Extraction of Urban Built-Up Areas Using Nighttime Light (NTL) and Multi-Source Data: A Case Study in Dalian City, China
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Study Area
2.2. Data Preparation
2.3. Method
2.3.1. POI Kernel Density Estimation Bandwidth Threshold
2.3.2. HSI, HSI and POI, HSI and POI, and LST Index Construction
2.3.3. SVM-Based Supervised Classification to Extract Built-Up Areas
2.4. Accuracy Evaluation
3. Results
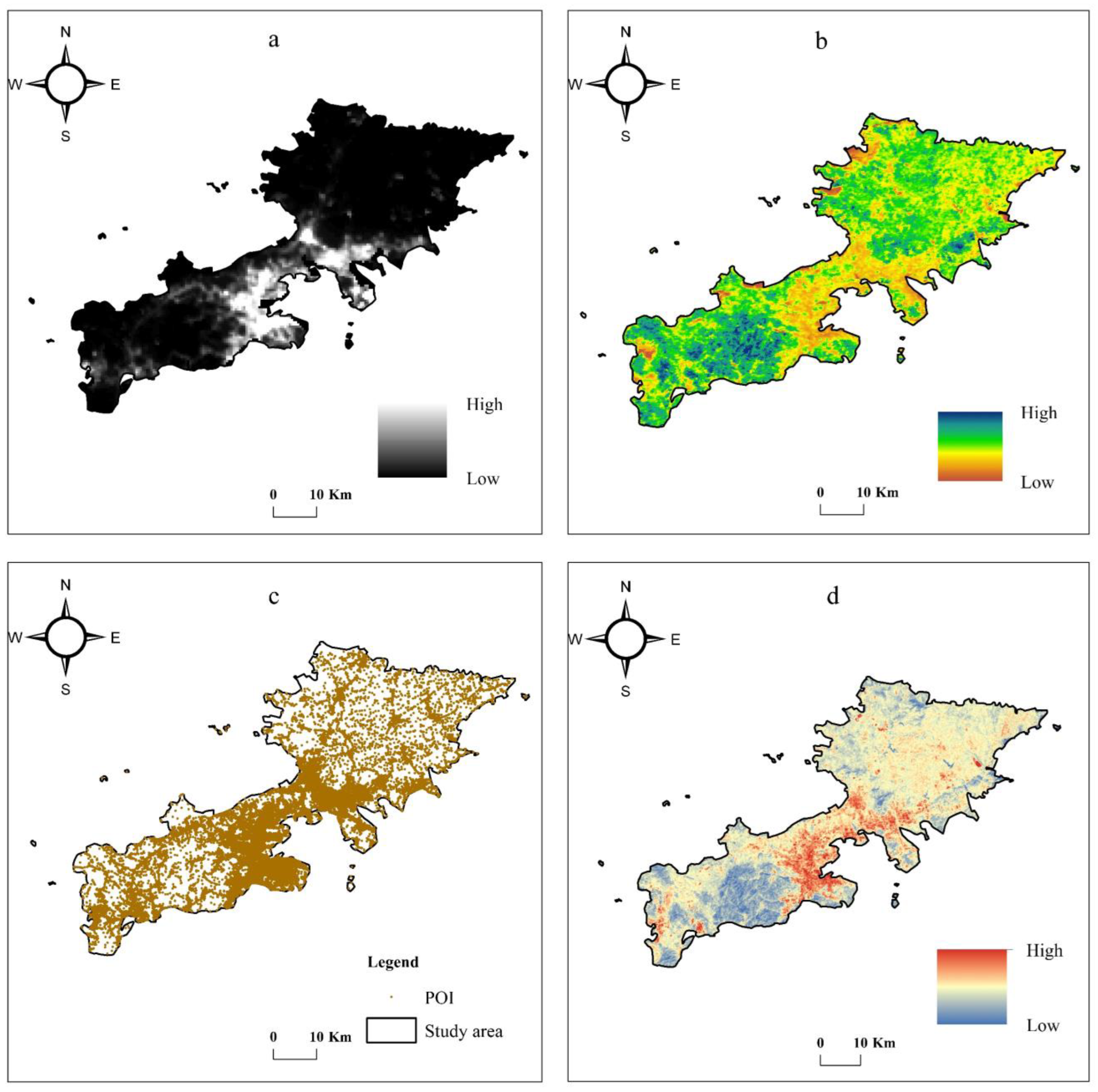
3.1. Analysis of POI Kernel Density Results
3.2. Spatial Distribution Characteristics of NPP-VIIRS, HSI, HP, and HPL
3.3. Visual Interpretation to Extract Urban Built-Up Areas
3.4. Comparative Analysis of Constructed Area Boundary Extraction
3.4.1. Comparative Analysis Based on the Results of the NPP-VIIRS and HSI Index
3.4.2. Comparative Analysis Based on the Results of the HSI and HP Index
3.4.3. Comparative Analysis Based on the Results of the HP Index and HPL Index
4. Discussion
4.1. HPL Index for Urban Built-Up Area Extraction Advantage
4.2. Selection of Support Vector Machine Methods
4.3. Constraints
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Superczynski, S.D.; Christopher, S.A. Exploring land use and land cover effects on air quality in Central Alabama using GIS and remote sensing. Remote Sens. 2011, 3, 2552–2567. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Rashid, H.; Manzoor, M.M.; Mukhtar, S. Pollution Urbanization and its effects on water resources: An exploratory analysis. Asian J. Water Environ. 2018, 15, 67–74. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, X.; Zhou, Y.; Yue, W.; Li, X.; Liu, Y.; Lu, D. Spatiotemporal patterns of summer urban heat island in Beijing, China using an improved land surface temperature. J. Clean. Prod. 2020, 257, 120529. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, L.; Dickinson, R.E.; Tian, Y.; Fang, J.; Li, Q.; Kaufmann, R.K.; Tucker, C.J.; Myneni, R.B. Evidence for a significant urbanization effect on climate in China. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2004, 101, 9540–9544. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Jiang, Z.; Liu, J.; Han, F. Traffic Congestion, Spatial Spillovers and Population Urbanization in China. Collect. Essayson Financ. Econ. 2019, 35, 104–112. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, H.; Zhan, Q.; Yang, C.; Wang, J. The multi-timescale temporal patterns and dynamics of land surface temperature using Ensemble Empirical Mode Decomposition. Sci. Total Environ. 2019, 652, 243–255. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, D.; Zhao, S.; Liu, S.; Zhang, L.; Zhu, C. Surface urban heat island in China’s 32 major cities: Spatial patterns and drivers. Remote Sens. Environ. 2014, 152, 51–61. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mallick, S.K.; Das, P.; Maity, B.; Rudra, S.; Pramanik, M.K.; Pradhan, B.; Sahana, M. Society Understanding future urban growth, urban resilience and sustainable development of small cities using prediction-adaptation-resilience (PAR) approach. Sustain. Cities Soc. 2021, 74, 103196. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Deren, L.; Xi, L. On luminous remote sensing data mining. Acta Geod. Cartogr. Sin. 2015, 44, 591–601. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sutton, P. Modeling population density with night-time satellite imagery and GIS. Comput. Environ. Urban Syst. 1997, 21, 227–244. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Imhoff, M.L.; Lawrence, W.T.; Elvidge, C.D.; Paul, T.; Levine, E.; Privalsky, M.V.; Brown, V. Using nighttime DMSP/OLS images of city lights to estimate the impact of urban land use on soil resources in the United States. Remote Sens. Environ. 1997, 59, 105–117. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Milesi, C.; Elvidge, C.D.; Nemani, R.R.; Running, S.W. Assessing the impact of urban land development on net primary productivity in the southeastern United States. Remote Sens. Environ. 2003, 86, 401–410. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Song, S.; Bailiang, Y.; Jianping, W.; Hongxing, L. Methods for Deriving Urban Built-up Area Using Night-light Data: Assessment and Application. Remote Sens. Technol. Appl. 2011, 26, 169–176. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Small, C.; Pozzi, F.; Elvidge, C.D. Spatial analysis of global urban extent from DMSP-OLS night lights. Remote Sens. Environ. 2005, 96, 277–291. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Deng, L.; Shen, Z.; Ke, Y. Built-up Area Extraction and Urban Expansion Analysis Based on Remote Sensing Images. J. Geo-Inf. Sci. 2018, 20, 996–1003. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Song, J.; Li, X.; Lin, T.; Zhang, G.; Ye, H.; He, X.; Ge, R. A Method of Extracting Urban Built-up Area Based on DMSP/OLS Nighttime Data and Google Earth. J. Geo-Inf. Sci. 2015, 17, 750–756. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pandey, B.; Joshi, P.; Seto, K.C. Geoinformation Monitoring urbanization dynamics in India using DMSP/OLS night time lights and SPOT-VGT data. Int. J. Appl. Earth Obs. 2013, 23, 49–61. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lu, D.S.; Tian, H.Q.; Zhou, G.M.; Ge, H.L. Regional mapping of human settlements in southeastern China with multisensor remotely sensed data. Remote Sens. Environ. Interdiscip. J. 2008, 112, 3668–3679. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Q.; Zhan, Q.; Li, J.; Yang, C.; Liu, W. Extracting Built⁃up Areas Using Luojia⁃1A Nighttime Light Imageries in Wuhan, China. Geomat. Inf. Sci. Wuhan Univ. 2021, 46, 30–39. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Q.; Schaaf, C.; Seto, K.C. The vegetation adjusted NTL urban index: A new approach to reduce saturation and increase variation in nighttime luminosity. Remote Sens. Environ. 2013, 129, 32–41. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, X.; Hu, G.; Ai, B.; Li, X.; Shi, Q. A normalized urban areas composite index (NUACI) based on combination of DMSP-OLS and MODIS for mapping impervious surface area. Remote Sens. 2015, 7, 17168–17189. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Wu, Z.; Chai, Y.; Dang, A.; Gong, J. Geography interact with big data: Dialogue and reflection. Geogr. Res. 2015, 34, 2207–2221. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Z.; Wang, H.; Qin, F.; Han, Z.; Miao, C. Mapping an Urban Boundary Based on Multi-Temporal Sentinel-2 and POI Data: A Case Study of Zhengzhou City. Remote Sens. 2020, 12, 4103. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.; Huang, C.; Zhao, M.; Hou, J.; Zhang, Y.; Gu, J. Mapping the population density in mainland China using NPP/VIIRS and points-of-interest data based on a random forests model. Remote Sens. 2020, 12, 3645. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Q.; Wang, J.; Peng, X.; Gong, P.; Shi, P. Urban built-up land change detection with road density and spectral information from multi-temporal Landsat TM data. Int. J. Remote Sens. 2002, 23, 3057–3078. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, Q.; Guo, L. Empirical approach to threshold determination for the delineation of built-up areas with road network data. PLoS ONE 2018, 13, e0194806. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Shao, Z.; Sumari, N.S.; Portnov, A.; Ujoh, F.; Musakwa, W.; Mandela, P.J. Urban sprawl and its impact on sustainable urban development: A combination of remote sensing and social media data. Geo-Spat. Inf. Sci. 2020, 24, 241–255. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, H.; Herfort, B.; Huang, W.; Zia, M.; Zipf, A.; Sensing, R. Exploration of OpenStreetMap missing built-up areas using twitter hierarchical clustering and deep learning in Mozambique. ISPRS J. Photogramm. 2020, 166, 41–51. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yan, Q.; Li, F.; Li, L. Research on Built-up Area Extraction via Brightness Correction Indexes based on Two Kinds of Nighttime Light Images. J. Geo-Inf. Sci. 2020, 22, 1714–1724. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zheng, H.; Gui, Z.; Li, F.; Wu, H. Urban Built-up Area Extraction Method Based on Nighttime Light lmages and Point of Interest Data. Geogr. Geo-Inf. Sci. 2019, 35, 25–32. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zheng, Z.; Chen, Y.; Wu, Z.; Zhang, Q. Method to reduce saturation of DMSP/OLS nighttime light data based on UNL. Natl. Remote Sens. Bull. 2018, 22, 161–173. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, J.; Zhang, X.; Tan, X.; Yuan, X. Extraction of Urban Built-Up Area Based on Deep Learning and Multi-Sources Data Fusion—The Application of an Emerging Technology in Urban Planning. Land 2022, 11, 1212. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, Y.; Zhao, G.; Zhang, Q. Spatial Distribution of Population Data Based on Nighttime Light and LUC Data in the SichuanChongqing Region. J. Geo-Inf. Sci. 2018, 20, 68–78. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zeng, C.; Zhou, Y.; Wang, S.; Yan, F.; Zhao, Q. Population spatialization in China based on night-time imagery and land use data. Int. J. Remote Sens. 2011, 32, 9599–9620. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, N.; Samson, E.L.; Liu, Y. Population bias in nighttime lights imagery. Remote Sens. Lett. 2019, 10, 913–921. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kumar, L.; Mutanga, O. Google Earth Engine Applications Since Inception: Usage, Trends, and Potential. Remote Sens. 2018, 10, 1509. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Heidenreich, N.-B.; Schindler, A.; Sperlich, S. Bandwidth selection for kernel density estimation: A review of fully automatic selectors. AStA Adv. Stat. Anal. 2013, 97, 403–433. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Li, C.; Wang, X.; Wu, Z.; Dai, Z.; Yin, J.; Zhang, C. An Improved Method for Urban Built-Up Area Extraction Supported by Multi-Source Data. Sustainability 2021, 13, 5042. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, X.; Yue, W.; Gao, D. Spatial improvement of human population distribution based on multi-sensor remote-sensing data: An input for exposure assessment. Int. J. Remote Sens. 2013, 34, 5569–5583. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Z.; Liu, C.; Alfredo, H. From AVHRR-NDVI to MODIS-EVI: Advances in vegetation index research. Acta Ecol. Sin. 2003, 23, 9. [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, J.; Shi, W.; Xiu, C. Urban Research Using Points of Interest Data in China. Sci. Geogr. Sin. 2021, 41, 140–148. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, J.; Li, B.; Ni, W.; Yan, W. An adaptively weighted multi-feature method for object-based change detection in high spatial resolution remote sensing images. Remote Sens. Lett. 2020, 11, 333–342. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lechner, A.M.; Stein, A.; Jones, S.D.; Ferwerda, J.G. Remote sensing of small and linear features: Quantifying the effects of patch size and length, grid position and detectability on land cover mapping. Remote Sens. Environ. 2009, 113, 2194–2204. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mantero, P.; Moser, G.; Serpico, S.B. Partially Supervised classification of remote sensing images through SVM-based probability density estimation. IEEE Trans. Geosci. Remote Sens. 2005, 43, 559–570. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, Z.; Gao, X. A novel method for identifying the boundary of urban built-up areas with POI data. Acta Geogr. Sin. 2016, 71, 928–939. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zha, Y.; Gao, J.; Ni, S. Use of normalized difference built-up index in automatically mapping urban areas from TM imagery. Int. J. Remote Sens. 2003, 24, 583–594. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, Y.; Shi, Y. Toward establishing the concept of physical urban area in China. Acta Geogr. Sin. 1995, 50, 289–301. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Z.; XiaoFan, Z.; Jing, Z.; Haiyan, T.; Boyu, G. An EVI-based method to reduce saturation of DMSP/OLS nighttime light data. Acta Geogr. Sin. 2015, 70, 1339–1350. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Roy Chowdhury, P.; Maithani, S. Monitoring growth of built-up areas in indo-gangetic plain using multi-sensor remote sensing data. J. Indian Soc. Remote Sens. 2010, 38, 291–300. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, Z.; Sharifi, A.; Dong, X.; Shen, L.; He, B.-J. Spatial variability and temporal heterogeneity of surface urban heat island patterns and the suitability of local climate zones for land surface temperature characterization. Remote Sens. 2021, 13, 4338. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, Z.-Q.; He, B.-J.; Li, L.-G.; Wang, H.-B.; Darko, A. Buildings Profile and concentric zonal analysis of relationships between land use/land cover and land surface temperature: Case study of Shenyang, China. Energy 2017, 155, 282–295. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, M.; He, C.; Liu, Z.; Dou, Y. How did urban land expand in China between 1992 and 2015? A multi-scale landscape analysis. PLoS ONE 2016, 11, e0154839. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Xu, T.; Coco, G.; Gao, J. Extraction of urban built-up areas from nighttime lights using artificial neural network. Geocarto Int. 2020, 35, 1049–1066. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- He, X.; Zhou, C.; Zhang, J.; Yuan, X. Using wavelet transforms to fuse nighttime light data and POI big data to extract urban built-up areas. Remote Sens. 2020, 12, 3887. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- He, X.; Zhang, Z.; Yang, Z. Extraction of urban built-up area based on the fusion of night-time light data and point of interest data. R. Soc. Open Sci. 2021, 8, 210838. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Suli, T.; Yufeng, L. Development and Application of Artificial Neural NetworkTechnology. Comput. Dev. Appl. 2009, 22, 59–61. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]








| Data | Resolution | Source | Acquisition Date |
|---|---|---|---|
| NPP-VIIRS | 500 m | http:/ngdc.noaa.gov/eog/ | 9 months in 2020 |
| EVI | 250 m | https://ladsweb.modaps.eosdis.nasa.gov | 12 months in 2020 |
| POI | https://lbs.amap.com/ | 31 December 2020 | |
| LST | 30 m | https://code.earthengine.google.com/ | 12 months in 2020 |
| Google Maps | 0.6 m | www.Amap.com | 1 January 2021 |
| Index | Optimal Threshold | Overall Accuracy | Kappa |
|---|---|---|---|
| NPP-VIIRS | 9 | 88.81% | 0.67 |
| HSI | 0.85 | 87.21% | 0.64 |
| HP | 0.02 | 90.01% | 0.72 |
| HPL | 0.05 | 91.41% | 0.77 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Li, X.; Song, Y.; Liu, H.; Hou, X. Extraction of Urban Built-Up Areas Using Nighttime Light (NTL) and Multi-Source Data: A Case Study in Dalian City, China. Land 2023, 12, 495. https://doi.org/10.3390/land12020495
Li X, Song Y, Liu H, Hou X. Extraction of Urban Built-Up Areas Using Nighttime Light (NTL) and Multi-Source Data: A Case Study in Dalian City, China. Land. 2023; 12(2):495. https://doi.org/10.3390/land12020495
Chicago/Turabian StyleLi, Xueming, Yishan Song, He Liu, and Xinyu Hou. 2023. "Extraction of Urban Built-Up Areas Using Nighttime Light (NTL) and Multi-Source Data: A Case Study in Dalian City, China" Land 12, no. 2: 495. https://doi.org/10.3390/land12020495
APA StyleLi, X., Song, Y., Liu, H., & Hou, X. (2023). Extraction of Urban Built-Up Areas Using Nighttime Light (NTL) and Multi-Source Data: A Case Study in Dalian City, China. Land, 12(2), 495. https://doi.org/10.3390/land12020495








