Local Factors Controlling Gully Development in a Mediterranean Environment
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
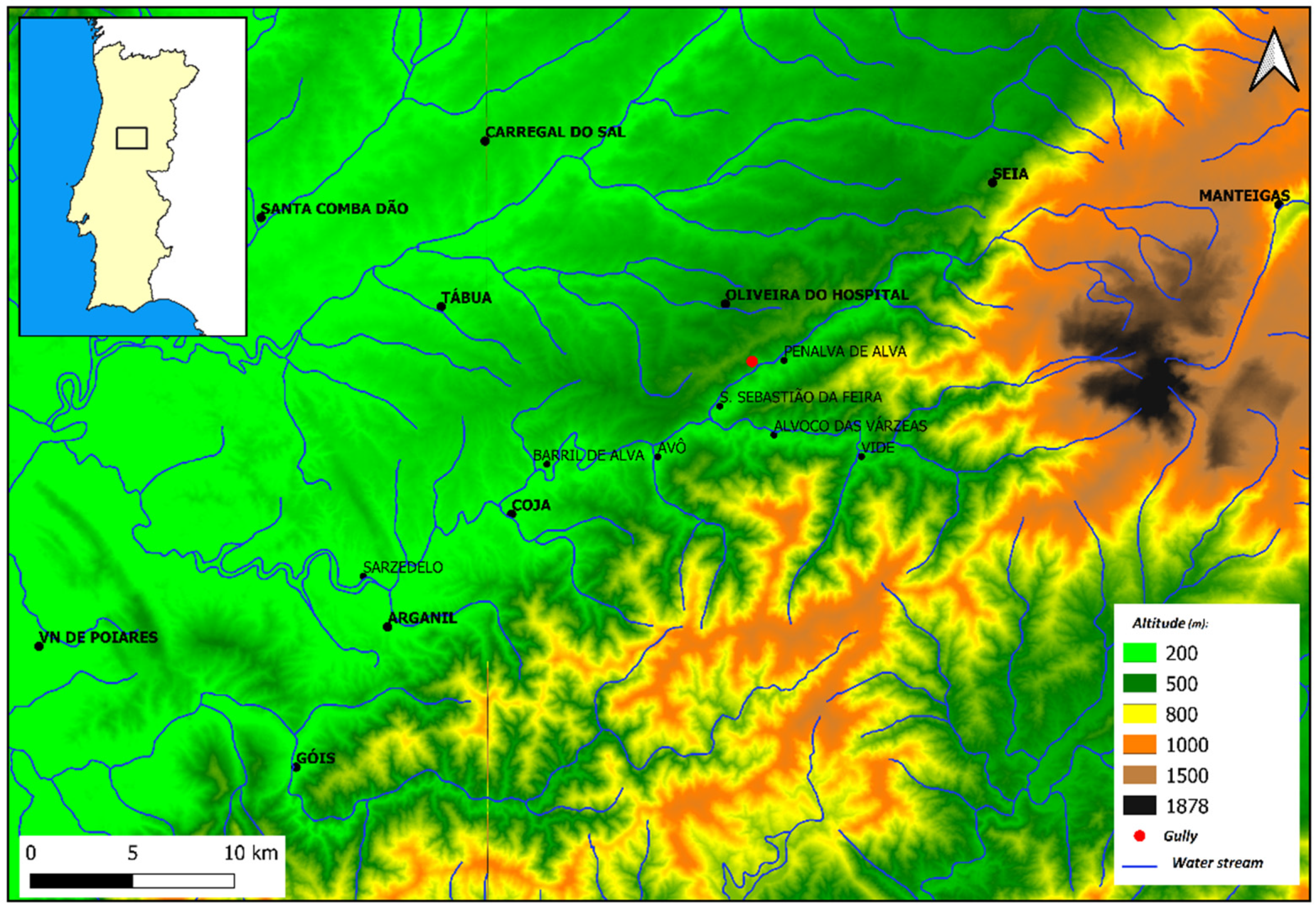
2.1. Study Area
2.2. Monitoring Morphological Changes in the Gully and Statistical Analysis
3. Results
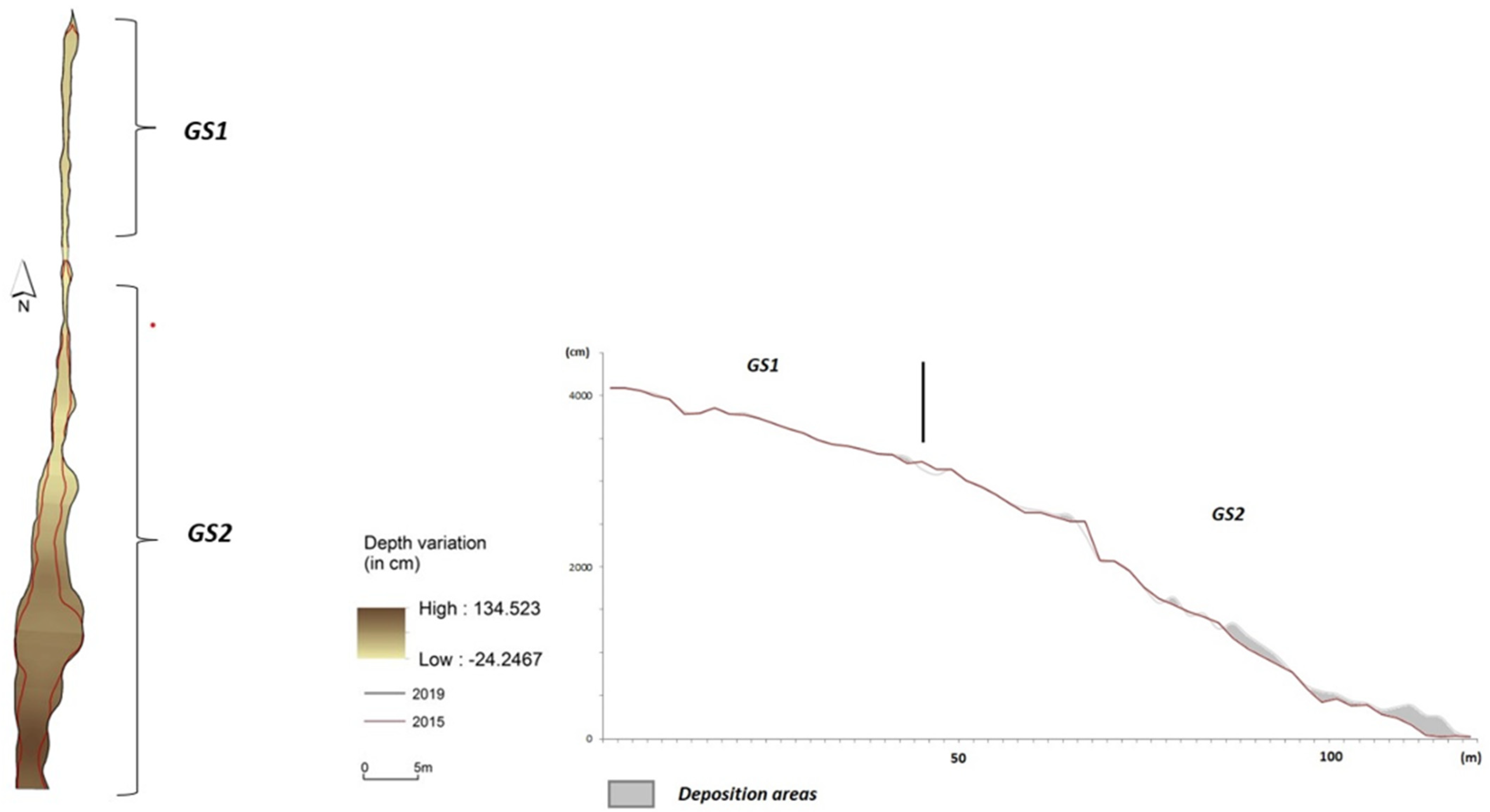
3.1. Gully Evolution
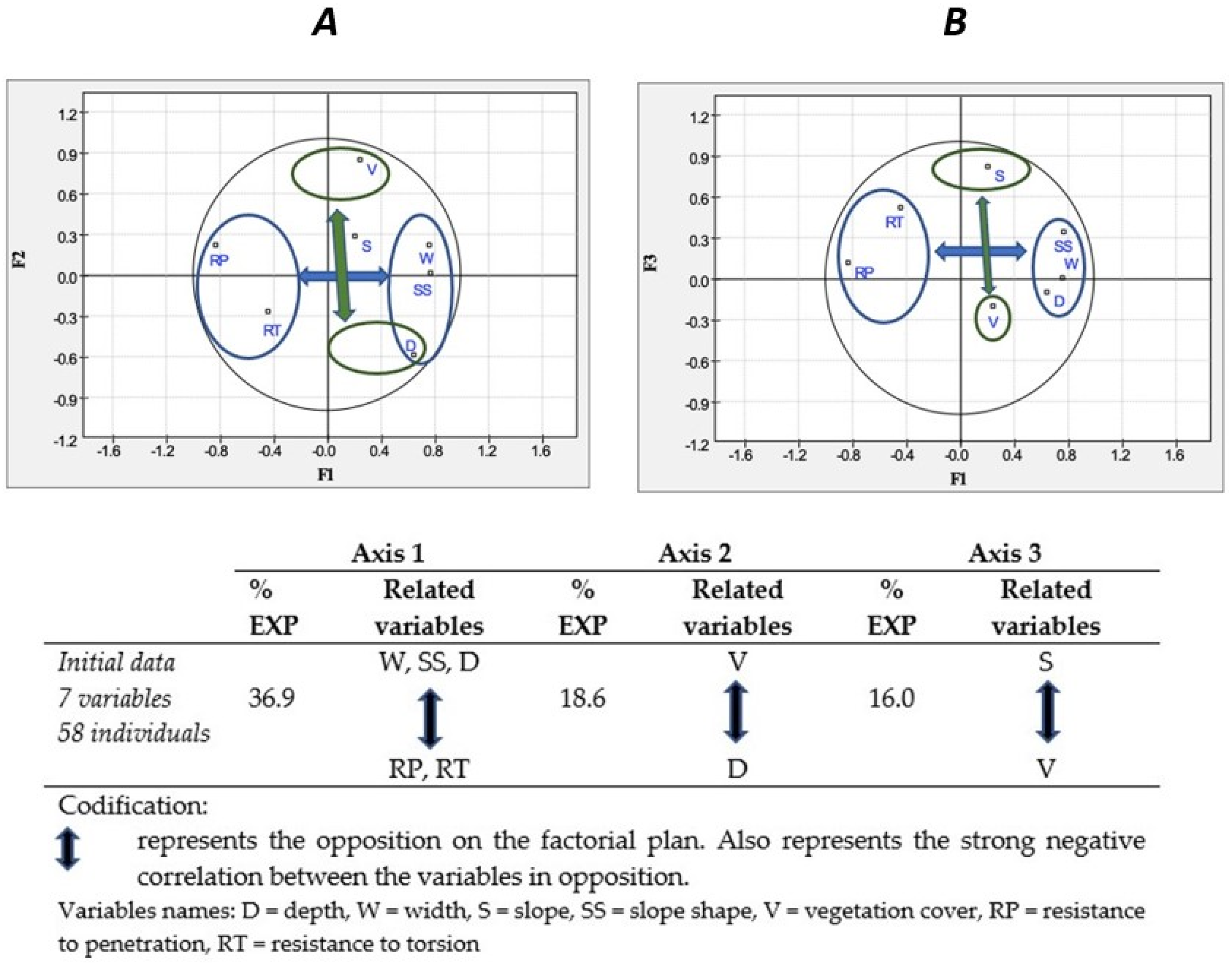
3.2. Key Factors of Enlargement and Depth Variation
4. Discussions
5. Conclusions, Limitations, and Further Research
Author Contributions
Funding
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Bufalo, M.; Nahon, D. Erosional processes of Mediterranean badlands: A new erosivity index for predicting sediment yield from gully erosion. Geoderma 1992, 52, 133–147. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Krause, A.; Franks, S.; Kalma, J.; Loughran, R.; Rowan, J. Multi parameter fingerprinting of sediment deposition in a small gullied catchment in SE Australia. Catena 2003, 53, 327–348. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Martinez-Casasnovas, J.A. A spatial information technology approach for the mapping and quantification of gully erosion. Catena 2003, 50, 293–308. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vente, J.; Poesen, J.; Arabkhedri, M.; Gert Verstraeten, G. The sediment delivery problem revisited. Prog. Phys. Geogr. 2007, 31, 155–178. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Bergonse, R.; Reis, E. Controlling factors of the size and location of large gully systems: A regression-based exploration using reconstructed pre-erosion topography. Catena 2011, 147, 621–631. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ben Slimane, A.; Raclot, D.; Evrard, O.; Sanaa, M.; Lefevre, I.; Le Bissonnais, Y. Relative contribution of rill/interrill and gully/channel erosion to small reservoir siltation in Mediterranean environments. Land Degrad. Dev. 2015, 27, 785–797. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ayele, G. A biophysical and economic assessment of a community-based rehabilitated gully in the Ethiopian highlands. Land Degrad. Dev. 2016, 27, 270–280. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Golosov, V.; Yermolaev, O.; Rysin, I.; Vanmaercke, M.; Zaytseva, M. Mapping and spatial-temporal assessment of gully density in the Middle Volga region, Russia. Earth Surf. Processes Landf. 2018, 43, 2818–2834. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Marzolff, I.; Pani, P. Dynamics and patterns of land levelling for agricultural reclamation of erosional badlands in Chambal Valley (Madhya Pradesh, India). Earth Surf. Processes Landf. 2018, 43, 524–542. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sidle, R.C.; Jarihani, B.; Kaka, S.I.; Koci, J.; Al-Shaibani, A. Hydrogeomorphic processes affecting dryland gully erosion: Implications for modelling. Prog. Phys. Geogr. Earth Environ. 2019, 43, 030913331881940. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Poesen, J. Soil erosion in the Anthropocene: Research needs. Earth Surf. Processes Landf. 2018, 43, 64–84. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cerdà, A. Parent Material and Vegetation Affect Soil Erosion in Eastern Spain. Soil Sci. Soc. Am. J. 2019, 63, 362–368. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Valentin, C.; Poesen, J.; Li, Y. Gully erosion: Impacts, factors and control. Catena 2005, 63, 132–153. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mekonnen, M.; Keesstra, S.D.; Baartman, J.E.; Ritsema, C.J.; Melesse, A.M. Evaluating sediment storage dams: Structural off-site sediment trapping measures in northwest Ethiopia. Cuad. Investig. Geogr. 2015, 41, 16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Assefa, E.; Hans-Rudolf, B. Farmers’ perception of land degradation and traditional knowledge in Southern Ethiopia—Resilience and stability. Land Degrad. Dev. 2016, 27, 1552–1561. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Foster, G.R. Understanding Ephemeral Gully Erosion. In Soil Conservation, Assessing the National Research Inventory; National Research Council, Board on Agriculture 2, National Academy Press: Washington, DC, USA, 1986; pp. 90–118. [Google Scholar]
- Poesen, J.; Nachtergaele, J.; Verstraeten, G.; Valentin, C. Gully erosion and environment change: Importance and research needs. Catena 2003, 50, 91–133. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wainwright, J.; Mathys, N.; Esteves, M. Gully erosion in mountain areas: Processes, measurement, modelling and regionalization. Earth Surf. Processes Landf. 2016, 31, 133–134. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brierley, G.; Stankoviansky, M. Geomorphic responses to land use change. Catena 2003, 51, 173–179. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Naimi, M. Dynamique de l’érosion par Ravinement Dans le Bassin Versant du Rif Occidental au Maroc. Sci. Changements Planétaires/Sécheresse 2003, 14, 95–100. [Google Scholar]
- Kefi, M.; Yoshino, K.; Setiawan, Y. Assessment and mapping of soil erosion risk by water in Tunisia using time series MODIS data. Paddy Water Environ. 2012, 10, 59–73. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Daba, S.; Rieger, W.; Strauss, P. Assessment of gully erosion in eastern Ethiopia using photogrammetric techniques. Catena 2003, 50, 273–291. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Walker, S.J.; van Dijk, A.I.J.M.; Wilkinson, S.N.; Hairsine, P.B. A comparison of hillslope drainage area estimation methods using high-resolution DEMs with implications for topographic studies of gullies. Earth Surf. Processes Landf. 2021, 46, 2229–2247. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, T.; Xu, X.; Erosion, G. Watershed Erosion Processes; Nature Switzerland AG 2021; Springer: Cham, Switzerland, 2021; pp. 41–67. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tang, J.; Liu, G.; Xie, Y.; Dun, X.; Wang, D.; Zhang, S. Ephemeral gullies caused by snowmelt: A ten-year study in northeastern China. Soil Tillage Res. 2021, 212, 105048. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Frankl, A.; Nyssen, J.; Vanmaercke, M.; Poesen, J. Gully prevention and control: Techniques, failures and effectiveness. Earth Surf. Processes Landf. 2021, 46, 220–238. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bogale, A.; Aynalem, D.; Adem, A.; Mekuria, W.; Tilahun, S. Spatial and temporal variability of soil loss in gully erosion in upper Blue Nile basin, Ethiopia. Appl. Water Sci. 2021, 10, 106. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Roy, S. Influence of Road-Stream Crossing on the Initiation of Gully: Case Study from the Terai Region of Eastern India. In Gully Erosion Studies from India and Surrounding Regions; Springer Nature: Cham, Switzerland, 2020; pp. 251–263. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nyssen, J.; Poesen, J.; Moeyersons, J.; Luyten, E.; Veyret-Picot, M.; Deckers, J.; Haile, M.; Govers, G. Impact of road building on gully erosion risk: A case study from the Northern Ethiopian Highlands. Earth Surf. Processes Landf. 2002, 27, 1267–1283. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Selkimäki, M.; González-Olabarria, J.R. Assessing gully erosion occurrence in forest lands in Catalonia (Spain). Land Degrad. Dev. 2017, 28, 616–627. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Luciano, L.; Adélia, N.; António, B.-G.; António, V. Soil Erosion after Wildfires in Portugal: What Happens When Heavy Rainfall Events Occur? Soil Erosion Edited by: Danilo Godone and Silvia Stanchi; InTech—Open Access Company: London, UK, 2012; ISBN 980-953-307-558-2. [Google Scholar]
- Nunes, J.P.; Seixas, J.; Keizer, J.J.; Ferreira, A.J.D. Sensitivity of runoff and soil erosion to climate change in two Mediterranean watersheds. Part II: Assessing impacts from changes in storm rainfall, soil moisture and vegetation cover. Hydrol. Process. 2009, 23, 1212–1220. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Meira-Castro, A.; Carvalho, J.; Meixedo, J. A qualitative description of soil parameters variation due to a prescribed fire in Portuguese northwestern forests using Fuzzy Boolean Nets—The case study of Cabreira mountain. Geoderma 2012, 191, 89–96. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Meira-Castro, A.; Shakesby, R.; Espinha Marques, J.; Doerr, S.; Meixedo, J.; Teixeira, J.; Chamine, H. Effects of prescribed fire on surface soil in a Pinus pinaster plantation, northern Portugal. Environ. Earth Sci. 2015, 73, 3011–3018. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Nunes, J.P.; Seixas, J.; Pacheco, N.R. Vulnerability of water resources, vegetation productivity and soil erosion to climate change in Mediterranean watersheds. Hydrol. Process. 2008, 22, 3115–3134. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Martins, B.; Meira-Castro, A.; Nunes, A.; Lourenço, L. The development of gullies in a Mediterranean environment: The example of the Corgo gully (central Portugal). Energy Rep. 2020, 6, 794–799. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Martins, B.; Castro, A.C.M.; Ferreira, C.; Lourenço, L.; Nunes, A. Gullies mitigation and control measures: A case study of the Seirós gullies (North of Portugal). Phys. Chem. Earth 2019, 109, 26–30. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Douglas, I.; Pietroniro, A. Predicting road erosion rates in selectively logged tropical rain forests. In Erosion Prediction in Ungauged Basins, Integrating Methods and Techniques, Proceedings of an International Symposium Sapporo, Japan, 8–9 July 2003; De Boer, D., Froehlich, W., Mizuyama, T., Eds.; IAHS Press: Wallingford, UK, 2003; pp. 199–205. [Google Scholar]
- Ezezika, O.C.; Adetona, O. Resolving the gully erosion problem in Southeastern Nigeria: Innovation through public awareness and community-based approaches. J. Soil Sci. Environ. Manag. 2011, 2, 286291. Available online: http://www.academicjournals.org/journal/JSSEM/articleabstract/8BBD5123409 (accessed on 15 October 2020).
- Kheir, R.; Wilson, J.; Deng, Y. Use of terrain variables for mapping gully erosion susceptibility in Lebanon. Earth Surf. Processes Landf. 2007, 32, 1770–1782. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nwilo, P.; Olayinka, D.; Uwadiegwu, I.; Adzandeh, A. An assessment and mapping of gully erosion hazards in Abia State: A GIS Approach. J. Sustain. Dev. 2011, 4, 196–211. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Nyssen, J.; Moeyersons, J.; Poesen, J.; Deckers, J.; Mitiku, H. The environmental significance of the remobilisation of ancient mass movements in the Atbara-Tekeze headwaters, Northern Ethiopia. Geomorphology 2002, 49, 303–322. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Deng, Q.; Qin, F.; Zhang, B.; Wang, H.; Luo, M.; Shu, C.; Liu, H.; Liu, G. Characterizing the morphology of gully cross-sections based on PCA: A case of Yuanmou Dry-Hot Valley. Geomorphology 2015, 228, 703–713. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mathys, N.; Brochot, S.; Meunier, M. L’érosion des Terres Noires dans les Alpes du sud: Contribution à l’estimation des valeurs annuelles moyennes (bassins versants expérimentaux de Draix, Alpes de Haute Provence, France). Rev. Geogr. Alp. 1996, 84, 17–27. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Prodanović, D.; Stanić, M.; Milivojević, V.; Simić, Z.; Arsić, M. DEM-based GIS algorithms for automatic creation of hydrological models data. J. Serb. Soc. Comput. Mech. 2009, 3, 64–85. [Google Scholar]
- Báčová, M.; Krása, J.; Devátý, J.; Kavka, P.A. GIS method for volumetric assessments of erosion rills from digital surface models. Eur. J. Remote Sens. 2009, 52 (Suppl. 1), 96–107. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Xu, Y.; Yue, D.; He, P. Point cloud segmentation of gully based on characteristic difference using airborne lidar data. Int. Arch. Photogramm. Remote Sens. Spat. Inf. Sci. 2017, XLII-2/W7, 307–311. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Khalili, A.; Raclot, D.; Habaeib, H.; Lamachère, J.M. Factores and processes of permanent gully evolution in a Mediterranean marly environment (Cape Bon, Tunisia). Hidrol. Sci. J. 2013, 58, 1519–1531. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zante, P.; Collinet, J.; Leclerc, G. Cartographie des Risques Érosifs sur le Bassin Versant de la Retenue Collinaire d’Abdessadok (Dorsale Tunisienne); Montpellier, France, 2003; Available online: https://agritrop.cirad.fr/553389/ (accessed on 28 November 2021).
- Junta de Energia Nuclear (JEN). A Província Uranífera do Centro de Portugal. Suas Características Estruturais, Tectónicas e Metalogénicas; Junta de Energia Nuclear: Lisboa, Portugal, 1968. [Google Scholar]
- Dias, R.; Ribeiro, A.; Coke, C.; Rodrigues, J.; Pereira, E.; Rebelo, J.; Moreira, N. Evolução Estrutural dos Sectores Setentrionais do Autóctone da Zona Centro-Ibérica, in Geologia de Portugal; Livraria Escolar Editora: Lisbon, Portugal, 2011. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, H.; Zhang, G.-H.; Li, N.-N.; Zhang, B.-J.; Yang, H.-Y. Variation in soil erodibility under five typical land uses in a small watershed on the Loess Plateau, China. Catena 2019, 174, 24–35. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Coelho, C.O.; Ferreira, A.J.; Laouina, A.; Boulet, A.-K.; Chaker, M.; Nafaa, R.; Naciri, R.; Regaya, K.; Hamza, A.; Carvalho, T.M.; et al. Changes in land-use and their impact on erosion rates and overland flow generation in the Maghreb region, Revue des sciences de l’eau. J. Water Sci. 2004, 17, 163–180. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Luk, S.-H.; Hamilton, H. Experimental effects of antecedent moisture and soil strength on rainwash erosion of two luvisols, Ontario. Geoderma 1986, 37, 29–43. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Marzolff, I.; Poesen, J. The potential of 3D gully monitoring with GIS using high-resolution aerial photography and a digital photogrammetry system. Geomorphology 2009, 111, 48–60. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- James, A.; Watson, D.; Hansen, W. Using LiDAR data to map gullies and headwater streams under forest canopy: South Carolina, USA. Catena 2007, 71, 132–144. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vandekerckhove, L.; Poesen, J.; Oostwoud Wijdenes, D. Thresholds for gully initiation and sedi-mentation in Mediterranean Europe. Earth Surf. Processes Landf. 2000, 25, 1201–1220. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dormann, C.F.; Elith, J.; Bacher, S.; Buchmann, C.; Carl, G.; Carré, G.; Marquéz, J.R.G.; Gruber, B.; Lafourcade, B.; Leitão, P.J.; et al. Collinearity: A review of methods to deal with it and a simulation study evaluating their performance. Ecography 2013, 36, 27–46. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vanmaercke, M.; Chen, Y.; Haregeweyn, N.; De Geeter, S.; Campforts, B.; Heyndrickx, W.; Tsunekawa, A.; Poesen, J. Predicting gully densities at sub-continental scales: A case study for the Horn of Africa. Earth Surf. Processes Landf. 2020, 45, 3763–3779. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bennett, S.J.; Wells, R.R. Gully erosion processes, disciplinary fragmentation, and technological innovation. Earth Surf. Processes Landf. 2019, 44, 46–53. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Shahabi, H.; Jarihani, B.; Tavakkoli Piralilou, S.; Chittleborough, D.; Avand, M.; Ghorbanzadeh, O. A Semi-Automated Object-Based Gully Networks Detection Using Different Machine Learning Models: A Case Study of Bowen Catchment, Queensland, Australia. Sensors 2019, 19, 4893. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Walker, S.J.; Wilkinson, S.N.; van Dijk, A.I.; Hairsine, P.B. A multi-resolution method to map and identify locations of future gully and channel incision. Geomorphology 2020, 358, 107115. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shruthi, R.B.V.; Kerle, N.; Jetten, V. Object-based gully feature extraction using high spatial resolution imagery. Geomorphology 2011, 134, 260–268. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Martha, T.R.; Kerle, N.; Jetten, V.; van Westen, C.J.; Kumar, K.V. Characterising spectral, spatial and morphometric properties of landslides for semi-automatic detection using object-oriented methods. Geomorphology 2010, 116, 24–36. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Remondino, F.; Barazzetti, L.; Nex, F. ISPRS—International Archives of the Photogrammetry. Remote Sens. Spat. Inf. Sci. 2011, XXXVIII-1/C22, 25–31. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Nachtergaele, J.; Poesen, J.; Vandekerckhove, L.; Oostwoud Wijdenes, D.; Roxo, M. Testing the ephemeral gully erosion model (EGEM) for two Mediterraneanenvironments. Earth Surf. Processes Landf. 2001, 26, 17–30. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nachtergaele, J.; Poesen, J.; ASteegen, A.; Takken, I.; Beuselinck, L.; Vandekerckhove, L.; Govers, G. The value of a physically based model versus an empirical approach in the prediction of ephemeral gully erosion for loess-derived soils. Geomorphology 2001, 40, 237–252. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kılıç, O. Effects of land use and land cover changes on soil erosion in semi-arid regions of Turkey; a case study in Almus lake watershed. Carpathian J. Earth Environ. Sci. 2021, 16, 129–138. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fernandes, J.; Bateira, C.; Soares, L.; Faria, A.; Oliveira, A.; Hermenegildo, C.; Moura, R.; Gonçalves, J. SIMWE model application on susceptibility analysis to bank gully erosion in Alto Douro Wine Region agricultural terraces. Catena 2017, 153, 39–49. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Olivares, B.; Verbist, K.; Silva, O.; Lobo, D.; Vargas, R. Evaluation of the USLE model to estimate water erosion in an Alfisol. Soil Sci. Plant Nutr. 2011, 11, 71–84. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Beckedahl, H.R.; Bowyer-Bower, T.A.S.; Dardis, G.F.; Hanvey, P.M. Geomorphic Effects of Soil Erosion; Moon, B.P., Dardis, G.F., Eds.; The Geomorphology of Southern Africa, Southern Book Co.: Johannesburg, South Africa, 1988; pp. 249–276. [Google Scholar]
- Kakembo, V.; Rowntree, K.M. The relationship between land use and soil erosion in the communal lands near Peddie Town, Eastern Cape, South Africa. Land Degrad. Dev. 2003, 14, 39–49. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Elwell, H.; Stocking, M. Vegetal cover to estimate soil erosion hazard in Rhodesia. Geoderma 1976, 15, 61–70. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- De Ploey, J. Modelling the erosional susceptibility of catchments in terms of energy. Catena 1990, 17, 175–183. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Francis, C.F.; Thornes, J.B. Runoff Hydrographs from Three Mediterranean Vegetation Cover Types. In Vegetation and Erosion: Processes and Environments; Thornes, J.B., Ed.; Wiley: Chichester, UK, 1990; pp. 363–385. [Google Scholar]
- Roxo, M.J. A Acção Antrópica no Processo de Degradação de Solos: A Serra de Serpa e Mértola. Ph.D. Thesis, Universidade Nova de Liboa, Lisboa, Portugal, 1994. [Google Scholar]
- Bochet, E.; Rubio, J.L.; Poesen, J. Modified topsoil islands within patchy Mediterranean vegetation in SE Spain. Catena 1999, 38, 23–44. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zuazo, V.H.D.; Martínez, J.R.F.; Pleguezuelo, C.R.R.; Raya, A.M.; Rodríguez, B.C. Soil-erosion and runoff prevention by plant covers in a mountainous area (SE Spain): Implications for sustainable agriculture. Environmentalist 2006, 26, 309–319. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sonneveld, B.; Keyzer, M.A. Land under pressure: Soil conservation concerns and opportunities for Ethiopia. Land Degrad. Dev. 2003, 14, 5–23. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Descroix, L.; Claude, J.-C. Spatial and temporal factors of erosion by water of black marl in the badlands of the French Southern Alps. Hydrol. Sci. J. 2002, 47, 227–242. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Desmet, P.J.J.; Govers, G. A GIS procedure for automatically calculating the USLE LS factor on topographically complex landscape units. J. Soil Water Conserv. 1996, 51, 427–433. [Google Scholar]
- Knapen, A.; Poesen, J. Soil erosion resistance effects on rill and gully initiation points and dimensions. Earth Surf. Processes Landf. 2009, 35, 217–228. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Daggupati, P.; Yen, H.; White, M.J.; Srinivasan, R.; Arnold, J.G.; Keitzer, C.S.; Sowa, S.P. Impact of model development, calibration and validation decisions on hydrological simulations in West Lake Erie Basin. Hydrol. Process. 2015, 29, 5307–5320. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nearing, M.A.; Foster, G.R.; Lane, L.J.; Finkner, S.C. A Process-Based Soil Erosion Model for USDA-Water Erosion Prediction Project Technology. Trans. ASAE 1989, 32, 1587–1593. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
| Coordinates | ||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| x | Y | Total length (m) | Mean width (m) | Maximum width value (m) | Mean depth (m) | Maximum depth value (m) | WDR * | SSAGH ** | Channel slope (m m−1) | Plan area (m2) |
| 40.3337 | −7.8471 | 116 | 1.33 | 9.30 | 2.02 | 6.65 | 2.1 | 0.39 | 0.36 | 333.5 |
| Depth Variation | Width Variation | WDR | Slope Shape | Vegetation Cover | Slope | Resist. to Penet. | Resist. to Torc. | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Width variation | Correlation Coefficient | 0.389 ** | 1 | 0.229 | 0.582 ** | 0.300 * | 0.214 | −0.529 ** | −0.126 |
| Sig. (2-tailed) | 0.003 | - | 0.084 | 0 | 0.022 | 0.107 | 0 | 0.344 | |
| Depth variation | Correlation Coefficient | 1 | 0.389 ** | −0.586 ** | 0.391 ** | −0.123 | −0.182 | −0.532 ** | −0.152 |
| Sig. (2-tailed) | 0.003 | 0 | 0.002 | 0.36 | 0.173 | 0 | 0.254 | ||
| N | 38 | 38 | 38 | 38 | 38 | 38 | 38 | 38 |
| Width Variation | Depth Variation | WDR | Slope Shape | Vegetation Cover | Slope | Resist. to Penet. | Resist. to Torc. | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Width variation of GS2 | Correlation Coefficient | 1 | 0.324 * | −0.707 ** | 0.367 * | −0.249 | −0.391 * | −0.566 ** | −0.166 |
| Sig. (2-tailed) | 0.047 | 0.000 | 0.024 | 0.132 | 0.015 | 0.000 | 0.319 | ||
| N | 38 | 38 | 38 | 38 | 38 | 38 | 38 | 38 |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Martins, B.; Nunes, A.; Meira-Castro, A.; Lourenço, L.; Hermenegildo, C. Local Factors Controlling Gully Development in a Mediterranean Environment. Land 2022, 11, 204. https://doi.org/10.3390/land11020204
Martins B, Nunes A, Meira-Castro A, Lourenço L, Hermenegildo C. Local Factors Controlling Gully Development in a Mediterranean Environment. Land. 2022; 11(2):204. https://doi.org/10.3390/land11020204
Chicago/Turabian StyleMartins, Bruno, Adélia Nunes, Ana Meira-Castro, Luciano Lourenço, and Carlos Hermenegildo. 2022. "Local Factors Controlling Gully Development in a Mediterranean Environment" Land 11, no. 2: 204. https://doi.org/10.3390/land11020204
APA StyleMartins, B., Nunes, A., Meira-Castro, A., Lourenço, L., & Hermenegildo, C. (2022). Local Factors Controlling Gully Development in a Mediterranean Environment. Land, 11(2), 204. https://doi.org/10.3390/land11020204








