Toward a Dualistic Growth? Population Increase and Land-Use Change in Rome, Italy
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
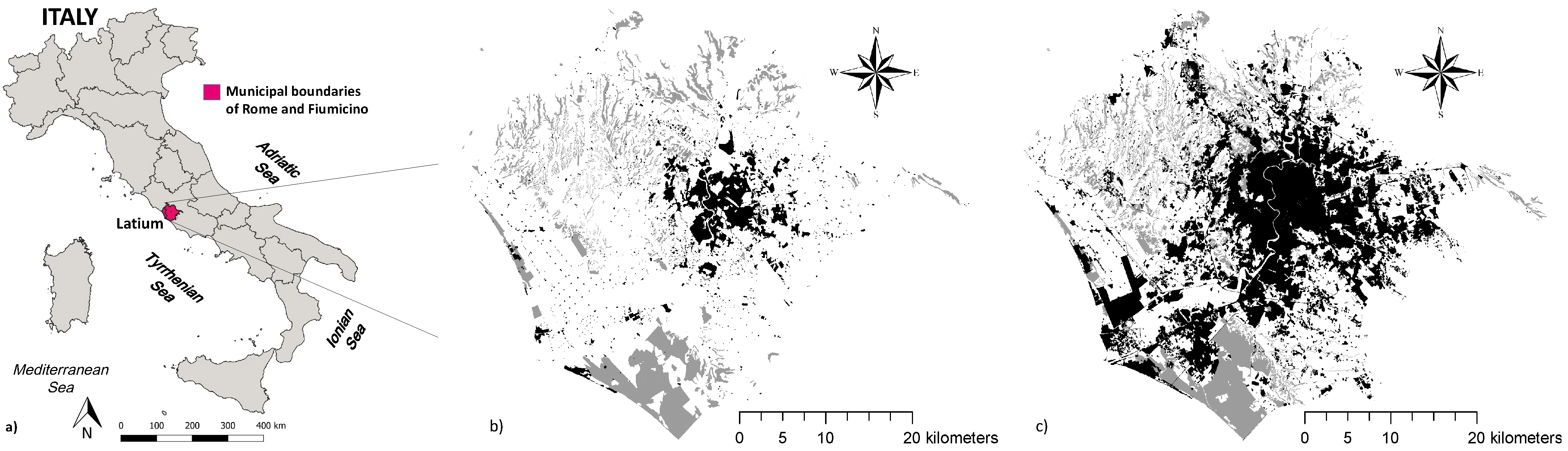
2.1. Study Area
2.2. Land-Use Maps
2.3. Land-Use Indicators
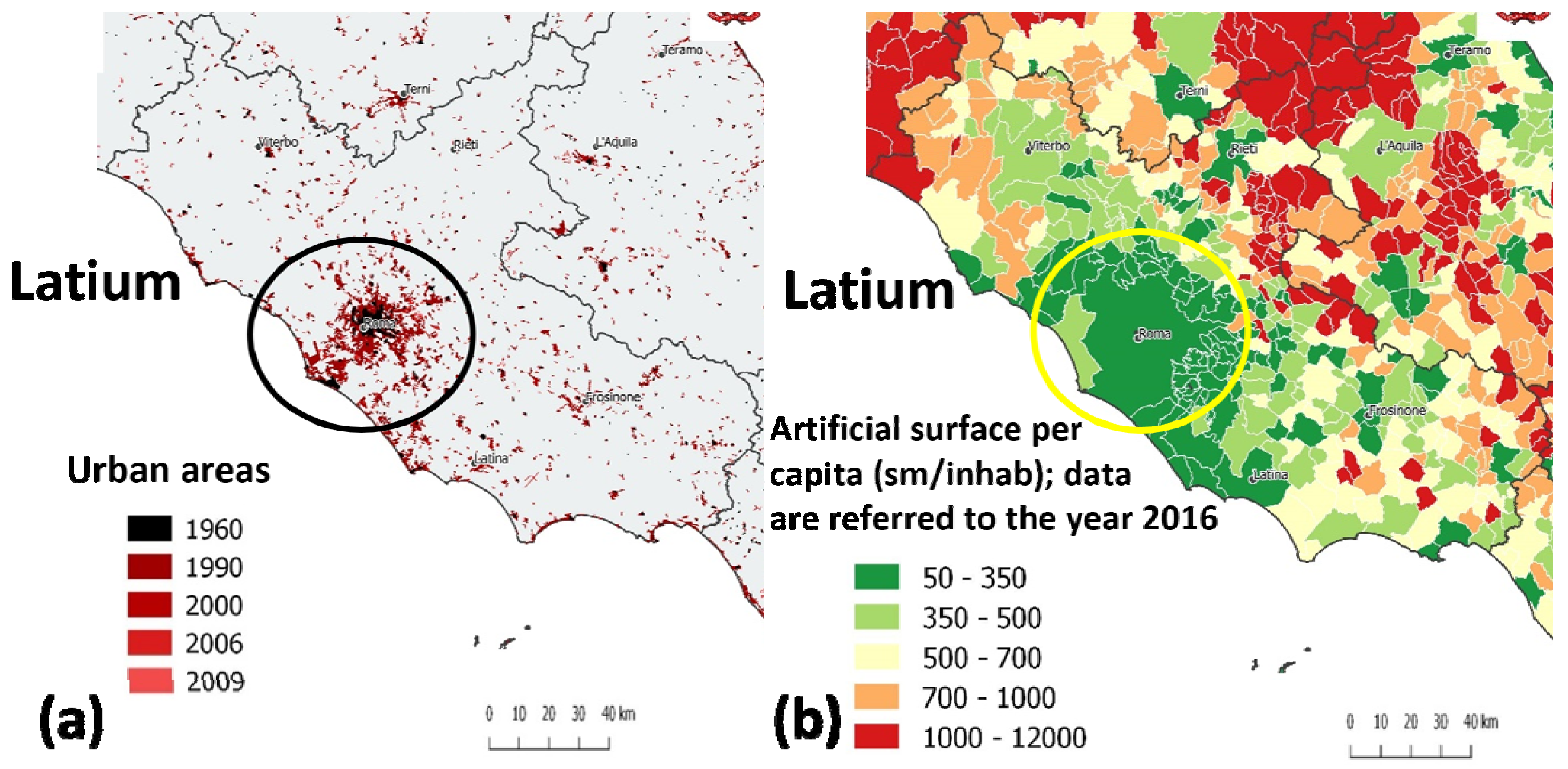
3. Results
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Bruegmann, R. Sprawl: A Compact History; University of Chicago Press: Chicago, IL, USA, 2005. [Google Scholar]
- Couch, C.; Petschel-Held, G.; Leontidou, L. (Eds.) Urban Sprawl in Europe: Landscape, Land-Use Change and Policy, 1st ed.; Wiley-Blackwell: Oxford, UK; Malden, MA, USA, 2007; ISBN 978-1-4051-3917-5. [Google Scholar]
- Brouwer, F.M.; Thomas, A.J.; Chadwick, M.J. Land Use Changes in Europe-Processes of Change, Environmental Transformations and Future Patterns; luwer AcademicPublishers: Dordrecht, The Netherlands, 1991. [Google Scholar]
- Lambin, E.F.; Turner, B.L.; Geist, H.J.; Agbola, S.B.; Angelsen, A.; Bruce, J.W.; Oliver, T.C.; Rodolf, D.; Gunther, F.; Carl, F.; et al. The causes of land-use and land-cover change: Moving beyond the myths. Glob. Environ. Chang. 2001, 11, 261–269. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pelorosso, R.; Leone, A.; Boccia, L. Land cover and land use change in the Italian central Apennines: A comparison of assessment methods. Appl. Geogr. 2009, 29, 35–48. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Simoniello, T.; Coluzzi, R.; Imbrenda, V.; Lanfredi, M. Land cover changes and forest landscape evolution (1985–2009) in a typical Mediterranean agroforestry system (high Agri Valley). Nat. Hazards Earth Syst. Sci. 2015, 15, 1201–1214. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Imbrenda, V.; Coluzzi, R.; Lanfredi, M.; Loperte, A.; Satriani, A.; Simoniello, T. Analysis of landscape evolution in a vulnerable coastal area under natural and human pressure. Geomat. Nat. Hazards Risk 2018, 9, 1249–1279. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Coluzzi, R.; D’Emilio, M.; Imbrenda, V.; Giorgio, G.A.; Lanfredi, M.; Macchiato, M.; Simoniello, T.; Telesca, V. Investigating climate variability and long-term vegetation activity across heterogeneous Basilicata agroecosystems. Geomat. Nat. Hazards Risk 2019, 10, 168–180. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Quaranta, G.; Salvia, R.; Salvati, L.; Paola, V.D.; Coluzzi, R.; Imbrenda, V.; Simoniello, T. Long-Term Impacts of Grazing Management on Land Degradation in a Rural Community of Southern Italy: Depopulation Matters. Land Degrad. Dev. 2020, 31, 1–16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Salvati, L.; Zambon, I.; Chelli, F.M.; Serra, P. Do Spatial Patterns of Urbanization and Land Consumption Reflect Different Socioeconomic Contexts in Europe? Sci. Total Environ. 2018, 625, 722–730. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- O’Sullivan, A. Urban Economics; McGraw-Hill/Irwin: New York, NY, USA, 2002. [Google Scholar]
- Oueslati, W.; Alvanides, S.; Garrod, G. Determinants of Urban Sprawl in European Cities. Urban Stud. 2015, 52, 1594–1614. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Capello, R.; Nijkamp, P. Urban Dynamics and Growth: Advances in Urban. Economics: 266; North Holland: Amsterdam, Holland, 2004; ISBN 978-0-444-51481-3. [Google Scholar]
- Coulson, N.E. Really Useful Tests of the Monocentric Model. Land Econ. 1991, 67, 299–307. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ahlfeldt, G. If Alonso Was Right: Modeling Accessibility and Explaining the Residential Land Gradient. J. Reg. Sci. 2011, 51, 318–338. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kazemzadeh-Zow, A.; Shahraki, S.Z.; Salvati, L.; Samani, N.N. A Spatial Zoning Approach to Calibrate and Validate Urban Growth Models. Int. J. Geogr. Inf. Sci. 2017, 31, 763–782. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Salvati, L.; Ciommi, M.T.; Serra, P.; Chelli, F.M. Exploring the Spatial Structure of Housing Prices Under Economic Expansion and Stagnation: The Role of Socio-Demographic Factors in Metropolitan Rome, Italy. Land Use Policy 2019, 81, 143–152. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schwarz, N. Urban Form Revisited—Selecting Indicators for Characterising European Cities. Landsc. Urban Plan. 2010, 96, 29–47. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kasanko, M.; Barredo, J.I.; Lavalle, C.; McCormick, N.; Demicheli, L.; Sagris, V.; Brezger, A. Are European Cities Becoming Dispersed? A Comparative Analysis of 15 European Urban Areas. Landsc. Urban Plan. 2006, 77, 111–130. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chelleri, L.; Schuetze, T.; Salvati, L. Integrating Resilience with Urban Sustainability in Neglected Neighborhoods: Challenges and Opportunities of Transitioning to Decentralized Water Management in Mexico City. Habitat Int. 2015, 48, 122–130. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Salvati, L.; Ferrara, A.; Chelli, F. Long-Term Growth and Metropolitan Spatial Structures: An Analysis of Factors Influencing Urban Patch Size under Different Economic Cycles. Geogr. Tidsskr./Dan. J. Geogr. 2018, 118, 56–71. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Imbrenda, V.; Quaranta, G.; Salvia, R.; Egidi, G.; Salvati, L.; ProkopovÃ, M.; Coluzzi, R.; Lanfredi, M. Land degradation and metropolitan expansion in a peri-urban environment. Geomat. Nat. Hazards Risk 2021, 12, 1797–1818. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Di Feliciantonio, C.; Salvati, L. ‘Southern’ Alternatives of Urban Diffusion: Investigating Settlement Characteristics and Socio-economic Patterns in Three Mediterranean Regions. Tijdschr. voor Econ. en Soc. Geogr. 2015, 106, 453–470. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- De Rosa, S.; Salvati, L. Beyond a ‘Side Street Story’? Naples from Spontaneous Centrality to Entropic Polycentricism, towards a ‘Crisis City’. Cities 2016, 51, 74–83. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cuadrado-Ciuraneta, S.; Durà-Guimerà, A.; Salvati, L. Not Only Tourism: Unravelling Suburbanization, Second-Home Expansion and “Rural” Sprawl in Catalonia, Spain. Urban Geogr. 2017, 38, 66–89. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cecchini, M.; Zambon, I.; Pontrandolfi, A.; Turco, R.; Colantoni, A.; Mavrakis, A.; Salvati, L. Urban Sprawl and the ‘Olive’ Landscape: Sustainable Land Management for ‘Crisis’ Cities. GeoJournal 2019, 84, 237–255. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schneider, A.; Woodcock, C.E. Compact, Dispersed, Fragmented, Extensive? A Comparison of Urban Growth in Twenty-Five Global Cities Using Remotely Sensed Data, Pattern Metrics and Census Information. Urban Stud. 2008, 45, 659–692. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Burger, M.; Meijers, E. Form Follows Function? Linking Morphological and Functional Polycentricity. Urban Stud. 2012, 49, 1127–1149. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Salvati, L. Agro-Forest Landscape and the ‘Fringe’ City: A Multivariate Assessment of Land-Use Changes in a Sprawling Region and Implications for Planning. Sci. Total Environ. 2014, 490, 715–723. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Veneri, P. The Identification of Sub-Centres in Two Italian Metropolitan Areas: A Functional Approach. Cities 2013, 31, 177–185. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Turok, I.; Mykhnenko, V. The Trajectories of European cities, 1960–2005. Cities 2007, 24, 165–182. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pili, S.; Grigoriadis, E.; Carlucci, M.; Clemente, M.; Salvati, L. Towards Sustainable Growth? A Multi-Criteria Assessment of (Changing) Urban Forms. Ecol. Indic. 2017, 76, 71–80. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Di Feliciantonio, C.; Salvati, L.; Sarantakou, E.; Rontos, K. Class Diversification, Economic Growth and Urban Sprawl: Evidences from a Pre-Crisis European city. Qual. Quant. 2018, 52, 1501–1522. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Salvati, L. The Dark Side of the Crisis: Disparities in Per Capita Income (2000–12) and the Urban–Rural Gradient in Greece. Tijdschr. Econ. Soc. Geogr. 2016, 107, 628–641. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Samat, N.; Hasni, R.; Elhadary, Y. Modelling Land Use Changes at the Peri-Urban Areas Using Geographic Information Systems and Cellular Automata Model. J. Sustain. Dev. 2011, 4, 72. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chorianopoulos, I.; Pagonis, T.; Koukoulas, S.; Drymoniti, S. Planning, Competitiveness and Sprawl in the Mediterranean City: The Case of Athens. Cities 2010, 27, 249–259. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Terzi, F.; Bolen, F. Urban Sprawl Measurement of Istanbul. Eur. Plan. Stud. 2009, 17, 1559–1570. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alphan, H. Land-Use Change and Urbanization of Adana, Turkey. Land Degrad. Dev. 2003, 14, 575–586. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Matteucci, S.D.; Morello, J. Environmental Consequences of Exurban Expansion in an Agricultural Area: The Case of the Argentinian Pampas Ecoregion. Urban Ecosyst. 2009, 12, 287–310. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kane, K.; Connors, J.P.; Galletti, C.S. Beyond Fragmentation at the Fringe: A Path-Dependent, High-Resolution Analysis of Urban Land Cover in Phoenix, Arizona. Appl. Geogr. 2014, 52, 123–134. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Anselm, N.; Brokamp, G.; Schütt, B. Assessment of Land Cover Change in Peri-Urban High Andean Environments South of Bogotá, Colombia. Land 2018, 7, 75. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- York, A.M.; Shrestha, M.; Boone, C.G.; Zhang, S.; Harrington, J.A.; Prebyl, T.J.; Swann, A.; Agar, M.; Antolin, M.F.; Nolen, B.; et al. Land Fragmentation under Rapid Urbanization: A cross-site analysis of southwestern cities. Urban Ecosyst. 2011, 14, 429–455. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Çakir, G.; Ün, C.; Baskent, E.Z.; Köse, S.; Sivrikaya, F.; Keleş, S. Evaluating Urbanization, Fragmentation and Land Use/Land Cover Change Pattern in Istanbul City, Turkey from 1971 TO 2002. Land Degrad. Dev. 2008, 19, 663–675. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Catalán, B.; Saurí, D.; Serra, P. Urban Sprawl in the Mediterranean? Patterns of Growth and Change in the Barcelona Metropolitan Region 1993–2000. Landsc. Urban. Plan. 2008, 85, 174–184. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Salvati, L.; Serra, P. Estimating Rapidity of Change in Complex Urban Systems: A Multidimensional, Local-Scale Approach. Geogr. Anal. 2016, 48, 132–156. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zambon, I.; Serra, P.; Sauri, D.; Carlucci, M.; Salvati, L. Beyond the ‘Mediterranean City’: Socioeconomic Disparities and Urban Sprawl in Three Southern European Cities. Geogr. Ann. Ser. B Hum. Geogr. 2017, 99, 319–337. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jarah, S.H.A.; Zhou, B.; Abdullah, R.J.; Lu, Y.; Yu, W. Urbanization and Urban Sprawl Issues in City Structure: A Case of the Sulaymaniah Iraqi Kurdistan Region. Sustainability 2019, 11, 485. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zambon, I.; Benedetti, A.; Ferrara, C.; Salvati, L. Soil Matters? A Multivariate Analysis of Socioeconomic Constraints to Urban Expansion in Mediterranean Europe. Ecol. Econ. 2018, 146, 173–183. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hassan, M.M. Monitoring Land Use/Land Cover Change, Urban Growth Dynamics and Landscape Pattern Analysis in Five Fastest Urbanized Cities in Bangladesh. Remote Sens. Appl. Soc. Environ. 2017, 7, 69–83. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Serra, P.; Vera, A.; Tulla, A.F.; Salvati, L. Beyond Urban–Rural Dichotomy: Exploring Socioeconomic and Land-Use Processes of Change in Spain (1991–2011). Appl. Geogr. 2014, 55, 71–81. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Attorre, F.; Bruno, M.; Francesconi, F.; Valenti, R.; Bruno, F. Landscape Changes of Rome through Tree-Lined Roads. Landsc. Urban Plan. 2000, 49, 115–128. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tsai, Y.-H. Quantifying Urban Form: Compactness versus “Sprawl”. Urban Stud. 2005, 42, 141–161. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Carlucci, M.; Grigoriadis, E.; Rontos, K.; Salvati, L. Revisiting a Hegemonic Concept: Long-Term ‘Mediterranean Urbanization’ in between City Re-Polarization and Metropolitan Decline. Appl. Spat. Anal. 2017, 10, 347–362. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gavalas, V.S.; Rontos, K.; Salvati, L. Who Becomes an Unwed Mother in Greece? Sociodemographic and Geographical Aspects of an Emerging Phenomenon. Popul. Space Place 2014, 20, 250–263. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Weber, C.; Petropoulou, C.; Hirsch, J. Urban Development in the Athens Metropolitan Area Using Remote Sensing Data with Supervised Analysis and GIS. Int. J. Remote Sens. 2005, 26, 785–796. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, Z.; Zhang, J.; Yang, G.; Schlaberg, J. Reverse Thinking: A New Method from the Graph Perspective for Evaluating and Mitigating Regional Surface Heat Islands. Remote Sens. 2021, 13, 1127. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Frenkel, A.; Ashkenazi, M. Measuring Urban Sprawl: How Can We Deal With It? Environ. Plann. B Plann. Des. 2008, 35, 56–79. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ioannidis, C.; Psaltis, C.; Potsiou, C. Towards a Strategy for Control of Suburban Informal Buildings Through Automatic Change Detection. Comput. Environ. Urban Syst. 2009, 33, 64–74. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lanfredi, M.; Coppola, R.; Simoniello, T.; Coluzzi, R.; D’Emilio, M.; Imbrenda, V.; Macchiato, M. Early Identification of Land Degradation Hotspots in Complex Bio-Geographic Regions. Remote. Sens. 2015, 7, 8154–8179. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Longhi, C.; Musolesi, A. European Cities in the Process of Economic Integration: Towards Structural Convergence. Ann. Reg. Sci. 2007, 41, 333–351. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Romano, B.; Zullo, F.; Fiorini, L.; Marucci, A.; Ciabò, S. Land Transformation of Italy Due to Half a Century of Urbanization. Land Use Policy 2017, 67, 387–400. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fiorini, L.; Zullo, F.; Marucci, A.; Romano, B. Land Take and Landscape Loss: Effect of Uncontrolled Urbanization in Southern italy. J. Urban Manag. 2019, 8, 42–56. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Salvati, L. Agricultural Land-Use Changes and Soil Quality: Evaluating Long-Term Trends in a Rural Mediterranean Region. Int. Sch. Res. Not. 2013, 2013, 18240. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Salvati, L.; De Zuliani, E.; Sabbi, A.; Cancellieri, L.; Tufano, M.; Caneva, G.; Savo, V. Land-cover changes and sustainable development in a rural cultural landscape of central Italy: Classical trends and counter-intuitive results. Int. J. Sustain. Dev. World Ecol. 2017, 24, 27–36. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Marchetti, M.; Marino, D.; De Toni, A.; Giaccio, V.; Giannelli, A.; Mastronardi, L. Soil Consumption, Territorial Dynamics and Ecosystem Services (in Italian); ISPRA (Italian National Institute for Environmental Protection and Research, see Reference), Annual Report 2017. Available online: https://www.isprambiente.gov.it/en/publications/reports/soil-consumption-in-italy-1 (accessed on 16 July 2021).
- Union Nations. Transforming Our World: The 2030 Agenda for Sustainable Development. A/RES/70/1.2015. Available online: http://www.un.org/en/ga/search/view_doc.asp?symbol=A/RES/70/1 (accessed on 16 July 2021).
- Antrop, M. Landscape Change and the Urbanization Process in Europe. Landsc. Urban Plan. 2004, 67, 9–26. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Anarfi, K.; Hill, R.A.; Shiel, C. Highlighting the Sustainability Implications of Urbanisation: A Comparative Analysis of Two Urban Areas in Ghana. Land 2020, 9, 300. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- OECD. Trends in Urbanisation and Urban Policies in OECD Countries: What Lessons for China? Organisation for Economic Co-Operation and Development and China Development Research Foundation. 2010. Available online: http://www.oecd.org/dataoecd/2/18/45159707.pdf (accessed on 16 July 2021).
- Robert, S.; Fox, D.; Boulay, G.; Grandclément, A.; Garrido, M.; Pasqualini, V.; Prévost, A.; Schleyer-Lindenmann, A.; Trémélo, M.-L. A Framework to Analyse Urban Sprawl in the French Mediterranean Coastal Zone. Reg. Environ. Chang. 2019, 19, 559–572. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pozoukidou, G.; Ntriankos, I. Measuring and Assessing Urban Sprawl: A Proposed Indicator System for the City of Thessaloniki, Greece. Remote Sens. Appl. Soc. Environ. 2017, 8, 30–40. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Herrschel, T. City Regions, Polycentricity and the Construction of Peripheralities Through Governance. Urban Res. Pract. 2009, 2, 240–250. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Brezzi, M.; Veneri, P. Assessing Polycentric Urban Systems in the OECD: Country, Regional and Metropolitan Perspectives. Eur. Plan. Stud. 2015, 23, 1128–1145. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Paül, V.; Tonts, M. Containing Urban Sprawl: Trends in Land Use and Spatial Planning in the Metropolitan Region of Barcelona. J. Environ. Plan. Manag. 2005, 48, 7–35. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Volgmann, K.; Münter, A. Understanding Metropolitan Growth in German Polycentric Urban Regions. Reg. Stud. 2020, 1–14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lagarias, A.; Sayas, J. Urban Sprawl in the Mediterranean: Evidence from coastal medium-sized cities. Reg. Sci. Inq. 2018, 10, 15–32. [Google Scholar]
- Guastella, G.; Oueslati, W.; Pareglio, S. Patterns of Urban Spatial Expansion in European Cities. Sustainability 2019, 11, 2247. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fertner, C.; Jørgensen, G.; Nielsen, T.A.S.; Nilsson, K.S.B. Urban Sprawl and Growth Management-Drivers, Impacts and Responses in Selected European and us Cities. Future Cities Environ. 2016, 2, 1–13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Meijers, E. Measuring polycentricity and its promises. Eur. Plan. Stud. 2008, 16, 1313–1323. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- European Environment Agency Urban Sprawl in Europe–The Ignored Challenge. Copenhagen, Denmark. 2006. Available online: https://www.eea.europa.eu/publications/eea_report_2006_10/eea_report_10_2006.pdf/view (accessed on 16 July 2021).
- Patacchini, E.; Zenou, Y.; Henderson, J.V.; Epple, D. Urban Sprawl in Europe. Brook. Whart. Pap. Urban Aff. 2009, 125–149. [Google Scholar]


| Class | 1949 | 1974 | 1999 | 2008 | 2016 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Arable Land | 6.277 | 2.777 | 2.505 | 2.342 | 2.199 |
| Crop Mosaic | 0.161 | 0.178 | 0.070 | 0.111 | 0.112 |
| Vineyards | 0.221 | 0.126 | 0.068 | 0.069 | 0.070 |
| Olive Groves | 0.039 | 0.056 | 0.056 | 0.062 | 0.063 |
| Woodlands | 1.018 | 0.551 | 0.634 | 0.631 | 0.631 |
| Pastures | 0.549 | 0.770 | 0.433 | 0.425 | 0.422 |
| Water Bodies | 0.062 | 0.036 | 0.035 | 0.036 | 0.035 |
| Impervious Land | 0.594 | 0.800 | 1.388 | 1.460 | 1.530 |
| Urban Parks | 0.144 | 0.090 | 0.172 | 0.174 | 0.174 |
| Class | 1949–1974 | 1974–1999 | 1999–2008 | 2008–2016 |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Arable Land | −2.23 | −0.39 | −0.72 | −0.77 |
| Crop Mosaic | 0.41 | −2.42 | 6.42 | 0.05 |
| Vineyards | −1.72 | −1.86 | 0.24 | 0.09 |
| Olive Groves | 1.79 | −0.06 | 1.22 | 0.21 |
| Woodlands | −1.84 | 0.61 | −0.05 | −0.01 |
| Pastures | 1.61 | −1.75 | −0.21 | −0.10 |
| Water Bodies | −1.70 | −0.05 | 0.09 | −0.23 |
| Impervious Land | 1.39 | 2.94 | 0.57 | 0.60 |
| Urban Parks | −1.51 | 3.67 | 0.11 | 0.03 |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2021 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Bianchini, L.; Egidi, G.; Alhuseen, A.; Sateriano, A.; Cividino, S.; Clemente, M.; Imbrenda, V. Toward a Dualistic Growth? Population Increase and Land-Use Change in Rome, Italy. Land 2021, 10, 749. https://doi.org/10.3390/land10070749
Bianchini L, Egidi G, Alhuseen A, Sateriano A, Cividino S, Clemente M, Imbrenda V. Toward a Dualistic Growth? Population Increase and Land-Use Change in Rome, Italy. Land. 2021; 10(7):749. https://doi.org/10.3390/land10070749
Chicago/Turabian StyleBianchini, Leonardo, Gianluca Egidi, Ahmed Alhuseen, Adele Sateriano, Sirio Cividino, Matteo Clemente, and Vito Imbrenda. 2021. "Toward a Dualistic Growth? Population Increase and Land-Use Change in Rome, Italy" Land 10, no. 7: 749. https://doi.org/10.3390/land10070749
APA StyleBianchini, L., Egidi, G., Alhuseen, A., Sateriano, A., Cividino, S., Clemente, M., & Imbrenda, V. (2021). Toward a Dualistic Growth? Population Increase and Land-Use Change in Rome, Italy. Land, 10(7), 749. https://doi.org/10.3390/land10070749







