Abstract
Environmental isotope tracers have been a useful tool in providing new insights into hydrologic processes. In Mexico, there have been several studies reporting different values for and for certain geographical areas. The objective of this study is to achieve the isotopic characterization of rainfall and groundwater and to report the comprehensive understanding of groundwater flow processes around and within the Calera aquifer and, consequently, its potential recharge sites. The samples used for the stable isotope analysis () were measured using a GV-Isoprime isotope-ratio mass spectrometer at the Isotopy Laboratory of the Water Center for Latin America and the Caribbean. The of precipitation ranged between −110.20‰ and 10.11‰, with a mean of −55.67‰ 27.81‰. The ranged between −17.80‰ and 2.74‰, with a mean of −9.44‰ 4.74‰. The of groundwater ranged between −81.92‰ and −36.45‰, with a mean of −66.05‰ 8.58‰. The ranged between −18.26‰ and −8.84‰, with a mean of −12.35‰ 2.12‰. The local meteoric water line of the Zacatecas state is. The groundwater samples were clustered into four groups. The clustering of the samples led to the finding that streamflows play a significant role in the hydrological balance as a source of local recharge to the aquifer.
1. Introduction
Environmental isotope tracers have been a useful tool in providing new insights into hydrologic processes; they integrate small-scale variability to provide an effective indication of catchment-scale processes [1]. The applications of environmental isotopes as hydrologic tracers in freshwater systems fall into two main categories according to the classification of Kendall and Doctor [1]: (i) tracers of water itself (water isotope hydrology) and (ii) tracers of the solutes in the water (solute isotope biogeochemistry).
Precipitation is an important collector of the major and minor pollutants present in the atmosphere; furthermore, it is an important component of total water resources, making it vital for irrigation, human use, as well as industrial and domestic purposes in inland regions [2,3]. The chemical composition of rainfall is determined by several mechanisms: the condensation of water vapor on cloud condensation nuclei, the capture of species inside the cloud droplets (rainout), and scavenging processes below the clouds (washout) [4,5]. Particularly, there are two factors that control the isotopic character of rainfall: (a) the temperature of condensation of the precipitation and (b) the ratio of water vapor that has already condensed into precipitation to the initial amount of water vapor in the air mass. Nevertheless, other factors such as altitude, latitude, inland distance along different storm tracks, environmental conditions at the source of the vapor, and humidity also influence the isotopic composition of precipitation [1]. Oxygen and hydrogen isotopes ( and ) can be used to determine the source of groundwater and surface waters; in nature, there is a similar systematic isotopic fractionation of stable hydrogen and oxygen; thus, their behavior in the hydrologic cycle is also similar. This similarity rises to a covariance between the stable hydrogen and oxygen isotopic concentration; the covariance was defined by Craig [6] as follows:
This relation defines the Global Meteoric Water Line (GMWL), and was obtained by using a linear regression method derived from the isotopic analysis of precipitation, snow water, and river water from all over the world; most of the precipitation in the world follows this relationship [7]. The slope and the intercept of this equation are useful in understanding the systematic isotopic fractionation controlled by the hydrologic cycle [8]. The slope and intercept of the “Local Meteoric Water Line” (LMWL) for precipitation from a specific region can be different from the GMWL [8]. The intercept, which is usually called the deuterium excess parameter (-excess, or ), has been used to describe different Meteoric Waterlines (MWLs), such that:
Arid and semiarid regions account for more than a third of the world’s land surface and are characterized by receiving less than 250 mm/year of rainfall [8]. In these regions where water scarcity is a major issue, the groundwater is often the principal water supply; furthermore, in these areas, groundwater resources may be fossil resources [8,9].
In Mexico, there have been several studies reporting different values for and . Kretzschmar and Frommen [10] identified the stable isotope composition for surface and groundwater samples in Baja California, based on a total of 135 samples. The authors reported significant variations in its isotopic signature depending on the type of water tested and depending on the study area; however, an LMWL was not presented. In the Gulf of Mexico area, different studies have presented LMWLs, particularly in the state of Veracruz. Lanchiet and Patterson [11] in a study made in the northern Central America report the meteoric line as . Afterwards, Goldsmith et al. [12] presented two LMWLs (2008–2009: ; 2009–2010: ); in the same region. Quezadas et al. [13] presented their LMWL () with data collected from 2007 to 2012. Other investigations have been carried out in southwestern Mexico, specifically in the states of Jalisco and Colima. Hernández-Antonio et al. [14] collected stable water isotopes from 40 wells around the Guadalajara metropolitan area to explain the groundwater flow dynamics, and authors concluded that local flow is associated with the infiltration of rainwater that occurs at higher altitudes. Hartosough et al. [15] sampled multiple components of the water cycle to test for differences before and during the North American Monsoon System (NAMS) in 2003–2004 and presented two meteoric lines (pre-monsoon: ; monsoon: ) for both periods.
The present study was carried out in Mexico, particularly in the northern zone of the Mexican state of Zacatecas, which is located in the central-northern part of the country. The objective of this study is to obtain the isotopic characterization of rainfall and groundwater, as well as to report the comprehensive understanding of groundwater flow processes around the Calera aquifer and, consequently, its potential recharge sites. By comparing the signatures, it is possible to identify possible groundwater recharge sites. Since isotopic meteoric lines vary with region, a local meteoric line needs to be determined. In this study, the relationship between and measured in the cumulative rainfall between each sampling time, as a time series based on samples, was collected for 2014 and 2015.
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Study Area
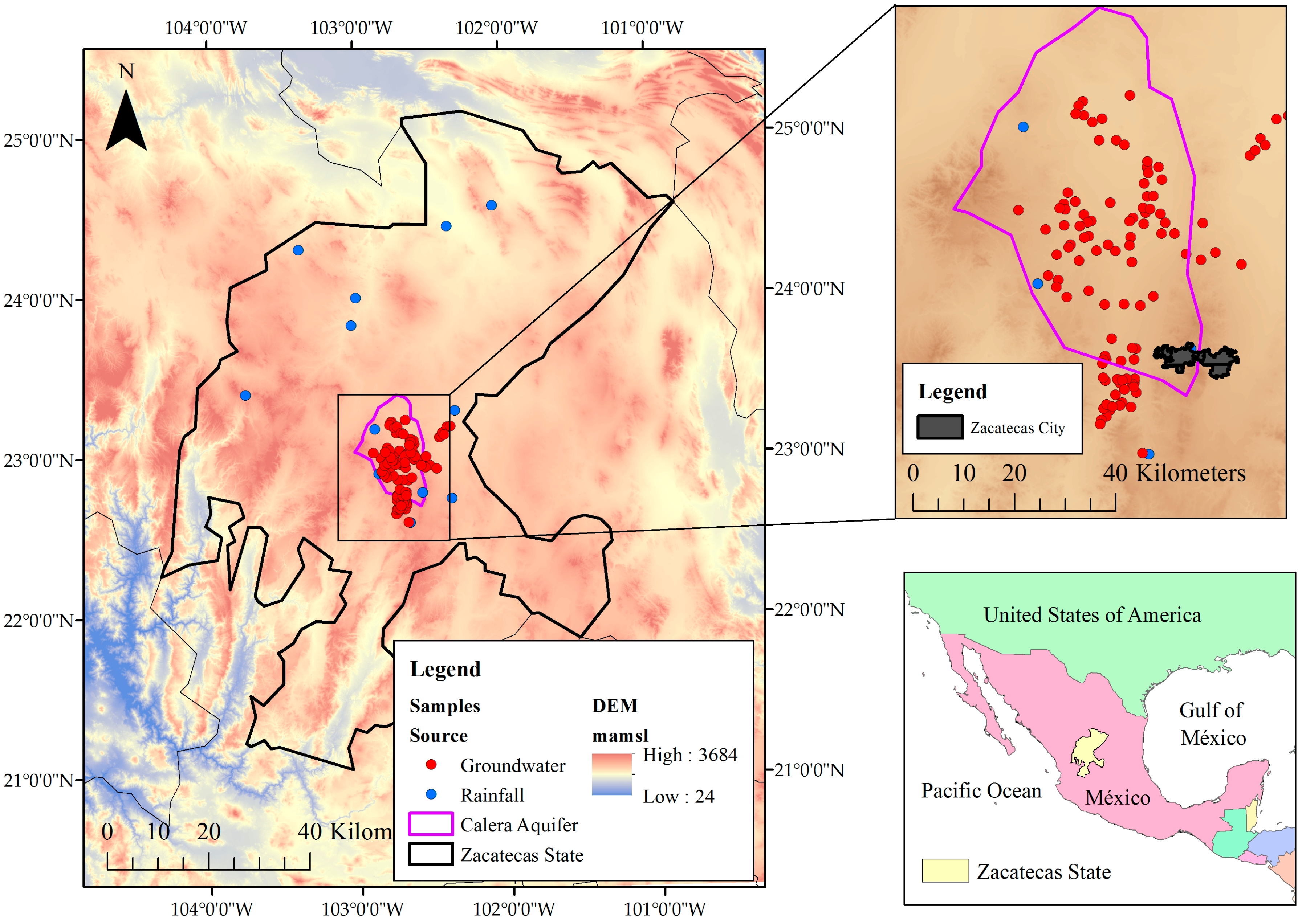
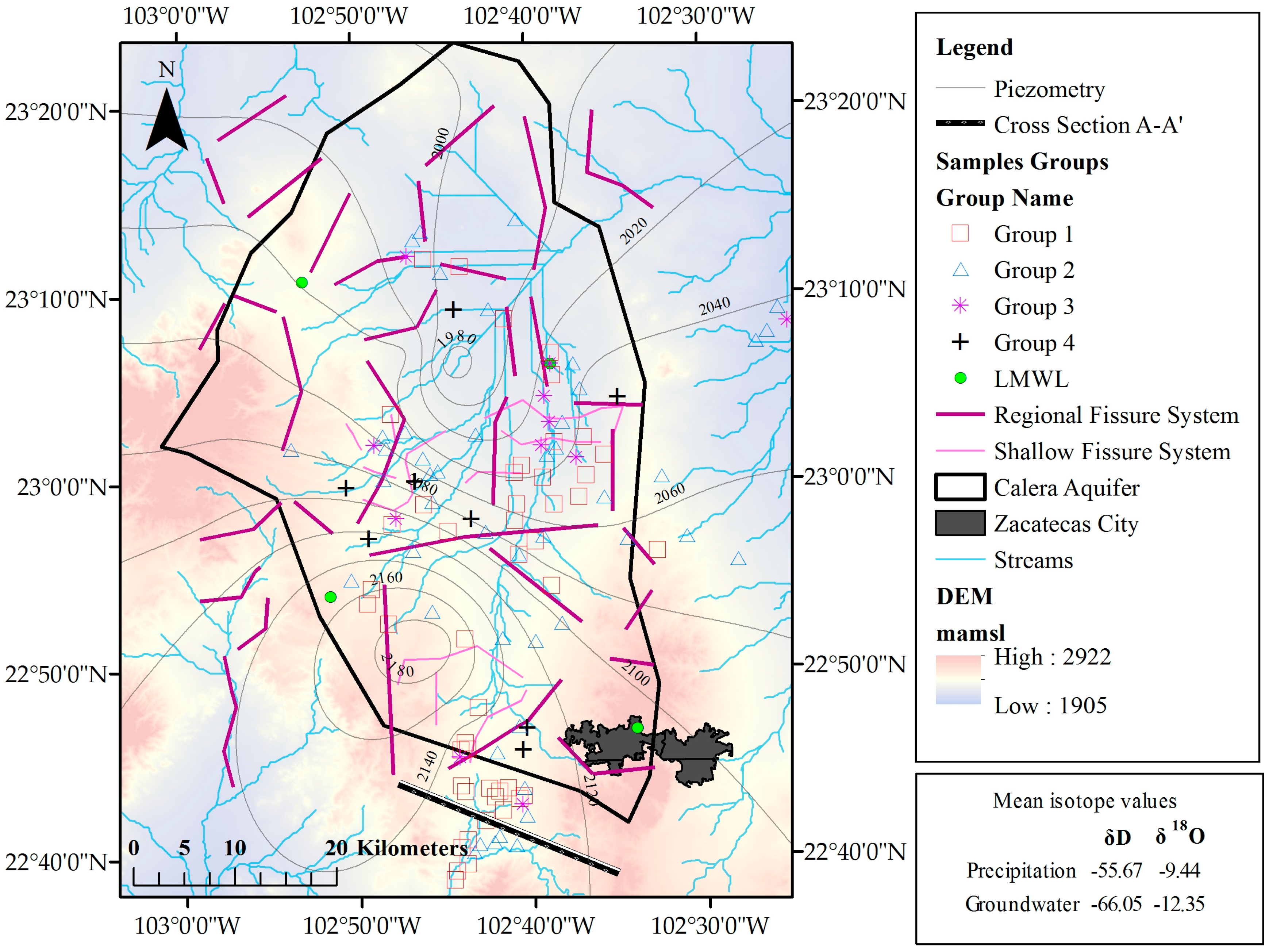
The Mexican state of Zacatecas is located at the central-northern part of the country; as a semiarid region, it is characterized by low rainfall values and consequently low surface runoff, but industrial activity and agricultural irrigation take place. In this region, groundwater is the main source that sustains economic development. The climate in Zacatecas is mainly arid, and half of the population lives in rural areas; therefore, irrigated agriculture is one of the most profitable economic activities. According to CONAGUA (National Commission of Water) [16], over 130 thousand hectares are irrigated with an annual volume of 330 hm3, producing annual groundwater levels drawdowns from 1 to 5 m, due in large part to rudimentary and outdated irrigation systems with efficiencies below 45%. This fact together with the incipient increase in population has caused a higher rate of water extraction to satisfy the demand for food and services [17]. The Calera aquifer is located in the central zone of the Zacatecas state, and has an area of 2087.6 km2, with a mean rainfall of 450 mm/year, resulting from a rainy season that occurs mainly between June and September and a potential evapotranspiration of 1900 mm/year. This aquifer is the main source of fresh water for agricultural and industrial activities, with an annual mean extraction of 125 mm3 [18]. The general map of the study area is shown in Figure 1.
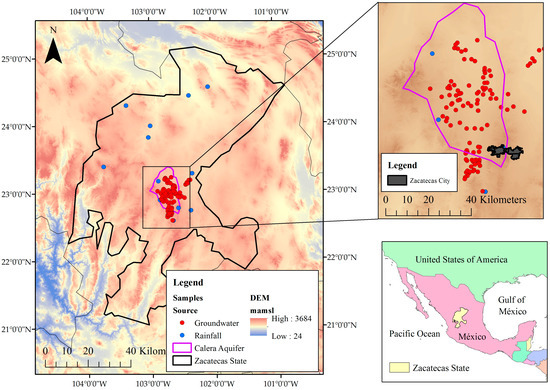
Figure 1.
The location of the study area. Groundwater (red dots) and precipitation (blue dots) samples are shown. A digital elevation model as the background is also shown.
2.2. Ordinary Least Squares Regression
The Ordinary Least Squares Regression method (OLSR) and the Reduced Major Axis (RMA) were used to determine the LMWL for Zacatecas. According to the report by Hughes and Crawford [19] for the OLSR, the slope () is given by:
The intercept (b) is given by:
For the RMA, the slope of the line of the best fit is given by:
The intercept is given by:
2.3. Sampling, Preservation, and Laboratory Analysis
The rainfall samples were collected using a 20-L plastic container lined with thermal insulation and reflective paper. Likewise, heavy mineral oil was used; this mineral oil behaves as a layer floating on the rainfall water, with the aim of minimizing evaporation. The mineral oil is inert; consequently, the isotopic composition of rainfall water will not be modified by its incorporation. Precipitation and groundwater samples were collected for oxygen and hydrogen isotopic analyses from 2014 to 2015. Rainwater samples were not filtered and collected in 50-mL bottles from the plastic containers. To avoid air bubbles being trapped within, both rainwater and groundwater sample bottles were filled to the brim [20]. Then, the sample bottles were stored in cool dry ice chests away from light in accordance with IAEA (International Atomic Energy Agency) [20] guidelines. A total of 144 water samples was taken as follows: 115 groundwater samples and 29 precipitation samples; the surface water was not sampled. Groundwater was sampled through wells at a depth ranging between 65 and 125 m below the ground surface. All 29 rainwater isotope data were used to determine the local meteoric water line.
The sampling locations were chosen according to the recommendations by Kendall and Doctor; the main recommendation was to consider the elevation of the sampling locations [1]. Rainfall sampling locations and a general map of the study area are shown in Table 1. The pH, EC (electrical conductivity), and temperature were measured in the field with HACH HQ430d equipment. The standard calibration was performed with a pH buffer of pH 4.01 and pH 7.00; for EC, the calibration was performed using KCl.

Table 1.
Rainfall sampling locations (elevation values are in meters above mean sea level).
The samples used for the stable isotope analysis () were measured using a GV-Isoprime isotope-ratio mass spectrometer at the Isotopy Laboratory of the Water Center for Latin America and the Caribbean, located at the Monterrey Institute of Technology and Higher Education, Nuevo León, México. Analyses for and are expressed in notation relative to the Vienna Standard Mean Ocean Water (VSMOW). The measurement precision for the stable isotopes was and for and , respectively.
3. Results
3.1. Isotopic Composition of Precipitation
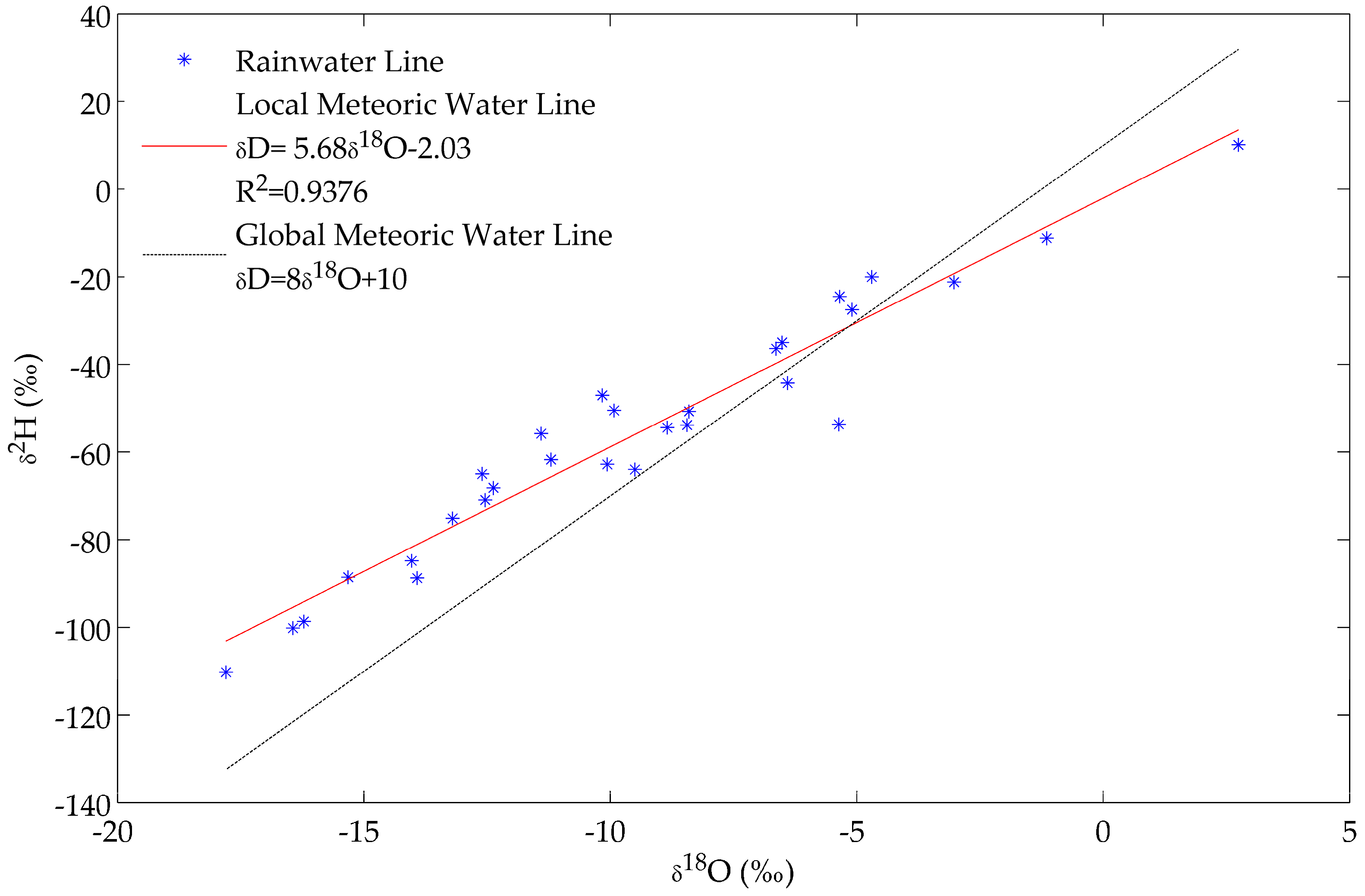
The isotopic signatures of 29 samples of precipitation in the Zacatecas state were analyzed. The data are presented in Table 2. The of precipitation ranged between −110.20‰ and 10.11‰, with a mean of −55.67‰ 27.81‰. The ranged between −17.80‰ and 2.74‰, with a mean of . The ranged between −11.81‰ and 35.80‰, with a mean of . The OLSR analysis showed the Local Meteoric Water Line (LMWL) for the studied region of Zacatecas state to be with a . The LMWL was plotted, and was found to have an intercept of −2.03, which is lower than the intercept of GMWL of 10. This difference may be due to the elevation of the sampling locations affecting the arrival of air masses, besides other possible influencing factors including air, temperature, secondary evaporation, moisture source, as well as the spatial and temporal variability of precipitation [21,22] (see Figure 2). The pH values of the research were measured in locations away from urban areas. The pH value reflects the acidic or alkaline degree of rainwater. The pH of rainwater in large cities is lower than that of the unpolluted area, which reflects the impact of anthropogenic activities on rainwater. The rainwater in Zacatecas state is significantly alkaline, suggesting an important effect of mineral dust from arid lands on rainwater, which is consistent with the report by Rao et al. [23].

Table 2.
Chemical and isotopic compositions of precipitation samples collected in the Zacatecas state (isotopic values are in ‰, EC (µS/cm), T in °C, pH and d-excess.
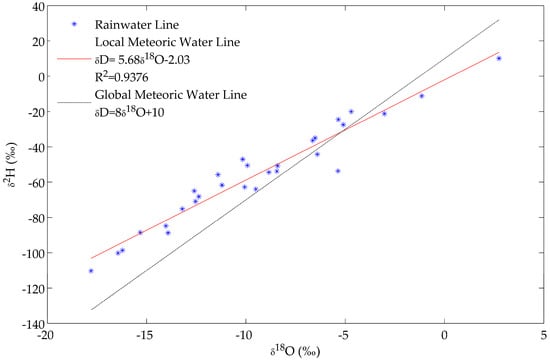
Figure 2.
Plot of Local Meteoric Water Line (LMWL) for precipitation samples and the Global Meteoric Water Line (GMWL).
3.2. Isotopic Composition of Groundwater and Recharge Sites
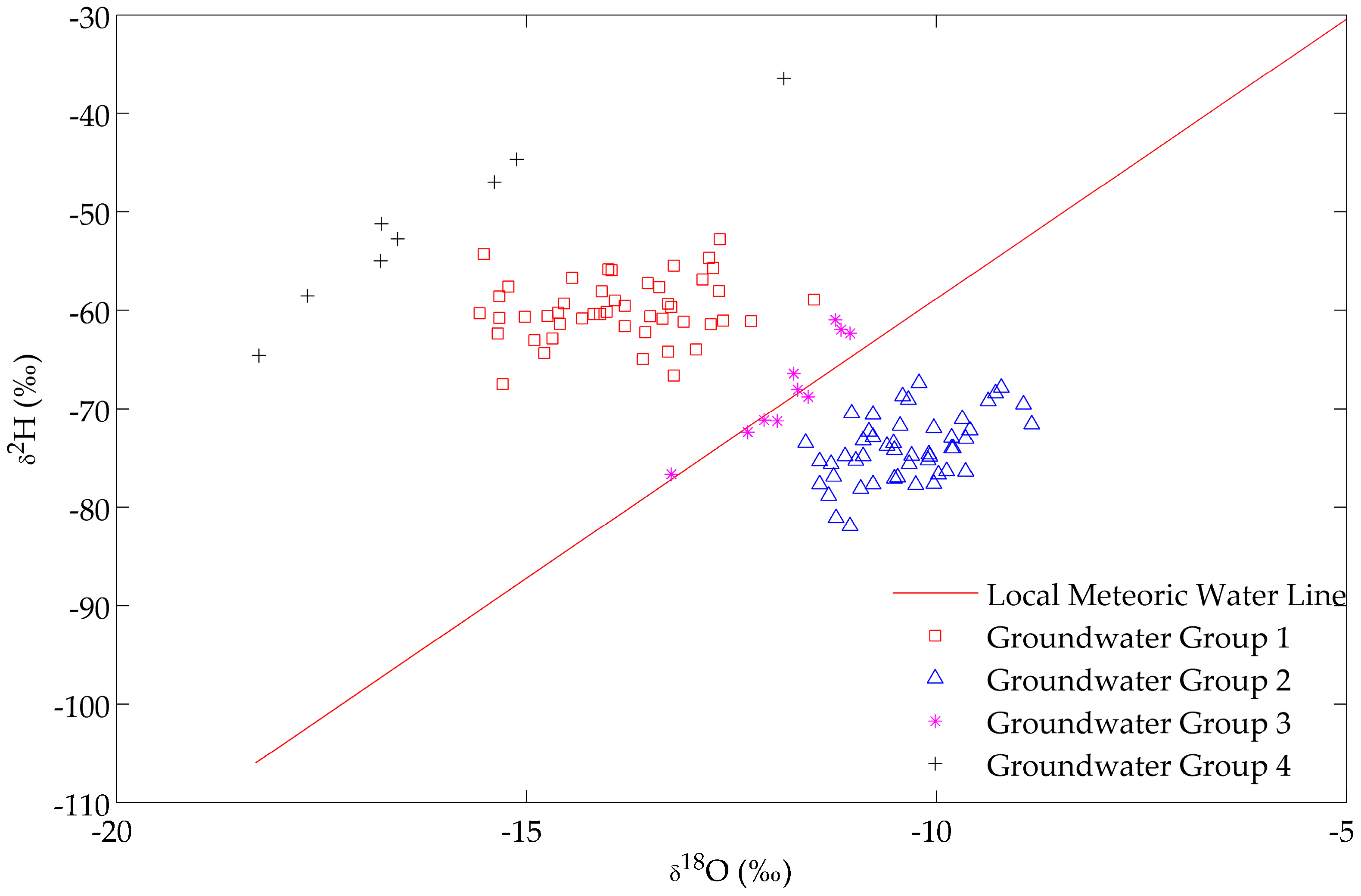
The stable isotope composition of groundwater reflects that precipitation in the recharge area seeps through the soil and the unsaturated zone to reach the water table. The potential infiltration of precipitation (only rain falling above a certain threshold rate contributes to recharge) into the soil and the unsaturated zone is, in principle, an isotopically non-fractionating process. In arid conditions, the movement of water can be upwards: water moves up in liquid and vapor phases in the unsaturated zone, eventually reaching the land surface to be lost as evaporation in the atmosphere [8]. Groundwater samples were obtained for a specific zone of Zacatecas, specifically around and within the Calera aquifer. The isotopic signatures of 115 samples of groundwater in and around the Calera aquifer were analyzed; the data are presented in the Supplementary File. The of groundwater ranged between −81.92‰ and −36.45‰, with a mean of −66.05‰ 8.58‰. The ranged between −18.26‰ and −8.84‰, with a mean of −12.35‰ 2.12‰. The ranged between −0.85‰ and 82.94‰, with a mean of 32.76‰ 23.71‰. There are different multivariate methods to group the samples; one widely-used method is the Hierarchical Cluster Analysis (HCA) approach, which has been used in the clustering of groundwater samples by several investigations [24,25,26]. Nevertheless, the groundwater samples in this study are clustered into four groups. These groups were established with respect to the distance from the LMWL (see Figure 3).
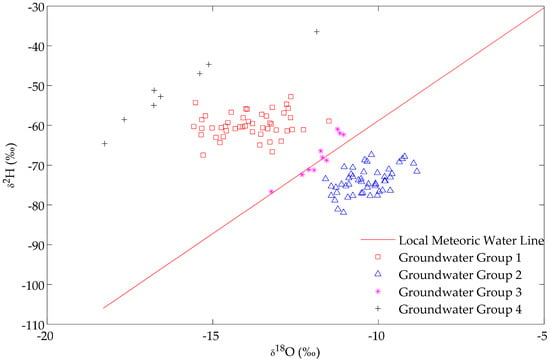
Figure 3.
Plot of vs. groundwater sampling groups and the LWML.
3.3. Deuterium Excess
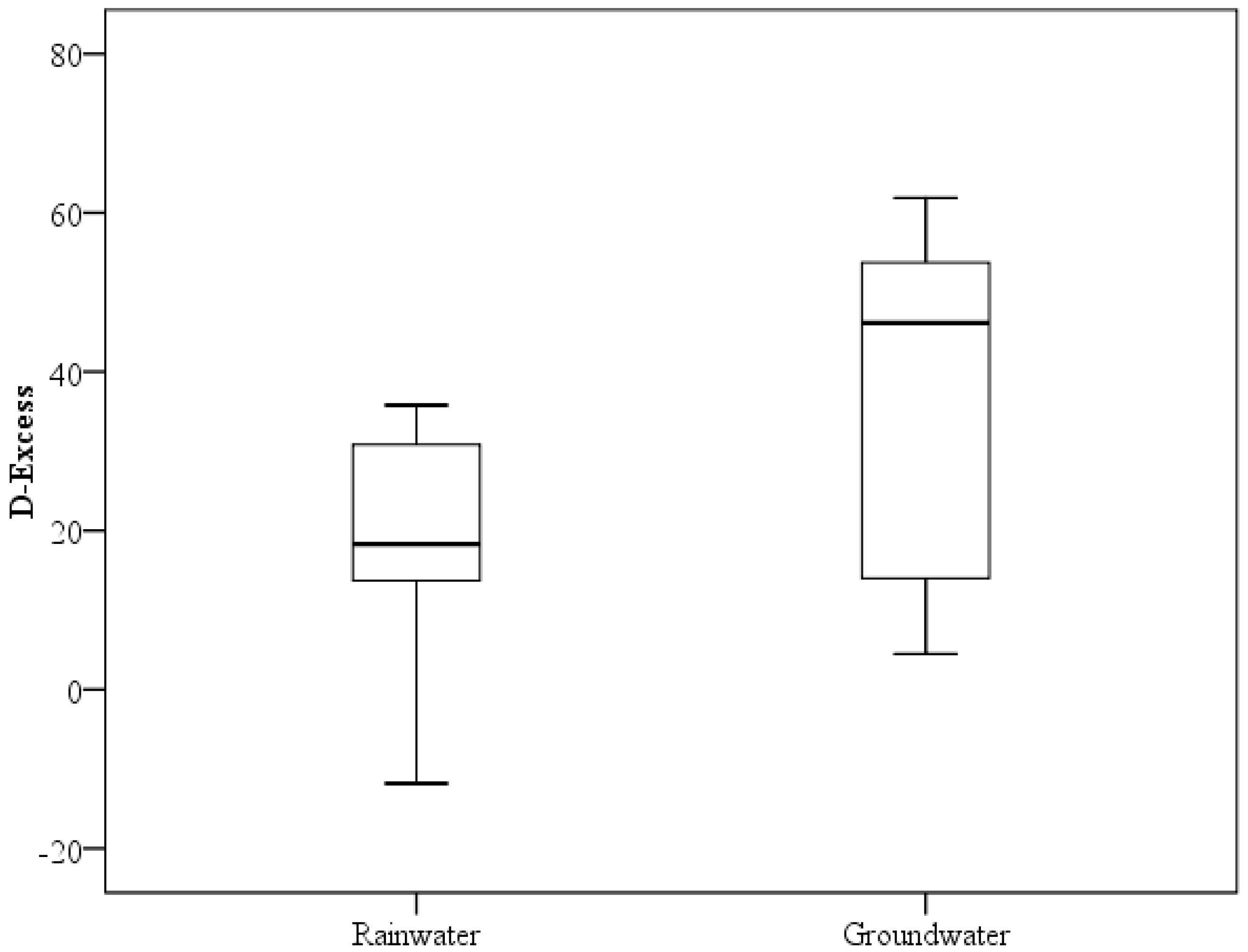
The isotopic composition of moisture in the marine atmosphere is controlled by air-sea interaction processes, and the d-excess value is fixed by these processes [27]. Figure 4 shows the statistical summaries of the d-excess values of rainwater and groundwater in the study area. The deuterium excess in precipitation and atmospheric water vapor provide information on the role of diffusive transport in the boundary layer at the evaporative source and on source temperatures that cannot be obtained from or individually available [28]. Rainwater samples in the study area present suggested d-excess values in the range of −11.81‰ and 35.80‰, with an average of 19.88‰. Of all the samples, 82.75% presented d-excess values higher than 10, which suggests the probable inputs of recycling water vapor and the contribution of possible surface flows to the rain clouds according to Fynn [29], where it was also established that low d-excess values may also have been derived from isolated local moist air masses having those characteristics. The d-excess value is a function of several factors, such as the temperature, humidity, and the isotopic characteristics of the ambient water vapor and the evaporating water.
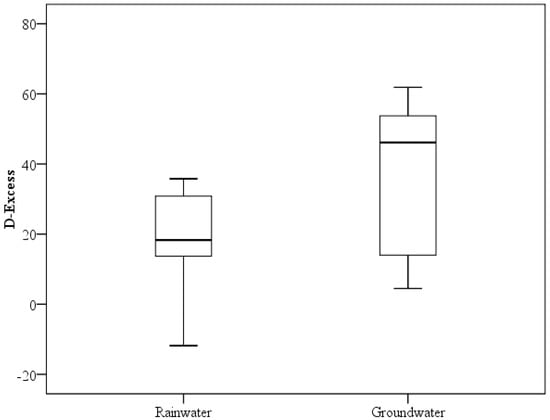
Figure 4.
Box-and-whisker plots showing the d-excess values of rainwater and groundwater.
The computed d-excess values of groundwater samples ranged between −0.85‰ and 82.94‰, with an average of 32.76‰. The average value of 32.76‰ was different from that of the local meteoric water line, making the evolutionary trend from precipitation in the study area to groundwater unclear. A higher variability of groundwater data was found, according to the research presented by Fynn et al. [29], and this variability suggests inputs from various sources and the spatial variability in the nature of the vadose zone. Variable infiltration rates are imposed by the spatial heterogeneity of the material of the vadose zone, leading to variable exposures of the infiltrated water to the effects of fractionation attending evaporation.
4. Discussion
Recharge to Aquifers
Stable isotope data can be used to evaluate possible sources of water for the Calera aquifer. All of the groundwater samples are shown in Figure 3, and they were subsequently clustered into four groups.
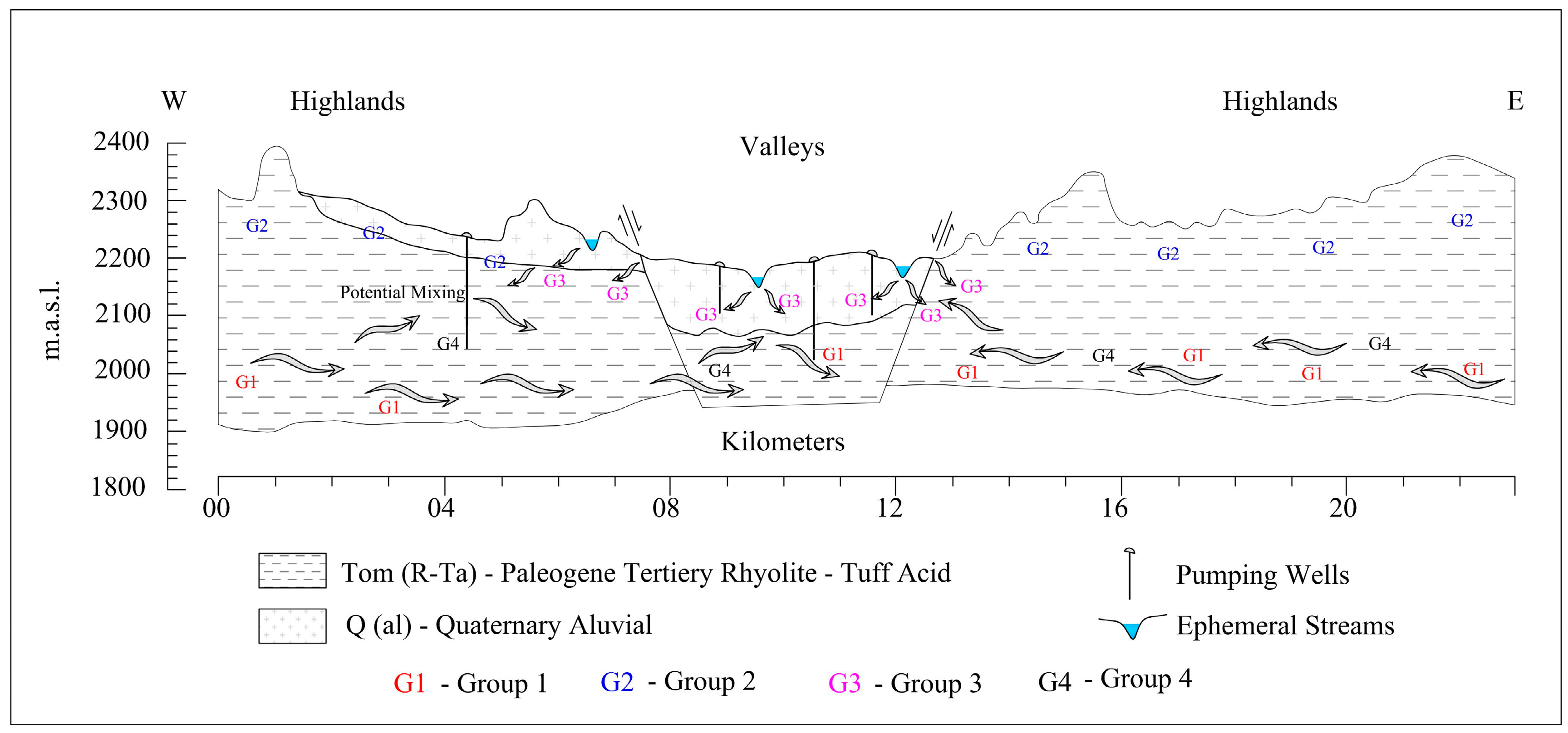
Groups 1 and 4 fall left on the LWML, which means this groundwater was recharged from the Calera aquifer; likely, the recharge originated in the southwest region out of the aquifer, as this area is characterized by a high density of streams and fissures and is consistent with the groundwater flow direction reported by Junez et al. [18]. Group 3 fits around the LMWL, indicating that these groundwater samples have been recharged from local precipitation. Furthermore, Figure 5 shows that these samples are closer than other samples to the streams in the study area. These streams can be classified as perched streams, as opposed to connected streams. They are hydraulically disconnected from the phreatic zone of the aquifer, which means that there is a vadose zone below the riverbed; consequently, they are losing streams and lose water mainly by outflow through the riverbed. The proximity of these groups to the streams may indicate that the streamflow represents one type of vertical recharge to the Calera aquifer, and this water can mix with other input flows in the aquifer. Besides, this group is close to the mountains, where the recharge from precipitation can appear, which is consistent with what was reported by Pacheco-Guerrero et al. [30], McCallum et al. [31], Shanafield and Cook [9], Goodrich et al. [32], and Shentis and Rosenathal [33]. Nevertheless, different types of horizontal recharge can be present in the aquifer. Two fissure systems are shown in Figure 5: shallow fissure and regional fissure systems; these fissures are potentially hydraulically connected with streams favoring the leakage from streams to the underlying unconfined aquifers. Group 2 falls right on the LWML, demonstrating that these samples have undergone some evaporation prior to infiltration [21,34].
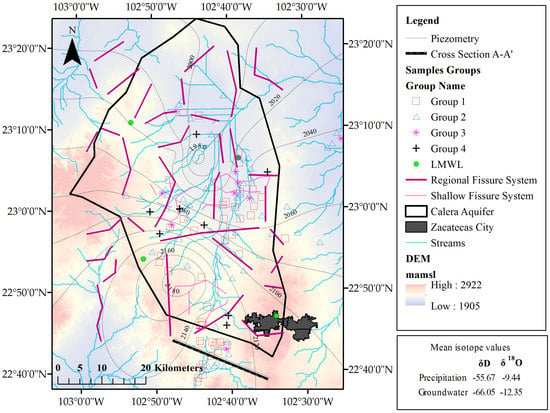
Figure 5.
Geospatial distribution of sampled groups, fissure systems, and streams in the study area.
The presence of different flow systems or mixing among them can impact the isotopic composition of the groundwater, leading to different cluster groups; there is a potential mixing of the regional groundwater system (G1, G4) with local systems (G3, G2) (Figure 6). The mixing probably results from the effect of fracture systems, as well as surface water and groundwater processes. Wassenaar et al. [35] reported groundwater data for and in Mexico; two of their sample points are in the Calera aquifer; namely, two of the sampled points by Wassenar et al. are in the study area. The authors reported values of −7.3 and −10.2 for and −63.2 and −73.9 for . These reported values are spatially consistent with the data reported in this investigation. The monitored altitude ranges between 1660 and 2703 mamsl, and there is not a relation found between the and altitude. Other geographical parameters such as the longitude or latitude can affect the relation with the , which is consistent with what was reported by Liu et al. [36].
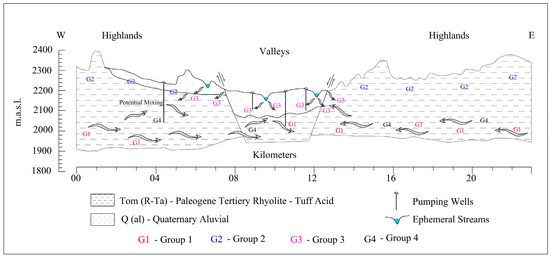
Figure 6.
Cross-section illustrating the groundwater flow conceptual model and the associated clusters.
Based on the isotopic composition of groundwater and clustering, a regional geochemical conceptual model (Figure 6) was proposed along a representative cross-section of the study area. The flow patterns are presented, and different hydrogeologic environments are represented with their associated clusters. The Paleogene tertiary rhyolite allows the movement of water through the fractures; moreover, the rhyolite is covered by quaternary alluvial. The composition of the groundwater from wells settled and close to ephemeral streams is close to the rainwater composition.
5. Conclusions
Environmental isotopes in groundwater of the Calera aquifer were used to identify different sources of water contributing to the groundwater recharge. This research examined the stable isotopic composition of precipitation in the Zacatecas state and groundwater around and within the Calera aquifer. The resultant LMWL for the Zacatecas state is. The slope and intercept values of the local meteoric water line are all lower than those of the global meteoric water line, and these differences are attributed to the continentality (~400 km away from sea), altitude (over 2000 mamsl), and the climatic conditions of the area affected by the humidity from the Pacific Ocean and the Gulf of Mexico. The d-excess values of groundwater on average seem to be higher than those of the local meteoric water line, due to groundwater having been subjected to several evaporative and infiltration processes. The clustering of the samples led to the finding that streamflow plays a significant role in the hydrological balance as a source of local recharge to the aquifer. The obtained results in this research contribute to the improvement of water management decisions with the objective of achieving an environmentally sustainable approach. In order to confirm the assumption that streamflow in the network drainage is the main groundwater recharge source, it will be necessary to examine the radioactive isotopic composition of groundwater (tritium and ). The presented data offer a tool for groundwater recharge assessment in arid and semiarid regions. Future research should analyze the isotopic stable composition of streamflow and the hydraulic linkage between fissure systems and rivers.
Supplementary Materials
The following are available online at www.mdpi.com/2073-4441/9/8/569/s1.
Acknowledgments
The authors express their gratitude to the Mexican National Council for Science and Technology (CONACYT) for financing the scholarship of the author Anuard Pacheco-Guerrero. We greatly appreciate the advice and professional comments from the two anonymous reviewers and the Editor. The authors also express their gratitude to the Isotopy Laboratory of the Water Center for Latin America and the Caribbean, Monterrey Institute of Technology and Higher Education, Nuevo León, México, for contributing to the isotopic analysis of all of the samples.
Author Contributions
Julián Gonzalez-Trinidad conceived of the subject of the article and elaborated the statistical analysis. Anuard Pacheco-Guerrero contributed to the writing of the paper, the data processing and the elaboration of the figures. Hugo Júnez-Ferreira participated in the composition of the manuscript, specifically in the results and discussion sections. Carlos Bautista-Capetillo contributed to the data processing and writing of the paper. Arturo Hernández-Antonio contributed to the precipitation and groundwater isotopic composition analysis.
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
References
- Kendall, C.; Doctor, D.H. Stable Isotope Applications in Hydrologic Studies. In Treatise on Geochemistry, 1st ed.; Drever, J.I., Ed.; Elsevier: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 2003; Volume 5, pp. 319–364. ISBN 978-0-08-098300-4. [Google Scholar]
- Bu-Li, C.; Xiao-Yan, L. Stable isotopes reveal sources of precipitation in the Qinghai Lake Basin of the northeastern Tibetan Plateau. Sci. Total Environ. 2015, 527, 26–37. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Prathibha, P.; Kothai, P.; Saradhi, I.V.; Pandit, G.G.; Puranik, V.D. Chemical characterization of precipitation at a coastal site in Trombay, Mumbai, India. Environ. Monit. Assess. 2010, 168, 45–53. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jinzhu, M.; Zhang, P.; Gaofeng, Z.; Yunquan, W.; Edmunds, W.M.; Zhenyu, D.; Jianhua, H. The composition and distribution of chemicals and isotopes in precipitation in the Shiyang River system, northwestern China. J. Hydrol. 2012, 436, 92–101. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Desboeufs, K.; Journet, E.; Rajot, J.L.; Chevailier, S.; Triquet, S.; Formenti, P.; Zakou, A. Chemistry of rain events in West Africa: Evidence of dust and biogenic influence in convective systems. Atmos. Chem. Phys. 2010, 10, 9283–9293. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Craig, H. Isotopic variations in meteoric waters. Science 1961, 133, 1702–1703. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hsin-Fu, Y.; Hung-I, L.; Cheng-Haw, L.; Kuo-Chin, H.; Chi-Shin, W. Identifying Seasonal Groundwater Recharge Using Environmental Stable Isotopes. Water 2014, 6, 2849–2861. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ingraham, N.L.; Caldwell, E.A.; Verhagen, B.T. Arid Catchments. In Isotope Tracers in Catchment Hydrology, 1st ed.; Kendall, C., McDonell, J.J., Eds.; Elsevier: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 1998; pp. 435–465. ISBN 978-0-444-81546-0. [Google Scholar]
- Shanafield, M.; Cook, P.G. Transmission losses, infiltration and groundwater recharge through ephemeral and intermittent streambeds: A review of applied methods. J. Hyhdrol. 2014, 511, 518–529. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kretzchmar, T.G.; Frommen, T. Stable isotope composition of surface and groundwater in Baja California, Mexico. Procedia Earth Planet. Sci. 2013, 7, 451–454. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lachniet, M.S.; Patterson, W.P. Oxygen isotope values of precipitation and surface waters in northern Central America (Belize and Guatemala) are dominated by temperature and amount effects. Earth Planet. Sci. Lett. 2009, 284, 435–446. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Goldsmith, G.R.; Muñoz-Villers, L.E.; Holwerda, F.; McDonell, J.J.; Asbjornsen, H.; Dawson, T.E. Stable isotopes reveal linkages among ecohydrological processes in a seasonally dry tropical montane cloud forest. Ecohydrology 2012, 5, 779–790. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Quezadas, P.; Cortés, A.; Inguaggiato, S.; Salas, M.R.; Cervantes, J.; Heilweil, M. Meteoric isotopic gradient on the windward side of the Sierra Madre Oriental area, Veracruz-Mexico. Geofís. Int. 2015, 54, 267–276. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hernández-Antonio, A.; Mahlknecht, J.; Tamez-Meléndez, C.; Ramos-Leal, J.; Ramírez-Orozco, A.; Parra, R.; Ornelas-Soto, N.; Eastoe, J. Groundwater flow processes and mixing in active volcanic systems: The case of Guadalajara (Mexico). Hydrol. Earth Syst. Sci. 2015, 19, 3937–3950. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hartsough, P.; Poulson, S.R.; Biondi, F.; Galindo-Estrada, I. Stable Isotope Characterization of the Ecohydrological Cycle at a Tropical. Arct. Antarct. Alp. Res. 2008, 40, 343–354. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Comisión Nacional del Agua (CONAGUA). Actualización de la Disponibilidad Media Anual de Agua Subterránea, Acuífero (3225) Calera; Diario Oficial de la Federación, Government of Mexico: Mexico City, Mexico, 2009.
- Junez-Ferreira, H.; Mojarro Davila, F.; Bautista-Capetillo, C.; Villalobos De Alba, A.; Steiner, J.L.; Avila-Carrasco, J. Quantitative and qualitative analysis of groundwater in aguanaval and chupaderos aquifers (Mexico). J. Earth Sci. Eng. 2013, 3, 425–436. [Google Scholar]
- Júnez-Ferreira, H.; Bautista-Capetillo, C.F.; González-Trinidad, J. Análisis geoestadístico espacial de cuatro iones mayoritarios y arsénico en el acuífero Calera, Zacatecas. Tecnol. Cienc. Agua 2013, 4, 175–181. [Google Scholar]
- Hughes, C.E.; Crawford, J. A new precipitation weighted method for determining the meteoric water line for hydrological applications demonstrated using Australian and global GNIP data. J. Hydrol. 2012, 464, 344–351. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- International Atomic Energy Agency (IAEA). Guidebook on Nuclear Techniques in Hydrology; IAEA Technical Report Series No. 91; IAEA: Vienna, Austria, 1983. [Google Scholar]
- Thivya, C.; Chidambaram, S.; Rao, M.S.; Gopalakrishnan, M.; Thilagavathi, R.; Prasanna, M.V.; Nepolian, M. Identification of Recharge Processes in Groundwater in Hard Rock Aquifers of Madurai District Using Stable Isotopes. Environ. Process. 2016, 3, 463–477. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rozanski, K.; Araguás-Araguás, L.; Gonfiantini, R. Isotopic Patterns in Modern Global Precipitation. Int. At. Energy Agency 1993, 78, 1–36. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rao, W.; Guillin, H.; Hongbin, T.; Jin, K.; Wang, S.; Chen, T. Chemical and Sr isotopic characteristics of rainwater on the Alxa Desert Plateau North China: Implication for air quality and ion sources. Atmos. Res. 2017, 193, 163–172. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cloutier, V.; Lefebre, R.; Therrien, R.; Savard, M.M. Multivariate statistical analysis of geochemical data as indicative of the hydrogeochemical evolution of groundwater in a sedimentary rock aquifer system. J. Hydrol. 2008, 353, 294–313. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moeck, C.; Radny, D.; Borer, P.; Rothardt, J.; Auckenthaler, A.; Berg, M.; Schirmer, M. Multicomponent statistical analysis to identify flow and transport processes in a highly-complex environment. J. Hydrol. 2016, 542, 437–449. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Montocoudiol, N.; Molson, J.; Lemieux, J.-M. Groundwater geochemistry of the Outaouais Region (Québec, Canada): A regional-scale study. Hydrogeol. J. 2015, 23, 377. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gat, J.R. Oxygen and hydrogen isotopes in the hydrologic cycle. Ann. Rev. Earth Planet Sci. 1996, 24, 225–262. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cappa, C.D.; Hendricks, M.B.; DePaolo, D.J.; Cohen, R.C. Isotopic fractionation of water during evaporation. J. Geophys. Res. Atmos. 2003, 108, 1–10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fynn, O.F.; Yidana, S.M.; Chegbeleh, L.P.; Yiran, G.B. Evaluating groundwater recharge processes using stable isotope signatures—The Nabogo catchment of the White Volta, Ghana. Arab J. Geosci. 2016, 9, 279. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pacheco-Guerrero, A.; Goodrich, D.C.; González-Trinidad, J.; Júnez-Ferreira, H.E.; Bautista-Capetillo, C.F. Flooding in ephemeral streams: Incorporating transmission losses. J. Maps 2017, 13, 350–357. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McCallum, A.; Andersen, M.S.; Acworth, R.I. A New Method for Estimating Recharge to Unconfined Aquifers Using Differential River Gauging. Groundwater 2014, 52, 291–297. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Goodrich, D.C.; Williams, D.G.; Unkrich, C.L.; Hogan, J.F.; Scott, R.L.; Hultine, K.R.; Pool, D.; Coes, A.L.; Miller, S. Comparison of Methods to Estimate Ephemeral Channel Recharge, Walnut Gulch, San Pedro River Basin, Arizona. In Groundwater Recharge in a Desert Environment: The Southwestern United States; Hogan, J.F., Phillips, F.M., Scanlon, B.R., Eds.; American Geophysical Union: Washington, DC, USA, 2013; Volume 9, pp. 77–99. [Google Scholar]
- Shentsis, I.; Rosenthal, E. Recharge of aquifers by flood events in an arid region. Hydrol. Process. 2003, 17, 695–712. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Baskaran, S.; Ransley, T.; Brodie, R.S.; Baker, P. Investigating groundwater-river interactions using environmental tracers. Aust. J. Earth Sci. 2009, 56, 13–19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wassenaar, L.I.; Van Wilgenburg, S.L.; Larson, K.; Hobson, K.A. A groundwater isoscape (δD, δ18O) for Mexico. J. Geochem. Explor. 2009, 102, 123–136. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, J.; Song, X.; Sun, X.; Yuan, G.; Liu, X.; Wang, S. Isotopic composition of precipitation over Arid Northwestern China and its implications for the water vapor origin. J. Geogr. Sci. 2009, 19, 164–174. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
© 2017 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).