Abstract
Urban–rural land transition and the coordination of coupled human–environmental systems are two important issues in the process of global urban–rural development. Although existing studies have explored the coupling coordination degree (CCD) of human–environmental interactions under the context of urbanization, few studies have taken land transitions into consideration. In this study, we investigated the dynamics of CCD in China from 2001 to 2018 using multisource remote sensing data and quantified the CCD changes in land transitions among urban construction land (UCL), rural residential land (RRL), and non-construction land (NCL). The CCD alterations mainly occurred in the decline in NCL stock, the increase in UCL stock, and especially the losses during RRL to NCL transfers. We urge academics and government decision-makers to pay more attention to the CCD transfers and losses during urban–rural transitions. This study provides scientific guidance for the development of urban–rural integration and is expected to assist the coordinated evaluation of human–environmental interactions in the process of sustainable development.
1. Introduction
Coupled human–environmental systems are complex, dynamic, and interrelated systems with important feedback across social and natural components [1]. Since the entering of the Anthropocene, human activities have conversed with the biophysical environment. Rapid urbanization and industrialization have greatly benefited economic growth, poverty reduction, and the pursuit of human welfare [2,3]. Uncontrolled land expansion and resource consumption, however, have posed great challenges to biodiversity, climate change, and geological hazard [4,5,6]. The degradation and collapse of natural systems will limit and threaten the adaptability of human systems. Socioeconomic development and land expansion have direct and indirect feedback between natural resources and the environment, and they are intertwined in the coordination of human–environmental relationships [7,8]. The adaptability of human systems can be largely limited and threatened as environmental systems degrade and collapse. Humans should consciously utilize and rebuild the natural environment in accordance with natural laws [9]. The goal of coupled human–environmental systems is to achieve regional and global sustainable development by coordinating the human–environment interactions.
Land, as an important component of production and a space carrier, reflects the socio-economic activities and environmental changes that occur on it [10]. The vast majority of the Earth’s land surface can be considered rural, including residential, agricultural, and natural areas [11]. Rural areas are directly related to the global biodiversity, as well as a range of other environmental impacts. Urban areas, in contrast, occupy only a small part of the land surface, including both built-up and non-built-up land in urban areas. In addition, the vast majority of all economic activities take place in cities, and cities are responsible for more than 60% of the use of natural resources.
Urban–rural development and land transition is a complex mechanism, with strategies and factor transformation between urban and rural areas [12,13]. Socioeconomic development and political decision-making are often the main influencing factors that lead to land use changes, which in turn affects the development of urban and rural societies [14]. However, the rural degradation caused by the unequal migration of factors from rural to urban areas, resulting from the uncontrolled urban sprawl, must be addressed [15]. Urban–rural construction land expansion and the coordination of coupled human–environmental systems are two prominent factors of urban–rural transformations and development [16]. Therefore, it is very important to understand the change inhuman–environmental relationships under the urban–rural transfer.
As an international hotpot in the field of geoscience and sustainable development science, the interaction and coupling mechanism of human–environmental systems has made great progress [17,18,19]. The coupling coordination degree (CCD) model is widely used to evaluate the coordination of the human-environmental relationship. The coordinated development of the system refers to the harmonious and consistent development of its subsystems and the relationship between them, which can explain the sustainable development. More and more interdisciplinary projects have been integrating social and ecological sciences to analyze human–environmental interactions, including urbanization–environment [20,21], society–ecology [22], economy–energy–environment [23], etc. Liu et al. (2020) [19] propose a conceptual framework "Coupled Human and Natural Cube", providing a more comprehensive and systematic research paradigm for revealing the evolution and mechanism of human–environment systems. Most studies use statistical data as the input parameters of the model and construct the index system from the social economic system and resource environment system. However, the limitations of traditional methods are that they cannot reflect the pixel-level spatial information and the results are extremely uncertain. Furthermore, most research has taken multi study units such as cities, provinces, urban agglomerations and basins, focusing on the horizontal comparison between regions [24,25,26,27]. However, few studies pay attention to the dynamic changes in human–environmental relationships within cities.
The rapid development of remote sensing technologies and the popularity of open-access multisource products have greatly promoted Earth observation research on the regional/global scale by forming a rich remote sensing data cube [28]. Remote sensing data can directly reflect the dynamic structure formed by the interaction between human socioeconomic activities and the eco-environment in a specific area of the Earth’s surface [9]. Nighttime light (NTL) data has been widely used in a variety of applications that include identifying urban/rural areas, assessing the intensity of socioeconomic activity, to list a few [24,29,30]. Impervious surface areas (i.e., artificial surface) have been used to investigate the spatial–temporal changes in land entities [31,32]. Medium and high-resolution remote sensing images are valuable data sources that can be used to evaluate multi-dimensional eco-environmental assessments [33,34]. RS data can also facilitate our understanding of CHANS within and across scales due to its flexible spatiotemporal observation capability. Xu et al. (2021) [35] quantified the coupling mechanism of urban human–environment interactions; Tang et al. (2021) [20] assessed the local and tele-coupling coordination degree of urbanization and eco-environment via remote sensing data. In addition, multi-source remote sensing data has a good effect on evaluating urban development boundaries and observing urban expansion [36,37,38]. On the basis of existing research, this study aims to quantify the dynamic changes in human–environment relationships that occur throughout urban–rural land transitions within cities.
In this article, we intend to provide a novel bottom-up perspective on human–environmental interactions throughout land transitions, taking advantage of multi-source remote sensing data. Taking China as the study area, which is undergoing a critical stage of urban and rural development and reform [39]. The purpose of this work is to: (1) identify the land transitions and assess the human activity intensity; (2) evaluate the national spatio-temporal change in CCD between human activity intensity and regional eco-environment; and (3) investigate the CCD dynamics during land transitions, especially the increments and losses throughout the urban–rural transfer. The theoretical and methodological knowledge, as well as the results of this study, provide deep insights into the human–environmental interaction mechanism, greatly benefiting land-use management decision-making.
2. Study Area and Materials
2.1. Study Area
China is located on the northwest coast of the Pacific Ocean, comprising vast territory, rich natural resources, and various climate conditions [40]. As the largest developing country worldwide, China is experiencing rapid urbanization and urban–rural transformation while trying to adhere to the harmonious coexistence between humans and environments as the basic national strategy [41]. The urbanization rate increased from 10.64% in 1949 to 59.58% in 2018, with 774 million people migrating from rural regions to cities, resulting in the largest urban expansion in recorded human history [42,43]. China actively promotes the healthy and sustainable urbanization developing path that emphasizes the establishment of green, low-carbon, and high-efficiency new urbanization over the past 70 years [44,45]. China has undertaken a number of large environmental initiatives, including the preservation of natural forests and the conversion of cropland to forests and grasslands [46]. Two main strategies have been issued, i.e., the Beautiful China Initiative and Rural Revitalization Strategy, aiming to achieve human–environment harmony and the sustainable development of a thriving society [47].
2.2. Materials
In this study, we used three public remote sensing datasets; detailed descriptions can be found in Table 1. Considering the data quality and accessibility, the temporal coverage of selected data covers the years 2001, 2005, 2010, 2015, and 2018. Necessary preprocessing steps such as splicing and resampling were carried out. In addition, the vector data of the city boundaries were acquired from the National Catalogue Service.

Table 1.
Description of the data used in the study.
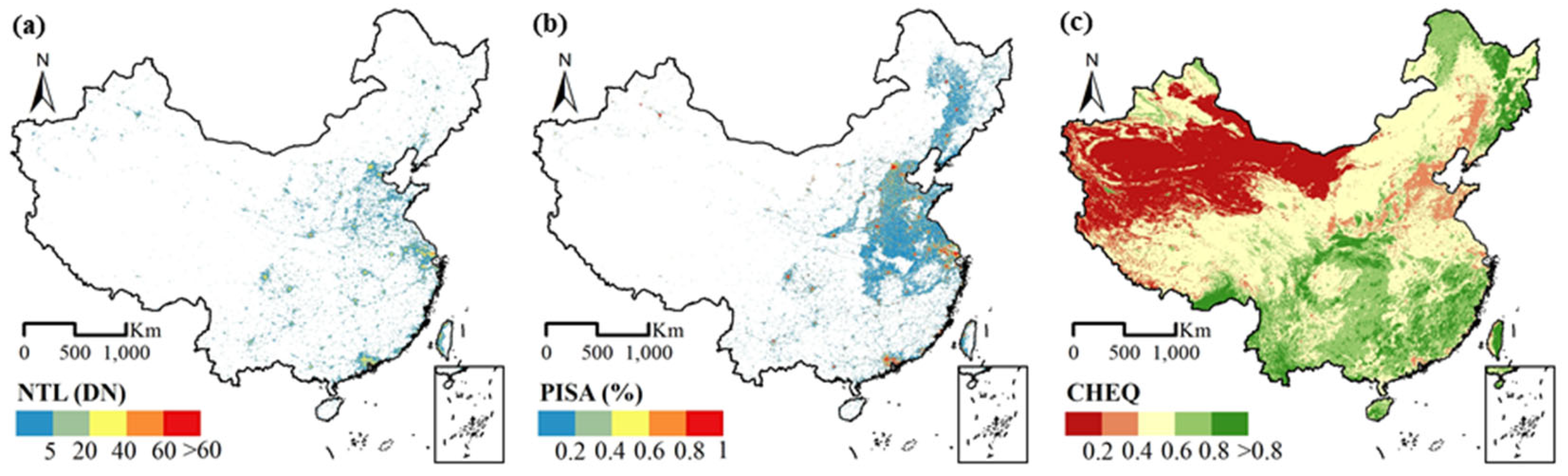
The NTL dataset was derived from Chen et al., (2021) [48], which is a harmonized global NTL dataset with a spatial resolution of 15 arc-seconds (approximately 500 m near the equator) and a temporal span from 1992 to 2018 using nW·cm−2·sr−1 as the unit (Figure 1a). This dataset was generated via cross-sensor calibration model and a modified self-encoder model with two datasets: DMSP/OLS data (2000–2012) and composited monthly NPP/VIIRS data (2013–2018). The derived dataset presented great accuracy, temporal consistency with reduced overflow effect.
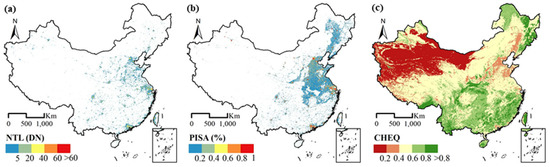
Figure 1.
The spatial distribution of (a) NTL, (b) PISA, and (c) CHEQ in the year 2018.
The GAIA mapped the dynamics global annual artificial impervious surface areas at 30m resolution from 1985 to 2018 using full archives of Landsat images with a consistent mapping approach [49]. The mean overall accuracy of GAIA is above 90% with temporally consistent urban expansion that ensures a monotonous manner from non-urban to urban areas. We aggregated the raw GAIA data to 1000 m in the form of the percentage of impervious surface area (PISA), as shown in Figure 1b.
The remote sensing monitoring data of regional eco-environment were obtained from CHEQ with the resolution of 1000 m, as shown in Figure 1c. The Remote Sensing Ecology Index (RSEI) is widely used as an eco-environment evaluation model, which includes four dimensions, i.e., heat, greenness, dryness, and wetness [50]. CHEQ added an abundance index to the RSEI model to improve underestimation. CHEQ is an environmental evaluation index provided by the official government; thus, with great consistency throughout the nation.
3. Methods
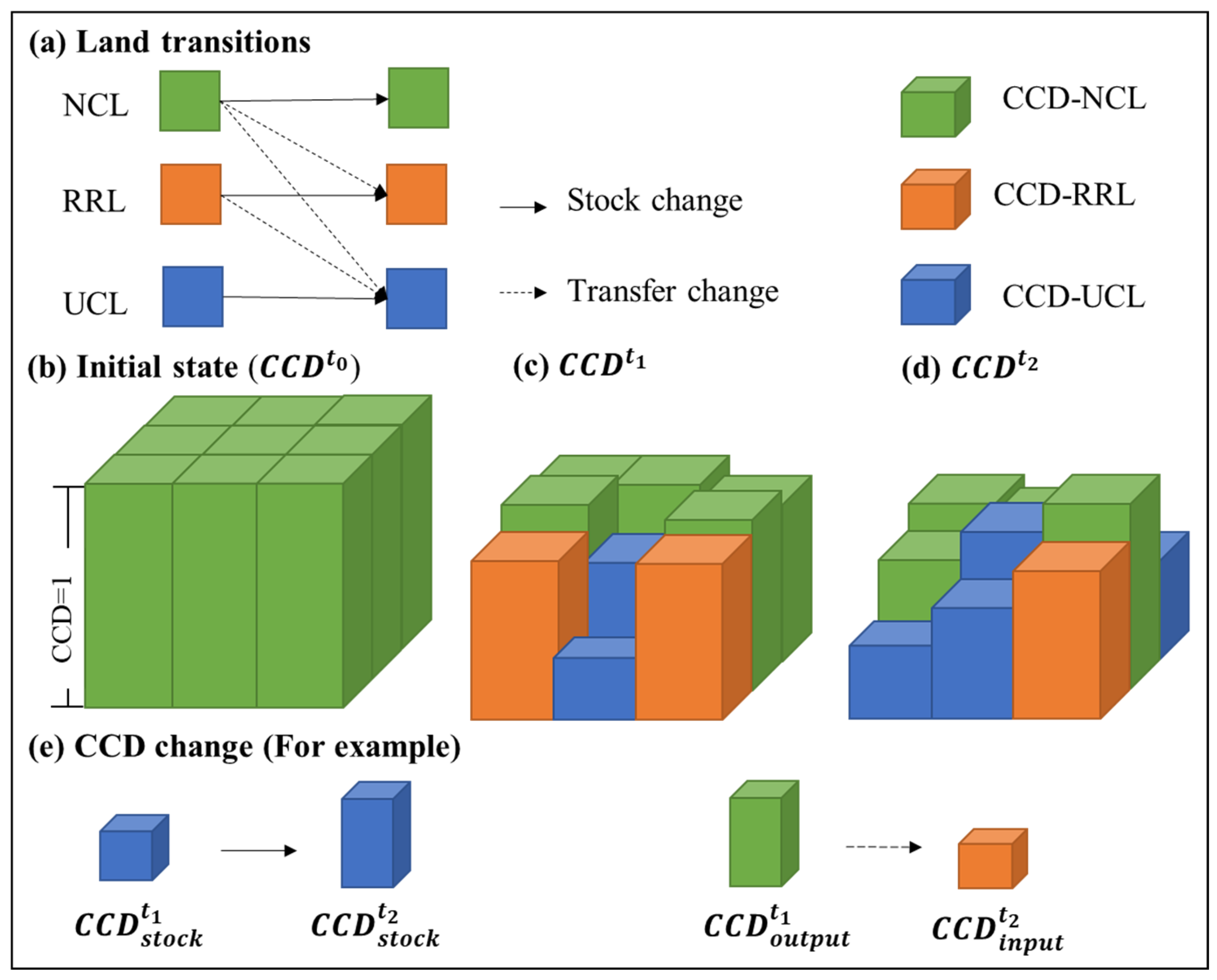
This study quantifies the dynamic process of CHANS from the perspective of urban–rural land transitions. Coupling coordination degree (CCD) is used to evaluate the coordination of CHANS. The conceptual pixel-wise model is shown in Figure 2. The detailed steps are as follows: (1) identifying the spatial patterns of urban construction land (UCL), rural residential land (RRL), and non-construction land (NCL); (2) calculating human activity intensity on UCL and RRL; (3) deriving the CCD between human activity intensity and regional eco-environment; and (4) quantifying CCD dynamics in land transitions.
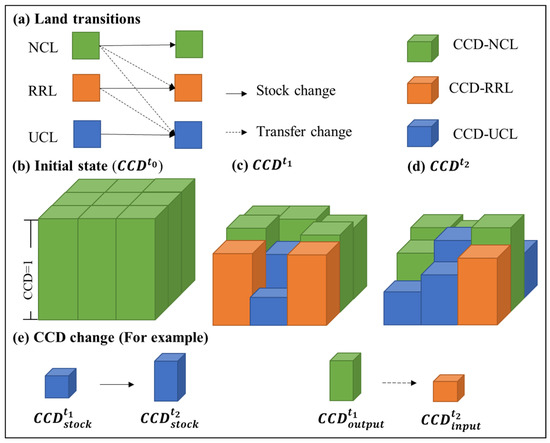
Figure 2.
The conceptual pixel-wise remote sensing-based model for CCD quantification during land transitions.
3.1. Identifying Urban–Rural Land Transitions
According to the national standard of “code for classification of urban land use and planning standards of development land” [51], we divided land cover into urban construction land (UCL), rural residential land (RRL), and non-construction land (NCL). Non-construction land is related to the eco-environment, including water area, agricultural, and forested land. Construction land is highly related to scopes of human socioeconomic activities. The NTL data was used to identify urban and rural areas [52]. The percentage of impervious surface area (PISA) was used to identify construction land and non-construction land [31,38]. The area without PISA is identified as NCL. We used the threshold method to distinguish the urban–rural boundary [53]. The area where the DN value of NTL exceeds threshold is defined as UCL; otherwise, it is categorized as RCL.
Given the changing dynamics of land types in different time periods, the process of urban–rural transitions can be identified. Among them, the constant region with no change is called stock land, and the changing area is called transfer land. It is assumed that the transitions between urban and rural areas, as well as the transformation between non-construction land and construction land, are irreversible.
3.2. Human Activity Intensity Assessment
The human activity intensity describes the effects and influences of human activities on land surfaces [7]. The human activity derived from NTL data is often used to evaluate the human activities intensity in urban cores [54]. However, the limitation of solely relying on NTL data lies in neglecting weak urbanization scenes and overestimating urban parks and green spaces caused by light scattering. Taking advantage of both impervious data and NTL data, we propose a human activity intensity index (HAI) that includes two dimensions: land-use intensity (L) and socio-economic activity intensity (S):
where L is PISA; if a region is classified as UCL, [53]; if the region is classified as RRL, ; the HAI of NCL is equal to 0.
3.3. Coupling Coordination Degree Model
In this study, the coupling coordination degree (CCD) model was applied to investigate the interactive coupling relationship between human activity and the regional eco-environment. Coupling, which originated from physics, is a phenomenon in which two or more subsystems in the whole physical system interact with each other through miscellaneous interactions. The CCD model has been widely applied to depict the non-linear interactive associations among multiple systems in various disciplines [4,55]. The input data to the CCD model need to be normalized according to the positive or negative effects on the system. The positive coupling between human activity and the eco-environment is encouraged in UCL (positively normalized). For RCL and NCL, the intervention of human activities is considered as a negative effect (negative normalized). Note that the environmental system is also positively normalized. The calculation of CCD follows [56]:
where H represents the human system and E represents the environment system. In UCL, H = HAI, and R = REE; in RCL and NCL, H = 1 − HAI, and E = REE. CDD ranges from 0 to 1, where the higher value indicates the higher the coordination of CHANS. is the adjustment coefficient assigned to 2 in this study. and , respectively, describe the contribution ratio of H and E. In order to highlight the efficiency gap between the two systems according to the synergy theory, these two parameters are calculated, and [57].
3.4. The CCD Transfer Model
According to the land attributes, the CCD can be divided into CCD-NCL, CCD-RRL, and CCD-UCL. As each pixel has a land attribute and a value of CCD, we use the sum of CCD to evaluate regional CHANS. NCL is the initial state for all pixels, assuming that the CCD value of all pixels is 1 (Figure 2b). The CCD state at the time point t is defined as the ratio of the sum of the current CCD and the initial CCD, as shown in Equation (3). Figure 2c,d shows the evolution process of the coordination with urban–rural transitions. Therefore, the change in CCD includes the change in stock land and the change in transfer land (Figure 2e). The difference in CCD between output and input in the land transfer process is called loss (Equation (4)). The CCD loss between and , i.e., , is calculated as:
4. Results
4.1. Land Transitions and Human Activity Intensity
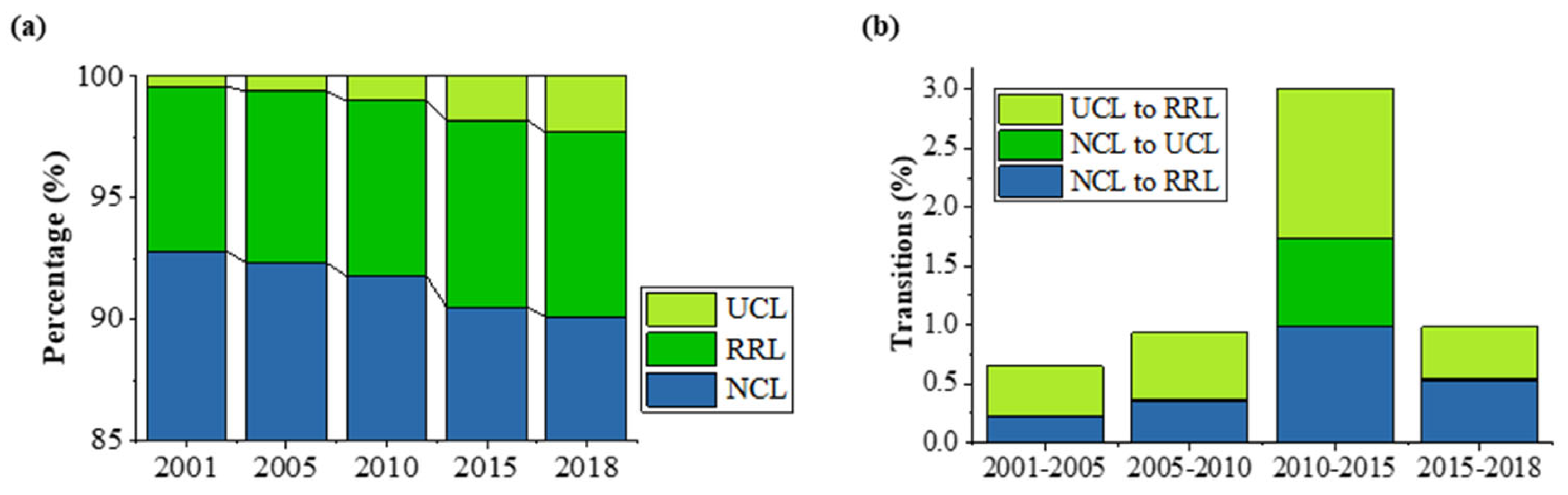
Figure 3a shows the land transitions in China from 2001 to 2018. The proportion of UCL in the national area expanded from 0.40% to 2.31%, and RRL expanded from 6.82% to 7.73%. Given the continuous spread of urban–rural construction land, NCL declined from 92.77% to 90.06%. The transitions from RRL to UCL and from UCL to RRL are dominant, while only a small amount of UCL transitioned to NCL. Most expansions of urban–rural construction areas occurred during the period of 2010-2015, as shown in Figure 3b. After 2015, the expansion rate of RRL decreased notably, while the expansion rate of UCL continued to increase.
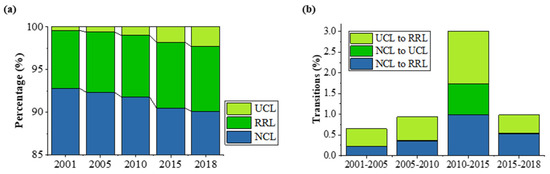
Figure 3.
Land transitions and the corresponding statistics (a) percentage of the area of UCL, RRL and NCL, respectively, (b) transition percentage From UCL to RRL, NCL to UCL and NCL to RRL, respectively.
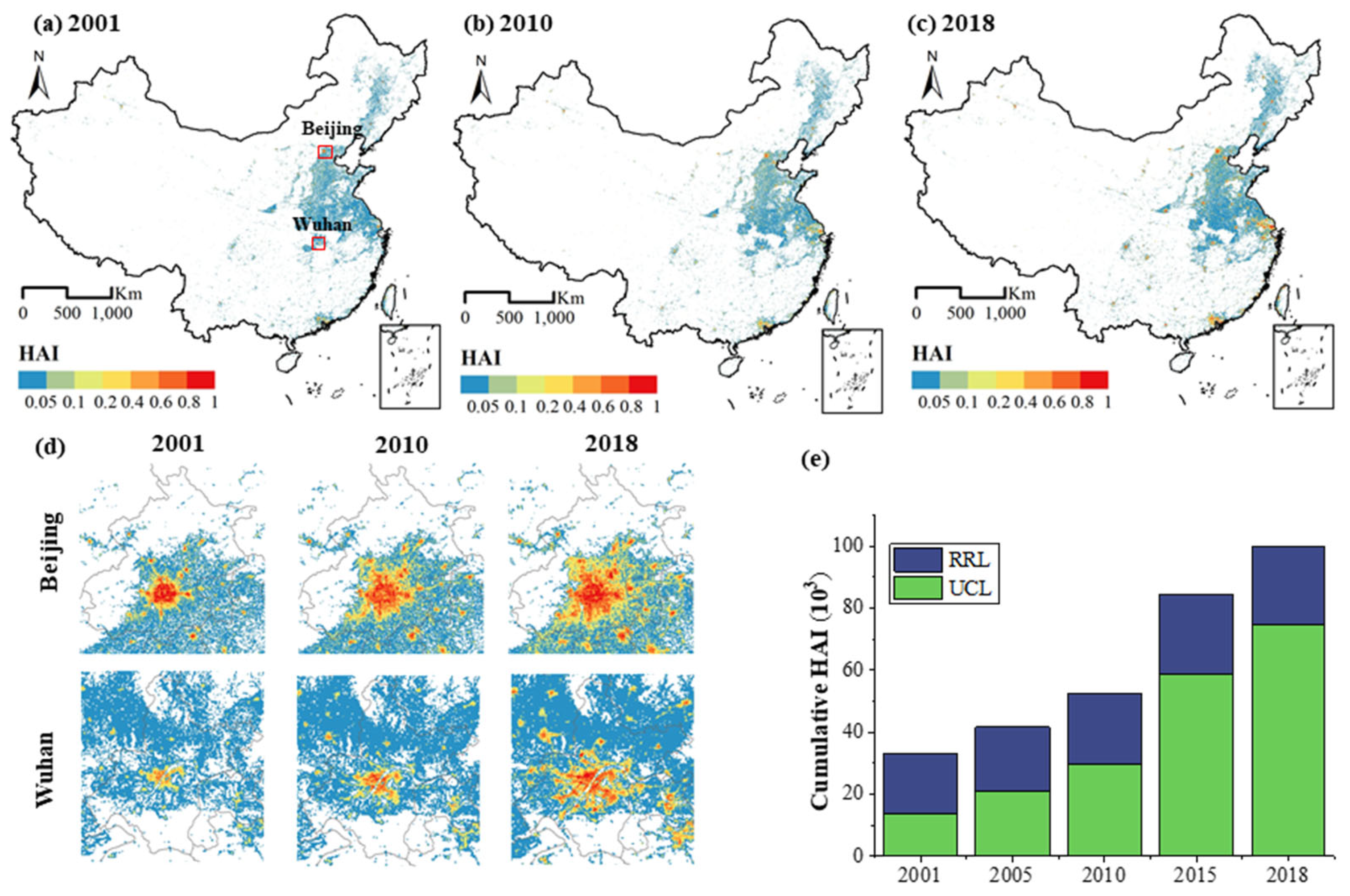
Figure 4a–c shows the spreading process of human activities under the context of urban expansion. The average intensity of human activity in UCL was 0.28, while that in RCL was only 0.03, pointing to the notable difference in human activity intensity in urban and rural areas. As shown in Figure 4e, with the increase in cumulative human activity intensity, UCL gradually obtained more proportions, highlighting the exacerbated urban–rural difference. In 2001, the proportion of urban human activities was only 40.89%, while this number reached 74.72% in 2018. Figure 4d shows saptial results of human activity intensity, taking example of Beijing and Wuhan.
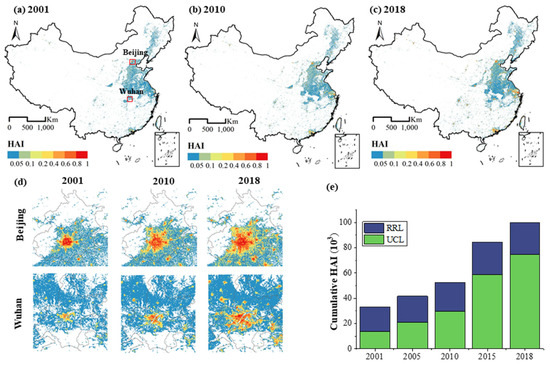
Figure 4.
Human activity intensity of China from 2001 to 2018.
4.2. The Spatial–Temporal Pattern of CCD
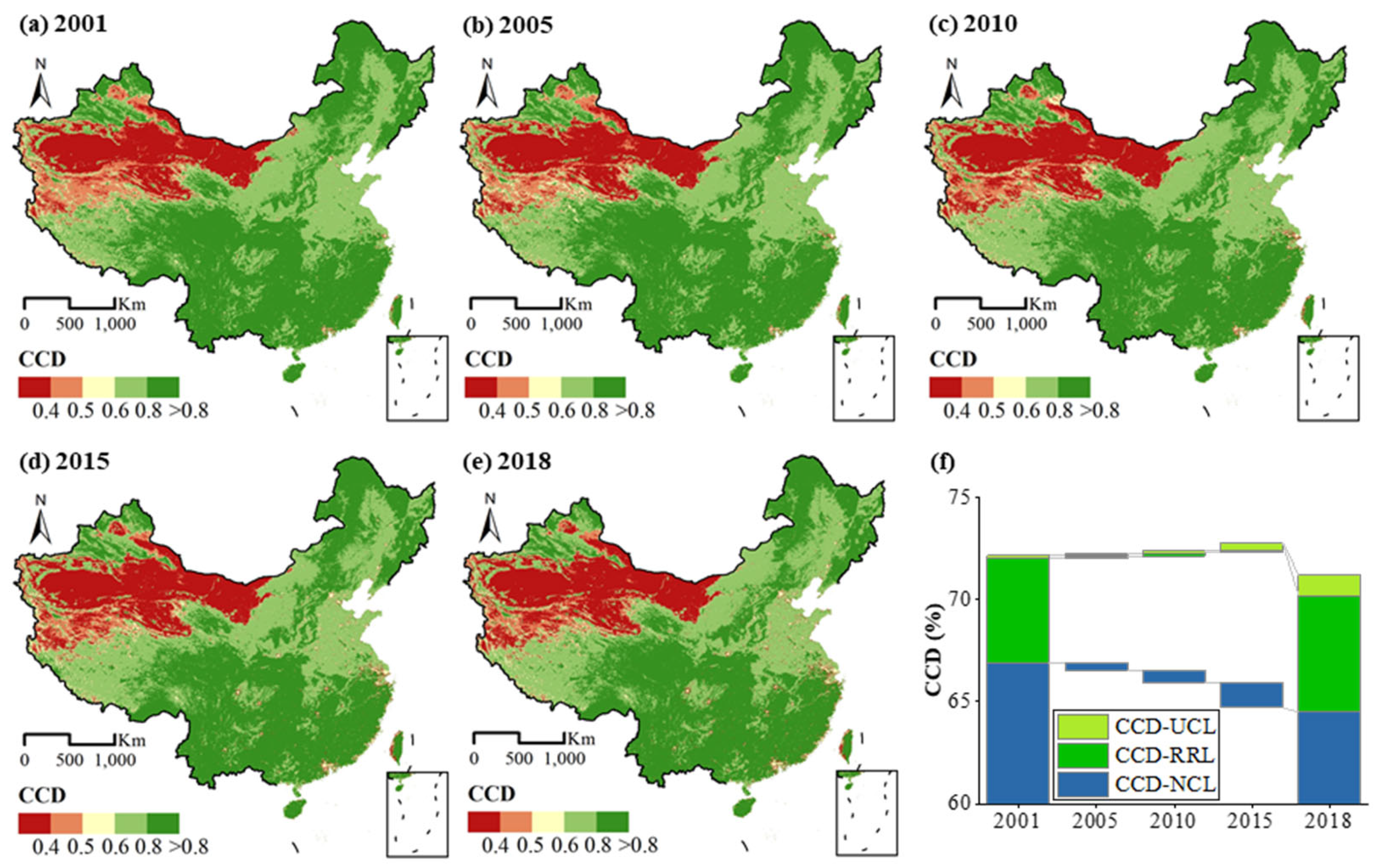
Figure 5 shows the spatiotemporal pixel-wise dynamics of CCD from 2001 to 2018 at the national level. The national CCD decreased from 72.17% in 2001 to 71.21% in 2018. The CCD-NCL decreased from 66.90% to 64.47%, while the CCD-UCL increased from 0.18% to 1.02%. The macroscopic results of CCD were similar to the pattern of the eco-environment. The lower CCD in the west was due to the low coupling effect caused by the lower eco-environment quality and the lower human activity intensity. The south region of the Yangtze River presented a considerably high coordination degree.
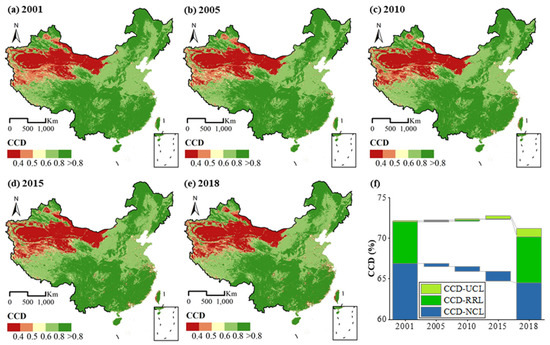
Figure 5.
Annual CCD in China from 2001 to 2018. (a) 2001; (b) 2005; (c) 2010; (d) 2015; (e) 2018; (f) CCD change of China of UCL,RRl and NCL from 2001–2018.
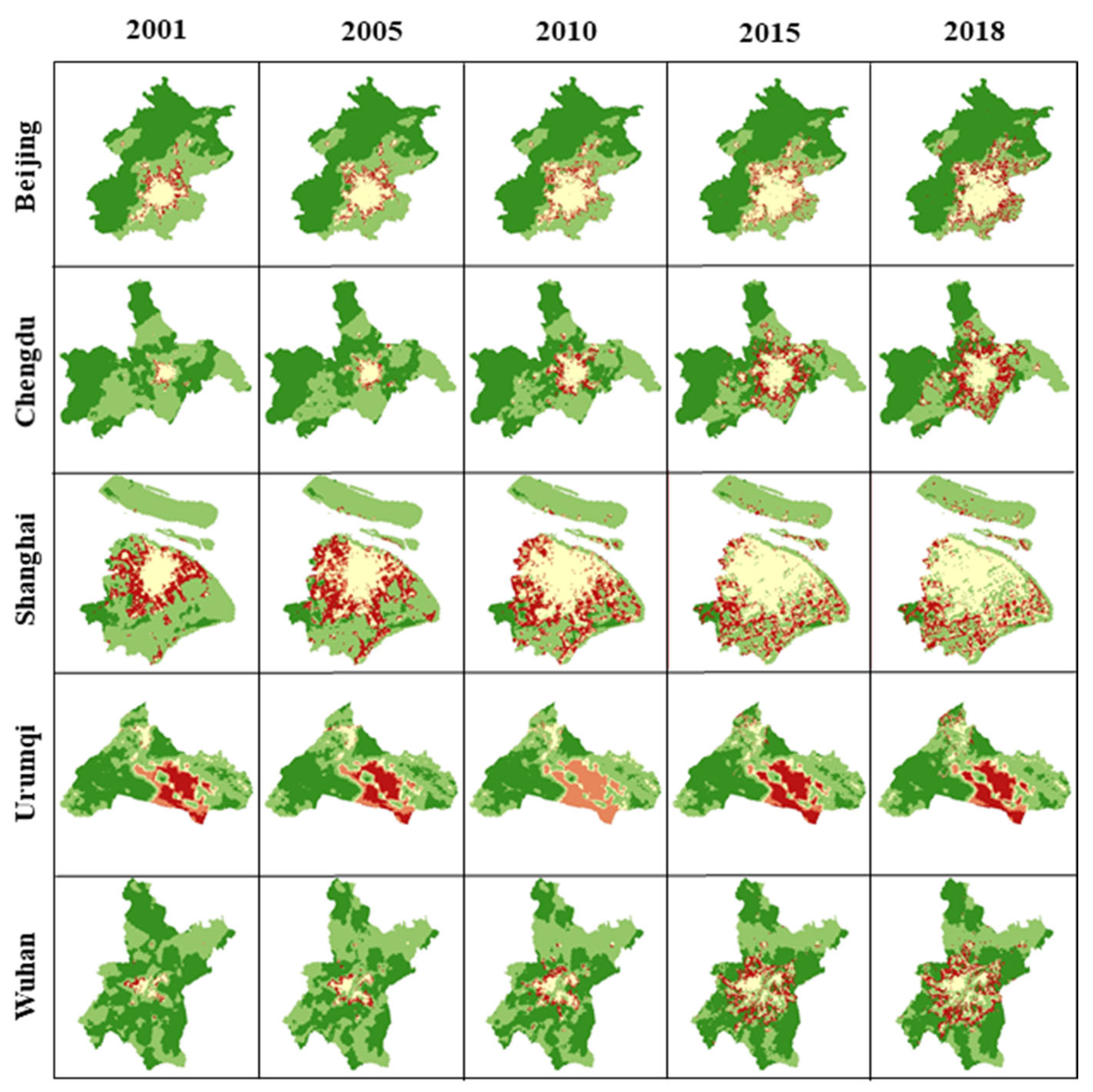
The CDD dynamics in five selected cities, i.e., Beijing, Chengdu, Shanghai, Urumqi, and Wuhan, are shown in Figure 6. In general, CCD dynamics correspond well with urban expansion. With the expansion of RRL and NCL, higher CCD areas were replaced by lower CCD areas. In addition, the CCD of urban cores and rural boundaries has been increased.
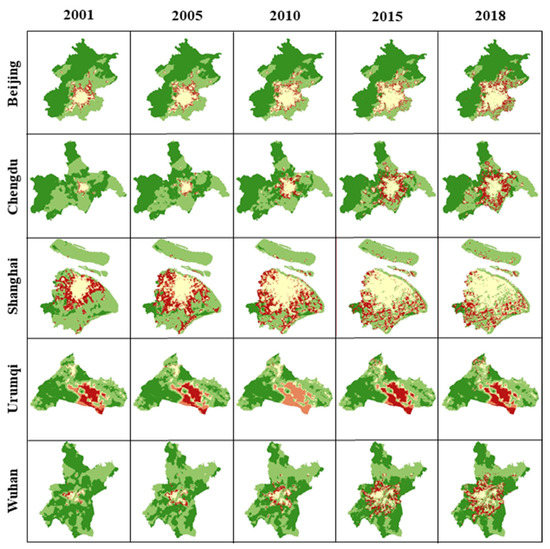
Figure 6.
The CCD change in five selected cities (Beijing, Chengdu, Shanghai, Urumqi, and Wuhan).
4.3. Quantifying the Transfer Process of CCD
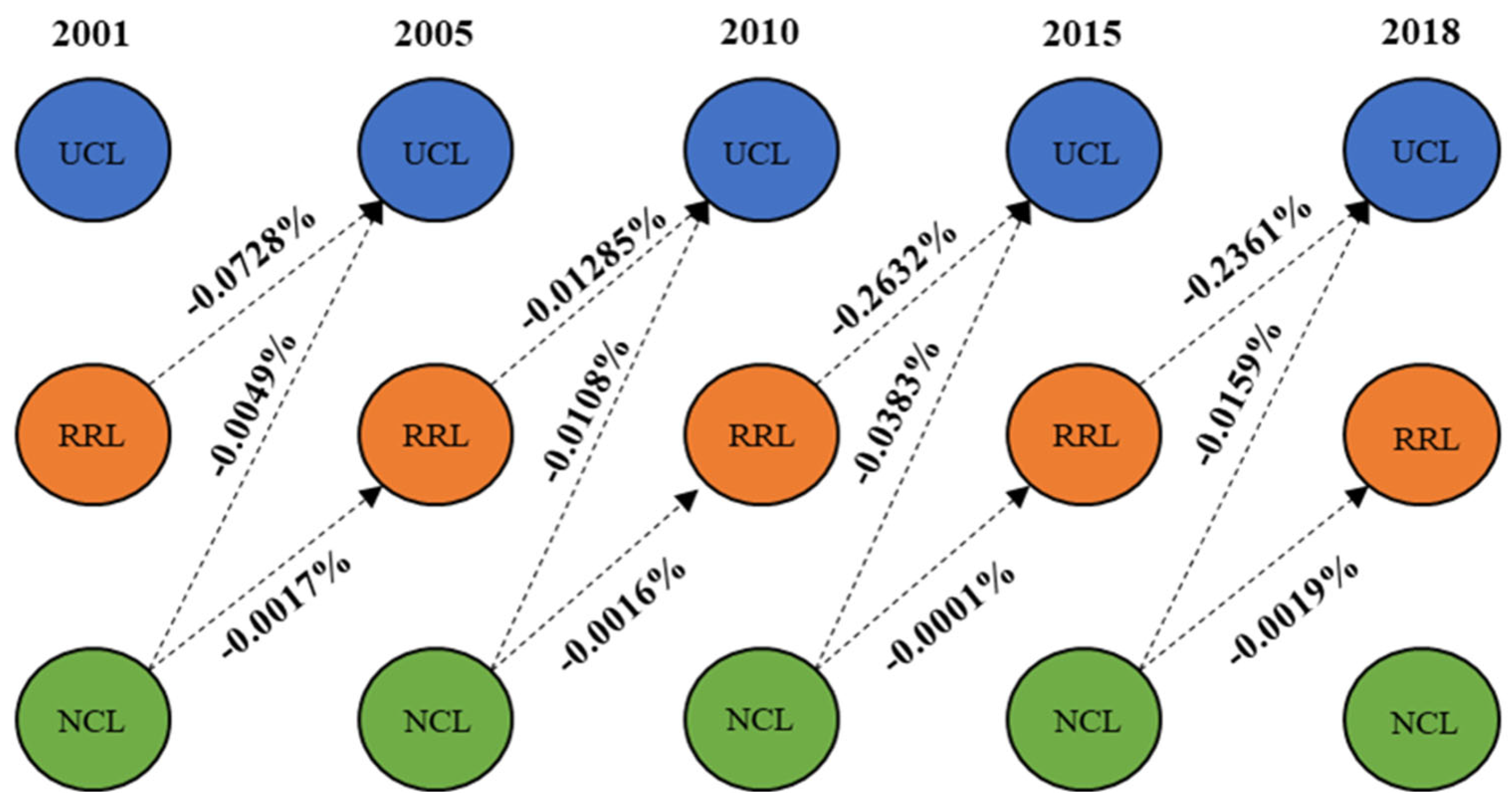
Table 2 depicts the CCD changes in land stocks, as well as the input and output during the land transitions. The major reason for the transition in CCD-NCL was the stock change and output to RRL. During the investigated period, NCL contributed a total of 2.09% to UCL and RRL. The CCD-RRL on stock land has not been altered substantially. The input from NCL and the output to UCL were the two dominant modifications in CCD-RRL. Furthermore, input from CCD-RRL, which was 0.64% in total (more than three times the growth of CCD-UCL in 2001), was the key cause for the increase in CCD-UCL. We further quantify the flow of CHANS in the process of land transitions from the standpoint of land stock and transfer.

Table 2.
The change in CCD-NCL, CCD-RRL, and CCD-UCL from 2001 to 2018 in China.
Note that if the land transition occurs, we should expect to observe differences between the output and input values, leading to the CCD losses (CCD-loss). This is related to the disparity in the value of human–environment relationship coordination among the regional systems of UCL, RCL, and URNL. Figure 7 shows the CCD losses in land transfers. For example, from 2001 to 2005, the CCD-RRL output was 0.1521%, whereas the CCD-UCL input was only 0.0793%, leading to a loss of -0.0728%. It was observed that when NCL transferred to RRL and UCL, a minor amount of CCD losses occurred. Significant losses occur mostly during the transition from RRL to UCL. Therefore, the key sources that contributed to the change in CCD in China are changes in NCL and UCL stock land as well as CCD losses during the transition from RCL to UCL.
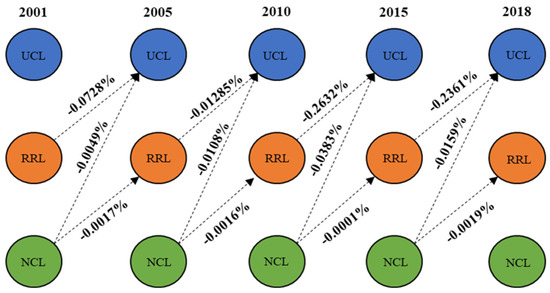
Figure 7.
The CCD losses during land transitions.
5. Discussion
5.1. Changes and Losses of CCD Related to UCL
UCL is the predominant component for human socioeconomic activities, as well as a crucial region in the study of the interaction between human and environmental systems. The processes related to CCD-UCL include UCL stock changes and transfers from RCL and NCL. Most existing efforts have concentrated primarily on estimating UCL stock and incremental changes while ignoring the losses suffered throughout the transfer processes.
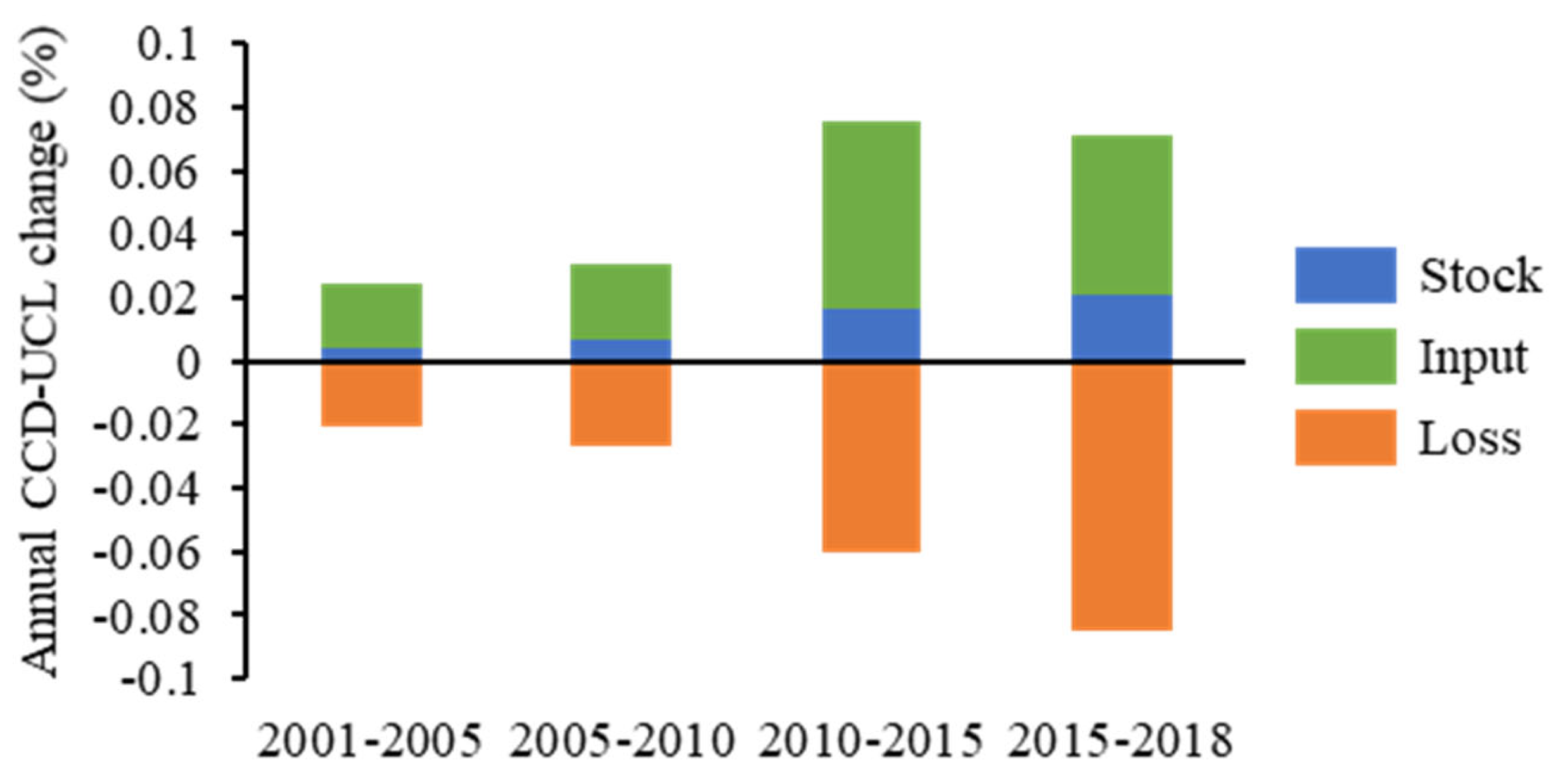
Take 2001-2005 as an example. When ignoring the transfer and loss, the growth of CCD-UCL was 0.0984%, including 0.0179% from the stock, and 0.0793% and 0.0012% input from RCL and NCL, respectively. The above finding is consistent with the conclusion from many studies that CCD-UCL tends to show improvement in the process of urbanization, leading to the positive impact of urbanization on the CHANS system. However, when considering the losses during the land transfer process, the CCD related to UCL decreased by 0.0598% from 2001 to 2005. Despite the increase in UCL stock, the losses of RCL and NCL transfer portions were -0.0728% and -0.0049%, respectively. Figure 8 shows the change in annual average stock, input, and losses associated with CCD-UCL during the investigated period. CCD-UCL increased in tandem with the increase in UCL-related losses. Although the rate of CCD growth slowed from 2015 and 2018, the average annual loss increased. From Table 2, we can observe that the losses during RRL-UCL transitions continued to increase, owing to the growing disparity between urban and rural areas.
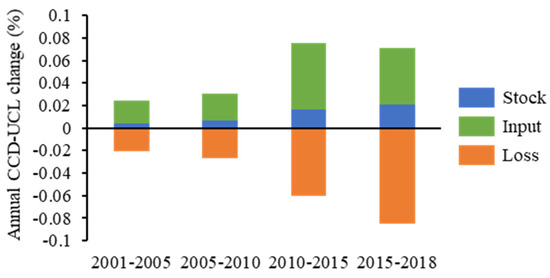
Figure 8.
Stock, input, and losses of CCD related to UCL.
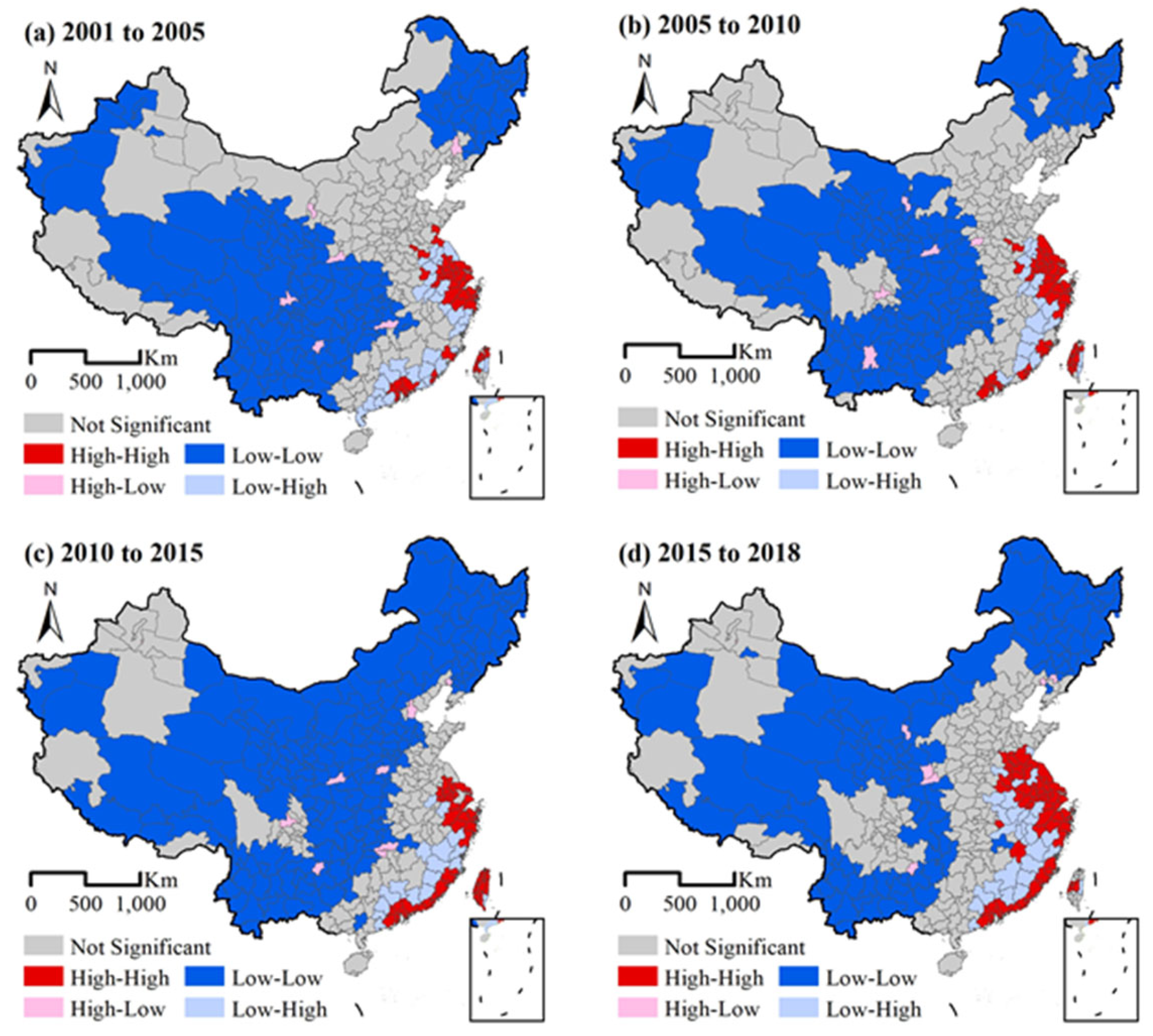
We further investigated the UCL-related CCD declines in 331 cities. The local autocorrelation analysis method was used to explore the spatial clustering characteristics of CCD, as shown in Figure 9. The distribution of UCL transfer loss presented a pattern of "high in the east and low in the west", indicating that LL-type high-loss cities were mainly distributed on China’s eastern coast, the most urbanized region in China. HH-type cities are mainly located in the west and north.
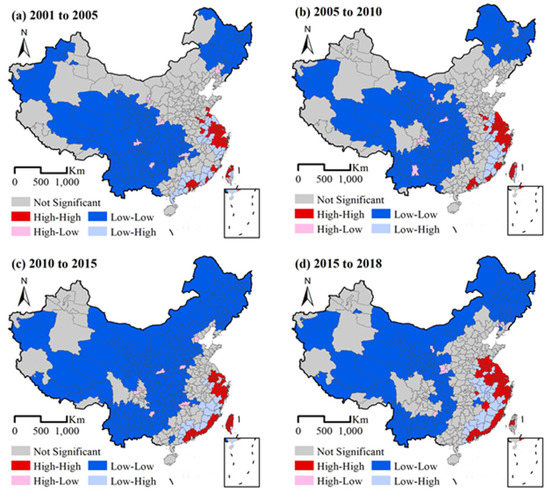
Figure 9.
Moran of UCL-related loss distribution.
5.2. Sustainable Development Strategies
We discuss two strategies for the sustainable development of CHANS. Development and protection are, in most cases, contradictory perspectives. In this study, we re-emphasized the importance of viewing the development and protection from the perspective of coordination of human–environmental relationships through quantitative results.
Protection entails restraining UCL’s expansion and maintaining the eco-environment quality. As the pixel-wise CCD values of RRL and NCL are much higher than UCL, the areas of RRL and NCL are crucial for the overall coordination degree of the whole CHANS. The average inventory value of 1% national area of CCD-NCL, CCD-RRL, and CCD-UCL in 2018 is 71.81%, 75.1%, and 44%, respectively. Moreover, the CCD-NCL stock fluctuations were solely determined by the environmental system. As the area of NCL exceeds 90% of the national area, changes in eco-environmental quality are expected to have a substantial impact on the change in CCD. Many existing policies, e.g., restoring farmland to forests and establishing the red line of cultivated land, have focused on improving the eco-environmental quality.
Development entails enhancing the quality of urbanization and reducing the urban–rural divide. The improvement in urbanization quality is expected to lead to the stock increase in CCD-UCL, and the average annual CCD growth of 1% national area in the research period is 1.25%. However, the average loss of urban–rural transfer was 4.6%. It can be observed that the average annual loss increased given the widened gap between urban and rural regions. Such an observation emphasizes the significance of rural regeneration.
In general, we need to pay attention to the positive and negative effects of land transitions on CHANS. The progressive growth of human–environmental connections is expected to greatly benefit sustainable development.
5.3. Future Work
Further investigations are needed from the following three aspects. (1) Future studies can enhance the CCD evaluation framework in the context of land transitions, including improving the identification of land transition processes using multi-source remote sensing data and establishing a more refined assessment model of CHANS during land transitions, considering land use/cover change (LUCC). (2) The loss caused by urban–rural transfer can be further investigated as few studies have been undertaken to explore this issue. Future efforts can be made to determine what, where, and how losses occur during land transitions. (3) Future studies can expand our proposed model to include other critical components of the eco-environment, such as the interaction between human activities with heat, carbon, water, as well as other elements.
6. Conclusions
Land transitions and human activity changes, as the core component of urbanization, have a significant impact on the coordination and stability of urban development. In this study, we proposed a novel remote sensing-based bottom-up model to quantify the evolution, transfer, and loss in the coordination of human–environmental relationships during urban–rural transitions. We used the nighttime light data and impervious surface area data to evaluate the human activity intensity by identifying urban construction land (UCL), rural residential land (RRL), and non-construction land (NCL). On the other hand, we mapped the spatiotemporal coupling coordination degree (CCD) of the human–land relationship in China from 2001 to 2018. On this basis, we further investigated the CCD changes in land stock and changes due to land transfer. The conclusions are as follows: (1) The proportion of UCL in China increased from 0.40% in 2001 to 2.31% in 2018, while NCL decreased from 92.78% to 90.09%. As the human activity intensity increased during the investigated period, the cumulative human activities shifted significantly from RRL to UCL. (2) CCD has seen a slight decrease from 2001 (72.17%) to 2018 (71.21%). The CCD changes mainly occurred due to the decline in NCL stock, the increase in UCL stock, as well as the CCD loss during transitions from RRL to NCL. (3) From the perspective of CCD stock and transfer changes, we analyzed and discussed the contradictory relationship and relevance between ecological protection and urbanization expansion. In the end, planners and researchers must take into account the tradeoff between urban–rural land transition and human–environmental interactions for sustainability development.
Author Contributions
Conceptualization, B.C. and Z.S.; methodology, B.C.; software, B.C.; investigation, B.C.; writing—original draft preparation, B.C.; writing—review and editing, B.C. and Z.S.; visualization, B.C. and X.H.; supervision, S.F.; funding acquisition, Z.S. All authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript.
Funding
This research was funded by the National Natural Science Foundation of China (Grant number 42090012), Zhuhai Industry University Research Cooperation Project of China (Grant number ZH22017001210098PWC), Sichuan Science and Technology Program (Grant number 2022YFN0031), Zhizhuo Research Fund on Spatial-Temporal Artificial Intelligence (Grant number ZZJJ202202).
Institutional Review Board Statement
Not applicable.
Informed Consent Statement
Not applicable.
Data Availability Statement
All data and materials are available upon request.
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
References
- Liu, J.; Dietz, T.; Carpenter, S.R.; Alberti, M.; Folke, C.; Moran, E.; Pell, A.N.; Deadman, P.; Kratz, T.; Lubchenco, J.; et al. Complexity of Coupled Human and Natural Systems. Science 2007, 317, 1513–1516. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Guan, X.; Wei, H.; Lu, S.; Dai, Q.; Su, H. Assessment on the Urbanization Strategy in China: Achievements, Challenges and Reflections. Habitat Int. 2018, 71, 97–109. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wei, C.; Shenglu, Z.; Shaohua, W. Measuring Smart Land Use in Urban–Rural Regions of China: A Case Study of Pukou, Nanjing City. Growth Change 2018, 49, 189–202. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, H.; Huang, B.; Yang, C. Assessing the Coordination between Economic Growth and Urban Climate Change in China from 2000 to 2015. Sci. Total Environ. 2020, 732, 139283. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bai, X.; Shi, P.; Liu, Y. Realizing China’s Urban Dream. Nature 2014, 509, 158–160. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Ding, Q.; Shao, Z.; Huang, X.; Altan, O.; Zhuang, Q.; Hu, B. Monitoring, Analyzing and Predicting Urban Surface Subsidence: A Case Study of Wuhan City, China. Int. J. Appl. Earth Obs. Geoinf. 2021, 102, 102422. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Z.; Shi, P.; Chen, J.; Toshiaki, I. Human Activity Intensity of Land Surface: Concept, Methods and Application in China. J. Geogr. Sci. 2016, 26, 1349–1361. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, L.; Fang, X.; Wu, J. How Does the Local-Scale Relationship between Ecosystem Services and Human Wellbeing Vary across Broad Regions? Sci. Total Environ. 2021, 816, 151493. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, S.; Fu, B.; Zhao, W.; Liu, Y.; Wei, F. Structure, Function, and Dynamic Mechanisms of Coupled Human–Natural Systems. Curr. Opin. Environ. Sustain. 2018, 33, 87–91. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, Y.; Bao, W.; Wang, Y.; Liu, Y. Measurement of Urban-Rural Integration Level and Its Spatial Differentiation in China in the New Century. Habitat Int. 2021, 117, 102420. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- van Vliet, J.; Birch-Thomsen, T.; Gallardo, M.; Hemerijckx, L.M.; Hersperger, A.M.; Li, M.; Tumwesigye, S.; Twongyirwe, R.; van Rompaey, A. Bridging the Rural-Urban Dichotomy in Land Use Science. J. Land Use Sci. 2020, 15, 585–591. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, Y.; Liu, Y.; Li, Y.; Du, G. Quantifying Spatio-Temporal Patterns of Urban Expansion in Beijing during 1985–2013 with Rural-Urban Development Transformation. Land Use Policy 2018, 74, 220–230. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qu, Y.; Long, H. The Economic and Environmental Effects of Land Use Transitions under Rapid Urbanization and the Implications for Land Use Management. Habitat Int. 2018, 82, 113–121. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yanbo, Q.; Guanghui, J.; Yaya, T.; Shang, R.; Shuwen, W.; Yuling, L. Urban–Rural Construction Land Transition(URCLT) in Shandong Province of China: Features Measurement and Mechanism Exploration. Habitat Int. 2019, 86, 101–115. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, R.; Zhang, J.; Xu, Q.; Luo, X. Urban-Rural Spatial Transformation Process and Influences from the Perspective of Land Use: A Case Study of the Pearl River Delta Region. Habitat Int. 2020, 104, 102234. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, C.; Zhang, X.; Wang, K.; Yuan, S.; Yang, L.; Skitmore, M. Urban–Rural Construction Land Transition and Its Coupling Relationship with Population Flow in China’s Urban Agglomeration Region. Cities 2020, 101, 102701. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ferraro, P.J.; Sanchirico, J.N.; Smith, M.D. Causal Inference in Coupled Human and Natural Systems. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2019, 116, 5311–5318. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Fang, C.; Liu, H.; Wang, S. The Coupling Curve between Urbanization and the Eco-Environment: China’ s Urban Agglomeration as a Case Study. Ecol. Indic. 2021, 130, 108107. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, H.; Fang, C.; Fang, K. Coupled Human and Natural Cube: A Novel Framework for Analyzing the Multiple Interactions between Humans and Nature. J. Geogr. Sci. 2020, 30, 355–377. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tang, P.; Huang, J.; Zhou, H.; Fang, C.; Zhan, Y.; Huang, W. Local and Telecoupling Coordination Degree Model of Urbanization and the Eco-Environment Based on RS and GIS: A Case Study in the Wuhan Urban Agglomeration. Sustain. Cities Soc. 2021, 75, 103405. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cai, B.; Shao, Z.; Fang, S.; Huang, X.; Huq, M.E.; Tang, Y.; Li, Y.; Zhuang, Q. Finer-Scale Spatiotemporal Coupling Coordination Model between Socioeconomic Activity and Eco-Environment: A Case Study of Beijing, China. Ecol. Indic. 2021, 131, 108165. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Z.; Fang, C.; Cheng, S.; Wang, J. Evolution of Coordination Degree of Eco-Economic System and Early-Warning in the Yangtze River Delta. J. Geogr. Sci. 2013, 23, 147–162. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zuo, Y.; Shi, Y.-L.; Zhang, Y.-Z. Research on the Sustainable Development of an Economic-Energy-Environment (3E) System Based on System Dynamics (SD): A Case Study of the Beijing-Tianjin-Hebei Region in China. Sustainability 2017, 9, 1727. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Zheng, Z.; Wu, Z.; Chen, Y.; Yang, Z.; Marinello, F. Exploration of Eco-Environment and Urbanization Changes in Coastal Zones: A Case Study in China over the Past 20 Years. Ecol. Indic. 2020, 119, 106847. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, Y.; Wang, S.; Zhou, C. Understanding the Relation between Urbanization and the Eco-Environment in China’s Yangtze River Delta Using an Improved EKC Model and Coupling Analysis. Sci. Total Environ. 2016, 571, 862–875. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Y.; Yang, L.; Jiang, W. Coupling Coordination and Spatiotemporal Dynamic Evolution between Social Economy and Water Environmental Quality—A Case Study from Nansi Lake Catchment, China. Ecol. Indic. 2020, 119, 106870. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fang, X.; Shi, X.; Phillips, T.K.; Du, P.; Gao, W. The Coupling Coordinated Development of Urban Environment towards Sustainable Urbanization: An Empirical Study of Shandong Peninsula, China. Ecol. Indic. 2021, 129, 107864. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, H.; Gong, P.; Wang, J.; Wang, X.; Ning, G.; Xu, B. Production of Global Daily Seamless Data Cubes and Quantification of Global Land Cover Change from 1985 to 2020—IMap World 1.0. Remote Sens. Environ. 2021, 258, 112364. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gao, B.; Huang, Q.; He, C.; Ma, Q. Dynamics of Urbanization Levels in China from 1992 to 2012: Perspective from DMSP/OLS Nighttime Light Data. Remote Sens. 2015, 7, 1721–1735. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Zhu, Z.; Zhou, Y.; Seto, K.C.; Stokes, E.C.; Deng, C.; Pickett, S.T.A.; Taubenböck, H. Understanding an Urbanizing Planet: Strategic Directions for Remote Sensing. Remote Sens. Environ. 2019, 228, 164–182. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, Q.; Wu, J.; He, C.; Hu, G. Reprint of “Spatial Scaling of Urban Impervious Surfaces across Evolving Landscapes: From Cities to Urban Regions”. Landsc. Urban Plan. 2019, 187, 132–144. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, C.; Huang, X.; Zhu, Z.; Chen, H.; Tang, X.; Gong, J. Automatic Extraction of Built-up Area from ZY3 Multi-View Satellite Imagery: Analysis of 45 Global Cities. Remote Sens. Environ. 2019, 226, 51–73. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, D.; Chen, T.; Zhen, N.; Niu, R. Monitoring the Effects of Open-Pit Mining on the Eco-Environment Using a Moving Window-Based Remote Sensing Ecological Index. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 2020, 27, 15716–15728. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Firozjaei, M.K.; Fathololoumi, S.; Weng, Q.; Kiavarz, M.; Alavipanah, S.K. Remotely Sensed Urban Surface Ecological Index (RSUSEI): An Analytical Framework for Assessing the Surface Ecological Status in Urban Environments. Remote Sens. 2020, 12, 2029. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, D.; Yang, F.; Yu, L.; Zhou, Y.; Li, H.; Ma, J.; Huang, J.; Wei, J.; Xu, Y.; Zhang, C.; et al. Quantization of the Coupling Mechanism between Eco-Environmental Quality and Urbanization from Multisource Remote Sensing Data. J. Clean. Prod. 2021, 321, 128948. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, X.; Gong, P.; Zhou, Y.; Wang, J.; Bai, Y.; Chen, B.; Hu, T.; Xiao, Y.; Xu, B.; Yang, J.; et al. Mapping Global Urban Boundaries from the Global Artificial Impervious Area (GAIA) Data. Environ. Res. Lett. 2020, 15, 094044. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, Z.; Jiao, L.; Lan, T.; Zhou, Z.; Cui, H.; Li, C.; Xu, G.; Liu, Y. Mapping Hierarchical Urban Boundaries for Global Urban Settlements. Int. J. Appl. Earth Obs. Geoinf. 2021, 103, 102480. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Y.; Zhang, X.; Kong, X.; Wang, R.; Chen, L. Identifying the Relationship between Urban Land Expansion and Human Activities in the Yangtze River Economic Belt, China. Appl. Geogr. 2018, 94, 163–177. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, Y.; Chen, Z.; Xu, G.; Tian, Z. Built-up Land Efficiency in Urban China: Insights from the General Land Use Plan (2006–2020). Habitat Int. 2016, 51, 31–38. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wei, W.; Guo, Z.; Xie, B.; Zhou, J.; Li, C. Quantitative Simulation of Socio-Economic Effects in Mainland China from 1980 to 2015: A Perspective of Environmental Interference. J. Clean. Prod. 2020, 253, 119939. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ge, Q.; Fang, C.; Jiang, D. Geographical Missions and Coupling Ways between Human and Nature for the Beautiful China Initiative. Dili Xuebao/Acta Geogr. Sin. 2020, 75, 1109–1119. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lu, L.; Guo, H.; Corbane, C.; Li, Q. Urban Sprawl in Provincial Capital Cities in China: Evidence from Multi-Temporal Urban Land Products Using Landsat Data. Sci. Bull. 2019, 64, 955–957. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Kuang, W. 70 Years of Urban Expansion across China: Trajectory, Pattern, and National Policies. Sci. Bull. 2020, 65, 1970–1974. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, M.; Liang, L.; Wang, Z.; Zhang, W.; Yu, J.; Liang, Y. Geographical Thoughts on the Relationship between ‘Beautiful China’ and Land Spatial Planning. J. Geogr. Sci. 2020, 30, 705–723. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hua, Y.-d.; Hu, K.-m.; Qiu, L.-y.; Dong, H.-a.; Ding, L.; Lo, S.-L. Exploring the Interaction Relationship between Beautiful China-SciTech Innovation Using Coupling Coordination and Predictive Analysis: A Case Study of Zhejiang; Springer: Dordrecht, The Netherlands, 2021; ISBN 0123456789. [Google Scholar]
- Zhuang, Q.; Wu, S.; Huang, X.; Kong, L.; Yan, Y.; Xiao, H.; Li, Y.; Cai, P. Monitoring the Impacts of Cultivated Land Quality on Crop Production Capacity in Arid Regions. Catena 2022, 214, 106263. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fang, C.; Wang, Z.; Liu, H. Beautiful China Initiative: Human-Nature Harmony Theory, Evaluation Index System and Application. J. Geogr. Sci. 2020, 30, 691–704. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, Z.; Yu, B.; Yang, C.; Zhou, Y.; Yao, S.; Qian, X.; Wang, C.; Wu, B.; Wu, J. An Extended Time Series (2000–2018) of Global NPP-VIIRS-like Nighttime Light Data from a Cross-Sensor Calibration. Earth Syst. Sci. Data 2021, 13, 889–906. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gong, P.; Li, X.; Wang, J.; Bai, Y.; Chen, B.; Hu, T.; Liu, X.; Xu, B.; Yang, J.; Zhang, W.; et al. Annual Maps of Global Artificial Impervious Area (GAIA) between 1985 and 2018. Remote Sens. Environ. 2020, 236, 111510. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, H.; Wang, M.; Shi, T.; Guan, H.; Fang, C.; Lin, Z. Prediction of Ecological Effects of Potential Population and Impervious Surface Increases Using a Remote Sensing Based Ecological Index (RSEI). Ecol. Indic. 2018, 93, 730–740. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liang, X.; Ji, X.; Guo, N.; Meng, L. Assessment of Urban Heat Islands for Land Use Based on Urban Planning: A Case Study in the Main Urban Area of Xuzhou City, China. Environ. Earth Sci. 2021, 80, 308. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chu, L.; Oloo, F.; Sudmanns, M.; Tiede, D.; Hölbling, D.; Blaschke, T.; Teleoaca, I. Monitoring Long-Term Shoreline Dynamics and Human Activities in the Hangzhou Bay, China, Combining Daytime and Nighttime EO Data. Big Earth Data 2020, 4, 242–264. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cheon, S.H.; Kim, J.A. Quantifying the Influence of Urban Sources on Night Light Emissions. Landsc. Urban Plan. 2020, 204, 103936. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Z.; Peijun, S.; Jin, C.; Toshiaki, I. Application of Compound Night Light Index Derived from DMSP/OLS Data to Urbanization Analysis in China in the 1990s. Acta Geogr. Sin. 2003, 58, 893–902. [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, B. The Dynamic Coupling Model and Its Application of Urbanization and Eco-Environment in Hexi Corridor. J. Geogr. Sci. 2005, 15, 491. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fang, C.; Liu, H.; Li, G. International Progress and Evaluation on Interactive Coupling Effects between Urbanization and the Eco-Environment. J. Geogr. Sci. 2016, 26, 1081–1116. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shen, L.; Huang, Y.; Huang, Z.; Lou, Y.; Ye, G.; Wong, S.W. Improved Coupling Analysis on the Coordination between Socio-Economy and Carbon Emission. Ecol. Indic. 2018, 94, 357–366. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).