Active and Passive Carbon Fractions in Contrasting Cropping Systems, Tillage Practices, and Soil Types
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Site Description
2.2. Treatment and Sampling Details
2.3. Crop Management
2.4. Soil Analysis
2.4.1. Soil Properties
2.4.2. TOC and its Fractions
2.5. Computation of Stratification Ratio (SR)
2.6. Computation of TOC/TN Stock
2.7. Data Analysis
3. Results
3.1. Total Organic Carbon and Total Nitrogen
3.2. Active Carbon and Passive Carbon
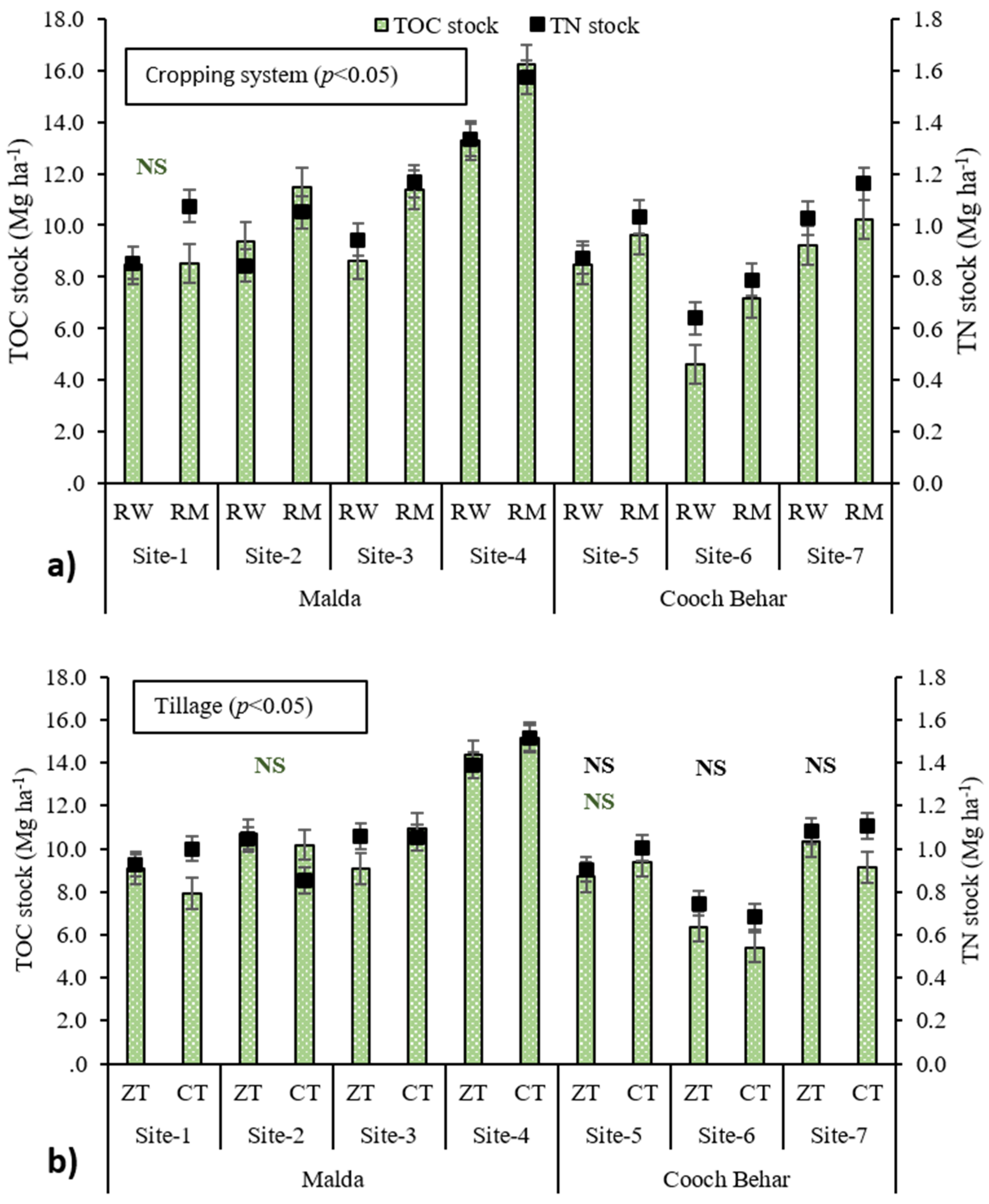
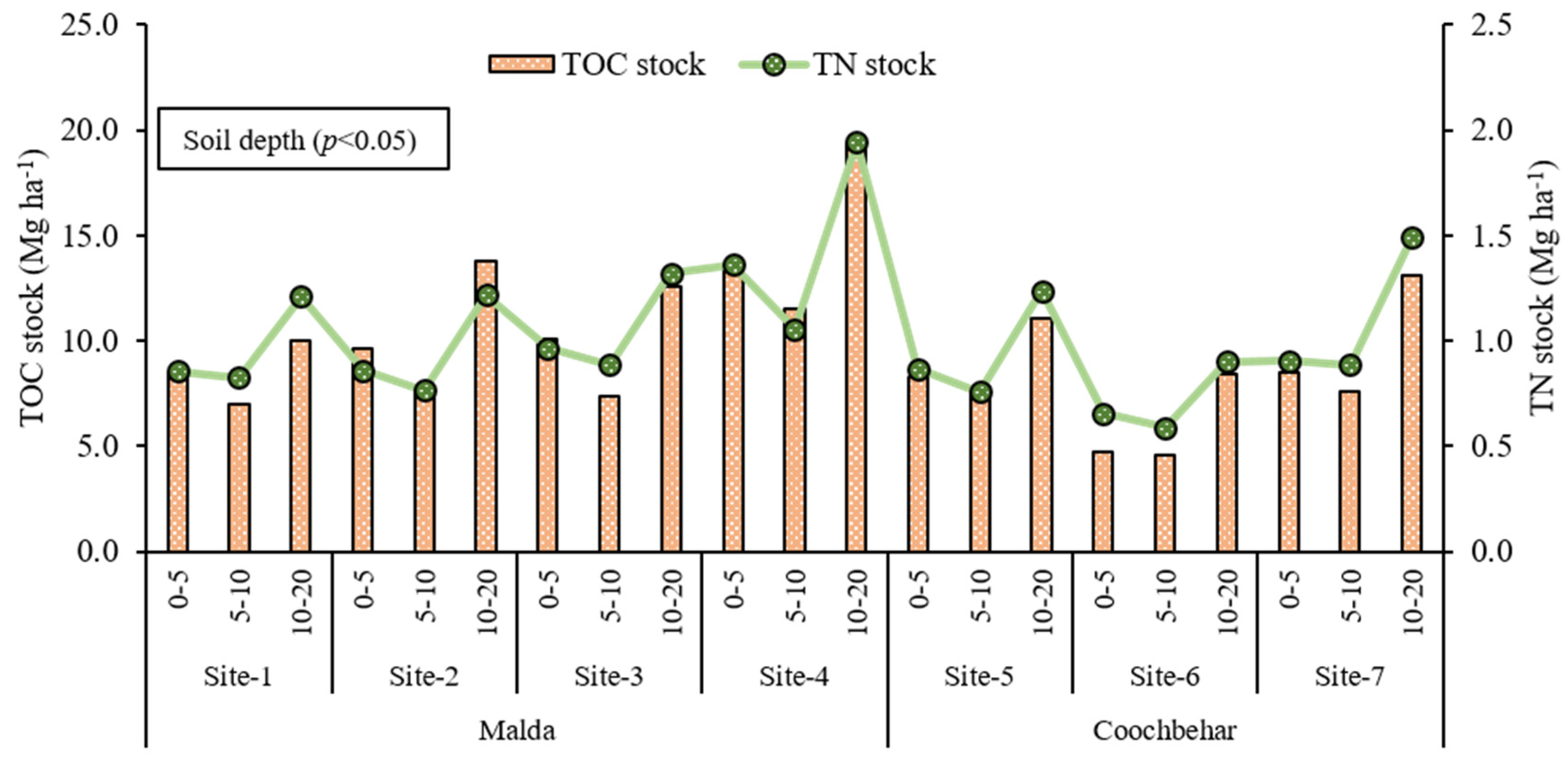
3.3. Bulk Density, TOC Stock, and TN Stock
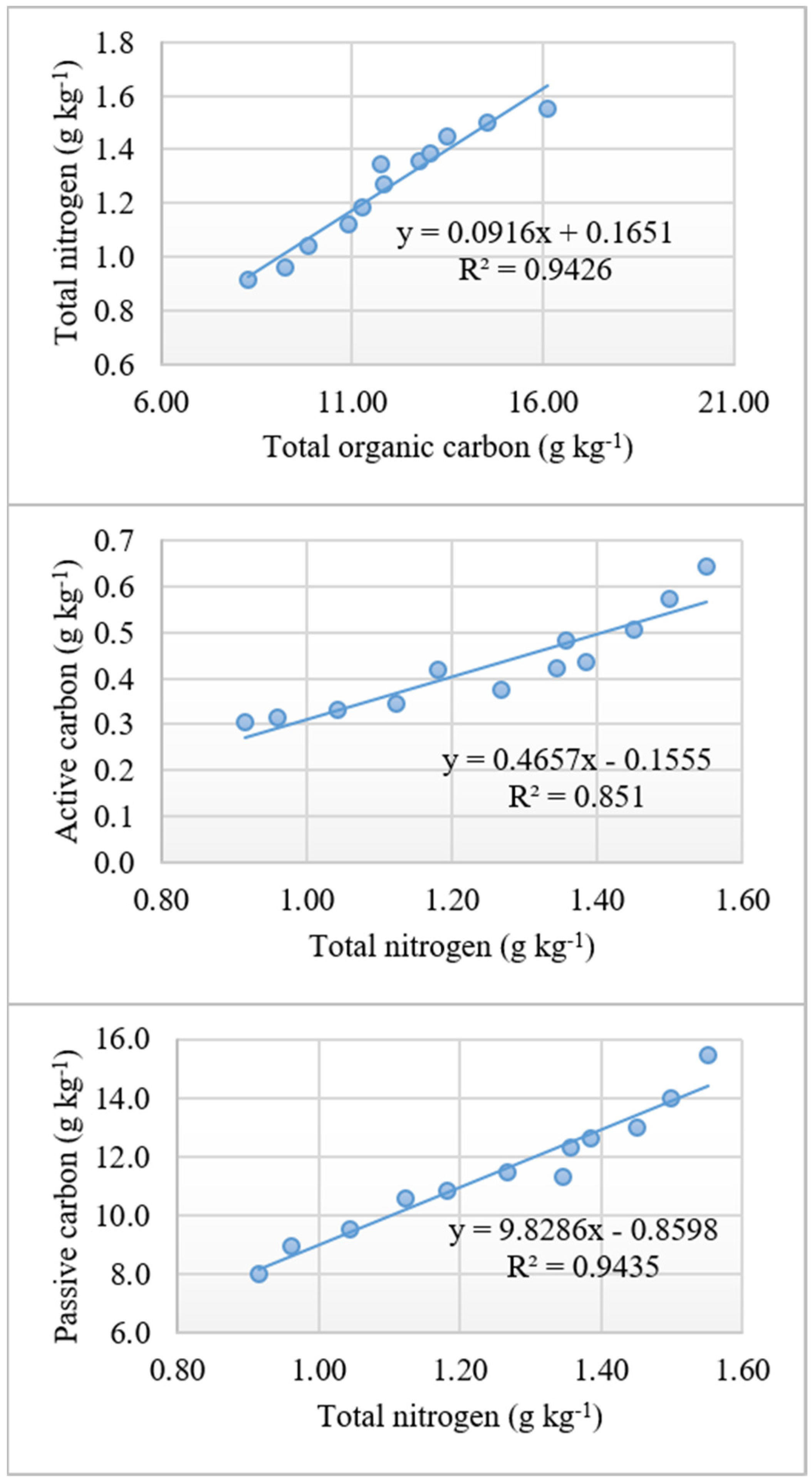
3.4. Relationship of TOC, AC, and PC with TN
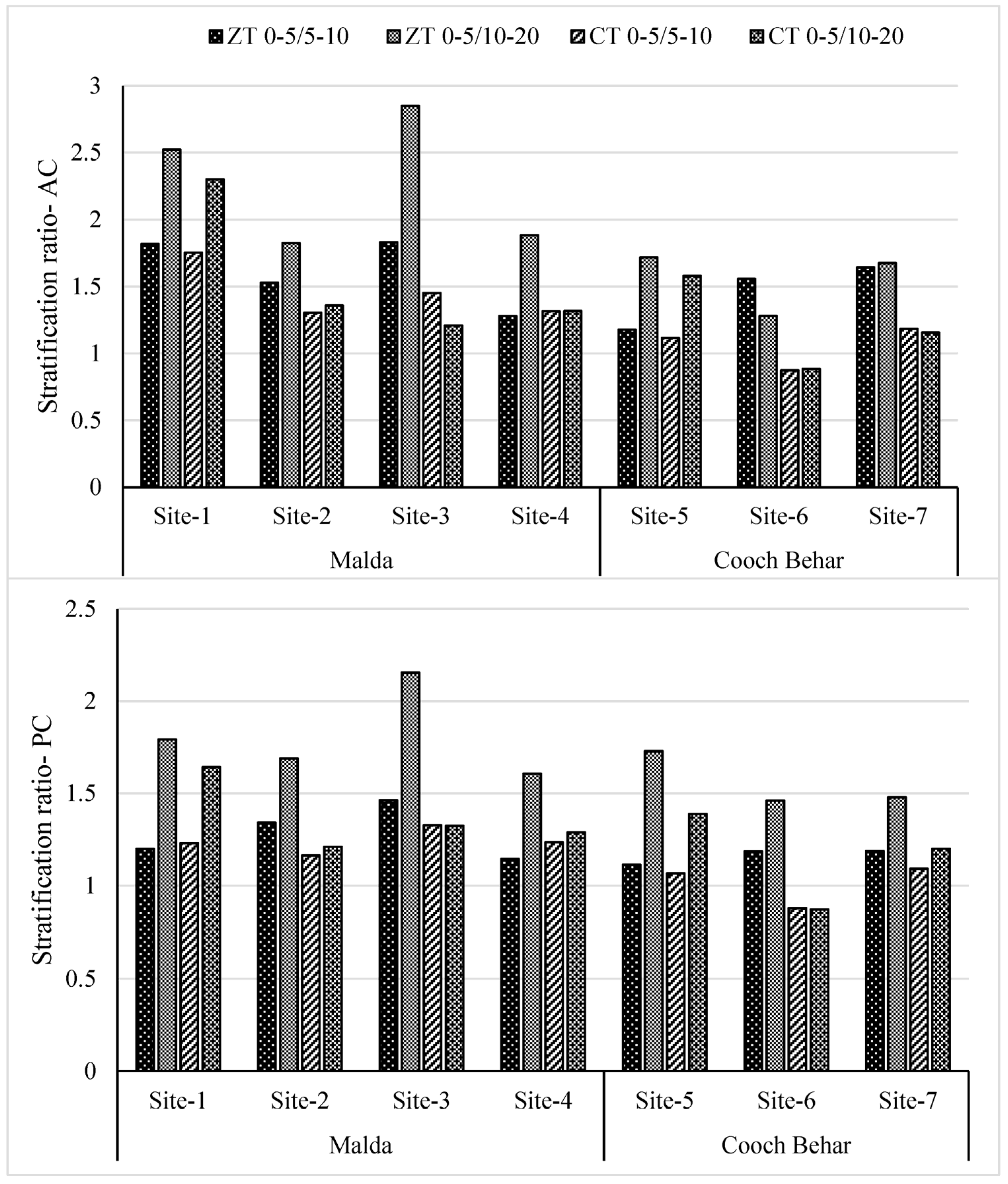
3.5. Stratification of AC and PC
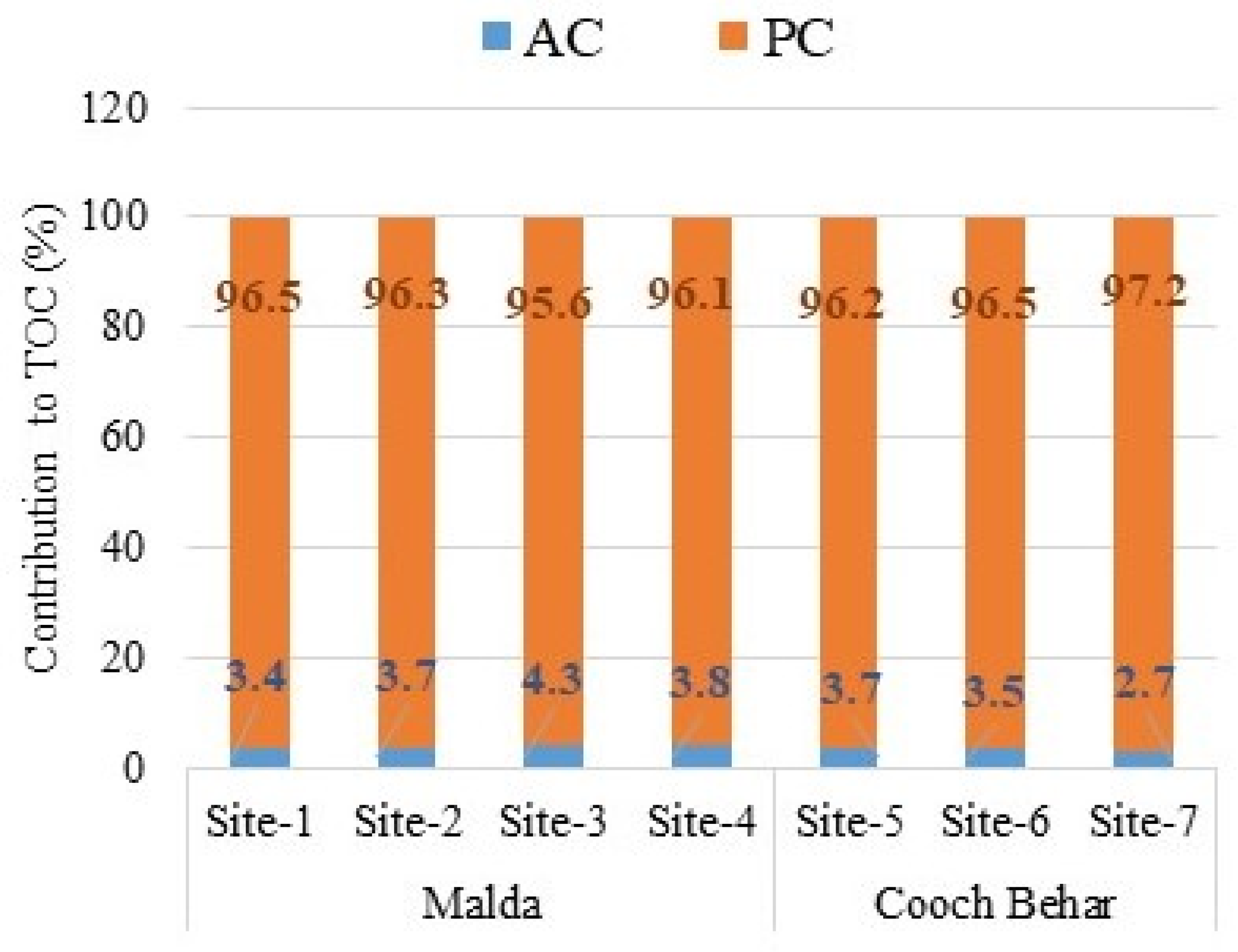
3.6. Contribution of AC and PC to TOC and the Ratio of AC/PC
4. Discussion
4.1. Effect of Cropping System on C Fractions
4.2. Effect of Tillage on C Fractions
4.3. Interaction Effect of Tillage and Cropping System on C Fractions
4.4. Effect of Tillage and Cropping System on TOC and TN Stock
4.5. Relationship of AC, PC, TOC, and TN
4.6. Effect of Tillage on Stratification of AC and PC
4.7. Overall Effect of Conservation Agriculture among the Sites
4.8. Contribution of AC and PC to TOC and Their Ratio in Soil
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Islam, S.; Gathala, M.K.; Tiwari, T.P.; Timsina, J.; Laing, A.M.; Maharjan, S.; Chowdhury, A.K.; Bhattacharya, P.M.; Dhar, T.; Mitra, B.; et al. Conservation agriculture based sustainable intensification: Increasing yields and water productivity for smallholders of the Eastern Gangetic Plains. Field Crops Res. 2019, 238, 1–17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sinha, A.K.; Ghosh, A.; Dhar, T.; Bhattacharya, P.M.; Mitra, B.; Rakesh, S.; Paneru, P.; Srestha, S.R.; Manandhar, S.; Beura, K.; et al. Trends in key soil parameters under conservation agriculture-based sustainable intensification farming practices in the Eastern Ganga Alluvial Plains. Soil Res. 2019, 57, 883–893. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- FAO. Climate-Smart Agriculture Sourcebook; Food and Agriculture Organization of the United Nations: Rome, Italy, 2017; Available online: https://www.fao.org/climate-smart-agriculture-sourcebook/en/ (accessed on 5 March 2018).
- Dinesha, S.; Panda, M.R.; Pradhan, D.; Rakesh, S.; Dey, A.N.; Bhat, J.A.; Pandey, R. Ecosystem carbon budgeting under Swietenia macrophylla King plantation in sub humid foothills of Eastern Himalayans of India. Environ. Dev. Sustain. 2023. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lal, R. Soil carbon sequestration in agroecosystems of India. J. Indian Soc. Soil Sci. 2015, 63, 125–143. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sarkar, D.; Kar, S.K.; Chattopadhyay, A.; Shikha; Rakshit, A.; Tripathi, V.K.; Dubey, P.K.; Abhilash, P.C. Low input sustainable agriculture: A viable climate-smart option for boosting food production in a warming world. Ecol. Indic. 2020, 115, 106412. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- IPCC. Land-climate interactions. In Climate Change and Land: An IPCC Specials Report on Climate Change, Desertification, Land Degradation, Sustainable Land Management, Food Security, and Greenhouse Gas Fluxes in Terrestrial Ecosystems; Summary for Policymakers; Cambridge University Press: Cambridge, UK, 2019; Available online: https://www.ipcc.ch/site/assets/uploads/2019/08/2c.-Chapter-2_FINAL.pdf (accessed on 1 February 2020).
- Sarkar, D.; Dubey, P.K.; Chaurasiya, R.; Sankar, A.; Shikha; Chatterjee, N.; Ganguly, S.; Meena, V.S.; Meena, S.K.; Parewa, H.P.; et al. Organic interventions conferring stress tolerance and crop quality in agroecosystems during the UN Decade on Ecosystem Restoration. Land Degrad. Dev. 2021, 32, 4797–4816. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sarkar, D.; Rakshit, A. Amalgamation of farmers’ bio-priming knowledge in integrated nutrient management for sustainable management of red cabbage soil under Middle Gangetic Plains, India. Environ. Manag. 2022. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sahoo, U.K.; Singh, S.L.; Gogoi, A.; Kenye, A.; Sahoo, S.S. Active and passive soil organic carbon pools as affected by different land use types in Mizoram, Northeast India. PLoS ONE 2019, 14, e0219969. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Belay-Tedla, A.; Zhou, X.; Su, B.; Wan, S.; Luo, Y. Labile, recalcitrant, and microbial carbon and nitrogen pools of a tallgrass prairie soil in the US Great Plains subjected to experimental warming and clipping. Soil Biol. Biochem. 2009, 41, 110–116. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- de Moraes Sá, J.C.; Séguy, L.; Tivet, F.; Lal, R.; Bouzinac, S.; Borszowskei, P.R.; Briedis, C.; dos Santos, J.B.; da Cruz Hartman, D.; Bertoloni, C.G.; et al. Carbon depletion by plowing and its restoration by no-till cropping systems in oxisols of subtropical and tropical agro-ecoregions in Brazil. Land Degrad. Dev. 2015, 26, 531–543. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sahoo, S.; Mukhopadhyay, P.; Mowrer, J.; Maity, P.P.; Maity, A.; Sinha, A.K.; Sow, P.; Rakesh, S. Tillage and N-source affect soil fertility, enzymatic activity, and crop yield in a maize–rice rotation system in the Indian Terai zone. Front. Environ. Sci. 2022. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- de Moraes Sá, J.C.; Lal, R. Stratification ratio of soil organic matter pools as an indicator of carbon sequestration in a tillage chronosequence on a Brazilian Oxisol. Soil Tillage Res. 2009, 103, 46–56. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sahoo, S.; Mukhopadhyay, P.; Sinha, A.K.; Bhattacharya, P.M.; Rakesh, S.; Kumar, R.; Padbhushan, R.; Bijay-Singh Parmar, B.; Vishwakarma, A.; Kumar, A.; et al. Yield, nitrogen-use efficiency, and distribution of nitratenitrogen in the soil profile as influenced by irrigation and fertilizer nitrogen levels under zero-till wheat in the eastern Indo-Gangetic plains of India. Front. Environ. Sci. 2022, 10, 970017. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zotarelli, L.; Zatorre, N.P.; Boddey, R.M.; Urquiaga, S.; Jantalia, C.P.; Franchini, J.C.; Alves, B.J.R. Influence of no-tillage and frequency of a green manure legume in crop rotations for balancing N outputs and preserving soil organic C stocks. Field Crops Res. 2012, 132, 185–195. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Babujia, L.C.; Hungria, M.; Franchini, J.C.; Brookes, P.C. Microbial biomass and activity at various soil depths in a Brazilian oxisol after two decades of no-tillage and conventional tillage. Soil Biol. Biochem. 2010, 42, 2174–2181. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alvarez, R.; Steinbach, H.S. A review of the effects of tillage systems on some soil physical properties, water content, nitrate availability and crops yield in the Argentine Pampas. Soil Tillage Res. 2009, 104, 1–15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ansari, M.A.; Choudhury, B.U.; Layek, J.; Das, A.; Lal, R.; Mishra, V.K. Green manuring and crop residue management: Effect on soil organic carbon stock, aggregation, and system productivity in the foothills of Eastern Himalaya (India). Soil Tillage Res. 2022, 218, 105318. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, X.; Xue, J.F.; Zhang, X.Q.; Kong, F.L.; Chen, F.; Lal, R.; Zhang, H.L. Stratification and storage of soil organic carbon and nitrogen as affected by tillage practices in the North China Plain. PLoS ONE 2015, 10, e0128873. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rakesh, S.; Sarkar, D.; Sinha, A.K.; Shikha; Mukhopadhyay, P.; Danish, S.; Fahad, S.; Datta, R. Carbon mineralization rates and kinetics of surface-applied and incorporated rice and maize residues in Entisol and Inceptisol soil types. Sustainability 2021, 13, 7212. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rakesh, S.; Sarkar, D.; Shikha; Sankar, A.; Sinha, A.K.; Mukhopadhyay, P.; Rakshit, A. Protocols for determination and evaluation of organic carbon pools in soils developed under contrasting pedogenic processes and subjected to varying management situations. In Soil Analysis: Recent Trends and Applications; Rakshit, A., Ghosh, S., Chakraborty, S., Philip, V., Datta, A., Eds.; Springer: Singapore, 2020; pp. 87–105. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, L.; Hu, N.; Zhang, Z.; Xu, J.; Tao, B.; Meng, Y. Short-term responses of soil organic carbon and carbon pool management index to different annual straw return rates in a rice–wheat cropping system. Catena 2015, 135, 283–289. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Haynes, R.J. Labile organic matter fractions as central components of the quality of agricultural soils: An overview. Adv. Agron. 2005, 5, 221–268. [Google Scholar]
- Wiesenberg, G.L.B.; Dorodnikov, M.; Kuzyakov, Y. Source determination of lipids in bulk soil and soil density fractions after four years of wheat cropping. Geoderma 2010, 156, 267–277. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Duval, M.E.; Galantini, J.A.; Martínez, J.M.; Limbozzi, F. Labile soil organic carbon for assessing soil quality: Influence of management practices and edaphic conditions. Catena 2018, 171, 316–326. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ren, C.; Zhao, F.; Shi, Z.; Chen, J.; Han, X.; Yang, G.; Feng, Y.; Ren, G. Differential responses of soil microbial biomass and carbon-degrading enzyme activities to altered precipitation. Soil Biol. Biochem. 2017, 115, 1–10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, W.; Wen, S.; Zhang, Y.; Gregory, A.S.; Xu, M.; Shah SA, A.; Hartley, I.P. Long-term fertilization enhances soil carbon stability by increasing the ratio of passive carbon: Evidence from four typical croplands. Plant Soil 2022, 478, 579–595. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Geraei, D.S.; Hojati, S.; Landi, A.; Cano, A.F. Total and labile forms of soil organic carbon as affected by land use change in southwestern Iran. Geoderma Reg. 2016, 7, 29–37. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Awale, R.; Emeson, M.A.; Machado, S. Soil organic carbon pools as early indicators for soil organic matter stock changes under different tillage practices in Inland Pacific Northwest. Front. Ecol. Evol. 2017, 5, 96. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Wani, S.A. Assessment of changes in soil organic carbon fractions and enzyme activities under apple growing ecosystems in temperate North-Western Himalayas. Resour. Environ. Sustain. 2021, 6, 100036. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Somasundaram, J.; Reeves, S.; Wang, W.; Heenan, M.; Dalal, R. Impact of 47 years of no tillage and stubble retention on soil aggregation and carbon distribution in a vertisol. Land Degrad. Dev. 2017, 28, 1589–1602. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qiu, L.; Hao, M.; Wu, Y. Potential impacts of climate change on carbon dynamics in a rain-fed agro-ecosystem on the Loess Plateau of China. Sci. Total Environ. 2017, 577, 267–278. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mi, W.; Sun, Y.; Zhao, C.; Wu, L. Soil organic carbon and its labile fractions in paddy soil as influenced by water regimes and straw management. Agric. Water Manag. 2019, 224, 105752. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Choudhary, M.; Datta, A.; Jat, H.S.; Yadav, A.K.; Gathala, M.K.; Sapkota, T.B.; Das, A.K.; Sharma, P.C.; Jat, M.L.; Singh, R.; et al. Changes in soil biology under conservation agriculture based sustainable intensification of cereal systems in Indo-Gangetic Plains. Geoderma 2018, 313, 193–204. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kumar, A.; Rana, K.S.; Choudhary, A.K.; Bana, R.S.; Sharma, V.K.; Prasad, S.; Tyagi, V. Energy budgeting and carbon footprints of zero-tilled pigeonpea–wheat cropping system under sole or dual crop basis residue mulching and Zn-fertilization in a semi-arid agro-ecology. Energy 2021, 231, 120862. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Harish, M.N.; Choudhary, A.K.; Dass, A.; Singh, V.K.; Pooniya, V.; Varatharajan, T. Tillage and phosphorus management in maize (Zea mays) in maize-wheat cropping system. Indian J. Agric. Sci. 2021, 91, 117–122. [Google Scholar]
- Bana, R.S.; Singh, D.; Nain, M.S.; Kumar, H.; Kumar, V.; Sepat, S. Weed control and rice yield stability studies across diverse tillage and crop establishment systems under on-farm environments. Soil Res. 2020, 204, 104729. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Singh, U.; Choudhary, A.K.; Sharma, S. Agricultural practices modulate the bacterial communities, and nitrogen cycling bacterial guild in rhizosphere: Field experiment with soybean. J. Sci. Food Agric. 2021, 101, 2687–2695. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Srinivasarao, C.; Kundu, S.; Yashavanth, B.S.; Rakesh, S.; Akbari, K.N.; Sutaria, G.S.; Vora, V.D.; Hirpara, D.S.; Gopinath, K.A.; Chary, G.R.; et al. Influence of 16 years of fertilization and manuring on carbon sequestration and agronomic productivity of groundnut in vertisol of semi-arid tropics of Western India. Carbon Manag. 2020, 12, 13–24. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rakesh, S.; Sinha, A.K.; Juttu, R.; Sarkar, D.; Jogula, K.; Reddy, S.B.; Raju, B.; Danish, S.; Datta, R. Does the accretion of carbon fractions and their stratification vary widely with soil orders? A case-study of an Alfisol and an Entisol of sub-tropical eastern India. Land Degrad. Dev. 2022, 33, 2039–2049. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Reddy, S.B.; Srinivasarao, C.; Rao, P.C.; Lal, R.; Rakesh, S.; Kundu, S.; Singh, R.N.; Dubey, P.K.; Abhilash, P.C.; Venkateswara Rao, K.; et al. Greenhouse gases emissions and agronomic productivity as influenced by varying levels of N fertilizer and tank silt in degraded semiarid Alfisol of Southern India. Land Degrad. Dev. 2022. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bhattacharyya, R.; Das, T.K.; Sudhishri, S.; Dudwal, B.; Sharma, A.R.; Bhatia, A.; Singh, G. Conservation agriculture effects on soil organic carbon accumulation and crop productivity under a rice-wheat cropping system in the western Indo-Gangetic Plains. Eur. J. Agron. 2015, 70, 11–21. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kolapo, A.; Didunyemi, A.J.; Aniyi, O.J.; Obembe, O.E. Adoption of multiple sustainable land management practices and its effects on productivity of smallholder maize farmers in Nigeria. Resour. Environ. Sustain. 2022, 10, 100084. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shekhawat, K.; Rathore, S.S.; Kandpal, B.K.; Premi, O.P.; Singh, D.; Chauhan, B.S. Crop establishment techniques affect productivity, sustainability, and soil health under mustard-based cropping systems of Indian semi-arid regions. Soil Tillage Res. 2016, 158, 137–146. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nandan, R.; Singh, S.S.; Kumar, V.; Singh, V.; Hazra, K.K.; Nath, C.P.; Malik, R.K.; Poonia, S.P.; Solanki, C.H. Crop establishment with conservation tillage and crop residue retention in rice-based cropping systems of Eastern India: Yield advantage and economic benefit. Paddy Water Environ. 2018, 16, 477–492. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Singh, V.K.; Dwivedi, B.S.; Singh, S.K.; Mishra, R.P.; Shukla, A.K.; Rathore, S.S.; Shekhawat, K.; Majumdar, K.; Jat, M.L. Effect of tillage and crop establishment, residue management and K fertilization on yield, K use efficiency and apparent K balance under rice-maize system in north-western India. Field Crops Res. 2018, 224, 1–12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sarkar, D.; Rakesh, S.; Sinha, A.K.; Mukhopadhyay, P. Forms of phosphorus in some acidic Entisols of subtropical Eastern India. Int. J. Plant Soil Sci. 2017, 19, 1–9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jackson, M.L. Soil Chemical Analysis; Prentice-Hall of India Pvt. Ltd.: New Delhi, India, 1973. [Google Scholar]
- Cresswell, H.; Hamilton, G.J. Bulk density and pore space relations. In Soil Physical Measurement and Interpretation for Land Evaluation; McKenzie, N., Coughlan, K., Cresswell, H., Eds.; CSIRO Publishing: Clayton, Australia, 2002; Volume 5, pp. 35–58. [Google Scholar]
- Bouyoucos, G.J. Hydrometer methods improves for making particle size analysis of soils. Agron. J. 1962, 54, 464–465. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Anonyms. Official Methods of the Association of Official Analytical Chemists, 12th ed.; Horwitz, W., Ed.; Benjamin Franklin Station: Washington, DC, USA, 1975; pp. 15–18. [Google Scholar]
- Baker, K.F. The determination of organic carbon in soil using a probe-colorimeter. Lab. Pract. 1976, 25, 82–83. [Google Scholar]
- Weil, R.R.; Islam, K.R.; Stine, M.A.; Gruver, J.B.; Samson-Liebig, S.E. Estimating active carbon for soil quality assessment: A simplified method for laboratory and field use. Am. J. Altern. Agric. 2003, 18, 3–17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aziz, I.; Bangash, N.; Mahmood, T.; Islam, K.R. Impact of no-till and conventional tillage practices on soil chemical properties. Pak. J. Bot. 2015, 47, 297–303. [Google Scholar]
- Franzluebbers, A.J. Soil organic matter stratification ratio as an indicator of soil quality. Soil Tillage Res. 2002, 66, 95–106. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pluske, W.; Murphy, D.; Sheppard, J. Fact Sheets Total Organic Carbon—NSW. 2015. Available online: http://www.soilquality.org.au/factsheets/total-organic-carbon-nsw (accessed on 1 March 2018).
- Benbi, D.K.; Brar, K.; Toor, A.S.; Sharma, S. Sensitivity of labile soil organic carbon pools to long-term fertilizer, straw and manure management in rice-wheat system. Pedosphere 2015, 25, 534–545. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pezzolla, D.; Marconi, G.; Turchetti, B.; Zadra, C.; Agnelli, A.; Veronesi, F.; Onofri, A.; Benucci, G.M.N.; Buzzini, P.; Albertini, E.; et al. Influence of exogenous organic matter on prokaryotic and eukaryotic microbiota in an agricultural soil. A multidisciplinary approach. Soil Biol. Biochem. 2015, 82, 9–20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tatzber, M.; Klepsch, S.; Soja, G.; Reichenauer, T.; Spiegel, H.; Gerzabek, M.H. Determination of soil organic matter features of extractable fractions using capillary electrophoresis: An organic matter stabilization study in a carbon-14-labeled long-term field experiment. In Labile Organic Matter—Chemical Compositions, Function, and Significance in Soil and the Environment; He, Z., Wu, F., Eds.; SSSA Special Publication: Madison, WI, USA, 2015; Volume 62, pp. 23–40. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Somasundaram, J.; Chaudhary, R.S.; Awanish Kumar, D.; Biswas, A.K.; Sinha, N.K.; Mohanty, M.; Hati, K.M.; Jha, P.; Sankar, M.; Patra, A.K.; et al. Effect of contrasting tillage and cropping systems on soil aggregation, carbon pools and aggregate-associated carbon in rainfed Vertisols. Eur. J. Soil Sci. 2018, 69, 879–891. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jat, H.S.; Datta, A.; Choudhary, M.; Yadav, A.K.; Choudhary, V.; Sharma, P.C.; Gathala, M.K.; Jat, M.L.; McDonald, A. Effects of tillage, crop establishment and diversification on soil organic carbon, aggregation, aggregate associated carbon and productivity in cereal systems of semi-arid Northwest India. Soil Tillage Res. 2019, 190, 128–138. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bongiorno, G.; Bünemann, E.K.; Oguejiofor, C.U.; Meier, J.; Gort, G.; Comans, R.; Mäder, P.; Brussaard, L.; de Goede, R. Sensitivity of labile carbon fractions to tillage and organic matter management and their potential as comprehensive soil quality indicators across pedoclimatic conditions in Europe. Ecol. Indic. 2019, 99, 38–50. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bastida, F.; Torres, I.F.; Hernández, T.; Bombach, P.; Richnow, H.H.; García, C. Can the labile carbon contribute to carbon immobilization in semiarid soils? Priming effects and microbial community dynamics. Soil Biol. Biochem. 2013, 57, 892–902. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hurisso, T.T.; Culman, S.W.; Horwath, W.R.; Wade, J.; Cass, D.; Beniston, J.W.; Bowles, T.M.; Grandy, A.S.; Franzluebbers, A.J.; Schipanski, M.E.; et al. Comparison of permanganate-oxidizable carbon and mineralizable carbon for assessment of organic matter stabilization and mineralization. Soil Sci. Soc. Am. J. 2016, 80, 1352–1364. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Calderón, F.J.; Culman, S.; Six, J.; Franzluebbers, A.J.; Schipanski, M.; Beniston, J.; Grandy, S.; Kong AY, Y. Quantification of soil permanganate oxidizable C (POXC) using infrared spectroscopy. Soil Sci. Soc. Am. J. 2017, 81, 277–288. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Singh, S.; Nouri, A.; Singh, S.; Anapalli, S.; Lee, J.; Arelli, P.; Jagadamma, S. Soil organic carbon and aggregation in response to thirty-nine years of tillage management in the southeastern US. Soil Tillage Res. 2020, 197, 104523. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Datta, A.; Choudhary, M.; Sharma, P.C.; Priyanka Jat, H.S.; Jat, M.L.; Kar, S. Stability of humic acid carbon under conservation agriculture practices. Soil Tillage Res. 2022, 216, 105240. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cyle, K.T.; Hill, N.; Young, K.; Jenkins, T.; Hancock, D.; Schroeder, P.A.; Thompson, A. Substrate quality influences organic matter accumulation in the soil silt and clay fraction. Soil Biol. Biochem. 2016, 103, 138–148. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Hadas, A.; Kautsky, L.; Goek, M.; Kara, E.E. Rates of decomposition of plant residues and available nitrogen in soil, related to residue composition through simulation of carbon and nitrogen turnover. Soil Biol. Biochem. 2004, 36, 255–266. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Carbonell-Bojollo, R.; González-Sánchez, E.J.; de Torres MR, R.; Ordóñez-Fernández, R.; Domínguez-Giménez, J.; Basch, G. Soil organic carbon fractions under conventional and no-till management in a long-term study in southern Spain. Soil Res. 2015, 53, 113–124. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yadav, G.S.; Lal, R.; Meena, R.S.; Babu, S.; Das, A.; Bhowmik, S.N.; Datta, M.; Layak, J.; Saha, P. Conservation tillage and nutrient management effects on productivity and soil carbon sequestration under double cropping of rice in north eastern region of India. Ecol. Indic. 2019, 105, 303–315. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alvear, M.; Rosas, A.; Rouanet, J.L.; Borie, F. Effects of three soil tillage systems on some biological activities in an Ultisol from southern Chile. Soil Tillage Res. 2005, 82, 195–202. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fontana, M.; Berner, A.; Mäder, P.; Lamy, F.; Boivin, P. Soil organic carbon and soil bio-physicochemical properties as co-influenced by tillage treatment. Soil Sci. Soc. Am. J. 2015, 79, 1435–1445. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Follett, R.F. Soil management concepts and carbon sequestration in cropland soils. Soil Tillage Res. 2001, 61, 77–92. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rahmati, M.; Eskandari, I.; Kouselou, M.; Feiziasl, V.; Mahdavinia, G.R.; Aliasgharzad, N.; McKenzie, B.M. Changes in soil organic carbon fractions and residence time five years after implementing conventional and conservation tillage practices. Soil Tillage Res. 2020, 200, 104632. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.; Ji, H.; Wang, R.; Guo, S.; Gao, C. Impact of root diversity upon coupling between soil C and N accumulation and bacterial community dynamics and activity: Result of a 30-year rotation experiment. Geoderma 2017, 292, 87–95. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Angers, D.A.; Eriksen-Hamel, N.S. Full-inversion tillage and organic carbon distribution in soil profiles: A meta-analysis. Soil Sci. Soc. Am. J. 2008, 72, 1370–1374. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, L.; Hu, N.; Yang, M.; Zhan, X.; Zhang, Z. Effects of different tillage and straw return on soil organic carbon in a rice-wheat rotation system. PLoS ONE 2014, 9, e88900. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Six, J.; Bossuyt, H.; Degryze, S.; Denef, K. A history of research on the link between (micro) aggregates, soil biota, and soil organic matter dynamics. Soil Tillage Res. 2004, 79, 7–31. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Devine, S.; Markewitz, D.; Hendrix, P.; Coleman, D. Soil aggregates and associated organic matter under conventional tillage, no-tillage, and forest succession after three decades. PLoS ONE 2014, 9, e84988. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Kibet, L.C.; Blanco-Canqui, H.; Jasa, P. Long-term tillage impacts on soil organic matter components and related properties on a Typic Argiudoll. Soil Tillage Res. 2016, 155, 78–84. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chalise, K.S.; Singh, S.; Wegner, B.R.; Kumar, S.; Pérez-Gutiérrez, J.D.; Osborne, S.L.; Nleya, T.; Guzman, J.; Rohila, J.S. Cover crops and returning residue impact on soil organic carbon, bulk density, penetration resistance, water retention, infiltration, and soybean yield. Agron. J. 2018, 110, 99–108. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Maiga, A.; Alhameid, A.; Singh, S.; Polat, A.; Singh, J.; Kumar, S.; Osborne, S. Responses of soil organic carbon, aggregate stability, carbon and nitrogen fractions to 15 and 24 years of no-till diversified crop rotations. Soil Res. 2019, 57, 149–157. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Duan, B.; Man, X.; Cai, T.; Xiao, R.; Ge, Z. Increasing soil organic carbon and nitrogen stocks along with secondary forest succession in permafrost region of the Daxing’an mountains, northeast China. Glob. Ecol. Conserv. 2020, 24, e01258. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alvarez, R. A review of nitrogen fertilizer and conservation tillage effects on soil organic carbon storage. Soil Use Manag. 2005, 21, 38–52. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Metay, A.; Jose, A.A.M.; Martial, B.; Thomas, B.; Jean, M.D.; Brigitte, F.; Christian, F.; Florent, M.; Robert, O.; Eric, S. Storage and forms of organic carbon in a no-tillage under cover crops system on clayey Oxisol in dryland rice production (Cerrados, Brazil). Soil Tillage Res. 2007, 94, 122–132. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liang, B.C.; VandenBygaart, A.J.; MacDonald, J.D.; Cerkowniak, D.; McConkey, B.G.; Desjardins, R.L.; Angers, D.A. Revisiting no-till’s impact on soil organic carbon storage in Canada. Soil Tillage Res. 2020, 198, 104529. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Roy, D.; Datta, A.; Jat, H.S.; Choudhary, M.; Sharma, P.C.; Singh, P.K.; Jat, M.L. Impact of long-term conservation agriculture on soil quality under cereal based systems of North West India. Geoderma 2022, 405, 115391. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Holden, S.R.; Treseder, K.K. A meta-analysis of soil microbial biomass responses to forest disturbances. Front. Microbiol. 2013, 4, 163. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Eze, S.; Palmer, S.M.; Chapman, P.J. Soil organic carbon stock and fractional distribution in upland grasslands. Geoderma 2018, 314, 175–183. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, D.; Huang, Y.; Sun, H.; An, S. The restoration age of Robinia pseudoacacia plantation impacts soil microbial biomass and microbial community structure in the Loess Plateau. Catena 2018, 165, 192–200. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lewis, D.B.; Castellano, M.J.; Kaye, J.P. Forest succession, soil carbon accumulation, and rapid nitrogen storage in poorly remineralized soil organic matter. Ecology 2014, 95, 2687–2693. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wuest, S.B.; Williams, J.D.; Gollany, H.T. Tillage and perennial grass effects on ponded infiltration for seven semi-arid loess soils. J. Soil Water Conserv. 2006, 61, 218–223. [Google Scholar]
- Jokela, W.E.; Grabber, J.H.; Karlen, D.L.; Balser, T.C.; Palmquist, D.E. Cover crop and liquid manure effects on soil quality indicators in a corn silage system. Agron. J. 2009, 101, 727–737. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Culman, S.W.; Snapp, S.S.; Freeman, M.A.; Schipanski, M.E.; Beniston, J.; Lal, R.; Drinkwater, L.E.; Franzluebbers, A.J.; Glover, J.D.; Grandy, A.S.; et al. Permanganate oxidizable carbon reflects a processed soil fraction that is sensitive to management. Soil Sci. Soc. Am. J. 2012, 76, 494–504. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Melero, S.; López-Garrido, R.; Murillo, J.M.; Moreno, F. Conservation tillage: Short-and long-term effects on soil carbon fractions and enzymatic activities under Mediterranean conditions. Soil Tillage Res. 2009, 104, 292–298. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Balogh, J.; Pintér, K.; Fóti, S.; Cserhalmi, D.; Papp, M.; Nagy, Z. Dependence of soil respiration on soil moisture, clay content, soil organic matter, and CO2 uptake in dry grasslands. Soil Biol. Biochem. 2011, 43, 1006–1013. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Y.; Gao, Y.; Zhang, Y.; Huang, D.; Li, X.; McLaughlin, N.; Zhang, X.; Chen, X.; Zhang, S.; Gregorich, E.; et al. Linking Rock-Eval parameters to soil heterotrophic respiration and microbial residues in a black soil. Soil Biol. Biochem. 2023, 178, 108939. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- von Lützow, M.; Kögel-Knabner, I.; Ekschmitt, K.; Flessa, H.; Guggenberger, G.; Matzner, E.; Marschner, B. SOM fractionation methods: Relevance to functional pools and to stabilization mechanisms. Soil Biol. Biochem. 2007, 39, 2183–2207. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, J.; Zhang, J.; Lambers, H.; Wu, J.; Qin, G.; Li, Y.; Wang, F. Intensified rainfall in the wet season alters the microbial contribution to soil carbon storage. Plant Soil 2022, 476, 337–351. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Matus, F.J. Fine silt and clay content is the main factor defining maximal C and N accumulations in soils: A meta-analysis. Sci. Rep. 2021, 11, 6438. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, J.Q.; Zhang, X.; Bourg, I.C.; Stone, H.A. 4D imaging reveals mechanisms of clay-carbon protection and release. Nat. Commun. 2021, 12, 622. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, H.; Zhang, J.; Ai, Z.; Wu, Y.; Xu, H.; Li, Q.; Xue, S.; Liu, G. 16-Year fertilization changes the dynamics of soil oxidizable organic carbon fractions and the stability of soil organic carbon in soybean-corn agroecosystem. Agric. Ecosyst. Environ. 2018, 265, 320–330. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, P.; Li, Y.; Liu, S.; Ding, Z.; Zhang, A.; Tang, X. The quantity and stability of soil organic carbon following vegetation degradation in a salt-affected region of Northeastern China. Catena 2022, 211, 105984. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]




| Parameter | Districts | Malda | Coochbehar | ||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Location | Site-1 | Site-2 | Site-3 | Site-4 | Site-5 | Site-6 | Site-7 | ||
| TOC (g kg−1) | CS | RW | 10.24 | 11.40 | 10.64 | 14.54 | 12.96 | 6.63 | 12.40 |
| RM | 9.57 | 13.13 | 13.12 | 17.13 | 13.60 | 9.05 | 12.51 | ||
| (p < 0.05) | 0.008 | 0.000 | 0.000 | 0.000 | 0.014 | 0.000 | NS | ||
| T | ZT | 10.67 | 12.76 | 11.29 | 15.73 | 13.24 | 8.74 | 13.49 | |
| CT | 9.15 | 11.76 | 12.48 | 15.93 | 13.32 | 6.94 | 11.43 | ||
| (p < 0.05) | 0.000 | 0.009 | 0.001 | NS | NS | 0.000 | 0.000 | ||
| D | 0 to 5 | 12.45 | 14.80 | 15.39 | 18.74 | 15.56 | 8.37 | 14.31 | |
| 5 to 10 | 10.12 | 11.72 | 10.97 | 15.72 | 14.24 | 7.95 | 12.43 | ||
| 10 to 20 | 7.15 | 10.27 | 9.29 | 13.04 | 10.04 | 7.20 | 10.64 | ||
| (p < 0.05) | 0.000 | 0.000 | 0.000 | 0.000 | 0.000 | 0.000 | 0.000 | ||
| TN (g kg−1) | CS | RW | 1.01 | 1.04 | 1.15 | 1.48 | 1.31 | 0.95 | 1.38 |
| RM | 1.20 | 1.21 | 1.36 | 1.62 | 1.45 | 1.03 | 1.42 | ||
| (p < 0.05) | 0.000 | 0.000 | 0.001 | 0.020 | 0.001 | NS | NS | ||
| T | ZT | 1.08 | 1.25 | 1.29 | 1.51 | 1.35 | 1.05 | 1.42 | |
| CT | 1.13 | 1.00 | 1.22 | 1.59 | 1.41 | 0.93 | 1.38 | ||
| (p < 0.05) | NS | 0.000 | NS | NS | NS | 0.028 | NS | ||
| D | 0 to 5 | 1.26 | 1.32 | 1.47 | 1.89 | 1.63 | 1.16 | 1.53 | |
| 5 to 10 | 1.19 | 1.15 | 1.32 | 1.44 | 1.37 | 1.04 | 1.45 | ||
| 10 to 20 | 0.86 | 0.90 | 0.98 | 1.31 | 1.14 | 0.78 | 1.21 | ||
| (p < 0.05) | 0.000 | 0.000 | 0.000 | 0.000 | 0.000 | 0.000 | 0.000 | ||
| AC (g kg−1) | CS | RW | 0.37 | 0.41 | 0.43 | 0.51 | 0.46 | 0.30 | 0.32 |
| RM | 0.33 | 0.44 | 0.62 | 0.74 | 0.47 | 0.30 | 0.32 | ||
| (p < 0.05) | 0.000 | 0.005 | 0.000 | 0.000 | NS | NS | NS | ||
| T | ZT | 0.37 | 0.47 | 0.49 | 0.61 | 0.50 | 0.30 | 0.37 | |
| CT | 0.33 | 0.38 | 0.56 | 0.64 | 0.43 | 0.30 | 0.27 | ||
| (p < 0.05) | 0.001 | 0.000 | 0.000 | 0.015 | 0.000 | NS | 0.000 | ||
| D | 0 to 5 | 0.53 | 0.54 | 0.72 | 0.78 | 0.56 | 0.33 | 0.40 | |
| 5 to 10 | 0.30 | 0.38 | 0.44 | 0.60 | 0.49 | 0.28 | 0.28 | ||
| 10 to 20 | 0.22 | 0.34 | 0.41 | 0.50 | 0.34 | 0.30 | 0.28 | ||
| (p < 0.05) | 0.000 | 0.000 | 0.000 | 0.000 | 0.000 | 0.003 | 0.000 | ||
| PC (g kg−1) | CS | RW | 9.87 | 10.99 | 10.21 | 14.03 | 12.51 | 6.33 | 12.09 |
| RM | 9.24 | 12.69 | 12.50 | 16.39 | 13.13 | 8.74 | 12.19 | ||
| (p < 0.05) | 0.014 | 0.000 | 0.000 | 0.000 | 0.014 | 0.000 | NS | ||
| T | ZT | 10.30 | 12.30 | 10.80 | 15.11 | 12.75 | 8.44 | 13.12 | |
| CT | 8.81 | 11.39 | 11.91 | 15.30 | 12.89 | 6.64 | 11.16 | ||
| (p < 0.05) | 0.000 | 0.014 | 0.001 | NS | NS | 0.000 | 0.000 | ||
| D | 0 to 5 | 11.92 | 14.25 | 14.67 | 17.96 | 15.00 | 8.04 | 13.90 | |
| 5 to 10 | 9.82 | 11.34 | 10.53 | 15.12 | 13.75 | 7.67 | 12.15 | ||
| 10 to 20 | 6.93 | 9.93 | 8.88 | 12.54 | 9.70 | 6.90 | 10.36 | ||
| (p < 0.05) | 0.000 | 0.000 | 0.000 | 0.000 | 0.000 | 0.000 | 0.000 | ||
| Parameter | Malda | Coochbehar | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Site-1 | Site-2 | Site-3 | Site-4 | Site-5 | Site-6 | Site-7 | |
| TOC | 0.007 | NS | 0.011 | 0.011 | 0 | 0 | NS |
| TN | NS | 0 | NS | 0.001 | NS | NS | NS |
| AC | NS | NS | NS | 0 | NS | NS | NS |
| PC | 0.007 | NS | 0.009 | 0.015 | 0 | 0 | NS |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Rakesh, S.; Sinha, A.K.; Sarkar, D.; Roy, D.; Bodiga, D.; Sahoo, S.; Jha, P.K.; Dubey, P.K.; Rakshit, A. Active and Passive Carbon Fractions in Contrasting Cropping Systems, Tillage Practices, and Soil Types. Land 2023, 12, 365. https://doi.org/10.3390/land12020365
Rakesh S, Sinha AK, Sarkar D, Roy D, Bodiga D, Sahoo S, Jha PK, Dubey PK, Rakshit A. Active and Passive Carbon Fractions in Contrasting Cropping Systems, Tillage Practices, and Soil Types. Land. 2023; 12(2):365. https://doi.org/10.3390/land12020365
Chicago/Turabian StyleRakesh, S., Abhas Kumar Sinha, Deepranjan Sarkar, Dewali Roy, Divya Bodiga, Samaresh Sahoo, Prakash Kumar Jha, Pradeep Kumar Dubey, and Amitava Rakshit. 2023. "Active and Passive Carbon Fractions in Contrasting Cropping Systems, Tillage Practices, and Soil Types" Land 12, no. 2: 365. https://doi.org/10.3390/land12020365
APA StyleRakesh, S., Sinha, A. K., Sarkar, D., Roy, D., Bodiga, D., Sahoo, S., Jha, P. K., Dubey, P. K., & Rakshit, A. (2023). Active and Passive Carbon Fractions in Contrasting Cropping Systems, Tillage Practices, and Soil Types. Land, 12(2), 365. https://doi.org/10.3390/land12020365










