A Dynamic Performance and Differentiation Management Policy for Urban Construction Land Use Change in Gansu, China
Abstract
1. Introduction
1.1. Background
1.2. Aim and Question
2. Literature Review
2.1. Research Method and Model
2.2. Response Planning and Policy
3. Research Design
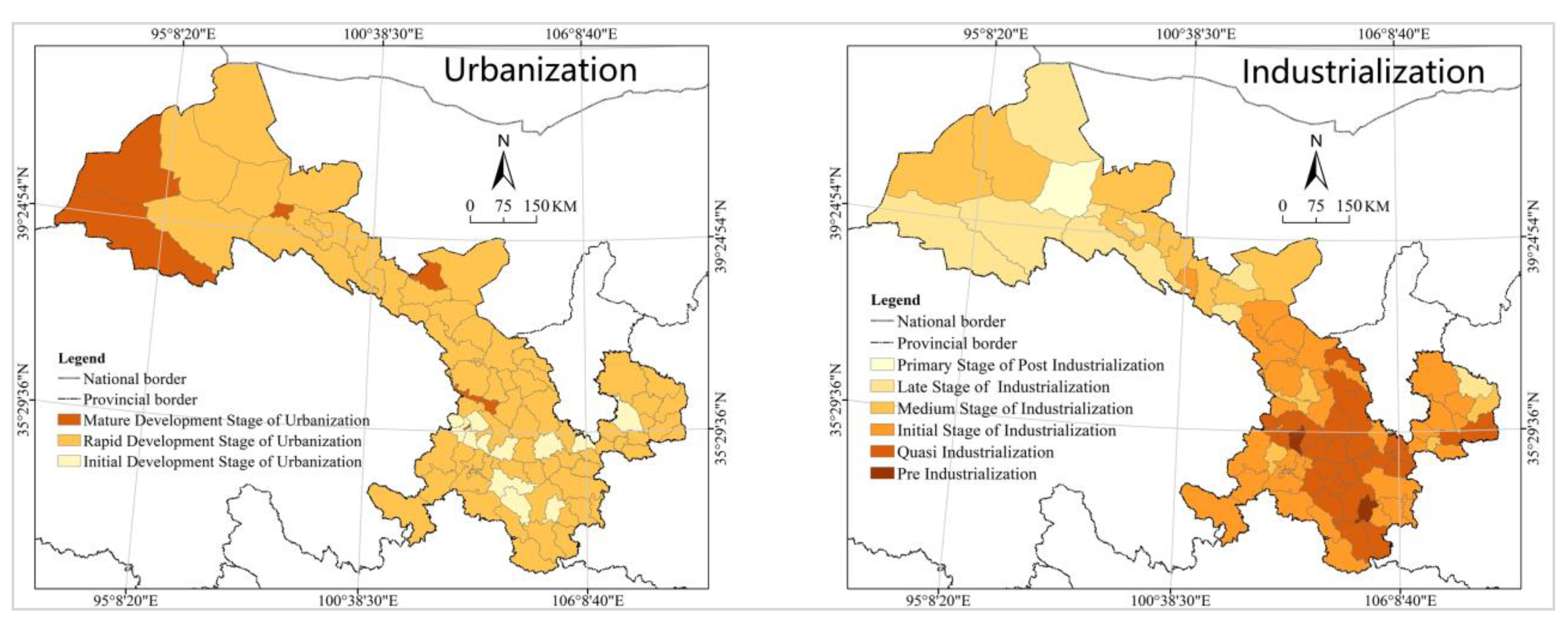
3.1. Study Area: Gansu Province, China
3.2. Index Selection and Data Sources
3.3. Research Methods
3.3.1. Spatial Heterogeneity and Agglomeration Methods: CV, GI, CR, HHI
3.3.2. Evolution Model Analysis Method: Boston Consulting Group Matrix (BCG)
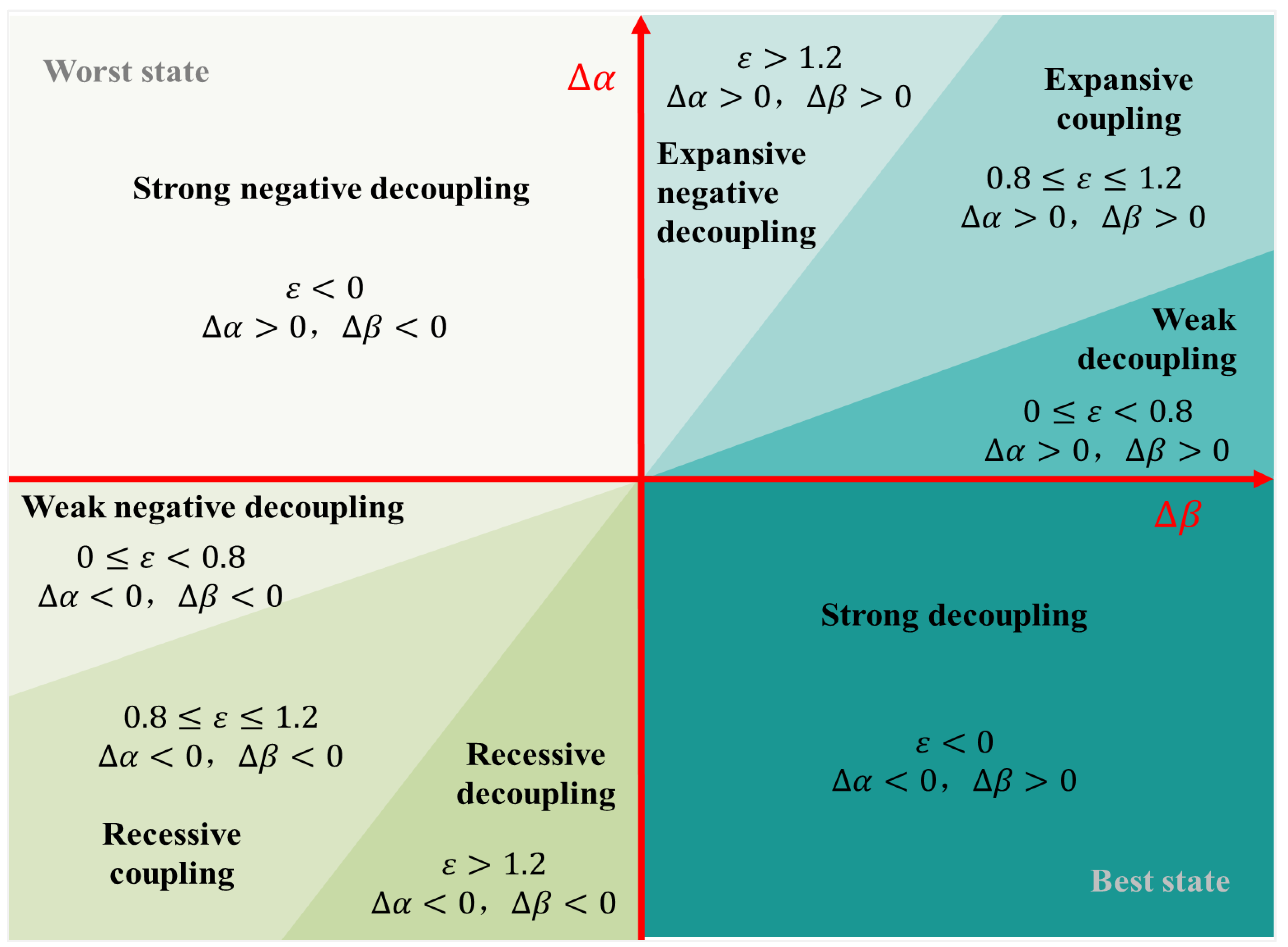
3.3.3. Performance Evaluation Method: Decoupling Model
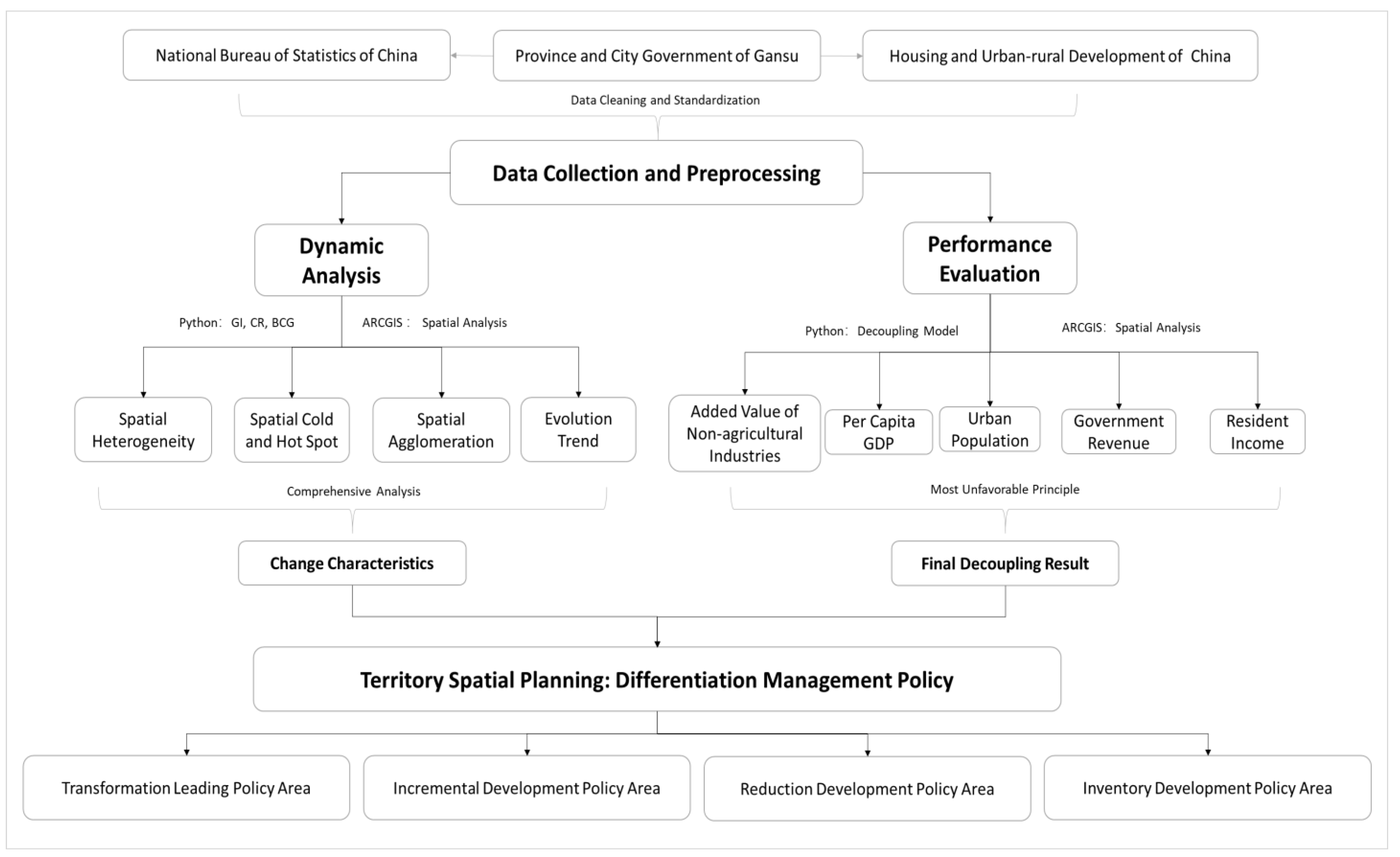
3.4. Research Steps
4. Results
4.1. Dynamic of Urban Construction Land
4.1.1. Change Characteristics
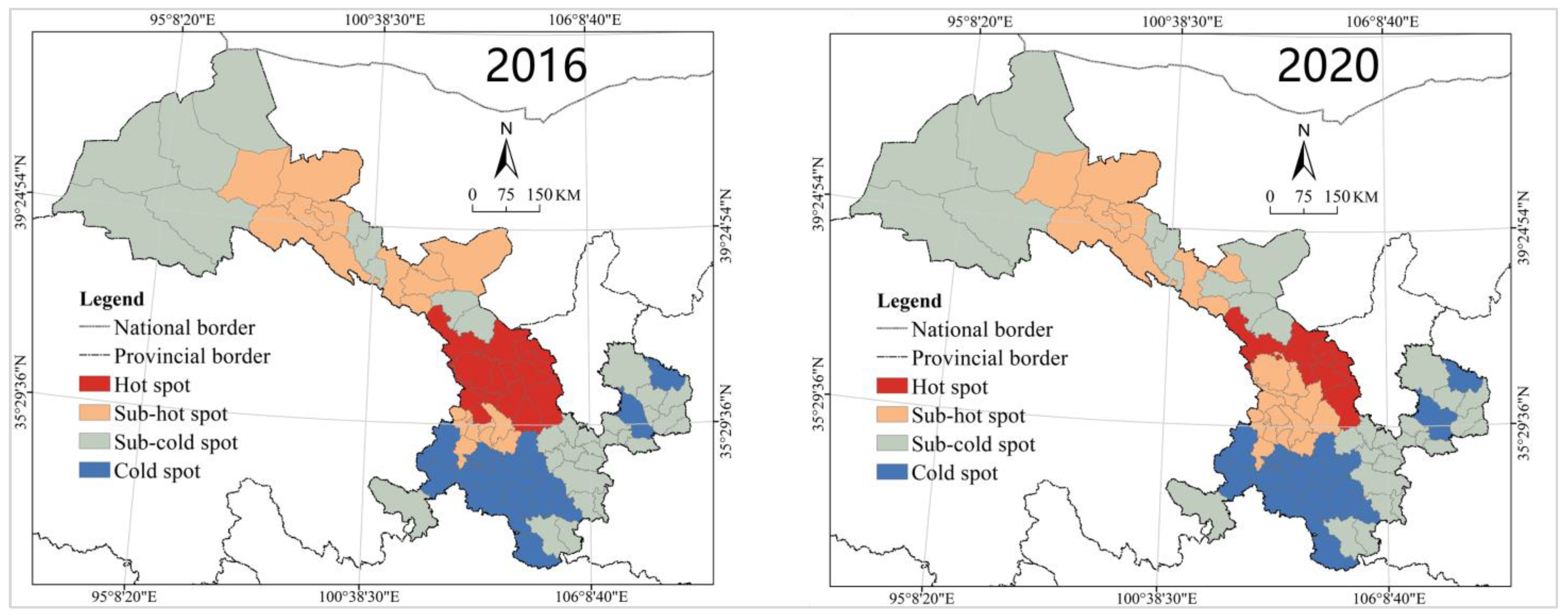
4.1.2. Evolution Trend
4.2. Performance of Urban Construction Land Change
4.2.1. Different Dimensions Analysis
Added Value of Non-Agricultural Industries
Per Capita GDP
Urban Population
Government Revenue
Resident Income
4.2.2. Final Decoupling Result
5. Discussion
5.1. Extended Thinking
5.1.1. Comparison with Other Regions in China
5.1.2. Comparison with Other Countries in the World
5.2. Territory Spatial Planning: Differentiation Management Policy
5.2.1. Transformation Leading Policy Area
5.2.2. Incremental Development Policy Area
5.2.3. Inventory Development Policy Area
5.2.4. Reduction Development Policy Area
5.3. Innovation and Deficiency
6. Conclusions
- (1)
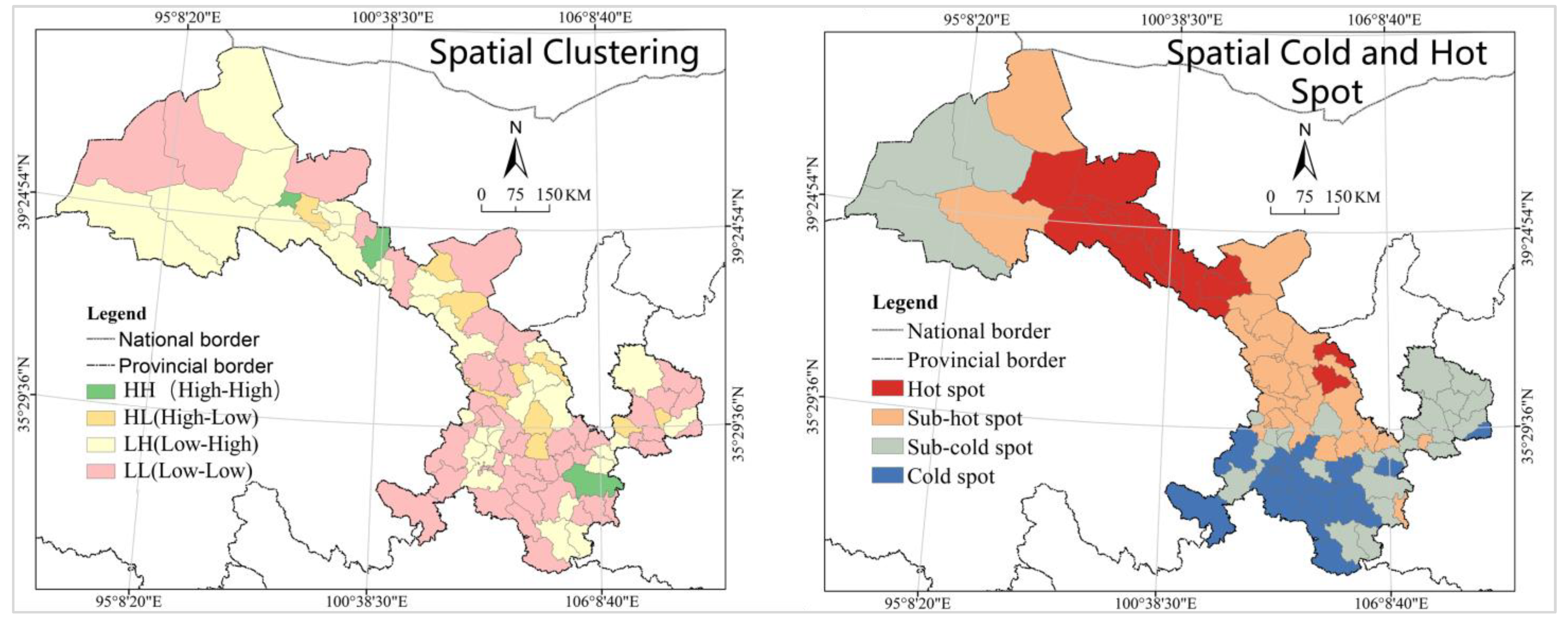
- Urban construction land has a solid spatial pattern with large intercity differences, but the level of spatial heterogeneity is decreasing. The cold and the hot spots are significantly clustered, with the cold spot space remaining stable for a long time, and the hot spot space shrinking in spatial coverage;
- (2)
- The change of urban construction land is dominated by expansion, and there is a small number of cities in shrinking and stagnation stages. The change of urban construction land is characterized by clustering and agglomeration;
- (3)
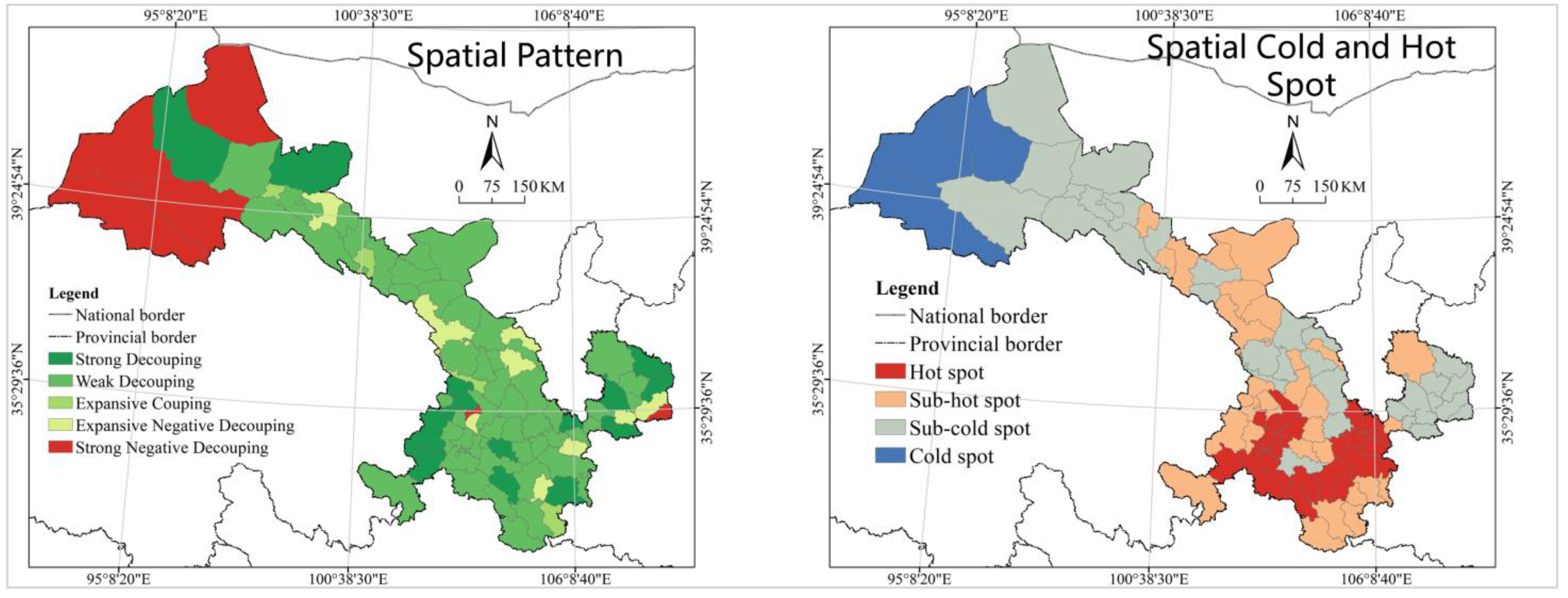
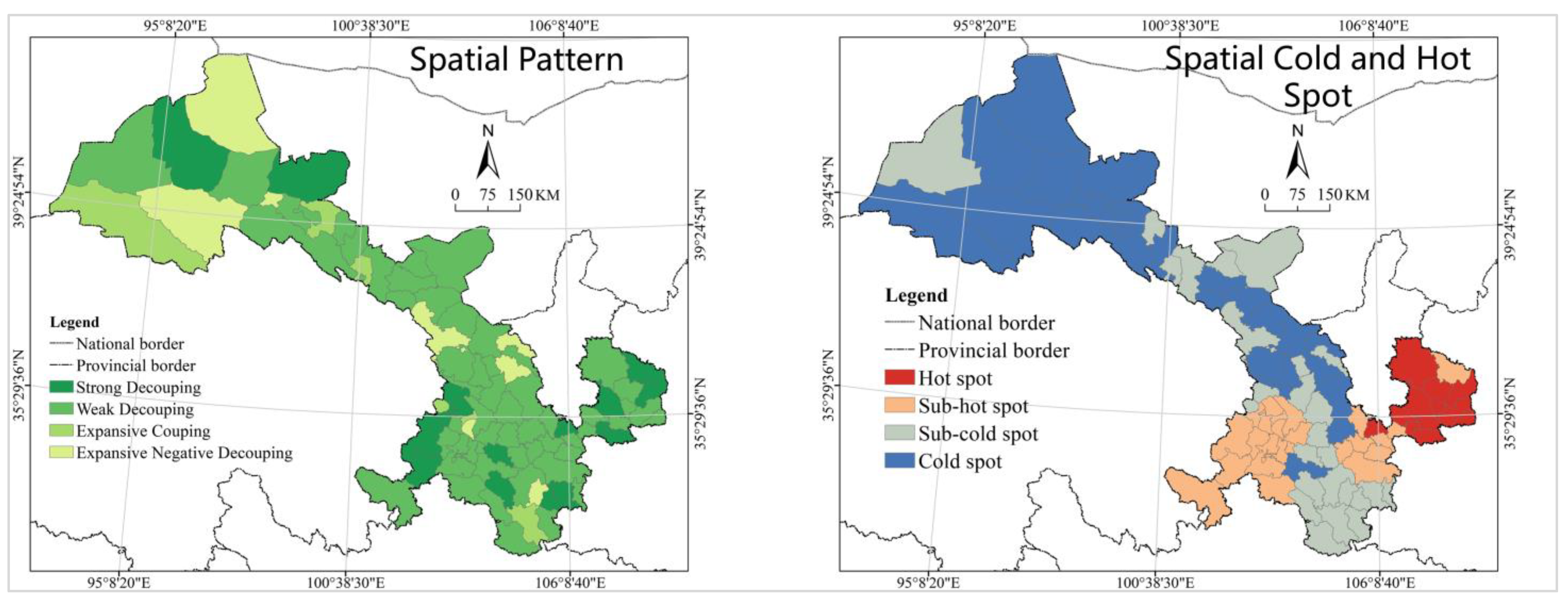
- The unhealthy trend of urban construction land evolution and the large number of cities in the question and dog classes urgently require the strengthening of spatial planning management and the formulation and the implementation of targeted spatial governance policies. The spatial pattern of gradient change takes shape with the town belt of Hexi Corridor as the hot spot, the provincial capital metropolitan area as the sub-hot spot, and Longnan as the cold spot and sub-cold spot;
- (4)
- Urban construction land change is in an incongruous relationship with population growth, economic development, and income increase, and most cities are in strong negative decoupling. It should be noted that the analysis results in different dimensions differ slightly in the dominant decoupling types and spatial distribution patterns, and in order to simplify the analysis this paper employs the equal-weighted superposition analysis method; however, in the practical application, the differentiated weighted superposition analysis method can be considered to calculate the final results so as to improve the accuracy of the analysis and the practicality of the results;
- (5)
- This paper puts forward the policy design method of differential management of urban construction land and takes the lead in applying it to territory spatial planning. Based on the decoupling relationship between urban construction land change and population and economic and income growth and in accordance with the trend of urban construction land evolution, the study area is divided into four types of study areas: incremental, inventory, reduction development policy area, and transformation leading policy area. For each type of city in the policy areas, this paper proposes a targeted policy design direction, forming a governance system of “control by zoning and management by class,” which significantly improves the accuracy of territory spatial planning.
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Kaya, I.A.; Gorgun, E.K. Land use and land cover change monitoring in Bandirma (Turkey) using remote sensing and geographic information systems. Environ. Monit. Assess. 2020, 192, 430. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sfa, F.E.; Nemiche, M.; Rayd, H. A generic macroscopic cellular automata model for land use change: The case of the Draa valley. Ecol. Complex. 2020, 43, 100851. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- He, C.Y.; Zhang, J.X.; Liu, Z.F.; Huang, Q.X. Characteristics and progress of land use/cover change research during 1990–2018. J. Geogr. Sci. 2022, 32, 537–559. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Leta, M.K.; Demissie, T.A.; Traenckner, J. Modeling and prediction of land use land cover change dynamics based on land change modeler (LCM) in Nashe Watershed, Upper Blue Nile basin, Ethiopia. Sustainability 2021, 13, 3740. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Osman, T.; Shaw, D.; Kenawy, E. An integrated land use change model to simulate and predict the future of greater Cairo metropolitan region. J. Land Use Sci. 2018, 13, 565–584. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gaur, S.; Mittal, A.; Bandyopadhyay, A.; Holman, I.; Singh, R. Spatio-temporal analysis of land use and land cover change: A systematic model inter-comparison driven by integrated modelling techniques. Int. J. Remote Sens. 2020, 41, 9229–9255. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Molotoks, A.; Smith, P.; Dawson, T.P. Impacts of land use, population, and climate change on global food security. Food Energy Secur. 2021, 10, e261. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lambin, E.F.; Meyfroidt, P. Global land use change, economic globalization, and the looming land scarcity. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2011, 108, 3465–3472. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Y.A.; Wu, K.N.; Cao, H.L. Land-use change and its driving factors in Henan province from 1995 to 2015. Arab. J. Geosci. 2022, 15, 247. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, W.W.; Jin, H.Y.; Chen, Y.; Hu, X.; Li, Z.R.; Kidd, A.; Liu, C.L. Spatial mismatch analyses of school land in China using a spatial statistical approach. Land Use Policy 2021, 108, 105543. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiang, S.; Meng, J.J.; Zhu, L.K.; Cheng, H.R. Spatial-temporal pattern of land use conflict in China and its multilevel driving mechanisms. Sci. Total Environ. 2021, 801, 149697. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, J.H.; Shi, Z.H.; Chu, X.P.; Shen, Y. The effect of the spatial misallocation of land supply on entrepreneurial activity. Appl. Econ. Lett. 2021, 28, 949–953. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aguejdad, R.; Houet, T.; Hubert-Moy, L. Spatial validation of land use change models using multiple assessment techniques: A case study of transition potential models. Environ. Modeling Assess. 2017, 22, 591–606. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- MohanRajan, S.N.; Loganathan, A.; Manoharan, P. Survey on land use/land cover (LU/LC) change analysis in remote sensing and GIS environment: Techniques and Challenges. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 2020, 27, 29900–29926. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yasir, M.; Sheng, H.; Huang, B.H.; Rahman, S.U. Coastline extraction and land use change analysis using remote sensing (RS) and geographic information system (GIS) technology—A review of the literature. Rev. Environ. Health 2021, 35, 453–460. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Arefin, R.; Meshram, S.G.; Santos, C.A.G. Comparison of land use/land cover change of fused image and multispectral image of landsat mission: A case study of Rajshahi, Bangladesh. Environ. Earth Sci. 2021, 80, 578. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aal, A.K.A.; Kamel, M.; Alyami, S.H. Environmental analysis of land use and land change of najran city: GIS and remote sensing. Arab. J. Sci. Eng. 2020, 45, 8803–8816. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rahman, A.; Kumar, S.; Fazal, S.; Siddiqui, M.A. Assessment of land use/land cover change in the north-west district of Delhi using remote sensing and GIS Techniques. J. Indian Soc. Remote Sens. 2012, 40, 689–697. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Suribabu, C.R.; Bhaskar, J.; Neelakantan, T.R. Land use/cover change detection of Tiruchirapalli City, India, using integrated remote sensing and GIS tools. J. Indian Soc. Remote Sens. 2012, 40, 699–708. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zadbagher, E.; Becek, K.; Berberoglu, S. Modeling land use/land cover change using remote sensing and geographic information systems: Case study of the Seyhan Basin, Turkey. Environ. Monit. Assess. 2018, 190, 494. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Obeidat, M.; Awawdeh, M.; Lababneh, A. Assessment of land use/land cover change and its environmental impacts using remote sensing and GIS techniques, Yarmouk River basin, north Jordan. Arab. J. Geosci. 2019, 12, 685. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Enoguanbhor, E.C.; Gollnow, F.; Nielsen, J.O.; Lakes, T.; Walker, B.B. Land cover change in the Abuja city-region, Nigeria: Integrating GIS and remotely sensed data to support land use planning. Sustainability 2019, 11, 1313. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abuelaish, B.; Olmedo, M.T.C. Scenario of land use and land cover change in the gaza strip using remote sensing and GIS models. Arab. J. Geosci. 2016, 9, 274. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Toure, S.I.; Stow, D.A.; Clarke, K.; Weeks, J. Patterns of land cover and land use change within the two major metropolitan areas of Ghana. Geocarto Int. 2020, 35, 209–223. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Halpern, A.B.W.; Meadows, M.E. Fifty years of land use change in the Swartland, Western Cape, South Africa: Characteristics, causes and consequences. S. Afr. Geogr. J. 2013, 95, 38–49. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cabanillas, F.J.J.; Aliseda, J.M.; Gallego, J.A.G. Land cover and land use change in the central Spanish-Portuguese border region. Bol. Asoc. Geogr. Esp. 2012, 60, 369. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Gibas, P.; Majorek, A. Analysis of land-use change between 2012–2018 in Europe in terms of sustainable development. Land 2020, 9, 46. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lubowski, R.N.; Plantinga, A.J.; Stavins, R.N. What drives land-use change in the United States? A national analysis of landowner decisions. Land Econ. 2008, 84, 529–550. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Terama, E.; Clarke, E.; Rounsevell, M.D.A.; Fronzek, S.; Carter, T.R. Modelling population structure in the context of urban land use change in Europe. Reg. Environ. Chang. 2019, 19, 667–677. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abijith, D.; Saravanan, S. Assessment of land use and land cover change detection and prediction using remote sensing and CA Markov in the northern coastal districts of Tamil Nadu, India. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 2021. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khwarahm, N.R.; Najmaddin, P.M.; Ararat, K.; Qader, S. Past and future prediction of land cover land use change based on earth observation data by the CA-Markov model: A case study from Duhok governorate, Iraq. Arab. J. Geosci. 2021, 14, 1544. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fitawok, M.B.; Derudder, B.; Minale, A.S.; Van Passel, S.; Adgo, E.; Nyssen, J. Modeling the impact of urbanization on land-use change in Bahir Dar city, Ethiopia: An integrated cellular automata-markov chain Approach. Land 2020, 9, 115. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nasiri, V.; Darvishsefat, A.A.; Rafiee, R.; Shirvany, A.; Hemat, M.A. Land use change modeling through an integrated multi-layer perceptron neural network and markov chain analysis (case study: Arasbaran region, Iran). J. For. Res. 2019, 30, 943–957. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nath, B.; Wang, Z.H.; Ge, Y.; Islam, K.; Singh, R.P.; Niu, Z. Land use and land cover change modeling and future potential landscape risk assessment using markov-CA model and analytical hierarchy process. ISPRS Int. J. Geo-Inf. 2020, 9, 134. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Al-sharif, A.A.A.; Pradhan, B. Monitoring and predicting land use change in Tripoli Metropolitan City using an integrated Markov chain and cellular automata models in GIS. Arab. J. Geosci. 2014, 7, 4291–4301. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- ZiaeeVafaeyan, H.; Moattar, M.H.; Forghani, Y. Land use change model based on bee colony optimization, Markov chain and a neighborhood decay cellular automaton. Nat. Resour. Modeling 2018, 31, e12151. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gounaridis, D.; Chorianopoulos, I.; Symeonakis, E.; Koukoulas, S. A random forest-cellular automata modelling approach to explore future land use/cover change in Attica (Greece), under different socio-economic realities and scales. Sci. Total Environ. 2018, 646, 320–335. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Levy, P.; van Oijen, M.; Buys, G.; Tomlinson, S. Estimation of gross land-use change and its uncertainty using a Bayesian data assimilation approach. Biogeosciences 2018, 15, 1497–1513. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abdullahi, S.; Pradhan, B. Land use change modeling and the effect of compact city paradigms: Integration of GIS-based cellular automata and weights-of-evidence techniques. Environ. Earth Sci. 2018, 77, 251. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mustafa, A.; Rienow, A.; Saadi, I.; Cools, M.; Teller, J.; Must, H. Comparing support vector machines with logistic regression for calibrating cellular automata land use change models. Eur. J. Remote Sens. 2018, 51, 391–401. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mustafa, A.; Saadi, I.; Cools, M.; Teller, J. A Time monte carlo method for addressing uncertainty in land-use change models. Int. J. Geogr. Inf. Sci. 2018, 32, 2317–2333. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Samie, A.; Deng, X.Z.; Jia, S.Q.; Chen, D.D. Scenario-based simulation on dynamics of land-use-land-cover change in Punjab Province, Pakistan. Sustainability 2017, 9, 1285. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rahnama, M.R.; Wyatt, R. Projecting land use change with neural network and GIS in northern Melbourne for 2014–2050. Aust. Geogr. 2021, 52, 149–170. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kumar, S.; Merwade, V.; Rao, P.S.C.; Pijanowski, B.C. Characterizing long-term land use/cover change in the United States from 1850 to 2000 using a nonlinear bi-analytical model. Ambio 2013, 42, 285–297. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brown, C.; Holman, I.; Rounsevell, M. How modelling paradigms affect simulated future land use change. Earth Syst. Dyn. 2021, 12, 211–231. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Avashia, V.; Parihar, S.; Garg, A. Evaluation of classification techniques for land use change mapping of Indian cities. J. Indian Soc. Remote Sens. 2020, 48, 877–908. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Karimi, M.; Mesgari, M.S.; Sharifi, M.A.; Pilehforooshha, P. Developing a methodology for modelling land use change in space and time. J. Spat. Sci. 2017, 62, 261–280. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Basse, R.M.; Charif, O.; Bodis, K. Spatial and temporal dimensions of land use change in cross border region of Luxembourg. Development of a hybrid approach integrating GIS, cellular automata and decision learning tree models. Appl. Geogr. 2016, 67, 94–108. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kocabas, V.; Dragicevic, S. Bayesian networks and agent-based modeling approach for urban land-use and population density change: A BNAS model. J. Geogr. Syst. 2013, 15, 403–426. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, N.H.; Brown, D.G.; An, L.; Yang, S.; Ligmann-Zielinska, A. Comparative performance of logistic regression and survival analysis for detecting spatial predictors of land-use change. Int. J. Geogr. Inf. Sci. 2013, 27, 1960–1982. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ralha, C.G.; Abreu, C.G.; Coelho, C.G.C.; Zaghetto, A.; Macchiavello, B.; Machado, R.B. A multi-agent model system for land-use change simulation. Environ. Model. Softw. 2013, 42, 30–46. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jjumba, A.; Dragicevic, S. High resolution urban land-use change modeling: Agent iCity approach. Appl. Spat. Anal. Policy 2013, 5, 291–315. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schwarz, N.; Kahlenberg, D.; Haase, D.; Seppelt, R. ABMland—A tool for agent-based model development on urban land use change. JASSS-J. Artif. Soc. Soc. Simul. 2012, 15, 8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pullanikkatil, D.; Palamuleni, L.; Ruhiiga, T. Assessment of land use change in Likangala River catchment, Malawi: A remote sensing and DPSIR approach. Appl. Geogr. 2016, 71, 9–23. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Palmer, B.J.; Hill, T.R.; Mcgregor, G.K.; Paterson, A.W. An Assessment of coastal development and land use change using the DPSIR framework: Case studies from the Eastern Cape, South Africa. Coast. Manag. 2011, 39, 158–174. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Okten, S.S.O.; Aysu, A.; Say, N. Residential land use change and urban sprawl through analytic hierarchy process (AHP) in Mersin, Turkey. Environ. Eng. Manag. J. 2021, 20, 1833–1842. [Google Scholar]
- Mohammady, M. Land use change optimization using a new ensemble model in Ramian County, Iran. Environ. Earth Sci. 2021, 80, 780. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Coral, C.; Bokelmann, W.; Bonatti, M.; Carcamo, R.; Sieber, S. Agency and structure: A grounded theory approach to explain land-use change in the Mindo and western foothills of Pichincha, Ecuador. J. Land Use Sci. 2020, 15, 547–569. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Buya, S.; Tongkumchum, P.; Owusu, B.E. Modelling of land-use change in Thailand using binary logistic regression and multinomial logistic regression. Arab. J. Geosci. 2020, 13, 437. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wilson, S.A.; Wilson, C.O. Modelling the impacts of civil war on land use and land cover change within Kono District, Sierra Leone: A socio-geospatial approach. Geocarto Int. 2013, 28, 476–501. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Arnold, C.; Wilson, E.; Hurd, J.; Civco, D. 30 Years of land cover change in Connecticut, USA: A case study of long-term research, dissemination of results, and their use in land use planning and natural resource conservation. Land 2020, 9, 255. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Spalding, A.K. Exploring the evolution of land tenure and land use change in Panama: Linking land policy with development outcomes. Land Use Policy 2017, 61, 543–552. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pareglio, S. The case for policy intervention in land use change: A critical assessment. Ital. J. Agron. 2013, 8, 217–223. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sanchez, J.M.T.; Maseda, R.C. Forcing and avoiding change. Exploring change and continuity in local land-use planning in Galicia (Northwest of Spain) and The Netherlands. Land Use Policy 2016, 50, 74–82. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, S.; Wang, T.; Yan, C.Z. Assessing the role of policies on land-use/cover change from 1965 to 2015 in the Mu Us Sandy Land, northern China. Sustainability 2017, 9, 1164. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qu, S.J.; Hu, S.G.; Li, W.D.; Wang, H.; Zhang, C.R.; Li, Q.F. Interaction between urban land expansion and land use policy: An analysis using the DPSIR framework. Land Use Policy 2020, 99, 104856. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vu, H.T.D.; Tran, D.D.; Schenk, A.; Nguyen, C.P.; Vu, H.L.; Oberle, P.; Trinh, V.C.; Nestmann, F. Land use change in the Vietnamese Mekong Delta: New evidence from remote sensing. Sci. Total Environ. 2022, 813, 151918. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sims, K.R.E.; Schuetz, J. Local regulation and land-use change: The effects of wetlands bylaws in Massachusetts. Reg. Sci. Urban Econ. 2009, 39, 409–421. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, B.; Robinson, D.T. Comparison of statistical approaches for modelling land-use change. Land 2018, 7, 144. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huber, R.; Rigling, A.; Bebi, P.; Brand, F.S.; Briner, S.; Buttler, A.; Elkin, C.; Gillet, F.; Gret-Regamey, A.; Hirschi, C.; et al. Sustainable land use in mountain regions under global change: Synthesis across scales and disciplines. Ecol. Soc. 2013, 18, 36. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huber, R.; Bugmann, H.; Buttler, A.; Rigling, A. Sustainable land-use practices in European mountain regions under global change: An integrated research approach. Ecol. Soc. 2013, 18, 37. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Koomen, E.; Koekoek, A.; Dijk, E. Simulating land-use change in a regional planning context. Appl. Spat. Anal. Policy 2011, 4, 223–247. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schmidt, S. Land use planning tools and institutional change in Germany: Recent developments in local and regional planning. Eur. Plan. Stud. 2009, 17, 1907–1921. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Milhorance, C.; Bursztyn, M.; Sabourin, E. From policy mix to policy networks: Assessing climate and land use policy interactions in Mato Grosso, Brazil. J. Environ. Policy Plan. 2020, 22, 381–396. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Danilo, V.D. The evolution process of Chicago’s industrial land-use policy. Urban Res. Pract. 2019, 11, 478–491. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dai, B.; Gu, X.K.; Xie, B.M. Policy framework and mechanism of life cycle management of industrial land (LCMIL) in China. Land Use Policy 2021, 99, 104997. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Teka, K.; Van Rompaey, A.; Poesen, J. Assessing the role of policies on land use change and agricultural development since 1960s in northern Ethiopia. Land Use Policy 2012, 30, 944–951. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, L.Y.; Qi, Z.X.; Xian, S.; Yao, D. Agricultural land use change in chongqing and the policy rationale behind it: A multiscale perspective. Land 2021, 10, 275. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Song, X.Q.; Ouyang, Z.; Li, Y.S.; Li, F.D. Cultivated land use change in China, 1999–2007: Policy development perspectives. J. Geogr. Sci. 2012, 22, 1061–1078. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Balikci, S.; Giezen, M.; Arundel, R. The paradox of planning the compact and green city: Analyzing land-use change in Amsterdam and Brussels. J. Environ. Plan. Manag. 2021. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hersperger, A.M.; Oliveira, E.; Pagliarin, S.; Palka, G.; Verburg, P.; Bolliger, J.; Gradinaru, S. Urban land-use change: The role of strategic spatial planning. Glob. Environ. Chang.-Hum. Policy Dimens. 2018, 51, 32–42. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Adhikari, S.; Fik, T.; Dwivedi, P. Proximate causes of land-use and land-cover change in Bannerghatta national park: A spatial statistical model. Forests 2017, 8, 342. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ganguly, K.; Kumar, R.; Reddy, K.M.; Rao, P.J.; Saxena, M.R.; Shankar, G.R. Optimization of spatial statistical approaches to identify land use/land cover change hot spots of Pune region of Maharashtra using remote sensing and GIS techniques. Geocarto Int. 2017, 32, 777–796. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sidharthan, R.; Bhat, C.R. Incorporating spatial dynamics and temporal dependency in land use change models. Geogr. Anal. 2012, 44, 321–349. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jimenez-Moreno, M.J.; Gonzalez-Guillen, M.D.; Escalona-Maurice, M.; Valdez-Lazalde, J.R.; Aguirre-Salado, C.A. Comparison of spatial methods to detect urban land-use change. Rev. Chapingo Ser. Cienc. For. Y Del Ambiente 2011, 17, 389–406. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, H.; Liu, Y.X.; Cai, L.P.; Fan, D.L.; Wang, Y.J.; Yao, Y. Regional differentiation in the ecological effects of land cover change in China. Land Degrad. Dev. 2021, 33, 346–357. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, C.M.; Zhang, X.L.; Wang, K.; Yuan, S.F.; Yang, L.X.; Skitmore, M. Urban-rural construction land transition and its coupling relationship with population flow in China’s urban agglomeration region. Cities 2020, 101, 102701. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gao, X.W.; Liu, T.; Cao, G.Z. On the influencing factors of metropolitan and non-metropolitan urban land expansion in Yangtze Delta region. Hum. Geogr. 2012, 126, 88–93. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dadi, D.; Azadi, H.; Senbeta, F.; Abebe, K.; Taheri, F.; Stellmacher, T. Urban sprawl and its impacts on land use change in Central Ethiopia. Urban For. Urban Green. 2016, 16, 132–141. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tomao, A.; Mattioli, W.; Fanfani, D.; Ferrara, C.; Quaranta, G.; Salvia, R.; Salvati, L. Economic downturns and land-use change: A spatial analysis of urban transformations in Rome (Italy) using a geographically weighted principal component analysis. Sustainability 2021, 13, 11293. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Du, D.N. The causal relationship between land urbanization quality and economic growth: Evidence from capital cities in China. Qual. Quant. 2017, 51, 2707–2723. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, L.; Zhang, P.Y.; Hou, W. Land use/cover change and driving forces in Southern Liaoning province since 1950s. Chin. Geogr. Sci. 2005, 15, 131–136. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cheng, J.; Zhao, J.M.; Zhu, D.L.; Zhang, H. Limits of land capitalization and its economic effects: Evidence from China. Land 2022, 10, 1346. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, D.X.; Chan, R.C.K. On ‘Land Finance’ in urban China: Theory and practice. Habitat Int. 2018, 75, 96–104. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Carruthers, J.I.; Mulligan, G.F. Land absorption in US metropolitan areas: Estimates and projections from regional adjustment models. Geogr. Anal. 2007, 39, 78–104. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Han, H.L.; Li, H. Coupling coordination evaluation between population and land urbanization in Ha-Chang urban agglomeration. Sustainability 2020, 12, 357. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ouyang, D.; Zhu, X.; Liu, X.; He, R.; Wan, Q. Spatial differentiation and driving factor analysis of urban construction land change in county-level city of Guangxi, China. Land 2021, 10, 691. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- He, S.J.; Liu, L.; Yang, G.B.; Wang, F.L. Housing differentiation and housing poverty in Chinese low-income urban neighborhoods under the confluence of state-market forces. Urban Geogr. 2017, 38, 729–751. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, S.; Zhang, C.; Qi, J. The key factors driving the development of new towns by mother cities and regions: Evidence from China. ISPRS Int. J. Geo-Inf. 2021, 10, 223. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, S.; Zhao, K.; Zhang, P. Spatial inequality in China’s housing market and the driving mechanism. Land 2021, 10, 841. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Miyamoto, S.; Chacon, A.; Hossain, M.; Martinez, L. Soil salinity of urban turf areas irrigated with saline water I Spatial variability. Landsc. Urban Plan. 2005, 71, 233–241. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bain, J.S. Industrial Organization; Harvard University Press: Cambridge, MA, USA, 1959. [Google Scholar]
- Li, L.; Zhao, K.; Wang, X.; Zhao, S.; Liu, X.; Li, W. Spatio-temporal evolution and driving mechanism of urbanization in small cities: Case study from Guangxi. Land 2022, 11, 415. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pesce, A. The Decoupling of Emerging Economies: Theoretical and Empirical Puzzle. J. Econ. Surv. 2017, 31, 602–631. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, J.D.; Wang, P.; Cui, L.B.; Huang, S.; Song, M.L. Decomposition and decoupling analysis of CO2 emissions in OECD. Appl. Energy 2018, 231, 937–950. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tapio, P. Towards a theory of decoupling: Degrees of decoupling in the EU and the case of road traffic in Finland between 1970 and 2001. Transp. Policy 2005, 12, 137–151. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Longhofer, W.; Jorgenson, A. Decoupling reconsidered: Does world society integration influence the relationship between the environment and economic development? Soc. Sci. Res. 2017, 65, 17–29. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, P.; Hu, J.; Zhao, K.; Chen, H.; Zhao, S.; Li, W. Dynamics and decoupling analysis of carbon emissions from construction industry in China. Buildings 2022, 12, 257. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, P.X.; Cao, H. Simulating uneven urban spatial expansion under various land protection strategies: Case study on Southern Jiangsu urban agglomeration. ISPRS Int. J. Geo-Inf. 2019, 8, 521. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, X.W.; Liang, C.; Shi, J.B.; Li, M.D. Spatiotemporal dynamics and urban land-use transformation in the rapid urbanization of the Shanghai metropolitan area in the 1980s–2000s. J. Environ. Inform. 2012, 20, 103–114. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xue, Q.R.; Yang, X.H.; Wu, F.F. A three-stage hybrid model for the regional assessment, spatial pattern analysis and source apportionment of the land resources comprehensive supporting capacity in the Yangtze River Delta urban agglomeration. Sci. Total Environ. 2020, 711, 134428. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ren, X.Y.; He, Y.F.; Wang, Z.M. Spatial-temporal characteristics of construction land expansion and occupation of cultivated land in urban agglomeration of central and southern Liaoning province based on remote sensing. Remote Sens. Land Resour. 2020, 32, 98–105. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Y.S.; Feng, Y.F.; Guo, G.H.; Wang, F.; Cai, S.R. The Spatio-temporal characteristics of construction land expansion in China’s typical urban agglomerations in Recent 30 years: A case study of the Beijing-Tianjin-Hebei urban agglomeration and the Guangdong-Hong Kong—Macao greater bay area. J. South China Norm. Univ. 2022, 54, 79–90. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ouyang, X.; Zhu, X.; He, Q.Y. Study of Spatio-temporal pattern and driving mechanism of urban land expansion in urban agglomeration: A case study of the Changsha-Zhuzhou-Xiangtan urban agglomeration. Resour. Environ. Yangtze Basin 2020, 29, 1298–1309. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, X.; He, S.M.; Huang, T.T.; Wang, Y. Analysis of spatial-temporal pattern characteristics and driving factors of urban land expansion: Taking central plains city cluster as an example. Ecol. Econ. 2020, 36, 105–111. [Google Scholar]
- Tang, C.C.; Li, Y.P. Geo-information Tupu process of land use/cover change in polycentric urban agglomeration: A case study of Changsha-Zhuzhou-Xiangtan urban agglomeration. Geogr. Res. 2020, 39, 2626–2641. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Y.L.; Cai, E.X.; Jing, Y.; Gong, J.; Wang, Z.Y. Analyzing the decoupling between rural-to-urban migrants and urban land expansion in Hubei province, China. Sustainability 2018, 10, 345. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, M.; Shi, Y.Y.; Duan, W.K.; Chen, A.Q.; Wang, N.; Hao, J.M. Spatiotemporal decoupling of population, economy and construction land changes in Hebei province. Sustainability 2019, 11, 6794. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, C.C.; Liu, Y.F.; Kong, X.S.; Li, J.W. Spatiotemporal decoupling between population and construction land in urban and Rural Hubei province. Sustainability 2017, 9, 1258. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sperandelli, D.I.; Dupas, F.A.; Pons, N.A.D. Dynamics of urban sprawl, vacant land, and green spaces on the metropolitan fringe of Sao Paulo, Brazil. J. Urban Plan. Dev. 2013, 139, 274–279. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Asabere, S.B.; Acheampong, R.A.; Ashiagbor, G.; Beckers, S.C.; Keck, M.; Erasmi, S.; Schanze, J.; Sauer, D. Urbanization, land use transformation and spatio-environmental impacts: Analyses of trends and implications in major metropolitan regions of Ghana. Land Use Policy 2020, 96, 104707. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cutsinger, J.; Galster, G.; Wolman, H.; Hanson, R.; Towns, D. Verifying the multi-dimensional nature of metropolitan land use: Advancing the understanding and measurement of sprawl. J. Urban Aff. 2005, 27, 235–259. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, J.J.; Su, F.Z. Spatial pattern of construction land distribution in bays along the coast of Vietnam. ISPRS Int. J. Geo-Inf. 2020, 9, 707. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fader, M.; Gerten, D.; Krause, M.; Lucht, W.; Cramer, W. Spatial decoupling of agricultural production and consumption: Quantifying dependences of countries on food imports due to domestic land and water constraints. Environ. Res. Lett. 2013, 8, 014046. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ciaian, P.; Kancs, D.; Espinosa, M. The impact of the 2013 CAP reform on the decoupled payments’ capitalization into land values. J. Agric. Econ. 2018, 69, 306–337. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Acs, S.; Hanley, N.; Dallimer, M.; Gaston, K.J.; Robertson, P.; Wilson, P.; Armsworth, P.R. The effect of decoupling on marginal agricultural systems: Implications for farm incomes, land use and upland ecology. Land Use Policy 2010, 27, 550–563. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Serra, T.; Zilberman, D.; Gil, J.M.; Featherstone, A. The effects of decoupling on land allocation. Appl. Econ. 2009, 41, 2323–2333. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- De Molina, M.G.; Fernandez, D.S.; Infante-Amate, J.; Aguilera, E.; Traver, J.V.; Guzman, G.I. Decoupling food from land: The evolution of Spanish agriculture from 1960 to 2010. Sustainability 2017, 9, 2348. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Millones, M.; Parmentier, B.; Rogan, J.; Schmook, B. Using food flow data to assess sustainability: Land use displacement and regional decoupling in Quintana Roo, Mexico. Sustainability 2017, 8, 1145. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pikaar, I.; Matassa, S.; Bodirsky, B.L.; Weindl, I.; Humpenoder, F.; Rabaey, K.; Boon, N.; Bruschi, M.; Yuan, Z.G.; van Zanten, H.; et al. Decoupling livestock from land use through industrial feed production pathways. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2018, 52, 7351–7359. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Velado-Alonso, E.; Morales-Castilla, I.; Gomez-Sal, A. Recent land use and management changes decouple the adaptation of livestock diversity to the environment. Sci. Rep. 2021, 10, 21035. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nelson, A.E.; Forbes, A.A. Urban land use decouples plant-herbivore-parasitoid interactions at multiple spatial scales. PLoS ONE 2014, 9, e102127. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Smart, M.D.; Otto, C.R.V.; Carlson, B.L.; Roth, C.L. The influence of spatiotemporally decoupled land use on honey bee colony health and pollination service delivery. Environ. Res. Lett. 2018, 13, 084016. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gupta, S. Decoupling: A step toward sustainable development with reference to OECD countries. Int. J. Sustain. Dev. World Ecol. 2015, 22, 510–519. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Verburg, P.H.; Alexander, P.; Evans, T.; Magliocca, N.R.; Malek, Z.; Rounsevell, M.D.A.; van Vliet, J. Beyond land cover change: Towards a new generation of land use models. Curr. Opin. Environ. Sustain. 2019, 38, 77–85. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Azadi, H.; Barati, A.A.; Rafiaani, P.; Taheri, F.; Gebrehiwot, K.; Witlox, F.; Lebailly, P. Evolution of land use-change modeling: Routes of different schools of knowledge. Landsc. Ecol. Eng. 2017, 13, 319–332. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shu, H.; Xiong, P.P. Reallocation planning of urban industrial land for structure optimization and emission reduction: A practical analysis of urban agglomeration in China’s Yangtze River delta. Land Use Policy 2019, 81, 604–623. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abrantes, P.; Fontes, I.; Gomes, E.; Rocha, J. Compliance of land cover changes with municipal land use planning: Evidence from the Lisbon metropolitan region (1990–2007). Land Use Policy 2016, 51, 120–134. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, J.; Jung, S. Industrial land use planning and the growth of knowledge industry: Location pattern of knowledge-intensive services and their determinants in the Seoul metropolitan area. Land Use Policy 2020, 95, 104632. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jun, M.J. Forecasting urban land-use demand using a metropolitan input-output model. Environ. Plan. A 2005, 37, 1311–1328. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tang, Y.; Yuan, Y.B.; Zhong, Q.Y. Evaluation of land comprehensive carrying capacity and spatio-temporal analysis of the Harbin-Changchun urban agglomeration. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2021, 18, 521. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kline, J.D.; Thiers, P.; Ozawa, C.P.; Yeakley, J.A.; Gordon, S.N. How well has land-use planning worked under different governance regimes? A case study in the Portland, OR-Vancouver, WA metropolitan area, USA. Landsc. Urban Plan. 2014, 131, 51–63. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Peng, J.; Liu, Q.H.; Blaschke, T.; Zhang, Z.M.; Liu, Y.X.; Hu, Y.N.; Wang, M.; Xu, Z.H.; Wu, J.S. Integrating land development size, pattern, and density to identify urban-rural fringe in a metropolitan region. Landsc. Ecol. 2020, 35, 2045–2059. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tao, Z.; Jiang, G.H.; Li, G.Y.; Zhou, D.Y.; Qu, Y.B. Neglected idle rural residential land (IRRL) in metropolitan suburbs: Spatial differentiation and influencing factors. J. Rural Stud. 2020, 78, 163–175. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xiao, R.; Huang, X.; Yu, W.X.; Lin, M.; Zhang, Z.H. Interaction relationship between built-up land expansion and demographic-social-economic urbanization in Shanghai-Hangzhou Bay metropolitan region of Eastern China. Photogramm. Eng. Remote Sens. 2019, 85, 231–240. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Y.H.; Zhang, Q. Human-environment interactions in China: Evidence of land-use change in Beijing-Tianjin-Hebei metropolitan region. Hum. Ecol. Rev. 2014, 20, 26–35. [Google Scholar]
- Hu, H.B.; Wu, L.Y.; Zhan, Y.L.; Zhang, S.H. Spatial and temporal pattern analysis of land use in Yangtze River Delta based on remote sensing and GIS in intelligent environment. Adv. Civ. Eng. 2021, 2021, 5561977. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, C.J.; Wu, Y.M.; Ye, X.Y.; Wu, B.J.; Kudva, S. The direct and indirect drag effects of land and energy on urban economic growth in the Yangtze River Delta, China. Environ. Dev. Sustain. 2020, 21, 2945–2962. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rienow, A.; Kantakumar, L.N.; Ghazaryan, G.; Droge-Rothaar, A.; Sticksel, S.; Trampnau, B.; Thonfeld, F. Modelling the spatial impact of regional planning and climate change prevention strategies on land consumption in the Rhine-Ruhr Metropolitan Area 2017–2030. Landsc. Urban Plan. 2022, 217, 104284. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]









| Indicator | Grade | Parameter Value Range | |
|---|---|---|---|
| Gini Index (GI) | Strong | GI < 0.4 | |
| Medium | 0.6 > GI ≥ 0.4 | ||
| Weak | GI ≥ 0.6 | ||
| Concentration Rate (CR) | Oligopoly type I | CR4 ≥ 85% | |
| Oligopoly type II | 85% > CR4 ≥ 75% | CR8 ≥ 75% | |
| Oligopoly type III | 75% > CR4 ≥ 50% | 85% > CR8 ≥ 75% | |
| Oligopoly type IV | 50% > CR4 ≥ 35% | 75% > CR8 ≥ 45% | |
| Oligopoly type V | 35% > CR4≥30% | 45% > CR8 ≥ 40% | |
| Competitive type | CR4 < 30% | CR8 < 40% | |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Ma, Y.; Zhang, P.; Zhao, K.; Zhou, Y.; Zhao, S. A Dynamic Performance and Differentiation Management Policy for Urban Construction Land Use Change in Gansu, China. Land 2022, 11, 942. https://doi.org/10.3390/land11060942
Ma Y, Zhang P, Zhao K, Zhou Y, Zhao S. A Dynamic Performance and Differentiation Management Policy for Urban Construction Land Use Change in Gansu, China. Land. 2022; 11(6):942. https://doi.org/10.3390/land11060942
Chicago/Turabian StyleMa, Yajun, Ping Zhang, Kaixu Zhao, Yong Zhou, and Sidong Zhao. 2022. "A Dynamic Performance and Differentiation Management Policy for Urban Construction Land Use Change in Gansu, China" Land 11, no. 6: 942. https://doi.org/10.3390/land11060942
APA StyleMa, Y., Zhang, P., Zhao, K., Zhou, Y., & Zhao, S. (2022). A Dynamic Performance and Differentiation Management Policy for Urban Construction Land Use Change in Gansu, China. Land, 11(6), 942. https://doi.org/10.3390/land11060942








