Spatial Distribution, Environmental Risk and Safe Utilization Zoning of Soil Heavy Metals in Farmland, Subtropical China
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
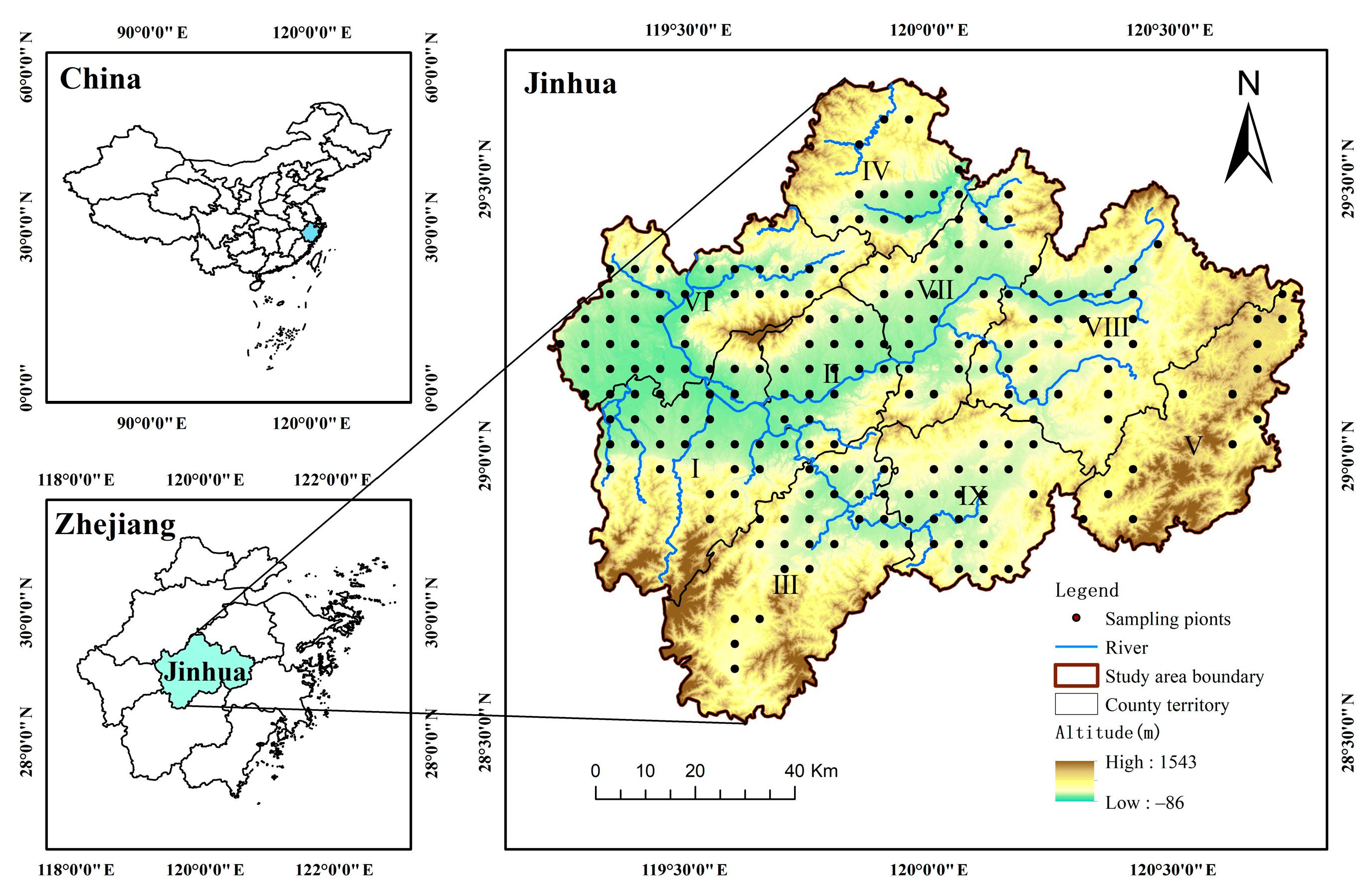
2.1. Study Area
2.2. Soil Sampling and Laboratory Analyses
2.3. Data Processing and Statistical Analysis
2.3.1. Ordinary Kriging
2.3.2. Indicator Kriging
2.3.3. Hot Spot Analysis
2.3.4. Influence Index of Comprehensive Quality of Soil (IICQs)
2.3.5. Statistical Analysis
3. Results and Discussion
3.1. Concentration Characteristics of Soil HMs
3.2. Spatial Distribution Characteristics of Soil HM Concentration
3.3. Environmental Risk of Soil HM Concentration
3.4. Safe Utilization Zoning of Soil HMs in Farmland
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Karim, Z.; Qureshi, B.A.; Mumtaz, M.; Qureshi, S. Heavy metal concentration in urban soils as an indicator of anthropogenic and natural influences on landscape of Karachi—A multivariate spatio-temporal analysis. Ecol. Indic. 2014, 42, 20–31. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xie, X.F.; Pu, L.J.; Zhu, M.; Meadows, M.; Sun, L.C.; Wu, T.; Bu, X.G.; Xu, Y. Differential effects of various reclamation treat-ments on soil characteristics: An experimental study of newly reclaimed tidal mudflats on the east China coast. Sci. Total Environ. 2021, 768, 144996. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, X.; Gao, P.; Li, D.; Liu, J.; Tang, W. Risk assessment for and microbial community changes in farmland soil contami-nated with heavy metals and metalloids. Ecotoxicol. Environ. Saf. 2019, 185, 109685. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, B.; Zhou, Y.; Jiang, Y.; Ji, W.; Fu, Z.; Shao, S.; Li, S.; Huang, M.; Zhou, L.; Shi, Z. Spatio-temporal variation and source changes of potentially toxic elements in soil on a typical plain of the Yangtze River Delta, China (2002–2012). J. Environ. Manag. 2020, 271, 110943. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nicholson, F.A.; Smith, S.R.; Alloway, B.J.; Carlton-Smith, C.; Chambers, B.J. An inventory of heavy metals inputs to agricultural soils in England and Wales. Sci. Total Environ. 2003, 311, 205–219. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Micó, C.; Recatalá, L.; Peris, M.; Sánchez, J. Assessing heavy metal sources in agricultural soils of an European Mediterrane-an area by multivariate analysis. Chemosphere 2006, 65, 863–872. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Singh, A.; Sharma, R.K.; Agrawal, M.; Marshall, F. Health risk assessment of heavy metals via dietary intake of foodstuffs from the wastewater irrigated site of a dry tropical area of India. Food Chem. Toxicol. 2010, 48, 611–619. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Deng, M.; Zhu, Y.; Shao, K.; Zhang, Q.; Ye, G.; Shen, J. Metals source apportionment in farmland soil and the prediction of metal transfer in the soil-rice-human chain. J. Environ. Manag. 2020, 260, 110092. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Marrugo-Negrete, J.; Pinedo-Hernández, J.; Díez, S. Assessment of heavy metal pollution, spatial distribution and origin in agricultural soils along the Sinú River Basin, Colombia. Environ. Res. 2017, 154, 380–388. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Adimalla, N.; Chen, J.; Qian, H. Spatial characteristics of heavy metal contamination and potential human health risk assessment of urban soils: A case study from an urban region of south India. Ecotoxicol. Environ. Saf. 2020, 194, 110406. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Baltas, H.; Sirin, M.; Gökbayrak, E.; Ozcelik, A.E. A case study on pollution and a human health risk assessment of heavy metals in agricultural soils around Sinop province, Turkey. Chemosphere 2020, 241, 125015. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, F.; Wu, Q.-Y.; Lü, J.-S.; Dong, Y.-L.; Cao, W.-T.; Kang, R.-F.; Cao, J.-F. Spatial Characteristics and Environmental Risk of Heavy Metals in Typical Gold Mining Area of Shandong Province. Huan Jing Ke Xue 2016, 37, 3144–3150. [Google Scholar]
- Adhikary, P.P.; Dash, C.J.; Bej, R.; Chandrasekharan, H. Indicator and probability kriging methods for delineating Cu, Fe, and Mn contamination in groundwater of Najafgarh Block, Delhi, India. Environ. Monit. Assess. 2010, 176, 663–676. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hossain, M.; Patra, P.K. Contamination zoning and health risk assessment of trace elements in groundwater through geostatistical modelling. Ecotoxicol. Environ. Saf. 2020, 189, 110038. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Meirvenne, M.V.; Goovaerts, P. Evaluating the probability of exceeding a site-specific soil cadmium contamination thresh-old. Geoderma 2001, 102, 75–100. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brus, D.J.; De Gruijter, J.J.; Walvoort, D.J.J.; De Vries, F.; Bronswijk, J.J.B.; Römkens, P.F.A.M. Mapping the Probability of Exceeding Critical Thresholds for Cadmium Concentrations in Soils in the Netherlands. J. Environ. Qual. 2002, 31, 1875–1884. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Y.; Ma, Z.; Lv, J.; Bi, J. Identifying sources and hazardous risks of heavy metals in topsoils of rapidly urbanizing East China. J. Geogr. Sci. 2016, 26, 735–749. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Ord, J.K.; Getis, A. Local Spatial Autocorrelation Statistics: Distributional Issues and an Application. Geogr. Anal. 1995, 27, 286–306. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, B.; Shao, S.; Fu, Z.; Li, Y.; Ni, H.; Chen, S.; Zhou, Y.; Jin, B.; Shi, Z. Identifying heavy metal pollution hot spots in soil-rice systems: A case study in South of Yangtze River Delta, China. Sci. Total Environ. 2019, 658, 614–625. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kowalska, J.B.; Mazurek, R.; Gasiorek, M.; Setlak, M.; Zaleski, T.; Waroszewski, J. Soil pollution indices conditioned by me-dieval metallurgical activity—A case study from Krakow (Poland). Environ. Pollut. 2016, 218, 1023–1036. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, Y.; Chen, Q.; Deng, M.; Japenga, J.; Li, T.; Yang, X.; He, Z. Heavy metal pollution and health risk assessment of agricultural soils in a typical peri-urban area in southeast China. J. Environ. Manag. 2018, 207, 159–168. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Doabi, S.A.; Karami, M.; Afyuni, M.; Yeganeh, M. Pollution and health risk assessment of heavy metals in agricultural soil, atmospheric dust and major food crops in Kermanshah province, Iran. Ecotoxicol. Environ. Saf. 2018, 163, 153–164. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Varol, M. Assessment of heavy metal contamination in sediments of the Tigris River (Turkey) using pollution indices and multivariate statistical techniques. J. Hazard. Mater. 2011, 195, 355–364. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mazurek, R.; Kowalska, J.; Gąsiorek, M.; Zadrożny, P.; Józefowska, A.; Zaleski, T.; Kępka, W.; Tymczuk, M.; Orłowska, K. Assessment of heavy metals contamination in surface layers of Roztocze National Park forest soils (SE Poland) by indices of pollution. Chemosphere 2017, 168, 839–850. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alonso, D.L.; Pérez, R.; Okio, C.K.; Castillo, E. Assessment of mining activity on arsenic contamination in surface water and sediments in southwestern area of Santurbán paramo, Colombia. J. Environ. Manag. 2020, 264, 110478. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, S.; Zhao, H.; Wu, K.; Zhang, Z.; Hou, Y.; Chen, T.; Jin, Q. Evaluation of heavy metal distribution characteristics of agricultural soil–rice system in a high geological background area according to the influence index of comprehensive quality (IICQ). Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 2020, 27, 20920–20933. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bartholomew, C.J.; Li, N.; Li, Y.; Dai, W.; Nibagwire, D.; Guo, T. Characteristics and health risk assessment of heavy metals in street dust for children in Jinhua, China. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 2020, 27, 5042–5055. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xie, X.; Wu, T.; Zhu, M.; Jiang, G.; Xu, Y.; Wang, X.; Pu, L. Comparison of random forest and multiple linear regression models for estimation of soil extracellular enzyme activities in agricultural reclaimed coastal saline land. Ecol. Indic. 2021, 120, 106925. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tang, H.; Ke, Z.; Yan, M.; Wang, W.; Nie, H.; Li, B.; Zhang, J.; Xu, X.; Wang, J. Concentrations, Distribution, and Ecological Risk Assessment of Heavy Metals in Daya Bay, China. Water 2018, 10, 780. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Ćujić, M.; Dragović, S.; Đorđević, M.; Dragović, R.; Gajić, B. Reprint of ”Environmental assessment of heavy metals around the largest coal fired power plant in Serbia”. Catena 2017, 148, 26–34. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Goovaerts, P.; Webster, R.; Dubois, J.P. Assessing the risk of soil contamination in the Swiss Jura using indicator geostatistics. Environ. Ecol. Stat. 1997, 4, 31–48. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Parchomenko, A.; Borsky, S. Identifying phosphorus hot spots: A spatial analysis of the phosphorus balance as a result of manure application. J. Environ. Manag. 2018, 214, 137–148. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Getis, A.; Ord, J.K. The Analysis of Spatial Association by Use of Distance Statistics. Geogr. Anal. 2010, 24, 189–206. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Anselin, L. Local Indicators of Spatial Association-LISA. Geogr. Anal. 1995, 27, 93–115. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ministry of Environmental Protection (MEP); Ministry of Land and Resources (MLR). The National Soil Pollution Condition Investigation Report [EB/OL]. 2014. Available online: http://www.gov.cn/foot/site1/20140417/782bcb88840814ba158d01.pdf (accessed on 16 December 2020).
- Slessarev, E.W.; Lin, Y.; Bingham, N.L.; Johnson, J.E.; Dai, Y.; Schimel, J.P.; Chadwick, O.A. Water balance creates a threshold in soil pH at the global scale. Nat. Cell Biol. 2016, 540, 567–569. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, J.H.; Liu, X.J.; Zhang, Y.; Shen, J.L.; Han, W.X.; Zhang, W.F.; Christie, P.; Goulding, K.W.T.; Vitousek, P.M.; Zhang, F. Significant Acidification in Major Chinese Croplands. Science 2010, 327, 1008–1010. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Ministry of Ecology and Environment (MEE). Soil Environmental Quality Risk Control Standard for Soil Contamination of Agricultural Land (GB15618–2018). 2018. Available online: http://www.mee.gov.cn/ywgz/fgbz/bz/bzwb/trhj/201807/W020190626595212456114.pdf (accessed on 16 December 2020).
- Sun, C.; Liu, J.; Wang, Y.; Sun, L.; Yu, H. Multivariate and geostatistical analyses of the spatial distribution and sources of heavy metals in agricultural soil in Dehui, Northeast China. Chemosphere 2013, 92, 517–523. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, S.; Cai, L.-M.; Wen, H.-H.; Luo, J.; Wang, Q.-S.; Liu, X. Spatial distribution and source apportionment of heavy metals in soil from a typical county-level city of Guangdong Province, China. Sci. Total Environ. 2019, 655, 92–101. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Q.H.; Dong, Y.X.; Zheng, W.; Zhou, G.H. Soil geochemical baseline values and environmental background values in Zhejiang, China. Geol. Bull. China 2007, 26, 590–597. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, Y.Y.; Ma, J.; Wei, H.Y.; Shi, T.R. Heavy metals in typical farmland soils of Zhejiang Province: Levels, sources and ecological risks. Ecol. Environ. Sci. 2019, 28, 1233–1241. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar]
- Heuvelink, G.; Webster, R. Modelling soil variation: Past, present, and future. Geoderma 2001, 100, 269–301. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, P.; Mao, R.; Shao, H.; Gao, Y. An investigation on the distribution of eight hazardous heavy metals in the suburban farmland of China. J. Hazard. Mater. 2009, 167, 1246–1251. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- El Sebai, T.; Lagacherie, B.; Soulas, G.; Martin-Laurent, F. Spatial variability of isoproturon mineralizing activity within an agricultural field: Geostatistical analysis of simple physicochemical and microbiological soil parameters. Environ. Pollut. 2007, 145, 680–690. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kelepertzis, E. Accumulation of heavy metals in agricultural soils of Mediterranean: Insights from Argolida basin, Peloponnese, Greece. Geoderma 2014, 221–222, 82–90. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiao, W.; Chen, W.; Chang, A.C.; Page, A.L. Environmental risks of trace elements associated with long-term phosphate fertilizers applications: A review. Environ. Pollut. 2012, 168, 44–53. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Biasioli, M.; Barberis, R.; Ajmone-Marsan, F. The influence of a large city on some soil properties and metals concentration. Sci. Total Environ. 2006, 356, 154–164. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Luo, L.; Ma, Y.; Zhang, S.; Wei, D.; Zhu, Y.-G. An inventory of trace element inputs to agricultural soils in China. J. Environ. Manag. 2009, 90, 2524–2530. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yan, X.; Zhao, W.; Yang, X.; Liu, C.; Zhou, Y. Input–output balance of cadmium in typical agriculture soils with historical sewage irrigation in China. J. Environ. Manag. 2020, 276, 111298. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, S.J.; Wang, X.D.; Guo, G.L.; Yan, Z.G. Status and environmental management of soil mercury pollution in China: A review. J. Environ. Manag. 2021, 277, 111442. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Facchinelli, A.; Sacchi, E.; Mallen, L. Multivariate statistical and GIS-based approach to identify heavy metal sources in soils. Environ. Pollut. 2001, 114, 313–324. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wei, B.; Yang, L. A review of heavy metal contaminations in urban soils, urban road dusts and agricultural soils from China. Microchem. J. 2010, 94, 99–107. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huo, X.-N.; Zhang, W.-W.; Sun, D.-F.; Li, H.; Zhou, L.-D.; Li, B.-G. Spatial Pattern Analysis of Heavy Metals in Beijing Agricultural Soils Based on Spatial Autocorrelation Statistics. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2011, 8, 2074–2089. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Lin, Y.-P.; Chu, H.-J.; Wu, C.-F.; Chang, T.-K.; Chen, C.-Y. Hotspot Analysis of Spatial Environmental Pollutants Using Kernel Density Estimation and Geostatistical Techniques. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2010, 8, 75–88. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yu, T.; Hou, W.L.; Hou, Q.Y.; Ma, W.J.; Xia, X.Q.; Li, Y.T.; Yan, B.Z.; Yang, Z.F. Safe utilization and zoning on natural selenium-rich land resources: A case study of the typical area in Enshi County, China. Environ. Geochem. Health 2020, 42, 2803–2818. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wei, H.B.; Luo, M.J.; Zheng, S.; Wu, K.N. Risk zoning and governance of heavy metal pollution in agricultural land. Chin. J. Agric. Resour. Reg. Plan. 2018, 39, 82–87. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar]



| Division Basis | Soil Pollution Level | Safe Utilization Zoning |
|---|---|---|
| IICQs ≤ 1 | Clean | Safe utilization zone |
| 1 < IICQs ≤ 2 | Slightly exceeded | Basic safe utilization zone |
| 2 < IICQs ≤ 3 | Moderately exceeded | Low-risk monitoring zone |
| 3 < IICQs ≤ 5 | Highly exceeded | Medium-risk warning zone |
| IICQs > 5 | Severely exceeded | High-risk restricted zone |
| As | Cd | Cr | Cu | Hg | Pb | Ni | Zn | pH | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Mean (mg kg−1) | 6.37 | 0.18 | 36.73 | 18.60 | 0.11 | 32.48 | 11.95 | 76.05 | 5.34 |
| SD | 3.67 | 0.10 | 26.49 | 10.47 | 0.16 | 8.31 | 11.78 | 26.15 | 0.78 |
| CV (%) | 57.56 | 53.07 | 72.12 | 56.29 | 152.24 | 25.59 | 98.55 | 34.39 | 15.00 |
| Kurtosis | 5.44 | 5.20 | 20.92 | 16.21 | 125.97 | 1.80 | 57.56 | 7.03 | 2.71 |
| Skewness | 1.89 | 1.73 | 3.84 | 2.94 | 10.23 | 1.00 | 6.54 | 2.05 | 1.47 |
| JBV (mg kg−1) | 6.49 | 0.19 | 39.07 | 18.08 | 0.10 | 35.12 | 12.45 | 72.13 | — |
| ZBV (mg kg−1) | 9.20 | 0.07 | 52.90 | 17.60 | 0.09 | 23.70 | 24.60 | 70.60 | — |
| RSV (mg kg−1) | 30.00 | 0.30 | 150.00 | 50.00 | 0.50 | 70.00 | 60.00 | 200.00 | — |
| Element | Model | C0 | C0 + C | C/(C0 + C) | Range (m) | R2 | RSS |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| As | exponential | 0.122 | 0.289 | 0.576 | 38,700 | 0.860 | 1.88 × 10−3 |
| Cd | exponential | 0.037 | 0.294 | 0.874 | 8900 | 0.539 | 5.82 × 10−4 |
| Cr | exponential | 0.147 | 0.296 | 0.502 | 32,400 | 0.623 | 3.40 × 10−3 |
| Cu | exponential | 0.123 | 0.252 | 0.502 | 31,200 | 0.580 | 3.13 × 10−3 |
| Hg | exponential | 0.034 | 0.422 | 0.919 | 8400 | 0.528 | 1.53 × 10−3 |
| Ni | exponential | 0.191 | 0.384 | 0.501 | 77,100 | 0.819 | 5.15 × 10−3 |
| Pb | exponential | 0.005 | 0.064 | 0.926 | 12,600 | 0.660 | 7.63 × 10−5 |
| Zn | exponential | 0.009 | 0.091 | 0.904 | 11,700 | 0.803 | 7.05 × 10−5 |
| Grade | Area (km2) | Proportion (%) |
|---|---|---|
| Safe utilization zone | 2144.47 | 89.35 |
| Basic safe utilization zone | 206.08 | 8.58 |
| Low-risk monitoring zone | 33.74 | 1.41 |
| Medium-risk warning zone | 14.59 | 0.61 |
| High-risk restricted zone | 1.12 | 0.05 |
| Total | 2400.00 | 100 |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2021 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Guo, W.; Wu, T.; Jiang, G.; Pu, L.; Zhang, J.; Xu, F.; Yu, H.; Xie, X. Spatial Distribution, Environmental Risk and Safe Utilization Zoning of Soil Heavy Metals in Farmland, Subtropical China. Land 2021, 10, 569. https://doi.org/10.3390/land10060569
Guo W, Wu T, Jiang G, Pu L, Zhang J, Xu F, Yu H, Xie X. Spatial Distribution, Environmental Risk and Safe Utilization Zoning of Soil Heavy Metals in Farmland, Subtropical China. Land. 2021; 10(6):569. https://doi.org/10.3390/land10060569
Chicago/Turabian StyleGuo, Weiwei, Tao Wu, Guojun Jiang, Lijie Pu, Jianzhen Zhang, Fei Xu, Hongmei Yu, and Xuefeng Xie. 2021. "Spatial Distribution, Environmental Risk and Safe Utilization Zoning of Soil Heavy Metals in Farmland, Subtropical China" Land 10, no. 6: 569. https://doi.org/10.3390/land10060569
APA StyleGuo, W., Wu, T., Jiang, G., Pu, L., Zhang, J., Xu, F., Yu, H., & Xie, X. (2021). Spatial Distribution, Environmental Risk and Safe Utilization Zoning of Soil Heavy Metals in Farmland, Subtropical China. Land, 10(6), 569. https://doi.org/10.3390/land10060569






