Community Participation Strategy for Sustainable Urban Regeneration in Xiamen, China
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Literature Review
2.1. Urban Regeneration and Sustainable Urban Development
2.2. Community Regeneration and Community Participation
3. Research Methodology
4. Reproducing Community Revitalization for Urban Regeneration in China
4.1. Transition Period in Urban Regeneration
4.1.1. Location of Xiamen
4.1.2. Challenges to Xiamen’s Urban Development
4.2. Utilizing Community Public Participation for Rural Regeneration in Zengcuoan
4.2.1. Location of the Village
4.2.2. Overview of the Stages of Development in Zengcuoan
The Stages of Development as a Traditional Fishing Village
Stages of Development in Cultural and Creative Fishing Villages
4.3. Utilizing Collaborative Workshops for Reproducing Community Vitality
4.3.1. Challenges and Difficulties in the Development of Zengcuoan
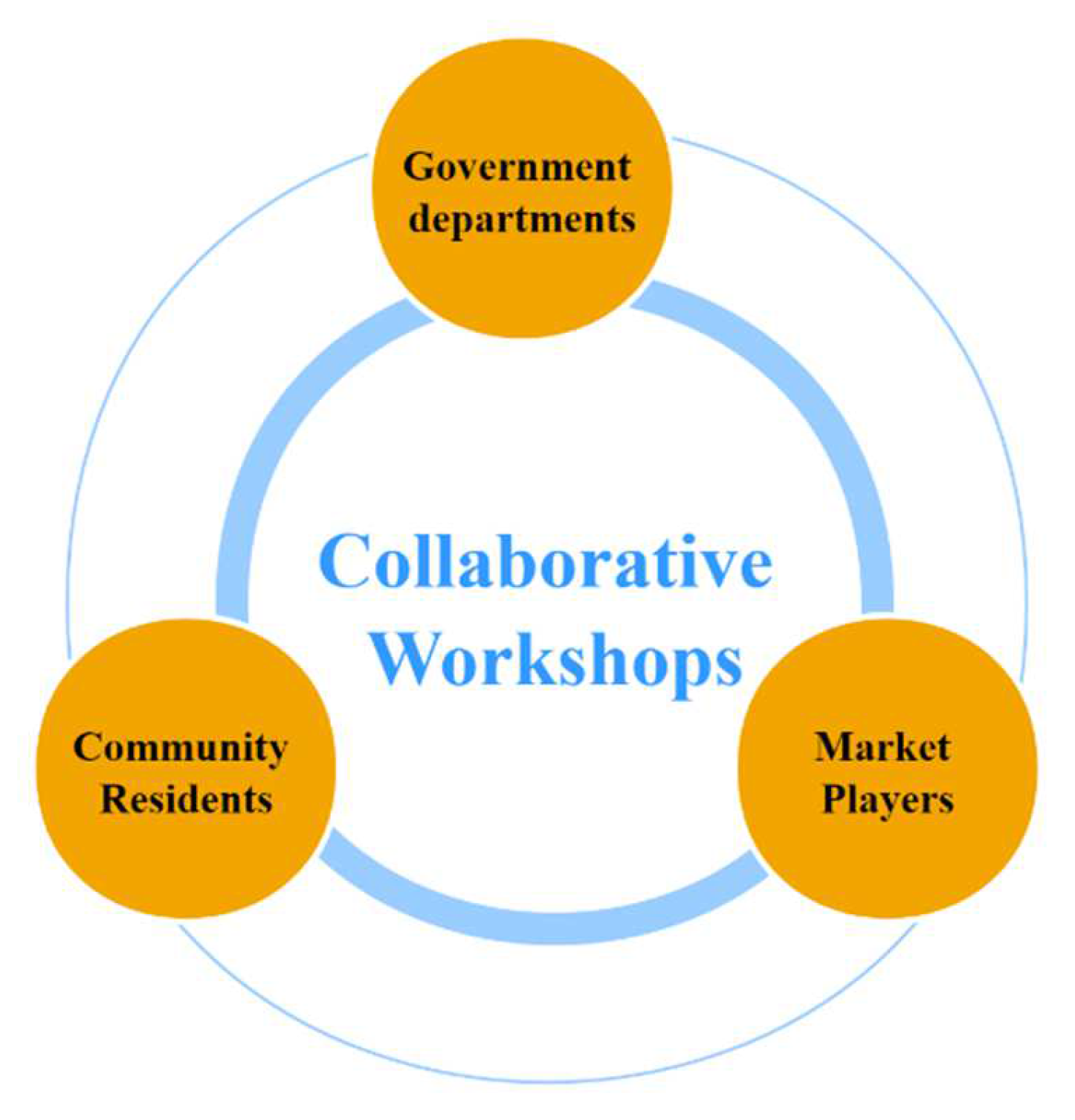
4.3.2. Collaborative Workshops for Community Participation
5. Discussion and Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Zheng, H.W.; Shen, G.Q.; Wang, H. A review of recent studies on sustainable urban renewal. Habitat Int. 2014, 41, 272–279. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Yang, L.; Ao, Y.; Ke, J.; Lu, Y.; Liang, Y. To walk or not to walk? Examining non-linear effects of streetscape greenery on walking propensity of older adults. J. Transp. Geogr. 2021, 94, 103099. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- He, B.-J.; Ding, L.; Prasad, D. Relationships among local-scale urban morphology, urban ventilation, urban heat island and outdoor thermal comfort under sea breeze influence. Sustain. Cities Soc. 2020, 60, 102289. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tan, Y.; Xu, H.; Zhang, X. Sustainable urbanization in China: A comprehensive literature review. Cities 2016, 55, 82–93. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, X.; Chan, C.K.C.; Yang, L. Economic restructuring and migrant workers’ coping strategies in China’s Pearl River Delta. Third World Q. 2021, 42, 812–830. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sharifi, A. Urban sustainability assessment: An overview and bibliometric analysis. Ecol. Indic. 2021, 121, 107102. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, L.; Zheng, W.; Hong, J.; Liu, Y.; Liu, G. Paths and strategies for sustainable urban renewal at the neighborhood level: A framework for decision-making. Sustain. Cities Soc. 2020, 55, 102074. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, Y.; Lan, F.; Zhou, T. An experience-based mining approach to supporting urban renewal mode decisions under a multi-stakeholder environment in China. Land Use Policy 2021, 106, 105428. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Valeriu, I.; Ristea, A. Commercial facilities and urban regeneration. Amfiteatru Econ. J. 2010, 12, 99–114. [Google Scholar]
- Chiesura, A. The role of urban parks for the sustainable city. Landsc. Urban Plan. 2004, 68, 129–138. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Adams, D.; Hastings, E.M. Urban renewal in Hong Kong: Transition from development corporation to renewal authority. Land Use Policy 2001, 18, 245–258. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abu-Dayyeh, N. Prospects for historic neighborhoods in atypical Islamic cities: The view from Amman, Jordan. Habitat Int. 2006, 30, 46–60. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Q. Resilience thinking as a system approach to promote China’s sustainability transitions. Sustainability 2020, 12, 5008. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Boyko, C.T.; Gaterell, M.R.; Barber, A.R.; Brown, J.; Bryson, J.R.; Butler, D.; Caputo, S.; Caserio, M.; Coles, R.; Cooper, R.; et al. Benchmarking sustainability in cities: The role of indicators and future scenarios. Glob. Environ. Chang. 2012, 22, 245–254. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brinkerhoff, J.M. Government-nonprofit partnership: A defining framework. Public Adm. Dev. 2002, 22, 19–30. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bromley, R.D.; Tallon, A.R.; Thomas, C.J. City centre regeneration through residential development: Contributing to sustainability. Urban Stud. 2005, 42, 2407–2429. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bryson, J.R.; Lombardi, R. Balancing product and process sustainability against business profitability: Sustainability as a competitive strategy in the property development process. Bus. Strategy Environ. 2010, 18, 97–107. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bügl, R.; Stauffacher, M.; Kriese, U.; Pollheimer, D.L.; Scholz, R.W. Identifying stakeholders’ views on sustainable urban transition: Desirability, utility and probability assessments of scenarios. Eur. Plan. Stud. 2012, 20, 1667–1687. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Couch, C.; Dennemann, A. Urban regeneration and sustainable development in Britain. Cities 2000, 17, 137–147. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Couch, C.; Sykes, O.; Borstinghaus, W. Thirty years of urban regeneration in Britain, Germany and France: The importance of context and path dependency. Prog. Plan. 2011, 75 Pt 1, 1–52. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hastings, A. Unravelling the process of ’partnership‘ in urban regeneration policy. Urban Stud. 1996, 33, 253–268. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gotham, K.F. Growth machine up-links: Urban renewal and the rise and fall of a pro-growth coalition in a US city. Crit. Sociol. 2000, 26, 268–300. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, J.; He, Z.; Ma, H. Comparison of collective-led and state-led land development in china from the perspective of institutional arrangements: The case of Guangzhou. Land 2022, 11, 226. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, W.; Zhang, X.; Wu, G. The network governance of urban renewal: A comparative analysis of two cities in China. Land Use Policy 2021, 106, 105448. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Turcu, C. Local experiences of urban sustainability: Researching Housing Market Renewal interventions in three English neighbourhoods. Prog. Plan. 2012, 78, 101–150. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Liu, G.; Chen, S.; Gu, J. Urban renewal simulation with spatial, economic and policy dynamics: The rent-gap theory-based model and the case study of Chongqing. Land Use Policy 2019, 86, 238–252. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, H.; Yang, J.; Li, T.; Jin, Y.; Sun, D. Morphological and functional polycentric structure assessment of megacity: An integrated approach with spatial distribution and interaction. Sustain. Cities Soc. 2022, 80, 103800. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xie, P.; Yang, J.; Sun, W.; Xiao, X.; Xia, J.C. Urban scale ventilation analysis based on neighborhood normalized current model. Sustain. Cities Soc. 2022, 80, 103746. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pan, W.; Du, J. Towards sustainable urban transition: A critical review of strategies and policies of urban village renewal in Shenzhen, China. Land Use Policy 2021, 111, 105744. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lai, Y.; Jiang, L.; Xu, X. Exploring spatio-temporal patterns of urban village redevelopment: The case of Shenzhen, China. Land 2021, 10, 976. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Smith, R.W. A theoretical basis for participatory planning. Policy Sci. 1973, 4, 275–295. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cilliers, E.J.; Timmermans, W. The importance of creative participatory planning in the public place-making process. Environ. Plan. B Plan. Des. 2014, 41, 413–429. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Legacy, C. Is there a crisis of participatory planning? Plan. Theory 2017, 16, 425–442. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Szetey, K.; Moallemi, E.; Ashton, E.; Butcher, M.; Sprunt, B.; Bryan, B. Participatory planning for local sustainability guided by the Sustainable Development Goals. Ecol. Soc. 2021, 26, 16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Salter, J.D.; Campbell, C.; Journeay, M.; Sheppard, S.R. The digital workshop: Exploring the use of interactive and immersive visualisation tools in participatory planning. J. Environ. Manag. 2009, 90, 2090–2101. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cao, Y.; Tang, X. Evaluating the Effectiveness of Community Public Open Space Renewal: A Case Study of the Ruijin Community, Shanghai. Land 2022, 11, 476. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Z.; Xiang, S.; Zhu, J.; Guo, S. The method and practice of street renewal based on innovative design thinking. J. Landsc. Res. 2020, 12, 23–27. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, X.; Aoki, N. Paradox between neoliberal urban redevelopment, heritage conservation, and community needs: Case study of a historic neighbourhood in Tianjin, China. Cities 2019, 85, 156–169. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nasca, T.F.; Changfoot, N.; Hill, S.D. Participatory planning in a low-income neighbourhood in Ontario, Canada: Building capacity and collaborative interactions for influence. Community Dev. J. 2019, 54, 622–642. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Natarajan, L.; Lock, S.J.; Rydin, Y.; Lee, M. Participatory planning and major infrastructure: Experiences in REI NSIP regulation. Town Plan. Rev. 2019, 90, 117–139. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Katsui, H.; Koistinen, M. The participatory research approach in non-Western countries: Practical experiences from Central Asia and Zambia. Disabil. Soc. 2008, 23, 747–757. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, J.; Yang, X.; Wang, H. Age-friendly regeneration of urban settlements in China: Game and incentives of stakeholders in decision-making. Land Use Policy 2021, 111, 105745. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Y.; Fan, P.; Liu, Y. What makes better village development in traditional agricultural areas of China? Evidence from long-term observation of typical villages. Habitat Int. 2019, 83, 111–124. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, J.; Krishnamurthy, S.; Roders, A.P.; Van Wesemael, P. Community participation in cultural heritage management: A systematic literature review comparing Chinese and international practices. Cities 2020, 96, 102476. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, X.; Chen, W.; Cundy, A.B.; Chang, A.C.; Jiao, W. Analysis of influencing factors on public perception in contaminated site management: Simulation by structural equation modeling at four sites in China. J. Environ. Manag. 2018, 210, 299–306. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Yang, J.; Yang, R.; Chen, M.H.; Su, C.H.; Zhi, Y.; Xi, J. Effects of rural revitalization on rural tourism. J. Hosp. Tour. Manag. 2021, 47, 35–45. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Warburton, D. Community and Sustainable Development: Participation in the Future; Routledge: London, UK, 1998; pp. 1–276. [Google Scholar]
- Wondirad, A.; Ewnetu, B. Community participation in tourism development as a tool to foster sustainable land and resource use practices in a national park milieu. Land Use Policy 2019, 88, 104155. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cheng, T.M.; Wu, H.C.; Wang, J.T.; Wu, M.R. Community Participation as a mediating factor on residents’ attitudes towards sustainable tourism development and their personal environmentally responsible behaviour. Curr. Issues Tour. 2019, 22, 1764–1782. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rahman, M.K.; Masud, M.M.; Akhtar, R.; Hossain, M.M. Impact of community participation on sustainable development of marine protected areas: Assessment of ecotourism development. Int. J. Tour. Res. 2022, 24, 33–43. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]







Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Yang, J.; Yang, L.; Ma, H. Community Participation Strategy for Sustainable Urban Regeneration in Xiamen, China. Land 2022, 11, 600. https://doi.org/10.3390/land11050600
Yang J, Yang L, Ma H. Community Participation Strategy for Sustainable Urban Regeneration in Xiamen, China. Land. 2022; 11(5):600. https://doi.org/10.3390/land11050600
Chicago/Turabian StyleYang, Jinkun, Linchuan Yang, and Haitao Ma. 2022. "Community Participation Strategy for Sustainable Urban Regeneration in Xiamen, China" Land 11, no. 5: 600. https://doi.org/10.3390/land11050600
APA StyleYang, J., Yang, L., & Ma, H. (2022). Community Participation Strategy for Sustainable Urban Regeneration in Xiamen, China. Land, 11(5), 600. https://doi.org/10.3390/land11050600







