Evaluation of the Health Promotion Capabilities of Greenway Trails: A Case Study in Hangzhou, China
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Literature Review
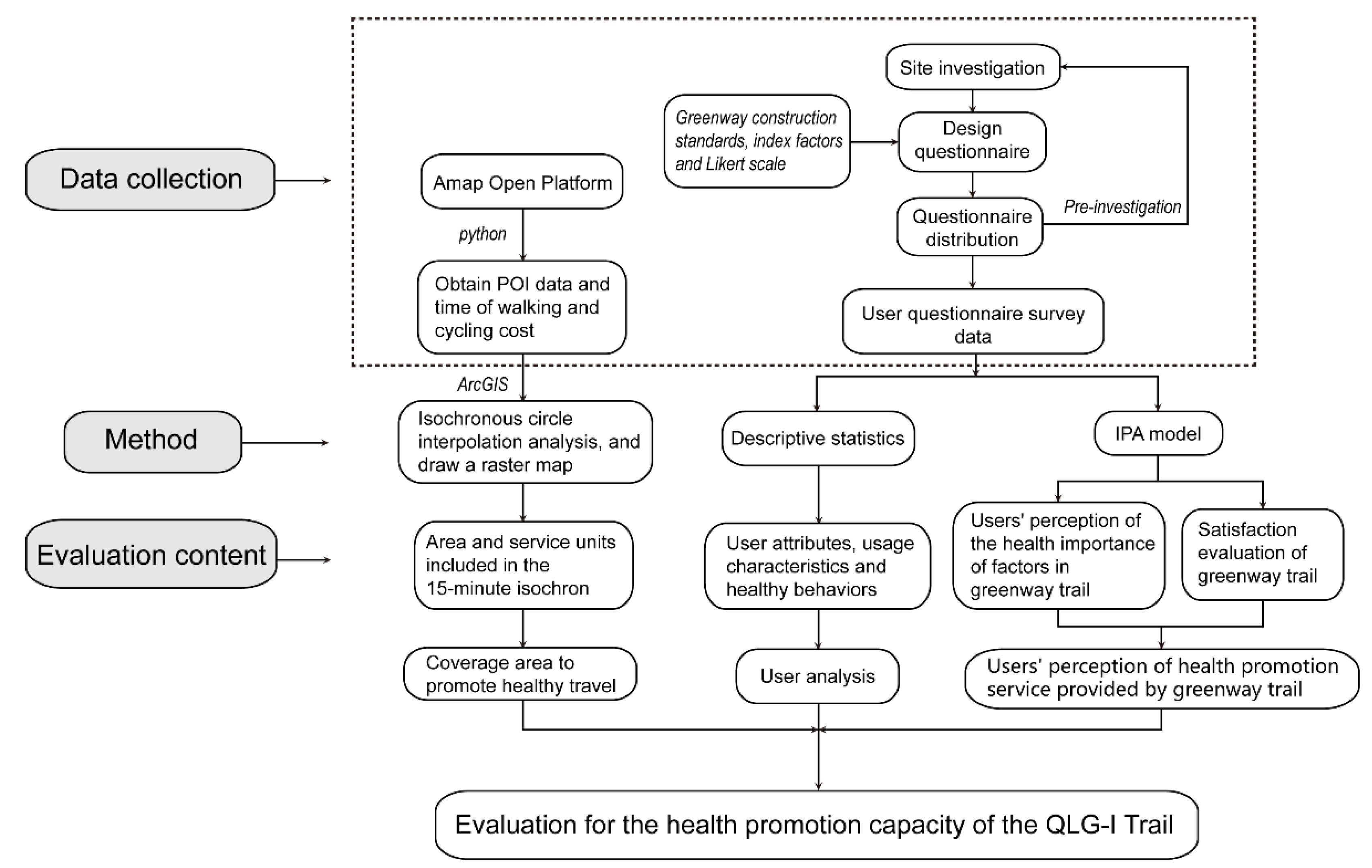
3. Methods
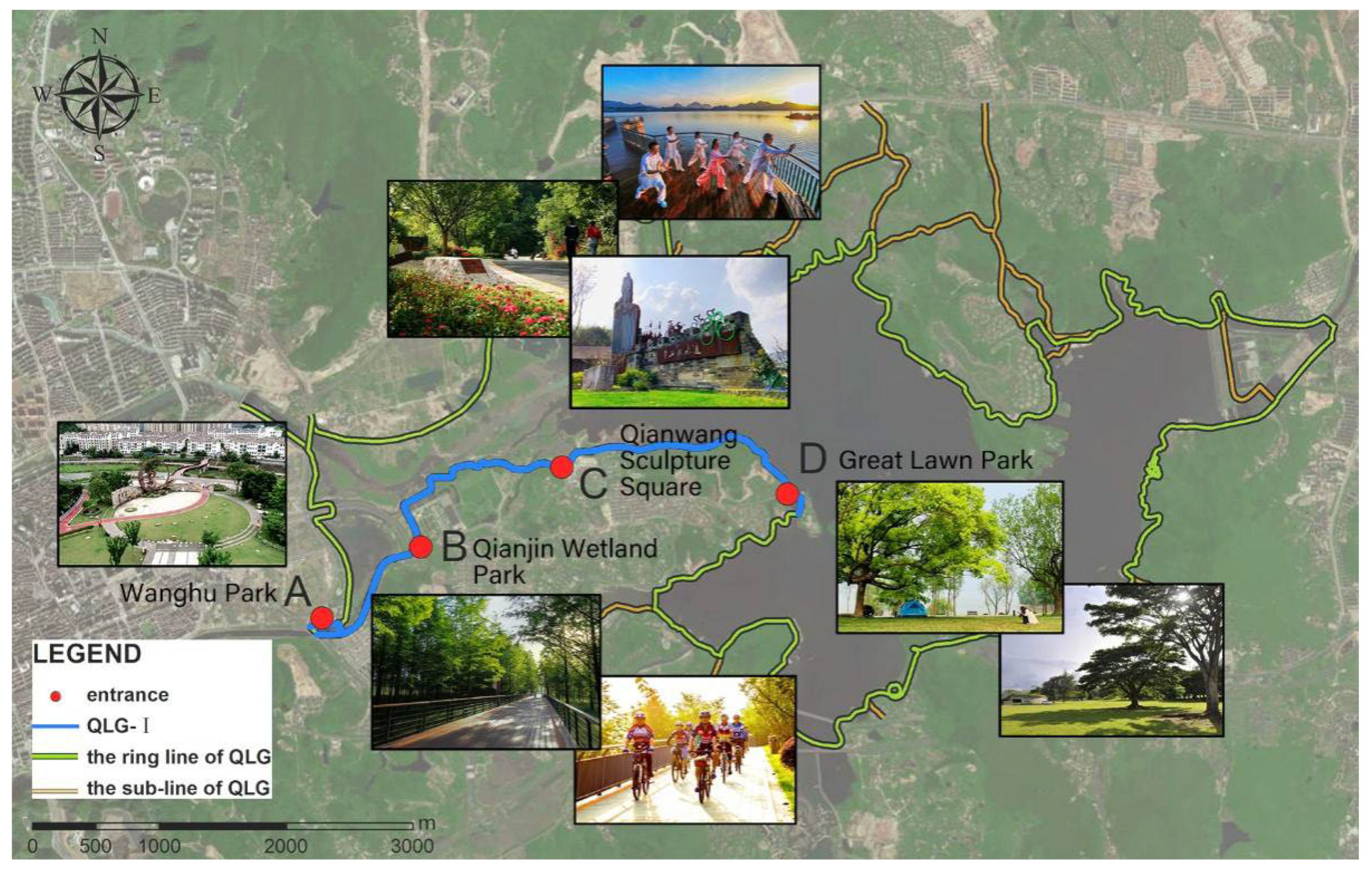
3.1. Study Area
3.2. Data Collection
3.2.1. POI Data and Travel Time Cost Data
3.2.2. Questionnaire Design and Site Investigation
3.3. Data Analysis
4. Results
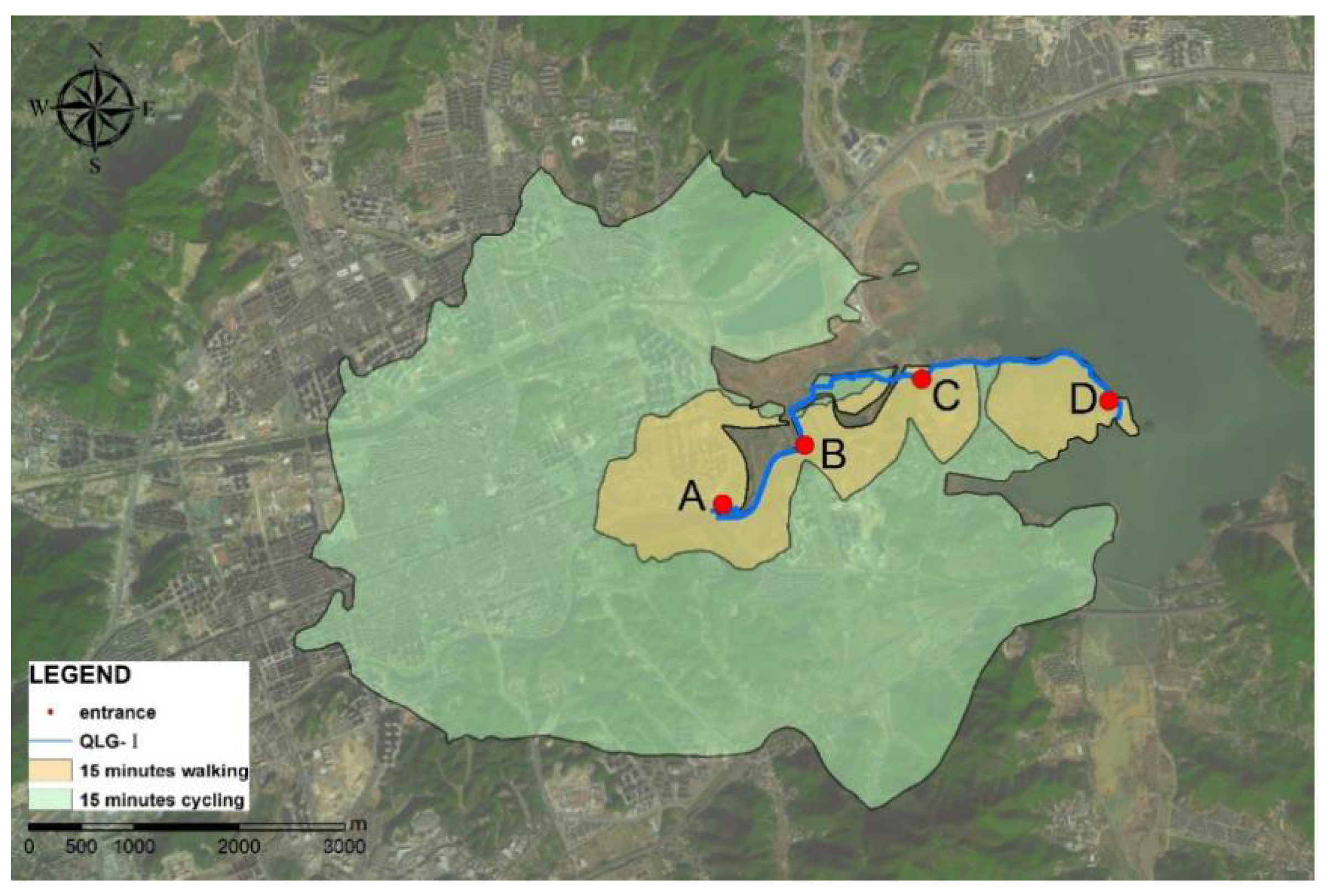
4.1. The Scope for Promoting Healthy Travel of the QLG-I Trail
4.1.1. The Walking and Cycling Accessibility of the QLG-I Trail
4.1.2. The Promoting Healthy Travel Range of the QLG-I Trail
4.2. The User Analysis of the QLG-I Trail
4.2.1. User Attributes and Use Characteristics
4.2.2. Health Awareness and Health-Promoting Behaviour of Users
4.3. The Perceptual Evaluation of the Trail Attributes in Terms of Health Promotion
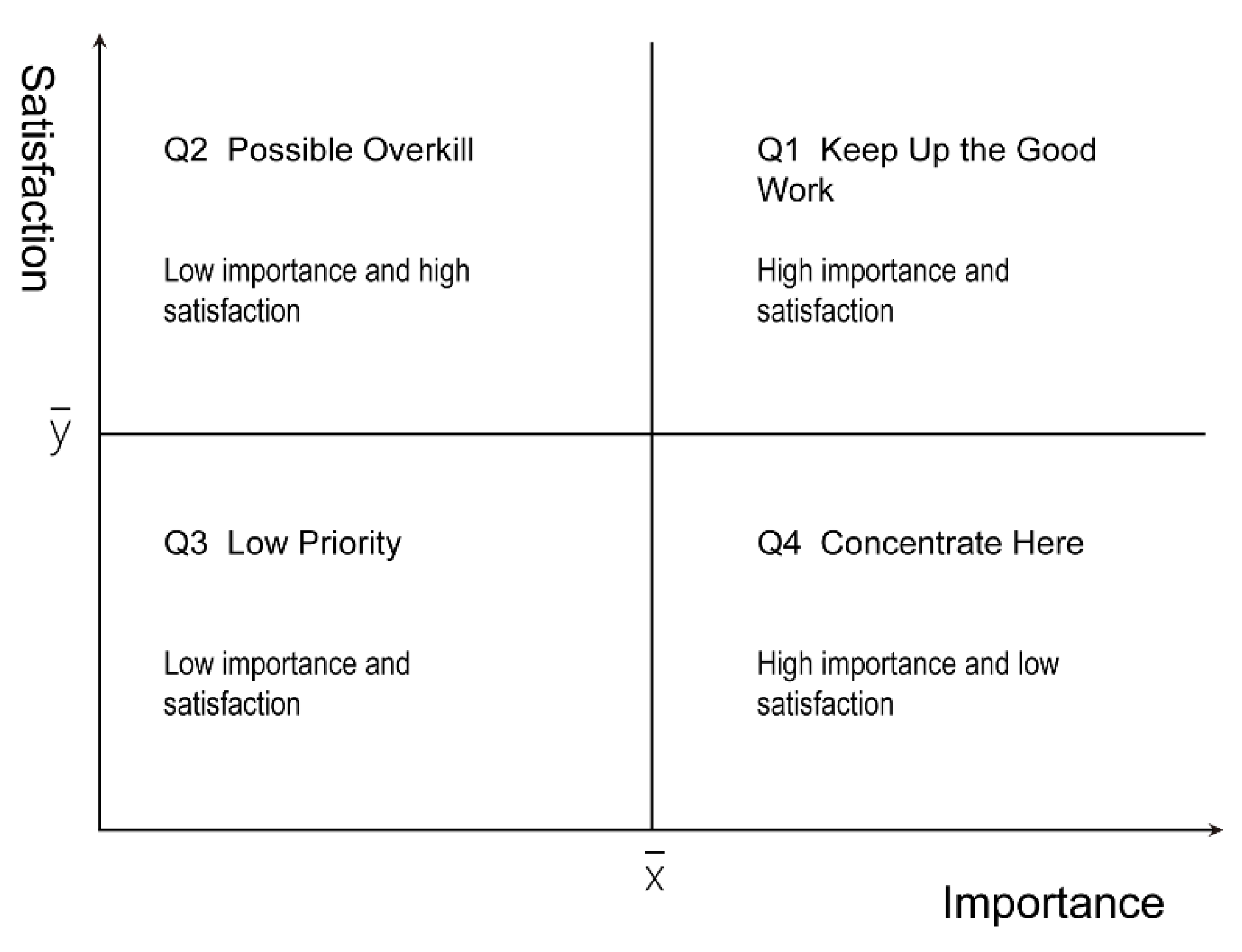
4.3.1. IPA of Factors That Affect Health Promotion
4.3.2. Satisfaction Evaluation of the QLG-I Trail
4.3.3. IPA Chart
5. Discussion and Conclusions
5.1. Research Contribution
5.2. Promotion of Healthy Travel
5.3. Health-Promoting Behaviour
5.4. Trail Attributes Affecting the Health Promotion of Country Greenways
5.5. Public Participation
5.6. Research Limitations and Future Directions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
Appendix A
| Evaluation Factors | Index Factors 1 | Explanation |
|---|---|---|
| Road Quality | S1 Width | Standard width 4 m |
| S2 Comfort of pavement for people | Suitable for walking, jogging or biking | |
| S3 Connectivity with other branches | Greenway entrances or exits are easy to reach | |
| S4 Protective fence | Waterfront guardrail, mountain rock enclosure | |
| S5 Wheelchair accessible | Walking or cycling barrier-free, serving special groups | |
| Supporting facilities | S6 Signage system | Information signs, guidance signs and warning signs |
| S7 Parking lot | Bicycle or car parking lot | |
| S8 Lighting system | Combination of different lamps | |
| S9 Commercial service facilities | Retail stores, bicycle rental, greenway relays | |
| S10 Public health | Toilets, dustbins, hand sinks | |
| Natural environment | S11 Terrain diversity | Wetlands, hills, fields, lakes and mountains |
| S12 Colourful plant landscape | Metasequoia forest, wet plants, farmland, flower bushes | |
| S13 Scenery line | Ridgeline, wood line, lakeshore line | |
| S14 Meteorological landscape | Landscapes that change over time or seasons like sunrise, rain, or dusk | |
| S15 Biological landscape | Birds, fish, squirrels and so on | |
| Regional cultural characteristics | S16 Greenway theme reflects | Green ecology, health or sports |
| S17 Historical allusions | Wuyue culture | |
| S18 Traditional construction techniques | Seal cutting, carving, masonry technology | |
| S19 Application of local materials | Bricks, stones, tiles and Bamboo | |
| S20 Sense of belonging | Willing to be close, stay and enjoy | |
| Management and maintenance | S21 Cleanliness | Normal environmental cleanliness |
| S22 Security guards patrol | Security personnel, guardhouses, alarms | |
| S23 The facilities are fully equipped | All facilities can be used normally | |
| S24 Plant conservation | Whether the plant has pests and diseases and its growth status | |
| S25 Fire safety | Fire-fighting facilities, emergency escape routes |
References
- World Health Organization. Health Promotion Glossary of Terms 2021; World Health Organization: Geneva, Switzerland, 2021. [Google Scholar]
- Lortet, P. The greenway concept: Lane for non-motorized traffic, leisure area and tool of heritage development. Espaces 1998, 150, 17–24. [Google Scholar]
- Lindsey, G. Use of urban greenways: Insights from Indianapolis. Landsc. Urban Plan. 1999, 45, 145–157. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Coutts, C. Greenway accessibility and physical-activity behavior. Environ. Plan. B Plan. Des. 2008, 35, 552–563. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Chen, Y.; Gu, W.; Liu, T.; Yuan, L.; Zeng, M. Increasing the use of urban greenways in developing countries: A case study on Wutong Greenway in Shenzhen, China. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2017, 14, 554. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Lindsey, G.; Wilson, J.; Anne Yang, J.; Alexa, C. Urban greenways, trail characteristics and trail use: Implications for design. J. Urban Des. 2008, 13, 53–79. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Price, A.E.; Reed, J.A.; Muthukrishnan, S. Trail user demographics, physical activity behaviors, and perceptions of a newly constructed greenway trail. J. Community Health 2012, 37, 949–956. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mundet, L.; Coenders, G. Greenways: A sustainable leisure experience concept for both communities and tourists. J. Sustain. Tour. 2010, 18, 657–674. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lovely, S.A. The Greenway Trail in Community Development: An Examination of Value, Representation, and Distribution of Benefits among Stakeholders; Virginia Polytechnic Institute and State University: Blacksburg, VA, USA, 2020. [Google Scholar]
- Fábos, J.D. Greenway planning in the United States: Its origins and recent case studies. Landsc. Urban Plan. 2004, 68, 321–342. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Burkhard, B.; Kroll, F.; Nedkov, S.; Müller, F. Mapping ecosystem service supply, demand and budgets. Ecol. Indic. 2012, 21, 17–29. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Geijzendorffer, I.R.; Martín-López, B.; Roche, P.K. Improving the identification of mismatches in ecosystem services assessments. Ecol. Indic. 2015, 52, 320–331. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mouchet, M.A.; Lamarque, P.; Martín-López, B.; Crouzat, E.; Gos, P.; Byczek, C.; Lavorel, S. An interdisciplinary methodological guide for quantifying associations between ecosystem services. Glob. Environ. Chang. 2014, 28, 298–308. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fields, B.; Thomas, J.; Wagner, J.A. Living with water in the Era of climate change: Lessons from the Lafitte Greenway in Post-Katrina New Orleans. J. Plan. Educ. Res. 2017, 37, 309–321. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, S. Urban greenway system design under “Integration” strategy: A case study in Shunyi District, Beijing. Urban Transp. China 2012, 10, 7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, F.; Nie, R.; Zhang, J.E. Greenway implementation influence on Agricultural Heritage Sites (AHS): The case of Liantang Village of Zengcheng District, Guangzhou City, China. Sustainability 2018, 10, 434. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Baker, T. Ecology of greenways. Landsc. J. 1994, 13, 175. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kiel, B.E. Greenways in America: The Ecosystem Services of Urban Greenways and Their Neighborhood Benefits; Fordham University: Bronx, NY, USA, 2017. [Google Scholar]
- Larson, L.R.; Keith, S.J.; Fernandez, M.; Hallo, J.C.; Shafer, C.S.; Jennings, V. Ecosystem services and urban greenways: What’s the public’s perspective? Ecosyst. Serv. 2016, 22, 111–116. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yahner, T.G.; Korostoff, N.; Johnson, T.P.; Battaglia, A.M.; Jones, D.R. Cultural landscapes and landscape ecology in contemporary greenway planning, design and management: A case study. Landsc. Urban Plan. 1995, 33, 295–316. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xie, B.; Lu, Y.; Zheng, Y. Casual evaluation of the effects of a large-scale greenway intervention on physical and mental health: A natural experimental study in China. Urban For. Urban Green. 2022, 67, 127419. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, W.; Yang, J.; Ma, L.; Huang, C. Factors affecting the use of urban green spaces for physical activities: Views of young urban residents in Beijing. Urban For. Urban Green. 2015, 14, 851–857. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thompson, C.W.; Roe, J.; Aspinall, P.; Mitchell, R.; Clow, A.; Miller, D. More green space is linked to less stress in deprived communities: Evidence from salivary cortisol patterns. Landsc. Urban Plan. 2012, 105, 221–229. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Thompson, C.W.; Peter, A.; Jenny, R.; Lynette, R.; David, M. Mitigating stress and supporting health in deprived urban communities: The importance of green space and the social environment. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2016, 13, 440. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dallat, M.A.T.; Soerjomataram, I.; Hunter, R.F.; Tully, M.A.; Cairns, K.J.; Kee, F. Urban greenways have the potential to increase physical activity levels cost-effectively. Eur. J. Public Health 2013, 24, 190–195. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Tang, H.; Hong, Q.; Xu, B. Landscape performance assessment of phase I of greenway around Qingshan Lake National Forest Park, Zhejiang Province. J. Zhejiang AF Univ. 2020, 37, 1177–1185. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ortega, E.; Martín, B.; LóPez-Lambas, M.E.; Soria-Lara, J.A. Evaluating the impact of urban design scenarios on walking accessibility: The case of the Madrid ‘Centro’ district. Sustain. Cities Soc. 2021, 74, 103156. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xia, N.; Cheng, L.; Chen, S.; Wei, X.; Zong, W.; Li, M. Accessibility based on Gravity-Radiation model and Google Maps API: A case study in Australia. J. Transp. Geogr. 2018, 72, 178–190. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Southworth, M. Designing the walkable city. J. Urban Plann. Dev. 2005, 131, 246–257. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, L.; Dong, C. Research on park layout and accessibility of Nanjing main urban area based on GIS technology. Landsc. Archit. 2019, 12, 69–75. [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, X.; Melbourne, S.; Sarkar, C.; Chiaradia, A.; Webster, C. Effects of green space on walking: Does size, shape and density matter? Urban Stud. 2020, 57, 3402–3420. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, N.; Liu, Z.; Lin, Y.; De Meulder, B. User, public, and professional perceptions of the greenways in the Pearl River Delta, China. Sustainability 2019, 11, 7211. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Wu, J. Post occupancy evaluation (POE) on the Zengcheng Greenway System in Guangdong Province. Chin. Landsc. Architect. 2011, 27, 39–43. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Keith, S.J.; Boley, B.B. Importance-performance analysis of local resident greenway users: Findings from three Atlanta BeltLine Neighborhoods. Urban For. Urban Green. 2019, 44, 126426. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Žlender, V.; Ward Thompson, C. Accessibility and use of peri-urban green space for inner-city dwellers: A comparative study. Landsc. Urban Plan. 2017, 165, 193–205. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Jenny, R.; Peter, A.; Thompson, C.W. Understanding relationships between health, ethnicity, place and the role of urban green space in deprived urban communities. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2016, 13, 681. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Millington, C.; Ward Thompson, C.; Rowe, D.; Aspinall, P.; Fitzsimons, C.; Nelson, N.; Mutrie, N. Development of the Scottish Walkability Assessment Tool (SWAT). Health Place 2009, 15, 474–481. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Martilla, J.A.; James, J.C. Importance-performance analysis. J. Mark. 1977, 41, 77–79. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qin, J.; Zhou, X.; Sun, C.; Leng, H.; Lian, Z. Influence of green spaces on environmental satisfaction and physiological status of urban residents. Urban For. Urban Green. 2013, 12, 490–497. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fletcher, J.E.; Kaiser, R.A.; Groger, S. An assessment of the importance and performance of park impact fees in funding park and recreation infrastructure. J. Park Recreat. Adm. 1992, 10, 75–87. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, B.; Wu, G.; Ma, J. Strategy of landscape ecological restoration of Xi’an Jiangcungou Landfill Site based on IPA analysis. Chin. Landsc. Architect. 2020, 36, 68–72. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xiong, C.; Tang, H.; Xu, B.; Hong, Q. Using characteristics and satisfaction of country greenway. J. Zhejiang AF Univ. 2019, 36, 154–161. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- O’Sullivan, D.; Morrison, A.; Shearer, J. Using desktop GIS for the investigation of accessibility by public transport: An isochrone approach. Int. J. Geogr. Inf. Sci. 2000, 14, 85–104. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, Z.; Jin, F. Scope, shape, and structural characteristics of traffic circles of equal travel time in Beijing. Prog. Geogr. 2016, 35, 389–398. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Yang, Y.; Li, J.; Huang, Q.; Xia, J.; Li, J.; Liu, D.; Tan, Q. Performance assessment of sponge city infrastructure on stormwater outflows using isochrone and SWMM models. J. Hydrol. 2021, 597, 126151. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Śleszyński, P.; Olszewski, P.; Dybicz, T.; Goch, K.; Niedzielski, M.A. The ideal isochrone: Assessing the efficiency of transport systems. Res. Transp. Bus. Manag. 2022, 100779. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kolcsár, R.; Szilassi, P. Assessing accessibility of urban green spaces based on isochrone maps and street resolution population data through the example of Zalaegerszeg, Hungary. Carpath. J. Earth Env. 2018, 13, 31–36. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Wolff, D.L.; Fitzhugh, E.C.; Bassett, D.R.; Cherry, C.R. Greenway siting and design: Relationships with physical activity behaviors and user characteristics. J. Phys. Act. Health 2014, 11, 1105. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Akpinar, A. Factors influencing the use of urban greenways: A case study of Aydın, Turkey. Urban For. Urban Green. 2016, 16, 123–131. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, J.; Lee, H.-S.; Jeong, D.; Shafer, C.S.; Chon, J. The relationship between user perception and preference of greenway trail characteristics in urban areas. Sustainability 2019, 11, 4438. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Le, N.D.; Zidek, J.V. Statistical Analysis of Environmental Space-Time Processes; Springer Science & Business Media: New York, NY, USA, 2006. [Google Scholar]
- Oliver, M.A.; Webster, R. Kriging: A method of interpolation for geographical information systems. ISPRS Int. J. Geoinf. 1990, 4, 313–332. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Helms, J.E.; Henze, K.T.; Sass, T.L.; Mifsud, V.A. Treating Cronbach’s Alpha reliability coefficients as data in counseling research. Couns. Psychol. 2006, 34, 630–660. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, M.; Han, C.; Guan, Q.; Huang, Y.; Xie, Z. A universal parallel scheduling approach to polyline and polygon vector data buffer analysis on conventional GIS platforms. Trans. GIS 2020, 24, 1630–1654. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Browning, M.; Lee, K. Within what distance does “Greenness” best predict physical health? A systematic review of articles with GIS buffer analyses across the Lifespan. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2017, 14, 675. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Melicher, J.; Špulerová, J. Application of landscape-ecological approach for greenways planning in rural agricultural landscape. Environments 2022, 9, 30. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Carlier, J.; Moran, J. Landscape typology and ecological connectivity assessment to inform Greenway design. Sci. Total Environ. 2019, 651, 3241–3252. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fňukalová, E.; Zýka, V.; Romportl, D. The network of green infrastructure based on ecosystem services supply in Central Europe. Land 2021, 10, 592. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, X.; Jiang, B.; Chen, M.; Bai, Y.; Yang, G. Strengthening the effectiveness of nature reserves in representing ecosystem services: The Yangtze River Economic Belt in China. Land Use Policy 2020, 96, 104717. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dang, H.; Li, J.; Zhang, Y.; Zhou, Z. Evaluation of the equity and regional management of some urban green space ecosystem services: A case study of main urban area of Xi’an City. Forests 2021, 12, 813. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Coutts, C. Multiple case studies of the influence of land-usetype on the distribution of uses along urban river greenways. J. Urban Plan. Dev. 2009, 135, 31–38. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Keith, S.J.; Larson, L.R.; Shafer, C.S.; Hallo, J.C.; Fernandez, M. Greenway use and preferences in diverse urban communities: Implications for trail design and management. Landsc. Urban Plan. 2018, 172, 47–59. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- James, P.; Banay, R.F.; Hart, J.E.; Laden, F. A review of the health benefits of greenness. Curr. Epidemiol. Rep. 2015, 2, 131–142. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Dorwart, C.E. Views from the path: Evaluating physical activity use patterns and design preferences of older adults on the Bolin Creek Greenway Trail. J. Aging Phys. Act. 2015, 23, 513–523. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chi, W.; Lin, G. The use of community greenways: A case study on a linear greenway space in high dense residential areas, Guangzhou. Land 2019, 8, 188. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Zhou, Y. Multiple functional greenway network planning: A case study in Shenzhen. Urban Transp. China 2012, 10, 24–29. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- West, S.T.; Shores, K.A. The impacts of building a greenway on proximate residents’ physical activity. J. Phys. Act. Health 2011, 8, 1092–1097. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- West, S.T.; Shores, K.A. Does building a greenway promote physical activity among proximate residents? J. Phys. Act. Health 2015, 12, 52–57. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xie, B.; Lu, Y.; Wu, L.; An, Z. Dose-response effect of a large-scale greenway intervention on physical activities: The first natural experimental study in China. Health Place 2021, 67, 102502. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, M.; Ding, L.; Kou, H.; Tan, S.; Long, H. Effects and environmental features of Mountainous Urban Greenways (MUGs) on physical activity. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2021, 18, 8696. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chang, P. Effects of the built and social features of urban greenways on the outdoor activity of older adults. Landsc. Urban Plan. 2020, 204, 103929. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Luo, P.; Miao, Y.; Zhao, J. Effects of auditory-visual combinations on students’ perceived safety of urban green spaces during the evening. Urban For. Urban Green. 2021, 58, 126904. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- South, E.C.; Kondo, M.C.; Cheney, R.A.; Branas, C.C. Neighborhood blight, stress, and health: A walking trial of urban greening and ambulatory heart rate. Am. J. Public Health 2015, 105, 909–913. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ahn, H.; Lee, J.; Hong, A. Does urban greenway design affect air pollution exposure? A case study of Seoul, South Korea. Sustain. Cities Soc. 2021, 72, 103038. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, X. The practice of environment design for public fitness in greenway—Taking the greenway around the Century Park in Shanghai as the example. Chin. Landsc. Archit. 2019, 35, 98–102. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cahyani; Hamzah, B.; Syarif, E. Greenway model as a support of Makassar smart city. IOP Conf. Ser. Earth Environ. Sci. 2020, 473, 012121. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chi, W.; Lin, G. A study on community greenways of Haizhu in Guangzhou from the perspective of Everyday Urbanism. In Proceedings of the Fábos Conference on Landscape and Greenway Planning, Amherst, MA, USA, 28–30 March 2019. [Google Scholar]
- Lim, Y.; Im, D.-U.; Lee, J. Promoting the sustainability of city communities through ‘Voluntary Arts Activities’ at regenerated cultural arts spaces: A focus on the combination of the ‘Democratization of Culture’ and ‘Cultural Democracy’ perspectives. Sustainability 2019, 11, 4400. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Cheng, C.; Randhir, T.O. A sustainability evaluation and dynamic modeling tool for landscape and urban planning policy scenarios. In Proceedings of the Fábos Conference on Landscape and Greenway Planning, Budapest, Hungary, 8–11 July 2010; Volume 3. [Google Scholar]
- Gábor, P. AngelGREEN: Green network development strategy of the 13th district of Budapest. In Proceedings of the Fábos Conference on Landscape and Greenway Planning, Budapest, Hungary, 8–11 July 2010; Volume 3. [Google Scholar]
- Boone-Heinonen, J.; Casanova, K.; Richardson, A.S.; Gordon-Larsen, P. Where can they play? Outdoor spaces and physical activity among adolescents in U.S. urbanized areas. Prev. Med. 2010, 51, 295–298. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Van Hecke, L.; Ghekiere, A.; Van Cauwenberg, J.; Veitch, J.; De Bourdeaudhuij, I.; Van Dyck, D.; Clarys, P.; Van De Weghe, N.; Deforche, B. Park characteristics preferred for adolescent park visitation and physical activity: A choice-based conjoint analysis using manipulated photographs. Landsc. Urban Plan. 2018, 178, 144–155. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
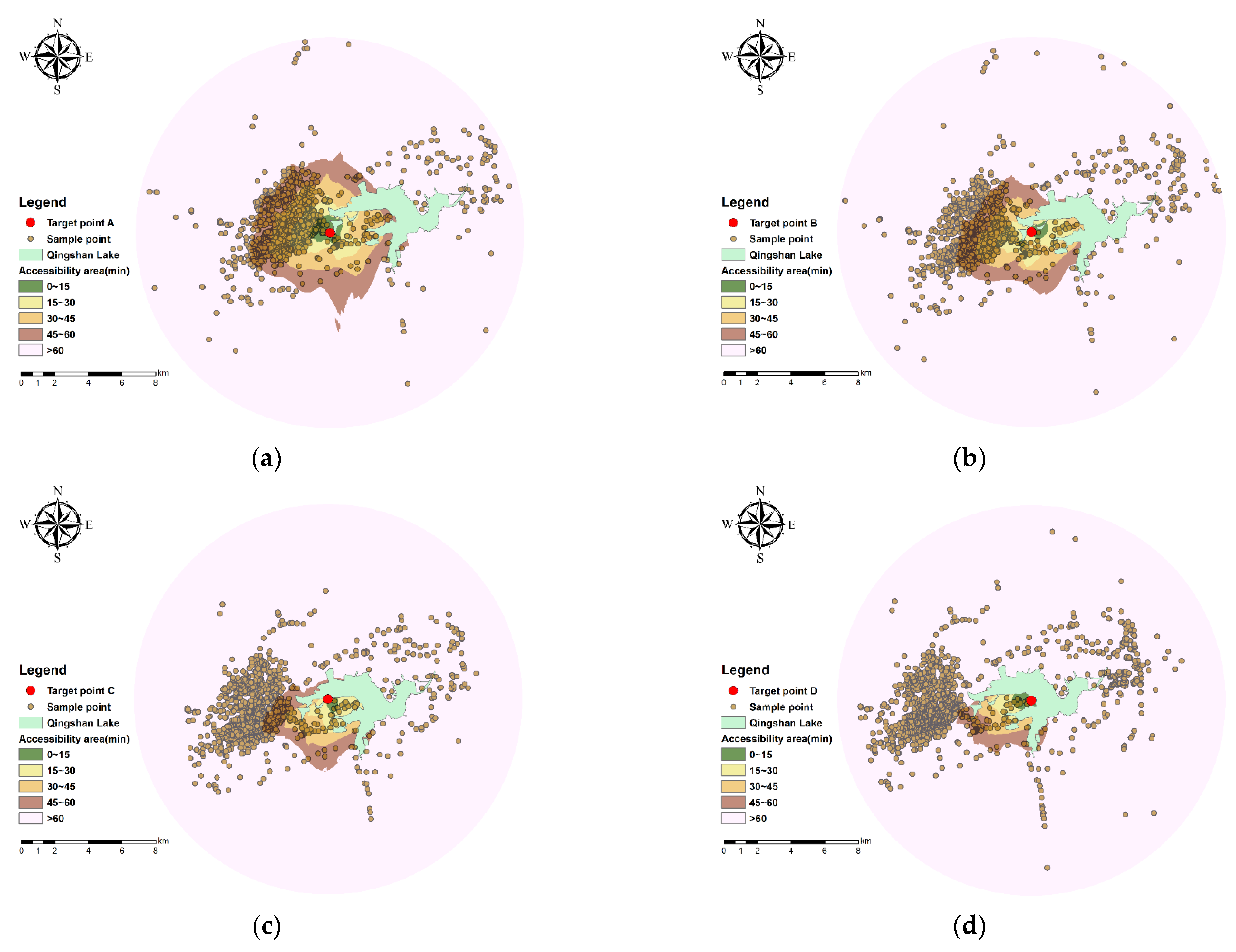
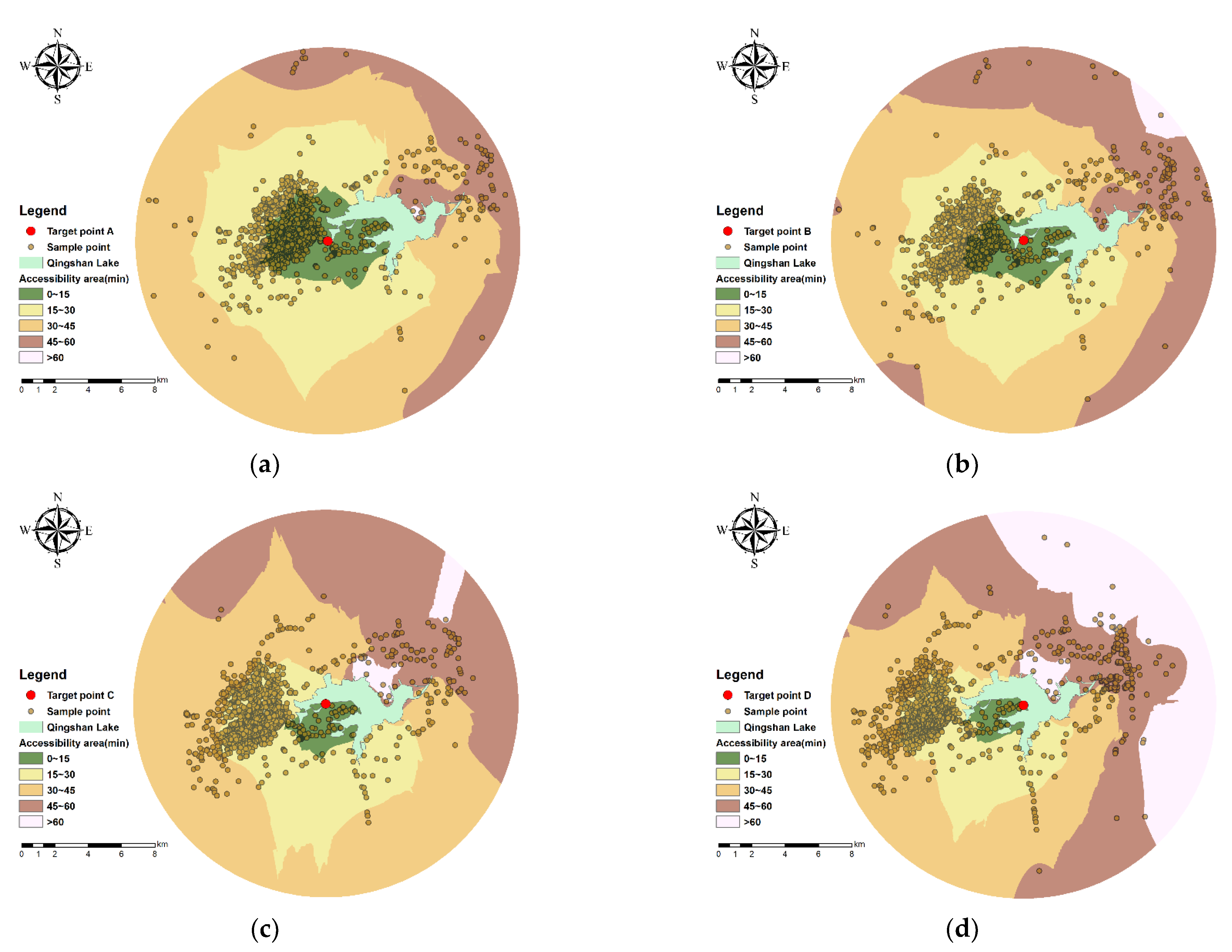

| Target Point Name | Number of Sample Points in the Buffer | Walking | Cycling | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| S (km2) | n | S (km2) | n | ||
| A | 1622 | 2.18 | 90 | 29.13 | 1175 |
| B | 1689 | 0.84 | 8 | 17.74 | 700 |
| C | 1596 | 0.55 | 5 | 8.7 | 150 |
| D | 1592 | 0.93 | 15 | 5.78 | 48 |
| Total (de-duplication) | 2116 | 4.35 | 113 | 29.21 | 1175 |
| Category | Percentage (%) | Category | Percentage (%) | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Gender | Female | 51.2 | Frequency of Use | Every day | 24.9 |
| Male | 48.8 | Multiple times a week | 37.8 | ||
| Age Group | <18 | 1.0 | Once a week | 14.9 | |
| 18–35 | 49.3 | Once a month | 11.4 | ||
| 36–55 | 36.3 | Less than once a month | 10.9 | ||
| >55 | 13.4 | Transportation | Walking | 50.2 | |
| Residence | Around the greenway | 42.8 | Cycling | 27.9 | |
| Downtown | 45.8 | Public transit | 4.5 | ||
| Outside of the Lin’an District, in downtown Hangzhou | 7.5 | Driving | 17.4 | ||
| Outside of Hangzhou city and other areas within Zhejiang Province | 2.5 | Time Period of Use | Before 7:00 | 8.0 | |
| Outside of Zhejiang Province | 1.5 | 7:00–9:00 | 33.3 | ||
| 9:00–13:00 | 6.0 | ||||
| 13:00–17:00 | 5.5 | ||||
| 17:00–20:00 | 46.3 | ||||
| After 20:00 | 1.0 |
| Q: Do You Think You Need Physical Exercise? | Exercise Very Necessary | Necessary | Comparatively Necessary | Normal | No Need |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Frequency | 68 | 96 | 19 | 15 | 3 |
| Percentage (%) | 33.8 | 47.8 | 9.5 | 7.5 | 1.5 |
| Classification | Specific Contents | Percentage (%) |
|---|---|---|
| Physical exercise | Walking, running, cycling, and yoga | 40.8 |
| Social interaction | Chatting, parties, team activities, and playing with children | 8.1 |
| Entertainment and leisure | Hanging out, walking the dog, fishing, taking pictures, picnicking, and taking a nap | 15.3 |
| Natural experience | Enjoying the sunset, listening to the calls of insects and birds, and smelling the fragrance of flowers | 28.1 |
| Others | Traffic, maintenance, work, study, and inspection | 7.8 |
| Category | Health-Promoting Behaviours | Fisher’s Exact Probability Method Test Value | p Value | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Physical Exercise | Social Interaction | Entertainment and Leisure | Natural Experience | ||||
| Gender | Female | 79 (43.4%) | 17 (9.3%) | 34 (18.7%) | 52 (28.6%) | 1.595 | 0.665 |
| Male | 78 (45.1%) | 14 (8.1%) | 25 (14.5%) | 56 (32.4%) | |||
| Age Group | <35 | 79 (43.2%) | 16 (8.7%) | 32 (17.5%) | 56 (30.6%) | 2.333 | 0.893 |
| 36–55 | 57 (46.0%) | 10 (8.1%) | 22 (17.7%) | 35 (28.2%) | |||
| >55 | 21 (43.8%) | 5 (10.4%) | 5 (10.4%) | 17 (35.4%) | |||
| Residence | Around the greenway | 75 (47.5%) | 12 (7.6%) | 26 (16.5%) | 45 (28.5%) | 12.575 | 0.045 1 |
| Downtown | 66 (41.3%) | 17 (10.6%) | 29 (18.1%) | 48 (30.0%) | |||
| Outside downtown | 6 (18.2%) | 2 (6.1%) | 8 (24.2%) | 17 (51.5%) | |||
| Evaluation Factors | Index Factors | Importance Perception | Satisfaction Evaluation | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Average ± Standard Deviation | Overall Average | Average ± Standard Deviation | Overall Average | ||
| Road quality | S1 Width | 4.22 ± 0.62 | 4.43 | 4.02 ± 0.61 | 3.94 |
| S2 Comfort of pavement for people | 4.57 ± 0.58 | 4.21 ± 0.61 | |||
| S3 Connectivity with other branches | 4.19 ± 0.67 | 4.02 ± 0.61 | |||
| S4 Protective fence | 4.64 ± 0.62 | 3.74 ± 0.86 | |||
| S5 Wheelchair accessible | 4.55 ± 0.66 | 3.73 ± 0.90 | |||
| Supporting facilities | S6 Signage system | 4.30 ± 0.69 | 4.11 | 4.02 ± 0.70 | 3.46 |
| S7 Parking lot | 3.96 ± 0.76 | 2.99 ± 1.08 | |||
| S8 Lighting system | 4.34 ± 0.67 | 3.79 ± 0.74 | |||
| S9 Commercial service facilities | 3.80 ± 0.74 | 3.36 ± 0.78 | |||
| S10 Public health | 4.16 ± 0.66 | 3.16 ± 1.02 | |||
| Natural environment | S11 Terrain diversity | 4.35 ± 0.72 | 4.37 | 4.24 ± 0.57 | 4.33 |
| S12 Colourful plant landscape | 4.50 ± 0.67 | 4.39 ± 0.64 | |||
| S13 Scenery line | 4.30 ± 0.74 | 4.35 ± 0.59 | |||
| S14 Meteorological landscape | 4.36 ± 0.72 | 4.36 ± 0.62 | |||
| S15 Biological landscape | 4.32 ± 0.69 | 4.30 ± 0.64 | |||
| Regional cultural characteristics | S16 Greenway theme reflects | 4.05 ± 0.77 | 3.63 | 4.19 ± 0.56 | 4.08 |
| S17 Historical allusions | 3.63 ± 0.97 | 4.13 ± 0.66 | |||
| S18 Traditional construction techniques | 3.25 ± 1.11 | 3.98 ± 0.68 | |||
| S19 Application of local materials | 3.19 ± 1.15 | 4.00 ± 0.64 | |||
| S20 Sense of belonging | 4.01 ± 0.76 | 4.11 ± 0.67 | |||
| Management and maintenance | S21 Cleanliness | 4.58 ± 0.60 | 4.47 | 3.53 ± 1.02 | 3.83 |
| S22 Security guards patrol | 4.52 ± 0.60 | 3.73 ± 0.82 | |||
| S23 The facilities are fully equipped | 4.34 ± 0.67 | 3.99 ± 0.73 | |||
| S24 Plant conservation | 4.35 ± 0.67 | 4.14 ± 0.67 | |||
| S25 Fire safety | 4.57 ± 0.61 | 3.75 ± 0.98 | |||
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Xu, B.; Shi, Q.; Zhang, Y. Evaluation of the Health Promotion Capabilities of Greenway Trails: A Case Study in Hangzhou, China. Land 2022, 11, 547. https://doi.org/10.3390/land11040547
Xu B, Shi Q, Zhang Y. Evaluation of the Health Promotion Capabilities of Greenway Trails: A Case Study in Hangzhou, China. Land. 2022; 11(4):547. https://doi.org/10.3390/land11040547
Chicago/Turabian StyleXu, Bin, Qingxia Shi, and Yaping Zhang. 2022. "Evaluation of the Health Promotion Capabilities of Greenway Trails: A Case Study in Hangzhou, China" Land 11, no. 4: 547. https://doi.org/10.3390/land11040547
APA StyleXu, B., Shi, Q., & Zhang, Y. (2022). Evaluation of the Health Promotion Capabilities of Greenway Trails: A Case Study in Hangzhou, China. Land, 11(4), 547. https://doi.org/10.3390/land11040547






