Abstract
Archaeological work began in 1928 at Yinxu (also known as Yin Ruins), the site of the capital of the late Shang Dynasty, and the continuous excavations have yielded the discovery of numerous remains and relics. The late Shang Dynasty was the zenith of China’s Bronze Age, and research on various aspects of Yinxu has gained attention among Chinese and international archaeologists. The layout of Yinxu, especially the water conservancy systems, has become a popular subject of research in recent years. Nevertheless, quantitative research is lacking in the existing literature. Using geographic information systems (GIS) allows such research to be carried out. This study used the hydrology and density analysis modules of ArcGIS software to study the water system and urban layout of Yinxu quantitatively. The results show that the water conservancy system altered the surface runoff pattern of the city and effectively harnessed limited local water resources. The system, centered on artificial channels, was built during the Second Phase of Yinxu, largely because of climate change and the city’s expansion. Its construction, in turn, profoundly affected the layout of the city. Dwellings and handicraft workshops clustered around areas with abundant water resources; together with the Huan River, the large-scale water conservancy facilities acted as partitions that practically isolated the “central zone”, creating a wall-less defense system that differs from other capital cities in the Bronze Age of China.
1. Introduction
A capital city is the political, economic, and cultural center of a country that embodies the formation and development of civilizations. By studying ancient capital cities, scholars can explore social organizations, handicrafts development, and ideas and beliefs of early states [1,2,3,4,5]. Among the elements that constitute a capital city, the water conservancy system plays a vital role in urban development because water provides a fundamental resource for production and domestic activities. Moreover, the control and distribution of water resources, as well as the construction and maintenance of water conservancy facilities, are concrete expressions of a city’s power structure and organizational capabilities [6]. Thus, water conservancy systems and urban layout/planning are closely related, and both constitute the focus of archaeological research on capital cities.
For more than a century, archaeologists have studied water conservancy systems and the layouts of capital cities such as Ur, Babylon, Memphis, Thebes, Mycenae, and Mohenjo-Daro, which have greatly enriched people’s understanding of the world’s early civilizations such as Mesopotamia and ancient Egypt, India, and Greece [7,8,9,10,11,12]. The Chinese archaeological community has also taken a keen interest in the excavation and research of ancient capitals. In 1928, when modern Chinese archaeology was in its infancy, the Institute of History and Linguistics of the Academia Sinica organized an archaeological excavation at Yinxu. Subsequent fieldwork was conducted at the sites of Erlitou, Zhengzhou Shang city, Yanshi Shang city, Zhouyuan, Zhenghan ancient city, Chang’an, and Luoyang [13,14,15,16,17,18,19]. Along with those excavations, a wealth of studies on water conservancy systems and the layout of ancient capital cities have been conducted, and fruitful research results have been achieved [20,21,22,23,24,25,26,27].
Of these archaeological studies of Chinese ancient cities that have already been or are being carried out, Yinxu holds special significance. It represents the economic, cultural, and technological high point in early China and reveals the prosperity of the Chinese Bronze Age urban civilization. In addition, fieldwork at the site is the longest ongoing excavation project and covers the largest excavation area in the history of Chinese archaeology. In the course of the work, rich and detailed archaeological materials have been discovered, enabling archaeologists to conduct comprehensive and multi-faceted research. Existing studies on Yinxu have led to an in-depth understanding of the city’s cultural stages, cultural evolution, and its relationships with surrounding areas. Although water conservancy systems and urban layout have received greater attention in recent years [26,28], there are still many unresolved questions. Studies are still dominated by qualitative and inductive research methods, while studies based on quantitative spatial analysis are rare.
GIS has been used in archaeology since the 1980s [29,30,31,32]. It is a powerful tool for spatial analysis [33,34], enabling archaeologists to quantitatively investigate a wide range of archaeological inquiries, including ancient urban layouts [35,36]. This study uses the powerful spatial analysis functions of GIS to explore the spatial characteristics of various remains at Yinxu to gain a deeper understanding of the city’s water conservancy system and urban layout based on the previous research.
2. Regional Settings and Research Background
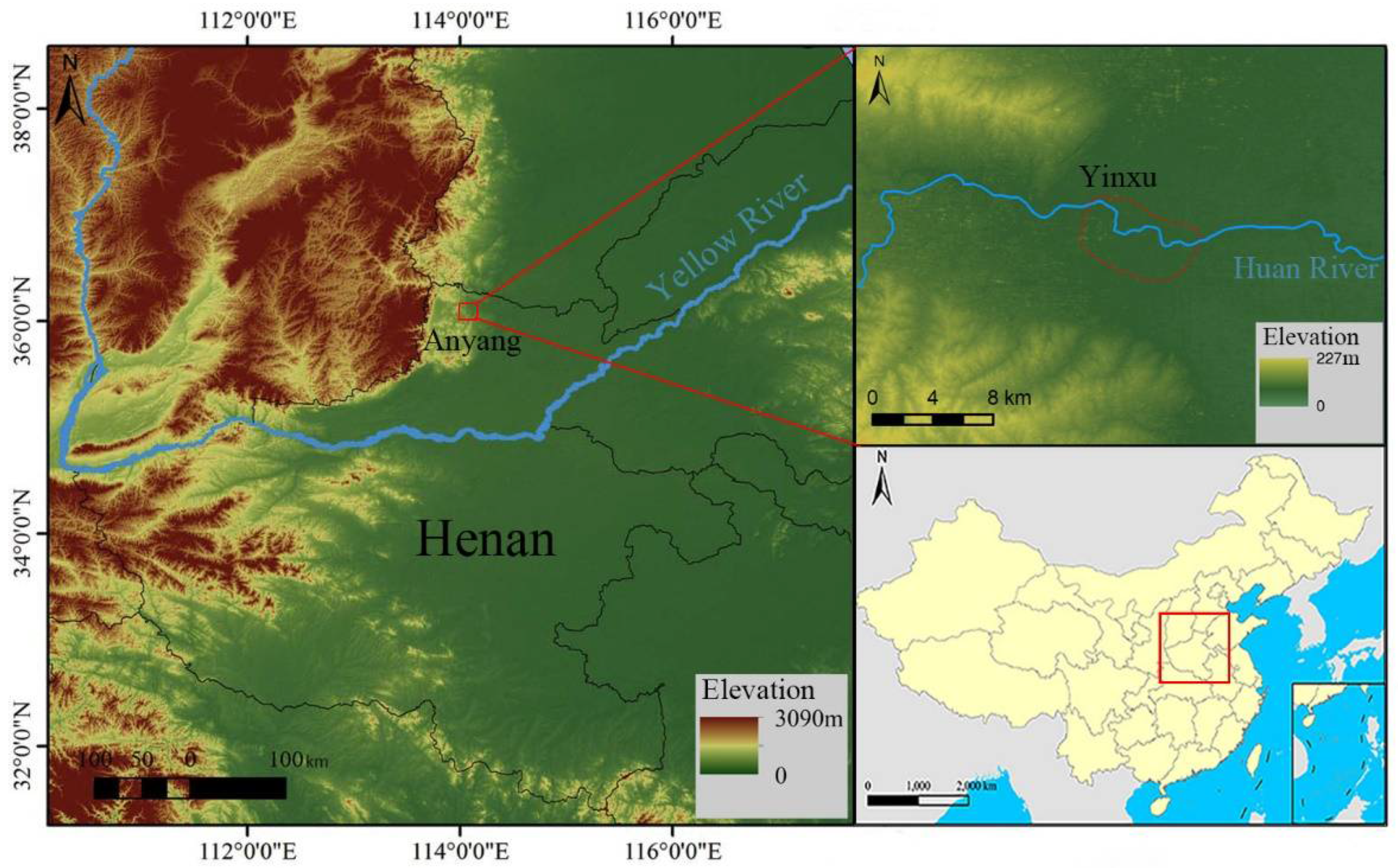
Yinxu is located northwest of the city of Anyang in the central Chinese province of Henan (36°00′–36°10′ N, 114°10′–114°35′ E). The elevation of the site is 65–110 m above sea level, and the average annual temperature is 10–14 °C. Annual precipitation is 500–800 mm, and evaporation is 1500–2000 mm. The area belongs to the warm temperate semi-humid continental monsoon climate zone. The site is located on the alluvial fan of the Huan River at the eastern foot of the Taihang Mountains (Figure 1), and it covers a total area of approximately 36,000,000 m2. Excavation of the Yin Ruins site began in 1928. During more than 90 years of excavations, various remains such as the foundations of palaces and ancestral temples, royal mausoleums, tombs, handicraft workshops, and civilian dwellings have been discovered along with a large number of relics, including inscribed oracle bones, potteries, bronzes, jades, and other bone objects. Based on these findings, academics consider the Yin Ruins to be the capital city of the late Shang Dynasty. Due to its important academic value, the site was listed among China’s first group of national key cultural relic protected units and is a World Cultural Heritage site.
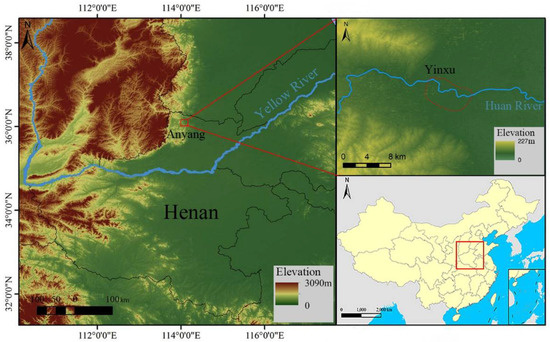
Figure 1.
Geographical location of the Yinxu.
Scholars have extensively studied the phases and ages of Yinxu. Dong divided the Yinxu culture into five phases according to their inscriptions [37]. Zou initially divided Yinxu culture into three phases (early, middle, and late) but later revised them into four following the excavation of the Dasikong site [38,39]. The Anyang work team at the Institute of Archaeology of the Chinese Academy of Social Sciences later formally proposed a new four-phase classification [40]. Subsequently, scholars reclassified remains from before King Pan Geng as belonging to the mid-Shang Dynasty rather than the late Shang culture. This change had a substantial impact on the phase division [41]. Following the Xia-Shang-Zhou Chronology Project, an academic consensus formed on the time frame of the Yinxu culture, which is the chronology adopted in this study (Table 1).

Table 1.
Cultural phase division of Yinxu.
Archaeological features concerning productive and domestic activities in the city, including the water conservancy system, have been one of the focuses of excavation and research at the Yinxu. Field excavations during the last century have uncovered several large handicraft workshop areas such as at Dasikongcun, Miaopubeidi, and Xiaomintun, and water facilities such as the great ditch, pool garden, and drainages connected to the Huan River around the palace-and-temple zone. In recent years, fieldwork has revealed a water conservancy system—the most important discovery of which is the artificial channels. These channels are located south of the palace-and-temple zone. They consist of the main channel and several branch channels that run northwest to southeast through the core area of Yinxu. There are many handicraft workshops and dwellings at both ends of the channels. Based on the stratigraphy, the channels were dug during the Second Phase of Yin, except for a few branch channels [24].
Based on the excavated materials, scholars have conducted extensive research on the water conservancy system of Yinxu and the layout of the city. Zheng explored the distribution of clans within the Yinxu based on oracle bone inscriptions and bronze inscriptions [43]. Yue et al. conducted the first exploration of the layout of the ancestral temple area and discussed the nature of the great ditch near the palace [44] and the function of the pool garden [45]. Chang compared the space planning of the copper casting workshops and stated that the copper casting technique developed at Yin was passed down and disseminated [46]. Tang et al. reconstructed the road and water networks at Yin based on their fieldwork and suggested that they were intended to serve handicraft workshops [24]. Nevertheless, He argued that the great ditch near the palace-and-temple zone is a defensive facility and that there is insufficient evidence to suggest that the artificial channels were used to supply water for handicraft production [28].
These archaeological discoveries and the pioneering studies have provided solid field data and instructive interpretations about the site structure, allowing us a preliminary understanding of the water conservancy system and the city’s layout at Yinxu; however, there are still questions that have not received sufficient attention in previous studies. For example, how did the water system alter the surface runoff pattern of the city? Why was the complex water system built? How did the construction of the water conservancy system affect the city’s layout? This article will elaborate on these questions.
3. Materials and Methods
3.1. Data Sources
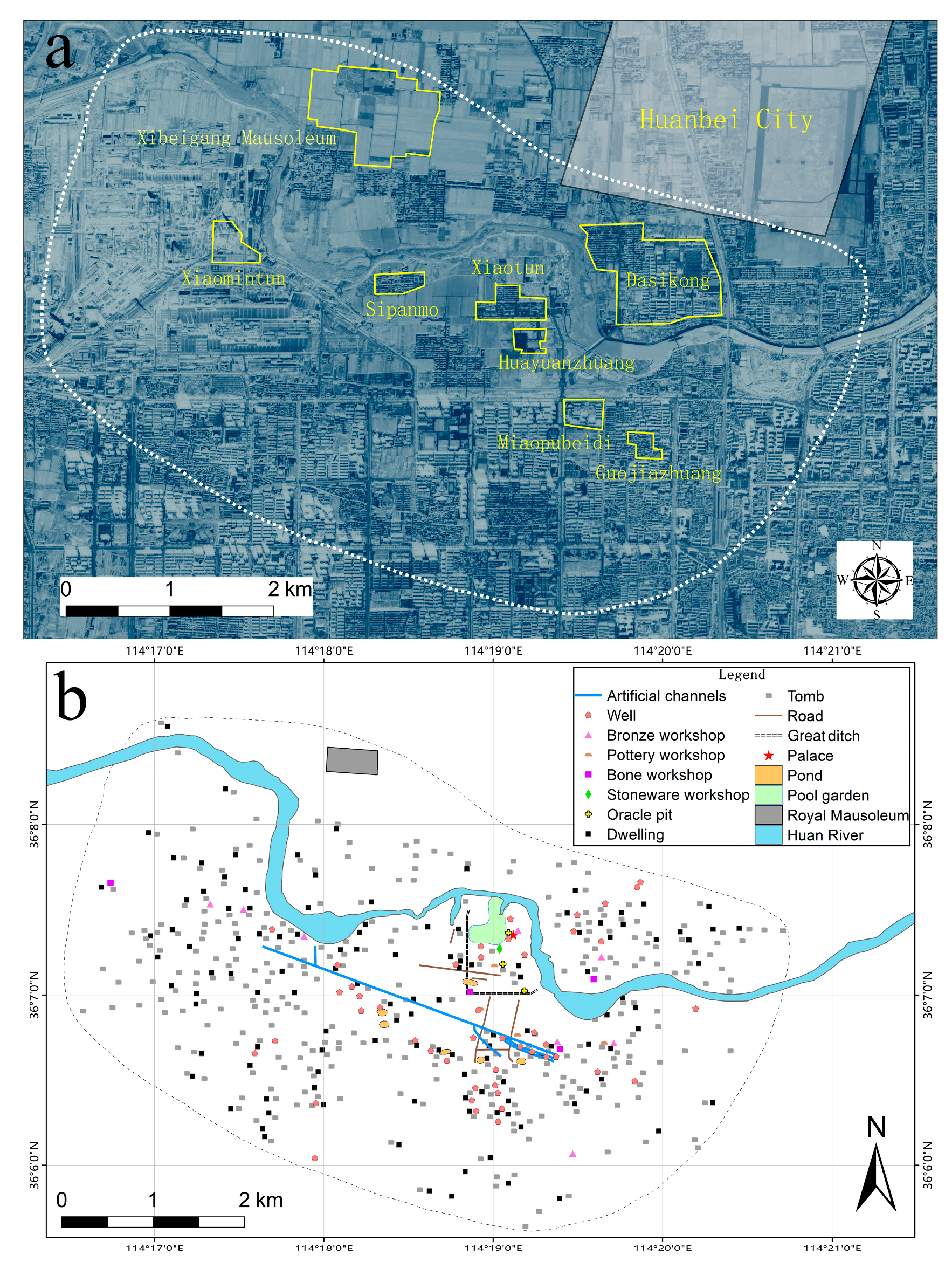
This study examined the urban layout of the city of Yinxu through spatial analysis based on GIS. The basic topographic data of the study area were obtained from a digital elevation model (DEM) with a spatial resolution of 12.5 m. The DEM was collected with the Advanced Land Observing Satellite (ALOS) Phased Array type L-Band Synthetic Aperture Radar (PALSAR). Spatial information on archaeological relics such as residential houses, tombs, roads, channels, and handicraft workshops within the Yinxu site area was derived from published reports and research papers. This study included various other types of remains based on published maps [21,24]. We scanned and imported the maps of remains into ArcGIS software, used Google Earth to find reference points of significant geographical features as registration points, recorded the corresponding geographical coordinates, and performed georeferencing of the distribution map with the help of the registration points. We vectorized various types of remains on the georeferenced map and generated point/polyline/polygon and other features in shapefile format, and superimposed those features on the DEM to obtain the site distribution map used in this study (Figure 2). According to the comparison with published excavation reports, our map accurately reflected the distribution of various archaeological remains within the study area.
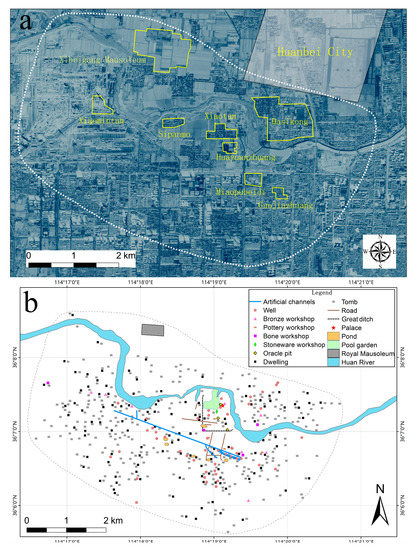
Figure 2.
(a) Satellite image of Yinxu site area showing toponyms mentioned in this article; (b) vectorized map showing major archaeological features within Yinxu site area.
Three specific points need to be noted. First, to date, thousands of small dwelling sites and tens of thousands of small tombs have been excavated at Yinxu. Due to inaccuracies in early field records, many tomb and dwelling sites lack precise geographic coordinates, so those data were not used in the study. Second, the remains of tombs and dwellings occupy a specific area, but most are smaller than the spatial range of a single pixel in the DEM used in this study (12.5 m × 12.5 m). Therefore, the tomb and dwelling remains are represented by points rather than polygons. In addition, based on the effect of the depth of channels on elevation, we adjusted the elevation value of the grids where artificial channels are located according to their depths published in excavation reports. This specifically involved performing georeferencing of the channel network at Yinxu and then drawing each segment of the channel before transferring them to the raster. We then used the grid calculator to subtract the elevation values according to the depth of each section, from which we finally obtained a new DEM file with the calculated channel depths.
3.2. Analysis Methods
The main spatial analysis methods in this study are hydrological analysis and density analysis. For the hydrological analysis, the Hydrology module in ArcGIS was used to calculate the flow accumulation, and comparative research was conducted on the influence of the artificial channels on the surface runoff in the area before and after construction. We also took hydrological considerations into account when locating dwellings, reservoirs, and handicraft workshops. Flow accumulation is a physical quantity that expresses the surface runoff value per unit area as a grid matrix. First, it was assumed that each grid of the DEM has a unit of water volume, and the water flow direction is determined according to the natural law of water flow from high to low elevation, so the amount of water passing through each grid in the area can be obtained. In practice, an area with a relatively large flow accumulation would not necessarily generate streams or rivers; nevertheless, it suggests an area where more water flow will converge and pass through when precipitation occurs, and thus, it has better potential conditions for water storage, diversion, and utilization. The flow accumulation method has been widely used in archaeology to investigate regional water availability and its influence on the spatial distribution of settlements in ancient times [31,47].
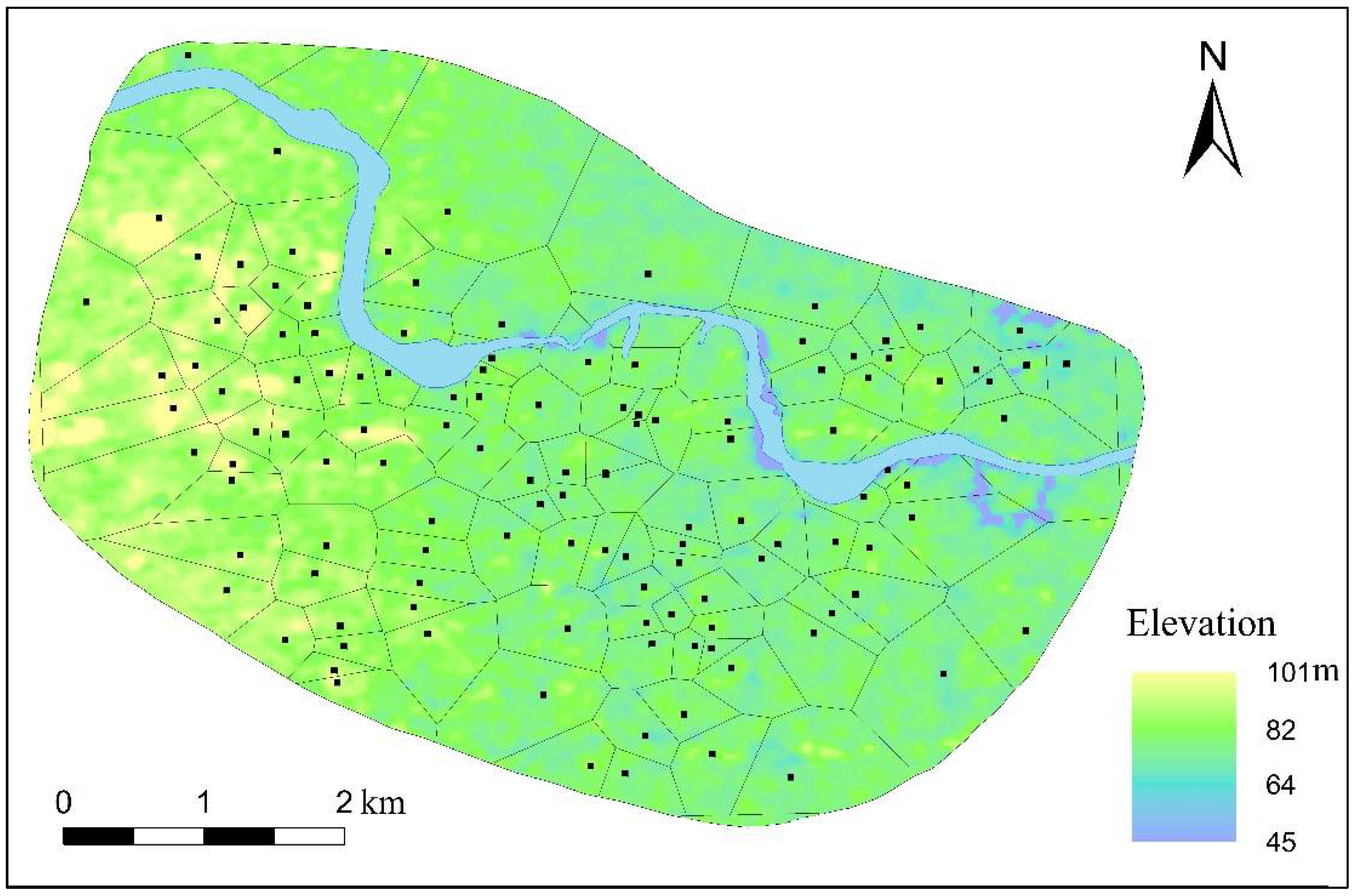
To investigate the spatial distribution characteristics of the study area, we used the cluster and outlier analysis tool in the spatial statistics module in ArcGIS. In this module, Anselin Local Moran’s I was calculated to statistically identify areas of high- and low-value clusters. According to the density of features located within a specific area and its neighboring areas, modes were divided into HH (high–high cluster, a high value surrounded by high values); HL (high–low outlier, a high-value outlier surrounded by low values); LH (low–high outlier, a low outlier surrounded by high values); and LL (low–low cluster, a low value surrounded by low values). At Yinxu, previous studies suggest that it was composed of dozens or even hundreds of clan towns [48]. For each clan, members lived together and were buried together. This custom means that the dwellings and tombs of a particular clan were spatially clustered, and thus, the distribution of clan members’ burials generally reflects where they were active during their lifetimes. We divided our distribution map based on the locations of dwellings using Thiessen’s polygon method (Figure 3) because it provides a reasonable model to fit the reality of “living together and being buried together” at Yinxu. The total number of tombs in each polygon was used to calculate Anselin Local Moran’s I, based on which we quantitatively analyze the cluster pattern of Yinxu.
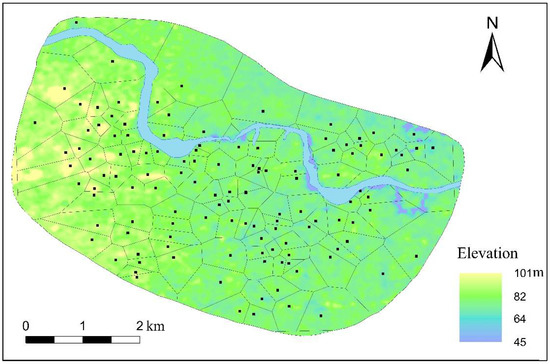
Figure 3.
Thiessen’s polygon division based on dwellings at Yinxu.
We also used kernel density analysis in the Density Module to investigate the layout characteristics at Yinxu. Kernel density analysis searches features within a circular area around a specific point, calculates the density, and finally generates a continuous density surface. It is one of the most widely used spatial analysis methods in archaeology, mainly for revealing the clustered or dispersed areas of point features [49,50,51]. In this study, point features mainly refer to warrior tombs, and we used this method to explore the changing pattern of the warrior tomb distribution in different phases at Yinxu.
4. Results and Discussion
4.1. Construction of the Water System at Yinxu
Human-built water conservancy facilities, such as channels, ponds, and wells, together with the Huan River, constitute the water network of Yinxu. Among these water conservancy facilities, the artificial channels require the largest amount of engineering work and play a central role in the water network [24]. The channels extend from the northwest to the southeast across the entire Yinxu area; they connect with the Huan River on the northwest side via a branch channel, and the southeast section flows toward a cluster of handicraft workshops near the Miaopubeidi.
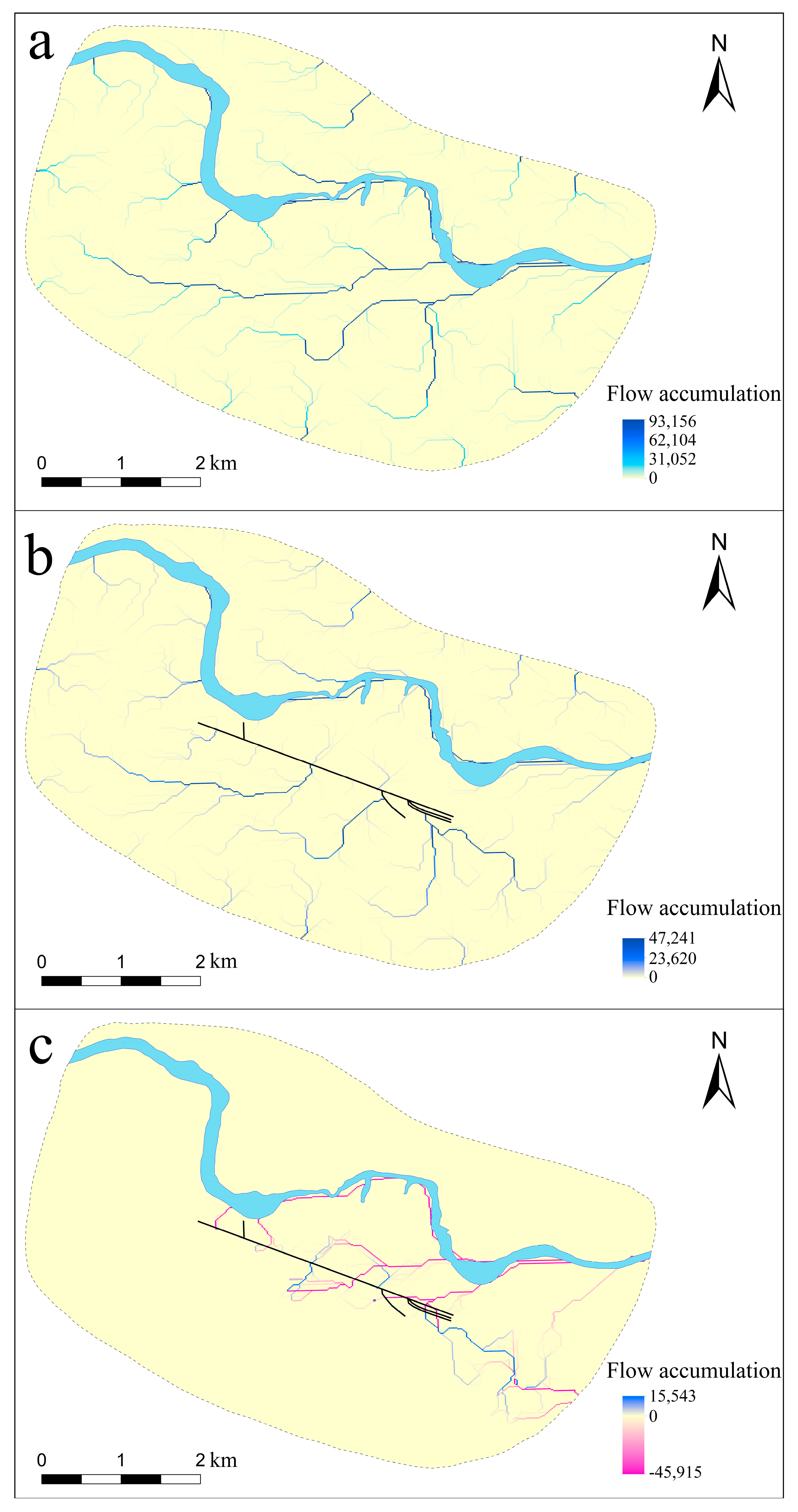
Scholars have discussed the function of the channels at length, but no research has been conducted from the perspective of their influence on surface runoff. We analyzed the flow accumulation in the study area. The results showed that surface runoff at the site was very different before and after the construction of the artificial channels (Figure 4). Prior to their construction, the rainfall runoffs converged and flowed across most of the site area, and two tributaries with a large amount of flow accumulation formed in the middle of Yinxu and finally flowed into the Huan River from the southwest to the northeast. After the construction, a number of runoffs changed directions and flowed into the channels, and the two tributaries that previously had large flow accumulations were blocked by the channels, so they no longer flowed through the city’s central area. In addition, the maximum value of flow accumulation (accumulated raster numbers) within the site area decreased from 93,156 to 47,241, indicating that the water volume entering the Huan River declined significantly. The above analysis results showed that the artificial channels collected runoff from the surrounding slopes that would have directly flowed into the Huan River, thus extensively altering the surface runoff pattern of Yinxu and effectively reallocating water resources of the city.
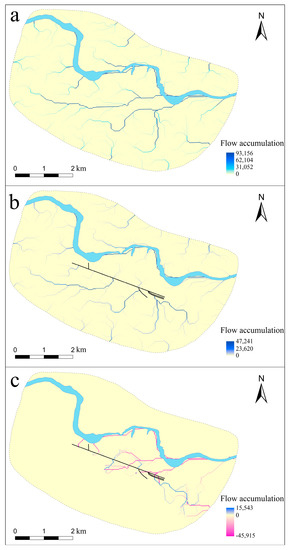
Figure 4.
(a) Flow accumulation before channel construction at Yinxu; (b) flow accumulation after channel construction at Yinxu; (c) change in flow accumulation before and after channel construction at Yinxu.
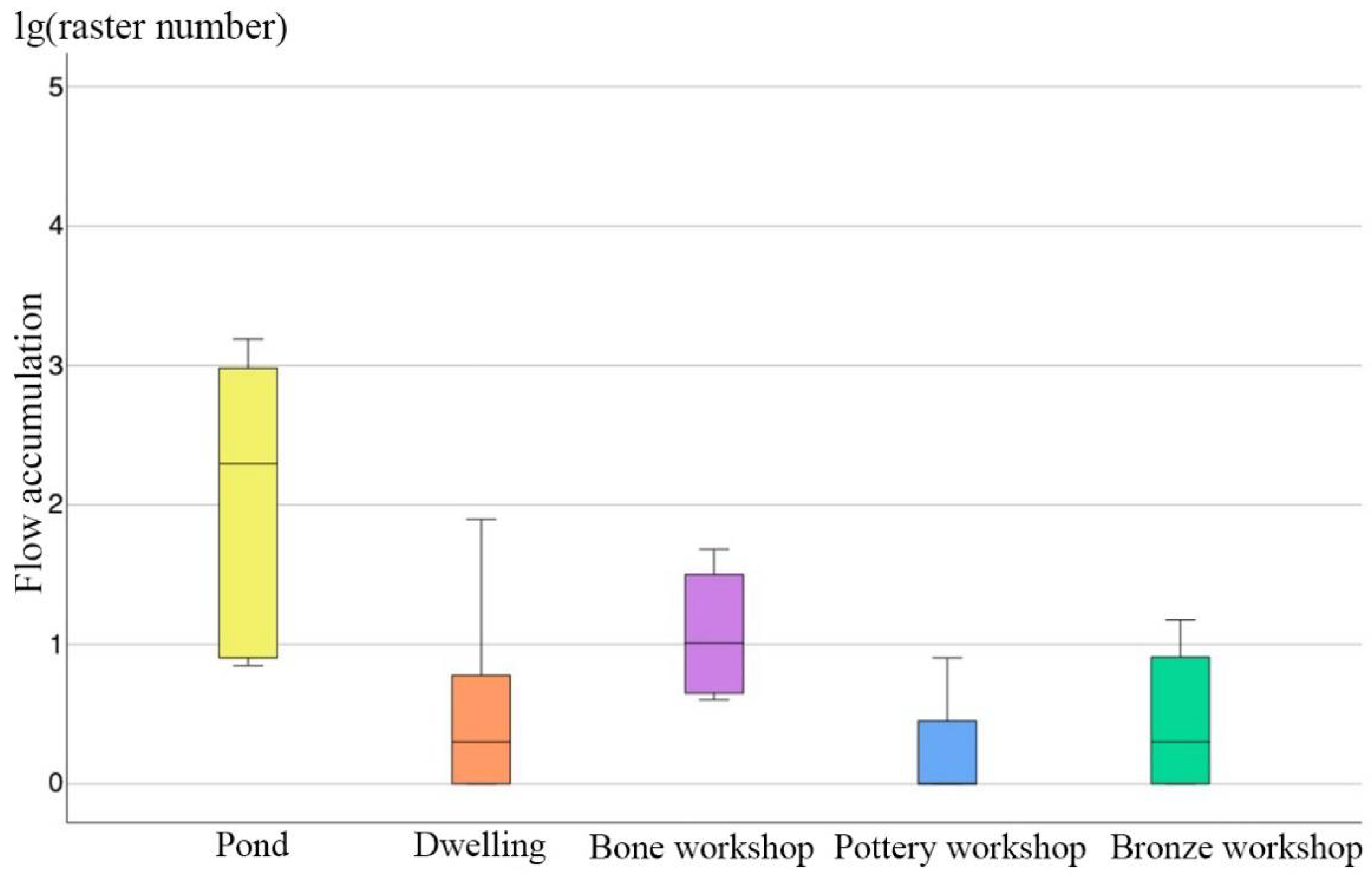
Another important type of water conservancy facility at Yinxu is the ponds distributed on both sides of the channels. Some scholars have suggested that they were not intentionally made but just borrow pits that formed following earth removal. To analyze the role of these ponds further in the entire urban water system, we extracted the flow accumulation within the coverage areas of the pond. For comparison, we set a buffer zone radius of 50 m for dwelling sites and handicraft workshops and similarly extracted the average flow accumulation for these buffer zones. Using these data, we created boxplots (Figure 5). The results show that, compared with other types of remains such as dwellings and handicraft workshops, the ponds are primarily located in areas with a large flow accumulation, and some were even dug exactly at the nodes where water flows converge. During precipitation, water naturally converges and flows through them, so the ponds effectively act as reservoirs to store surface water in the city area.
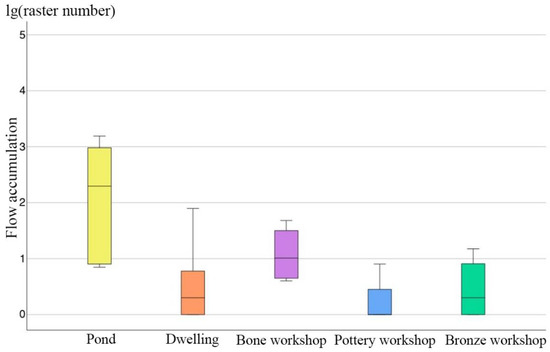
Figure 5.
Flow accumulation of different types of archaeological features at Yinxu. Values were processed with a logarithm.
Therefore, the construction of water conservancy facilities, such as the artificial channels and ponds, in the capital city of Yinxu was intentionally planned and located. These facilities effectively take advantage of local topography to intercept and redistribute the surface runoff that originally flowed into the Huan River to optimize local water utilization.
4.2. Driving Forces of Constructing the Water System
A water conservancy system is a fundamental resource for production and domestic use in cities with dense populations. However, in the case of Yinxu, why did people build labor-consuming facilities such as the artificial channels and ponds across the site area within a relatively short period (mostly during the Second Phase)? Was it indispensable? In the existing literature, scholars have attributed the construction of the artificial channels to providing water for production in the southern handicraft areas along Miaopubeidi, Liujiazhuang, and Tiesan Road [24]. Based on the clear orientation of the channels and their spatial relationship with the handicraft area, we believe that they indeed provided water for production, such as pottery and copper casting. However, this still does not fully explain the necessity of building the channels. First, the bronze workshop in the Miaopubeidi and the pottery workshop around Liujiazhuang were built during the First Phase of Yinxu, but the artificial channels were built no earlier than the Second Phase. In other words, the existence of the channels was not a prerequisite for handicraft workshops. Scholars have also pointed out that well water could have been used for production in handicraft areas [28]. Second, if the only purpose of the channels was to provide water to the handicraft area, it would have been possible to build a closer channel connected to the Huan River without having to divert water from the northwest across the entire city. Thus, the reasons for constructing the channels still require further exploration.
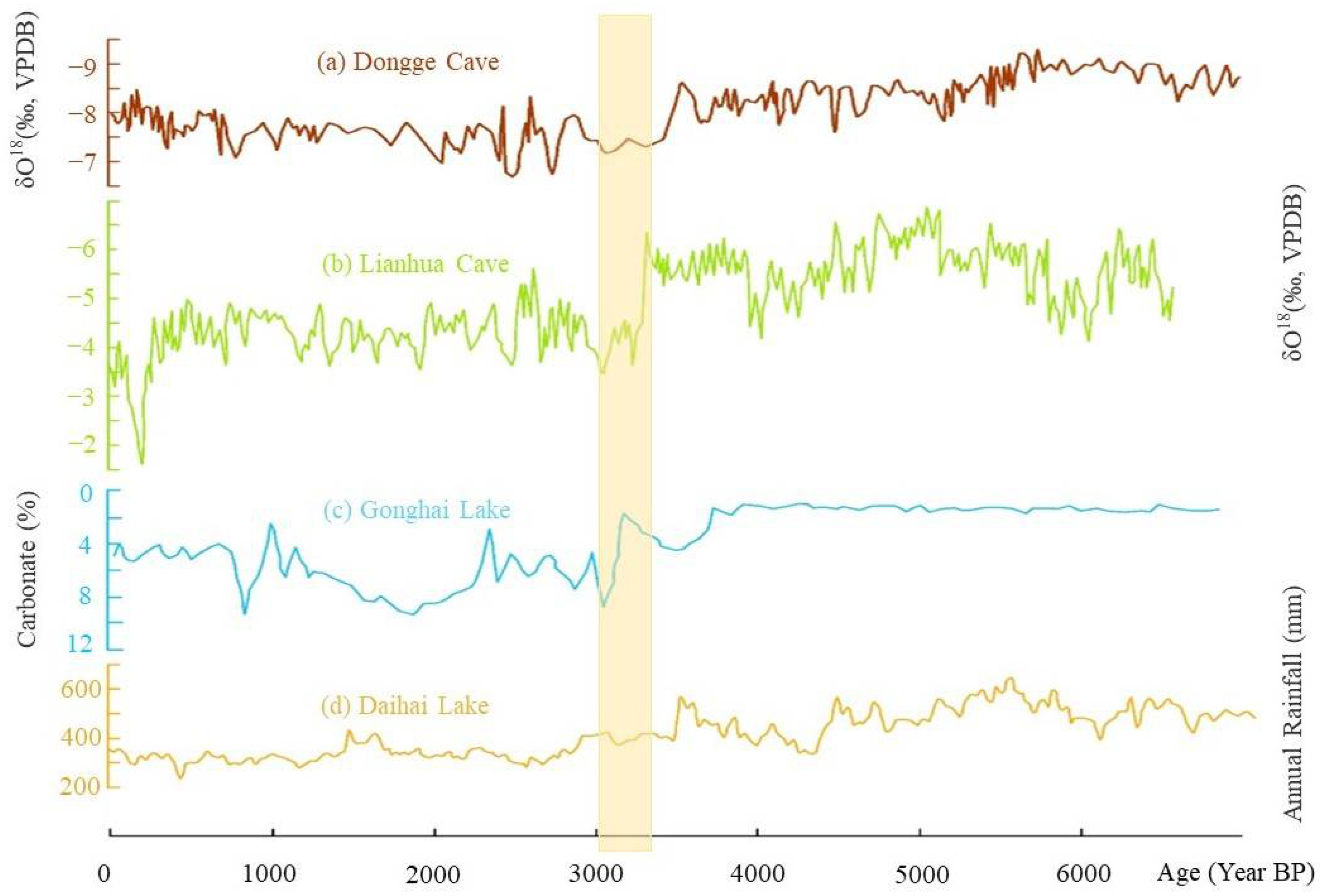
A possibly overlooked factor in the existing literature is climate change. This may have been an important driving force for constructing the water conservancy system at Yinxu, especially these artificial channels. It is usually assumed that the climate of the Shang period was warm and humid [52,53], similar to the current climate in the middle and lower reaches of the Yangtze River [54]. However, scholars have comprehensively investigated the oracle bone inscriptions, the depth of water wells, and the remains of animals and plants discovered at the Yinxu and concluded that the climate changed from warm and humid to cool and dry between the First and Second Phase [55]. We collected multiproxy data on paleoclimatic reconstruction in the East Asian monsoon region, and the results showed that significant climate change in fact occurred at some point during the Yinxu period [56,57,58,59]. This change may be the most drastic and significant climate change event during the Bronze Age (Figure 6). The North China Plains, where Yinxu is located, may have experienced its driest and coldest period since the Holocene Climatic Optimum. Therefore, available surface water and groundwater in the Yinxu area might have decreased at that time. A significant increase in well depth during the Second Phase of Yinxu provides strong evidence of this inference [55,60].
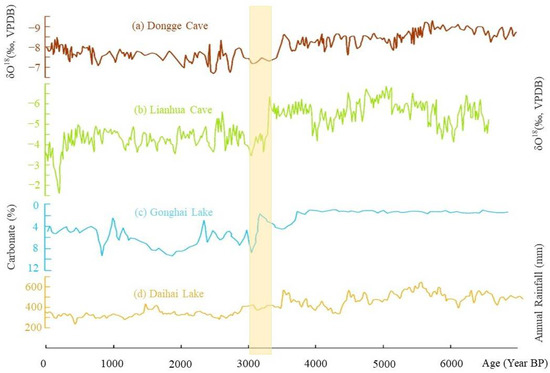
Figure 6.
Proxies of climatic changes around the study area during the past 6000 years: (a) δ18O sequences from Dongge Cave [56]; (b) δ18O sequences from Lianhua Cave [57]; (c) carbonate sequences from Gonghai Lake [58]; (d) annual rainfall reconstruction based on pollen assemblages at Daihai Lake [59]. Light-yellow strip indicates the Yinxu period (~3250–~3000 BP).
On the other hand, the population and handicraft industries expanded significantly in the Second Phase of Yinxu. In the First Phase, only a small number of settlements were distributed at the bend of the Huan River, but from the Second Phase, the number of settlements grew in the vast area south of the artificial channels, and bronze casting, pottery, and bone workshops in the southern area expanded the scale of their production activities. This led to a significant increase in demand for water. Affected by the dual factors of climate change and urban expansion, the original means of supplying water via wells was no longer sufficient to meet residents’ needs for production and domestic activities; hence, they built artificial channels to utilize natural water sources that drained into the Huan River as well as to intercept surface runoff from the southwest. Together with the ponds and the widely distributed wells, these artificial channels constituted a new water supply and storage system, which effectively guaranteed water for production and domestic use at Yinxu.
4.3. Influence of the Water System on the Layout of the City
4.3.1. Dwellings and Handicraft Workshops
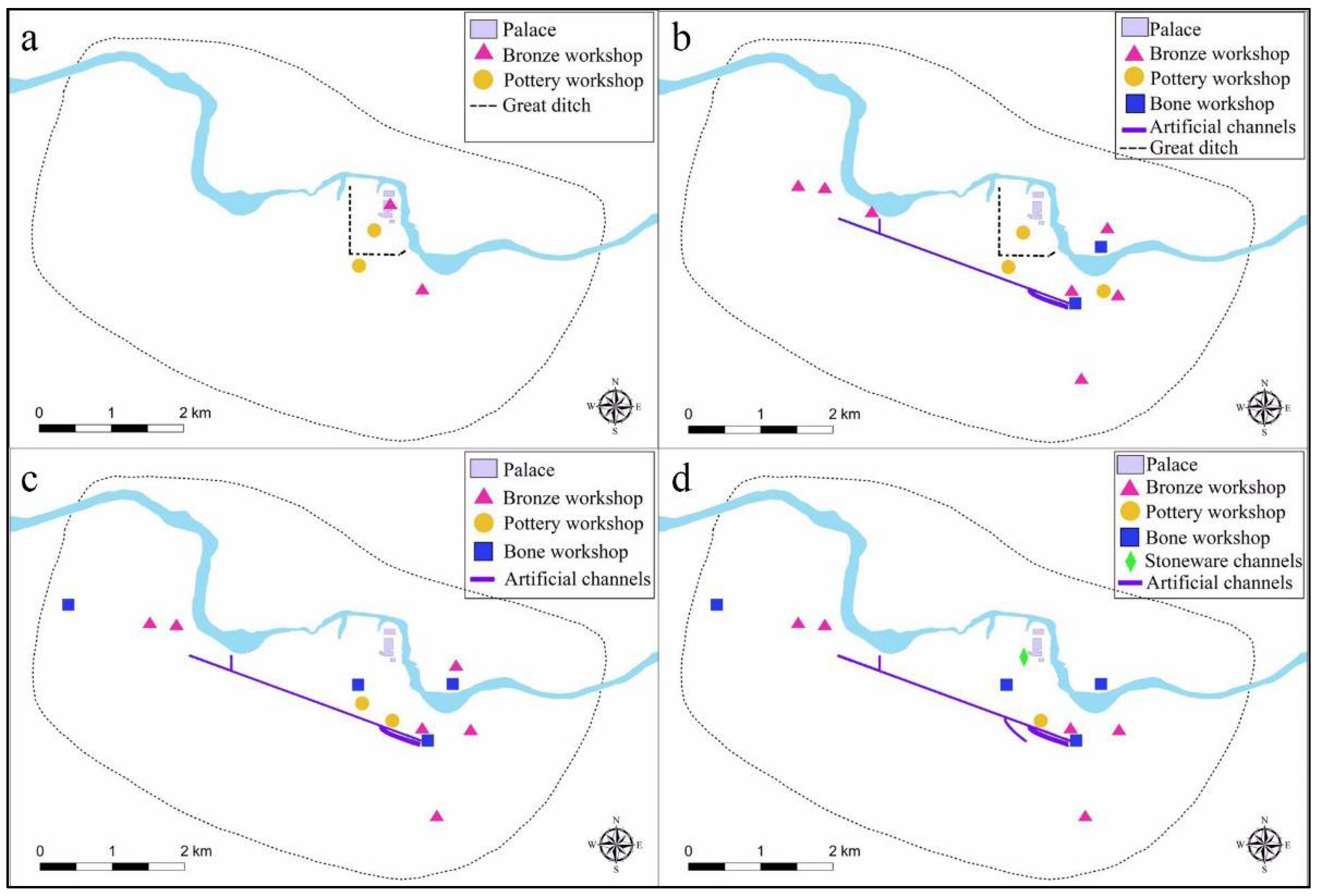
In the previous section, we pointed out that providing water for production and domestic use to dwellings and handicraft workshops was a reason for constructing water conservancy facilities. However, there may not be a simple causal relationship between the two. Instead, it could be a positive feedback relationship of mutual causality. We found that, during the Second Phase of Yinxu, handicraft workshops, such as bronze casting, pottery making, bone carving, and stoneware/jade making, were agglomerated near the southeastern end of the channels and continuously expanded, eventually forming the most comprehensive handicraft workshop area at Yinxu (Figure 7). In addition, most dwellings were distributed around the streams formed by surface runoff, in areas with relatively elevated terrain and low flow accumulation. In other words, dwelling sites were close to water flows but avoided low-lying areas with high flow accumulation (Figure 5). As such, the construction of the water conservancy system greatly affected the distribution of dwellings and handicraft workshops.
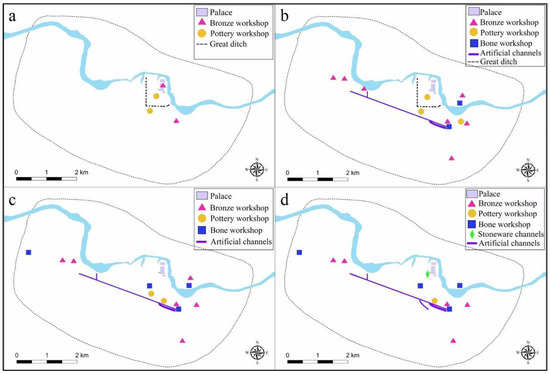
Figure 7.
Distribution map of artificial channels and handicraft workshops at Yinxu in different phases: (a) First Phase; (b) Second Phase; (c) Third Phase; (d) Fourth Phase. Numbers and scales of handicraft workshops increased and expanded since the Second Phase with the construction of artificial channels.
4.3.2. The Defense System Based on the Water System
A notable feature distinguishing Yinxu from other large urban centers in Bronze Age China is the lack of defensive facilities, such as city walls and moats. Some scholars have previously suggested that the pool garden and the great ditch near the palace-and-temple zone played a role in defense, but the great ditch was filled and abandoned during the Second Phase. Subsequently, how did the Shang royals construct a city defense system against enemy regimes and power space for elites? What role did the water system play in it?
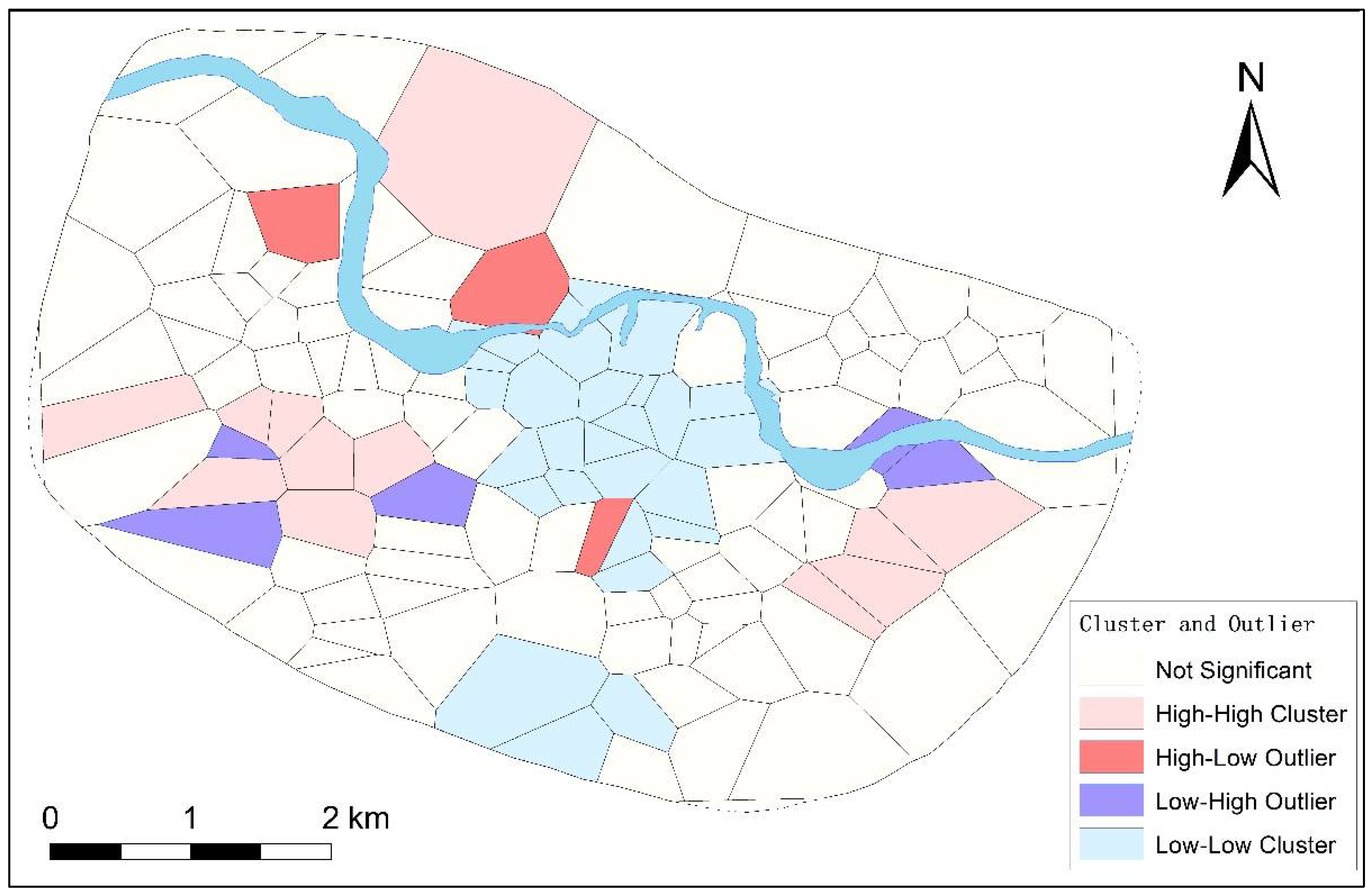
To further explore these questions, we first used the cluster and outlier tool to analyze the polygons, and the results are shown in Figure 8. The results showed a large blue area near the palace-and-temple zone, suggesting a LL mode (Low number of tombs and dwellings in the specific polygonal area, and low number in its surrounding areas). This area extends to Huayuanzhuang in the east, the bend of the Huan River in the north, Sipanmo in the west, and the artificial channels in the south, covering about 2,000,000 m2. It contains crucial remains, such as the palace-and-temple zone, a square, a pool garden, the great ditch, artificial channels, and road systems. Since this area sits at the center of the Yinxu site, in this study, it is referred to as the “central zone”.
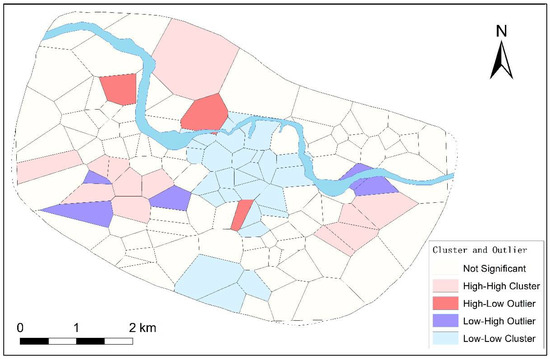
Figure 8.
Cluster and outlier analysis result.
Scholars have discussed the nature of this central zone. Comparing the area of the Xiaotun palace-and-temple zone to the total area of the Yinxu site, Yue found that the ratio was only 1:57, which was much lower than the ratio of palace area (for royals specifically) to the total area ratios in other large Bronze Age cities (Erlitou 1:30, Yanshi 1:20, Huanbei 1:21). Yue speculated that the palace-and-temple zone should have covered a larger area [44]. We agree that the land area of the Xiaotun palace-and-temple zone at Yinxu is too small compared to the entire site. From the cluster and outlier analysis results, the boundary of the LL clustered area accords with Yue’s speculation. Calculating this central zone (2,000,000 m2) as a proportion of the entire Yinxu area (36,000,000 m2) gives a ratio of 1:18, which is closer to the ratios of other Bronze Age capital cities (Erlitou, Yanshi, and Huanbei). Therefore, we speculate that the central zone was the actual palace area, and the artificial channels played the role of a boundary to divide the inside palace area for royals and the outside zones mainly for the commoners.
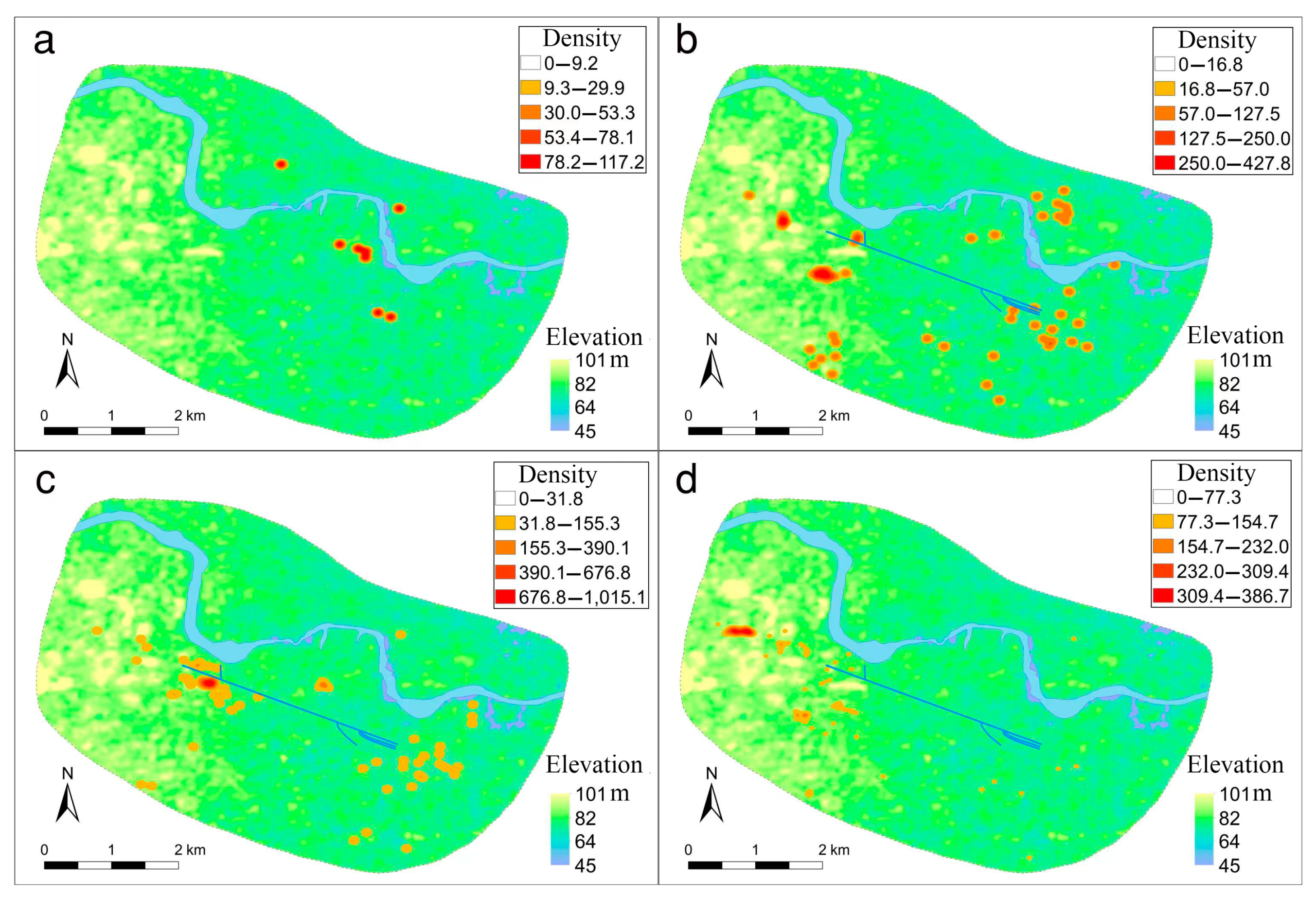
Another perspective from which to examine the influence of water conservancy facilities on the Yinxu defense system is to analyze the distribution of its military power and its spatial relationships with water. An army is an essential foundation upon which countries establish and maintain their rule, and its primary function is to contain anything that might threaten the ruling class. During the Shang Dynasty, Shang kings had powerful armies, and they were tasked with suppressing external threats, maintaining internal order, participating in social ceremonies, and supervising handicraft production [61]. By understanding the distribution of military power during each phase, we can study the focal points of the city’s layout. From a review of the existing literature and excavation reports, we determined the distribution of warrior tombs at the Yinxu during the different phases [62,63,64,65,66,67,68,69,70,71,72,73,74,75,76,77,78,79]. Using the kernel density analysis of warrior tombs yielded the following results (Figure 9).
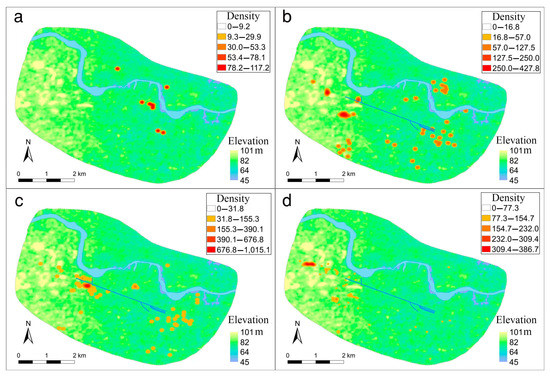
Figure 9.
Distribution of warrior burial sites at Yinxu in different phases: (a) First Phase; (b) Second Phase; (c) Third Phase; (d) Fourth Phase.
In the First Phase, warrior tombs were few, and they were primarily distributed in the areas of Xiaotun, Dasikong, and Miaopubeidi, that is, around the palace-and-temple zone (Figure 9a). The reason for their location is that, at the time, the capital had only just been moved south of the Huan River to Yinxu from Huanbei, and the city was not yet highly developed. The Shang royals and elites lived in this area; hence, the army was concentrated within a relatively small and limited area.
During the Second Phase, the distribution of warrior burial sites expanded significantly (Figure 9b). Their range expanded from the concentrated distribution in the bend of the Huan River during the First Phase into all directions. The figures show that military forces were distributed at both ends of the artificial channels. Although they are not very concentrated, the initial influence of the channels on the construction of the defense system can be seen.
During the Third Phase, the distribution of warrior burial sites was still relatively extensive, but with significant concentrations at the east and west ends of the artificial channels (Figure 9c). The influence of the water system on the defense system was particularly evident at this stage: the northwest end and the southeast end of the main channel left narrow passes, and many troops guarded the “passes”. The channels to the south and the Huan River to the north together constituted the defense system of the central zone of Yinxu.
In the Fourth Phase, the distribution of warrior tombs displayed new characteristics, with almost all of them concentrating on the west side of the site (Figure 9d). We believe that this was due to a change in defense targets of Shang royals, from an internally ruled class to the competing political regimes. During this period, the power of the Zhou to the west was in its ascendancy, and Shang’s relationships with the city-states to the northwest were also unstable, leading to frequent conflicts [80]. Within this context, the Shang deployed most of the capital’s military forces at the northwest pass as the last line of defense of the capital. Comparatively, the function of the artificial channels as the boundary of the royal zone and commoners’ zone was significantly weakened.
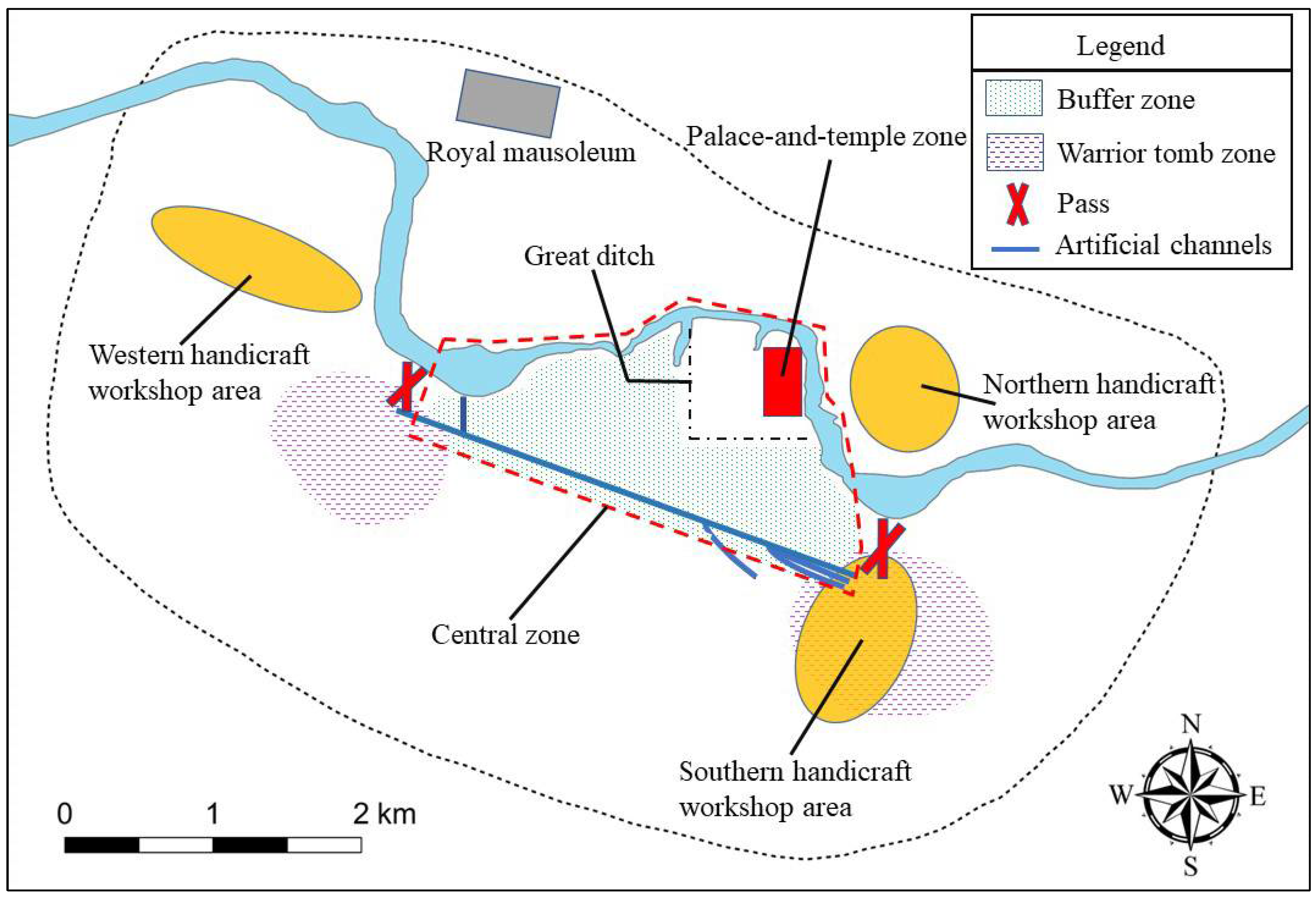
Spatial analyses using the cluster–outlier and kernel density methods allow us to understand the impact of water systems on the construction of Yinxu’s defense system. Palace walls can be seen in the early capitals of Erlitou, Yanshi, Zhengzhou, and Huanbei, as well as in historical capitals such as Chang’an, Luoyang, Kaifeng, and Beijing. Palace walls are a type of defensive wall built within a large city. Their primary function is to separate commoners from the royals and to construct a power zone belonging to the ruling class. However, no palace walls have been found at Yinxu, even after fieldwork for over 90 years. Due to the significant difference in the number of burial sites and dwellings in the central zone and surrounding areas, we speculate that the ruling class might have issued military or administrative orders to restrict the establishment of settlements in the vicinity. As a result, a large unoccupied area was created as a buffer zone between the artificial channels and the Xiaotun palace-and-temple zone, and the artificial channels acted as a “wall” (Figure 10). Physical anthropology studies and isotope analysis have shown that the Anyang area had become a melting pot during the Shang Dynasty, not only of local peoples but also of many citizens and enslaved people from northeastern and western China and beyond [81,82]. Studies in Chinese classical literature have also suggested the social contradictions between the royals and the common people during the late Shang Dynasty [83] and found that these internal conflicts were the main reason for the social unrest in the Shang society [84].
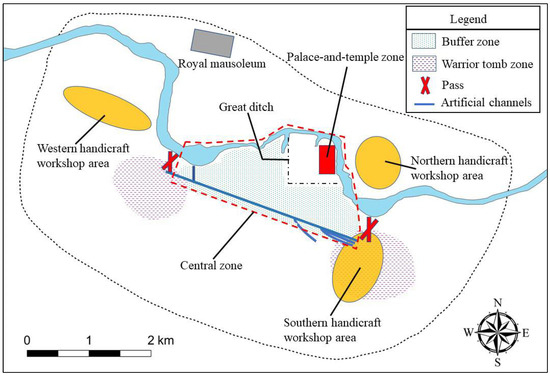
Figure 10.
Schematic diagram of the Yinxu defense system. The nearly enclosed “central zone” is shown in the red frame surrounded by the Huan River, artificial channels, and passes.
In summary, the diverse residents in the city and conflicts between classes were all potential threats that Shang kings had to consider. Nevertheless, for unknown reasons, the rulers did not build city walls but took advantage of the existing artificial channels as partitions and stationed troops to create a boundary between the palace-and-temple zone and the commoners’ zone (Figure 10); this served to delineate spaces of power and guard against internal threats. This idea was implemented in the Second Phase of Yinxu with the construction of the channels and then significantly strengthened in the Third Phase but finally weakened in the Fourth Phase as the focus of the defense system shifted.
5. Conclusions
Using GIS-based spatial analysis, we found that residents at Yinxu built a water conservancy system by digging large artificial channels connected to natural water systems and excavated ponds where water flows converged. This system altered the city’s surface runoff pattern and reconfigured the limited water resources within the city. It is possible that this water conservancy system was not planned from the outset of the city’s construction but was built due to the dual factors of climate change and the capital’s expansion (especially handicraft industries) during the Second Phase. The construction of this water conservancy system also influenced the layout of Yinxu. First, the population and handicraft industries gathered in areas with abundant water resources, causing the Miaopubeidi and neighborhoods at the southeastern end of the artificial channels to develop into a synthetical workshop area for the bronze casting, pottery making, bone carving, and stoneware/jade making. Second, artificial channels, together with the Huan River and the many soldiers stationed at the “passes” at either end of the channels, formed a nearly enclosed “central zone”. The artificial channels were utilized as a part of the city’s defense system for guarding against potential threats from both inside and outside the capital city.
As one of the longest excavated and most influential sites in the past hundred years of Chinese archaeology, Yinxu has yielded a wealth of field material that has greatly enriched our understanding of this late Shang dynasty capital. This research provides a case study of generating insight into water conservancy systems and urban layouts in the Chinese ancient capital cities. We expect the methodology in this research also applies to global archaeological investigations in similar contexts where urban centers have developed, and hydraulic facilities have been constructed such as in Mesopotamia, Egypt, and the Indus Valley. However, there are still many specific or broad questions to be studied. For example, why did Yinxu adopt a “wall-less” defense system that differs from those in most Bronze Age urban centers? How was the water system built in other early urban centers both in China and the rest of the world? What role did water management and utilization play in the process of social stratification and complexity? The solution to these questions, on the one hand, depends on new archaeological discoveries, and on the other hand, it depends on how to use new methods and technologies to unearth deeper information based on existing field materials. In this sense, GIS-based spatial analyses have opened a new window for present and future archaeologists.
Author Contributions
Conceptualization, Y.W. and Z.Q.; methodology, Y.W. and Z.Q.; software, Y.W. and Z.Q.; writing—original draft preparation, Y.W. and Z.Q.; writing—review and editing, Z.Q., W.H., and M.S.; visualization, Y.W. and Z.Q.; supervision, Z.Q. and W.H.; project administration, Z.Q.; funding acquisition, Z.Q. and W.H. All authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript.
Funding
This research was funded by the National Social Science Fund of China (Grant# 19CKG028, 20&ZD225, 21BKG003), the National Key Research and Development Program of China (Grant# 2020YFC1521605), and the Archaeology Research Fund of ‘South-to-North Water Diversion Project (Grant#KT-201809).
Data Availability Statement
The data are contained within this article.
Acknowledgments
We thank two anonymous reviewers for their comments and suggestions. We are grateful to Jigen Tang for his guidance on the acquisition of map data.
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
References
- Xu, L. The Study About Urban Settlements of Xia, Shang And Zhou Dynasty. Sandai Archaeol. 2004, 38–57. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar]
- Earle, T. Bronze Age Economics: The Beginnings of Political Economies; Westview Press: Boulder, CO, USA, 2002; ISBN 978-042-950-199-9. [Google Scholar]
- Gates, C. Ancient Cities: The Archaeology of Urban Life in the Ancient Near East and Egypt, Greece, and Rome; Routledge: New York, NY, USA, 2003; ISBN 978-041-512-182-8. [Google Scholar]
- Marcus, J.; Sabloff, J. (Eds.) The Ancient City: New Perspectives on Urbanism in the Old and New World; SAR Press: Santa Fe, NM, USA, 2008; ISBN 978-1-934691-02-1. [Google Scholar]
- Smith, M.E. Empirical Urban Theory for Archaeologists. J. Archaeol. Method Theory 2011, 18, 167–192. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Wittfogel, K.A. Oriental Despotism: A Comparative Study of Total Power; Yale University Press: New Haven, CN, USA, 1957; ISBN 978-039-474-701-9. [Google Scholar]
- Crouch, D.P. Water Management in Ancient Greek Cities; Oxford University Press: New York, NY, USA, 1993; ISBN 978-019-507-280-4. [Google Scholar]
- Viollet, P.L. Water Engineering in Ancient Civilizations: 5000 Years of History; CRC Press: Boca Raton, FL, USA, 2017; ISBN 978-113-847-447-5. [Google Scholar]
- Bunbury, J.; Jeffreys, D. Real and Literary Landscape in Ancient Egypt. Camb. Archaeol. J. 2011, 21, 65–76. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rost, S. Water management in Mesopotamia from the sixth till the first millennium B.C. WIREs Water 2017, 4, e1230. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Driaux, D. Water supply of ancient Egyptian settlements: The role of the state. Overview of a relatively equitable scheme from the Old to New Kingdom (ca. 2543–1077 BC). Water Hist. 2016, 8, 43–58. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Jansen, M. Water Supply and Sewage Disposal at Mohenjo-Daro. World Archaeol. 1989, 21, 177–192. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fang, Y. Briefing on the excavation of the Erlitou site in Yanshi, Henan. Archaeology 1965, 5, 215–224. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar]
- Henan Provincial Institute of Cultural Heritage and Archaeology. Investigation and excavation of outer enceinte in Zhengzhou Shang city site. Archaeology 2004, 3, 40–50. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar]
- Institute of Archaeology CASS. Yanshi City; Science Press: Beijing, China, 2013; ISBN 978-703-038-699-1. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar]
- The Institute of Archaeology CASS. Erlitou (1999–2006); Wenwu Press: Beijing, China, 2014; ISBN 978-750-104-107-7. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar]
- Wang, X.; Gu, F.; Cao, H.; Li, Z. The Palace and Pool Garden of Yanshi Shang City, Henan. Archaeology 2006, 6, 13–31. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar]
- Qian, G. The Excavation About the Ancient Wall of Luoyang City of Han and Wei Dynasty. Acta Archaeol. 1998, 3, 361–404. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar]
- Zhouyuan Archaeological Team. Exploration and excavation of zhouyuan site in Baoji City, Shaanxi Province, 2014–2015. Archaeology 2016, 7, 32–44. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar]
- Du, J. The Discovery about the Palace and Pool Garden of the Early Shang Dynasty. Archaeology 2006, 11, 55–65. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar]
- He, Y. The Study of the Layout and Headstream of the Handicraft Industry in Yinxu. Archaeology 2019, 6, 75–88. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar]
- Hou, W. Changing Capital Region Settlement Patterns and Social Reorganization in the Early Phase of the Shang Capital at Zhengzhou. Jianghan Archaeol. 2018, 2, 57–67. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar]
- Cao, H.; Gu, F.; Chen, G. A New Understanding of the Water Conservancy Facilities and the Layout of the City Site at the Yanshi Shang City. Cult. Relics South. China 2021, 6, 192–197. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, X. The Water Conservancy Research of Shang Dynasty; China Social Science Press: Beijing, China, 2010; ISBN 978-751-614-225-7. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, Y. The Preliminary Understanding of Water Resources Utilization in the Zhouyuan, Western Zhou Dynasty. J. Natl. Mus. Chin. Hist. 2019, 1, 60–68. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar]
- Tang, J.; Yue, H.; He, Y.; Niu, S.; Yue, Z.; Jing, Z. The Road and Water Networks of the Huanbei Shang City and Yinxu Sites. Acta Archaeol. 2016, 202, 319–342. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar]
- Xu, H. Archaeological Research on Pre-Qin Dynasty Cities; Beijing Yanshan Preass: Beijing, China, 2000; ISBN 978-754-021-338-1. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar]
- He, Y. The waterway system and related questions about Huanbei Shang City and Yinxu. Archaeology 2021, 9, 82–94+2. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar]
- Heinrich, A.R.; Gall, M.J. Zooarchaeology and GIS: Enslaved and Free Black Diet at a Late Eighteenth- to Mid-Nineteenth-Century Delaware Farm, New Castle County, Delaware, United States. Int. J. Hist. Archaeol. 2021, 6, 1–34. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, J.; Wang, L. The study of settlements archaeology supported by spatial analysis. Remote Sens. Inf. 2006, 3, 51–53+94. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar]
- Conolly, J.; Lake, M. Geographical Information Systems in Archaeology; Cambridge University Press: New York, NY, USA, 2006; ISBN 978-052-179-744-3. [Google Scholar]
- Gupta, N.; Devillers, R. Geographic Visualization in Archaeology. J. Archaeol. Method Theory 2017, 4, 852–885. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Earley-Spadoni, T.; Harrower, M.J. Spatial archaeology: Mapping the ancient past with the humanities and the sciences. Int. J. Humanit. Arts Comput. 2020, 14, 176–196. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Verhagen, P. Digital Geoarchaeology; Siart, C., Forbriger, M., Bubenzer, O., Eds.; Springer: New York, NY, USA, 2018; Chapter 2; pp. 11–25. ISBN 978-331-925-314-5. [Google Scholar]
- Lock, G.; Pouncett, J. Spatial thinking in archaeology: Is GIS the answer? J. Archaeol. Sci. 2017, 84, 129–135. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.; Kong, Y.; Ma, H. An Attempt to Represent the Spatial Structure of Historical City with GIS: A Case of Dongjing, the Capital of the Northern Song Dynasty. Geo-Inf. Sci. 2007, 5, 43–49. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar]
- Dong, Z. The Oracle from Houjiazhuang Village in Anyang, Field Archaeological Report; The Commercial Press: Beijing, China, 1936; Volume 1, pp. 91–96. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar]
- Zou, H. On the newly discovered Yinshang cultural sites in Zhengzhou. Acta Archaeol. 1956, 3, 77–103. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar]
- Zou, H. Try to discuss the staging of Yin Ruins culture. J. Beijing Univ. Philos. Soc. Sci. 1964, 4, 39–60. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar]
- Zheng, Z. Briefing on the excavation of Dasikong Village in Anyang in 1962. Archaeology 1964, 8, 381–384. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar]
- Tang, J. The Culture Studies of Middle Shang Dynasty. Acta Archaeol. 1999, 4, 393–420. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar]
- Xia-Shang-Zhou Chronology Project Expert Group. The Phase Results Report of Xia-Shang-Zhou Chronology Project: 1996–2000; World Publishing Corporation: Beijing, China, 2010; (In Chinese). ISBN 7-5062-4138-2/K 4. [Google Scholar]
- Zheng, R. The preliminary study in distribution about ethnic group of Dayishang in Yinxu site. Cult. Relics Cent. China 1995, 3, 84–93. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar]
- Yue, H.; Yue, Z.; He, Y. The preliminary study of the layout about the region of the palace and temple in Yinxu site. Sandai Archaeol. 2006, 328–343. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar]
- Yue, H.; He, H.; Yue, Z. Some questions about the layout of Yinxu City. Sandai Archaeology 2011, 1, 248–278. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar]
- Chang, H. Spatial planning analysis about bronze casting workshop of Xia and Shang Dynasty. Cult. Relics Cent. China 2018, 203, 68–81. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar]
- Comer, D.C. Tourism and Archaeological Heritage Management at Petra; Springer: New York, NY, USA, 2012; ISBN 978-1-4614-1480-3. [Google Scholar]
- Yue, Z. The study about cultural landscape of the Yinxu Phase IV through archaeological material. Cult. Relics South. China 2020, 4, 74–81. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar]
- Baxter, M.J.; Beardah, C.C. Some Archaeological Applications of Kernel Density Estimates. J. Archaeol. Sci. 1997, 24, 347–354. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Grove, M. A Spatio-Temporal Kernel Method for Mapping Changes in Prehistoric Land-Use Patterns. Archaeometry 2011, 53, 1012–1130. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sayer, D.; Wienhold, M. A GIS-Investigation of Four Early Anglo-Saxon Cemeteries: Ripley’s K-function Analysis of Spatial Groupings Amongst Graves. Soc. Sci. Comput. Rev. 2013, 31, 71–89. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, K. Preliminary research on climate change in China in the past 5000 years. Sci. China 1973, 2, 168–189. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, Z.; Xu, H.; Li, Y.; Yang, X.; Jing, Z.; Tang, J. Characteristics And Environmental Significance of Soil Profile Pollen in Yinxu Site. Quat. Sci. 2007, 3, 461–468. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar]
- Wang, S.; Yue, H.; Yue, Z. The High-resolution Ratio of Ecological Environment During The Yin Dynasty. Cult. Relics South. China 2016, 2, 148–157. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wei, J. A Exploration of Climate Change in the Central Plains during the Shang Dynasty. Archaeol. Cult. Relics 2007, 6, 44–50. [Google Scholar]
- Dykoski, C.A.; Edwards, R.L.; Cheng, H.; Yuan, D.; Cai, Y.; Zhang, M.; Lin, Y.; Qing, J.; An, Z.; Revenaugh, J. A high-resolution, absolute-dated Holocene and deglacial Asian monsoon record from Dongge Cave, China. Earth Planet. Sci. Lett. 2005, 233, 71–86. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cosford, J.; Qing, H.; Eglington, B.; Mattey, D.; Yuan, D.; Zhang, M.; Cheng, H. East Asian monsoon variability since the Mid-Holocene recorded in a high-resolution, absolute-dated aragonite speleothem from eastern China. Earth Planet. Sci. Lett. 2008, 275, 296–307. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, F.; Xu, Q.; Chen, J.; Birks, H.J.B.; Liu, J.; Zhang, S.; Jin, L.; An, C.; Telford, R.J.; Cao, X.; et al. East Asian summer monsoon precipitation variability since the last deglaciation. Sci. Rep. 2015, 5, 11896. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Xu, Q.; Xiao, J.; Li, Y.; Tian, F.; Nakagawa, T. Pollen-based quantitative reconstruction of holocene climate changes in the daihai lake area, inner Mongolia, China. J. Clim. 2010, 23, 2856–2868. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yue, H. Revisiting the Concept about “Huangquan” of Shang Dynasty. Cult. Relics Cent. China 2018, 5, 38–48. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar]
- Meng, X.; Li, G.; Li, Y. The state-controlled handicraft workshop in the Yinxu, the capital city of Yin Dynasty. Yindu J. 2014, 35, 13–20. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar]
- Liu, Y. The Disscussion About the Combination of Bronze Weapons in the Tomb of Yinxu Site in Anyang. Archaeology 2002, 3, 63–75. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar]
- Yang, X. The excavation of eastern Sanjiazhuang of Anyang Yin Ruins. Archaeology 1983, 2, 126–132. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar]
- Li, J. The recording of the bronze artifact unearthed in Xiaotun—The middle chapter: Blade Ware. Acta Archaeol. Sin. 1949, 4, 1–69. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar]
- Zheng, R. Briefing on the excavation of the Tomb of Yin in the North of the Anyang Nursery in autumn,1984. Archaeology 1989, 2, 123–138. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar]
- Gu, F. The two Yin tombs in the south of Dasikong Village in Anyang in 1986. Archaeology 1989, 07, 591–597. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar]
- Xu, G. The No. 26 tomb which in the southeast of Guojiazhuang, Anyang City, Henan Province. Archaeology 1998, 373, 36–47. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar]
- Yang, X. Briefing on the excavation of M539 in Dasikong Village, Anyang, Henan in 1980. Archaeology 1992, 6, 509–517. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar]
- Xu, G. A Yin Dynasty tomb in the southeast of The Dasikong Village of Anyang. Archaeology 1988, 10, 509–517. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar]
- Zheng, Z. The two Yin Dynasty tombs in the north of Xiaotun Village, Anyang. Acta Archaeol. Sin. 1981, 4, 491–518. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar]
- Xu, G. Briefing on the excavation of the tomb of Yin in the southeast of Xuejiazhuang in Anyang. Archaeology 1986, 12, 1067–1072. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar]
- Gu, F. The 1984–1988 Excavation Report of Yin Dynasty Tombs in the North of Dasikong Village, Anyang. Acta Archaeol. Sin. 1994, 115, 471–497. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar]
- Xu, G. The excavation about the Yin Dynasty tomb of Hougang in Anyang in 1991. Archaeology 1993, 10, 880–903. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar]
- Meng, X. The 269th tomb in the east of Qijiazhuang, Yinxu. Acta Archaeol. Sin. 1991, 3, 325–352. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar]
- Zhao, Q.; Zhao, S.; Liu, X.; Zhang, J. The briefing on the excavation of the Yin Dynasty tomb in Dasikong Village, Anyang City, Henan Province in the spring of 1958. Archaeology 1958, 10, 51–62. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar]
- Zhou, D.; Liu, Y. The excavation of the Yin Dynasty tomb in Gaolouzhuang Village, Anyang City in the autumn of 1958. Archaeology 1963, 4, 213–216. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar]
- Yang, X. The excavation of the Yin Dynasty tomb in the southeast of Gaolouzhuang Village, Anyang City in the summer of 1987. Archaeology 1988, 10, 875–881. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar]
- Yang, X.; Yang, B. The excavation of the 1713th tomb in the western of Yinxu, Anyang. Archaeology 1986, 8, 703–712. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar]
- Dai, F. The excavation of the Yin Dynasty tomb in Meiyuanzhuang Village, Anyang City in the autumn of 1987. Archaeology 1991, 2, 125–142. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar]
- Sun, Y.; Lin, H. Geography and States in Shang Dynasty; China Social Science Press: Beijing, China, 2010; ISBN 978-750-048-924-5. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar]
- Yuan, H. A Comprehensive Study of Human Bones in Small and Medium- Sized Tombs in Yinxu. Ph.D. Thesis, Jilin University, Changchun, China, 2010. (In Chinese). [Google Scholar]
- Cheung, C.; Jing, Z.; Tang, J.; Richards, M.P. Social dynamics in early Bronze Age China: A multi-isotope approach. J. Archaeol. Sci. Rep. 2017, 16, 90–101. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, M. The class struggle between the nobility and the commoners of Shang Dynasty, as reflected in the Pangeng-Shangshu. J. Zhengzhou Univ. Philos. Soc. Sci. Ed. 1978, 2, 75–81. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar]
- Li, M. The ecological environment of Yinxu and the migration of Pangeng. Hist. Res. 1991, 1, 111–120. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar]
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).