The Effects of Terrain Factors and Cultural Landscapes on Plateau Forest Distribution in Yushu Tibetan Autonomous Prefecture, China
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
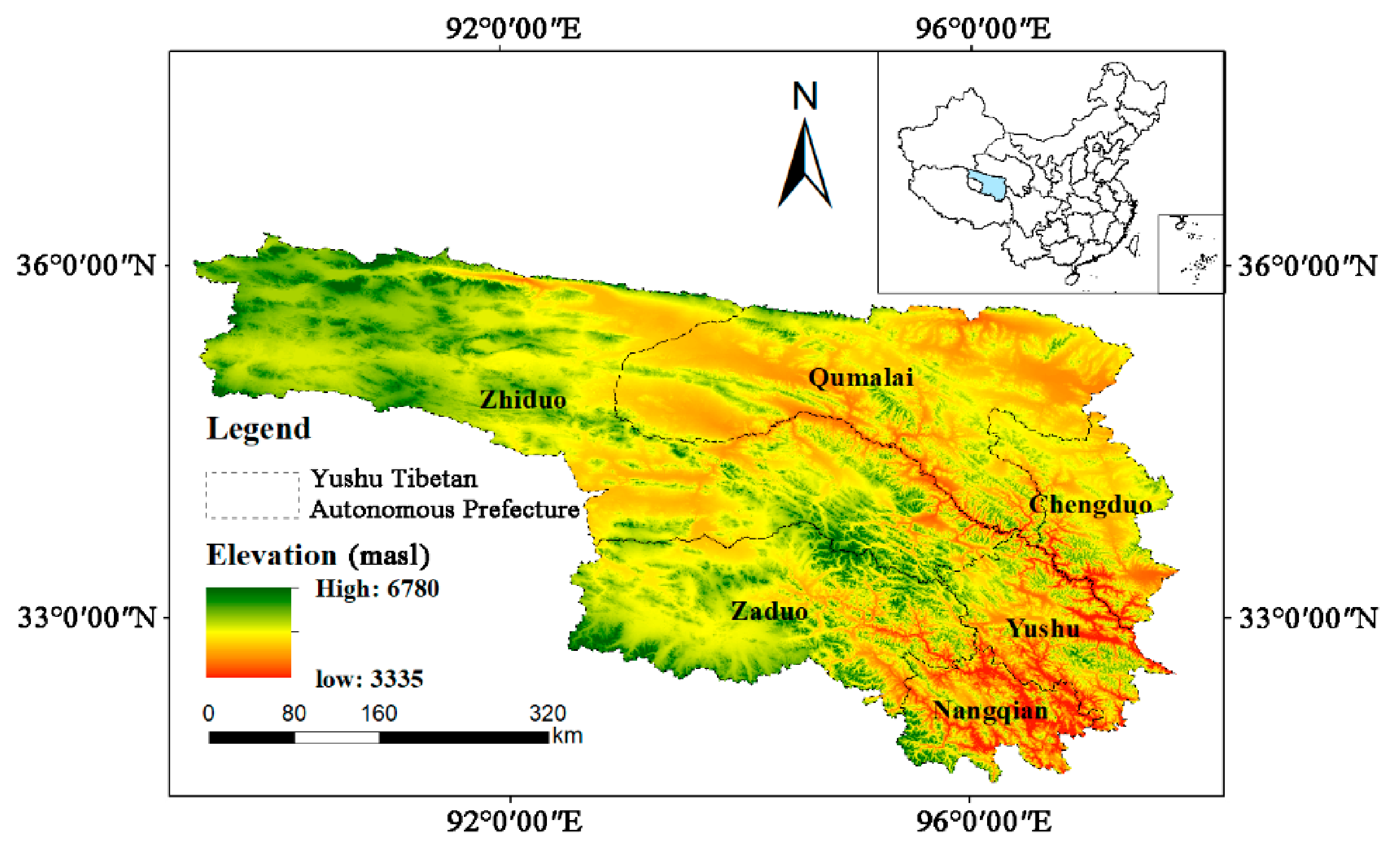
2.1. Study Area
2.2. Data Collection
2.3. Methods
2.3.1. Spatial Sampling Analysis of Terrain Factors and Forest Landscape
2.3.2. Correlation between Terrain Factors and Forest Landscape Distribution Patterns and Nonlinear Regression Tests
2.3.3. Spatial Relationship Function of Temple, Village and Forest Landscapes
2.3.4. Monte Carlo Significance Test of Pc(rq) Function
2.3.5. The Establishment of Buffer Zone
3. Results
3.1. Spatiotemporal Variation Characteristic of Forest Landscape as a Function of Altitude and Slope
3.2. Regression Model Analysis of Terrain Factors
3.3. Spatiotemporal Variation Characteristics of Forest Landscape as a Function of Different Cultural Landscapes
3.4. Spatiotemporal Variation Characteristic of Forest Landscape under the Influence of Temples
4. Discussion
4.1. The Influence of Terrain Factors on Forest Landscape Distribution
4.2. The Influence of Culture Landscapes on Forest Distribution
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Balmford, A.; Moore, J.L.; Brooks, T.; Burgess, N.; Hansen, L.A.; Williams, P.; Rahbek, C. Conservation Conflicts Across Africa. Science 2001, 291, 2616–2619. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pimm, S.L.; Raven, P. Extinction by numbers. Nature 2000, 403, 843–845. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sala, O.E.; Chapin, F.S.; Armesto, J.J.; Berlow, E.L.; Bloomfield, J.B.; Dirzo, R.H.; Huber-Sanwald, E.; Huenneke, L.F.; Jackson, R.B.; Kinzig, A.P.; et al. Global biodiversity scenarios for the Year 2100. Science 2000, 287, 1770–1774. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Teixeira, A.M.G.; Soares-Filho, B.S.; Freitas, S.R.; Metzger, J.P. Modeling landscape dynamics in an Atlantic Rainforest region: Implications for conservation. For. Ecol. Manag. 2009, 257, 1219–1230. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ayram, C.A.C.; Mendoza, M.E.; Etter, A.; Salicrup, D.R.P. Potential Distribution of Mountain Cloud Forest in Michoacán, Mexico: Prioritization for Conservation in the Context of Landscape Connectivity. Environ. Manag. 2017, 60, 86–103. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Spracklen, D.V.; Righelato, R. Tropical montane forests are a larger than expected global carbon store. Biogeosci. Discuss 2013, 10, 18893–18924. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Feng, X.; Wu, X.; Shen, D.; Zhu, J. Association analysis of forest topography and vegetation spatial pattern based on DEM. Fujian For. Sci. Technol. 2015, 1, 26–30. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zeng, H.D. Application of Digital Terrain Information and Geostatistics to Forest Spatial Pattern Analysis—A Case on Wuyi Mt. Area. Geoinf. Sci. 2005, 2, 82–88. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Andrews, A. Fragmentation of Habitat by Roads and Utility Corridors: A Review. Aust. Zool. 1990, 26, 130–141. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Collinge, S.K. Ecological consequences of habitat fragmentation: Implications for landscape architecture and planning. Landsc. Urban Plan. 1996, 36, 59–77. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Linehan, J.; Gross, M.; Finn, J. Greenway planning: Developing a landscape ecological network approach. Landsc. Urban Plan. 1995, 33, 179–193. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Walker, R.; Craighead, L. Analyzing Wildlife Movement Corridors in Montana Using GIS. In Proceedings of the 1997 ESRI User Conference, Redlands, CA, USA, 8–11 July 1997. [Google Scholar]
- Deng, X.; Huang, J.; Rozelle, S.; Uchida, E. Growth, population and industrialization, and urban land expansion of China. J. Urban Econ. 2008, 63, 96–115. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Castella, J.C.; Kam, S.P.; Dang, D.Q.; Verburg, P.H.; Chu, T.H. Combining top-down and bottom-up modelling approaches of land use/cover change to support public policies: Application to sustainable management of natural resources in northern Vietnam. Land Use Policy 2007, 24, 531–545. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rosati, L.; Fipaldini, M.; Marignani, M.; Blasi, C. Effects of fragmentation on vascular plant diversity in a Mediterranean forest archipelago. Bot. Ital. 2010, 144, 38–46. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bürgi, M. A case study of forest change in the Swiss lowlands. Landsc. Ecol. 1999, 14, 567–576. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xin, C.; Chen, J.; Chen, L.J.; Liao, A.P.; Sun, F.D.; Yang, L.I.; Lei, L.I. Preliminary analysis of spatiotemporal pattern of global land surface water. Sci. China Earth Sci. 2014, 57, 2330–2339. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kazak, J.; Wang, T.; Szewrański, S. Analysis of Land Use Transformation Potential in Spatial Management. Real Estate Manag. Valuat. 2015, 23, 5–14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Zhang, Z.; Zinda, J.A.; Li, W. Forest transitions in Chinese villages: Explaining community-level variation under the returning forest to farmland program. Land Use Policy 2017, 64, 245–257. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Jamon, V.D.H.; Ozdogan, M.; Burnicki, A.; Zhu, A.X. Evaluating forest policy implementation effectiveness with a cross-scale remote sensing analysis in a priority conservation area of Southwest China. Appl. Geogr. 2014, 47, 177–189. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cullotta, S.; Barbera, G. Mapping traditional cultural landscapes in the Mediterranean area using a combined multidisciplinary approach: Method and application to Mount Etna (Sicily; Italy). Landsc. Urban Plan. 2011, 100, 98–108. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiao, Y.; Liang, L.; Okuro, T.; Takeuchi, K. Ecosystem Services and Biodiversity of Traditional Agricultural Landscapes: A Case Study of the Hani Terraces in Southwest China. In Biocultural Landscapes; Springer: Dordrecht, The Netherlands, 2014; pp. 81–88. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Grace, D.; Jeuland, M. Preferences for Attributes of Sacred Groves and Temples along an Urbanization Gradient in the National Capital Region of India. Ecol. Econ. 2018, 152, 322–335. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bhagwat, S.A.; Nogué, S.; Willis, K.J. Cultural drivers of reforestation in tropical forest groves of the Western Ghats of India. For. Ecol. Manag. 2014, 329, 393–400. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Chen, J.; Yifang, B.; Songnian, L. China: Open access to Earth land-cover map. Nature 2014, 514, 434. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Kuenzer, C.; Leinenkugel, P.; Vollmuth, M.; Dech, S. Comparing global land-cover products—Implications for geoscience applications: An investigation for the trans-boundary Mekong Basin. Int. J. Remote Sens. 2014, 35, 2752–2779. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Leinenkugel, P.; Kuenzer, C.; Oppelt, N.; Dech, S. Characterisation of land surface phenology and land cover based on moderate resolution satellite data in cloud prone areas—A novel product for the Mekong Basin. Remote Sens. Environ. 2013, 136, 180–198. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, J.; Chen, J.; Liao, A.; Cao, X.; Chen, L.; Chen, X.; He, C.; Han, G.; Peng, S.; Lu, M. Global land cover mapping at 30 m resolution: A POK-based operational approach. ISPRS J. Photogramm. Remote Sens. 2015, 103, 7–27. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Vemu, S.; Bhaskar, P.U. Change Detection in Landuse and landcover using Remote Sensing and GIS Techniques. Int. J. Eng. Sci. Technol. 2010, 2, 7758–7762. [Google Scholar]
- Balogun, I.A.; Adeyewa, D.Z.; Balogun, A.A.; Morakinyo, T.E. Analysis of urban expansion and land use changes in Akure, Nigeria, using remote sensing and geographic information system (GIS) techniques. J. Geogr. Reg. Plan. 2011, 4, 533–541. [Google Scholar]
- Hu, Z.; Lo, C.P. Modeling urban growth in Atlanta using logistic regression. Comput. Environ. Urban Syst. 2007, 31, 667–688. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qi, W.; Meng, J.; Mao, X. Scenario simulation and landscape pattern assessment of land use change based on neighborhood analysis and auto-logistic model: A case study of Lijiang River Basin. Geogr. Res. 2014, 33, 1073–1084. [Google Scholar]
- Basse, R.M.; Omrani, H.; Charif, O.; Gerber, P.; Bódis, K. Land use changes modelling using advanced methods: Cellular automata and artificial neural networks. The spatial and explicit representation of land cover dynamics at the cross-border region scale. Appl. Geogr. 2014, 53, 160–171. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bryan, C.P.; Daniel, G.B.; Gaurav, A.M. Using neural networks and GIS to forecast land use changes: A Land Transformation Model. Comput. Environ. Urban Syst. 2002, 26, 553–575. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kamusoko, C.; Aniya, M.; Adi, B.; Manjoro, M. Rural sustainability under threat in Zimbabwe—Simulation of future land use/cover changes in the Bindura district based on the Markov-cellular automata model. Appl. Geogr. 2009, 29, 435–447. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Poelmans, L.; Rompaey, A.V. Complexity and performance of urban expansion models. Comput. Environ. Urban Syst. 2010, 34, 17–27. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Verburg, P.H.; Soepboer, W.; Veldkamp, A. Modeling the Spatial Dynamics of Regional Land Use: The CLUE-S Model. Environ. Manag. 2002, 30, 391. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ran, Y.H.; Xin, L.I.; Institute, E.E.; Sciences, C.A.O. First comprehensive fine-resolution global land cover map in the world from China—Comments on global land cover map at 30-m resolution. Sci. China 2015, 58, 1677–1678. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ministry of Land and Resources of the People’s Republic of China. TD/T 1055-2019, Technical Regulation of the Third Nationwide Land Survey. Available online: http://gi.mnr.gov.cn/201901/t20190129_2391915.html (accessed on 2 June 2019).
- Cui, N.; Luo, G.; Du, S. Analysis of Spatial-Temporal Variation of Grassland Landscape Pattern Based on Terrain Factors in Qinghai Yushu Tibetan Autonomous Prefecture, China. In Proceedings of the 26th International Conference on Geoinformatics, Kunming, China, 28–30 June 2018. [Google Scholar]
- Qinghai Information Center. Available online: http://www.qhei.org.cn/ (accessed on 11 May 2019).
- Yang, Y.; Zhang, X.; Yu, H.; Lv, Z. The Spatial Distribution of China’s Forest Biomass and Its Influencing Factors. J. Southwest For. Univ. 2015, 35, 45–52. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, X.; Ke, B.; Huang, Z.; Yang, G.; Huang, G.; Hu, Q.; Sun, L. Quantification of Forest Carbon Storage in Tibetan Plateau. For. Environ. Sci. 2020, 36, 9–19. [Google Scholar]
- Zhuo-Ma, C.; Huang, Q.; Guo, L.; Xue, D.Y. Distribution and Dynamic Change of Land Use of Monastery and Settlement in YuShu Tibetan Autonomous Prefecture in Three River Headwater Region. J. Minzu Univ. China 2016, 25, 5–11. [Google Scholar]
- Wei, F.U.; Junquan, Z.; Guozhen, D.U. Research on tibetan traditional ecological ethics and the qinghai- tibet plateau ecological and environmental protection. Ecol. Econ. 2013, 2, 420–423. [Google Scholar]




| Year | R2 | F | p | ||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Closed Forest Land | Shrubbery | Open Forest Land | Closed Forest Land | Shrubbery | Open Forest Land | Closed Forest Land | Shrubbery | Open Forest Land | |
| 1990 | 0.977 | 0.863 | 0.993 | 41.647 | 18.843 | 141.443 | 0.023 | 0.023 | 0.007 |
| 2000 | 0.979 | 0.884 | 0.993 | 46.457 | 22.907 | 145.416 | 0.021 | 0.017 | 0.007 |
| 2005 | 0.978 | 0.883 | 0.993 | 43.882 | 22.640 | 145.372 | 0.022 | 0.018 | 0.007 |
| 2010 | 0.978 | 0.878 | 0.993 | 43.882 | 21.571 | 146.769 | 0.022 | 0.019 | 0.007 |
| 2015 | 0.979 | 0.878 | 0.993 | 47.119 | 21.571 | 152.407 | 0.021 | 0.019 | 0.007 |
| Year | R2 | p | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Closed Forest Land | Shrubbery | Open Forest Land | Closed Forest Land | Shrubbery | Open Forest Land | |
| 1990 | 0.987 | 0.988 | 0.986 | 0.012 | 0.010 | 0.011 |
| 2000 | 0.984 | 0.991 | 0.985 | 0.014 | 0.009 | 0.012 |
| 2005 | 0.984 | 0.991 | 0.985 | 0.014 | 0.009 | 0.012 |
| 2010 | 0.984 | 0.991 | 0.986 | 0.014 | 0.009 | 0.011 |
| 2015 | 0.982 | 0.990 | 0.985 | 0.015 | 0.010 | 0.011 |
| Point | Year | Pc(rq) | |||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 km | 2 km | 3 km | 4 km | 5 km | 6 km | 7 km | 8 km | 9 km | 10 km | ||
| Temple | 1990–1995 | 0.951 | 1.118 * | 1.140 * | 1.305 * | 1.404 * | 1.484 * | 1.464 * | 1.405 * | 1.382 * | 1.341 * |
| 1995–2000 | 1.581 * | 1.509 * | 1.793 * | 1.700 * | 1.660 * | 1.597 * | 1.549 * | 1.471 * | 1.412 * | 1.371 * | |
| 2000–2010 | 1.498 * | 1.602 * | 1.614 * | 1.583 * | 1.493 * | 1.487 * | 1.444 * | 1.422 * | 1.433 * | 1.419 * | |
| 2010–2015 | 1.431 * | 1.517 * | 1.652 * | 1.621 * | 1.596 * | 1.601 * | 1.563 * | 1.482 * | 1.434 * | 1.376 * | |
| Village | 1990–1995 | 1.139 | 1.125 | 1.239 * | 1.245 * | 1.207 * | 1.132 * | 1.096 * | 1.062 * | 1.025 | 0.991 |
| 1995–2000 | 1.371 * | 1.499 * | 1.395 * | 1.361 * | 1.273 * | 1.187 * | 1.113 * | 1.032 | 1.012 | 0.988 * | |
| 2000–2010 | 1.260 * | 1.312 * | 1.225 * | 1.158 * | 1.156 * | 1.108 * | 1.051 | 1.004 | 0.983 | 0.973 | |
| 2010–2015 | 1.351 * | 1.391 * | 1.324 * | 1.335 * | 1.256 * | 1.164 * | 1.102 * | 1.046 | 1.014 | 0.992 | |
| Year | Types | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Closed Forest Land (%) | Shrubbery (%) | Open Forest Land (%) | Sum (%) | |
| 1990 | 3.435 | 25.415 | 20.075 | 48.925 |
| 1995 | 1.729 | 30.131 | 13.801 | 45.661 |
| 2000 | 3.522 | 24.680 | 20.174 | 48.376 |
| 2005 | 3.522 | 24.697 | 20.215 | 48.434 |
| 2010 | 3.525 | 24.697 | 20.165 | 48.386 |
| 2015 | 3.526 | 24.708 | 20.151 | 48.386 |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2021 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Cui, N.; Zou, H.; Zhang, M.; Guo, L. The Effects of Terrain Factors and Cultural Landscapes on Plateau Forest Distribution in Yushu Tibetan Autonomous Prefecture, China. Land 2021, 10, 345. https://doi.org/10.3390/land10040345
Cui N, Zou H, Zhang M, Guo L. The Effects of Terrain Factors and Cultural Landscapes on Plateau Forest Distribution in Yushu Tibetan Autonomous Prefecture, China. Land. 2021; 10(4):345. https://doi.org/10.3390/land10040345
Chicago/Turabian StyleCui, Naixin, Huiting Zou, Moshi Zhang, and Luo Guo. 2021. "The Effects of Terrain Factors and Cultural Landscapes on Plateau Forest Distribution in Yushu Tibetan Autonomous Prefecture, China" Land 10, no. 4: 345. https://doi.org/10.3390/land10040345
APA StyleCui, N., Zou, H., Zhang, M., & Guo, L. (2021). The Effects of Terrain Factors and Cultural Landscapes on Plateau Forest Distribution in Yushu Tibetan Autonomous Prefecture, China. Land, 10(4), 345. https://doi.org/10.3390/land10040345






