Does Transport Infrastructure Inequality Matter for Economic Growth? Evidence from China
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Literature Review
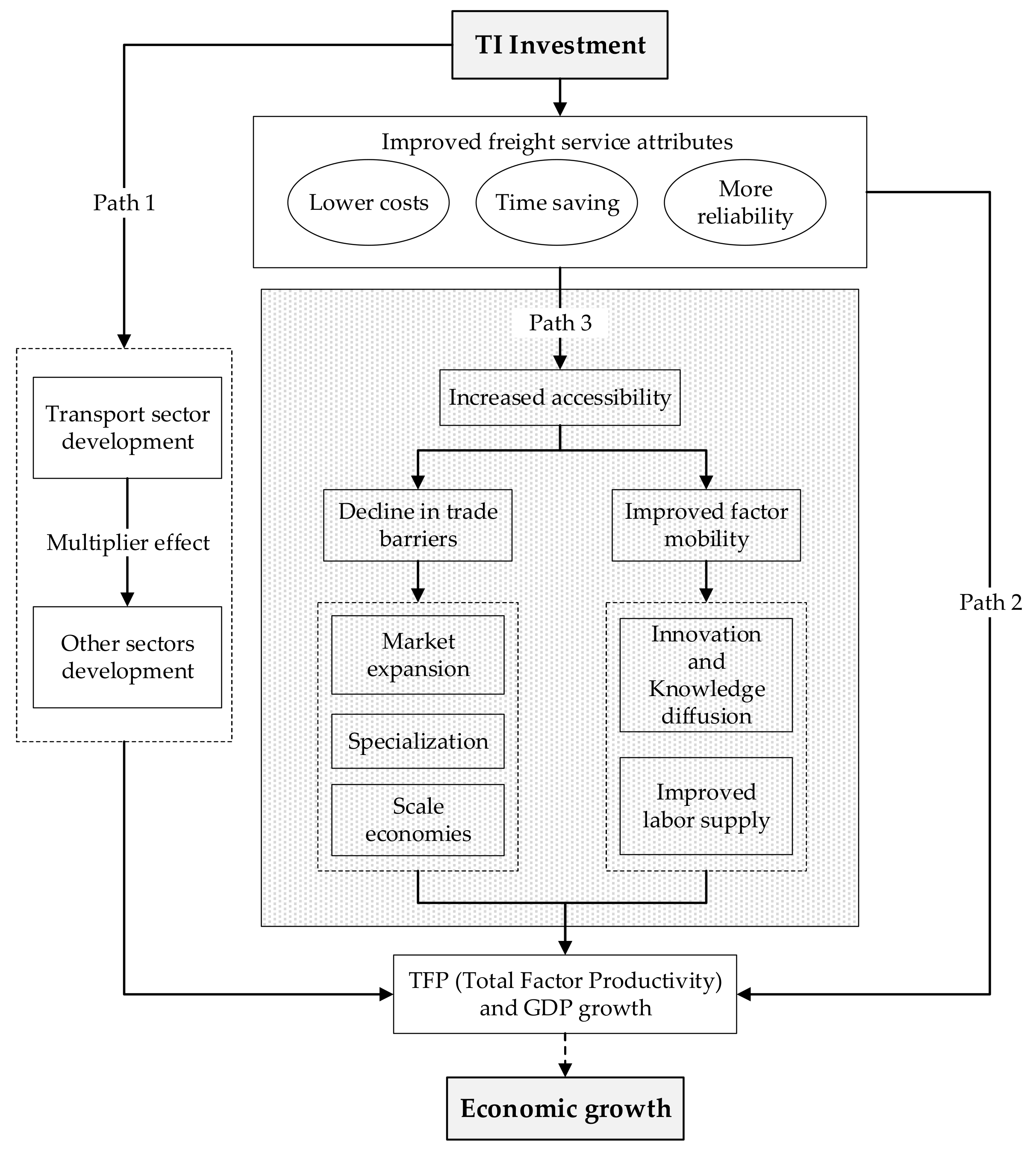
2.1. TI Investment and Economic Growth
2.2. TI Distribution and Economic Growth
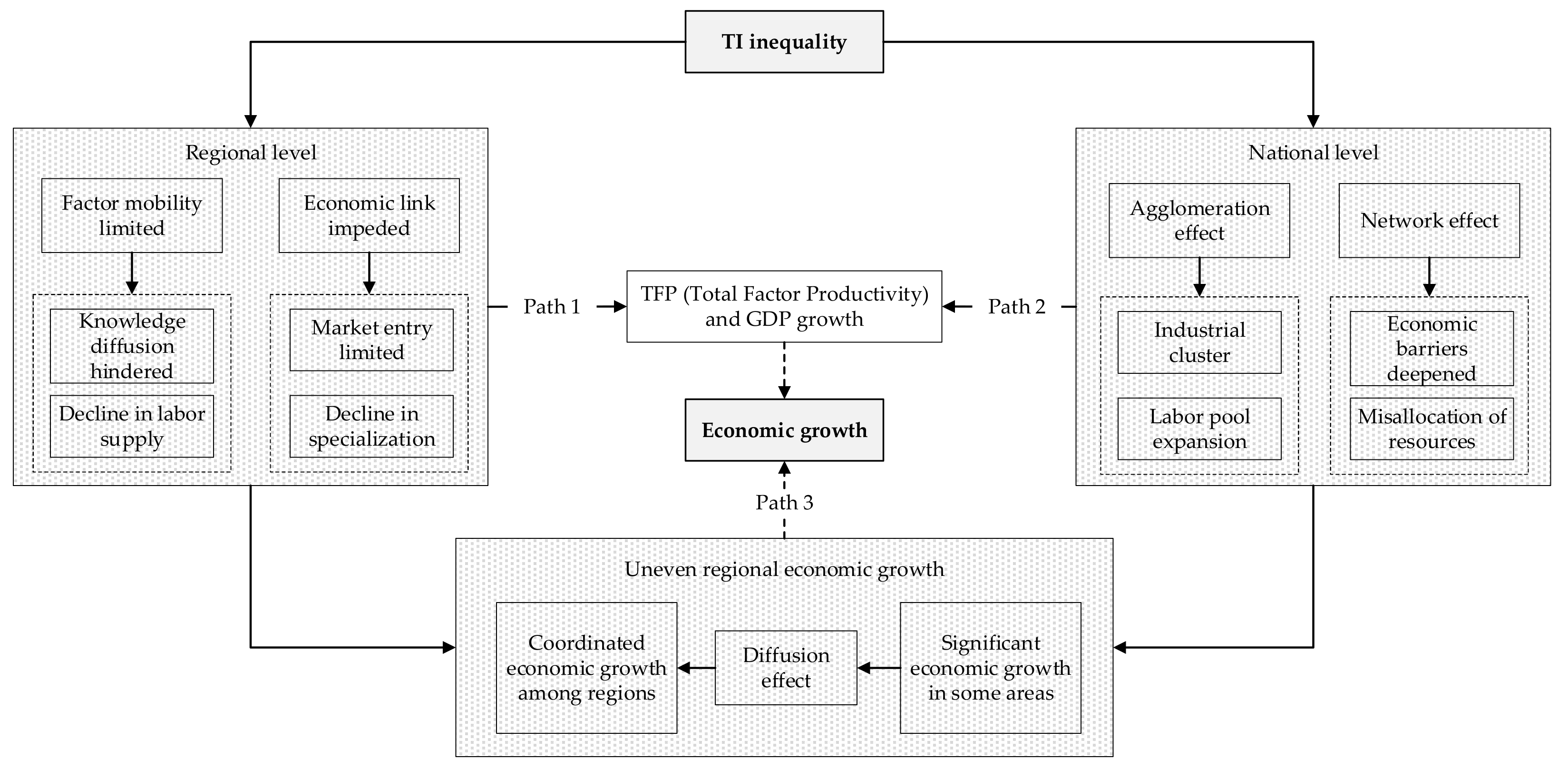
2.3. TI Inequality and Economic Growth
3. Case Study
4. Methodology
4.1. Indicators and Data
4.2. TI Inequality Measures
4.3. Granger Causality Analysis
5. Result of the Data Analysis
5.1. Trends of TI Inequality
5.2. Values of the Granger Causality Test
5.2.1. Panel Unit Root Tests
5.2.2. Panel Cointegration Tests
5.2.3. Granger Tests of Causality
6. Discussion
6.1. Equilibrium Relationships between TI Inequality and Economic Growth
6.2. Causal Linkages between TI Inequality and Economic Growth
6.2.1. At the National Level
6.2.2. At the Regional Level
7. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
Appendix A. National and Regional Gini Coefficients and Their Contribution Rates
| Year | NER | NCR | ECR | SCR | MYL | MYT | SWR | NWR | Inter-Regional | National |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1982 | 0.1163 | 0.1258 | 0.1502 | 0.0479 | 0.2833 | 0.1198 | 0.0945 | 0.0070 | 0.1621 | 0.2352 |
| 1983 | 0.1180 | 0.1251 | 0.1504 | 0.0504 | 0.2820 | 0.1177 | 0.0909 | 0.0104 | 0.1609 | 0.2334 |
| 1984 | 0.1126 | 0.1261 | 0.1557 | 0.0526 | 0.2799 | 0.1147 | 0.0844 | 0.0095 | 0.1592 | 0.2300 |
| 1985 | 0.1007 | 0.1244 | 0.1630 | 0.0579 | 0.2797 | 0.1121 | 0.0909 | 0.0065 | 0.1601 | 0.2271 |
| 1986 | 0.0872 | 0.1259 | 0.1632 | 0.0602 | 0.2832 | 0.1078 | 0.0900 | 0.0066 | 0.1581 | 0.2271 |
| 1987 | 0.0751 | 0.1211 | 0.1625 | 0.0636 | 0.2876 | 0.1063 | 0.0869 | 0.0214 | 0.1603 | 0.2269 |
| 1988 | 0.0712 | 0.1166 | 0.1693 | 0.0278 | 0.2864 | 0.1053 | 0.0893 | 0.0272 | 0.1700 | 0.2314 |
| 1989 | 0.0707 | 0.1194 | 0.1720 | 0.0306 | 0.2849 | 0.0971 | 0.0935 | 0.0242 | 0.1667 | 0.2284 |
| 1990 | 0.0657 | 0.1169 | 0.1844 | 0.0759 | 0.2804 | 0.1007 | 0.0978 | 0.0237 | 0.1589 | 0.2243 |
| 1991 | 0.0643 | 0.1231 | 0.1866 | 0.0779 | 0.2763 | 0.1004 | 0.1009 | 0.0234 | 0.1564 | 0.2222 |
| 1992 | 0.0594 | 0.1265 | 0.1839 | 0.0770 | 0.2731 | 0.1017 | 0.1039 | 0.0242 | 0.1532 | 0.2194 |
| 1993 | 0.0588 | 0.1223 | 0.1968 | 0.0681 | 0.2662 | 0.1029 | 0.1082 | 0.0384 | 0.1525 | 0.2180 |
| 1994 | 0.0534 | 0.1086 | 0.2004 | 0.0337 | 0.2620 | 0.1038 | 0.1120 | 0.0424 | 0.1569 | 0.2193 |
| 1995 | 0.0514 | 0.0896 | 0.2086 | 0.0201 | 0.2550 | 0.0852 | 0.1150 | 0.0566 | 0.1594 | 0.2174 |
| 1996 | 0.0501 | 0.0870 | 0.2079 | 0.0138 | 0.2546 | 0.0814 | 0.1191 | 0.0647 | 0.1570 | 0.2158 |
| 1997 | 0.0513 | 0.0879 | 0.2100 | 0.0121 | 0.2652 | 0.0773 | 0.1271 | 0.0651 | 0.1542 | 0.2171 |
| 1998 | 0.0493 | 0.0754 | 0.2218 | 0.0102 | 0.2882 | 0.0697 | 0.1304 | 0.0674 | 0.1486 | 0.2181 |
| 1999 | 0.0469 | 0.0491 | 0.2278 | 0.0161 | 0.2962 | 0.0679 | 0.1778 | 0.0698 | 0.1483 | 0.2282 |
| 2000 | 0.0456 | 0.0404 | 0.2306 | 0.0334 | 0.2943 | 0.0657 | 0.1833 | 0.0447 | 0.1443 | 0.2246 |
| 2001 | 0.0915 | 0.0506 | 0.0960 | 0.0338 | 0.2884 | 0.0950 | 0.2644 | 0.2434 | 0.1520 | 0.2420 |
| 2002 | 0.0850 | 0.0427 | 0.0999 | 0.0303 | 0.2884 | 0.0678 | 0.2363 | 0.2440 | 0.1500 | 0.2331 |
| 2003 | 0.0827 | 0.0411 | 0.0863 | 0.0315 | 0.2888 | 0.0665 | 0.2313 | 0.2421 | 0.1461 | 0.2297 |
| 2004 | 0.0783 | 0.0496 | 0.0866 | 0.0361 | 0.2895 | 0.0649 | 0.2286 | 0.2446 | 0.1389 | 0.2238 |
| 2005 | 0.0845 | 0.0609 | 0.0941 | 0.0376 | 0.2799 | 0.0583 | 0.2124 | 0.2427 | 0.1394 | 0.2180 |
| 2006 | 0.1069 | 0.0683 | 0.1140 | 0.0480 | 0.1344 | 0.0585 | 0.1550 | 0.1651 | 0.1363 | 0.1842 |
| 2007 | 0.1101 | 0.0761 | 0.1147 | 0.0475 | 0.1472 | 0.0591 | 0.1448 | 0.1524 | 0.1409 | 0.1877 |
| 2008 | 0.1199 | 0.0888 | 0.1148 | 0.0524 | 0.1591 | 0.0612 | 0.1291 | 0.1423 | 0.1461 | 0.1932 |
| 2009 | 0.1220 | 0.0914 | 0.1191 | 0.0541 | 0.1667 | 0.0679 | 0.1297 | 0.1317 | 0.1529 | 0.2016 |
| 2010 | 0.1228 | 0.0974 | 0.1148 | 0.0550 | 0.1699 | 0.0715 | 0.1186 | 0.1242 | 0.1582 | 0.2074 |
| 2011 | 0.1233 | 0.1011 | 0.1174 | 0.0555 | 0.1717 | 0.0747 | 0.1168 | 0.1131 | 0.1631 | 0.2119 |
| 2012 | 0.1252 | 0.1093 | 0.1185 | 0.0556 | 0.1770 | 0.0612 | 0.1168 | 0.1129 | 0.1663 | 0.2150 |
| 2013 | 0.1158 | 0.1088 | 0.1207 | 0.0579 | 0.1821 | 0.0601 | 0.1185 | 0.1079 | 0.1651 | 0.2137 |
| 2014 | 0.1104 | 0.1122 | 0.1204 | 0.0518 | 0.1872 | 0.0677 | 0.1204 | 0.1003 | 0.1666 | 0.2156 |
| 2015 | 0.1028 | 0.1112 | 0.1195 | 0.0552 | 0.1914 | 0.0689 | 0.1207 | 0.0914 | 0.1678 | 0.2177 |
| Year | Intra-Regional | Inter-Regional | Residual Term | Year | Intra-Regional | Inter-Regional | Residual Term |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1982 | 0.0810 | 0.6891 | 0.2299 | 1999 | 0.0892 | 0.6501 | 0.2608 |
| 1983 | 0.0806 | 0.6894 | 0.2300 | 2000 | 0.0904 | 0.6422 | 0.2675 |
| 1984 | 0.0800 | 0.6920 | 0.2281 | 2001 | 0.1013 | 0.6280 | 0.2706 |
| 1985 | 0.0810 | 0.7050 | 0.2139 | 2002 | 0.0955 | 0.6433 | 0.2612 |
| 1986 | 0.0808 | 0.6965 | 0.2227 | 2003 | 0.0951 | 0.6363 | 0.2686 |
| 1987 | 0.0797 | 0.7063 | 0.2140 | 2004 | 0.0966 | 0.6209 | 0.2825 |
| 1988 | 0.0757 | 0.7345 | 0.1898 | 2005 | 0.0949 | 0.6396 | 0.2655 |
| 1989 | 0.0767 | 0.7302 | 0.1932 | 2006 | 0.0810 | 0.7401 | 0.1789 |
| 1990 | 0.0818 | 0.7084 | 0.2098 | 2007 | 0.0804 | 0.7504 | 0.1692 |
| 1991 | 0.0832 | 0.7042 | 0.2126 | 2008 | 0.0789 | 0.7563 | 0.1648 |
| 1992 | 0.0847 | 0.6984 | 0.2169 | 2009 | 0.0783 | 0.7585 | 0.1632 |
| 1993 | 0.0850 | 0.6994 | 0.2156 | 2010 | 0.0748 | 0.7628 | 0.1624 |
| 1994 | 0.0814 | 0.7155 | 0.2031 | 2011 | 0.0738 | 0.7700 | 0.1561 |
| 1995 | 0.0769 | 0.7330 | 0.1900 | 2012 | 0.0719 | 0.7737 | 0.1544 |
| 1996 | 0.0772 | 0.7277 | 0.1950 | 2013 | 0.0727 | 0.7722 | 0.1551 |
| 1997 | 0.0803 | 0.7100 | 0.2096 | 2014 | 0.0737 | 0.7730 | 0.1534 |
| 1998 | 0.0828 | 0.6814 | 0.2358 | 2015 | 0.0732 | 0.7708 | 0.1560 |
| Year | NER | NCR | ECR | SCR | MYL | MYT | SWR | NWR |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1982 | 0.1444 | 0.0284 | 0.0016 | 0.1270 | 0.1762 | 0.1166 | 0.1828 | 0.1421 |
| 1983 | 0.1379 | 0.0277 | 0.0020 | 0.1297 | 0.1750 | 0.1165 | 0.1856 | 0.1451 |
| 1984 | 0.1391 | 0.0270 | 0.0028 | 0.1292 | 0.1767 | 0.1145 | 0.1871 | 0.1436 |
| 1985 | 0.1424 | 0.0264 | 0.0034 | 0.1307 | 0.1620 | 0.1117 | 0.1991 | 0.1433 |
| 1986 | 0.1418 | 0.0256 | 0.0041 | 0.1297 | 0.1799 | 0.1074 | 0.1918 | 0.1388 |
| 1987 | 0.1410 | 0.0235 | 0.0051 | 0.1280 | 0.1781 | 0.1030 | 0.1916 | 0.1500 |
| 1988 | 0.1399 | 0.0226 | 0.0055 | 0.1638 | 0.1666 | 0.0941 | 0.1896 | 0.1421 |
| 1989 | 0.1348 | 0.0233 | 0.0060 | 0.1657 | 0.1654 | 0.0919 | 0.1958 | 0.1405 |
| 1990 | 0.1482 | 0.0236 | 0.0072 | 0.1225 | 0.1712 | 0.0925 | 0.2106 | 0.1423 |
| 1991 | 0.1474 | 0.0263 | 0.0075 | 0.1228 | 0.1701 | 0.0885 | 0.2134 | 0.1406 |
| 1992 | 0.1506 | 0.0286 | 0.0081 | 0.1201 | 0.1676 | 0.0857 | 0.2156 | 0.1389 |
| 1993 | 0.1457 | 0.0314 | 0.0091 | 0.1348 | 0.1609 | 0.0782 | 0.2146 | 0.1403 |
| 1994 | 0.1411 | 0.0343 | 0.0087 | 0.1724 | 0.1522 | 0.0714 | 0.2065 | 0.1321 |
| 1995 | 0.1391 | 0.0327 | 0.0077 | 0.1976 | 0.1485 | 0.0679 | 0.1994 | 0.1300 |
| 1996 | 0.1344 | 0.0356 | 0.0075 | 0.2044 | 0.1514 | 0.0637 | 0.1967 | 0.1291 |
| 1997 | 0.1276 | 0.0349 | 0.0068 | 0.1952 | 0.1788 | 0.0577 | 0.1969 | 0.1217 |
| 1998 | 0.1160 | 0.0351 | 0.0072 | 0.1828 | 0.2040 | 0.0540 | 0.2035 | 0.1146 |
| 1999 | 0.0999 | 0.0347 | 0.0064 | 0.1675 | 0.2037 | 0.0452 | 0.2505 | 0.1029 |
| 2000 | 0.0938 | 0.0317 | 0.0047 | 0.1418 | 0.2117 | 0.0500 | 0.2666 | 0.1093 |
| 2001 | 0.0811 | 0.0107 | 0.0043 | 0.0874 | 0.1419 | 0.1007 | 0.2953 | 0.1773 |
| 2002 | 0.0771 | 0.0102 | 0.0041 | 0.0812 | 0.1451 | 0.1111 | 0.2985 | 0.1774 |
| 2003 | 0.0842 | 0.0100 | 0.0048 | 0.0766 | 0.1541 | 0.1077 | 0.2922 | 0.1751 |
| 2004 | 0.0898 | 0.0095 | 0.0088 | 0.0696 | 0.1598 | 0.1034 | 0.2836 | 0.1789 |
| 2005 | 0.0896 | 0.0092 | 0.0087 | 0.0672 | 0.1673 | 0.0990 | 0.2843 | 0.1797 |
| 2006 | 0.1081 | 0.0249 | 0.0023 | 0.0187 | 0.2173 | 0.1604 | 0.1852 | 0.2021 |
| 2007 | 0.0991 | 0.0250 | 0.0030 | 0.0165 | 0.2267 | 0.1482 | 0.2066 | 0.1944 |
| 2008 | 0.1012 | 0.0247 | 0.0039 | 0.0147 | 0.2268 | 0.1421 | 0.2244 | 0.1833 |
| 2009 | 0.0911 | 0.0251 | 0.0041 | 0.0133 | 0.2224 | 0.1424 | 0.2431 | 0.1803 |
| 2010 | 0.0827 | 0.0224 | 0.0047 | 0.0130 | 0.2135 | 0.1628 | 0.2544 | 0.1717 |
| 2011 | 0.0820 | 0.0218 | 0.0049 | 0.0127 | 0.2097 | 0.1623 | 0.2628 | 0.1699 |
| 2012 | 0.0793 | 0.0240 | 0.0048 | 0.0126 | 0.2053 | 0.1639 | 0.2596 | 0.1786 |
| 2013 | 0.0779 | 0.0260 | 0.0045 | 0.0138 | 0.2004 | 0.1639 | 0.2618 | 0.1791 |
| 2014 | 0.0777 | 0.0256 | 0.0042 | 0.0142 | 0.1940 | 0.1614 | 0.2675 | 0.1818 |
| 2015 | 0.0769 | 0.0259 | 0.0042 | 0.0146 | 0.1871 | 0.1679 | 0.2738 | 0.1766 |
References
- Ye, X.; Ma, L.; Ye, K.; Chen, J.; Xie, Q. Analysis of Regional Inequality from Sectoral Structure, Spatial Policy and Economic Development: A Case Study of Chongqing, China. Sustainability 2017, 9, 633. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Chen, J.; Chen, J.; Miao, Y.; Song, M.; Fan, Y. Unbalanced development of inter-provincial high-grade highway in China: Decomposing the Gini coefficient. Transp. Res. Part D Transp. Environ. 2016, 48, 499–510. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bajar, S.; Rajeev, M. The Impact of Infrastructure Provisioning on Inequality in India: Does the Level of Development Matter? J. Comp. Asian Dev. 2016, 15, 122–155. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Inderst, G. “Infrastructure Investment, Private Finance, and Institutional Investors: Asia from a Global Perspective”; ADBI Working Paper 555; Asian Development Bank Institute: Tokyo, Japan, 2016. [Google Scholar]
- Chakrabarti, S. Can highway development promote employment growth in India? Transp. Policy 2018, 69, 1–9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Agbelie, B.R.D.K. An empirical analysis of three econometric frameworks for evaluating economic impacts of transportation infrastructure expenditures across countries. Transp. Policy 2014, 35, 304–310. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Crescenzi, R.; Rodríguez-Pose, A. Infrastructure and regional growth in the European Union*. Pap. Reg. Sci. 2012, 91, 487–513. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Banister, D.; Berechman, Y. Transport investment and the promotion of economic growth. J. Transp. Geogr. 2001, 9, 209–218. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ozbay, K.; Ozmen-Ertekin, D.; Berechman, J. Contribution of transportation investments to county output. Transp. Policy 2007, 14, 317–329. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aschauer, D.A. Is Government Spending Productive? J. Monet. Econ. 1989, 23, 177–200. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hong, J.; Chu, Z.; Wang, Q. Transport infrastructure and regional economic growth: Evidence from China. Transportation 2011, 38, 737–752. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, J.; Jin, F.; Mo, H.; Wang, F. Spatiotemporal evolution of China’s railway network in the 20th century: An accessibility approach. Transp. Res. Part A Policy Pract. 2009, 43, 765–778. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, T. Spatial structure convergence of China’s transportation system. Res. Transp. Econ. 2019, 78, 100768. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Démurger, S. Infrastructure Development and Economic Growth: An Explanation for Regional Disparities in China? J. Comp. Econ. 2001, 29, 95–117. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, X.; Dai, L.; Derudder, B. Spatial Inequality in the Southeast Asian Intercity Transport Network. Geogr. Rev. 2017, 107, 317–335. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fistung, F.D.; Miroiu, R.; Tătaru, D.; Iştoc, M.; Popescu, T. Transport in Support of the Process of Socio-economic Development of Romania, After 1990. Procedia Econ. Financ. 2014, 8, 313–319. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Rosenstein-Rodan, P.N. Problems of industrialisation of eastern and South-Eastern Europe. Econ. J. 1943, 53, 202–211. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Scitovsky, T. Two concepts of external economies. J. Political Econ. 1954, 62, 143–151. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Luo, X.; Zhu, N.; Zou, H. China’s Lagging Region Development and Targeted Transportation Infrastructure Investments. Ann. Econ. Financ. 2014, 15, 365–409. [Google Scholar]
- Jiwattanakulpaisarn, P.; Noland, R.B.; Graham, D.J. Causal linkages between highways and sector-level employment. Transp. Res. Part A Policy Pract. 2010, 44, 265–280. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tong, T.; Yu, T.E.; Cho, S.; Jensen, K.; De La Torre Ugarte, D. Evaluating the spatial spillover effects of transportation infrastructure on agricultural output across the United States. J. Transp. Geogr. 2013, 30, 47–55. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, H.; Ahn, S.; Ulfarsson, G.F. Transportation infrastructure investment and the location of new manufacturing around South Korea’s West Coast Expressway. Transp. Policy 2018, 66, 146–154. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kanwal, S.; Rasheed, M.I.; Pitafi, A.H.; Pitafi, A.; Ren, M. Road and transport infrastructure development and community support for tourism: The role of perceived benefits, and community satisfaction. Tour. Manag. 2020, 77, 104014. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Park, J.S.; Seo, Y.; Ha, M. The role of maritime, land, and air transportation in economic growth: Panel evidence from OECD and non-OECD countries. Res. Transp. Econ. 2019, 78, 100765. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Atack, J.; Bateman, F.; Haines, M.; Margo, R.A. Did Railroads Induce or Follow Economic Growth? Urbanization and Population Growth in the American Midwest, 1850–1860. Soc. Sci. Hist. 2010, 34, 171–197. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fan, S.; Zhang, L.; Zhang, X. Growth, Inequality, and Poverty in Rural China: The Role of Public Investments; International Food Policy Research Institute: Washington, DC, USA, 2002. [Google Scholar]
- Canning, D.; Pedroni, P. Infrastructure, long-run economic growth and causality tests for cointegrated panels. Manch. Sch. 2008, 76SI, 504–527. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mahmoudzadeh, M.; Sadeghi, S. Fiscal spending and crowding out effect: A comparison between developed and developing countries. Inst. Econ. 2013, 5, 31–40. [Google Scholar]
- Rodriguez-Pose, A.; Crescenzi, R. Research and development, spillovers, innovation systems, and the genesis of regional growth in Europe. Reg. Stud. 2008, 42, 51–67. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lakshmanan, T.R. The broader economic consequences of transport infrastructure investments. J. Transp. Geogr. 2011, 19, 1–12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pradhan, R.P.; Bagchi, T.P. Effect of transportation infrastructure on economic growth in India: The VECM approach. Res. Transp. Econ. 2013, 38, 139–148. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiang, X.; He, X.; Zhang, L.; Qin, H.; Shao, F. Multimodal transportation infrastructure investment and regional economic development: A structural equation modeling empirical analysis in China from 1986 to 2011. Transp. Policy 2017, 54, 43–52. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vickerman, R. Recent Evaluation of Research into the Wider Economic Benefits of Trans Port Infrastructure Investments; OECD/ITF Joint Transport Research Centre Discussion Papers 2007/9; OECD Publishing: Paris, France, 2007. [Google Scholar]
- Duan, L.; Sun, W.; Zheng, S. Transportation network and venture capital mobility: An analysis of air travel and high-speed rail in China. J. Transp. Geogr. 2020, 88, 102852. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, F.; Zhang, D.; Sun, C. China’s regional balanced development based on the investment in power grid infrastructure. Renew. Sustain. Energy Rev. 2016, 53, 1549–1557. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chatman, D.G.; Noland, R.B. Do Public Transport Improvements Increase Agglomeration Economies? A Review of Literature and an Agenda for Research. Transp. Rev. 2011, 31, 725–742. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Beyazit, E. Are wider economic impacts of transport infrastructures always beneficial? Impacts of the Istanbul Metro on the generation of spatio-economic inequalities. J. Transp. Geogr. 2015, 45, 12–23. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wei, W.; Zhang, W.; Wen, J.; Wang, J. TFP growth in Chinese cities: The role of factor-intensity and industrial agglomeration. Econ. Model. 2019, 91, 534–549. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pe’Er, A.; Keil, T. Are all startups affected similarly by clusters? Agglomeration, competition, firm heterogeneity, and survival. J. Bus. Ventur. 2013, 28, 354–372. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ottaviano, G.; Thisse, J. Chapter 58—Agglomeration and Economic Geography. In Handbook of Regional and Urban Economics; Henderson, J.V., Thisse, J., Eds.; Elsevier: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 2004; Volume 4, pp. 2563–2608. [Google Scholar]
- Fujita, M.; Krugman, P.R.; Venables, A. The Spatial Economy: Cities, Regions, and International Trade; The MIT Press: Cambridge, UK, 1999. [Google Scholar]
- Banerjee, A.; Duflo, E.; Qian, N. On the Road: Access to Transportation Infrastructure and Economic Growth in China. J. Dev. Econ. 2020, 145, 102442. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Wetwitoo, J.; Kato, H. High-speed rail and regional economic productivity through agglomeration and network externality: A case study of inter-regional transportation in Japan. Case Stud. Transp. Policy 2017, 5, 549–559. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vickerman, R. Can high-speed rail have a transformative effect on the economy? Transp. Policy 2018, 62, 31–37. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- He, D.; Yin, Q.; Zheng, M.; Gao, P. Transport and regional economic integration: Evidence from the Chang-Zhu-Tan region in China. Transp. Policy 2019, 79, 193–203. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dehghan Shabani, Z.; Safaie, S. Do transport infrastructure spillovers matter for economic growth? Evidence on road and railway transport infrastructure in Iranian provinces. Reg. Sci. Policy Pract. 2018, 10, 49–63. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Su, H.W.; Bai, S.Y.; Hong, Y. Foreign Metropolitan Vicinity-Ideas in Development of Changchun and Jilin Regions; Yang, W., Liang, J.G., Eds.; Trans Tech Publications Ltd.: Durnten-Zurich, Switzerland, 2013; Volume 409-410. [Google Scholar]
- Antonio Ricci, L. Economic geography and comparative advantage: Agglomeration versus specialization. Eur. Econ. Rev. 1999, 43, 357–377. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, J.; Wen, J.; Jiang, B. Spatial Spillover Effects of Transport Infrastructure in Chinese New Silk Road Economic Belt. Int. J. E-Navig. Marit. Econ. 2017, 6, 1–8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, N.; de Roo, G.; de Jong, M.; Storm, S. Does the expansion of a motorway network lead to economic agglomeration? Evidence from China. Transp. Policy 2016, 45, 218–227. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Webb, C.; Bywaters, P.; Scourfield, J.; McCartan, C.; Bunting, L.; Davidson, G.; Morris, K. Untangling child welfare inequalities and the ‘Inverse Intervention Law’ in England. Child. Youth Serv. Rev. 2020, 111, 104849. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Krafft, C.; Alawode, H. Inequality of opportunity in higher education in the Middle East and North Africa. Int. J. Educ. Dev. 2018, 62, 234–244. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mookherjee, D.; Shorrocks, A. A decomposition analysis of the trend in UK income inequality. Econ. J. 1982, 92, 886–902. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vandenbulcke, G.; Steenberghen, T.; Thomas, I. Mapping accessibility in Belgium: A tool for land-use and transport planning? J. Transp. Geogr. 2009, 17, 39–53. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cavallaro, F.; Bruzzone, F.; Nocera, S. Spatial and social equity implications for High-Speed Railway lines in Northern Italy. Transp. Res. Part A Policy Pract. 2020, 135, 327–340. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, S.; Wan, Y.; Zhang, A. Does China’s high-speed rail development lead to regional disparities? A network perspective. Transp. Res. Part A Policy Pract. 2020, 138, 299–321. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Graham, D.J.; Gibbons, S. Quantifying Wider Economic Impacts of agglomeration for transport appraisal: Existing evidence and future directions. Econ. Transp. 2019, 19, 100121. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cohen, J.P.; Paul, C.J.M. Agglomeration economies and industry location decisions: The impacts of spatial and industrial spillovers. Reg. Sci. Urban Econ. 2005, 35, 215–237. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Iacono, M.; Levinson, D. Mutual causality in road network growth and economic development. Transp. Policy 2016, 45, 209–217. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Chen, Y.; Salike, N.; Luan, F.; He, M. Heterogeneous effects of inter- and intra-city transportation infrastructure on economic growth: Evidence from Chinese cities. Camb. J. Reg. Econ. Soc. 2016, 9, 571–587. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Démurger, S.; Woo, W.; Sachs, J.; Bao, S.; Chang, G.; Mellinger, A. Geography, Economic Policy, and Regional Development in China. Asian Econ. Pap. 2002, 1, 146–197. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Ningjie, Y.; Rui, C. Research on the Development of Urban Infrastructure in China Based on Cluster Analysis. In Proceedings of the 2010 International Conference on Management and Service Science, Wuhan, China, 24–26 August 2010. [Google Scholar]
- Zhou, G. Western Region Development: The Change for the Western Provinces. China Institute of Calculation on National Economy; 2009. Available online: http://www.stats.gov.cn/ztjc/tjzdgg/hsyjh1/yjhxsjlh/hsfx/200911/t20091130_69166.html (accessed on 16 September 2017). (In Chinese)
- Feitelson, E.; Salomon, I. The implications of differential network flexibility for spatial structures. Transp. Res. Part A Policy Pract. 2000, 34, 459–479. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yi, Y.; Kim, E. Spatial economic impact of road and railroad accessibility on manufacturing output: Inter-modal relationship between road and railroad. J. Transp. Geogr. 2018, 66, 144–153. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rana, I.A.; Bhatti, S.S.; E Saqib, S. The spatial and temporal dynamics of infrastructure development disparity—From assessment to analyses. Cities 2017, 63, 20–32. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sen, A. On Economic Inequality; Clarendon Press: Oxford, UK, 1997. [Google Scholar]
- Yitzhaki, S. Relative deprivation and the GINI coefficient. Q. J. Econ. 1979, 93, 321–324. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Runciman, W.G. Relative Deprivation and Social Justice: A Study of Attitudes to Social Inequality in Twentieth-Century Britain; University of California Press: Berkeley and Los Angeles, CA, USA, 1966. [Google Scholar]
- Hong, X. A New Subgroup Decomposition of the Gini Coefficient. China Econ. Q. 2008, 8, 307–324. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar]
- Silber, J. Factor components, population subgroups and the computation of the gini index of inequality. Rev. Econ. Stat. 1989, 71, 107–115. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Granger, C.W.J. Investigating Causal Relations by Econometric Models and Cross-spectral Methods. Econometrica 1969, 37, 424–438. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tong, T.; Yu, T.E. Transportation and economic growth in China: A heterogeneous panel cointegration and causality analysis. J. Transp. Geogr. 2018, 73, 120–130. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, N.; De Jong, M.; Storm, S.; Mi, J. Transport Infrastructure, Spatial Clusters and Regional Economic Growth in China. Transp. Rev. 2012, 32, 3–28. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xi, Y. Excessive Agglomeration and Labor Crowding Effect: An Empirical Study of China’s Manufacturing Industry. Am. Int. J. Humanit. Soc. Sci. 2016, 2, 45–54. [Google Scholar]
- Hou, Q.; Li, S. Transport infrastructure development and changing spatial accessibility in the Greater Pearl River Delta, China, 1990–2020. J. Transp. Geogr. 2011, 19, 1350–1360. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]




| Index | Year | NER | NCR | ECR | SCR | MYL | MYT | SWR | NWR |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Average GDP per capita (CNY) | 81–85 | 866 | 1239 | 1551 | 615 | 528 | 503 | 397 | 576 |
| 86–90 | 1750 | 2324 | 2826 | 1458 | 1062 | 1013 | 807 | 1107 | |
| 91–95 | 3867 | 5348 | 7276 | 4291 | 2277 | 2167 | 1967 | 2304 | |
| 96–00 | 7659 | 12,044 | 15,735 | 8799 | 4806 | 4589 | 4127 | 4510 | |
| 01–05 | 12,106 | 21,908 | 26,538 | 14,060 | 8872 | 7687 | 6451 | 7737 | |
| 06–10 | 25,343 | 43,699 | 49,309 | 28,237 | 23,034 | 17,164 | 14,441 | 16,421 | |
| 11–15 | 47,646 | 71,500 | 78,402 | 50,679 | 44,054 | 35,550 | 30,661 | 32,230 | |
| Average annual GDP per capita growth rate | 81–85 | 11.38% | 11.57% | 9.76% | 16.10% | 14.29% | 13.42% | 12.26% | 12.20% |
| 86–90 | 14.12% | 12.56% | 11.20% | 18.65% | 13.50% | 13.76% | 16.07% | 12.73% | |
| 91–95 | 20.96% | 22.90% | 27.85% | 27.42% | 20.59% | 20.78% | 23.00% | 18.56% | |
| 96–00 | 9.90% | 12.44% | 9.77% | 9.35% | 10.34% | 10.44% | 8.95% | 10.11% | |
| 01–05 | 11.78% | 14.73% | 13.73% | 12.06% | 17.68% | 13.39% | 13.04% | 13.46% | |
| 06–10 | 16.59% | 13.17% | 11.42% | 14.80% | 20.03% | 18.61% | 17.77% | 16.88% | |
| 11–15 | 9.06% | 8.04% | 8.33% | 10.18% | 9.01% | 11.88% | 13.33% | 10.86% |
| Year | Railways in Operation | Highways | Expressway | Navigable Inland Waterways | Regular Civil Aviation Routes |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1980 | 5.33 | 88.83 | 0 | 10.85 | 19.53 |
| 1985 | 5.52 | 94.24 | 0 | 10.91 | 27.72 |
| 1990 | 5.79 | 102.83 | 0.05 | 10.92 | 50.68 |
| 1995 | 6.24 | 115.70 | 0.21 | 11.06 | 112.90 |
| 2000 | 6.87 | 167.98 | 1.63 | 11.93 | 150.29 |
| 2005 | 7.54 | 334.52 | 4.10 | 12.33 | 199.85 |
| 2010 | 9.12 | 400.82 | 7.41 | 12.42 | 276.51 |
| 2015 | 12.10 | 457.73 | 12.35 | 12.70 | 531.72 |
| Index | Year | NER | NCR | ECR | SCR | MYL | MYT | SWR | NWR |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Density of Railways in Operation | 1982 | 152.85 | 149.43 | 84.87 | 55.89 | 60.58 | 105.32 | 55.36 | 11.36 |
| 1985 | 152.81 | 162.94 | 84.87 | 57.98 | 63.16 | 107.55 | 55.76 | 12.31 | |
| 1990 | 152.63 | 175.15 | 88.93 | 57.26 | 66.27 | 111.01 | 55.91 | 12.27 | |
| 1995 | 152.15 | 183.96 | 92.03 | 57.47 | 67.77 | 116.04 | 57.31 | 13.25 | |
| 2000 | 152.82 | 208.48 | 85.69 | 53.29 | 70.56 | 123.47 | 62.24 | 15.58 | |
| 2005 | 169.88 | 264.10 | 150.64 | 121.09 | 97.14 | 155.23 | 82.94 | 16.81 | |
| 2010 | 178.76 | 289.52 | 195.27 | 164.99 | 123.02 | 193.89 | 92.90 | 24.97 | |
| 2015 | 216.47 | 398.30 | 272.76 | 246.63 | 157.87 | 253.50 | 126.72 | 34.23 | |
| Density of Highways | 1982 | 1253 | 2354 | 2067 | 2892 | 802 | 2218 | 1393 | 185 |
| 1985 | 1304 | 2416 | 2273 | 2984 | 805 | 2270 | 1470 | 189 | |
| 1990 | 1444 | 2653 | 2673 | 3238 | 907 | 2389 | 1627 | 206 | |
| 1995 | 1568 | 3299 | 3029 | 4353 | 980 | 2526 | 1783 | 221 | |
| 2000 | 1663 | 4123 | 3515 | 5102 | 1351 | 2844 | 2334 | 249 | |
| 2005 | 2169 | 4912 | 6612 | 5809 | 1651 | 4464 | 3160 | 420 | |
| 2010 | 4364 | 11,368 | 12,919 | 9019 | 3985 | 10,281 | 6223 | 863 | |
| 2015 | 4833 | 13,161 | 13,751 | 10,363 | 4305 | 11,832 | 7333 | 1034 |
| Variables | T-Statistic | Test Critical Values | Test Results | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1% Level | 5% Level | 10% Level | |||
| LN GDP per capita | 0.2130 | −3.6617 | −2.9604 | −2.6192 | Non-stationary |
| LN Gini | −2.0163 | −3.6463 | −2.9540 | −2.6158 | Non-stationary |
| DLN GDP per capita | −4.2575 | −3.6617 | −2.9604 | −2.6192 | Stationary |
| DLN Gini | −5.1610 | −3.6537 | −2.9571 | −2.6174 | Stationary |
| Region | Variables | t-Statistic | Test Critical Values | Test Results | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1% Level | 5% Level | 10% Level | ||||
| NER | LN XLN | 1.3609 | −3.6617 | −2.9604 | −2.6192 | N-S |
| LN Y | −1.3423 | −3.6463 | −2.9540 | −2.6158 | N-S | |
| DLN X | −3.3933 | −3.6617 | −2.9604 | −2.6192 | S | |
| DLN Y | −5.2417 | −3.6537 | −2.9571 | −2.6174 | S | |
| NCR | LN X | 0.5232 | −3.6617 | −2.9604 | −2.6192 | N-S |
| LN Y | −2.0774 | −3.6702 | −2.9640 | −2.6210 | N-S | |
| DLN X | −4.2549 | −3.6617 | −2.9604 | −2.6192 | S | |
| DLN Y | −3.6975 | −3.6537 | −2.9571 | −2.6174 | S | |
| ECR | LN X | −3.5384 | −3.7241 | −2.9862 | −2.6326 | S |
| LN Y | −1.4893 | −3.6463 | −2.9540 | −2.6158 | N-S | |
| DLN X | −3.5155 | −3.6892 | −2.9719 | −2.6251 | S | |
| DLN Y | −5.6792 | −3.6537 | −2.9571 | −2.6174 | S | |
| SCR | LN X | −1.7943 | −3.6537 | −2.9571 | −2.6174 | N-S |
| LN Y | −2.5410 | −3.6537 | −2.9571 | −2.6174 | N-S | |
| DLN X | −3.4223 | −3.6537 | −2.9571 | −2.6174 | S | |
| DLN Y | −4.0468 | −3.6537 | −2.9571 | −2.6174 | S | |
| MYL | LN X | 0.6064 | −3.6537 | −2.9571 | −2.6174 | N-S |
| LN Y | −1.4890 | −3.6463 | −2.9540 | −2.6158 | N-S | |
| DLN X | −2.8692 | −3.6617 | −2.9604 | −2.6192 | S | |
| DLN Y | −5.7251 | −3.6537 | −2.9571 | −2.6174 | S | |
| MYT | LN X | 1.6019 | −3.6617 | −2.9604 | −2.6192 | N-S |
| LN Y | −1.7438 | −3.6463 | −2.9540 | −2.6158 | N-S | |
| DLN X | −3.0658 | −3.6617 | −2.9604 | −2.6192 | S | |
| DLN Y | −7.3149 | −3.6537 | −2.9571 | −2.6174 | S | |
| SWR | LN X | 0.7367 | −3.6537 | −2.9571 | −2.6174 | N-S |
| LN Y | −2.2785 | −3.6617 | −2.9604 | −2.6192 | N-S | |
| DLN X | −2.2922 | −3.6537 | −2.9571 | −2.6174 | N-S | |
| D LN Y | −2.2385 | −3.6617 | −2.9604 | −2.6192 | N-S | |
| DDLN X | −5.5125 | −3.6617 | −2.9604 | −2.6192 | S | |
| DDLN Y | −12.5963 | −3.6617 | −2.9604 | −2.6192 | S | |
| NWR | LN X | 0.6380 | −3.6537 | −2.9571 | −2.6174 | N-S |
| LN Y | −1.8947 | −3.6463 | −2.9540 | −2.6158 | N-S | |
| DLN X | −3.1207 | −3.6617 | −2.9604 | −2.6192 | S | |
| DLN Y | −6.0670 | −3.6537 | −2.9571 | −2.6174 | S | |
| Region | Variables | T-Statistic | Test Critical Values | Cointegra-Ted or Not | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1% Level | 5% Level | 10% Level | ||||
| National | et | −2.1714 | −2.6369 | −1.9513 | −1.6107 | YES |
| NER | −2.0824 | −2.6369 | −1.9513 | −1.6107 | YES | |
| NCR | −2.1574 | −2.6443 | −1.9525 | −1.6102 | YES | |
| SCR | −2.5639 | −2.6392 | −1.9517 | −1.6106 | YES | |
| MYL | −2.5824 | −2.6369 | −1.9513 | −1.6107 | YES | |
| MYT | −2.6609 | −2.6369 | −1.9513 | −1.6107 | YES | |
| SWR | −2.3068 | −2.64179 | −1.9521 | −1.6104 | YES | |
| NWR | −1.5687 | −2.63690 | −1.9513 | −1.6107 | NO | |
| Region | Null Hypothesis | Lags | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | 2 | 3 | 4 | ||
| National | DLN Y → DLN X | 3.5262 * (0.0705) | 1.7417 (0.1950) | 1.8218 (0.1713) | 1.7620 (0.1762) |
| DLN X → DLN Y | 0.0206 (0.8868) | 0.1153 (0.8915) | 0.0776 (0.9715) | 0.2105 (0.9295) | |
| NER | DLN Y → DLN X | 0.7148 (0.4048) | 0.9791 (0.3891) | 1.6584 (0.2037) | 1.3410 (0.2894) |
| DLN X → DLN Y | 0.4675 (0.4996) | 0.4133 (0.6657) | 0.4179 (0.7419) | 0.1432 (0.9639) | |
| NCR | DLN Y → DLN X | 0.1855 (0.6699) | 0.0770 (0.9261) | 0.0961 (0.9614) | 0.3607 (0.8336) |
| DLN X → DLN Y | 0.0262 (0.8726) | 0.0440 (0.9570) | 0.0818 (0.9693) | 0.0976 (0.9820) | |
| ECR | DLN Y → DLN X | 0.0964 (0.7584) | 0.0123 (0.9878) | 0.0747 (0.9730) | 0.0178 (0.9993) |
| DLN X → DLN Y | 1.0046 (0.3245) | 0.4900 (0.6182) | 0.3150 (0.8144) | 0.1907 (0.9405) | |
| SCR | DLN Y → DLN X | 3.4184 * (0.0747) | 2.9420 * (0.0705) | 2.0866 (0.1298) | 1.5555 (0.2247) |
| DLN X → DLN Y | 5.3792 ** (0.0276) | 2.2710 (0.1233) | 3.2121 ** (0.0418) | 3.4599 ** (0.0265) | |
| MYL | DLN Y → DLN X | 1.5690 (0.2204) | 1.2069 (0.3154) | 1.0066 (0.4077) | 1.1755 (0.3515) |
| DLN X → DLN Y | 2.0416 (0.1637) | 1.6915 (0.2039) | 1.1275 (0.3586) | 0.9727 (0.4443) | |
| MYT | DLN Y → DLN X | 0.2299 (0.6352) | 0.1625 (0.8509) | 0.2219 (0.8802) | 0.3536 (0.8385) |
| DLN X → DLN Y | 0.0038 (0.9510) | 1.0066 (0.3792) | 0.9428 (0.4362) | 0.7583 (0.5645) | |
| SWR | DDLN Y → DDLN X | 0.0348 (0.8534) | 0.0687 (0.9338) | 0.3587 (0.7834) | 0.5000 (0.7361) |
| DDLN X → DDLN Y | 0.2083 (0.6516) | 0.1728 (0.8423) | 0.4516 (0.7187) | 0.2876 (0.8824) | |
| NWR | DLN Y → DLN X | 0.2792 (0.6013) | 0.2078 (0.8137) | 1.1551 (0.3482) | 0.7927 (0.5437) |
| DLN X → DLN Y | 1.1499 (0.2924) | 0.5231 (0.5988) | 0.5850 (0.6309) | 0.6334 (0.6445) | |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2021 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Chen, A.; Li, Y.; Ye, K.; Nie, T.; Liu, R. Does Transport Infrastructure Inequality Matter for Economic Growth? Evidence from China. Land 2021, 10, 874. https://doi.org/10.3390/land10080874
Chen A, Li Y, Ye K, Nie T, Liu R. Does Transport Infrastructure Inequality Matter for Economic Growth? Evidence from China. Land. 2021; 10(8):874. https://doi.org/10.3390/land10080874
Chicago/Turabian StyleChen, Anyu, Yueran Li, Kunhui Ye, Tianyi Nie, and Rui Liu. 2021. "Does Transport Infrastructure Inequality Matter for Economic Growth? Evidence from China" Land 10, no. 8: 874. https://doi.org/10.3390/land10080874
APA StyleChen, A., Li, Y., Ye, K., Nie, T., & Liu, R. (2021). Does Transport Infrastructure Inequality Matter for Economic Growth? Evidence from China. Land, 10(8), 874. https://doi.org/10.3390/land10080874






