Object-Based Informal Settlement Mapping in Google Earth Engine Using the Integration of Sentinel-1, Sentinel-2, and PlanetScope Satellite Data
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
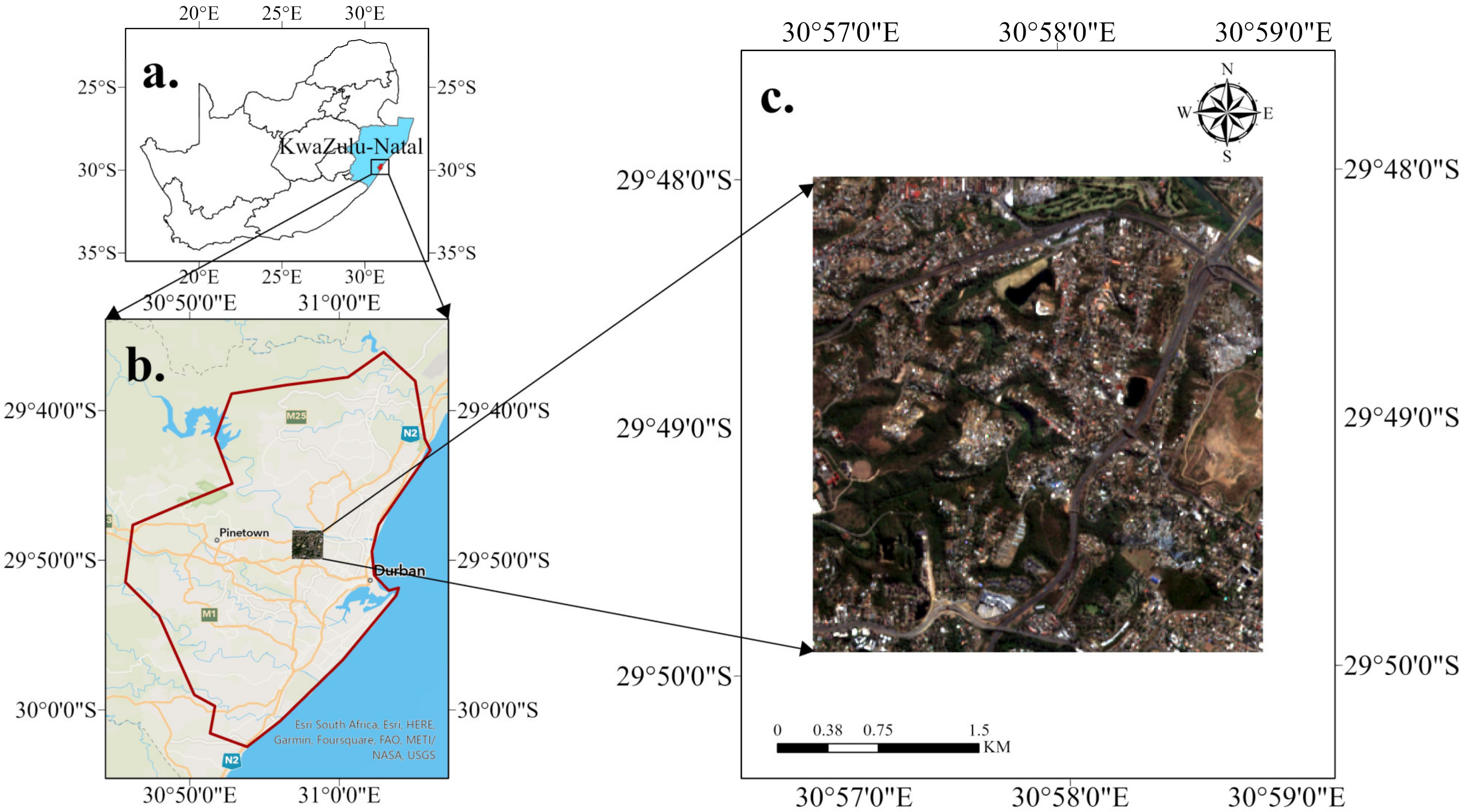
2.1. Study Area
2.2. Methodology
2.2.1. Data Collection, Pre-Processing, and Image Composition
2.2.2. Image Segmentation with SNIC
2.2.3. Texture Analysis
2.2.4. Object Based Image Classification
2.2.5. Accuracy Assessment
2.2.6. Feature Importance Assessment
3. Results
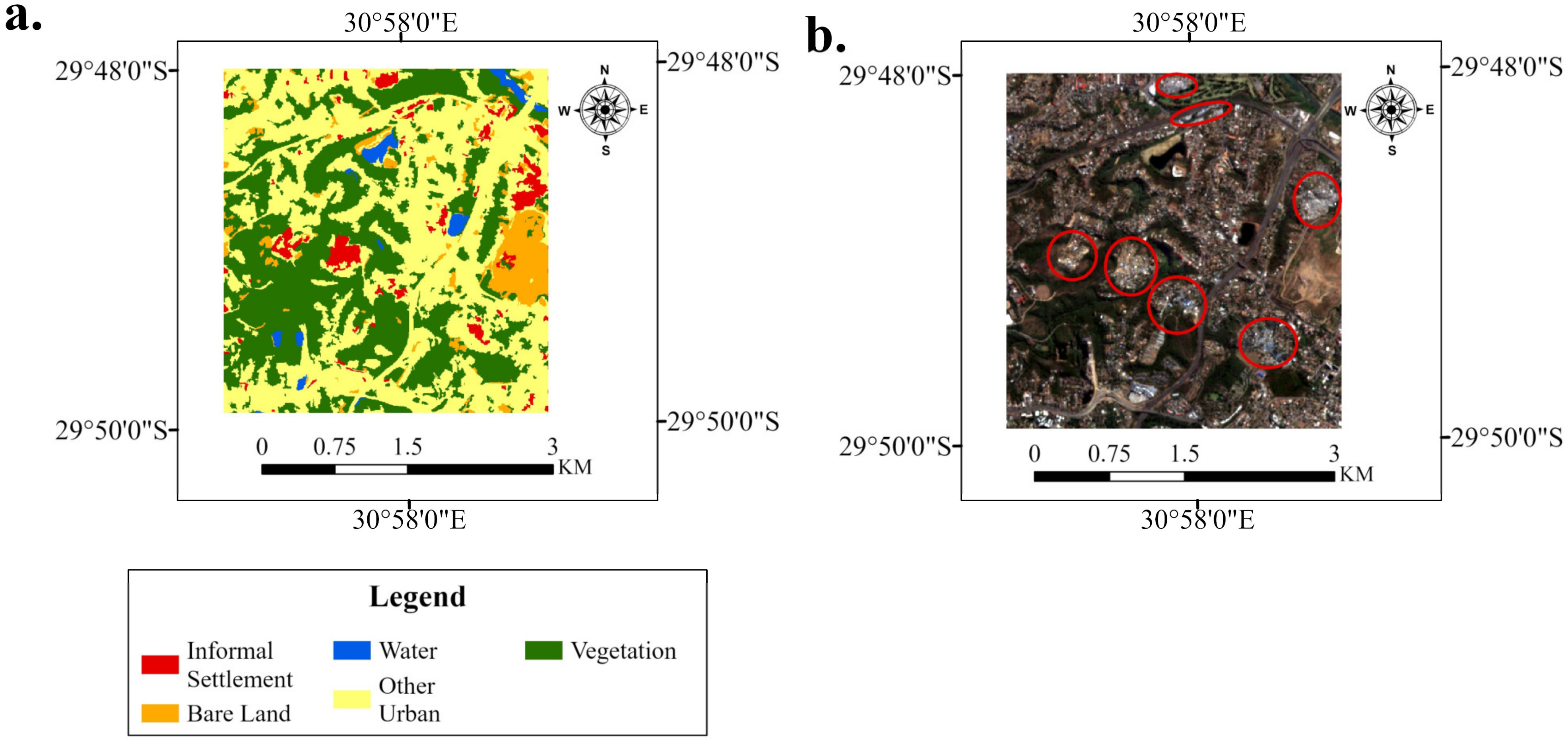
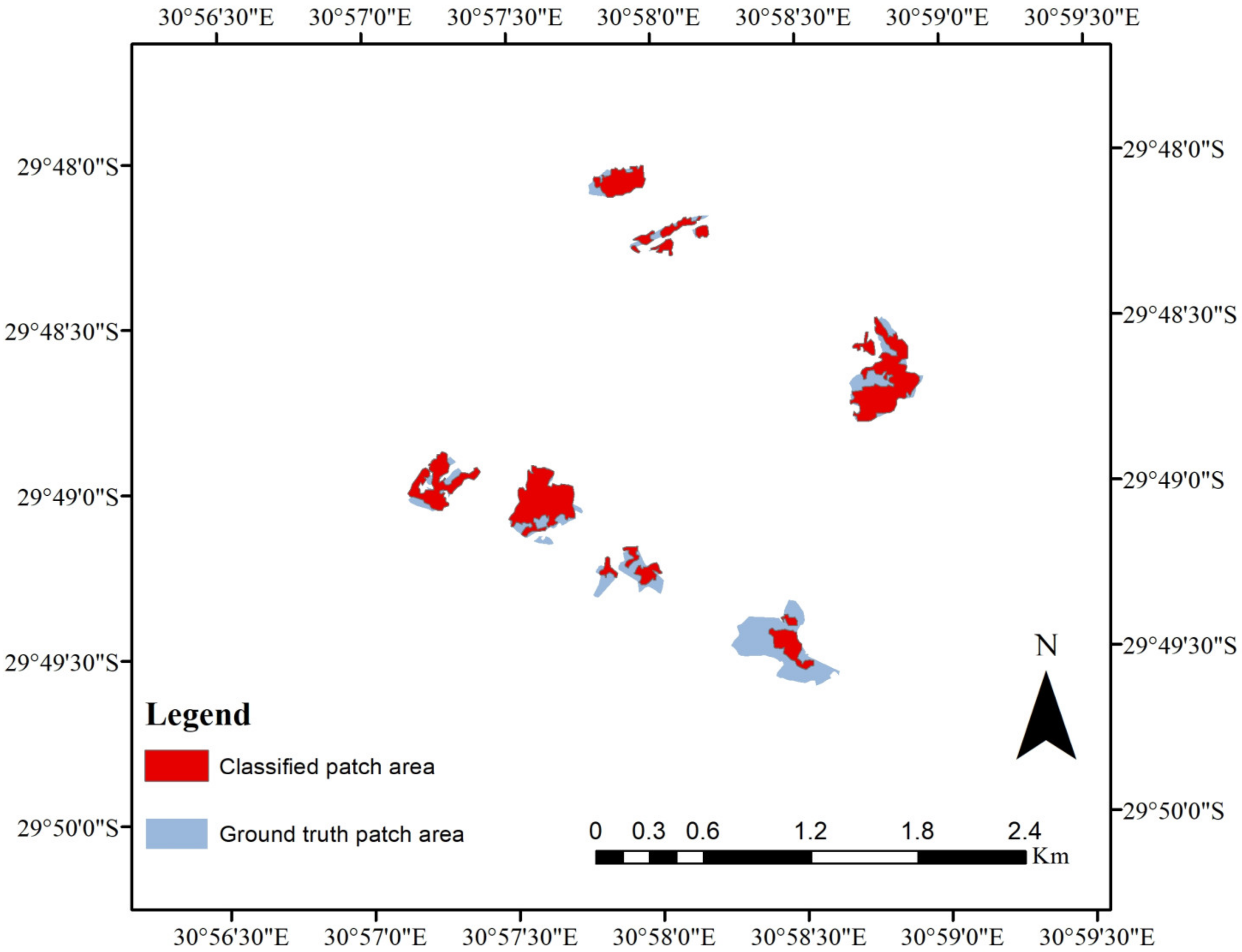
3.1. Accuracy Assessment of the LULC Map
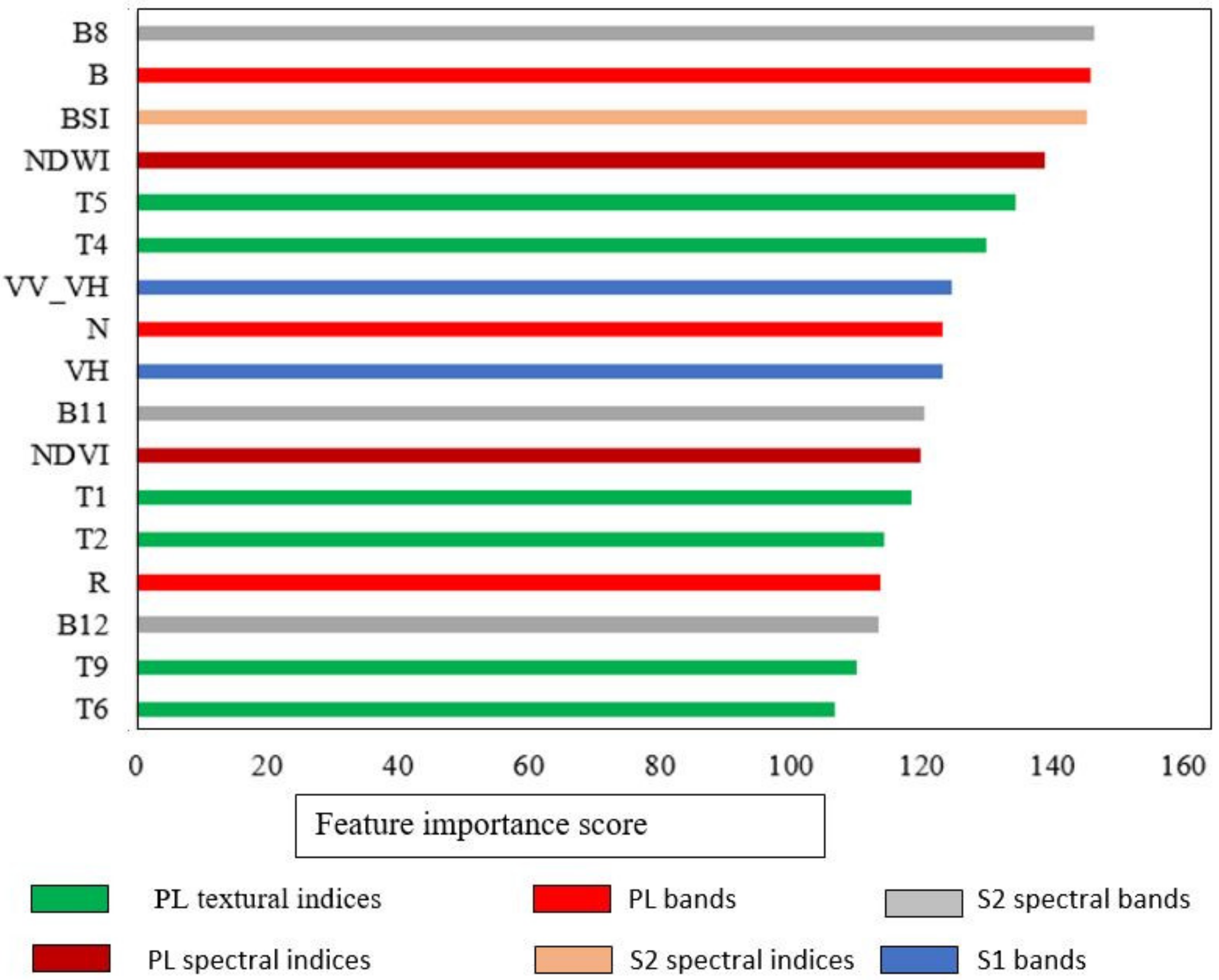
3.2. Relative Contribution of Input Variables in RF Classification
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Wurm, M.; Stark, T.; Zhu, X.X.; Weigand, M.; Taubenböck, H. Semantic segmentation of slums in satellite images using transfer learning on fully convolutional neural networks. ISPRS J. Photogramm. Remote Sens. 2019, 150, 59–69. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hofmann, P.; Taubenböck, H.; Werthmann, C. Monitoring and modelling of informal settlements-A review on recent developments and challenges. In Proceedings of the 2015 Joint Urban Remote Sensing Event (JURSE), Lausanne, Switzerland, 30 March–1 April 2015; pp. 1–4. [Google Scholar]
- Kuffer, M.; Thomson, D.R.; Boo, G.; Mahabir, R.; Grippa, T.; Vanhuysse, S.; Engstrom, R.; Ndugwa, R.; Makau, J.; Darin, E.; et al. The Role of Earth Observation in an Integrated Deprived Area Mapping “System” for Low-to-Middle Income Countries. Remote Sens. 2020, 12, 982. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- UN-Habitat. World Cities Report 2016: Urbanization and Development—Emerging Futures; World Cities Report; UN: Nairobi, Kenya, 2016; ISBN 978-92-1-058281-0. [Google Scholar]
- Fallatah, A.; Jones, S.; Wallace, L.; Mitchell, D. Combining Object-Based Machine Learning with Long-Term Time-Series Analysis for Informal Settlement Identification. Remote Sens. 2022, 14, 1226. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pratomo, J.; Kuffer, M.; Martinez, J.; Kohli, D. Coupling Uncertainties with Accuracy Assessment in Object-Based Slum Detections, Case Study: Jakarta, Indonesia. Remote Sens. 2017, 9, 1164. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Taubenböck, H.; Kraff, N.J.; Wurm, M. The morphology of the Arrival City—A global categorization based on literature surveys and remotely sensed data. Appl. Geogr. 2018, 92, 150–167. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kraff, N.J.; Wurm, M.; Taubenböck, H. The dynamics of poor urban areas—Analyzing morphologic transformations across the globe using Earth observation data. Cities 2020, 107, 102905. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Belenok, V.; Noszczyk, T.; Hebryn-Baidy, L.; Kryachok, S. Investigating anthropogenically transformed landscapes with remote sensing. Remote Sens. Appl. Soc. Environ. 2021, 24, 100635. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Farda, N.M. Multi-temporal Land Use Mapping of Coastal Wetlands Area using Machine Learning in Google Earth Engine. IOP Conf. Ser. Earth Environ. Sci. 2017, 98, 012042. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, J.; Kuffer, M.; Roy, D.; Pfeffer, K. Deprivation pockets through the lens of convolutional neural networks. Remote Sens. Environ. 2019, 234, 111448. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kuffer, M.; Pfeffer, K.; Sliuzas, R.; Baud, I. Extraction of Slum Areas From VHR Imagery Using GLCM Variance. IEEE J. Sel. Top. Appl. Earth Obs. Remote Sens. 2016, 9, 1830–1840. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mboga, N.; Persello, C.; Bergado, J.; Stein, A. Detection of Informal Settlements from VHR Images Using Convolutional Neural Networks. Remote Sens. 2017, 9, 1106. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Mudau, N.; Mhangara, P. Investigation of Informal Settlement Indicators in a Densely Populated Area Using Very High Spatial Resolution Satellite Imagery. Sustainability 2021, 13, 4735. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Prabhu, R.; Parvathavarthini, B. An enhanced approach for informal settlement extraction from optical data using morphological profile-guided filters: A case study of Madurai city. Int. J. Remote Sens. 2021, 42, 6688–6705. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fallatah, A.; Jones, S.; Mitchell, D. Object-based random forest classification for informal settlements identification in the Middle East: Jeddah a case study. Int. J. Remote Sens. 2020, 41, 4421–4445. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kohli, D.; Sliuzas, R.; Stein, A. Urban slum detection using texture and spatial metrics derived from satellite imagery. J. Spat. Sci. 2016, 61, 405–426. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Mugiraneza, T.; Nascetti, A.; Ban, Y. WorldView-2 Data for Hierarchical Object-Based Urban Land Cover Classification in Kigali: Integrating Rule-Based Approach with Urban Density and Greenness Indices. Remote Sens. 2019, 11, 2128. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Stark, T.; Wurm, M.; Zhu, X.X.; Taubenböck, H. Satellite-Based Mapping of Urban Poverty with Transfer-Learned Slum Morphologies. IEEE J. Sel. Top. Appl. Earth Obs. Remote Sens. 2020, 13, 5251–5263. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Leonita, G.; Kuffer, M.; Sliuzas, R.; Persello, C. Machine Learning-Based Slum Mapping in Support of Slum Upgrading Programs: The Case of Bandung City, Indonesia. Remote Sens. 2018, 10, 1522. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Kohli, D.; Warwadekar, P.; Kerle, N.; Sliuzas, R.; Stein, A. Transferability of Object-Oriented Image Analysis Methods for Slum Identification. Remote Sens. 2013, 5, 4209–4228. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Fallatah, A.; Jones, S.; Mitchell, D.; Kohli, D. Mapping informal settlement indicators using object-oriented analysis in the Middle East. Int. J. Digit. Earth 2019, 12, 802–824. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kohli, D.; Sliuzas, R.; Kerle, N.; Stein, A. An ontology of slums for image-based classification. Comput. Environ. Urban Syst. 2012, 36, 154–163. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Phan, T.N.; Kuch, V.; Lehnert, L.W. Land Cover Classification using Google Earth Engine and Random Forest Classifier—The Role of Image Composition. Remote Sens. 2020, 12, 2411. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shafizadeh-Moghadam, H.; Khazaei, M.; Alavipanah, S.K.; Weng, Q. Google Earth Engine for large-scale land use and land cover mapping: An object-based classification approach using spectral, textural and topographical factors. GISci. Remote Sens. 2021, 58, 914–928. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Teluguntla, P.; Thenkabail, P.S.; Oliphant, A.; Xiong, J.; Gumma, M.K.; Congalton, R.G.; Yadav, K.; Huete, A. A 30-m landsat-derived cropland extent product of Australia and China using random forest machine learning algorithm on Google Earth Engine cloud computing platform. ISPRS J. Photogramm. Remote Sens. 2018, 144, 325–340. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kelley, L.C.; Pitcher, L.; Bacon, C. Using Google Earth Engine to Map Complex Shade-Grown Coffee Landscapes in Northern Nicaragua. Remote Sens. 2018, 10, 952. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Yang, G.; Yu, W.; Yao, X.; Zheng, H.; Cao, Q.; Zhu, Y.; Cao, W.; Cheng, T. AGTOC: A novel approach to winter wheat mapping by automatic generation of training samples and one-class classification on Google Earth Engine. Int. J. Appl. Earth Obs. Geoinf. 2021, 102, 102446. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Achanta, R.; Susstrunk, S. Superpixels and polygons using simple non-iterative clustering. In Proceedings of the IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition (CVPR), Honolulu, HI, USA, 21–26 July 2017; pp. 4651–4660. [Google Scholar]
- Luo, C.; Qi, B.; Liu, H.; Guo, D.; Lu, L.; Fu, Q.; Shao, Y. Using Time Series Sentinel-1 Images for Object-Oriented Crop Classification in Google Earth Engine. Remote Sens. 2021, 13, 561. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qu, L.a.; Chen, Z.; Li, M.; Zhi, J.; Wang, H. Accuracy Improvements to Pixel-Based and Object-Based LULC Classification with Auxiliary Datasets from Google Earth Engine. Remote Sens. 2021, 13, 453. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vizzari, M. PlanetScope, Sentinel-2, and Sentinel-1 Data Integration for Object-Based Land Cover Classification in Google Earth Engine. Remote Sens. 2022, 14, 2628. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tassi, A.; Gigante, D.; Modica, G.; Di Martino, L.; Vizzari, M. Pixel- vs. Object-Based Landsat 8 Data Classification in Google Earth Engine Using Random Forest: The Case Study of Maiella National Park. Remote Sens. 2021, 13, 2299. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tassi, A.; Vizzari, M. Object-Oriented LULC Classification in Google Earth Engine Combining SNIC, GLCM, and Machine Learning Algorithms. Remote Sens. 2020, 12, 3776. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hall-Beyer, M. Practical guidelines for choosing GLCM textures to use in landscape classification tasks over a range of moderate spatial scales. Int. J. Remote Sens. 2017, 38, 1312–1338. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, K.; Dong, X.; Liu, Z.; Gao, W.; Hu, Z.; Wu, G. Mapping Tidal Flats with Landsat 8 Images and Google Earth Engine: A Case Study of the China’s Eastern Coastal Zone circa 2015. Remote Sens. 2019, 11, 924. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Li, M.; Zhang, R.; Luo, H.; Gu, S.; Qin, Z. Crop Mapping in the Sanjiang Plain Using an Improved Object-Oriented Method Based on Google Earth Engine and Combined Growth Period Attributes. Remote Sens. 2022, 14, 273. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mahdianpari, M.; Salehi, B.; Rezaee, M.; Mohammadimanesh, F.; Zhang, Y. Very Deep Convolutional Neural Networks for Complex Land Cover Mapping Using Multispectral Remote Sensing Imagery. Remote Sens. 2018, 10, 1119. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Mahdianpari, M.; Salehi, B.; Mohammadimanesh, F.; Brisco, B. An Assessment of Simulated Compact Polarimetric SAR Data for Wetland Classification Using Random Forest Algorithm. Can. J. Remote Sens. 2017, 43, 468–484. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Amani, M.; Brisco, B.; Afshar, M.; Mirmazloumi, S.M.; Mahdavi, S.; Mirzadeh, S.M.J.; Huang, W.; Granger, J. A generalized supervised classification scheme to produce provincial wetland inventory maps: An application of Google Earth Engine for big geo data processing. Big Earth Data 2019, 3, 378–394. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mahdianpari, M.; Salehi, B.; Mohammadimanesh, F.; Homayouni, S.; Gill, E. The FirstWetland Inventory Map of Newfoundland at a Spatial Resolution of 10 m Using Sentinel-1 and Sentinel-2 Data on the Google Earth Engine Cloud Computing Platform. Remote Sens. 2018, 11, 43. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Tavares, P.A.; Beltrao, N.E.S.; Guimaraes, U.S.; Teodoro, A.C. Integration of Sentinel-1 and Sentinel-2 for Classification and LULC Mapping in the Urban Area of Belem, Eastern Brazilian Amazon. Sensors 2019, 19, 1140. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Rao, P.; Zhou, W.; Bhattarai, N.; Srivastava, A.K.; Singh, B.; Poonia, S.; Lobell, D.B.; Jain, M. Using Sentinel-1, Sentinel-2, and Planet Imagery to Map Crop Type of Smallholder Farms. Remote Sens. 2021, 13, 1870. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bwangoy, J.-R.B.; Hansen, M.C.; Roy, D.P.; Grandi, G.D.; Justice, C.O. Wetland mapping in the Congo Basin using optical and radar remotely sensed data and derived topographical indices. Remote Sens. Environ. 2010, 114, 73–86. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, H.; Xiao, P.; Zhang, X.; Zhou, X.; Li, J.; Guo, R. Object-based island green cover mapping by integrating UAV multispectral image and LiDAR data. J. Appl. Remote Sens. 2021, 15, 034512. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Williams, D.; Máñez Costa, M.; Celliers, L.; Sutherland, C. Informal Settlements and Flooding: Identifying Strengths and Weaknesses in Local Governance for Water Management. Water 2018, 10, 871. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Marx, C.; Charlton, S. Global Report on Human Settlements; UN-HABITAT (Hg.): Durban, South Africa, 2003; pp. 195–223. [Google Scholar]
- Matarira, D.; Mutanga, O.; Naidu, M. Google Earth Engine for Informal Settlement Mapping: A Random Forest Classification Using Spectral and Textural Information. Remote Sens. 2022, 14, 5130. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Marfai, M.A.; Farda, N.M.; Khakhim, N.; Wicaksono, P.; Wicaksono, A. Tidal Correction Effects Analysis on Shoreline Mapping in Jepara Regency. J. Appl. Geospat. Inf. 2018, 2, 145–151. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Carrasco, L.; O’Neil, A.; Morton, R.; Rowland, C. Evaluating Combinations of Temporally Aggregated Sentinel-1, Sentinel-2 and Landsat 8 for Land Cover Mapping with Google Earth Engine. Remote Sens. 2019, 11, 288. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Abebe, M.S.; Derebew, K.T.; Gemeda, D.O. Exploiting temporal-spatial patterns of informal settlements using GIS and remote sensing technique: A case study of Jimma city, Southwestern Ethiopia. Environ. Syst. Res. 2019, 8, 6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Bouzekri, S.; Lasbet, A.A.; Lachehab, A. A New Spectral Index for Extraction of Built-Up Area Using Landsat-8 Data. J. Indian Soc. Remote Sens. 2015, 43, 867–873. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Diek, S.; Fornallaz, F.; Schaepman, M.E. Barest Pixel Composite for Agricultural Areas Using Landsat Time Series. Remote Sens. 2017, 9, 1245. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Nguyen, H.T.T.; Doan, T.M.; Tomppo, E.; McRoberts, R.E. Land Use/Land Cover Mapping Using Multitemporal Sentinel-2 Imagery and Four Classification Methods—A Case Study from Dak Nong, Vietnam. Remote Sens. 2020, 12, 1367. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vergni, L.; Vinci, A.; Todisco, F.; Santaga, F.S.; Vizzari, M. Comparing Sentinel-1, Sentinel-2, and Landsat-8 data in the early recognition of irrigated areas in central Italy. J. Agric. Eng. 2021, 52. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, T.; Liu, J.; Zheng, G.; Li, Y.; Xie, B. Quantitative assessment of urban wetland dynamics using high spatial resolution satellite imagery between 2000 and 2013. Sci Rep 2018, 8, 7409. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Achanta, R.; Shaji, A.; Smith, K.; Lucchi, A.; Fua, P.; Süsstrunk, S. SLIC superpixels compared to state-of-the-art superpixel methods. IEEE Trans. Pattern Anal. Mach. Intell. 2012, 34, 2274–2282. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Chen, Y.; Zhou, Y.n.; Ge, Y.; An, R.; Chen, Y. Enhancing Land Cover Mapping through Integration of Pixel-Based and Object-Based Classifications from Remotely Sensed Imagery. Remote Sens. 2018, 10, 77. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Prabhu, R.; Alagu Raja, R.A. Urban Slum Detection Approaches from High-Resolution Satellite Data Using Statistical and Spectral Based Approaches. J. Indian Soc. Remote Sens. 2018, 46, 2033–2044. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wurm, M.; Taubenböck, H.; Weigand, M.; Schmitt, A. Slum mapping in polarimetric SAR data using spatial features. Remote Sens. Environ. 2017, 194, 190–204. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zurqani, H.A.; Post, C.J.; Mikhailova, E.A.; Allen, J.S. Mapping Urbanization Trends in a Forested Landscape Using Google Earth Engine. Remote Sens. Earth Syst. Sci. 2019, 2, 173–182. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Malambo, L.; Heatwole, C.D. Automated training sample definition for seasonal burned area mapping. ISPRS J. Photogramm. Remote Sens. 2020, 160, 107–123. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, Y.; Zhu, W.; Wei, P.; Fang, P.; Zhang, X.; Yan, N.; Liu, W.; Zhao, H.; Wu, Q. Classification of Zambian grasslands using random forest feature importance selection during the optimal phenological period. Ecol. Indic. 2022, 135, 108529. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kpienbaareh, D.; Sun, X.; Wang, J.; Luginaah, I.; Bezner Kerr, R.; Lupafya, E.; Dakishoni, L. Crop Type and Land Cover Mapping in Northern Malawi Using the Integration of Sentinel-1, Sentinel-2, and PlanetScope Satellite Data. Remote Sens. 2021, 13, 700. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hamud, A.M.; Shafri, H.Z.M.; Shaharun, N.S.N. Monitoring Urban Expansion and Land Use/ Land cover Changes in Banadir, Somalia, using Google Earth Engine (GEE). IOP Conf. Ser. Earth Environ. Sci. 2021, 767, 012041. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Duque, J.C.; Patino, J.E.; Ruiz, L.A.; Pardo-Pascual, J.E. Measuring intra-urban poverty using land cover and texture metrics derived from remote sensing data. Landsc. Urban Plan. 2015, 135, 11–21. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lai, F.; Yang, X. Integrating spectral and non-spectral data to improve urban settlement mapping in a large Latin-American city. GISci. Remote Sens. 2020, 57, 830–844. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shekhar, S. Detecting slums from Quick Bird data in Pune using an object oriented approach. Int. Arch. Photogramm. Remote Sens. Spat. Inf. Sci. 2012, 39, 519–524. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Gevaert, C.M.; Persello, C.; Sliuzas, R.; Vosselman, G. Classification of Informal Settlements through the Integration of 2d and 3d Features Extracted from Uav Data. ISPRS Ann. Photogramm. Remote Sens. Spat. Inf. Sci. 2016, III-3, 317–324. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Myint, S.W.; Gober, P.; Brazel, A.; Grossman-Clarke, S.; Weng, Q. Per-pixel vs. object-based classification of urban land cover extraction using high spatial resolution imagery. Remote Sens. Environ. 2011, 115, 1145–1161. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hay Chung, L.C.; Xie, J.; Ren, C. Improved machine-learning mapping of local climate zones in metropolitan areas using composite Earth observation data in Google Earth Engine. Build. Environ. 2021, 199, 107879. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]


| Code | Texture Features | Textural Index Description |
|---|---|---|
| T1 | Angular second moment | Describes how uniform the distribution of grey levels is in the image |
| T2 | Contrast | Measures variations in intensity of neighbouring pixel pairs |
| T3 | Mean | Measures the mean of the grey level sum distribution of the image |
| T4 | Entropy | Quantifies the randomness of the grey-level intensity distribution |
| T5 | Variance | Measures how spread out the distribution of grey levels is in the image |
| T6 | Homogeneity | Measures the homogeneity of the image |
| Satellite | Band Types | Features |
|---|---|---|
| PL | Main channels | B (blue), G (green), R (red), NIR |
| Spectral indices | NDVI = , NDWI = | |
| Textural features | Angular second moment, contrast, variance, homogeneity, mean, entropy | |
| S2 | Main channels | B8, B11, B12 |
| Spectral index | BSI = | |
| S1 | Main channels | VV, VH |
| Ratio features | VH-VV |
| Class | Description |
|---|---|
| Informal settlement | Densely built housing units that are contiguous |
| Bare land | Exposed soil with neither grass, trees, nor built-up structures |
| Water | Water bodies like dams, rivers, ponds, and swamps |
| Other Urban | Housing units with regular layout pattern, residential, commercial, industrial, freeways, highways, tertiary or local roads |
| Vegetation | Area covered by grasslands, forests, croplands, small shrubs, sparse and dense trees |
| Informal Settlements | Bare Land | Water | Other Urban | Vegetation | PA | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Informal settlement | 44 | 0 | 0 | 10 | 0 | 81% |
| Bare land | 1 | 39 | 0 | 1 | 1 | 93% |
| Water | 0 | 0 | 26 | 0 | 0 | 100% |
| Other urban | 0 | 0 | 0 | 115 | 0 | 100% |
| Vegetation | 2 | 1 | 0 | 3 | 282 | 98% |
| UA | 94% | 98% | 100% | 89% | 100% | 96% |
| F-score | 87% | 95% | 100% | 94% | 99% |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Matarira, D.; Mutanga, O.; Naidu, M.; Vizzari, M. Object-Based Informal Settlement Mapping in Google Earth Engine Using the Integration of Sentinel-1, Sentinel-2, and PlanetScope Satellite Data. Land 2023, 12, 99. https://doi.org/10.3390/land12010099
Matarira D, Mutanga O, Naidu M, Vizzari M. Object-Based Informal Settlement Mapping in Google Earth Engine Using the Integration of Sentinel-1, Sentinel-2, and PlanetScope Satellite Data. Land. 2023; 12(1):99. https://doi.org/10.3390/land12010099
Chicago/Turabian StyleMatarira, Dadirai, Onisimo Mutanga, Maheshvari Naidu, and Marco Vizzari. 2023. "Object-Based Informal Settlement Mapping in Google Earth Engine Using the Integration of Sentinel-1, Sentinel-2, and PlanetScope Satellite Data" Land 12, no. 1: 99. https://doi.org/10.3390/land12010099
APA StyleMatarira, D., Mutanga, O., Naidu, M., & Vizzari, M. (2023). Object-Based Informal Settlement Mapping in Google Earth Engine Using the Integration of Sentinel-1, Sentinel-2, and PlanetScope Satellite Data. Land, 12(1), 99. https://doi.org/10.3390/land12010099









