface sediment microcosm using encapsulated phosphate buffer. Water Res. 2000, 34, 1447–1454. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Drtil, M.; Nemeth, P.N.; Kucman, K.; Bodik, I.; Kasperek, V. Acidobasic balances in the course of heterotrophic denitrification. Water Res. 1995, 29, 1353–1360. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Minzoni, F.; Bonetto, C.; Golterman, H.L. The nitrogen cycle in shallow water sediment systems of rice fields. Part 1: The denitrification process. Hydrobiologia 1988, 159, 189–202. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xing, G.X.; Cao, Y.C.; Shi, S.L.; Sun, G.Q.; Du, L.J.; Zhu, J.G. Denitrification in underground saturated soil in a rice paddy region. Soil Biol. Biochem. 2002, 34, 1593–1598. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kingsbury, J.A. Shallow Ground-Water Quality in Agricultural Areas of Northern Alabama and Middle Tennessee, 2000–2001; U.S. Geological Survey Water Resources Investigations Report 03-4181; U.S. Geological Survey: Nashville, TN, USA, 2003; p. 38.
- Kim, H.; Kaown, D.; Mayer, B.; Lee, J.; Hyun, Y.; Lee, K. Identifying the sources of nitrate contamination of groundwater in an agricultural area (Heaan basin, Korea) using isotope and microbial community analyses. Sci. Total Environ. 2015, 533, 566–575. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Böttcher, J.; Strebel, O.; Voerkelius, S.; Schmidt, H.L. Using isotope fractionation of nitrate-nitrogen and nitrate-oxygen for evaluation of microbial denitrification in a sandy aquifer. J. Hydrol. 1990, 114, 413–424. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Postma, D.; Boesen, C.; Kristiansen, H.; Larsen, F. Nitrate reduction in an unconfined sandy aquifer: Water chemistry, reduction processes, and geochemical modeling. Water Resour. Res. 1991, 27, 2027–2045. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kazemi, G.A.; Lehr, J.H.; Perrochet, P. Groundwater Age; Wiley-Interscience: Hoboken, NJ, USA, 2006. [Google Scholar]
- Murglet, D.; Tick, G.R. Understanding the sources and fate of nitrate in a highly developed aquifer system. J. Contam. Hydrol. 2013, 155, 69–81. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mengis, M.; Schiff, S.L.; Harris, M.; English, M.C.; Aravena, R.; Elgood, R.J.; MacLean, A. Multiple geochemical and isotopic approaches for assessing ground water NO3 elimination in a riparian zone. Ground Water 1999, 37, 448–457. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]









| Statistic | Depth (m) | pH | EC (μS/cm) | DO (mg/L) | Temp (°C) | Eh (mV) | HCO3 (mg/L) | F (mg/L) | Cl (mg/L) | Br (mg/L) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Min | 10.0 | 5.2 | 114.0 | 0.8 | 9.5 | 16.9 | 0.0 | 0.0 | 5.5 | 0.0 |
| Max | 240.0 | 7.7 | 1776.0 | 11.5 | 19.3 | 538.4 | 232.9 | 2.3 | 335.6 | 0.2 |
| Average | 56.1 | 6.2 | 334.1 | 7.1 | 15.0 | 233.8 | 53.0 | 0.1 | 33.2 | 0.0 |
| 25% | 48.0 | 6.0 | 229.5 | 5.7 | 14.6 | 193.0 | 25.6 | 0.0 | 17.9 | 0.0 |
| Median | 50.0 | 6.2 | 305.0 | 7.6 | 15.0 | 230.0 | 40.3 | 0.1 | 27.5 | 0.0 |
| 75% | 84.0 | 6.4 | 370.0 | 8.8 | 15.6 | 270.9 | 66.6 | 0.1 | 39.1 | 0.1 |
| Statistic | NO3–N (mg/L) | SO4 (mg/L) | Ca (mg/L) | Mg (mg/L) | Na (mg/L) | K (mg/L) | Fe (mg/L) | Mn (mg/L) | Si (mg/L) | Sr (mg/L) |
| Min | 0.01 | 0.0 | 4.2 | 0.7 | 5.3 | 0.6 | 0.0 | 0.0 | 5.3 | 0.0 |
| Max | 67.21 | 135.4 | 102.1 | 36.5 | 77.3 | 154.5 | 0.2 | 11.9 | 22.2 | 1.2 |
| Average | 17.63 | 12.2 | 29.2 | 6.8 | 21.8 | 4.2 | 0.04 | 0.19 | 15.2 | 0.3 |
| 25% | 7.88 | 2.8 | 18.4 | 3.5 | 15.6 | 1.3 | 0.03 | 0.07 | 14.1 | 0.2 |
| Median | 15.38 | 7.5 | 26.5 | 5.4 | 20.0 | 1.9 | 0.05 | 0.02 | 15.6 | 0.3 |
| 75% | 23.29 | 15.1 | 37.6 | 8.3 | 26.4 | 2.8 | 0.01 | 0.004 | 17.0 | 0.4 |
| Variables | pH | EC | DO | HCO3 | F | Cl | NO3 | SO4 | Ca | Mg | Na | K |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| pH | 1 | – | – | – | – | – | – | – | – | – | – | – |
| EC | −0.247 | 1 | – | – | – | – | – | – | – | – | – | – |
| DO | −0.173 | −0.130 | 1 | – | – | – | – | – | – | – | – | – |
| HCO3 | 0.627 | 0.079 | −0.628 | 1 | – | – | – | – | – | – | – | – |
| F | 0.663 | −0.289 | −0.389 | 0.530 | 1 | – | – | – | – | – | – | – |
| Cl | −0.266 | 0.794 | −0.172 | 0.087 | −0.265 | 1 | – | – | – | – | – | – |
| NO3 | −0.403 | 0.725 | 0.223 | −0.253 | −0.461 | 0.586 | 1 | – | – | – | – | – |
| SO4 | 0.022 | 0.327 | −0.415 | 0.239 | 0.037 | 0.247 | 0.007 | 1 | – | – | – | – |
| Ca | 0.015 | 0.865 | −0.262 | 0.372 | −0.064 | 0.782 | 0.601 | 0.379 | 1 | – | – | – |
| Mg | −0.015 | 0.764 | −0.311 | 0.341 | −0.029 | 0.728 | 0.431 | 0.521 | 0.777 | 1 | – | – |
| Na | −0.408 | 0.717 | 0.003 | −0.059 | −0.347 | 0.749 | 0.805 | −0.033 | 0.633 | 0.426 | 1 | – |
| K | −0.520 | 0.508 | 0.054 | −0.305 | −0.490 | 0.439 | 0.518 | 0.323 | 0.329 | 0.403 | 0.388 | 1 |
| Variables | PC1 | PC2 | PC3 | PC4 |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Ca | 0.904 | – | – | – |
| NO3 | 0.830 | (−0.336) | – | – |
| Na | 0.830 | – | (−0.383) | – |
| Cl | 0.828 | – | – | – |
| Mg | 0.706 | 0.306 | – | 0.416 |
| HCO3 | – | 0.792 | 0.450 | – |
| DO | – | −0.775 | – | – |
| Mn | – | 0.745 | – | – |
| pH | – | – | 0.893 | – |
| F | – | – | 0.560 | – |
| Fe | – | – | (−0.428) | 0.323 |
| SO4 | – | – | – | 0.825 |
| K | – | – | – | 0.734 |
| Eigenvalue | 3.5632 | 2.268 | 1.831 | 1.636 |
| Percentage variance explained | 27.407 | 17.449 | 14.083 | 12.585 |
| Cumulative percentage variance explained | 27.407 | 44.855 | 58.938 | 71.523 |
© 2016 by the authors; licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC-BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Kim, H.-s.; Park, S.-r. Hydrogeochemical Characteristics of Groundwater Highly Polluted with Nitrate in an Agricultural Area of Hongseong, Korea. Water 2016, 8, 345. https://doi.org/10.3390/w8080345
Kim H-s, Park S-r. Hydrogeochemical Characteristics of Groundwater Highly Polluted with Nitrate in an Agricultural Area of Hongseong, Korea. Water. 2016; 8(8):345. https://doi.org/10.3390/w8080345
Chicago/Turabian StyleKim, Hyun-su, and So-ra Park. 2016. "Hydrogeochemical Characteristics of Groundwater Highly Polluted with Nitrate in an Agricultural Area of Hongseong, Korea" Water 8, no. 8: 345. https://doi.org/10.3390/w8080345
APA StyleKim, H.-s., & Park, S.-r. (2016). Hydrogeochemical Characteristics of Groundwater Highly Polluted with Nitrate in an Agricultural Area of Hongseong, Korea. Water, 8(8), 345. https://doi.org/10.3390/w8080345