Abstract
University Lake, a shallow, artificial, urban lake adjacent to the campus of Louisiana State University, has a long history of water quality problems, including algal blooms, fish kills, and high concentrations of fecal indicator bacteria. Periodic dredging of the lake is necessary to prevent its return to swampland. This study was undertaken to elucidate the roles of allochthonous versus autochthonous nutrients as causes of water quality problems in the lake, with the expectation that this information would help identify strategies for lake restoration. Photosynthetic rates and concentrations of inorganic nutrients and phytoplankton pigments were measured over a period of one year. More than 90% of the chlorophyll a (chl a) in the lake was accounted for by Chlorophyceae, Cyanophyceae, and Bacillariophyceae. Concentrations of chl a, which averaged 75 μg L−1, fluctuated weekly during dry weather by as much as a factor of four. Phytoplankton growth rates were about 30% higher 1–2 days after rain events than after periods of dry weather, the implication being that allochthonous nutrient loading has a significant effect on the dynamics of the phytoplankton community in the lake. Therefore, dredging of sediments will likely produce no long-term improvement in water quality. More than 100 storm drains currently discharge into the lake, and diversion of those drains may be the most cost-effective strategy for effecting a long-term improvement in water quality.
1. Introduction
Urban lakes are often plagued by water quality problems related to street runoff, leaky sewer lines, and intentional discharges of wastewater [1,2,3,4]. The accumulation of nutrients in lake sediments and the recycling of those nutrients via resuspension of the sediments or, in the case of phosphate, release during anoxic conditions in the hypolimnion, exacerbate eutrophication problems associated with allochthonous nutrient loading [5,6]. In such cases dredging of contaminated sediments may be necessary to improve water quality [7,8]. University Lake (Baton Rouge, Louisiana) has a long history of water quality problems that reflect in part its shallow depth and the fact that approximately 140 outflows from storm drains enter the lake. The lake has been plagued by high fecal coliform counts for decades, and between 1957 and 1978 there were frequent fish kills in both University Lake and nearby urban lakes as a result of oxygen depletion caused by the decomposition of algal blooms [9]. A restoration effort initiated in 1977 involved the removal of nutrient-laden sediments and the repair of broken sewer lines. Post-restoration monitoring has revealed a reduction in fecal coliform counts and fewer fish kills since the 1980s; however, fecal coliform counts remain above attainment concentrations, and fish kills still occur, particularly during the warm summer months [10,11]. Blooms of cyanobacteria in lakes are associated with a variety of water quality problems, including fish kills, offensive odors, unpalatability of drinking water, unsightly algal scums, and, when the cyanobacteria die or are ingested, the release of water-soluble neurotoxins or hepatotoxins [12,13]. The focus of this study was to determine the relative importance of allochthonous versus autochthonous nutrients as causes of eutrophication and the conditions that lead to cyanobacterial blooms, with the expectation that this information would help guide lake restoration efforts.
2. Study Site
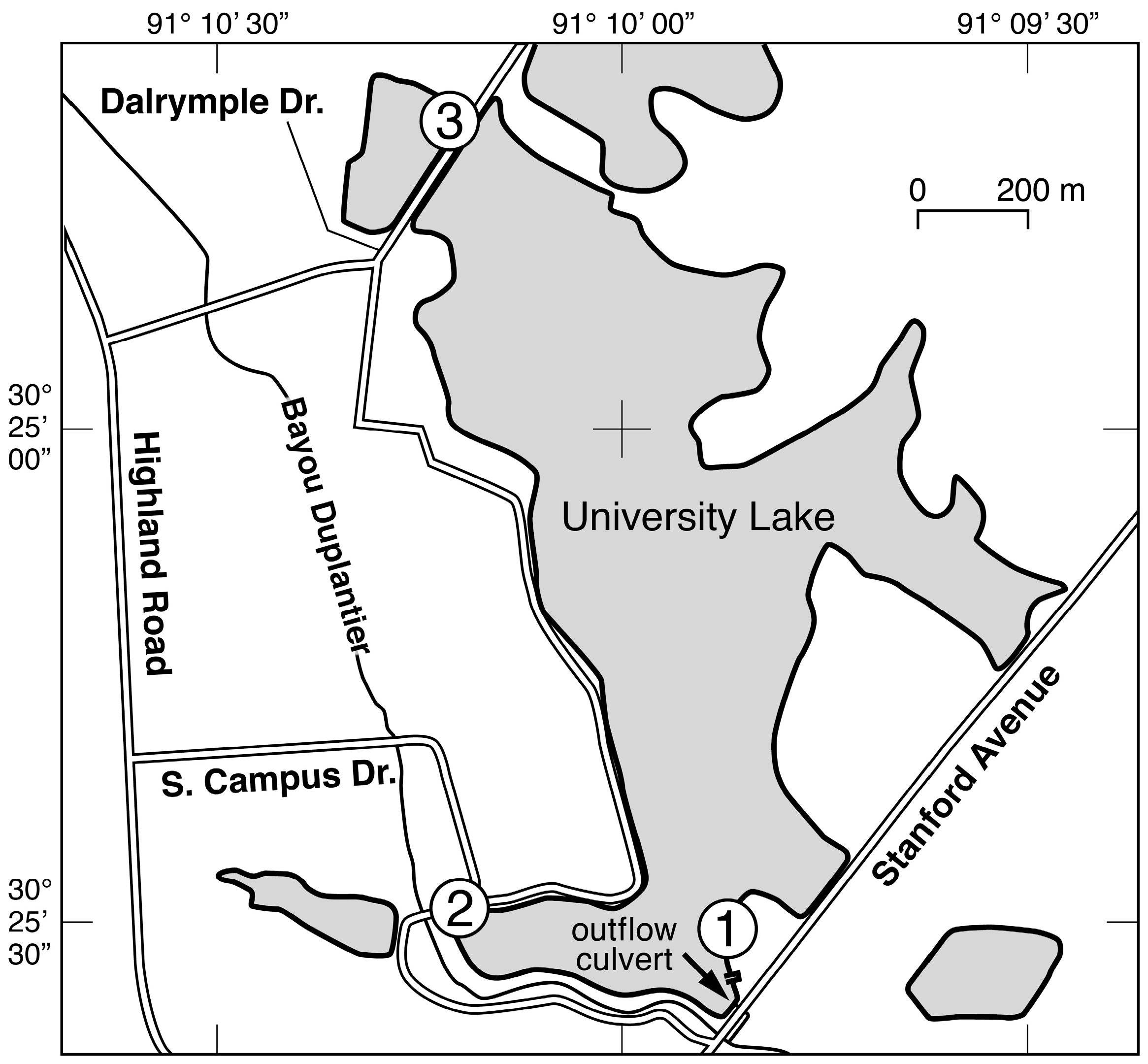
University Lake is an artificial lake located adjacent to the Louisiana State University (LSU) campus (Figure 1). The lake was created in the 1930s by dredging and damming a former cypress swamp after the trees had been cut for timber. The lake has an area of approximately 80 ha, an average depth of 0.86 m [14], and an average hydraulic retention time of about 50 days [10]. Climate in the area is subtropical, with an annual average temperature and rainfall of 19.9 °C and 154 mm, respectively [10]. The temperature of University Lake varies from a low of 14 °C in January to a high of 31 °C in August [14].
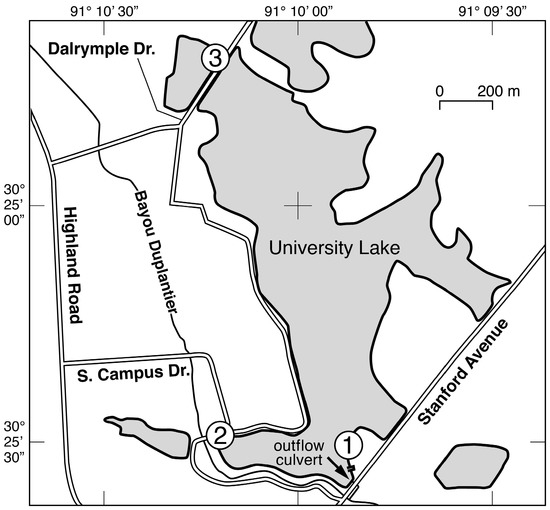
Figure 1.
Map of University Lake with the locations of the three sampling stations from which water samples were collected and the outflow from the lake to Bayou Duplantier.
3. Materials and Methods
Water samples were collected on approximately a weekly basis from 23 February 2011 to 15 February 2012 from three sites around the perimeter of the lake (Figure 1). In addition to this routine water sampling, additional samples were collected 1–2 days after an episodic event. An episodic event was defined to be at least one centimeter of precipitation recorded during a one-hour period at the LSU Southern Regional Climate Center weather station on the perimeter of University Lake. The time interval of 1–2 days was chosen to allow time for a response from the phytoplankton community. At each site, four 500 mL samples were collected from a depth of 30 cm with a Niskin bottle and transferred to pre-cleaned polypropylene bottles. Samples were collected at approximately 8 a.m. on each day. Site 1 was located adjacent to a popular recreational area, where a boat launch and dock facilitated collection of water samples. Site 2 was located adjacent to several LSU dormitories at a location where samples could be easily collected from the lake bank. Site 3 was located on a land bridge that separates University Lake from the adjacent Crest Lake, and a railed bridge provided a convenient location for sample collection.
After collection, all water samples were transported to a laboratory in the LSU Environmental Sciences Department, the transit time being approximately 10 min. The samples were processed for measurements of photosynthetic rates, respiration rates, and the concentrations of inorganic nutrients and photosynthetic pigments. The inorganic nutrients included ammonium + ammonia (hereafter ammonium), phosphate, nitrate + nitrite (hereafter nitrate), and silicate. Aliquots of water were filtered through glass fiber (Whatman GF/F) filters for pigment and inorganic nutrient analyses. The filters were immediately frozen, and the pigments collected on the filters subsequently extracted in acetone. Pigment analyses were carried out with a high-pressure liquid chromatograph (HPLC) (Agilent Technologies, Santa Clara, CA) according to the protocol of Bidigare et al. [15]. The HPLC system consisted of a Varian model 9012 HPLC equipped with a Varian model 9300 auto-sampler, a Timberline column heater, and a Waters Spherisorb 5 μm ODS-2 analytical column (diameter: 4.6 mm, length: 250 mm) and corresponding guard cartridge. Pigments were detected with a ThermoSeparation Products UV2000 detector. Inorganic nutrients were assayed on the sample filtrates with an OI Analytical Flow Solutions IV autoanalyzer using the colorimetric procedures described in Strickland and Parsons [16], with modifications for automated analysis.
Photosynthetic rates and respiration rates were determined from changes in the oxygen concentrations in whole-water samples incubated separately in replicate 60 mL glass BOD bottles in the light and dark for four hours. In all cases, both sets of incubations were carried out at a temperature of 20 °C. The light incubations were carried out at an irradiance of 400 μmol photons m−2 s−1 of 400–700 nm radiation provided by a bank of fluorescent lamps. We assumed this irradiance to be sufficient to saturate photosynthetic rates [17,18]. Oxygen concentrations were measured during the first eight months by Winkler titration [16] and during the final four months with a YSI model 5905 oxygen meter. The change in methodology was based on the fact that the oxygen meter measurements could be performed more quickly and easily than the Winkler titrations. Comparisons of oxygen concentrations measured on identical samples with the two methods revealed no significant difference (p > 0.10). To avoid artifacts associated with the formation of oxygen bubbles during the light incubations, water samples were initially bubbled with N2 gas for approximately 30 s to ensure that O2 concentrations remained below saturation during the subsequent incubations. Oxygen concentrations were assayed initially (after bubbling with N2) and at the end of all incubations. Gross oxygen production was calculated as the difference in the O2 concentrations in the light and dark bottles at the end of the incubation. Respiration was equated to the difference between the O2 concentrations in the dark bottle at the beginning and end of the incubation. Photosynthetic rates and respiration rates were converted to a carbon basis by assuming a photosynthetic quotient of 1.1 and a respiratory quotient of 0.9, respectively [19]. Assimilation ratios (grams carbon per gram chlorophyll per hour) were then calculated from the ratio of the carbon-normalized gross photosynthetic rate and the chlorophyll a (chl a) concentration.
Seasons of the year were defined as follows: spring, 22 March to 21 June; summer, 22 June to 21 September; fall, 22 September to 21 December; winter, 22 December to 21 March. A Kruskal–Wallis (KW) test was used to determine whether there were significant differences between event and non-event values of inorganic nutrient concentrations, assimilation ratios, pigment concentrations, and the ratio of respiration to photosynthesis. A KW test was also used to determine whether there were significant differences of chl a concentrations between sampling sites. Pearson product-moment correlation coefficients were used to determine whether there were significant correlations between pigment concentrations. In all statistical tests, the null hypothesis was rejected if the type I error rate (p) was less than 0.05. Multiple linear regression analysis was used to identify diagnostic pigments that accounted for a significant (p < 0.05) percentage of the variance of the chl a concentrations. Principal components analysis was used to identify patterns in the relationships between the diagnostic pigments identified in the multiple linear regression analysis.
4. Results
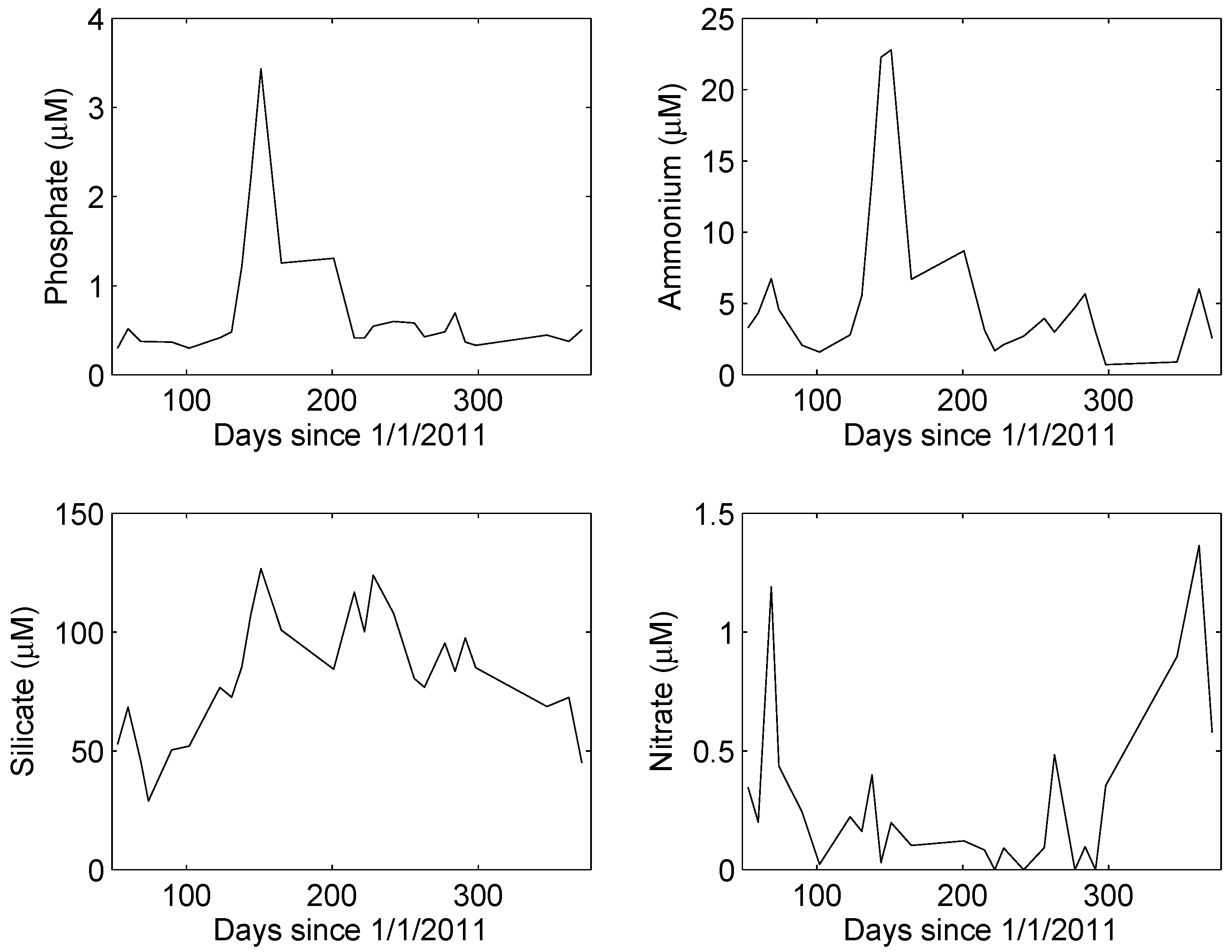
Rainfall during the one-year study totaled 141 mm, about 92% of the long-term average (154 mm y−1). Inorganic nutrient concentrations in University Lake under non-event conditions followed a distinctly non-random temporal pattern (Figure 2). Concentrations of phosphate and ammonium were highest during the spring, although rainfall was below average during the months of April, May, and June. Silicate concentrations were high during the late spring and summer and low during the winter. Nitrate concentrations, in contrast, were highest in the winter. A Kruskal–Wallis (KW) test revealed no significant differences in ammonium, phosphate, or silicate concentrations during non-event and post-event conditions (p > 0.32). However, the KW test revealed a significant difference in nitrate concentrations (p < 7 × 10−5), median concentrations during non-event, and post-event conditions being 0.16 and 0.60 μM, respectively.
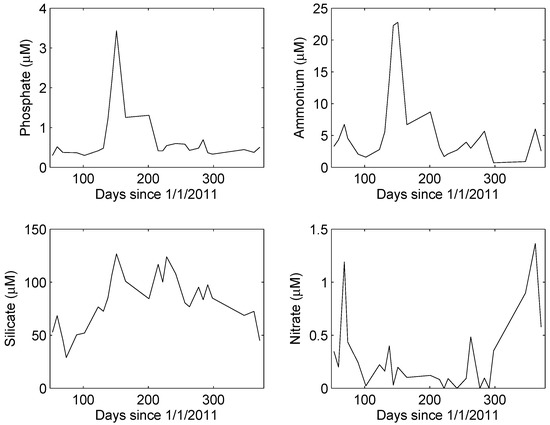
Figure 2.
Median concentrations of inorganic nutrients under non-episodic conditions. In each case, a runs test revealed the time series to be significantly non-random (p < 0.05).
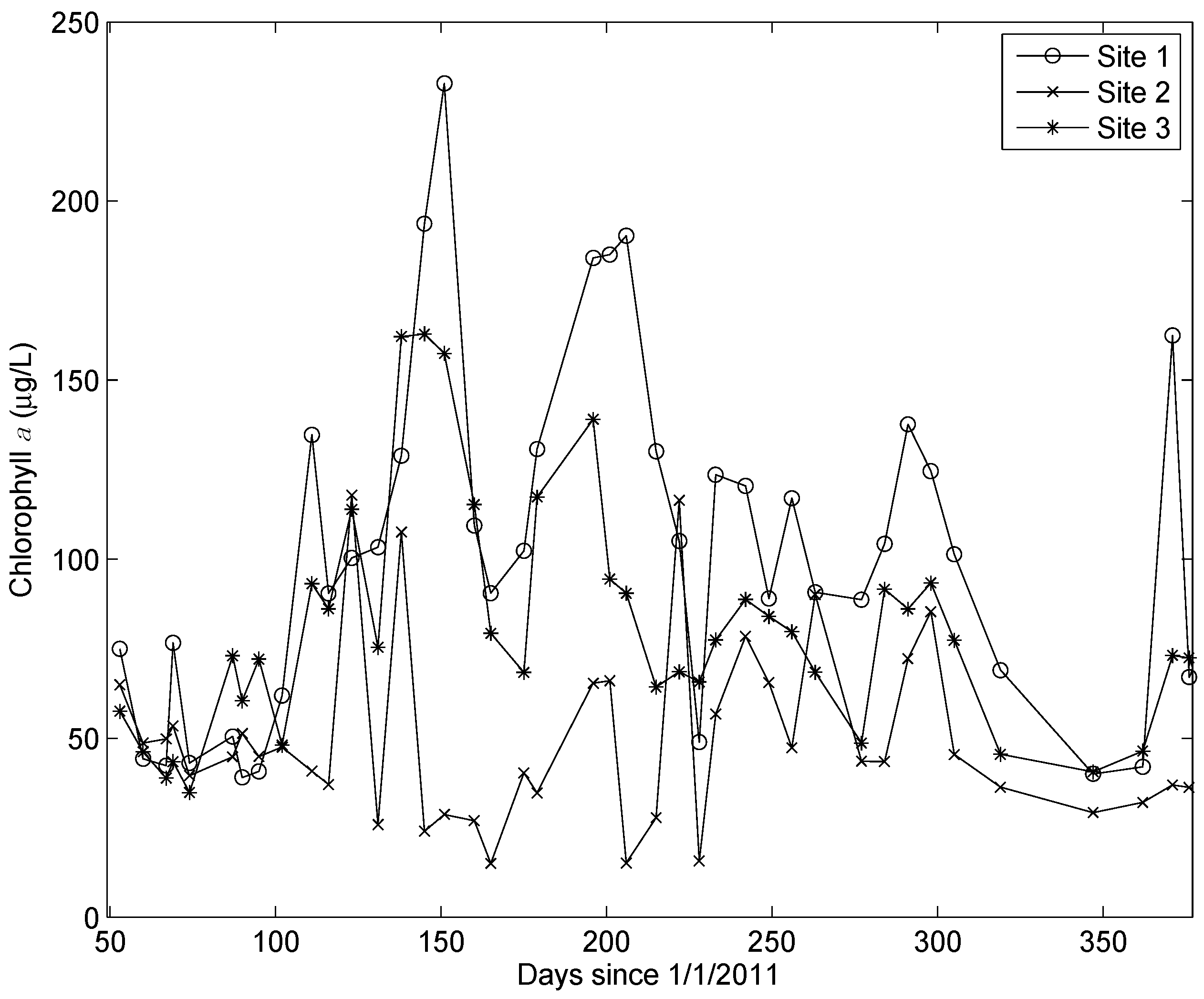
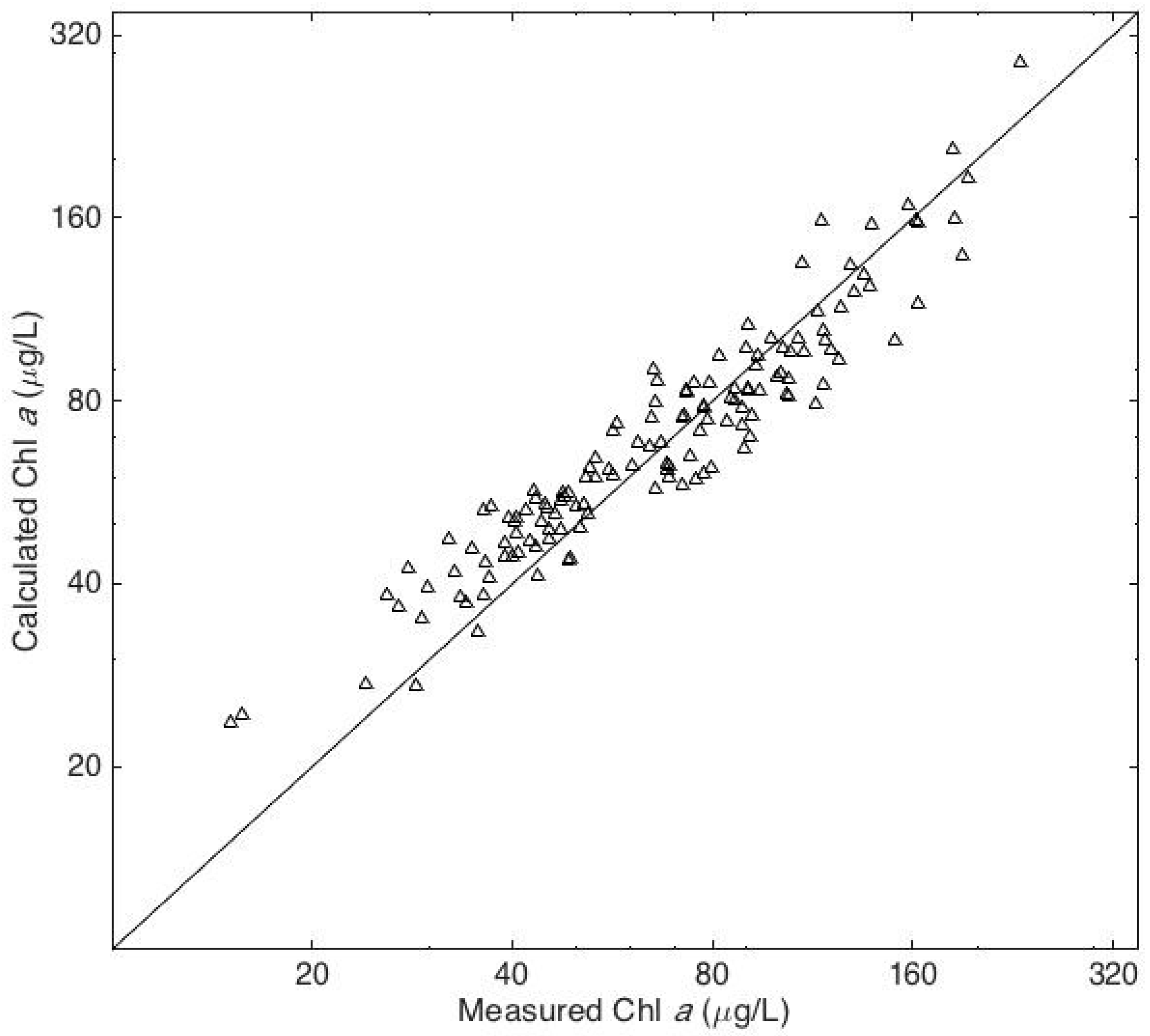
There was a highly significant difference in the chl a concentrations at the three sites. The highest concentrations consistently occurred at Site 1 and the lowest concentrations at Site 2 (Figure 3). The HPLC analyses revealed that 19’butanoyloxyfucoxanthin, 19’hexanoyloxyfucoxanthin, peridinin, and prasinoxanthin were undetectable on all occasions at all stations. These results imply the absence of Pelagophyceae, Prymnesiophyceae, Dinophyceae, and Prasinophyceae, respectively, in the algal community [20]. The accessory pigments routinely detected in the samples included α and β carotene, chl b, and the xanthophylls alloxanthin, diadinoxanthin, fucoxanthin, lutein, violaxanthin, and zeaxanthin. Chlorophyll c was detected in 20% of the samples. There was a very high correlation between chl b and lutein (r = 0.94, p < 10−64) and a very significant correlation between fucoxanthin and diadinoxanthin (r = 0.81, p < 10−32). Multiple linear regression analysis revealed that 87% of the variance in the chl a concentrations could be accounted for by variations in three accessory pigments: chl b, fucoxanthin, and zeaxanthin (Figure 4). The predictive equation was as follows:
where fuco and zea are the concentrations of fucoxanthin and zeaxanthin, respectively, and all concentrations are in units of micrograms per liter.
chl a = 6.3 + 5.7·chl b + 4.3·fuco + 2.0·zea
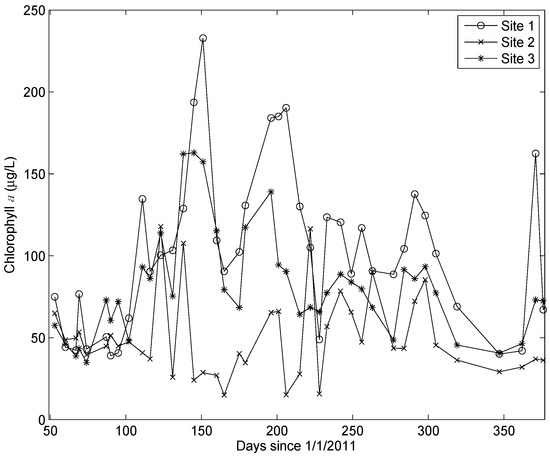
Figure 3.
Time series of the chl a concentrations at the three sites. A Kruskal–Wallis test indicated that the concentrations at the three sites were different at p < 3 × 10−9.
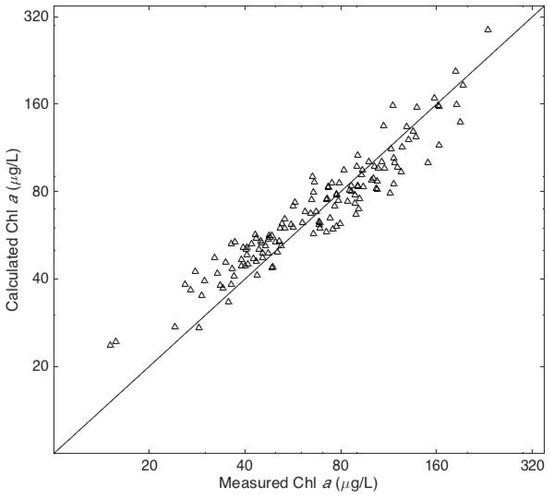
Figure 4.
Measured chl a concentrations and the concentrations predicted by multiple linear regression with chl b, fucoxanthin, and zeaxanthin as the independent variables.
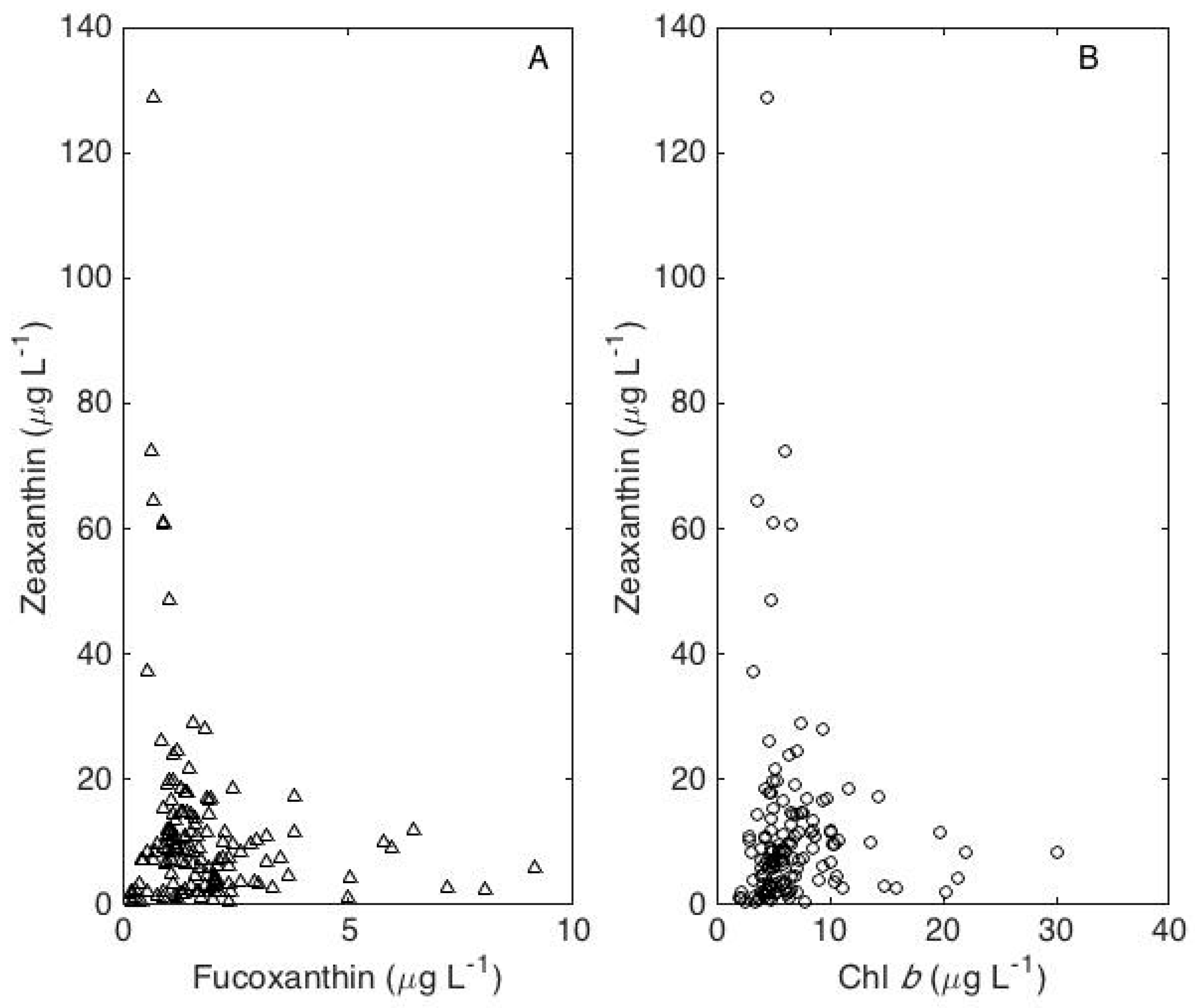
A principal components analysis of the chl b, fucoxanthin, and zeaxanthin concentrations identified a first principal component that accounted for 46% of the total variance and consisted of positive contributions from chl b and fucoxanthin and a negative contribution from zeaxanthin. High concentrations of fucoxanthin occurred only when zeaxanthin concentrations were low, and high concentrations of zeaxanthin occurred only when fucoxanthin concentrations were low (Figure 5A). Likewise, high concentrations of chl b occurred only when zeaxanthin concentrations were low, and high concentrations of zeaxanthin occurred only when chl b concentrations were low (Figure 5B).
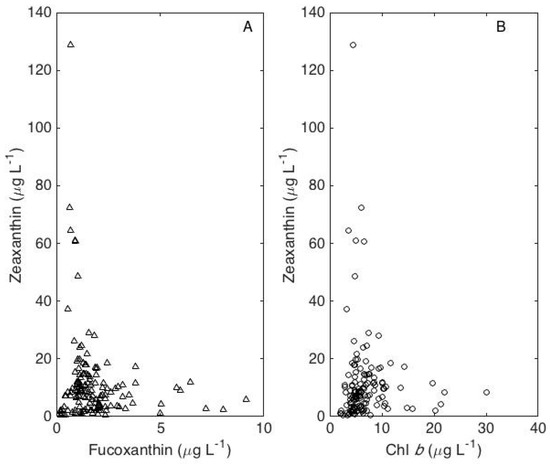
Figure 5.
Relationships between zeaxanthin and fucoxanthin (A) and between zeaxanthin and chl b (B).
There were 17 episodic events during the course of the study. A KW test revealed no significant difference (p > 0.3) in the concentrations of chl a, chl b, fucoxanthin, and zeaxanthin on non-event and post-event days. However, assimilation ratios were significantly higher (KW test, p < 0.0056) on post-event days; median values on non-event and post-event days were 3.1 (2.5–3.4) and 4.0 (3.3–4.9) g C g−1 chl a h−1, respectively, where the values in parentheses are the 95% confidence intervals. Ratios of respiration to photosynthesis were virtually identical on non-event and post-event days, median values being 0.14 and 0.13, respectively.
5. Discussion
Chlorophyll b is found in both Chlorophyceae and Prasinophyceae, but the absence of prasinoxanthin implies that all the chl b in University Lake is associated with Chlorophyceae [21]. This conclusion is supported by the very high correlation between chl b and lutein (r = 0.94, p < 0.001), which is diagnostic for Chlorophyceae [21]. Fucoxanthin is found in Bacillariophyceae, Prymnesiophyceae, Pelagophyceae, and Chrysophyceae [21]. However, the absence of 19’butanoyloxyfucoxanthin and 19’hexanoyloxyfucoxanthin rules out Pelagophyceae and Prymnesiophyceae, respectively [20,21]. Although both Bacillariophyceae and Chrysophyceae contain fucoxanthin, of the two only Bacillariophyceae contain diadinoxanthin [22]. In the absence of Prymnesiophyceae, Pelagophyceae, and Dinophyceae, diadinoxanthin is diagnostic for Bacillariophyceae. We found a good correlation between fucoxanthin and diadinoxanthin (r = 0.78, p < 0.001), the suggestion being that most of the fucoxanthin was associated with Bacillariophyceae. In the absence of Prasinophyceae, zeaxanthin would be associated only with Cyanobacteria and Chlorophyceae [20,22]. However, the absence of a significant correlation between zeaxanthin and either chl b (p = 0.56) or lutein (p = 0.39) suggests that most of the zeaxanthin was associated with Cyanobacteria.
The average composition of the phytoplankton community in University Lake can be estimated from the regression coefficients in Equation (1) and the average concentrations of chl a, chl b, fucoxanthin, and zeaxanthin, 75.3, 6.8, 1.8, and 11.5 μg L−1, respectively. Assuming the regression coefficients to be the ratios of chl a to chl b, fucoxanthin, and zeaxanthin in Chlorophyceae, Bacillariophyceae, and Cyanophyceae, respectively, we estimate that these three classes of phytoplankton accounted for 51%, 10%, and 31%, respectively, of the chl a in University Lake.
Variations in alloxanthin did not explain a significant percentage of the chl a variance, but alloxanthin was consistently present at low concentrations. Because alloxanthin is diagnostic for Cryptophyceae, it is clear that a small percentage of the phytoplankton community consisted of Cryptophyceae. Descy et al. [23] estimated the alloxanthin:chl a ratio to be 0.3 in freshwater cryptophytes. Dividing the average alloxanthin concentration in University Lake, 765 ng L−1, by 0.3 implies that Cryptophyceae accounted for about 3.4% of the chl a in University Lake. The pigment analysis could thus identify the classes of phytoplankton that accounted for about 95% of the chl a in University Lake.
The explanation for the negative contribution from zeaxanthin to the first principal component is apparent from an examination of the relationships between zeaxanthin and fucoxanthin (Figure 5A) and between zeaxanthin and chl b (Figure 5B). The fact that high concentrations of Cyanophyceae were invariably associated with low concentrations of both Chlorophyceae and Bacillariophyceae, and conversely, may reflect allelopathic interactions. Natural waters containing high concentrations of algae are frequently very inhibitory, and when large populations of Cyanophyceae are present, the filtrate from the water is algistatic to all species [24] (p. 469).
The assimilation ratios can be converted to growth rates by dividing them by the C:chl a ratio in the phytoplankton. Riemann et al. [25] estimated this ratio to average about 38.5 in several eutrophic lakes. After combining lacustrine results with data from marine enclosures, they noted that most of the C:chl a ratios fell in the range 27–67. If we assume the C:chl a ratio of the phytoplankton in University Lake to be 38.5, assimilation ratios of 3.1 and 4.0 g C g−1 chl a h−1 translate to growth rates of 0.08 and 0.10 h−1, respectively. Because the incubations were carried out at an irradiance of 400 μmol photons m−2 s−1, these rates can be considered light-saturated [26]. Assuming respiration rates during the day and night to be the same and equal to 13.5% of the gross photosynthetic rates (vide supra), these rates translate to 0.70 d−1 and 0.91 d−1 for growth on a 12:12 light/dark cycle. The former rate is very consistent with the average growth rate of 0.6 d−1 estimated by pigment labeling of phytoplankton growing in mesocosms in the Neuse River [27]. Despite the high chl a concentrations in the lake (75.3 μg L−1), light was probably sufficient to saturate photosynthetic rates at all depths. Assuming a mean spectral extinction coefficient of 14 m2 g−1 chl a [28], we estimate the visible light extinction coefficient to be 1.05 m−1. The irradiance at the bottom of the lake (0.86 m) is therefore estimated to be about 40% of the surface irradiance. Surface irradiance in Baton Rouge varies between an average of 510 and 885 μmol photons m−2 s−1 of 400–700 nm radiation in January and June, respectively.
One concern in a hypereutrophic lake such as University Lake is the possibility that oxygen concentrations will drop to dangerously low levels at night. At a chl a concentration of 75.3 μg L−1, respiration rates following storm events would be expected to be about (75.3 μg chl a L−1) × (4.0 μg C μg−1 chl a h−1) × (0.13) = 39 μg C L−1 h−1 = 3.3 μmol C L−1 h−1. Assuming a respiratory quotient of 0.9 and 12 hours between sunset and sunrise, this respiration would be sufficient to reduce oxygen concentrations by (3.3/0.9) × (12) = 44 μmol O2 L−1 = 1.41 mg O2 L−1. At a temperature of 31 °C, the saturation oxygen concentration in freshwater is about 7.4 mg L−1. The highest chl a concentration that we measured in our study was about 240 μg L−1, which would translate to a decrease of the O2 concentration during the night of 4.49 mg O2 L−1 following a storm. It is thus possible that, during the late summer, respiration rates following a storm might be sufficient to reduce the O2 to a concentration of ~3 mg L−1 but still above the concentration of 2 mg L−1 that is typically associated with hypoxia [29].
These calculations suggest that the creation of anoxic conditions in University Lake is unlikely to result from the respiration of the phytoplankton in the lake, but it might result from the dieoff and subsequent decomposition of a phytoplankton bloom. Assuming a C:chl a ratio of 38.5, it follows that a chl a concentration of 240 μg L−1 would be associated with a phytoplankton carbon concentration of 9.2 mg L−1. Assuming a respiratory quotient of 0.9, the complete decomposition of this carbon would theoretically consume about 27.4 mg O2 L−1. Thus, decomposition of roughly 25–35% of the biomass in such a bloom could lead to complete anoxia, depending on the temperature and extent of gas exchange with the atmosphere.
The fact that assimilation ratios increased by 30% 1–2 days after rain events is noteworthy. Median concentrations of ammonium, nitrate, phosphate, and silicate in the lake were 4.0, 0.2, 0.5, and 81 μM, respectively. The ammonium concentrations were consistently above concentrations that would be expected to limit phytoplankton growth [30], and silicate concentrations were consistently above concentrations that would be expected to limit diatom growth [24,31]. Phosphate concentrations that are limiting to phytoplankton growth are on the order of 10 nM [32,33], but the standard assay for molybdate-reactive phosphorus [34] gives a positive response for a large number of dissolved organo-phosphorus compounds [35], and it is therefore likely that the average molybdate-reactive phosphorus concentration of 0.5 μM is an overestimation of the inorganic phosphate concentration in University Lake. To the extent that phytoplankton biomass in the lake is limited by the concentration of a macronutrient, phosphate appears to be the most likely candidate, as is the case in many freshwater systems [36,37]. Assuming that phosphate is the limiting nutrient in University Lake, it is likely that an influx of phosphate from land runoff following a rain event would stimulate phytoplankton photosynthetic rates.
Given the 30% increase in assimilation ratios 1–2 days after rain events, the absence of a comparable change in phytoplankton biomass warrants comment. Grazing by herbivores seems an unlikely explanation. The very high biomass of phytoplankton in the lake would almost certainly be sufficient to saturate zooplankton feeding rates [38]. If the phytoplankton were in fact growing at roughly 0.7 d−1 prior to an event, then a 30% increase of that growth rate, in the absence of any increase in zooplankton grazing, would imply an increase of about 23% per day in the phytoplankton biomass.
Several factors may have contributed to the lack of a consistent increase in phytoplankton biomass after rain events. First, some time lag would be expected between the addition of nutrients and a change in the growth rate of the phytoplankton [39]. Second, and perhaps most importantly, in a lake as shallow as University Lake, many cells undoubtedly settle to the bottom during quiescent conditions and are then resuspended by even a small amount of turbulence. During periods of little or no rain, chl a concentrations in University Lake frequently varied by more than a factor of four from one week to the next. Such large changes, if caused by a combination of wind mixing and settling, could effectively obscure changes associated with nutrient input from land runoff.
6. Conclusions
The results of this study clearly characterize University Lake as hypereutrophic. The average chl a concentration at the three sampling sites, 75.3 μg L−1, is almost twice the average summer chl a concentration in Lake Washington at the peak of eutrophication prior to the diversion of nutrient inputs from wastewater treatment plants [40,41]. More than 80% of the chl a in the lake is accounted for by Chlorophyceae and Cyanophyceae. Phytoplankton growth rates in the lake are clearly responsive to impacts from land runoff, but the biomass of phytoplankton can vary dramatically on a timeframe of one week for reasons unrelated to rainfall. The most likely explanation for these changes is the settling of cells and their subsequent resuspension from the bottom of this shallow lake.
The implications of this study for the restoration and management of University Lake are consistent with current understanding that restoration efforts via dredging or similar activities will have only short-term effects on water quality unless allochthonous nutrient loading is controlled [42] (p. 79). In the case of University Lake, dredging is inevitable to prevent its return to swampland. However, any improvement of water quality will be temporary unless there is a reduction of the phytoplankton biomass in the lake. The fact that phytoplankton growth rates increase 1–2 days after storm events is strong evidence that allochthonous nutrient loading has a significant impact on the population dynamics of the phytoplankton community, despite the large reservoir of nutrients in the sediments. A potential solution to the problems caused by allochthonous nutrient loading would be to divert all or most of the storm drains that currently discharge into University Lake to Bayou Duplantier, the stream into which University Lake drains (Figure 1). An alternative strategy for mitigating the problems caused by algal blooms would be top-down control via manipulation of the fish population. However, the fish community in University Lake is quite diverse and includes bluegill, bream, and various species of bass (white, largemouth, yellow, smallmouth, and striped). It seems doubtful that the fish community can be manipulated in a way that would bring about effective control of the phytoplankton population by other than rather heroic efforts. University Lake must be periodically dredged to prevent its becoming a swamp again. Because the frequency and cost of the dredging are positively correlated with the quantities of particulate materials that wash into the lake with every storm, the next instance of dredging may be a good opportunity to seriously consider rerouting the storm drains that currently discharge into the lake. Because rerouting the storm drains need be done only once, whereas dredging must be done periodically for the foreseeable future, rerouting the storm drains would appear to be a cost-effective way to reduce the long-term costs of dredging and at the same time address the problems caused by allochthonous nutrient loading.
Acknowledgments
We gratefully acknowledge the analytical support provided by Robert Bidigare, Stephanie Christensen, and Fenina Butler (University of Hawaii) for performing the HPLC analyses of diagnostic pigments. This research was supported by the Environmental Research Support fund from the LSU College of the Coast and Environment.
Author Contributions
E.A.L. conceived and designed the experiments; B.N. performed the experiments; E.A.L. and B.N. analyzed the data; E.A.L. and B.N. wrote the paper.
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare no conflict of interest. The founding sponsors had no role in the design of the study; in the collection, analyses, or interpretation of data; in the writing of the manuscript; or in the decision to publish the results.
References
- Welch, E.B. The eventual recovery of Lake Sammamish following phosphorus diversion. J. Water Pollut. Control Fed. 1985, 57, 977–978. [Google Scholar]
- Effler, S.W.; Brooks, C.M.; Whitehead, K.A. Domestic waste inputs of nitrogen and phosphorus to Onondaga Lake, and water quality implications. Lake Reserv. Manag. 1996, 12, 127–140. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Effler, S.W.; Hennigan, R.D. Onondaga Lake, New York: Legacy of pollution. Lake Reserv. Manag. 1996, 12, 1–13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Edmondson, W.T.; Anderson, G.C.; Peterson, D.R. Artificial eutrophication of Lake Washington. Limnol. Oceanogr. 1956, 1, 47–53. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Welch, E.B.; Michaud, J.P.; Perkins, M.A. Alum control of internal phosphorus loading in a shallow lake. Water Resour. Bull. 1982, 18, 929–936. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Welch, E.B.; Rock, C.A.; Howe, R.C.; Perkins, M.A. Lake Sammamish response to waste-water diversion and increasing urban runoff. Water Res. 1980, 14, 821–828. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vanderdoes, J.; Verstraelen, P.; Boers, P.; Vanroestel, J.; Roijackers, R.; Moser, G. Lake restoration with and without dredging of phosphorus-enriched upper sediment layers. Hydrobiologia 1992, 233, 197–210. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- James, R.T.; Pollman, C.D. Sediment and nutrient management solutions to improve the water quality of Lake Okeechobee. Lake Reserv. Manag. 2011, 27, 28–40. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Knaus, R.; Malone, R. A historical overview of a successful lakes restoration project in Baton Rouge, Louisiana. Lake Reserv. Manag. 1984, 1, 412–415. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Norris, B. Composition and Physiological Changes of the University Lake Ecosystem Phytoplankton Community: Impacts of Seasonal and Episodic Events. Master’s Thesis, Environmental Sciences, Louisiana State University, Baton Rouge, LA, USA, 2012. [Google Scholar]
- Anonymous. The LSU Lakes are Dying. Can They be Saved? 225 Magazine, January 2010; 33–37. [Google Scholar]
- Carpenter, S.R.; Caraco, N.F.; Correll, D.L.; Howarth, R.W.; Sharpley, A.N.; Smith, V.H. Nonpoint pollution of surface waters with phosphorus and nitrogen. Ecol. Appl. 1998, 8, 559–568. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lagoutte, B.; Tunkelrott, M.-L.; Feraudet-Tarisse, C.; Dano, J.; Volland, H. Fast and Direct Extraction of Cell-associated Hepatotoxins from Toxic Cyanobacteria. Water Environ. Res. 2014, 86, 470–477. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mesmer, R. Impact of Urban Runoff on Phosphorus, Nitrogen, and Dissolved Oxygen in a Shallow Subtropical Lake. Master’s Thesis, Renewable Natural Resources, Louisiana State University, Baton Rouge, LA, USA, 2010. [Google Scholar]
- Bidigare, R.R.; Van Heukelem, L.; Trees, C.C. Analysis of algal pigments by high-performance liquid chromatography. In Algal Culturing Techniques; Andersen, R.A., Ed.; Academic Press: New York, NY, USA, 2005; pp. 327–345. [Google Scholar]
- Strickland, J.D.H.; Parsons, T.R. A Practical Handbook of Seawater Analysis, 2nd ed.; Bulletins of the Fisheries Research Board of Canada; Fisheries Research Board of Canada: Ottawa, ON, Canada, 1972; Volume 167, p. 310. [Google Scholar]
- Chalup, M.S.; Laws, E.A. A test of the assumptions and predictions of recent microalgal growth models with the marine phytoplankter Pavlova lutheri. Limnol. Oceanogr. 1990, 35, 583–596. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Laws, E.A.; Redalje, D.G.; Karl, D.M.; Chalup, M.S. A theoretical and experimental examination of the predictions of two recent models of phytoplankton growth. J. Theor. Biol. 1983, 105, 469–491. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Laws, E.A. Photosynthetic quotients, new production and net community production in the open ocean. Deep Sea Res. I 1991, 38, 143–167. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Letelier, R.M.; Bidigare, R.R.; Hebel, D.V.; Ondrusek, M.; Winn, C.D.; Karl, D.M. Temporal variability of phytoplankton community structure based on pigment analysis. Limnol. Oceanogr. 1993, 38, 1420–1437. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Paerl, H.W.; Valdes, L.M.; Pinckney, J.L.; Piehler, M.F.; Dyble, J.; Moisander, P.H. Phytoplankton photopigments as indicators of estuarine and coastal eutrophication. Bioscience 2003, 53, 953–964. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Smith, G.M. The Freshwater Algae of the United States, 2nd ed.; McGraw-Hill: New York, USA, 1950; p. 719. [Google Scholar]
- Descy, J.; Sarmiento, H.; Wiggins, H. Variability of phytoplankton pigment ratios across aquatic environments. Eur. J. Phycol. 2009, 44, 319–330. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hutchinson, G.E. Volume II: Introduction to Lake Biology and the Limnoplankton. In A Treatise on Limnology; John Wiley & Sons: New York, NY, USA, 1967; Volume 2, p. 1115. [Google Scholar]
- Riemann, B.; Simonsen, P.; Stensgaard, L. The carbon and chlorophyll content of phytoplankton from various nutrient regimes. J. Plankton Res. 1989, 11, 1037–1045. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Laws, E.A.; Bannister, T.T. Nutrient-and light-limited growth of Thalassiosira fluviatilis in continuous culture, with implications for phytoplankton growth in the ocean. Limnol. Oceanogr. 1980, 25, 457–473. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pinckney, J.L.; Richardson, T.L.; Millie, D.F.; Paerl, H.W. Application of photopigment biomarkers for quantifying microalgal community composition and in situ growth rates. Org. Geochem. 2001, 32, 585–595. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Atlas, D.A.; Bannister, T.T. Dependence of mean spectral extinction coefficient of phytoplankton on depth, water color, and species. Limnol. Oceanogr. 1980, 25, 157–159. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rabalais, N.N.; Diaz, R.J.; Levin, L.A.; Turner, R.E.; Gilbert, D.; Zhang, J. Dynamics and distribution of natural and human-caused hypoxia. Biogeosciences 2010, 7, 585–619. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sunda, W.G.; Hardison, D.R. Ammonium uptake and growth limitation in marine phytoplankton. Limnol. Oceanogr. 2007, 52, 2496–2506. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Harrison, P.J.; Conway, H.L.; Dugdale, R.C. Marine diatoms grown in chemostats under silicate or ammonium limitation.1. Cellular chemical composition and steady-state growth kinetics of Skeletonema costatum. Mar. Biol. 1976, 35, 177–186. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Laws, E.A.; Pei, S.; Bienfang, P.; Grant, S. Phosphate-limited growth and uptake kinetics of the marine prasinophyte Tetraselmis suecica (Kylin) Butcher. Aquaculture 2011, 322–323, 117–121. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Laws, E.A.; Pei, S.F.; Bienfang, P.; Grant, S.; Sunda, W.G. Phosphate-limited growth of Pavlova lutheri (prymnesiophyceae) in continuous culture: Determination of growth-rate-limiting substrate concentrations with a sensitive bioassay procedure. J. Phycol. 2011, 47, 1089–1097. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Murphy, J.; Riley, J.P. A modified single solution method for the determination of phosphate in natural waters. Anal. Chim. Acta 1962, 26, 31–36. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thomson-Bulldis, A.L.; Karl, D. Application of a novel method for phosphorus determinations in the oligotrophic North Pacific Ocean. Limnol. Oceanogr. 1998, 43, 1565–1577. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schindler, D.W. Factors regulating phytoplankton production and standing crop in the world’s freshwaters. Limnol. Oceanogr. 1978, 23, 478–486. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schindler, D.W. Evolution of phosphorus limitation in lakes. Science 1977, 195, 260–262. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Laws, E.A. Food-web structure and planktonic predator-prey relationships in two eutrophic European lakes: Stability constraints on carbon fluxes. Limnol. Oceanogr. 2008, 53, 760–772. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Caperon, J. Time lag in population growth response of Isochrysis galbana to a variable nitrate environment. Ecology 1969, 50, 188–192. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Edmondson, W.T.; Lehman, J.T. The effect of changes in the nutrient income on the condition of Lake Washington. Limnol. Oceanogr. 1981, 26, 1–29. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Edmondson, W.T. Eutrophication effects on the food chains of lakes. Memorie dell’Istituto Italiano di Idrobiologia 1993, 52, 113–132. [Google Scholar]
- Cooke, G.D.; Welch, E.B.; Peterson, S.A.; Nichols, S.A. Restoration and Management of Lakes and Reservoirs, 3rd ed.; CRC Press: Boca Raton, FL, USA, 2005; p. 616. [Google Scholar]
© 2017 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).