Spatial Planning Implementation Effectiveness: Review and Research Prospects
Abstract
:1. Introduction
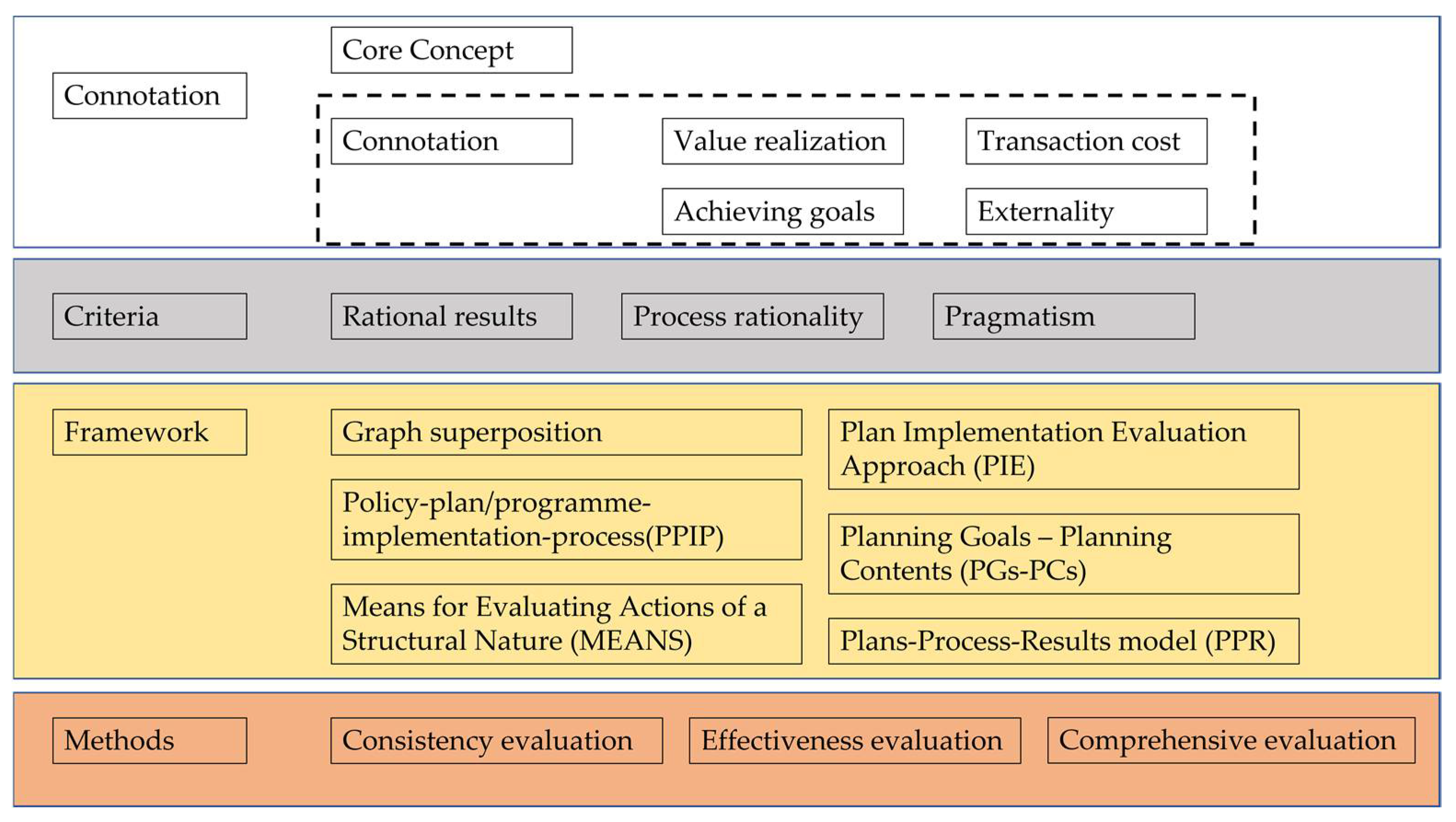
2. Connotation Discrimination of the Effect of Spatial Planning Implementation
2.1. The Core Concept of Spatial Planning Implementation Evaluation
2.2. Connotation of the Implementation Effect of Spatial Planning
2.2.1. Perspective of Value Realization
2.2.2. Perspective on Achieving Goals
2.2.3. Transaction Cost Perspective
2.2.4. Externality Perspective
3. Evaluation Criteria of the Implementation Effect of Spatial Planning
3.1. Rational Results
3.2. Process Rationality
3.3. Pragmatism
4. Evaluation Framework
4.1. Graph Superposition Method
4.2. The Policy-Plan/Programme-Implementation-Process Approach (PPIP)
4.3. Means for Evaluating Actions of a Structural Nature (MEANS)
4.4. Plan Implementation Evaluation Approach (PIE)
4.5. Plans-Process-Results Model (PPR)
4.6. Planning Goals—Planning Contents (PGs-PCs)
5. Evaluation Methods
5.1. Consistency Evaluation Method
5.2. Effectiveness Evaluation Method
5.3. Comprehensive Evaluation Method
6. Evolution of Spatial Planning Effectiveness Implementation Evaluation
6.1. The Evaluation Concept Changes from Complete Rationality to Limited Rationality
6.2. Research Methodology Changes from Simple Closed System to Complex Open System
6.3. The Research Perspective Shifts from the Map to the Main Body of Planning Implementation Behavior
7. Conclusions and Future Prospects
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Talen, E. Success, Failure, and Conformance: An Alternative Approach to Planning Evaluation. Environ. Plan. B Plan. Des. 1997, 24, 573–587. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Berke, P.; Backhurst, M.; Day, M.; Ericksen, N.; Laurian, L.; Crawford, J.; Dixon, J. What Makes Plan Implementation Successful? An Evaluation of Local Plans and Implementation Practices in New Zealand. Environ. Plan. B Plan. Des. 2006, 33, 581–600. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lyles, W.; Stevens, M. Plan Quality Evaluation 1994–2012: Growth and Contributions, Limitations, and New Directions. J. Plan. Educ. Res. 2014, 34, 433–450. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Talen, E.; Anselin, L.; Lee, S.; Koschinsky, J. Looking for logic: The zoning—Land use mismatch. Landsc. Urban Plan. 2016, 152, 27–38. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pressman, J.; Wildavsky, A. Implementation; University of California Press: Berkeley, CA, USA, 1984. [Google Scholar]
- Alexander, E.R.; Faludi, A. Planning and Plan Implementation: Notes on Evaluation Criteria. Environ. Plan. B Plan. Des. 1989, 16, 127–140. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Talen, E. Do Plans Get Implemented? A Review of Evaluation in Planning. J. Plan. Lit. 1996, 10, 248–259. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Laurian, L.; Day, M.; Berke, P.; Ericksen, N.; Backhurst, M.; Crawford, J.; Dixon, J. Evaluating Plan Implementation: A Conformance-Based Methodology. J. Am. Plan. Assoc. 2004, 70, 471–480. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Loh, C.G. Assessing and Interpreting Non-conformance in Land-use Planning Implementation. Plan. Pract. Res. 2011, 26, 271–287. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mastop, H.; Faludi, A. Evaluation of Strategic Plans: The Performance Principle. Environ. Plan. B Plan. Des. 1997, 24, 815–832. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Janin Rivolin, U. Conforming and Performing Planning Systems in Europe: An Unbearable Cohabitation. Plan. Pract. Res. 2008, 23, 167–186. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Feitelson, E.; Felsenstein, D.; Razin, E.; Stern, E. Assessing land use plan implementation: Bridging the performance-conformance divide. Land Use Policy 2017, 61, 251–264. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Calkins, H.W. The Planning Monitor: An Accountability Theory of Plan Evaluation. Environ. Plan. A Econ. Space 1979, 11, 745–758. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Baer, W.C. General Plan Evaluation Criteria: An Approach to Making Better Plans. J. Am. Plan. Assoc. 1997, 63, 329–344. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shen, X.; Wang, X.; Zhang, Z.; Lu, Z.; Lv, T. Evaluating the effectiveness of land use plans in containing urban expansion: An integrated view. Land Use Policy 2019, 80, 205–213. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Oliveira, V.; Pinho, P. Measuring success in planning: Developing and testing a methodology for planning evaluation. Town Plan. Rev. 2010, 81, 307–332. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shen, X.; Wang, X.; Zhang, Z.; Fei, L. Does non-conforming urban development mean the failure of zoning? A framework for conformance-based evaluation. Environ. Plan. B Urban Anal. City Sci. 2020, 48, 1279–1295. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Oliveira, V.; Pinho, P. Bridging the gap between planning evaluation and programme evaluation: The contribution of the PPR methodology. Evaluation 2011, 17, 293–307. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Oliveira, V.; Pinho, P. Evaluating Plans, Processes and Results. Plan. Theory Pract. 2009, 10, 35–63. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, L.-G.; Han, H.; Lai, S.-K. Do plans contain urban sprawl? A comparison of Beijing and Taipei. Habitat Int. 2014, 42, 121–130. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Healey, P. Urban Complexity and Spatial Strategies: Towards a Relational Planning for Our Times, 1st ed.; Routledge: London, UK, 2006. [Google Scholar]
- Li, G.; Xu, Z.; Wu, C.; Zhuo, Y.; Tong, X.; Wei, Y.; Shen, X. Inside or Outside? The Impact Factors of Zoning–Land Use Mismatch. Sustainability 2020, 12, 265. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Wu, Y.; Fan, P.; Li, B.; Ouyang, Z.; Liu, Y.; You, H. The Effectiveness of Planning Control on Urban Growth: Evidence from Hangzhou, China. Sustainability 2017, 9, 855. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Faludi, A. Dutch growth management: The two faces of success. Landsc. Urban Plan. 1992, 22, 93–106. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hopkins, L.D. Urban Development: The Logic of Making Plans; Island Press: Washington, WA, USA, 2001. [Google Scholar]
- Faludi, A. CONFORMANCE VS. PERFORMANCE: IMPLICATIONS FOR EVALUATION. Impact Assess. 1989, 7, 135–151. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Faludi, A. The Performance of Spatial Planning. Plan. Pract. Res. 2000, 15, 299–318. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Macmillan, S. Added value of good design. Build. Res. Inf. 2006, 34, 257–271. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Leung, H.-L. Land Use Planning Made Plain; University of Toronto Press: Toronto, ON, Canada, 2003. [Google Scholar]
- Liu, Y.; Zhou, Y. Territory spatial planning and national governance system in China. Land Use Policy 2021, 102, 105288. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pennington, M. Planning and the Political Market: Public Choice and the Politics of Government Failure; The Athlone Press: London, UK, 2000. [Google Scholar]
- Evans, A. Economics and Land Use Planning; Blackwell Publishing Ltd.: Oxford, UK, 2004. [Google Scholar]
- Chadwick, G. A Systems View of Planning: Towards a Theory of the Urban and Regional Planning Process; Pergamon Press: New York, NY, USA, 1981. [Google Scholar]
- Shahab, S.; Clinch, J.P.; O’Neill, E. Impact-based planning evaluation: Advancing normative criteria for policy analysis. Environ. Plan. B Urban Anal. City Sci. 2017, 46, 534–550. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alfasi, N.; Almagor, J.; Benenson, I. The actual impact of comprehensive land-use plans: Insights from high resolution observations. Land Use Policy 2012, 29, 862–877. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alexander, E.R. Planning, Policy and the Public Interest: Planning Regimes and Planners′ Ethics and Practices. Int. Plan. Stud. 2010, 15, 143–162. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alexander, E.R. A Transaction Cost Theory of Planning. J. Am. Plan. Assoc. 1992, 58, 190–200. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Buitelaar, E. The Cost of Making Land Use Decisions. In The Cost of Land Use Decisions: Applying Transaction Cost Economics to Planning & Development; Buitelaar, E., Ed.; Blackwell Publishing Ltd.: Oxford, UK, 2007; pp. 1–13. [Google Scholar]
- Lai, L.W.-C. Neo-Institutional Economics and Planning Theory. Plan. Theory 2005, 4, 7–19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dawkins, C.J. Transaction Costs and the Land Use Planning Process. J. Plan. Lit. 2000, 14, 507–518. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shahab, S.; Clinch, J.P.; O’Neill, E. Accounting for transaction costs in planning policy evaluation. Land Use Policy 2018, 70, 263–272. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Campbell, H.; Marshall, R. Utilitarianism’s Bad Breath? A Re-Evaluation of the Public Interest Justification for Planning. Plan. Theory 2002, 1, 163–187. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Laurian, L.; Crawford, J.; Day, M.; Kouwenhoven, P.; Mason, G.; Ericksen, N.; Beattie, L. Evaluating the Outcomes of Plans: Theory, Practice, and Methodology. Environ. Plan. B Plan. Des. 2010, 37, 740–757. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Talen, E. After the Plans: Methods to Evaluate the Implementation Success of Plans. J. Plan. Educ. Res. 1996, 16, 79–91. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alexander, E.R. Planning Rights: Toward Normative Criteria for Evaluating Plans. Int. Plan. Stud. 2002, 7, 191–212. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Oliveira, V.; Pinho, P. Evaluation in Urban Planning: Advances and Prospects. J. Plan. Lit. 2010, 24, 343–361. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Taylor, N. Urban Planning Theory since 1945; Sage Publications Ltd.: London, UK, 1998. [Google Scholar]
- Benveniste, G. The Politics of Expertise; Glendessary Press: Berkeley, CA, USA, 1972. [Google Scholar]
- Bulti, D.T.; Sori, N.D. Evaluating land-use plan using conformance-based approach in Adama city, Ethiopia. Spat. Inf. Res. 2017, 25, 605–613. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alterman, R.; Hill, M. Implementation of Urban Land Use Plans. J. Am. Inst. Plan. 1978, 44, 274–285. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chapin, T.S.; Deyle, R.E.; Baker, E.J. A Parcel-Based GIS Method for Evaluating Conformance of Local Land-Use Planning with a State Mandate to Reduce Exposure to Hurricane Flooding. Environ. Plan. B Plan. Des. 2008, 35, 261–279. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lyles, W.; Berke, P.; Smith, G. Local plan implementation: Assessing conformance and influence of local plans in the United States. Environ. Plan. B Plan. Des. 2015, 43, 381–400. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abbott, C.; Margheim, J. Imagining Portland′s Urban Growth Boundary: Planning Regulation as Cultural Icon. J. Am. Plan. Assoc. 2008, 74, 196–208. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dempsey, J.A.; Plantinga, A.J. How well do urban growth boundaries contain development? Results for Oregon using a difference-in-difference estimator. Reg. Sci. Urban Econ. 2013, 43, 996–1007. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alterman, R.; Calor, I. Between Informal and Illegal in the Global North: Planning Law, Enforcement, and Justifiable Noncompliance. In Comparative Approaches to Informal Housing around the Globe; Grashoff, U., Ed.; University College London (UCL) Press: London, UK, 2020. [Google Scholar]
- Iban, M.C. Lessons from approaches to informal housing and non-compliant development in Turkey: An in-depth policy analysis with a historical framework. Land Use Policy 2020, 99, 105104. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vedung, E. Public Policy and Program Evaluation; Transaction Publishers: Piscataway, NJ, USA, 1997. [Google Scholar]
- Zhong, T.; Mitchell, B.; Huang, X. Success or failure: Evaluating the implementation of China′s National General Land Use Plan (1997–2010). Habitat Int. 2014, 44, 93–101. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Han, H.-y.; Lai, S.-K.; Dang, A.-r.; Tan, Z.-b.; Wu, C.-f. Effectiveness of urban construction boundaries in Beijing: An assessment. J. Zhejiang Univ. Sci. A 2009, 10, 1285–1295. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Long, Y.; Han, H.; Lai, S.-K.; Mao, Q. Urban growth boundaries of the Beijing Metropolitan Area: Comparison of simulation and artwork. Cities 2013, 31, 337–348. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Long, Y.; Han, H.; Tu, Y.; Shu, X. Evaluating the effectiveness of urban growth boundaries using human mobility and activity records. Cities 2015, 46, 76–84. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Faludi, A. A decision-centred view of environmental planning. Landsc. Plan. 1985, 12, 239–256. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Faludi, A. Towards a Three-Dimensional Model of Planning Behaviour. Environ. Plan. A Econ. Space 1971, 3, 253–266. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shen, X.; Wang, L.; Wang, X.; Zhang, Z.; Lu, Z. Interpreting non-conforming urban expansion from the perspective of stakeholders’ decision-making behavior. Habitat Int. 2019, 89, 102007. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tian, L.; Shen, T. Evaluation of plan implementation in the transitional China: A case of Guangzhou city master plan. Cities 2011, 28, 11–27. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mastop, H.; Needham, B. Performance Studies in Spatial Planning: The State of the Art. Environ. Plan. B Plan. Des. 1997, 24, 881–888. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Needham, B.; Zwanikken, T.; Faludi, A. Strategies for Improving the Performance of Planning: Some Empirical Research. Environ. Plan. B Plan. Des. 1997, 24, 871–880. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pickvance, C. Physical Planning and Market Forces in Urban Development. In Critical Readings in Planning Theory; Paris, C., Ed.; Pergamon Press Ltd.: Oxford, UK, 1982; pp. 69–82. [Google Scholar]
- Hoch, C.J. Evaluating Plans Pragmatically. Plan. Theory 2002, 1, 53–75. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alexander, E.R. Institutional Transformation and Planning: From Institutionalization Theory to Institutional Design. Plan. Theory 2005, 4, 209–223. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alexander, E.R. If Planning Isn’t Everything, Maybe Its Something. Town Plan. Rev. 1981, 52, 131–142. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mayne, J. Addressing Attribution Through Contribution Analysis: Using Performance Measures Sensibly. Can. J. Program Eval. 2001, 16, 1–24. [Google Scholar]
- Seasons, M. Monitoring and Evaluation in Municipal Planning: Considering the Realities. J. Am. Plan. Assoc. 2003, 69, 430–440. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Carmona, M.; Sieh, L. Performance Measurement in Planning—Towards a Holistic View. Environ. Plan. C Gov. Policy 2008, 26, 428–454. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- He, J. Evaluation of Plan Implementation: Peri-urban Development and the Shanghai Master Plan 1999–2020. A+BE Archit. Built Environ. 2015, 5. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, T.; Huang, D.; Tan, X.; Kong, F. Planning consistency and implementation in urbanizing China: Comparing urban and land use plans in suburban Beijing. Land Use Policy 2020, 94, 104498. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- European, C.; Directorate-General for, R.; Urban, P. Evaluating Socio-Economic Programmes; European Union: Brussels, Belgium, 2009; Volume 1–6. [Google Scholar]
- Laurian, L.; Day, M.; Backhurst, M.; Berke, P.; Ericksen, N.; Crawford, J.; Dixon, J.; Chapman, S. What drives plan implementation? Plans, planning agencies and developers. J. Environ. Plan. Manag. 2004, 47, 555–577. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Berke, P.; Godschalk, D. Searching for the Good Plan: A Meta-Analysis of Plan Quality Studies. J. Plan. Lit. 2009, 23, 227–240. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Burby, R.J. Making Plans that Matter: Citizen Involvement and Government Action. J. Am. Plan. Assoc. 2003, 69, 33–49. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brody, S.D.; Highfield, W.E. Does Planning Work?: Testing the Implementation of Local Environmental Planning in Florida. J. Am. Plan. Assoc. 2005, 71, 159–175. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brody, S.D.; Highfield, W.E.; Thornton, S. Planning at the Urban Fringe: An Examination of the Factors Influencing Nonconforming Development Patterns in Southern Florida. Environ. Plan. B Plan. Des. 2006, 33, 75–96. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schmid, F.B.; Kienast, F.; Hersperger, A.M. The compliance of land-use planning with strategic spatial planning—insights from Zurich, Switzerland. Eur. Plan. Stud. 2021, 29, 1231–1250. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, Y.; Wu, C.; Li, B.; Luo, W. Research on Spatial-Temporal Evolution and its Mechanisms for Urban Planning Control Performance: A Case Study on Five Master Plans of Beijing During 1958–2004. City Plan. Rev. 2013, 37, 33–41. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar]
- Gennaio, M.-P.; Hersperger, A.M.; Bürgi, M. Containing urban sprawl—Evaluating effectiveness of urban growth boundaries set by the Swiss Land Use Plan. Land Use Policy 2009, 26, 224–232. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yue, W.; Zhang, L. Implementation Evaluation of Urban Master Planning Based on Spatial Consistency—A Case of Hangzhou. Econ. Geogr. 2014, 34, 47–53. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bacău, S.; Grădinaru, S.R.; Hersperger, A.M. Spatial plans as relational data: Using social network analysis to assess consistency among Bucharest’s planning instruments. Land Use Policy 2020, 92, 104484. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Faludi, A.; Altes, W.K. Evaluating communicative planning: A revised design for performance research. Eur. Plan. Stud. 1994, 2, 403–418. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Millard-Ball, A. The Limits to Planning: Causal Impacts of City Climate Action Plans. J. Plan. Educ. Res. 2012, 33, 5–19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Van Damme, L.; Galle, M.; Pen-Soetermeer, M.; Verdaas, K. Improving the Performance of Local Land-Use Plans. Environ. Plan. B Plan. Des. 1997, 24, 833–844. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mastop, H. Performance in Dutch Spatial Planning: An Introduction. Environ. Plan. B Plan. Des. 1997, 24, 807–813. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Limb, M.; Grodach, C.; Donehue, P.; Mayere, S. When plans are used to no effect: Considering implementation performance of greater Brisbane’s compact activity centre policies. Environ. Plan. B Urban Anal. City Sci. 2020, 48, 1860–1875. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, J.; Li, G.a.; Li, J.; Liu, A. Integrating conformance and performance for the evaluation of urban planning implementation from a goal-oriented perspective. Environ. Plan. B Urban Anal. City Sci. 2021, 49, 737–753. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Loh, C.G. Placemaking and implementation: Revisiting the performance principle. Land Use Policy 2019, 81, 68–75. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
| Category | Advantage | Limitations | |
|---|---|---|---|
| Criteria | Rational results | Simple and clear Easy to identify | Ignoring the complexity of the planning implementation process |
| Process rationality | Focus on the impact of planning on human decision-making behavior | Key elements of the evaluation are difficult to observe and measure Difficult to manipulate | |
| Pragmatism | Avoiding a disconnect between planning implementation and actual needs | Subjective Evaluation benchmarks are controversial | |
| Framework | Graph superposition | Quantitative spatial analysis Intuitive | Neglect of the planning implementation process and the actual role of planning |
| The policy-plan/programme-implementation-process Approach (PPIP) | Comprehensive content Broad impact | Lack of practical workability | |
| Means for Evaluating Actions of a Structural Nature (MEANS) | Synthesis | Need to collect a large amount of assessment information | |
| Plan Implementation Evaluation Approach (PIE) | Focus on the strength of the link between planning control policies and planning permissions | One-sidedness | |
| Plans-Process-Results model (PPR) | Include planning preparation in the assessment of plan implementation | Assessment data are difficult to obtain | |
| Planning Goals—Planning Contents (PGs-PCs) | Integration of planning objectives and planning content | Operational complexity | |
| Methods | Consistency evaluation | Intuitive, objective and easy to use | Consistency evaluation is not sufficient to capture the actual impact and effect of plan implementation |
| Effectiveness evaluation | Ability to assess the long-term impact of the plan Consider the impact of the planning implementation process | Lack of operability Ignoring the economic, social and ecological impact and effectiveness of the plan | |
| Comprehensive evaluation | Synthesis Ability to assess the effectiveness of planning implementation from multiple perspectives | Complex to operate and difficult to practice | |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Li, G.; Wang, L.; Wu, C.; Xu, Z.; Zhuo, Y.; Shen, X. Spatial Planning Implementation Effectiveness: Review and Research Prospects. Land 2022, 11, 1279. https://doi.org/10.3390/land11081279
Li G, Wang L, Wu C, Xu Z, Zhuo Y, Shen X. Spatial Planning Implementation Effectiveness: Review and Research Prospects. Land. 2022; 11(8):1279. https://doi.org/10.3390/land11081279
Chicago/Turabian StyleLi, Guan, Liping Wang, Cifang Wu, Zhongguo Xu, Yuefei Zhuo, and Xiaoqiang Shen. 2022. "Spatial Planning Implementation Effectiveness: Review and Research Prospects" Land 11, no. 8: 1279. https://doi.org/10.3390/land11081279
APA StyleLi, G., Wang, L., Wu, C., Xu, Z., Zhuo, Y., & Shen, X. (2022). Spatial Planning Implementation Effectiveness: Review and Research Prospects. Land, 11(8), 1279. https://doi.org/10.3390/land11081279






