Effects of Plant Growth Form and Water Substrates on the Decomposition of Submerged Litter: Evidence of Constructed Wetland Plants in a Greenhouse Experiment
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Study Site
2.2. Plant Litter Decomposition Experiment
2.3. Measurements of the Initial and Harvested Litter
2.4. Statistical Analysis
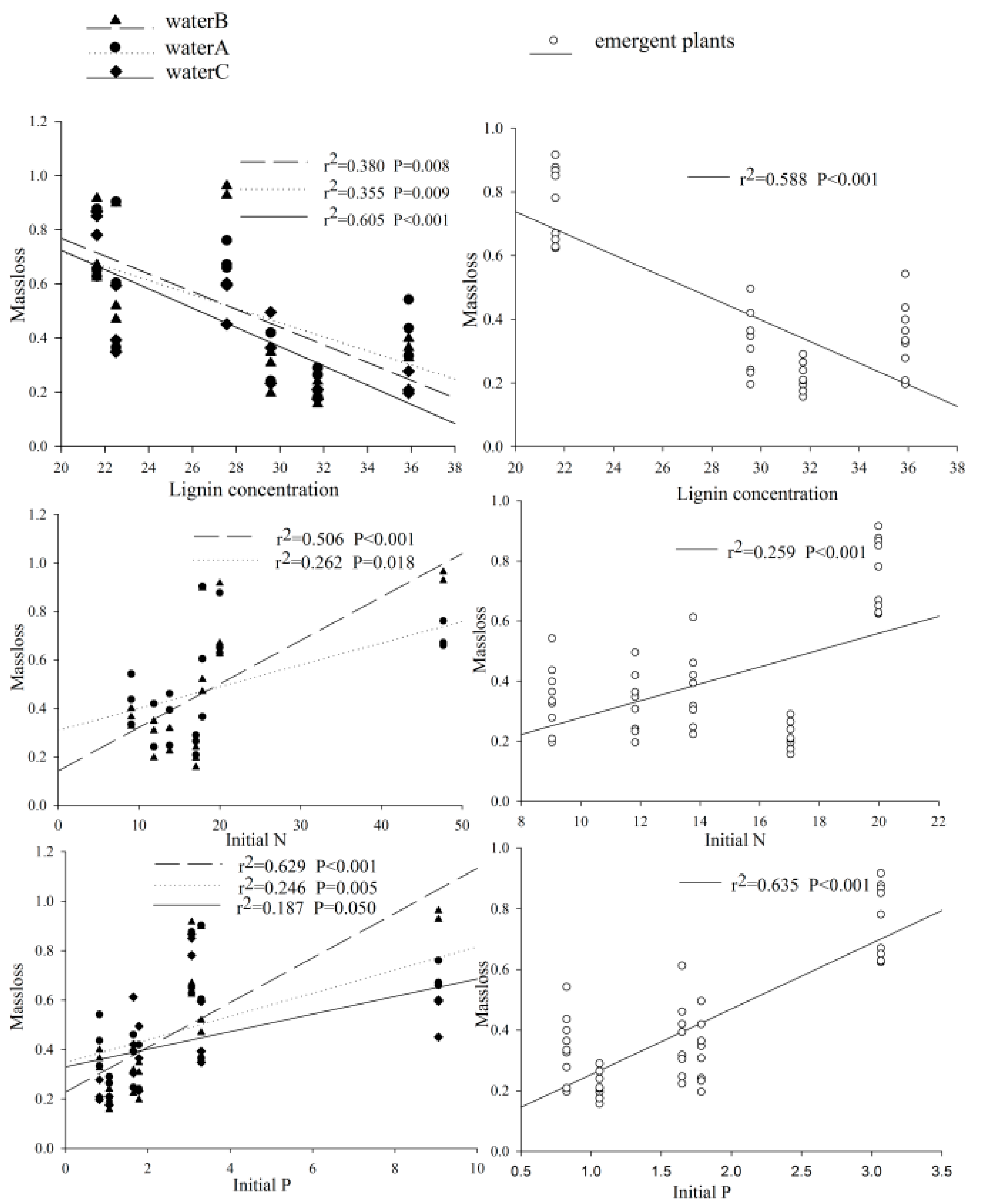
3. Results
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Acknowledgments
Author Contributions
Conflicts of Interest
Appendix A
| MS | TN−Change | TP−Change | TN−Loss | TP−Loss | |||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| R | p | R | p | R | p | R | p | R | p | ||
| Lignin | All | −0.653 | <0.001 | −0.256 | 0.067 | −0.012 | 0.935 | −0.269 | 0.054 | −0.435 | <0.001 |
| F | 0.354 | 0.164 | −0.813 | <0.001 | −0.992 | <0.001 | 0.682 | 0.003 | 0.757 | <0.001 | |
| E | −0.767 | <0.001 | 0.225 | 0.194 | 0.481 | 0.003 | −0.759 | <0.001 | −0.713 | <0.001 | |
| water A | −0.596 | 0.009 | −0.297 | 0.231 | 0.065 | 0.797 | −0.264 | 0.291 | −0.466 | 0.051 | |
| water B | −0.617 | 0.008 | −0.342 | 0.179 | −0.069 | 0.792 | −0.173 | 0.521 | −0.488 | 0.047 | |
| water C | −0.778 | <0.001 | −0.137 | 0.600 | −0.038 | 0.880 | −0.361 | 0.141 | −0.372 | 0.129 | |
| N | All | 0.520 | <0.001 | −0.281 | 0.028 | −0.391 | <0.001 | 0.490 | <0.001 | 0.453 | <0.001 |
| F | 0.354 | 0.165 | −0.813 | <0.001 | −0.992 | <0.001 | 0.682 | 0.003 | 0.757 | <0.001 | |
| E | 0.509 | <0.001 | −0.311 | 0.040 | −0.331 | 0.028 | 0.523 | <0.001 | 0.467 | 0.001 | |
| water A | 0.512 | 0.018 | −0.373 | 0.096 | −0.453 | 0.049 | 0.503 | 0.020 | 0.459 | 0.036 | |
| water B | 0.711 | <0.001 | −0.287 | 0.220 | −0.342 | 0.140 | 0.526 | 0.021 | 0.470 | 0.036 | |
| water C | 0.367 | 0.102 | −0.203 | 0.390 | −0.413 | 0.063 | 0.463 | 0.034 | 0.468 | 0.032 | |
| P | All | 0.594 | <0.001 | −0.173 | 0.184 | −0.329 | <0.001 | 0.447 | <0.01 | 0.430 | <0.001 |
| F | 0.354 | 0.164 | −0.813 | <0.001 | −0.992 | <0.001 | 0.682 | 0.003 | 0.757 | <0.001 | |
| E | 0.797 | <0.001 | −0.095 | 0.542 | −0.228 | 0.136 | 0.454 | 0.002 | 0.432 | 0.003 | |
| water A | 0.588 | 0.005 | −0.274 | 0.229 | −0.397 | 0.074 | 0.483 | 0.026 | 0.469 | 0.032 | |
| water B | 0.793 | <0.001 | −0.145 | 0.542 | −0.261 | 0.267 | 0.436 | 0.062 | 0.424 | 0.063 | |
| water C | 0.432 | 0.050 | −0.124 | 0.603 | −0.350 | 0.120 | 0.437 | 0.047 | 0.437 | 0.048 | |
Appendix B
| Latin Name | Initial TN (g/kg) | Initial TP (g/kg) | Lignin (%) |
|---|---|---|---|
| Salvinia natans | 17.83 | 3.30 | 22.50 |
| Lemna minor | 2.41 | 5.11 | 27.57 |
| Iris wilsonii | 19.99 | 3.07 | 21.63 |
| Zizania latifolia | 9.03 | 0.83 | 35.88 |
| Sparganium stoloniferum | 13.77 | 1.65 | - |
| Typha orientalis | 11.82 | 1.79 | 29.57 |
| Phragmites australis | 17.04 | 1.06 | 31.72 |
References
- Johnston, C.A. Sediment and nutrient retention by freshwater wetlands: Effects on surface water quality. Crit. Rev. Environ. Sci. Technol. 1991, 21, 491–565. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hoorens, B.; Aerts, R.; Stroetenga, M. Does initial litter chemistry explain litter mixture effects on decomposition? Oecologia 2003, 137, 578–586. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bonanomi, G.; Senatore, M.; Migliozzi, A.; De Marco, A.; Pintimalli, A.; Lanzotti, V.; Mazzoleni, S. Decomposition of submerged plant litter in a Mediterranean reservoir: A microcosm study. Aquat. Bot. 2015, 120, 169–177. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brinson, M.M.; Lugo, A.E.; Brown, S. Primary productivity, decomposition and consumer activity in freshwater wetlands. Annu. Rev. Ecol. Syst. 1981, 12, 123–161. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cotrufo, M.F.; Ngao, J.; Marzaioli, F.; Piermatteo, D. Inter-comparison of methods for quantifying above-ground leaf litter decomposition rates. Plant Soil 2010, 334, 365–376. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Morris, J.T.; Bradley, P.M. Effects of nutrient loading on the carbon balance of coastal wetland sediments. Limnol. Oceanogr. 1999, 44, 699–702. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liski, J.; Nissinen, A.; Erhard, M.; Taskinen, O. Climatic effects on litter decomposition from arctic tundra to tropical rainforest. Glob. Chang. Biol. 2003, 9, 575–584. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bünemann, E.; Bossio, D.A.; Smithson, P.; Frossard, E.; Oberson, A. Microbial community composition and substrate use in a highly weathered soil as affected by crop rotation and P fertilization. Soil Biol. Biochem. 2004, 36, 889–901. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vitousek, P.M. Nutrient Cycling and Limitation: Hawai’i as a Model System; Princeton University Press: Princeton, NJ, USA, 2004. [Google Scholar]
- IWA (International Water Association). Constructed Wetlands for Pollution Control: Processes, Performance, Design and Operation; IWA Publishing: London, UK, 2001. [Google Scholar]
- Chimney, M.J.; Pietro, K.C. Decomposition of macrophyte litter in a subtropical constructed wetland in south Florida (USA). Ecol. Eng. 2006, 27, 301–321. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kadlec, R.H.; Wallace, S. Treatment Wetlands; CRC Press: Boca Raton, FL, USA, 2009. [Google Scholar]
- Alvarez, J.A.; Bécares, E. Seasonal decomposition of Typha latifolia in a free-water surface constructed wetland. Ecol. Eng. 2006, 28, 99–105. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kleeberg, A. Impact of aquatic macrophyte decomposition on sedimentary nutrient and metal mobilization in the initial stages of ecosystem development. Aquat. Bot. 2013, 105, 41–49. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Carvalho, C.; Hepp, L.U.; Palma-Silva, C.; Albertoni, E.F. Decomposition of macrophytes in a shallow subtropical lake. Limnol.-Ecol. Manag. Inland Waters 2015, 53, 1–9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vymazal, J. Emergent plants used in free water surface constructed wetlands: A review. Ecol. Eng. 2013, 61, 582–592. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aerts, R. Climate, leaf litter chemistry and leaf litter decomposition in terrestrial ecosystems: A triangular relationship. Oikos 1997, 79, 439–449. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cornwell, W.K.; Cornelissen, J.H.; Amatangelo, K.; Dorrepaal, E.; Eviner, V.T.; Godoy, O.; Hobbie, S.E.; Hoorens, B.; Kurokawa, H.; Pérez-Harguindeguy, N. Plant species traits are the predominant control on litter decomposition rates within biomes worldwide. Ecol. Lett. 2008, 11, 1065–1071. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lan, Y.; Cui, B.; You, Z.; Li, X.; Han, Z.; Zhang, Y.; Zhang, Y. Litter decomposition of six macrophytes in a eutrophic shallow lake (Baiyangdian Lake, China). CLEAN-Soil Air Water 2012, 40, 1159–1166. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ren, L.; Yuan, Z.; Wang, H.; Wen, Z. Nitrogen resorption of three life--forms (trees, shrubs and grasses) in the semiarid region of north China. Acta Bot. Boreal.-Occident. Sin. 2004, 25, 497–502. [Google Scholar]
- Guo, P.; Jiang, H.; Yu, S.; Ma, Y.; Dou, R.; Song, X. Comparison of litter decomposition of six species of coniferous and broad-leaved trees in subtropical China. Chin. J. Appl. Environ. Biol. 2009, 15, 655–659. [Google Scholar]
- Cao, P.P.; Liu, M.S.; Tang, J.Y.; Teng, S.; Xu, C. A comparative study on the decomposition processes among some aquatic plants. Acta Ecol. Sin. 2014, 34, 3848–3858. [Google Scholar]
- Xie, Y.; Yu, D.; Ren, B. Effects of nitrogen and phosphorus availability on the decomposition of aquatic plants. Aquat. Bot. 2004, 80, 29–37. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Balasubramanian, D.; Arunachalam, K.; Das, A.; Arunachalam, A. Decomposition and nutrient release of Eichhornia crassipes (Mart.) Solms. under different trophic conditions in wetlands of eastern Himalayan foothills. Ecol. Eng. 2012, 44, 111–122. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, X.; Cui, B.; Yang, Q.; Lan, Y.; Wang, T.; Han, Z. Effects of plant species on macrophyte decomposition under three nutrient conditions in a eutrophic shallow lake, North China. Ecol. Model. 2013, 252, 121–128. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Newman, S.; Kumpf, H.; Laing, J.; Kennedy, W. Decomposition responses to phosphorus enrichment in an Everglades (USA) slough. Biogeochemistry 2001, 54, 229–250. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gulis, V.; Suberkropp, K. Leaf litter decomposition and microbial activity in nutrient-enriched and unaltered reaches of a headwater stream. Freshw. Biol. 2003, 48, 123–134. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gulis, V.; Ferreira, V.; Graca, M. Stimulation of leaf litter decomposition and associated fungi and invertebrates by moderate eutrophication: Implications for stream assessment. Freshw. Biol. 2006, 51, 1655–1669. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Breeuwer, A.; Heijmans, M.; Robroek, B.J.; Limpens, J.; Berendse, F. The effect of increased temperature and nitrogen deposition on decomposition in bogs. Oikos 2008, 117, 1258–1268. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Peterson, B.J.; Deegan, L.; Helfrich, J.; Hobbie, J.E.; Hullar, M.; Moller, B.; Ford, T.E.; Hershey, A.; Hiltner, A.; Kipphut, G. Biological responses of a tundra river to fertilization. Ecology 1993, 74, 653–672. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Royer, T.V.; Minshall, G.W. Effects of nutrient enrichment and leaf quality on the breakdown of leaves in a hardwater stream. Freshw. Biol. 2001, 46, 603–610. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pascoal, C.; Cássio, F. Contribution of fungi and bacteria to leaf litter decomposition in a polluted river. Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 2004, 70, 5266–5273. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cui, L.; Li, W.; Zhang, Y.; Wei, J.; Lei, Y.; Zhang, M.; Pan, X.; Zhao, X.; Li, K.; Ma, W. Nitrogen removal in a horizontal subsurface flow constructed wetland estimated using the first-order kinetic model. Water 2016, 8, 514. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Freschet, G.T.; Cornelissen, J.H.; Van Logtestijn, R.S.; Aerts, R. Evidence of the ‘plant economics spectrum’ in a subarctic flora. J. Ecol. 2010, 98, 362–373. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wen, J.; Yu, J.; Zhong, Y.; Pang, G.; Sun, L. Study on the treatment efficiency of natural wetland on eutrophic water and its mechanism. Ind. Water Treat. 2013, 33, 31–35. [Google Scholar]
- Iamchaturapatr, J.; Yi, S.W.; Rhee, J.S. Nutrient removals by 21 aquatic plants for vertical free surface-flow (VFS) constructed wetland. Ecol. Eng. 2007, 29, 287–293. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, A.; Wu, S.; Ni, L. Study of macrophytes nitrogen and phosphorus contents of the shallow lakes in the middle reaches of Changjiang River. Acta Hydrobiol. Sin. 2005, 29, 412. [Google Scholar]
- Pan, X.; Ping, Y.; Cui, L.; Li, W.; Zhang, X.; Zhou, J.; Yu, F.-H.; Prinzing, A. Plant litter submergence affects the water quality of a constructed wetland. PLoS ONE 2017, 12, e0171019. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kirschner, A.K.; Riegl, B.; Velimirov, B. Degradation of emergent and submerged macrophytes in an oxbow lake of an embanked backwater system: Implications for the terrestrialization process. Int. Rev. Hydrobiol. 2001, 86, 555–571. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hunt, H.; Ingham, E.; Coleman, D.; Elliott, E.; Reid, C. Nitrogen limitation of production and decomposition in prairie, mountain meadow, and pine forest. Ecology 1988, 69, 1009–1016. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Saranya, G.; Saravanan, P.; Dharmendira, K.M.; Renganathan, S. Equilibrium uptake and bioaccumulation of basic violet 14 using submerged macrophyte Hydrilla verticillata. CLEAN-Soil Air Water 2011, 39, 283–288. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kuehn, K.; Gessner, M.; Wetzel, R.; Suberkropp, K. Decomposition and CO2 evolution from standing litter of the emergent macrophyte Erianthus giganteus. Microb. Ecol. 1999, 38, 50–57. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kuehn, K.A.; Steiner, D.; Gessner, M.O. Diel mineralization patterns of standing-dead plant litter: Implications for CO2 flux from wetlands. Ecology 2004, 85, 2504–2518. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Poi de Neiff, A.; Neiff, J.J.; Casco, S.L. Leaf litter decomposition in three wetland types of the Paraná River floodplain. Wetlands 2006, 26, 558–566. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rejmánková, E.; Houdková, K. Wetland plant decomposition under different nutrient conditions: What is more important, litter quality or site quality? Biogeochemistry 2006, 80, 245–262. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gessner, M.O. Breakdown and nutrient dynamics of submerged Phragmites shoots in the littoral zone of a temperate hardwater lake. Aquat. Bot. 2000, 66, 9–20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liao, C.Z.; Luo, Y.Q.; Fang, C.M.; Chen, J.K.; Li, B. Litter pool sizes, decomposition, and nitrogen dynamics in Spartina alterniflora-invaded and native coastal marshlands of the Yangtze Estuary. Oecologia 2008, 156, 589–600. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Enríquez, S.; Duarte, C.M.; Sand-Jensen, K. Patterns in decomposition rates among photosynthetic organisms: The importance of detritus C: N: P content. Oecologia 1993, 94, 457–471. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- McLatchey, G.P.; Reddy, K. Regulation of organic matter decomposition and nutrient release in a wetland soil. J. Environ. Q. 1998, 27, 1268–1274. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brock, T.C.; Boon, J.J.; Paffen, B.G. The effects of the season and of water chemistry on the decomposition of Nymphaea alba L.; weight loss and pyrolysis mass spectrometry of the particulate matter. Aquat. Bot. 1985, 22, 197–229. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Webster, J.; Benfield, E. Vascular plant breakdown in freshwater ecosystems. Annu. Rev. Ecol. Syst. 1986, 17, 567–594. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, Y.; Ma, S.; Sun, J.; Wang, X.; Cheng, G.; Lu, X. Chemical diversity and incubation time affect non-additive responses of soil carbon and nitrogen cycling to litter mixtures from an alpine steppe soil. Soil Biol. Biochem. 2017, 109, 124–134. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]


| df | Mass Loss | TN Change | TP Change | TN Loss | TP Loss | ||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| F | p | F | p | F | p | F | p | F | p | ||
| Group 1: | |||||||||||
| Water (W) | 2 | 1.348 | 0.271 | 1.862 | 0.169 | 1.654 | 0.204 | 0.316 | 0.731 | 0.155 | 0.857 |
| Species (S) | 6 | 28.416 | <0.01 | 23.852 | <0.01 | 116.654 | <0.01 | 14.689 | <0.01 | 32.037 | <0.01 |
| W*S | 12 | 2.164 | 0.033 | 0.856 | 0.595 | 2.020 | 0.047 | 0.417 | 0.948 | 1.681 | 0.107 |
| Group 2: | |||||||||||
| Water (W) | 2 | 1.231 | 0.300 | 0.396 | 0.675 | 0.043 | 0.958 | 0.070 | 0.933 | 0.040 | 0.961 |
| Growth form (G) | 1 | 15.751 | <0.01 | 2.507 | 0.119 | 0.064 | 0.801 | 1.304 | 0.258 | 2.866 | 0.096 |
| W*G | 2 | 2.004 | 0.144 | 0.206 | 0.814 | 0.145 | 0.865 | 0.021 | 0.979 | 0.341 | 0.713 |
© 2017 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Ping, Y.; Pan, X.; Cui, L.; Li, W.; Lei, Y.; Zhou, J.; Wei, J. Effects of Plant Growth Form and Water Substrates on the Decomposition of Submerged Litter: Evidence of Constructed Wetland Plants in a Greenhouse Experiment. Water 2017, 9, 827. https://doi.org/10.3390/w9110827
Ping Y, Pan X, Cui L, Li W, Lei Y, Zhou J, Wei J. Effects of Plant Growth Form and Water Substrates on the Decomposition of Submerged Litter: Evidence of Constructed Wetland Plants in a Greenhouse Experiment. Water. 2017; 9(11):827. https://doi.org/10.3390/w9110827
Chicago/Turabian StylePing, Yunmei, Xu Pan, Lijuan Cui, Wei Li, Yinru Lei, Jian Zhou, and Jiaming Wei. 2017. "Effects of Plant Growth Form and Water Substrates on the Decomposition of Submerged Litter: Evidence of Constructed Wetland Plants in a Greenhouse Experiment" Water 9, no. 11: 827. https://doi.org/10.3390/w9110827
APA StylePing, Y., Pan, X., Cui, L., Li, W., Lei, Y., Zhou, J., & Wei, J. (2017). Effects of Plant Growth Form and Water Substrates on the Decomposition of Submerged Litter: Evidence of Constructed Wetland Plants in a Greenhouse Experiment. Water, 9(11), 827. https://doi.org/10.3390/w9110827






