- Article
Exploring the Residents’ Perceptions of Ecosystem Services and Disservices in Three-River-Source National Park
- Aiqing Li,
- Huaju Xue and
- Yanqin Wang
- + 2 authors
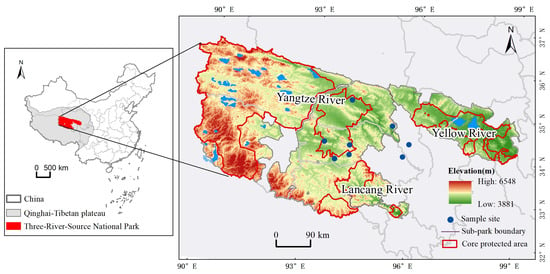
Understanding residents’ perceptions of ecosystem services (ES) and ecosystem disservices (EDS) is crucial for protected areas governance. This study, conducted in China’s Three-River-Source National Park (TNP), employed participatory rural appraisal and household questionnaires to examine local cognitive patterns of ES and EDS, along with their socio-spatial heterogeneity and perceived synergies and trade-offs among them. The key findings are as follows: (1) Cultural services received the highest scores, followed by regulating services, whereas provisioning services, especially food provisioning, were rated as relatively inadequate. Safety threats were considered the most severe EDS. Overall, a Matthew Effect emerged: services with high current perception scores showed an improving trend, while those with low scores deteriorated. (2) Spatially, ES/EDS evaluation scores exhibited a “core zone < general control zone < peripheral zone” gradient. Socio-demographic and economic factors also influenced residents’ perceptions; women and the elderly were especially more concerned about food and energy supply shortages and safety issues. (3) The relationships among the various ES and EDS are primarily synergistic rather than trade-offs. Specifically, gains in regulating services were associated with enhanced cultural services, while declines in provisioning services and intensified safety threats coincided with the deterioration of material EDS. These findings offer a scientific basis for managing protected areas in high-altitude, ecologically fragile regions and provide practical insights for balancing ecological conservation with community development.
11 January 2026