Cellular Automata in Modeling and Predicting Urban Densification: Revisiting the Literature since 1971
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Cellular Automata (CA) Model
3. Evolution of Urban Growth Models
3.1. Advancement of Urban CA Model to Study Densification
3.2. Integrated CA Models
4. Materials and Methods
4.1. Bibliometric Analysis
4.2. Literature Section
4.3. Literature Review
5. Key Findings: Mapping the Landscape of CA in the Five Decades since 1971
Bibliometric Analysis
6. Cellular Automata in Urban Densification
6.1. Data Collection
6.2. Driving Factors
| Author, Year | Built Factors | Environmental Factors | Socioeconomic Factors |
|---|---|---|---|
| Poelmans and Van Rompaey, 2010 [42] | ● | ● | ● |
| Al-shalabi et al., 2013 [32] | ● | ● | |
| Pijanowski et al., 2014 [55] | ● | ● | |
| Liu and Ma, 2011 [91] | ● | ● | |
| White and Engelen, 2000 [64] | ● | ||
| Wu, 2002 [92] | ● | ● | |
| Mustafa et al., 2018 [59] | ● | ● | ● |
| Shu et al., 2014 [93] | ● | ● |
6.3. Validation and Calibration of Urban CA Models
6.4. Prospects of CA Model in Urban Densification
6.4.1. Vector-Based CA Model
6.4.2. Three-Dimensional CA Model
7. Challenges, Limitations, and Potential
8. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Liu, X.; Ma, L.; Li, X.; Ai, B.; Li, S.; He, Z. Simulating urban growth by integrating landscape expansion index (LEI) and cellular automata. Int. J. Geogr. Inf. Sci. 2014, 28, 148–163. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lambin, E.F.; Turner, B.L.; Geist, H.J.; Agbola, S.B.; Angelsen, A.; Bruce, J.W.; Coomes, O.T.; Dirzo, R.; Fischer, G.; Folke, C. The causes of land-use and land-cover change: Moving beyond the myths. Glob. Environ. Chang. 2001, 11, 261–269. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rasoul, G.; Noushad, S. Smart growth strategy in urban development, principles and approaches. J. Geogr. Develop. 2008, 6, 163–180. [Google Scholar]
- Shi, L.; Shao, G.; Cui, S.; Li, X.; Lin, T.; Yin, K.; Zhao, J. Urban three-dimensional expansion and its driving forces—A case study of Shanghai, China. Chin. Geogr. Sci. 2009, 19, 291–298. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Teller, J. Regulating urban densification: What factors should be used? Build. Cities 2021, 2, 302–317. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mustafa, A.M.; Heppenstall, A.; Omrani, H.; Saadi, I.; Cools, M.; Teller, J. Modelling built-up expansion and densification with multinomial logistic regression, cellular automata and genetic algorithm. Comput. Environ. Urban Syst. 2018, 67, 147–156. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Gordon, P.; Richardson, H.W. Are compact cities a desirable planning goal? J. Am. Plan. Assoc. 1997, 63, 96–106. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kaur, M.; Hewage, K.; Sadiq, R. Investigating the impacts of urban densification on buried water infrastructure through DPSIR framework. J. Clean. Prod. 2020, 259, 120897. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Broitman, D.; Koomen, E. Residential Density Change: Densification and Urban Expansion. Geogr. Urban Process. (Sub-Top.) 2015, 54, 32–46. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Leao, S.; Bishop, I.; Evans, D. Simulating urban growth in a developing nation’s region using a CA-based model. J. Urban Plan. Dev. 2004, 130, 145–158. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Herold, M.; Goldstein, N.C.; Clarke, K.C. The spatiotemporal form of urban growth: Measurement, analysis and modeling. Remote Sens. Environ. 2003, 86, 286–302. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Poelmans, L.; Van Rompaey, A. Detecting and modelling spatial patterns of urban sprawl in highly fragmented areas: A case study in the Flanders–Brussels region. Landsc. Urban Plan. 2009, 93, 10–19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, H.; He, S.; Liu, X.; Dai, L.; Pan, P.; Hong, S.; Zhang, W. Simulating urban expansion using a cloud-based cellular automata model: A case study of Jiangxia, Wuhan, China. Landsc. Urban Plan. 2013, 110, 99–112. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Santé, I.; García, A.M.; Miranda, D.; Crecente, R. Cellular automata models for the simulation of real-world urban processes: A review and analysis. Landsc. Urban Plan. 2010, 96, 108–122. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tobler, W.R. A Computer Movie Simulating Urban Growth in the Detroit Region. Econ. Geogr. 1970, 46, 234–240. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Couclelis, H. Cellular Worlds: A Framework for Modeling Micro—Macro Dynamics. Environ. Plan. A 1985, 17, 585–596. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Phipps, M. Dynamical Behavior of Cellular Automata under the Constraint of Neighborhood Coherence. Geogr. Anal. 2010, 21, 197–215. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Batty, M. Urban Evolution on the Desktop: Simulation with the Use of Extended Cellular Automata. Environ. Plan. A 1998, 30, 1943–1967. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aburas, M.M.; Ho, Y.M.; Ramli, M.F.; Ash’aari, Z.H. The simulation and prediction of spatio-temporal urban growth trends using cellular automata models: A review. Int. J. Appl. Earth Obs. GeoInf. 2016, 52, 380–389. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liang, X.; Liu, X.; Li, D.; Zhao, H.; Chen, G. Urban growth simulation by incorporating planning policies into a CA-based future land-use simulation model. Int. J. Geogr. Inf. Sci. 2018, 32, 2294–2316. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tong, X.; Feng, Y. A review of assessment methods for cellular automata models of land-use change and urban growth. Int. J. Geogr. Inf. Sci. 2020, 34, 866–898. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Al-sharif, A.; Pradhan, B. A novel Approach for Predicting the Spatial Patterns of Urban Expansion by Combining the Chi-Squared Automatic Integration Detection Decision Tree, Markov Chain, and Cellular Automata Models in GIS. Geocarto Int. 2015, 30, 858–881. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Singh, A.K. Modelling Land Use Land Cover Changes Using Cellular Automata in a Geo-Spatial Environment. Master’s Thesis, ITC, Enschede, The Netherlands, 2003. [Google Scholar]
- Liu, Y. Modelling Urban Development with Geographical Information Systems and Cellular Automata: A Case Study of Sydney since 1971; Taylor and Francis: New York, NY, USA, 2001. [Google Scholar]
- Basse, R.; Omrani, H.; Charif, O.; Gerber, P.; Bódis, K. Land use changes modelling using advanced methods: Cellular automata and artificial neural networks. The spatial and explicit representation of land cover dynamics at the cross-border region scale. Appl. Geogr. 2014, 53, 160–171. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, X.; Yeh, A.G.O. Neural-network-based cellular automata for simulating multiple land use changes using GIS. Int. J. Geogr. Inf. Sci. 2002, 16, 323–343. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, X.; Liu, X.P. An extended cellular automaton using case-based reasoning for simulating urban. Int. J. Geogr. Inf. Sci. 2006, 20, 1109–1136. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, X.; Li, X.; Liu, L.; He, J.; Ai, B. A bottom-up approach to discover transition rules of cellular automata using ant intelligence. Int. J. Geogr. Inf. Sci. 2008, 22, 1247–1269. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mitsova, D.; Shuster, W.; Wang, X. A cellular automata model of land cover change to integrate urban growth with open space conservation. Landsc. Urban Plan. 2011, 99, 41–153. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mantelas, L.; Prastacos, P.; Hatzichristos, T.; Koutsopoulos, K. Using fuzzy cellular automata to access and simulate urban growth. GeoJournal 2012, 77, 13–28. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Y.; Feng, Y. A Logistic Based Cellular Automata Model for Continuous Urban Growth Simulation: A Case Study of the Gold Coast City, Australia. In Agent-Based Models of Geographical Systems; Heppenstall, A., Crooks, A., See, L., Batty, M., Eds.; Springer: Dordrecht, The Netherlands, 2012. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Al-Shalabi Al-Sharif, A.A.; Pradhan, B. Monitoring and predicting land use change in Tripoli Metropolitan City using an integrated Markov chain and cellular automata models in GIS. Arab. J. Geosci. 2013, 7, 4291–4301. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wagner, D.F. Cellular Automata and Geographic Information Systems. Environ. Plan. B Plan. Des. 1997, 24, 219–234. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sgandurra, D. An Introduction to Cellular Automata (Powerpoint presentation); Bio-inspired Models of Computation, Dipartimento di Informatica, Università di Pisa: Pisa, Italy, 16 October 2009. [Google Scholar]
- Rodríguez Puente, R.; Pérez Betancourt, Y.G.; Mufeti, K. Cellular Automata and Its Applications in Modeling and Simulating the Evolution of Diseases [Paper Presentation]; National Research Symposium: Windhoek, Namibia, 2015. [Google Scholar]
- Wolfram, S. Cellular automata as models of complexity. Nature 1984, 311, 419–424. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Grimm, N.; Grove, M.; Pickett, S.T.A.; Redman, C. Integrated Approaches to Long-Term Studies of Urban Ecological Systems; Springer: Boston, MA, USA, 2008. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Allen, J.; Lu, K. Modeling and Prediction of Future Urban Growth in the Charleston Region of South Carolina: A GIS-based Integrated Approach. Conserv. Ecol. 2003, 8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Amato, F.; Pontrandolfi, P.; Murgante, B. Using Spatiotemporal Analysis in Urban Sprawl Assessment and Prediction. In Computational Science and Its Applications–ICCSA 2014. ICCSA 2014. Lecture Notes in Computer Science; Springer: Cham, Switzerland, 2014; Volume 8580, pp. 758–773. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Verburg, P.; Overmars, K.; Huigen, M.; Groot, W.; Veldkamp, A. Analysis of the effects of land use change on protected areas in the Philippines. Appl. Geogr. 2006, 26, 153–173. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jokar Arsanjani, J.; Zipf, A.; Mooney, P.; Helbich, M. An Introduction to OpenStreetMap in Geographic Information Science: Experiences, Research, and Applications. In OpenStreetMap in GIScience; Jokar Arsanjani, J., Zipf, A., Mooney, P., Helbich, M., Eds.; Lecture Notes in Geoinformation and Cartography; Springer: Cham, Switzerland, 2015. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Poelmans, L.; Rompaey, A.V. Complexity and performance of urban expansion models. Comput. Environ. Urban Syst. 2010, 34, 17–27. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Verburg, P.; Dijst, M.; Schot, P.; Veldkamp, A. Land Use Change Modelling: Current Practice and Research Priorities. Geojournal 2004, 61, 309–324. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yagoub, M.M.; Bizreh, A.A. Prediction of Land Cover Change Using Markov and Cellular Automata Models: Case of Al-Ain, UAE, 1992–2030. J. Indian Soc. Remote Sens. 2014, 42, 665–671. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Clarke, K.C.; Hoppen, S.; Gaydos, L. A self-modifying cellular automaton model of historical urbanization in the San Francisco Bay area. Environ. Plan. B: Plan. Des. 1997, 24, 247–261. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Landis, J.; Zhang, M. The second generation of the California urban futures model. Environ. Plan. B Plan. Des. 1998, 25, 795–824. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Al-sharif, A.; Pradhan, B.; Shafri, H.; Mansor, S. Quantitative analysis of urban sprawl in Tripoli using Pearson’s Chi-Square statistics and urban expansion intensity index. IOP Conf. Ser. Earth Environ. Sci. 2014, 20, 012006. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, Z.; Lo, C. Modeling urban growth in Atlanta using logistic regression. Comput. Environ. Urban Syst. 2007, 31, 667–688. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, X.; Gong, P. Urban growth models: Progress and perspective. Sci. Bull. 2016, 61, 1637–1650. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, X.; Andersson, C. Assessing the impact of temporal dynamics on land-use change modeling. Comput. Environ. Urban Syst. 2004, 28, 107–124. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Batty, M. Urban Modelling: Algorithms, Calibrations, Predictions; Cambridge University Press: Cambridge, UK, 1976; p. 381. [Google Scholar]
- Clarke, K.; Gaydos, L. Loose-Coupling a Cellular Automaton Model and GIS: Long-Term Urban Growth Prediction for San Francisco and Washington/Baltimore. Int. J. Geogr. Inf. Sci. IJGIS 1998, 12, 699–714. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Matthews, R.; Gilbert, N.; Roach, A.; Polhill, J.G.; Gotts, N. Agent-based land-use models: A review of applications. Landsc. Ecol. 2007, 22, 1447–1459. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Liu, X.; Li, X.; Shi, X.; Huang, K.; Liu, Y. A multi-type ant colony optimization (MACO) method for optimal land use allocation in large areas. Int. J. Geogr. Inf. Sci. 2012, 26, 1325–1343. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pijanowski, B.; Brown, D.G.; Shellito, B.; Manik, G. Using neural networks and GIS to forecast land use changes: A Land Transformation Model. Comput. Environ. Urban Syst. 2002, 26, 553–575. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Waddell, P. UrbanSim: Modeling Urban Development for Land Use, Transportation, and Environmental Planning. J. Am. Plan. Assoc. 2002, 68, 297–314. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rahnama, M. Forecasting land-use changes in Mashhad Metropolitan area using Cellular Automata and Markov chain model for 2016–2030. Sustain. Cities Soc. 2021, 64, 102548. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Silva, E.A.; Clarke, K. Calibration of the SLEUTH urban growth model for Lisbon and Porto, Portugal. Comput. Environ. Urban Syst. 2002, 26, 525–552. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mustafa, A.M.; Rompaey, A.V.; Cools, M.; Saadi, I.; Teller, J. Addressing the determinants of built-up expansion and densification processes at the regional scale. Urban Stud. 2018, 55, 3279–3298. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Cao, X.; Luo, P.; Li, M.; Long, A. Research on the Simulation of Urban Land Use Change Based on GIS and CA Models—A Case Study of Longgang District, Shenzhen City. In Proceedings of the 2009 International Conference on Environmental Science and Information Application Technology, Wuhan, China, 4–5 July 2009; Volume 2, pp. 351–354. [Google Scholar]
- Ghadami, M.; Dittmann, A.; Safarrad, T. Lack of Spatial Approach in Urban Density Policies: The Case of the Master Plan of Tehran. Sustainability 2020, 12, 7285. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Batty, M. Artificial intelligence and smart cities. Environ. Plan. B Urban Anal. City Sci. 2018, 45, 3–6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mustafa, A.M.; Cools, M.; Saadi, I.; Teller, J. Coupling agent-based, cellular automata and logistic regression into a hybrid urban expansion model (HUEM). Land Use Policy 2017, 69, 529–540. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- White, R.; Engelen, G. Cellular Automata and Fractal Urban Form: A Cellular Modelling Approach to the Evolution of Urban Land-Use Patterns. Environ. Plan. A 1993, 25, 1175–1199. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Liu, Y.; Corcoran, J.; Feng, Y. Cellular automata. In International Encyclopedia of Human Geography; Elsevier: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 2020; pp. 101–104. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Y.; Dai, L.; Xiong, H. Simulation of urban expansion patterns by integrating auto-logistic regression, Markov chain and cellular automata models. J. Environ. Plan. Manag. 2015, 58, 1113–1136. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Almeida, C.; Gleriani, J.M.; Castejon, E.; Soares-Filho, B. Using neural networks and cellular automata for modelling intra-urban land-use dynamics. Int. J. Geogr. Inf. Sci. 2008, 22, 943–963. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xiao, Y.; Watson, M. Guidance on Conducting a Systematic Literature Review. J. Plan. Educ. Res. 2017, 39, 112–193. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Arsanjani, J.J.; Barron, C.; Bakillah, M.; Helbich, M. Assessing the quality of OpenStreetMap contributors together with their contributions. In Proceedings of the AGILE, Leuven, Belgium, 14–17 May 2013; pp. 14–17. [Google Scholar]
- Liu, Y.; Batty, M.; Wang, S.; Corcoran, J. Modelling urban change with cellular automata: Contemporary issues and future research directions. Prog. Hum. Geogr. 2019, 45, 3–24. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Musa, S.I.; Hashim, M.; Reba, M.N. A review of geospatial-based urban growth models and modelling initiatives. Geocarto Int. 2017, 32, 813–833. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aburas, M.M.; Ho, Y.; Ramli, M.F.; Ash’aari, Z.H. Improving the capability of an integrated CA-Markov model to simulate spatio-temporal urban growth trends using an Analytical Hierarchy Process and Frequency Ratio. Int. J. Appl. Earth Obs. Geoinf. 2017, 59, 65–78. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kang, J.; Fang, L.; Li, S.; Wang, X. Parallel Cellular Automata Markov Model for Land Use Change Prediction over MapReduce Framework. ISPRS Int. J. Geo-Inf. 2019, 8, 454. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Yang, Q.; Li, X. Nonlinear transition rules of urban cellular automata based on a Bayesian method. Acat Sci. Nat. Univ. Sunyatseni 2007, 46, 105–109. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar]
- Yang, Q.; Li, X.; Shi, X. Cellular automata for simulating land use changes based on support vector machines. Comput. Geosci. 2008, 34, 592–602. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Palme, M.; Ramirez, J.E. A Critical Assessment and Projection of Urban Vertical Growth in Antofagasta, Chile. Sustainability 2013, 5, 2840–2855. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Huang, C.; Homer, C.; Yang, L. Regional forest land cover characterisation using medium spatial resolution satellite data. In Remote Sensing of Forest Environments; Springer: Boston, MA, USA, 2003; pp. 389–410. [Google Scholar]
- Aristodemou, E.; Boganegra, L.M.; Mottet, L.; Pavlidis, D.; Constantinou, A.; Pain, C.C.; Robins, A.; ApSimon, H.M. How tall buildings affect turbulent air flows and dispersion of pollution within a neighbourhood. Environ. Pollut. 2018, 233, 782–796. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tang, U.W.; Wang, Z.S. Influences of urban forms on traffic-induced noise and air pollution: Results from a modelling system. Environ. Model. Softw. 2007, 22, 1750–1764. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Koziatek, O.; Dragićević, S. iCity 3D: A geosimualtion method and tool for three-dimensional modeling of vertical urban development. Landsc. Urban Plan. 2017, 167, 356–367. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jian, S.U.N.; Zhang, L.; Chunlu, P.E.N.G.; Zhongren, P.E.N.G.; Meng, X.U. CA-based urban land use prediction model: A case study on orange county, Florida, US. J. Transp. Syst. Eng. Inf. Technol. 2012, 12, 85–92. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, R.; Murayama, Y.; Morimoto, T. Scenario simulation studies of urban development using remote sensing and GIS: Review. Remote Sens. Appl. Soc. Environ. 2021, 22, 100474. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Anand, J.; Gosain, A.; Khosa, R. Prediction of land use changes based on Land Change Modeler and attribution of changes in the water balance of Ganga basin to land use change using the SWAT model. Sci. Total Environ. 2018, 644, 503–519. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ewing, R.H. Characteristics, causes, and effects of sprawl: A literature review. In Urban Ecology; Springer: New York, NY, USA, 2008; pp. 519–535. [Google Scholar]
- Mieszkowski, P.; Mills, E. The causes of metropolitan suburbanization. J. Econ. Perspect. 1993, 7, 135–147. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Pendall, R. Do land-use controls cause sprawl? Environ. Plan. B Plan. Des. 1999, 26, 555–571. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dieleman, F.; Wegener, M. Compact city and urban sprawl. Built Environ. 2004, 30, 308–323. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Landis, J. The California Urban Futures Model: A New Generation of Metropolitan Simulation Models. Environ. Plan. B Plan. Des. 1994, 21, 399–420. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Zhou, L.; Dang, X.; Mu, H.; Wang, B.; Wang, S. Cities are going uphill: Slope gradient analysis of urban expansion and its driving factors in China. Sci. Total Environ. 2021, 775, 145836. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, Y.; Newman, G.; Güneralp, B. A Review of Driving Factors, Scenarios, and Topics in Urban Land Change Models. Land 2020, 9, 246. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, C.; Ma, X. Analysis to driving forces of land use change in Lu’an mining area. Trans. Nonferrous Met. Soc. China 2011, 21, s727–s732. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, F. Calibration of stochastic cellular automata: The application to rural-urban land conversions. Int. J. Geogr. Inf. Sci. 2002, 16, 795–818. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shu, B.; Bakker, M.M.; Zhang, H.; Li, Y.; Qin, W.; Carsjens, G.J. Modeling urban expansion by using variable weights logistic cellular automata: A case study of Nanjing, China. Int. J. Geogr. Inf. Sci. 2017, 31, 1314–1333. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pontius, R.; Huffaker, D.; Denman, K. Useful techniques of validation for spatially explicit land-change models. Ecol. Model. 2004, 179, 445–461. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sargent, R. An introductory tutorial on verification and validation of simulation models. In Proceedings of the 2015 Winter Simulation Conference (WSC), Huntington Beach, CA, USA, 6–9 December 2015; pp. 1729–1740. [Google Scholar]
- Chung, C.; Fabbri, A. Validation of Spatial Prediction Models for Landslide Hazard Mapping. Nat. Hazards 2003, 30, 451–472. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vliet, J.V. Calibration and Validation of Land-Use Models. Ph.D. Thesis, Wageningen University, Wageningen, The Netherlands, 2013; p. 162. Available online: https://www.wur.nl/en/Publication-details.htm?publicationId=publication-way-343332353934 (accessed on 13 March 2022).
- Rykiel, E. Testing ecological models: The meaning of validation. Ecol. Model. 1996, 90, 229–244. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Soares-Filho, B.; Cerqueira, G.; Pennachin, C. Dinamica—A stochastic cellular automata model designed to simulate the landscape dynamics in an Amazonian colonization frontier. Ecol. Model. 2002, 154, 217–235. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, F. An Experiment on the Generic Polycentricity of Urban Growth in a Cellular Automatic City. Environ. Plan. B Plan. Des. 1998, 25, 731–752. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- González, P.B.; Gómez-Delgado, M.; Aguilera-Benavente, F. From raster to vector cellular automata models: A new approach to simulate urban growth with the help of graph theory. Comput. Environ. Urban Syst. 2015, 54, 119–131. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Triantakonstantis, D.P.; Mountrakis, G. Urban Growth Prediction: A Review of Computational Models and Human Perceptions. J. Geogr. Inf. Syst. 2012, 4, 555–587. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Benguigui, L.; Czamanski, D.; Roth, R. Modeling Cities in 3D: A Cellular Automaton Approach. Environ. Plan. B Plan. Des. 2008, 35, 413–430. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Semboloni, F. The Growth of an Urban Cluster into a Dynamic Self-Modifying Spatial Pattern. Environ. Plan. B Plan. Des. 2000, 27, 549–564. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Agius, T.; Sabri, S.; Kalantari, M. Three-Dimensional Rule-Based City Modelling to Support Urban Redevelopment Process. ISPRS Int. J. Geo Inf. 2018, 7, 413. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Alomía, G.; Loaiza, D.; Zúñiga, C.; Luo, X.; Asorey-Cacheda, R. Procedural modeling applied to the 3D city model of bogota: A case study. Virtual Real. Intell. Hardw. 2021, 3, 423–433. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, J.; Huang, B.; Chen, M.; Huang, Z. Modeling urban vertical growth using cellular automata—Guangzhou as a case study. Appl. Geogr. 2014, 53, 172–186. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Güneralp, B.; Zhou, Y.; ürge-Vorsatz, D.; Gupta, M.K.; Yu, S.; Patel, P.; Fragkias, M.; Li, X.; Seto, K.C. Global scenarios of urban density and its impacts on building energy use through 2050. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2017, 114, 8945–8950. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Vuckovic, M.; Loibl, W.; Tötzer, T.; Stollnberger, R. Potential of Urban Densification to Mitigate the Effects of Heat Island in Vienna, Austria. Environments 2019, 6, 82. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Barredo, J.; Kasanko, M.; McCormick, N.; Lavalle, C. Modelling dynamic spatial processes: Simulation of urban future scenarios through cellular automata. Landsc. Urban Plan. 2003, 64, 145–160. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shukla, A.; Jain, K.; Ramsankaran, R.; Rajasekaran, E. Understanding the macro-micro dynamics of urban densification: A case study of different sized Indian cities. Land Use Policy 2021, 107, 105469. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, L.; Omrani, H.; Zhao, Z.; Francomano, D.; Li, K.; Pijanowski, B. Analysis on urban densification dynamics and future modes in southeastern Wisconsin, USA. PLoS ONE 2019, 14, e0211964. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Saganeiti, L.; Mustafa, A.M.; Teller, J.; Murgante, B. Modeling urban sprinkling with cellular automata. Sustain. Cities Soc. 2020, 65, 102586. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guan, D.; Li, H.; Inohae, T.; Su, W.; Nagaie, T.; Hokao, K. Modeling urban land use change by the integration of cellular automaton and Markov model. Ecol. Model. 2011, 222, 3761–3772. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- García, A.M.; Santé-Riveira, I.; Boullón-Magán, M.; Crecente-Maseda, R. Calibration of an urban cellular automaton model by using statistical techniques and a genetic algorithm. Application to a small urban settlement of NW Spain. Int. J. Geogr. Inf. Sci. 2013, 27, 1593–1611. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nowak, A.; Kuś, M.; Urbaniak, J.; Zarycki, T. Simulating the coordination of individual economic decisions. Phys. A-Stat. Mech. Its Appl. 2000, 287, 613–630. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- White, S.H.; Rey, Á.M.; Sánchez, G.R. Modeling epidemics using cellular automata. Appl. Math. Comput. 2007, 186, 193–202. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sieburg, H.B.; McCutchan, H.W.; Clay, O.K.; Caballero, L.; Ostlund, J. Simulation of HIV-infection in artificial immune systems. Phys. D Nonlinear Phenom. 1990, 45, 208–227. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Omrani, H.; Tayyebi, A.; Pijanowski, B.C. Integrating the multi-label land-use concept and cellular automata with the artificial neural network-based Land Transformation Model: An integrated ML-CA-LTM modeling framework. GIScience Remote Sens. 2017, 54, 283–304. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Chaturvedi, V.; de Vries, W.T. Machine Learning Algorithms for Urban Land Use Planning: A Review. Urban Sci. 2021, 5, 68. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
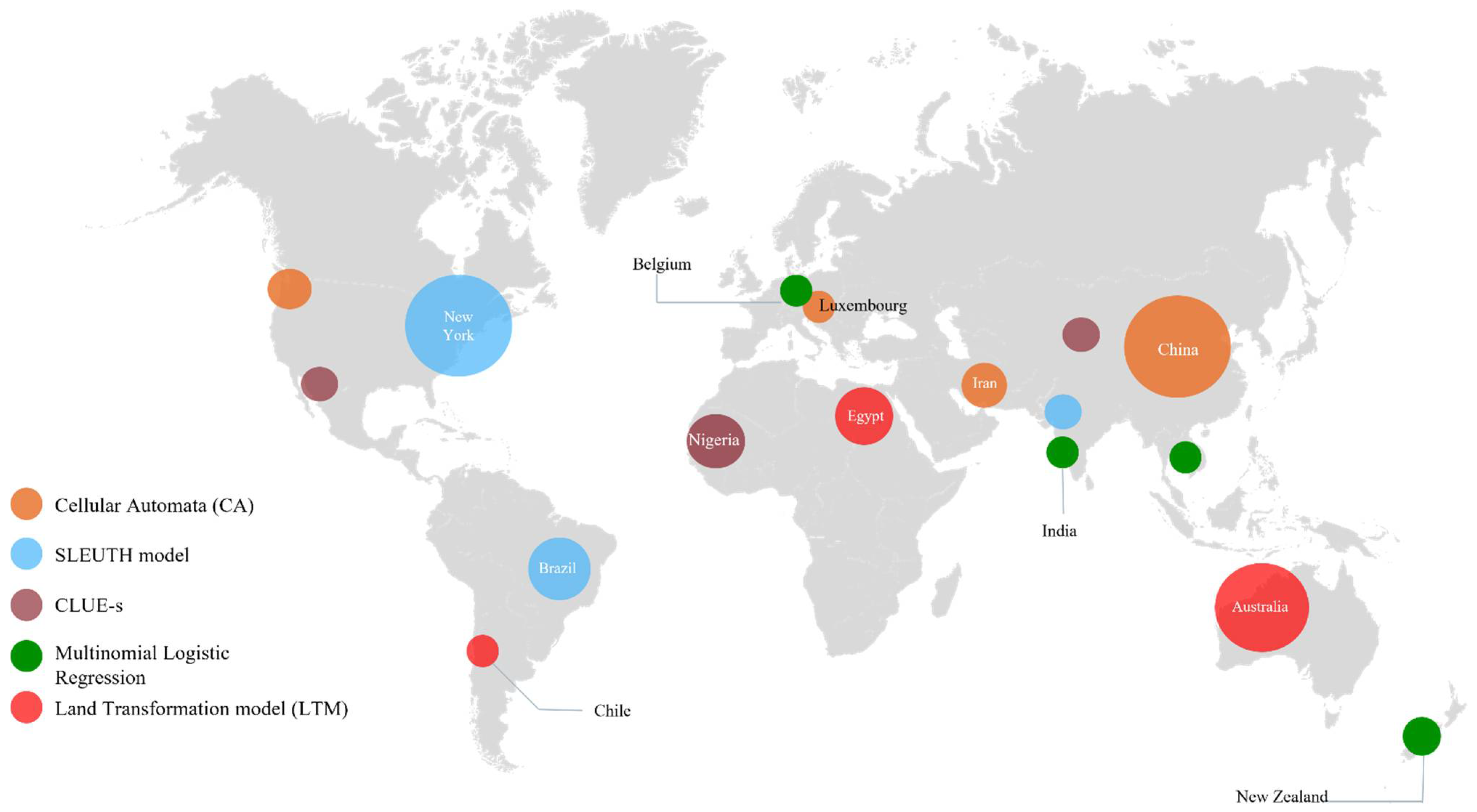

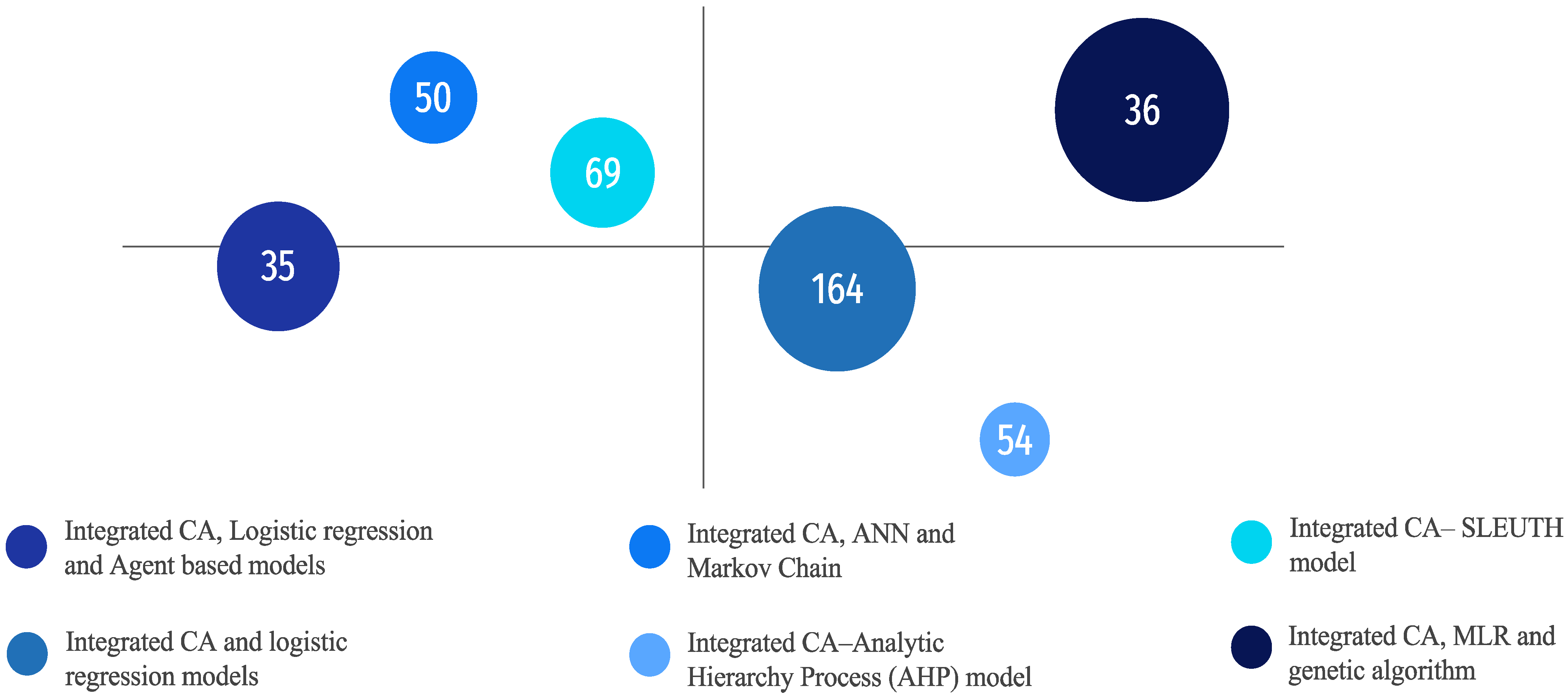




| Type of Model | Densification Process | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Urban | AND | Cellular Automata | AND | Infill developments |
| OR | Logistic Regression | OR | Growth models | |
| OR | SLEUTH | Expansion | ||
| OR | MCE-CA(Multicriteria Evaluation-Cellular Automata) | Densification |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Chakraborty, A.; Sikder, S.; Omrani, H.; Teller, J. Cellular Automata in Modeling and Predicting Urban Densification: Revisiting the Literature since 1971. Land 2022, 11, 1113. https://doi.org/10.3390/land11071113
Chakraborty A, Sikder S, Omrani H, Teller J. Cellular Automata in Modeling and Predicting Urban Densification: Revisiting the Literature since 1971. Land. 2022; 11(7):1113. https://doi.org/10.3390/land11071113
Chicago/Turabian StyleChakraborty, Anasua, Sujit Sikder, Hichem Omrani, and Jacques Teller. 2022. "Cellular Automata in Modeling and Predicting Urban Densification: Revisiting the Literature since 1971" Land 11, no. 7: 1113. https://doi.org/10.3390/land11071113
APA StyleChakraborty, A., Sikder, S., Omrani, H., & Teller, J. (2022). Cellular Automata in Modeling and Predicting Urban Densification: Revisiting the Literature since 1971. Land, 11(7), 1113. https://doi.org/10.3390/land11071113







