Strontium Removal in Seawater by Means of Composite Magnetic Nanoparticles Derived from Industrial Sludge
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Chemicals
2.2. Manufacturing of Composite Magnetic Nanoparticles
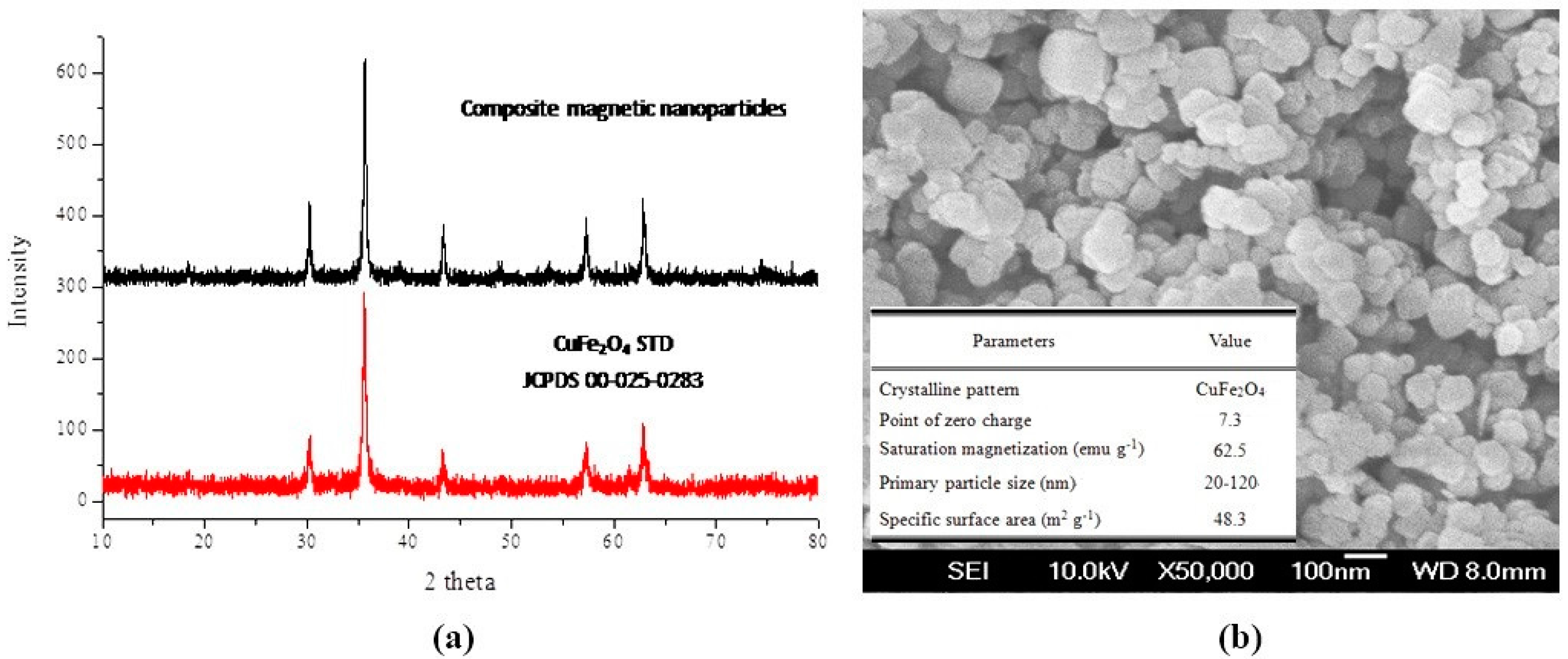
2.3. Characterization of the Composite Magnetic Nanoparticles
2.4. Batch Adsorption Experiments
3. Results and Discussion
3.1. Basic Properties of the Adsorbent
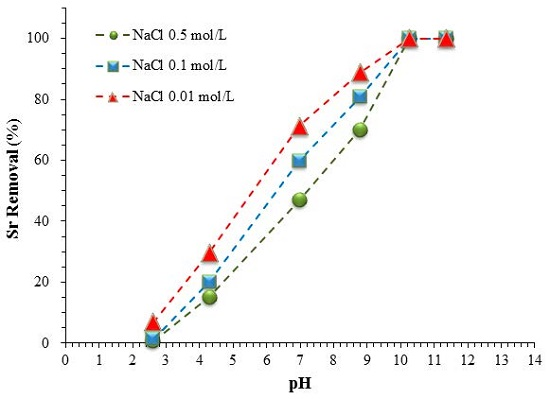
3.2. Effect of pH and Competitive Ions
3.2.1. pH Effect
3.2.2. Effect of Competitive Ions
3.3. Adsorption Kinetics
3.4. Isotherm Modeling
3.5. Comparison of the Sr Adsorption Capacity with Other Adsorbents
3.6. Sr Removal from Seawater
4. Conclusions
Acknowledgments
Author Contributions
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Baisden, P.A.; Choppin, G.R. Nuclear waste management and the nuclear fuel cycle. In Radiochemistry and Nuclear Chemistry; Encyclopedia of Life Support Systems (EOLSS): Oxford, UK, 2007. [Google Scholar]
- U.S. Environmental Protection Agency (USEPA). EPA Facts about Strontium-90; USEPA: Washington, DC, USA, 2002.
- Gerke, T.L.; Little, B.J.; Luxton, T.P.; Scheckel, K.G.; Maynard, J.B. Strontium concentrations in corrosion products from residential drinking water distribution systems. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2013, 47, 5171–5177. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chegrouche, S.; Mellah, A.; Barkat, M. Removal of strontium from aqueous solutions by adsorption onto activated carbon: Kinetic and thermodynamic studies. Desalination 2009, 235, 306–318. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dahl, S.G.; Allain, P.; Marie, P.J.; Mauras, Y.; Boivin, G.; Ammann, P.; Tsouderos, Y.; Delmas, P.D.; Christiansen, C. Incorporation and distribution of strontium in bone. Bone 2001, 28, 446–453. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nielsen, S.P. The biological role of strontium. Bone 2004, 35, 583–588. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mangano, J.J.; Sherman, J.D. Elevated in vivo strontium-90 from nuclear weapons test fallout among cancer decedents: A case-control study of deciduous teeth. Int. J. Health Serv. 2011, 41, 137–158. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ma, B.; Oh, S.; Shin, W.S.; Choi, S.J. Removal of Co2+, Sr2+ and Cs+ from aqueous solution by phosphate-modified montmorillonite (PMM). Desalination 2011, 276, 336–346. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ambashta, R.D.; Sillanpää, M.E.T. Membrane purification in radioactive waste management: A short review. J. Environ. Radioact. 2012, 105, 76–84. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- U.S. Department of Health and Human Services. Toxicological Profile for Strontium; Public Health Service, Agency for Toxic Substances and Disease Registry: Washington, DC, USA, 2004.
- Zhang, L.; Wei, J.Y.; Zhao, X.; Li, F.Z.; Jiang, F.; Zhang, M. Strontium(II) adsorption on Sb(III)/Sb2O5. Chem. Eng. J. 2015, 267, 245–252. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Raut, D.R.; Mohapatra, P.K.; Manchanda, V.K. A highly efficient supported liquid membrane system for selective strontium separation leading to radioactive waste remediation. J. Membr. Sci. 2012, 390–391, 76–83. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Park, Y.; Lee, Y.C.; Shin, W.S.; Choi, S.J. Removal of cobalt, strontium and cesium from radioactive laundry wastewater by ammonium molybdophosphate–polyacrylonitrile (AMP–PAN). Chem. Eng. J. 2010, 162, 685–695. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Murthy, Z.V.P.; Parmar, S. Removal of strontium by electrocoagulation using stainless steel and aluminum electrodes. Desalination 2011, 282, 63–67. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Faghihian, H.; Iravani, M.; Moayed, M.; Ghannadi-Maragheh, M. Preparation of a novel PAN–zeolite nanocomposite for removal of Cs+ and Sr2+ from aqueous solutions: Kinetic, equilibrium, and thermodynamic studies. Chem. Eng. J. 2013, 222, 41–48. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cho, Y.C.; Komarneni, S. Cation exchange equilibria of cesium and strontium with K-depleted biotite and muscovite. Appl. Clay Sci. 2009, 44, 15–20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sen Gupta, S.; Bhattacharyya, K.G. Adsorption of heavy metals on kaolinite and montmorillonite: A review. Phys. Chem. Chem. Phys. 2012, 14, 6698–6723. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tu, Y.J.; You, C.F.; Chang, C.K.; Chan, T.S.; Li, S.H. XANES evidence of molybdenum adsorption onto novel fabricated nano-magnetic CuFe2O4. Chem. Eng. J. 2014, 244, 343–349. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cao, C.Y.; Qu, J.; Yan, W.S.; Zhu, J.F.; Wu, Z.Y.; Song, W.G. Low-cost synthesis of flowerlike α-Fe2O3 nanostructures for heavy metal ion removal: Adsorption property and mechanism. Langmuir 2012, 28, 4573–4579. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tu, Y.J.; You, C.F.; Chang, C.K. Conversion of waste Mn-Zn dry battery as efficient nano-adsorbents for hazardous metals removal. J. Hazard. Mater. 2013, 258–259, 102–108. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Small, T.D.; Warren, L.A.; Ferris, F.G. Influence of ionic strength on strontium sorption to bacteria, Fe(III) oxide, and composite bacteria Fe(III) oxide surfaces. Appl. Geochem. 2001, 16, 939–946. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ghaemi, A.; Torab-Mostaedi, M.; Ghannadi-Maragheh, M. Characterizations of strontium(II) and barium(II) adsorption from aqueous solutions using dolomite powder. J. Hazard. Mater. 2011, 190, 916–921. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Krupicka, S.; Novak, P. Oxide spinels. Handb. Ferromagn. Mater. 1982, 3, 189–304. [Google Scholar]
- Tu, Y.J.; You, C.F.; Chang, C.K.; Wang, S.L.; Chan, T.S. Adsorption behavior of As(III) onto a copper ferrite generated from printed circuit board industry. Chem. Eng. J. 2013, 225, 433–439. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tu, Y.J.; You, C.F.; Chang, C.K. Kinetics and thermodynamics of adsorption for Cd on green manufactured nano-particles. J. Hazard. Mater. 2012, 235–236, 116–122. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tu, Y.J.; Chang, C.K.; You, C.F.; Lou, J.C. Recycling of Cu powder from industrial sludge by combined acid leaching, chemical exchange and ferrite process. J. Hazard. Mater. 2010, 181, 981–985. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tu, Y.J.; You, C.F.; Chang, C.K.; Wang, S.L.; Chan, T.S. Arsenate adsorption from water using a novel fabricated copper ferrite. Chem. Eng. J. 2012, 198–199, 440–448. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Denizli, A.; Salih, B.; Piskin, E. New sorbents for removal of heavy metal ions: Diamine-glow-discharge treated polyhydroxyethylmethacrylate microspheres. J. Chromatogr. A 1997, 773, 169–178. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, C.H.; Shih, Y.J.; Huang, Y.H.; Huang, C.P. Kinetic and thermodynamic studies for adsorptive removal of Sr2+ using waste iron oxide. J. Taiwan Inst. Chem. Eng. 2014, 45, 914–920. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tu, Y.J.; You, C.F.; Chen, Y.R.; Huang, C.P.; Huang, Y.H. Application of recycled iron oxide for adsorptive removal of strontium. J. Taiwan Inst. Chem. Eng. 2015, 53, 92–97. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Namasivayam, C.; Prathap, K. Uptake of molybdate by adsorption onto industrial solid waste Fe(III)/Cr(III) hydroxide: Kinetic and equilibrium studies. Environ. Technol. 2006, 27, 923–932. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lagergren, S. Zur Theorie der Sogenannten Adsorption geloester Stoffe; PA Norstedt & Söner: Stockholm, Sweden, 1898; Volume 24, pp. 1–39. [Google Scholar]
- Ho, Y.S.; McKay, G. The kinetics of sorption of divalent metals ions onto sphagnum moss peat. Water Res. 2000, 34, 735–742. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Freundlich, H.M.F. Ueber die adsorption in loesungen (Adsorption in solution). J. Phys. Chem. 1906, 57, 384–470. [Google Scholar]
- Langmuir, I. The adsorption of gases on plane surfaces of glass, Mica and Platinum. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 1918, 40, 1361–1368. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chiron, N.; Guilet, R.; Deydier, E. Adsorption of Cu(II) and Pb(II) onto a grafted silica: Isotherms and kinetic models. Water Res. 2003, 37, 3079–3086. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Y.H.; Di, Z.; Ding, J.; Wu, D.; Luan, Z.; Zhu, Y. Adsorption thermodynamic, kinetic and desorption studies of Pb2+ on carbon nanotubes. Water Res. 2005, 39, 605–609. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Khan, A.A.; Singh, R.P. Adsorption thermodynamics of carbofuran on Sn (IV) arsenosilicate in H+, Na+ and Ca2+ forms. Colloids Surf. 1987, 24, 33–42. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aksu, Z. Determination of the equilibrium, kinetic and thermodynamic parameters of the batch biosorption of nickel(II) ions onto chlorella vulgaris. Process Biochem. 2002, 38, 89–99. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yan, L.G.; Xu, Y.Y.; Yu, H.Q.; Xin, X.D.; Wei, Q.; Du, B. Adsorption of phosphate from aqueous solution by hydroxy-aluminum, hydroxy-iron and hydroxy-iron–aluminum pillared bentonites. J. Hazard. Mater. 2010, 179, 244–250. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cheng, Z.; Gao, Z.; Ma, W.; Sun, Q.; Wang, B.; Wang, X. Preparation of magnetic Fe3O4 particles modified sawdust as the adsorbent to remove strontium ions. Chem. Eng. J. 2012, 209, 451–457. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]






| Temperature (K) | Freundlich | Langmuir | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| KF | n | R2 | qm | KL | R2 | |
| 298 | 7.381 | 4.090 | 0.9788 | 19.72 | 0.248 | 0.9939 |
| 308 | 9.373 | 4.632 | 0.9853 | 21.05 | 0.439 | 0.9899 |
| 318 | 13.831 | 6.716 | 0.9744 | 23.04 | 1.130 | 0.9938 |
| Temperature (K) | Thermodynamic Constant | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| K (m·M−1) | ΔG° (kJ·mol−1) | ΔS° (J·mol−1·K−1) | ΔH° (kJ·mol−1) | |
| 298 | 9.88 | −5.68 | 9.38 | 2.11 |
| 308 | 12.39 | −6.45 | ||
| 318 | 15.43 | −7.23 | ||
| Adsorbents | pH | Temperature (K) | Sr adsorption Capacity (mg·g−1) | References |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| FeOOH (BT1) | 10.50 | 318 | 39.8 | [29] |
| FeOOH (BT1) | 10.50 | 303 | 38.5 | [29] |
| FeOOH (BT1) | 10.50 | 293 | 32.9 | [29] |
| FeOOH (BT9) | 11.22 | 323 | 29.9 | [30] |
| FeOOH (BT9) | 11.22 | 303 | 28.0 | [30] |
| FeOOH (BT9) | 11.22 | 288 | 27.0 | [30] |
| Composite magnetic nanoparticles | 10.25 | 318 | 23.0 | This study |
| Composite magnetic nanoparticles | 10.25 | 308 | 21.1 | This study |
| Composite magnetic nanoparticles | 10.25 | 298 | 19.7 | This study |
| Ammonium molybdophosphate polyacrylonitrile | 5.01 | 293 | 16.6 | [13] |
| Phosphate-modified montmorillonite | - | 298 | 12.6 | [8] |
| Magnetic Fe3O4 particles modified sawdust | 6.74 | 293 | 12.6 | [41] |
| Hydrous ferric oxide | 10.01 | 293 | 6.9 | [21] |
| Dolomite | 5.50 | 293 | 1.2 | [22] |
| Matrix | Adsorption pH | Sr (mg·L−1) | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| before Adsorption (mg·L−1) | after Adsorption (mg·L−1) | Removal (%) | ||
| Seawater | 10.37 (adjusted pH) | 7.98 | 1.08 | 86.5 |
| 8.21 (natural pH) | 7.98 | 3.01 | 62.3 | |
| 6.09 (adjusted pH) | 7.98 | 6.58 | 17.5 | |
| 3.13 (adjusted pH) | 7.98 | 7.79 | 2.4 | |
© 2016 by the authors; licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC-BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Tu, Y.-J.; You, C.-F.; Zhang, Z.; Duan, Y.; Fu, J.; Xu, D. Strontium Removal in Seawater by Means of Composite Magnetic Nanoparticles Derived from Industrial Sludge. Water 2016, 8, 357. https://doi.org/10.3390/w8080357
Tu Y-J, You C-F, Zhang Z, Duan Y, Fu J, Xu D. Strontium Removal in Seawater by Means of Composite Magnetic Nanoparticles Derived from Industrial Sludge. Water. 2016; 8(8):357. https://doi.org/10.3390/w8080357
Chicago/Turabian StyleTu, Yao-Jen, Chen-Feng You, Zhonghao Zhang, Yanping Duan, Jing Fu, and Di Xu. 2016. "Strontium Removal in Seawater by Means of Composite Magnetic Nanoparticles Derived from Industrial Sludge" Water 8, no. 8: 357. https://doi.org/10.3390/w8080357
APA StyleTu, Y.-J., You, C.-F., Zhang, Z., Duan, Y., Fu, J., & Xu, D. (2016). Strontium Removal in Seawater by Means of Composite Magnetic Nanoparticles Derived from Industrial Sludge. Water, 8(8), 357. https://doi.org/10.3390/w8080357