Abstract
Agricultural terraces provide farmers in hilly landscapes with effective ways to increase the area available for crops. They mitigate the risks of soil erosion and promote crop productivity by slowing surface water runoff and retaining moisture. As in other parts of the world, terraces have been constructed and used in the Mediterranean for millennia. The availability of terraced agriculture had important socio-economic, ecological, and environmental implications for past societies. However, the chronology of construction, use, and abandonment of terraces in different regions remains uncertain. A more robust set of chronological data will allow better assessment of whether terrace agriculture was a resilient strategy in the face of past economic or ecological instability and, in turn, inform how terraces could be used to address future agricultural and environmental challenges. In this paper, we review the application of luminescence dating to terrace sediments, the key challenges involved, and the currently published data which include over 250 luminescence ages. We also discuss the use of a multidisciplinary approach involving other geoarchaeological tools (e.g., use of GIS analyses, field-based luminescence readers, and micromorphology) to enhance the ways that past terrace systems can be understood. Terrace systems are inextricably linked to sustainable land use across the Mediterranean. Luminescence dating methods, therefore, have a crucial role to play in understanding the complexities of past and future landscape change.
1. Introduction
Agricultural terraces, which demonstrate an ingenious and sustainable way of transforming hilly slopes into arable land, are ubiquitous features of Mediterranean landscapes, stretching from Portugal to the Judean Highlands [1,2,3,4,5,6,7,8,9,10,11]. Outside this region, terraces are widely distributed in the tropics, scattered across Africa (notably in Ethiopia), in the Peruvian Andes, and in Asia from the Himalayas to the rice terraces of China and southeast Asia [2]. Whilst studies of agricultural terrace systems have been carried out in the Americas [12,13] and Asia [14,15,16,17], it is the Mediterranean terraces that have received most attention. Grove and Rackam [5] describe five principal types of historic terraces in the Mediterranean: step terraces, often parallel to the contour of the hillside; braided terraces, which zigzag up the slope being connected by switchbacks; pocket terraces with crescent-shaped walls, which often protect soil for individual trees; squarish terraced fields; and check-dams built across watercourses. Since the 1950s, modern false terraces built with mechanical earthmovers have become widespread. Over recent decades, terraces have been abandoned in many regions as agriculture declined including in Tuscany, Italy [18], the Guadalquivir valley and La Rioja in Spain [19,20], and the islands of the Aegean [7]. The abandonment of terraces in southern Europe has been attributed to a range of socio-economic, technological, and political factors, including the mechanisation of agriculture and the disappearance of traditional farming methods [21,22]. The history of terraces in the Mediterranean remains poorly understood. GIS-based techniques such as Historic Landscape Characterisation (HLC) have been used to map terraced landscapes in the eastern Mediterranean, and techniques such as retrogressive analysis have been used to define their temporal relationships [23,24], although such analyses tend to produce and rely on relative chronologies. Without robust absolute chronologies, it remains difficult to relate the construction of terraces to their original socio-economic and environmental context. Furthermore, terraces were maintained and reconstructed over long periods, so understanding construction phases can be complex and age estimates can be unreliable [25,26,27].
In earlier decades, before the advent of absolute dating techniques, indirect methods were frequently employed by landscape archaeologists to suggest chronologies for terrace construction; for example, on associations with nearby ancient buildings or other structures of known age (in Crete, Greece) [28], with surface finds (in Petra, Jordan) [29,30,31], or according to the attributes of the terrace walls [32]. Morphology and construction style may provide chronological indicators, but this could be frustrated by replication and re-use of established construction methods. Successive usage and maintenance work on the terraces can lead to an age underestimation in the common situation where terrace walls were refurbished but the soils behind them remained relatively intact [25,33]. Further, the spatial coincidence of settlements, scatters of cultural material, and terraces do not necessarily provide any firm indication that they were built or even used at the same time. In an earlier review by Frederick and Krahtopoulou [25], the authors discussed thirteen methods of dating terraces grouped into three categories: (i) from the surrounding landscape—where relation or association is established with ancient settlements or cultural material found in the vicinity; (ii) riser and wall attributes—dating via investigating the masonry style and phasing of wall structure; and (iii) deposit attributes—dating of ceramics or absolute dating of buried soils. Price and Nixon [28] expanded these criteria, listing nine criteria in descending order of strength: dateable material in the fill; ages of trees on terraces; terrace construction style; shared construction style with adjacent ancient structures; terraces built against ancient structures; extent and type of lichenisation of terraces; extent of degradation of terraces; relict landscapes; and antiquity on other grounds (e.g., pressure on agricultural resources). More recently, Quirós-Castillo and Nicosia [34] employed a different technique in which they conducted a detailed study of ~6 ha of terraced land in the Basque country and identified abandoned settlements by means of written sources, toponomy, and oral traditions coupled with geoarchaeological field survey and radiometric study of specific sites. Oral accounts proved helpful in identifying the extent of agricultural activities and abandonment of terraces, although they were often limited to the past few decades. In a study on the island of Madeira, Kiesow and Bork [35] conducted in-depth interviews with local residents which each lasted between one and four hours. By selecting their informants, the authors argued that they could sample very specialised knowledge about the historic use of terraces. Whilst they may provide invaluable information, such methods have disadvantages: not only are they time-consuming but the qualitative data they yield are inevitably subject to the vagaries of individual and social memory.
Using relative dating methods studies have suggested origins for Mediterranean terraces as long ago as the Bronze Age [11,28,33]. Nevertheless, considering the ubiquity of terraces in the region there remains a dearth of absolute chronological data. Terraces can be expensive to map and survey, and were often considered ‘boring’: they consequently attracted limited research using sophisticated techniques and models [36]. Tephrochronology has been used in a very small number of Mediterranean studies (e.g., Bronze Age terraces on Pseira, Crete) [37]. Lichen and cosmogenic isotope analyses have been attempted on the stones used for the terrace walls, but the techniques have not been very successful [25,38]. There is no single, universally-accepted method for dating agricultural terraces, but radiocarbon and luminescence dating are now the two most common techniques used to date terrace sediments, with the latter gaining ground over the former in the last few years. Given this context, the aim of this paper is to review recent applications of radiometric methods on agricultural terraces in the Mediterranean, with a particular focus on current advances and challenges in luminescence dating.
2. Radiocarbon Dating
Radiocarbon dating can be used in wide range of depositional settings, making it a preferred technique in the world of archaeology [39,40]. Its application to organic materials has been exploited in several studies to construct chronologies of agricultural terraces in the Mediterranean [7,41,42,43,44]. Methodological developments in accelerator mass spectrometry and refinements in calibration curves mean that even small samples can now be analysed with improved precision. The relative speed of analysis and ability to offer significantly better precision than OSL dating (~5–10% at 1σ) mean radiocarbon dating has been the chosen method in many studies [45,46].
A radiocarbon age, whether performed on charred material or a fraction of organic matter (bulk, humic acid, or humin), is assumed to reflect the latest organic inputs to the soil before burial under the terrace fill [43]. Since this assumption depends on a number of factors, including the absence of younger carbon infiltrating down from above, alteration of the A horizon, or reworking of older carbon, interpretation of such ages requires careful consideration [43,44,47]. It has been suggested that the humic fraction works well for dating younger soils, which proved accurate for Medieval terrace fills in Galicia, Spain [48,49]. However, for older contexts, the humin fraction is preferred because of its stability and insolubility [50]. For example, Puy and Balbo [47] obtained a single date of cal AD 647–778 (2σ) from an A horizon buried under a terrace fill in Ricote, southeast Spain, which led them to suggest that the irrigated terraces in the region originated with the arrival of Arabs and Berbers in the Iberian Peninsula. However, on reassessment, the authors found that the ages previously obtained in Ricote from the bulk organic fraction were significantly older than those yielded by the charred material [43]. Citing this example and a ~2500 year difference in chronology, Puy et al. [43] recommended (i) to avoid using the bulk organic fraction to determine absolute dates for the construction of terraces, and (ii) not to rely on single AMS dates as it is impossible to determine whether the dated material represents the most recent organic additions to the soil before it was buried or the age of pre-existing organic matter.
Statistical modelling may go some way to mitigating these issues by allowing incorporation of information such as archaeological context or material-specific background information. This can be used to recalculate uncertainty and refine the interpretation of radiocarbon dating results. Acabado [14] investigated Ifugao rice terraces in the Philippine Cordillera and used seven 14C dates to construct an absolute chronology for the stratigraphic and construction sequences of rice terraces, presenting a model which allowed the integration of relative stratigraphic information through a Bayesian statistical framework [51]. This approach has yet to be applied to terraces in the Mediterranean region.
As radiocarbon dating requires an organic sample, its application is strictly tied to the availability of dateable material. Hot dry summers, seasonally restricted rainfall (e.g., in the dry farming zones in the Levant), or acidic soils mean that scarcity of dateable material becomes an issue. In their investigations of terraced landscape on Mount Eitan in the Judean Highlands, Gadot et al. [52] noted that not only was it difficult to establish the source of charcoal found within terrace fills, but that issues of reworking of old charcoal and bioturbation by roots added uncertainties to the determined age. One way to circumvent these issues could be to generate several chronologies for a stratigraphy, with a parallel physical or chemical dataset to observe the degree of disturbance/alteration. In a different approach, Bruins et al. [46] described soft, powdery charcoal flecks as ‘charred organic material’ and used it to date terrace fills in Horvat Haluqim in the Negev Highlands. The authors argued that these flecks must have originated on site since they are fragile and their transportation from elsewhere would cause their disintegration and dispersal. They further argued that the incorporation of such soft charcoal flecks in a soil layer could only be possible by anthropogenic activities such as manuring [45]. Meanwhile, in the context of cultivated fluvial terraces, reworking and redeposition processes have been shown to affect radiocarbon dating of embedded organic material [53]. Beckers et al. [54], following a similar strategy, assumed a single and short erosion–transportation–deposition cycle for their sampled charcoal. This assumption was considered true since radiocarbon dates were in stratigraphic order and charcoal samples were found in context with sharp-edged pottery fragments, indicating short transport distances. In northwest Spain, Silva-Sánchez et al. [55] obtained compatible OSL and radiocarbon dates in terrace levels with a higher incidence of macrocharcoal (>2 mm), likely indicating fire around the time of deposition. In levels where radiocarbon dating was performed on both macrocharcoal and bulk sediment, the ages obtained from the bulk sediment suggested an older age than dates from the charcoal, interpreted as the result of local fires.
3. Luminescence Dating
Luminescence dating refers to a group of radiometric dating techniques that are used to determine the time elapsed since a sediment was last exposed to sunlight or sufficient heating. This technique has become the preferred method in the last two decades for dating ‘terrace’ sediments—sediments associated with agricultural terracing, either behind built structures or as earthworks [13,56,57]. The technique relies on the fact that minerals such as quartz and feldspars serve as micro dosimeters accumulating a dose in response to natural radioactivity in the environment [58,59]. These signals are depleted, or reset, when the minerals are exposed to either daylight or heat. After deposition and burial, luminescence grows in situ in response to ionising radiation in the sample and environment. This is the burial dose. In the laboratory, a series of calibration experiments are undertaken with radiation sources to quantify the natural luminescence signal equivalent to the burial dose—the ‘equivalent dose (De)’. In parallel, a combination of low-level radiometric measurements are undertaken to determine the palaeo-dose rate to the sample (Ḋ). The luminescence age is then determined as the quotient of equivalent dose over the estimate of environmental dose rate.
In theory, OSL dating is well-suited to the Mediterranean environment due to relatively high insolation [60,61]. OSL does not rely on the presence of organic matter, which is also an advantage in the region [62,63]. Quartz is the most commonly used mineral for dating agricultural terrace sediments due to its ubiquity and resistance to weathering. In laboratory analyses, the single aliquot regenerative-dose (SAR) protocol on quartz is routine, and it is not subject to the same fading-related issues as feldspars.
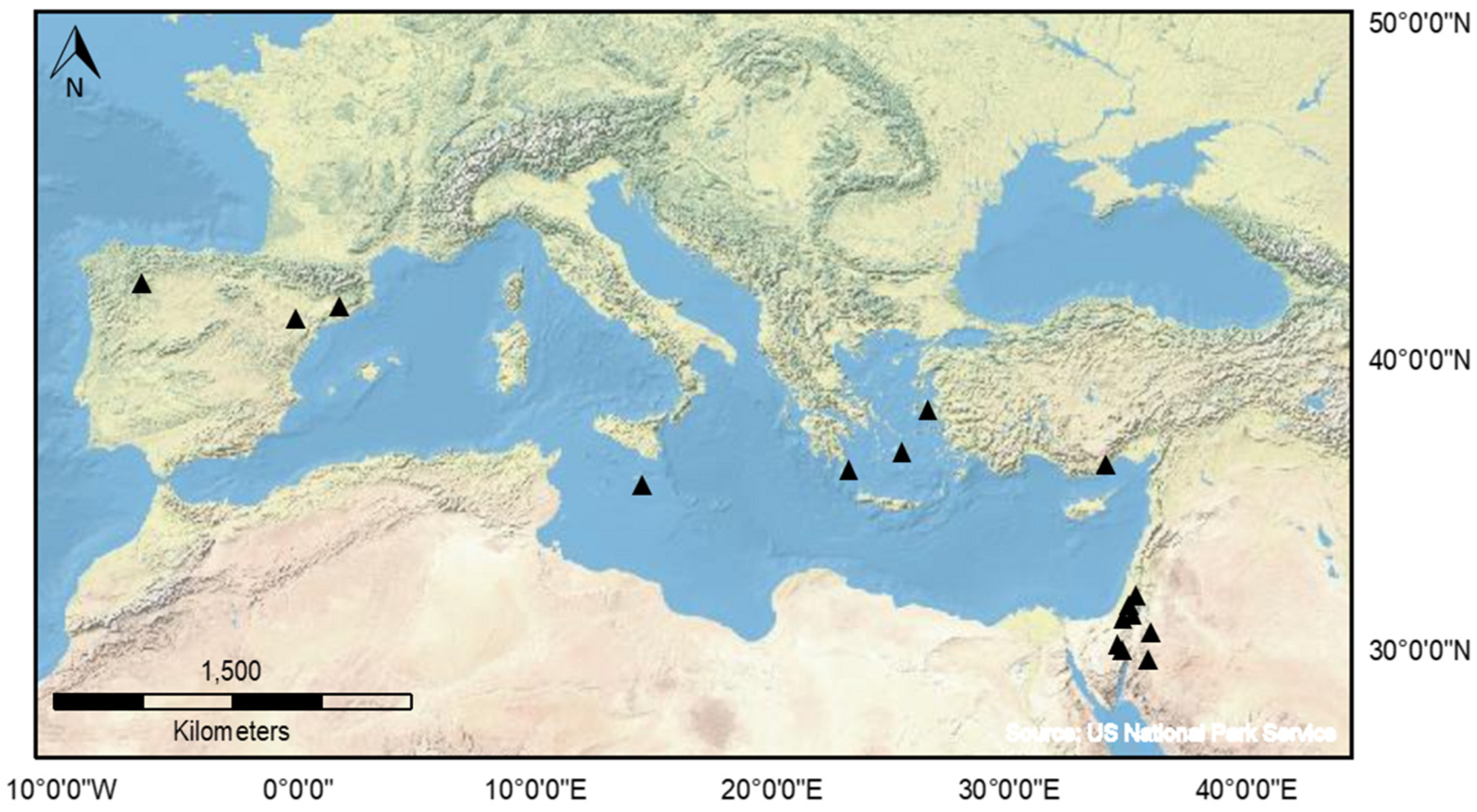
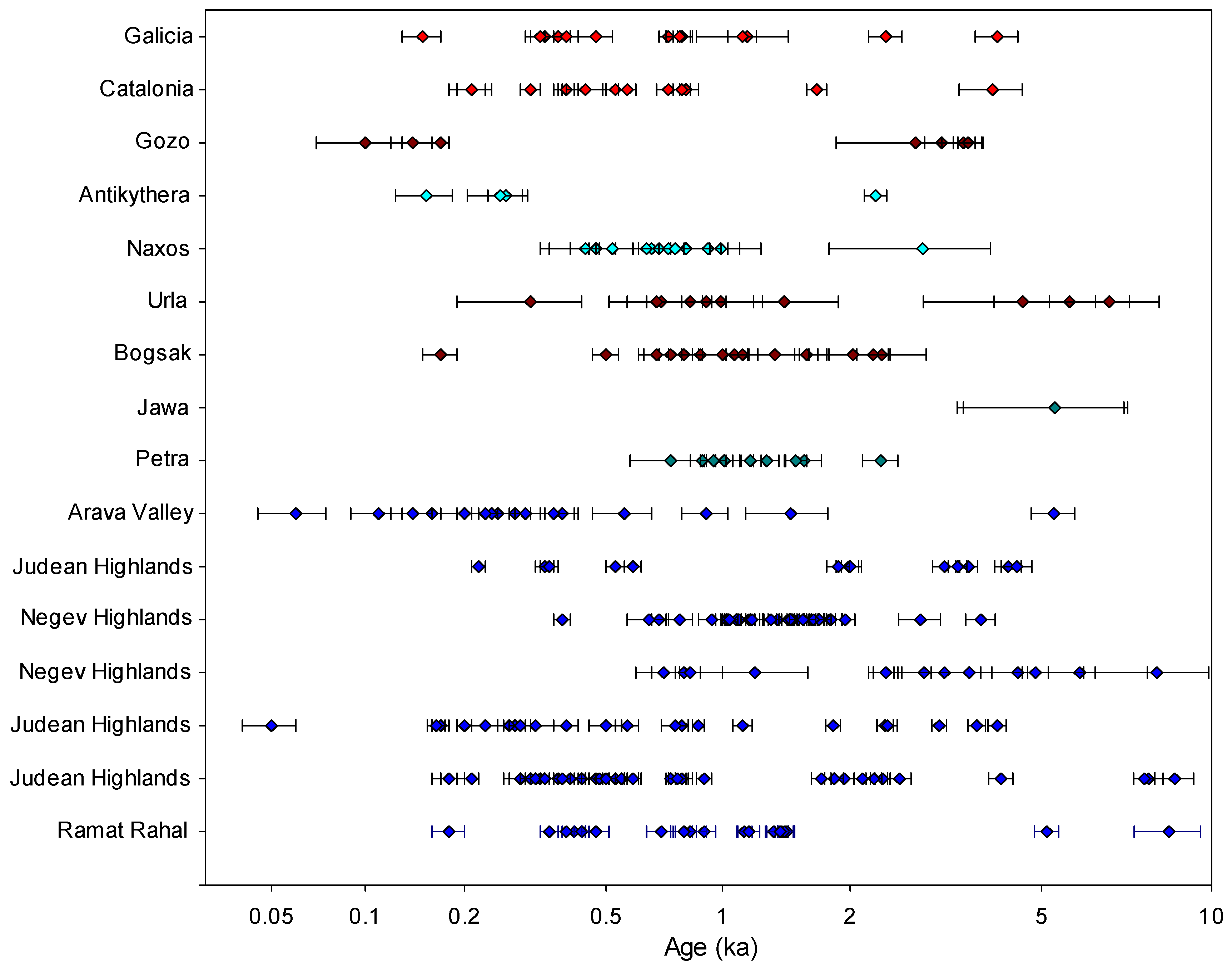
There are over 250 published OSL ages for sediment associated with agricultural terraces and earthworks across the Mediterranean region (Figure 1). Unlike other fields which routinely use luminescence dating to produce large datasets, studies of terraces are under-represented in the records. The published OSL ages are presented in Figure 2. As shown in Figure 1, there is currently a regional bias in the availability of published OSL records: over 150 ages are reported from the southern Levant, with no other region in the Mediterranean so tightly constrained, either spatially or chronologically. The data suggest that in the Negev Highlands, large-scale agricultural fields were constructed during the Byzantine and Early Islamic periods (4th−10th centuries CE), whilst in the Judean Highlands, widespread agricultural activities took place during the Late Mamluk and Early Ottoman periods (between the 13th and 19th centuries CE) [52,57,62,64,65,66,67,68]. Outside the Levant, terraced landscapes in other regions are now being investigated in Spain, Greece, and Turkey, with a large number of OSL dates—supported by proxy luminescence datasets now published—providing significant insights into terrace construction [56,69,70]. The published ages collectively represent many historic periods between the early Neolithic period and the 19th century with notable periods of intensification during the Roman–Byzantine/early medieval periods (1st millennium CE) and the later Middle Ages (c. 12th–17th centuries CE).
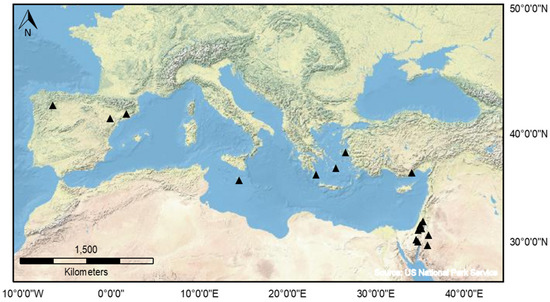
Figure 1.
Distribution of regional archaeological studies of terraced landscape in the Mediterranean which used luminescence dating as the main chronometric tool.
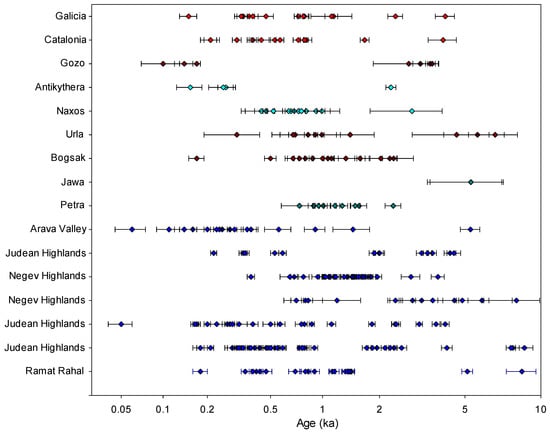
Figure 2.
Distribution of published luminescence ages from major studies of Mediterranean terraces (as listed in Table 1).
4. OSL Dating of Terrace Sediments: Current Challenges and Misconceptions
Of the published dataset, the majority of the age determinations were made on quartz using the standard SAR dating protocol. There are certain challenges and misconceptions surrounding luminescence dating that often discourage geoarchaeologists from using these techniques as a chronometric tool. In this section, we discuss these challenges with particular reference to dating sediments associated with agricultural terraces and conclude by offering several potential solutions.
4.1. Viability of Luminescence Signal for Dating
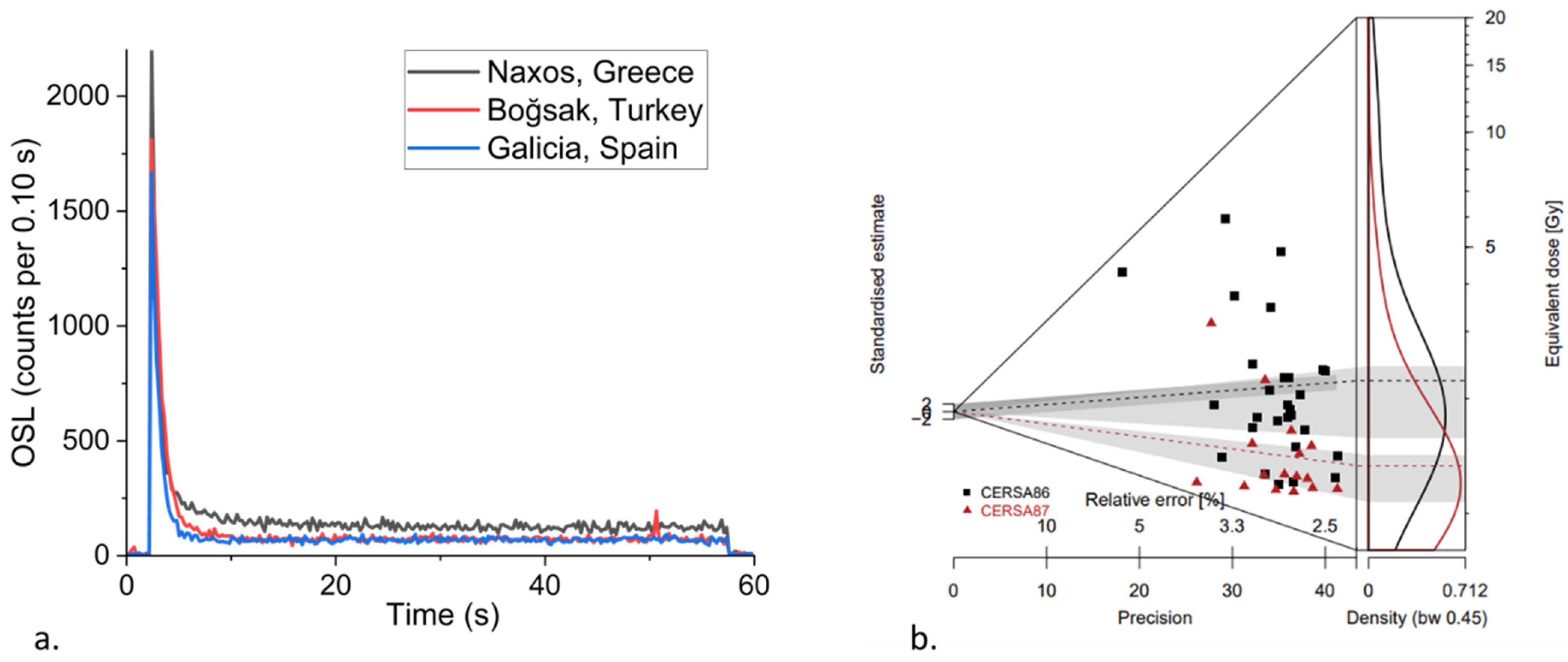
Although quartz is ubiquitous across the Mediterranean, it has variable luminescence responses, sensitivities, brightness, and stability of signals. As such, the viability of the quartz OSL signal for dating remains an open question in any new study. The OSL signal from quartz is composed of a number of components: the fast component is optimal because of its stability and because it is susceptible to bleaching [71,72]. Avni et al. [64] and Gadot et al. [52] examined quartz from the Negev Highlands and Judean Highlands and found it characterised by bright signals dominated by the fast component (Table 1). Beckers et al. [54] explored different integration limits in determining equivalent doses for their samples associated with run-off terrace in Jordan; they were successful in isolating the fast component and minimising the influence of the medium component in their final Des. Turner et al. [69] assessed the suitability of the SAR OSL protocol to quartz from different locations in Turkey, Greece, and Spain and showed that quartz in the wider Mediterranean region has the potential to act as a suitable dosimeter for luminescence dating techniques (Figure 3a).

Table 1.
Luminescence-dated agricultural terrace sites in the Mediterranean.
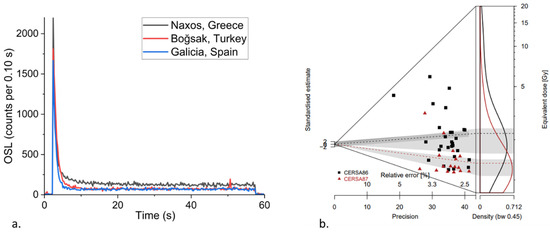
Figure 3.
(a) Examples of typical OSL decay curves dominated by fast component from small aliquots in samples from three different study regions in the Mediterranean. (b) Examples of two samples from agricultural terraces at Samos Monastery, Galicia, Spain which display degrees of heterogeneity or dispersion in their respective equivalent dose datasets. CERSA86 has an OD value of 63 % while CERSA87 has 37% (data plotted from Turner et al. [69]).
4.2. Partial Bleaching of Terrace Sediments
An essential requirement for luminescence dating is the exposure of luminescent minerals to adequate light at deposition to completely bleach, or reset, the luminescence signals prior to burial. Bleaching can occur during cycles of erosion, transportation, and deposition; hence, the luminescence age should represent the time elapsed since last burial. Due to the depositional histories to the sediment in terraces and earthworks, it is likely that the luminescent minerals are only partially bleached prior to burial, which can led to significant scatter in equivalent dose values (Figure 3b) and, hence, age [59,73]. This is more of an issue which may cause an age overestimation of the burial event [74] in contexts where exposure to light may be limited, particularly in terrace systems where sediments accumulate during episodic flash floods and runoff events [25,33,54,63]. Kouki [31] reported incomplete bleaching of sediments associated with fluvial and agricultural terraces in the Petra region. Likewise, Beckers et al. [54], in the context of dating terraces from the same region, observed a large scatter in dose values while using larger aliquots (6 mm) which confirmed the expected partial bleaching of the samples, and consequently replaced them with smaller aliquots. The effect of partial bleaching is more pronounced in such fluvial settings where terrace sediments have been washed and deposited, without being completely bleached first. Additionally, if the stored doses are smaller, the impact of partial bleaching becomes greater (e.g., Stavi et al. [68]). In contrast, Gadot et al. [52] studied an extensive dataset of OSL ages from the arid Judean Highlands. Based on the stratigraphic position of ages and quality assurance tests, they suggested that OSL signals in their samples were bleached during agricultural activities (either when the terrace wall was filled or during the latest episode of ploughing) and, thus, argued that their OSL ages were associated with episodes of terrace construction and use. Nevertheless, where partially bleached grains are present in samples, they can be used to identify distinct populations which represent earlier episodes of terrace construction and, therefore, provide evidence of soil being recycled from older features. Porat et al. [57] used a large dataset of over 900 aliquots from the Judean Highlands to reveal the finer details of terrace construction through time, that a set of individual OSL ages might have otherwise missed (Section 4.3). They suggested periods of terrace construction in the 14th–19th centuries AD and the Hellenistic–Roman and Early Islamic periods and only limited agricultural activity during the Bronze and Iron Ages.
4.3. Overdispersion and Choosing the Right Dose Model
There are several statistical approaches for reducing equivalent dose distributions to a burial dose, influencing the calculation of luminescence ages. Various arguments have been made on the most appropriate dose model for a given sample based on the protocol(s) used to determine equivalent doses, the heterogeneity or observed overdispersion in the distribution, the geomorphologic setting, and or the stratigraphic context. A further complication to dating terrace sediments is the potential for post-depositional mixing caused by bioturbation (disturbance of the sediment by plants and animals) or geomorphic processes (e.g., sediment slumping into gullies). Bioturbated samples may exhibit multi-modal De distributions, with modes both higher and lower than the dose distribution associated with the true burial age [75]. Beta-dose heterogeneity can also contribute to the scatter in equivalent doses: some grains in the matrix might experience a greater dose due to proximity to ‘hotspots’ (areas of high beta radiation), whereas grains distal to these will experience a lower dose [76].
As the choice of dose model significantly influences luminescence age, careful consideration needs to be given to samples that have heterogeneous equivalent dose distribution, or high overdispersion (e.g., incomplete bleaching, post depositional mixing, dosimetric variability; see discussion in Guerin et al. [77]). For those samples that show a homogeneity in equivalent dose values (overdispersion is low), such that estimates of De cluster around a central value and show a normal distribution, the central dose model (CDM) [78] might be preferable. Stavi et al. [68], in their study of run-off terraces in the Arava Valley, noted that their samples were characterised by very high degrees of scatter in equivalent doses; however, after discarding distinct outlying dose values, the equivalent doses showed a normal distribution and the authors argued for the use of the CDM. Gadot et al. [52], in their study of over 40 samples from terraces in the Judean Highlands, obtained overdispersion values in the range of 10–85%, and argued for the use of several dose models: CDM for samples returning normal dose distributions and either the minimum dose model (MDM) or the finite mixture model (FMM) for the remaining samples. Beckers et al. [54] also used a combination of different dose models to calculate ages for runoff terrace systems in the eastern Highlands of Jordan. There are arguments against using such models: Rodnight et al. [79] demonstrated that the MDM is influenced by low De values; Arnold and Roberts [80] questioned whether one can correctly identify the correct number of dose populations to successively implement FMM. Porat et al. [57] argued that, in poorly bleached samples, multi-grain small aliquots might be used as a surrogate for single grain measurements, and hence implemented both MDMs and FMMs. Overall, though, for Mediterranean terrace studies, CDM seems appears to be the model used most frequently in studies of Mediterranean terraces. Guerin et al. [77] highlighted the weaknesses associated with CDM and put forward a new average dose model (ADM). Based on experimental evidence, they argued that ADM leads to more accurate ages and shows better agreement with the independent control than CDM. Future studies could employ the ADM and examine its suitability for application on terrace sediments.
4.4. Choosing the Right Water Content Value for Dosimetry
Another key challenge in determining an accurate luminescence age is estimating the most representative water content. Water present in sediments attenuates radiation such that only a proportion of it is received by the mineral grain. The higher the water content, the lower the dose rate, which can have a significant impact on age determinations. Murray et al. [81] showed that a 1% change in lifetime average water content could lead to a 1% change in derived age; hence, dose rate calculations require careful consideration of incorporated water content values. Generally, if it is likely that the sample remained dry (for example in an arid region) or saturated (below the water table) during burial, uncertainties and assumption related to water content decrease. The problem becomes complex in conditions where the average water content is likely to vary throughout the burial history and, therefore, it is always recommended to consider the water content history of the sampling sites and landscape. Different studies in the Mediterranean have adopted different strategies to address this issue, and field water content is generally used in calculations. For example, authors conducting fieldwork at terrace sites in Israel [52,62,64] estimated water content between 5 ± 2% and 15 ± 5%, reflecting the proximity to surface and seasonal variations. For their study at Petra (Jordan), Beckers et al. [54] used sophisticated water balance models and available representative data from meteorological stations to estimate water content values. For terraces in Greece and Turkey, Kinnaird et al. [56] and Turner et al. [69] determined both fractional and saturation water content values from their samples to derive the most representative values for their final dose rate calculations (between 10 ± 5% and 15 ± 6%). Regardless of their approach, these authors have used a generous error term on their final water content values to account for potential variations during the burial history of the sample.
5. Multidisciplinarity: The Way Forward
Luminescence dating methods are now being used as the preferred geochronological tool to date agricultural terrace sediments. In this section, three key advances which have the potential to fundamentally change the way that researchers study ancient terrace systems are discussed. The integration of these developments into routine practice has the potential to revolutionise the field and provide new insights into the history of terrace systems.
5.1. Identifying the Best Sites for OSL Dating
One of the key factors which precedes luminescence dating (or use of any dating technique) is the collection of samples from the most appropriate agricultural terraces and terrace systems. To this end, desk-based techniques for historic landscape analysis can play an important role in advance of sampling in the field. This can include mapping the extent of current and past agricultural activities based on the distribution of terraces, field systems, irrigation channels, or communications networks. For example, Historic Landscape Characterisation (HLC) provides a holistic, generalising methodology that can be used to interpret how historic processes have resulted in distinctive patterns and combinations of features in existing landscapes [82]. As HLC is a generalising methodology, it is not necessarily concerned with individual historic features, but rather with groups of features and their articulation as components in larger spatiotemporal systems. An HLC provides a broad-scale, seamless overview of human activity across the landscape. This makes it particularly useful for examining the development of extensive terraced landscapes in the Mediterranean [23,24,83,84,85]. To create an HLC, units of different HLC ‘types’ are classified using Geographic Information Systems (GIS) based on data including modern and historic maps, aerial photographs, and satellite imagery. Other remotely sensed data can be integrated where available (e.g., lidar), as well as archaeological datasets and modern thematic landcover data [85,86]. The principal output of an HLC is a continuous geospatial dataset: a landscape mosaic which represents groups of features in the modern landscape linked by their historical development [23] (p. 219).
The classification system used in each HLC varies depending on project aims and objectives. It can employ a pre-defined regional typology; for example, the six broad Mediterranean terrace categories identified by Grove and Rackham [5]. Alternatively, the HLC may use a project-specific typology informed by previous research or by using techniques like retrogressive analysis [87,88,89]. This type of morphological generalisation may not account sufficiently for local issues (e.g., vertical aggradation [90]), but it can provide a classification that is wholly suitable for broad landscape assessment. The scale and resolution of remote sensing data generally mean that ground checks are required to finalise the selection of exact sampling locations, but HLC and other types of landscape analysis can be used successfully to identify suitable areas for fieldwork.
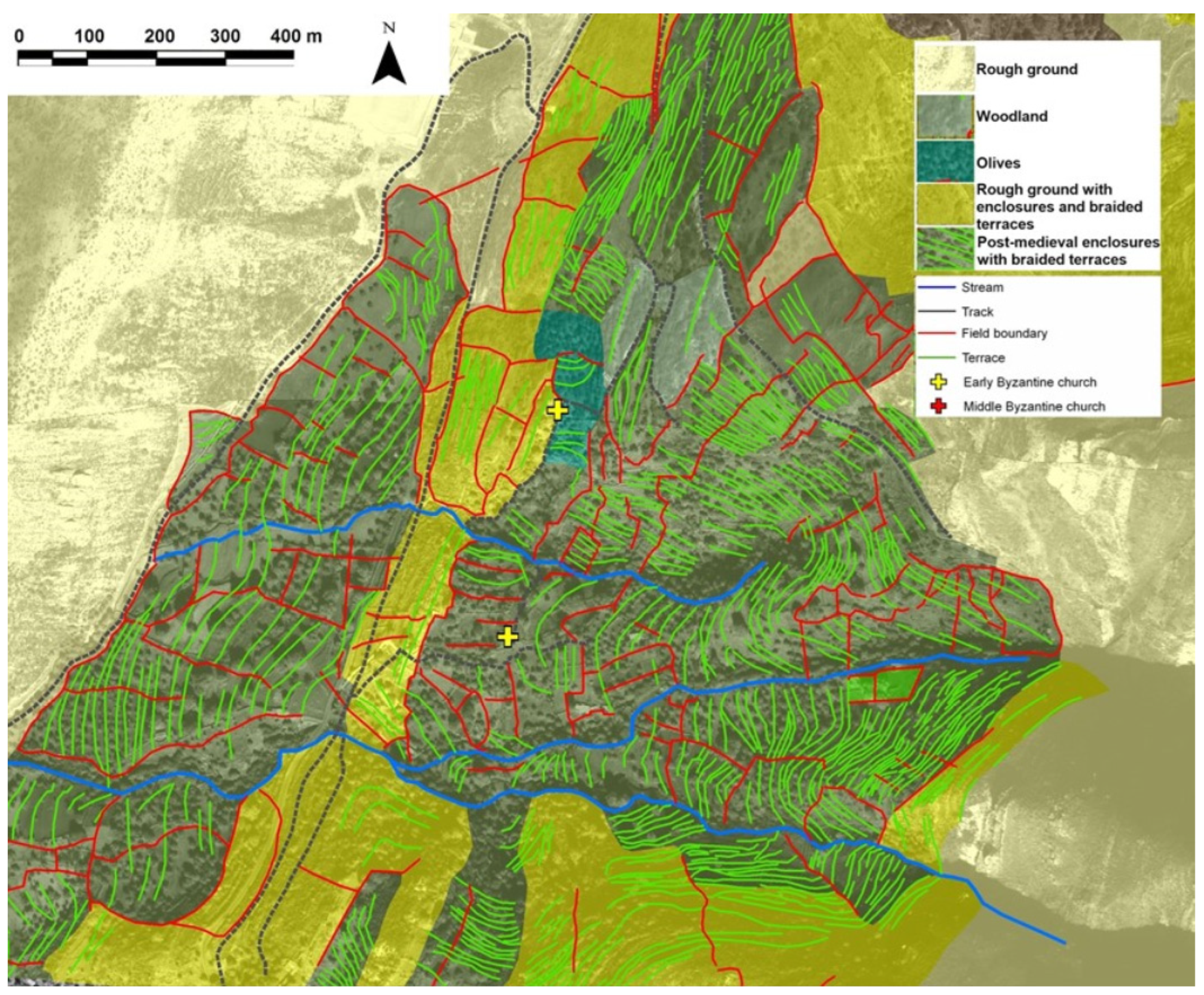
The applicability of this approach has been demonstrated on the island of Naxos, Greece, where HLC and retrogressive analysis have been used since 2006 to analyse historic landscape development [24]. The island of Naxos has tens of thousands of kilometres of observable terraces constructed in a range of periods. It would be impractical to examine them all on the ground. In the Aria valley study area (Figure 4), the HLC was used to identify potential sample locations chosen on the basis of their topographic position (upstream/downstream in the catchment); terrace type (braided contour terraces, check-dams); relationship to other land use (presence/absence of subsequent enclosure); and terrace condition (in use/not in use, relative preservation). During subsequent fieldwork, between three and six sample locations were chosen for analysis in each of several contiguous terrace systems. In this way, the development of terraces within systems as well as between systems could be evaluated.
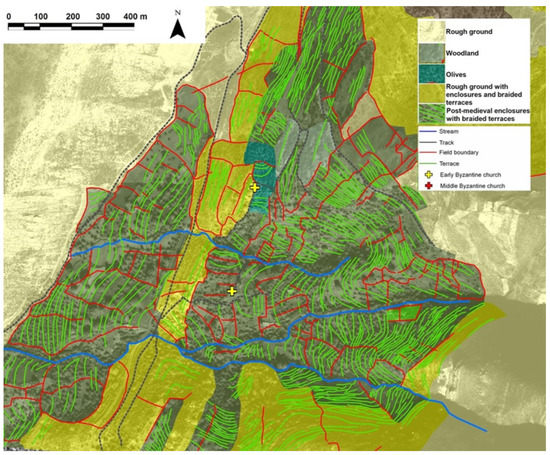
Figure 4.
HLC and retrogressive analysis of the Aria area, Naxos. (Includes IKONOS material© 2006, Space Imaging LLC. All rights reserved) [24].
5.2. Combining OSL Profiling and Dating
A practical consideration with luminescence dating is that it is a time-intensive technique and may take several months between collecting samples and determining associated ages, which has a direct bearing on the number of samples dated. The need for a large number of dated samples has led to attempts to reduce preparation time needed for samples by streamlining or paring down the process [91,92], or reducing measurement time by using a standardised growth curve (SGC) [93,94]. It is important to note that range finder methods provide suggested ages with large uncertainties, while SGCs require regionally based datasets which limit their application.
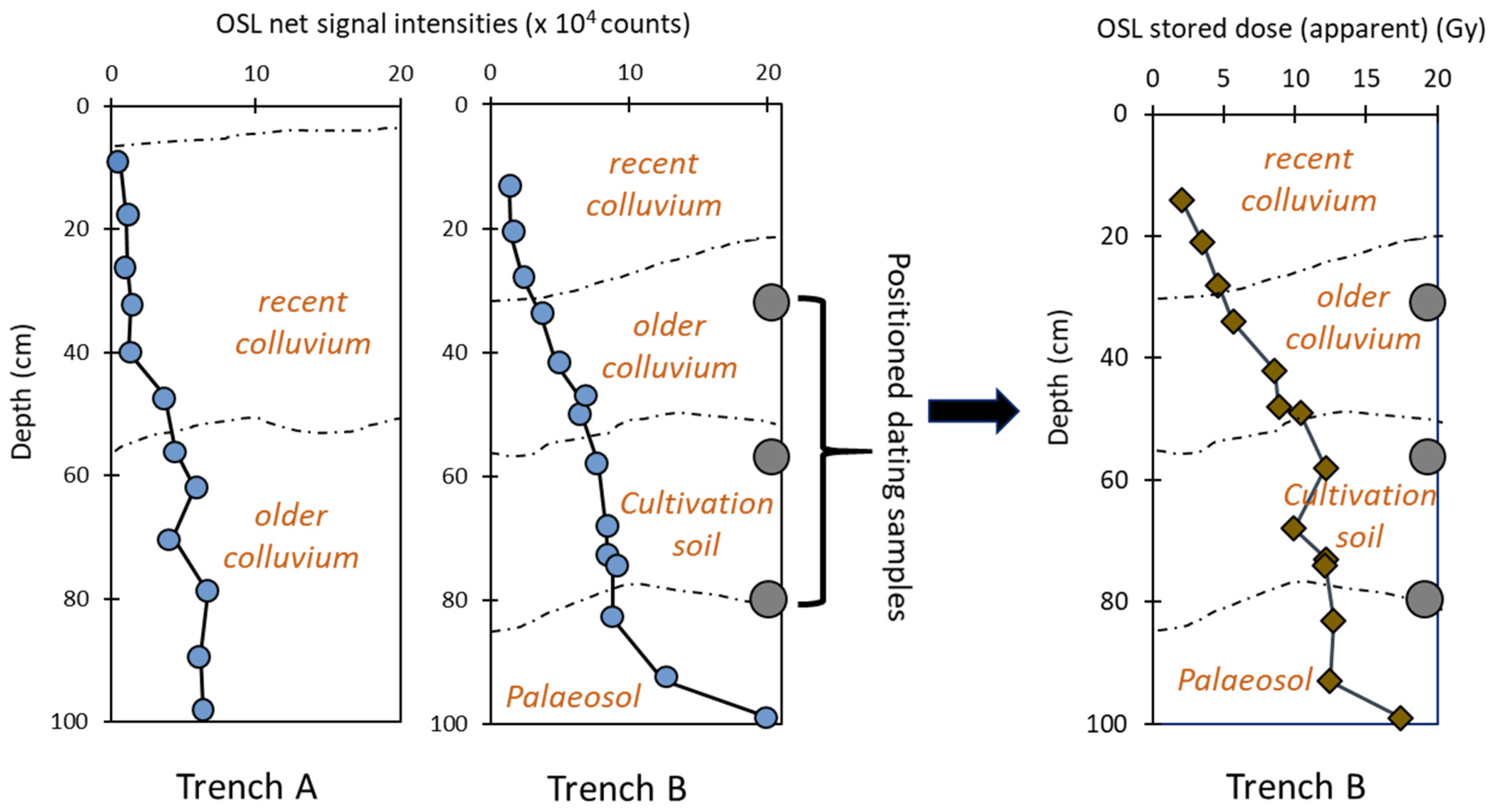
The development of the SUERC portable OSL reader has meant that it is now possible to quantify bulk luminescence behaviour rapidly in the field [95]. The first portable OSL readers were created just over a decade ago, and their utility in the field for generating real-time data has made them a powerful tool in a range of geological settings [96,97] (pp. 165–180). IRSL and OSL signal intensities, depletion indices and IRSL:OSL ratios can be determined in the field and assessed relative to the sedimentology and archaeology [98]. These nuanced data inform the selection of sampling points for full OSL dating [95,99]. Net signal intensities might act as a proxy for age in well-bleached sediment; and stratigraphic trends might inform on depositional processes, rates, and pathways. The samples collected for field profiling can be used retrospectively to determine apparent age estimates in the laboratory using simplified dating protocols. Kinnaird et al. [56] applied this methodology to sedimentary stratigraphies associated with agricultural terraces and earthworks in western Catalonia and demonstrated that progressions and breaks in signal intensities in luminescence profiles do exemplify changes in depositional processes and settings. A key advantage of combining field and laboratory methods, as shown in Figure 5, is that it allows assessment of the ‘chronology’ of the whole investigated section, instead of relying on dates/ages from a small number of selected samples. This further aids in the identification and relation of discrete sedimentary units to the construction or modification of the terrace [69]. Porat et al. [67] exploited this approach to construct a detailed chronology of agricultural terrace building and to understand the history of soil accumulation in the Judean Highlands.
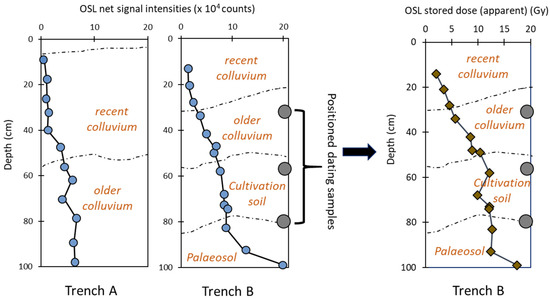
Figure 5.
Illustration of the utility of profiling in the field using two luminescence vs. depth profiles for sediment stratigraphies from two hypothetical trenches A and B. Here, for trench A, net signal intensities show a change in chronology, so this trench is selected for further analyses in the laboratory. This profiling not only allows fieldworkers to create hypotheses about earthwork development to select samples for subsequent laboratory screening but also to locate samples for OSL dating.
Quantitative luminescence ages are still required to be determined to evaluate how well signals from the portable equipment may be used as a proxy for age. Nevertheless, correlating a limited number of conventional full OSL dates with a large number of rapid portable measurements on small bulk samples is a powerful tool. Recently, Turner et al. [69] (2021) combined OSL profiling and dating to produce a large dataset which revealed the first evidence for intensive episodes of terrace building which occurred during the later Middle Ages in five widely-dispersed areas of Spain, Turkey, and Greece. In a different application, Vervust et al. [100] developed the approach of Kinnaird et al. [56] to produce intensity maps for the spatial variations in OSL and IRSL net signal intensities. This novel method not only helps to identify hiatuses and changes within stratigraphic sections, removing the inherent arbitrariness associated with sample collection (which is impossible to capture otherwise), but also provides a practical and cost-effective methodology suitable for dating earthworks around the world.
5.3. Interrogating Micromorphological Data with Luminescence Chronology
In recent years, the combination of soil and sediment micromorphology with OSL dating techniques has become increasingly widespread. Observations of micromorphological characteristics (e.g., shape, form, composition, structure, sedimentological and pedogenic history) of undisturbed deposits within archaeological and geological contexts provide insights on (1) depositional and/or sedimentary processes, (2) natural and cultural post-depositional alterations (e.g., transformations and disturbances), and (3) past climate and environmental histories [101,102]. Collectively, these techniques equip archaeologists with the ability to tease apart sediments and soils into their respective absolute and relative spatio-temporal contexts by placing sites into their broader stratigraphic frameworks. Kemp et al. [12] demonstrated the utility of using soil micromorphology in combination with OSL dating to evaluate how a single deposit can undergo various stages of sedimentation, soil formation, exhumation, and secondary soil formation. Naturally, each of these processes can result in the addition, removal, or translocation of fine grains and can, therefore, have implications for accurate age assessment. A similar approach was used at the Palaeolithic site of Kokkinopilos in Epirus, Greece, where soil micromorphology and OSL proved crucial for disentangling a dynamic sediment and soil environment consisting of spatially discontinuous marshy and dry areas driven by seasonal climate change and erosion [103]. Artefacts buried in argillic soils were confirmed to be of Pleistocene age by using micromorphology to identify undisturbed contexts best suited for OSL dating, effectively solving a debate about the age of the archaeological materials found at Kokkinopilos which had been ongoing since the 1960s [103,104,105,106]. Similar applications of soil micromorphology to aid OSL dating were used at other key Palaeolithic sites across the eastern Mediterranean, including Qesem Cave, Israel [107], Contrebandiers Cave, Morocco [108], Marathousa I, Greece [109,110], Stelida on the island of Naxos, Greece [111], Abric del Pastor, Iberia [112], and Uluzzo C Rockshelter, Italy [113].
Soil and sediment micromorphology also demonstrates how deposits can be altered through chemical or mechanical processes (both natural and cultural) which provide valuable information to inform OSL dating. Understanding post-depositional alteration of deposits is crucial for addressing issues of scatter when determining equivalent dose populations and for properly understanding deposits sampled for OSL dating. For example, at Kebara Cave in Israel, micromorphology was used to identify phosphatic-rich zones which were formed due to the dissolution of bone, which, in turn, resulted in different compositions of key elements needed to calculate OSL dose rates, including uranium, thorium, and potassium [102,114,115]. In less extreme examples, micromorphology can aid in detecting disturbances such as bioturbation caused by burrowing animals, insects, and plants; pedoturbation caused by fluctuating clays during soil formation; cryoturbation in periglacial environments; mechanical effects of water translocation; mineral alterations; and stress-related disturbances [101,116]. Each of these disturbances can have implications for adequate age assessment using OSL. Most recently, these lessons have become essential for understanding the ways in which agricultural terraces are used or disused over time [4,12,33,34,47,117,118].
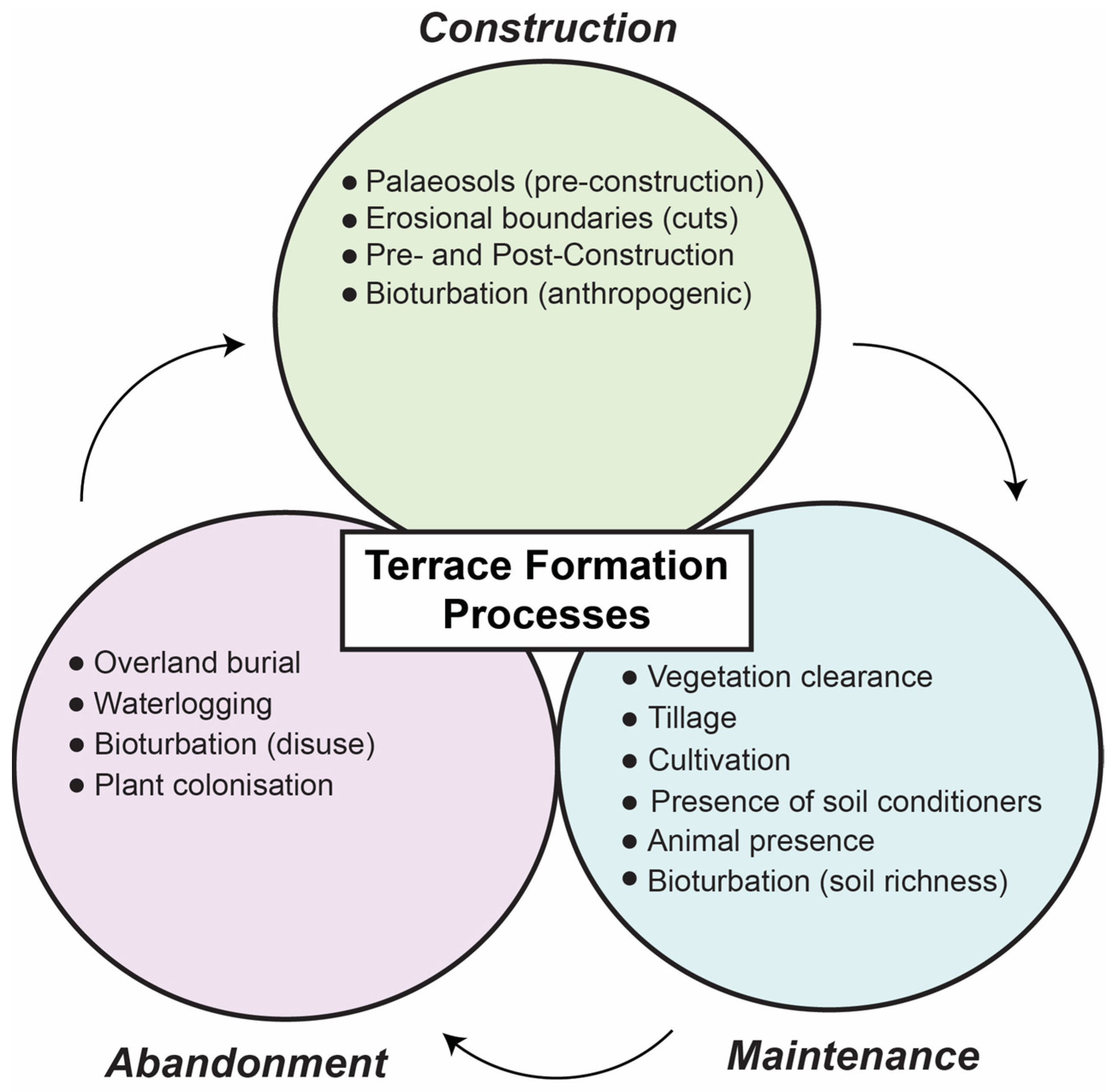
The three key elements of terrace formation processes, i.e., initial formation, maintenance, and abandonment (Figure 6), can be studied effectively using soil micromorphology. Typically, initial terrace construction involves cutting into culturally sterile (paleo) soils that represent a former period of landscape stability which can be compared to post-terrace soils. Identifying and evaluating pre-terrace soils is crucial for understanding initial terrace formation and evaluating how former landscapes have been altered over time through land use [117,118]. Typically, former soils become incorporated into terrace deposits during cultivation or from colluviation of upslope soils [101] (p. 136). Terrace deposits form during maintenance or use periods—which can also include vegetation clearance, tillage, irrigation, animal and insect activity, and the addition of soil conditioners to enhance productivity (e.g., charcoal for carbon or water to address salinization)—and will eventually be abandoned and face plant colonization; all these processes will leave diagnostic microscopic characteristics [119]. Future research designs seeking to incorporate soil micromorphology and OSL to study agricultural terracing can attempt to identify the various stages of terrace formation processes in the field, especially by taking advantage of handheld analytical techniques such as the portable X-ray Fluorescence (pXRF) Spectroscopy or portable OSL measurements.
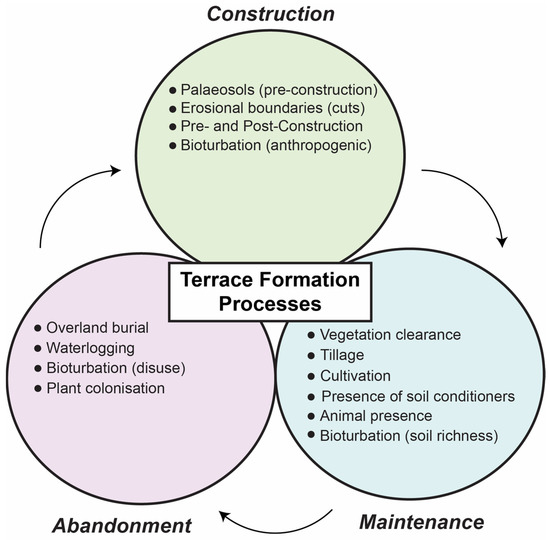
Figure 6.
Schematic representation of terrace formation processes that can be identified using soil and sediment micromorphology.
6. Conclusions
Agricultural terraces are widespread across the Mediterranean. Whilst there have been many studies on these terraces, it is only in the last two decades that substantial chronological data shedding light on the phases of terrace construction and development have started to be published, with luminescence dating becoming increasingly prominent. There are now over 250 luminescence ages from the Mediterranean but there are marked biases in available temporal and spatial data. Over two-thirds of published ages are from Israel, whilst the ages from other regions (e.g., Greece and Turkey) currently show that terraces were predominantly constructed and used during the later Middle Ages. Compared to other geological and geomorphological settings like arid or fluvial landscapes where large luminescence datasets are available, the lack of comprehensive chronologies from agricultural terraces could be attributed to the fact that dating these sediments is notoriously difficult. Major challenges include the incomplete bleaching or resetting of the luminescence signal which causes heterogeneity in generated datasets, necessitating more luminescence measurements and making the whole process more time- and cost-intensive. The recent adoption of GIS techniques like HLC has proven advantageous in identifying key sites for dating and contextualising results. Furthermore, the combination of conventional luminescence dating with field profiling and calibration addresses the issue of having limited numbers of dating samples per section by providing a way to evaluate complete stratigraphic profiles. This cost- and time-effective combination has been successfully demonstrated to date terrace systems in Spain, Turkey, and Greece. However, there remain several key regions in the Mediterranean with extensive terraced landscapes that have not yet seen research campaigns focused on the issue of dating. Andlar et al. [120] present a case for work on Croatian Adriatic terraced landscapes, where they identify nine classes of terraces. They highlight how the lack of a chronological framework inhibits appreciation of the region’s archaeology. The African shores of the Mediterranean are particularly neglected in this respect. The slopes of the Atlas Mountains in Morocco have long histories of terrace construction and use but there has been very little research on when terrace construction began in the region [121]. Studies of historic terrace systems are becoming increasingly important for understanding the complexities of human–environment interactions as the demand for sustainable land use continues to grow in the Mediterranean [122]. Applications of luminescence dating in conjunction with allied geoarchaeological techniques are becoming more relevant than ever to provide a more comprehensive understanding of the evolution of a landscape over time and the role of human activities in shaping it.
Author Contributions
Conceptualisation: A.S.; Writing—original draft preparation: A.S., C.S. and J.A.H.; Writing—review and editing: T.K. and S.T.; Funding acquisition: T.K. and S.T. All authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript.
Funding
This paper derives from the TerraSAgE project (Terraces as Sustainable Agricultural Environments) which is funded by the UK Arts and Humanities Research Council [grant number: AH/T000104/1].
Data Availability Statement
This review is based on previously published data as cited throughout the manuscript.
Acknowledgments
The authors thank the reviewers for their feedback and suggestions.
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
References
- Bradford, J. Ancient Landscapes: Studies in Field Archaeology; Bell: London, UK, 1957. [Google Scholar]
- Spencer, J.E.; Hale, G.A. The origin, nature, and distribution of agricultural terracing. Pac. Viewp. 1961, 2, 1–40. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Correia, T. Land abandonment: Changes in the land use patterns around the Mediterranean basin. Cah. Options Méditerr. 1993, 1, 97–112. [Google Scholar]
- French, C.A.; Whitelaw, T.M. Soil erosion, agricultural terracing and site formation processes at Markiani, Amorgos, Greece: The micromorphological perspective. Geoarchaeology 1999, 14, 151–189. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Grove, A.T.; Rackham, O. The Nature of Mediterranean Europe: An Ecological History; Yale University Press: London, UK, 2003. [Google Scholar]
- Bevan, A.; Conolly, J. Terraced fields and Mediterranean landscape structure: An analytical case study from Antikythera, Greece. Ecol. Model. 2011, 222, 1303–1314. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bevan, A.; Conolly, J.; Colledge, S.; Frederick, C.; Palmer, C.; Siddall, R.; Stellatou, A. The long-term ecology of agricultural terraces and enclosed fields from Antikythera, Greece. Hum. Ecol. 2013, 41, 255–272. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rackham, O.; Moody, J.; Nixon, L.; Price, S. Some field systems in Crete. Br. Sch. Athens Stud. 2010, 18, 269–284. [Google Scholar]
- Petanidou, T.; Kizos, T.; Soulakellis, N. Socioeconomic dimensions of changes in the agricultural landscape of the Mediterranean basin: A case study of the abandonment of cultivation terraces on Nisyros Island, Greece. Environ. Manag. 2008, 41, 250–266. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- García-Ruiz, J.M.; Lana-Renault, N. Hydrological and erosive consequences of farmland abandonment in Europe, with special reference to the Mediterranean region—A review. Agric. Ecosyst. Environ. 2011, 140, 317–338. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gibson, S. Agricultural terraces and settlement expansion in the highlands of early Iron Age Palestine: Is there any correlation between the two? In Studies in the Archaeology of the Iron Age in Israel and Jordan; A&C Black: London, UK, 2001; pp. 113–146. [Google Scholar]
- Kemp, R.; Branch, N.; Silva, B.; Meddens, F.; Williams, A.; Kendall, A.; Vivanco, C. Pedosedimentary, cultural and environmental significance of paleosols within pre-hispanic agricultural terraces in the southern Peruvian Andes. Quat. Int. 2006, 158, 13–22. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Borejsza, A.; López, I.R.; Frederick, C.D.; Bateman, M.D. Agricultural slope management and soil erosion at La Laguna, Tlaxcala, Mexico. J. Archaeol. Sci. 2008, 35, 1854–1866. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Acabado, S. A Bayesian approach to dating agricultural terraces: A case from the Philippines. Antiquity 2009, 83, 801–814. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Henck, A.; Taylor, J.; Lu, H.; Li, Y.; Yang, Q.; Grub, B.; Breslow, S.J.; Robbins, A.; Elliott, A.; Hinckley, T.; et al. Anthropogenic hillslope terraces and swidden agriculture in Jiuzhaigou National Park, northern Sichuan, China. Quat. Res. 2010, 73, 201–207. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiang, Y.; Li, S.; Cai, D.; Chen, W.; Liu, Y.; Yu, Z. The genesis and paleoenvironmental records of Longji agricultural terraces, southern China: A pilot study of human–environment interaction. Quat. Int. 2014, 321, 12–21. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiang, Y.; Li, S.; Chen, W.; Cai, D.; Liu, Y. The evolution of crop cultivation and paleoenvironment in the Longji Terraces, southern China: Organic geochemical evidence from paleosols. J. Environ. Manag. 2017, 202, 524–531. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Agnoletti, M.; Conti, L.; Frezza, L.; Santoro, A. Territorial analysis of the agricultural terraced landscapes of Tuscany (Italy): Preliminary results. Sustainability 2015, 7, 4564–4581. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lasanta, T.; Arnáez, J.; Oserín, M.; Ortigosa, L.M. Marginal lands and erosion in terraced fields in the Mediterranean mountains. Mt. Res. Dev. 2001, 21, 69–76. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ales, R.F.; Martin, A.; Ortega, F.; Ales, E.E. Recent changes in landscape structure and function in a Mediterranean region of SW Spain (1950–1984). Landsc. Ecol. 1992, 7, 3–18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tarolli, P.; Rizzo, D.; Brancucci, G. Terraced landscapes: Land abandonment, soil degradation, and suitable management. In World Terraced Landscapes: History, Environment, Quality of Life; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2019; pp. 195–210. [Google Scholar]
- Moreno-de-las-Heras, M.; Lindenberger, F.; Latron, J.; Lana-Renault, N.; Llorens, P.; Arnáez, J.; Romero-Díaz, A.; Gallart, F. Hydro-geomorphological consequences of the abandonment of agricultural terraces in the Mediterranean region: Key controlling factors and landscape stability patterns. Geomorphology 2019, 333, 73–91. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Turner, S.; Crow, J. Unlocking historic landscapes in the Eastern Mediterranean: Two pilot studies using Historic Landscape Characterisation. Antiquity 2010, 84, 216–229. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Crow, J.; Turner, S.; Vionis, A.K. Characterizing the historic landscapes of Naxos. J. Mediterr. Archaeol. 2011, 24, 111–137. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Frederick, C.D.; Krahtopoulou, A. Deconstructing agricultural terraces: Examining the influence of construction method on stratigraphy, dating and archaeological visibility. In Landscape and Land Use in Postglacial Greece; A&C Black: London, UK, 2000; pp. 79–94. [Google Scholar]
- Wilkinson, T.J. Archaeological Landscapes of the Near East; University of Arizona Press: Tucson, AZ, USA, 2003. [Google Scholar]
- Gibson, S. The Archaeology of Agricultural Terraces in the Mediterranean zone of the southern Levant and the use of the optically stimulated luminescence (OSL) dating method. In Soils and Sediments as Archives of Landscape Change: Geoarchaeology and Landscape Change in the Subtropics and Tropics (Erlanger Geographische Arbeiten42); ACADEMIA: San Francisco, CA, USA, 2015; pp. 295–314. [Google Scholar]
- Price, S.; Nixon, L. Ancient Greek agricultural terraces: Evidence from texts and archaeological survey. Am. J. Archaeol. 2005, 109, 665–694. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lavento, M. Archaeological investigations of ancient water systems in Jordan. In Transference. Interdisciplinary Communications 2008/2009; CAS: Oslo, Norway, 2010. [Google Scholar]
- Lavento, M.; Huotari, M. A water management system around Jabal Harun, Petra–its design and significance. In Proceedings of the 11th International Conference on the History of Water Management and Hydraulic Engineering in the Mediterranean Region, Israel, 7–12 May 2001; Volume 1, pp. 93–106. [Google Scholar]
- Kouki, P. Archaeological Evidence of Land Tenure in the Petra Region, Jordan: Nabataean-Early Roman to Late Byzantine. J. Mediterr. Archaeol. 2009, 22, 29–56. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, W.E. Pylos regional archaeological project, part IV: Change and the human landscape in a modern Greek village in Messenia. Hesperia 2001, 70, 49–98. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Krahtopoulou, A.; Frederick, C. The stratigraphic implications of long-term terrace agriculture in dynamic landscapes: Polycyclic terracing from Kythera Island, Greece. Geoarchaeology Int. J. 2008, 23, 550–585. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Quirós-Castillo, J.A.; Nicosia, C. Reconstructing past terraced agrarian landscapes in the Ebro Valley: The deserted village of Torrentejo in the Basque Country, Spain. Geoarchaeology 2019, 34, 684–697. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kiesow, S.; Bork, H.R. Agricultural terraces as a proxy to landscape history on Madeira island, Portugal. Ler História 2017, 31, 127–152. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brown, A.; Walsh, K.; Fallu, D.; Cucchiaro, S.; Tarolli, P. European agricultural terraces and lynchets: From archaeological theory to heritage management. World Archaeol. 2020, 52, 566–588. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Betancourt, P.P.; Hope Simpson, R. The agricultural system of Bronze age Pseira. Cretan Stud. 1992, 3, 47–54. [Google Scholar]
- Rackham, O.; Moody, J. The Making of the Cretan Landscape; Manchester University Press: Manchester, UK, 1996. [Google Scholar]
- Bayliss, A. Rolling out revolution: Using radiocarbon dating in archaeology. Radiocarbon 2009, 51, 123–147. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Taylor, R.E.; Bar, O. Radiocarbon Dating: An Archaeological Perspective. Am. J. Archaeol. 2018, 122. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Beckers, B.; Berking, J.; Schütt, B. Ancient water harvesting methods in the drylands of the Mediterranean and Western Asia. Etopoi. J. Anc. Stud. 2013. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rendu, C.; Passarrius, O.; Calastrenc, C.; Julia, R.; Llubes, M.; Illes, P.; Campmajo, P.; Jodry, C.; Crabol, D.; Bille, E.; et al. Reconstructing past terrace fields in the Pyrenees: Insights into land management and settlement from the Bronze Age to the Early Modern era at Vilalta (1650 masl, Cerdagne, France). J. Field Archaeol. 2015, 40, 461–480. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Puy, A.; Balbo, A.L.; Bubenzer, O. Radiocarbon dating of agrarian terraces by means of buried soils. Radiocarbon 2016, 58, 345–363. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- González Reyero, S.; Sánchez-Palencia, F.J.; López-Sáez, J.A.; Pérez-Díaz, S.; Ruiz-Alonso, M.; Romero Perona, D.; Vallés Iriso, J.; Álvarez-Ayuso, E. Agrarian landscapes in the Iberian Iron Age: Mountain communities and land use in southeastern Iberia. Geoarchaeology 2019, 34, 252–271. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bruins, H.J.; van der Plicht, J. Iron Age Agriculture-A Critical Rejoinder to “Settlement Oscillations in the Negev Highlands Revisited: The Impact of Microarchaeological Methods”. Radiocarbon 2017, 59, 1. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bruins, H.J.; Van Der Plicht, J.; Haiman, M. Desert habitation history by 14C dating of soil layers in rural building structures (Negev, Israel): Preliminary results from Horvat Haluqim. Radiocarbon 2012, 54, 391–406. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Puy, A.; Balbo, A.L. The genesis of irrigated terraces in al-Andalus. A geoarchaeological perspective on intensive agriculture in semi-arid environments (Ricote, Murcia, Spain). J. Arid Environ. 2013, 89, 45–56. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ferro-Vázquez, C.; Martínez-Cortizas, A.; Nóvoa-Muñoz, J.C.; Ballesteros-Arias, P.; Criado-Boado, F. 1500 years of soil use reconstructed from the chemical properties of a terraced soil sequence. Quat. Int. 2014, 346, 28–40. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ferro-Vázquez, C.; Kaal, J.; Santos Arévalo, F.; Criado Boado, F. Molecular fingerprinting of 14C dated soil organic matter fractions from archaeological settings in NW Spain. Radiocarbon 2018, 61, 101–130. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pessenda, L.C.; Gouveia, S.E.; Aravena, R. Radiocarbon dating of total soil organic matter and humin fraction and its comparison with 14C ages of fossil charcoal. Radiocarbon 2001, 43, 595–601. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Buck, C.E.; Cavanagh, W.G.; Litton, C.D. Bayesian Approach to Interpreting Archaeological Data; Wiley Chichester: Chichester, UK, 1996. [Google Scholar]
- Gadot, Y.; Davidovich, U.; Avni, G.; Avni, Y.; Piasetzky, M.; Faershtein, G.; Golan, D.; Porat, N. The formation of a Mediterranean terraced landscape: Mount Eitan, Judean Highlands, Israel. J. Archaeol. Sci. Rep. 2016, 6, 397–417. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gillespie, R.; Prosser, I.P.; Dlugokencky, E.; Sparks, R.J.; Wallace, G.; Chappell, J. AMS dating of alluvial sediments on the southern tablelands of New South Wales, Australia. Radiocarbon 1992, 34, 29–36. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Beckers, B.; Schütt, B.; Tsukamoto, S.; Frechen, M. Age determination of Petra’s engineered landscape–optically stimulated luminescence (OSL) and radiocarbon ages of runoff terrace systems in the Eastern Highlands of Jordan. J. Archaeol. Sci. 2013, 40, 333–348. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Silva-Sánchez, N.; Kinnaird, T.; Fernández-Ferreiro, M.; López-Salas, E.; Turner, S.; Sánchez-Pardo, J.-C. Written in soil and paper. Investigating environmental transformations of a monastic landscape by combining geoarchaeology and palynology with historical analysis at Samos (Galicia). J. Archaeol. Sci. Rep. 2022, 45, 103575. [Google Scholar]
- Kinnaird, T.; Bolos, J.; Turner, A.; Turner, S. Optically-stimulated luminescence profiling and dating of historic agricultural terraces in Catalonia (Spain). J. Archaeol. Sci. 2017, 78, 66–77. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Porat, N.; Davidovich, U.; Avni, Y.; Avni, G.; Gadot, Y. Using OSL measurements to decipher soil history in archaeological terraces, Judean Highlands, Israel. Land Degrad. Dev. 2018, 29, 643–650. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aitken, M.J. Introduction to Optical Dating: The Dating of Quaternary Sediments by the Use of Photon-Stimulated Luminescence; Clarendon Press: Oxford, UK, 1998. [Google Scholar]
- Duller, G.A. Single-grain optical dating of Quaternary sediments: Why aliquot size matters in luminescence dating. Boreas 2008, 37, 589–612. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Granger, D.E.; Muzikar, P.F. Dating sediment burial with in situ-produced cosmogenic nuclides: Theory, techniques, and limitations. Earth Planet. Sci. Lett. 2001, 188, 269–281. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Walsh, K.; Berger, J.F.; Roberts, C.N.; Vanniere, B.; Ghilardi, M.; Brown, A.G.; Woodbridge, J.; Lespez, L.; Estrany, J.; Glais, A.; et al. Holocene demographic fluctuations, climate and erosion in the Mediterranean: A meta data-analysis. Holocene 2019, 29, 864–885. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Davidovich, U.; Porat, N.; Gadot, Y.; Avni, Y.; Lipschits, O. Archaeological investigations and OSL dating of terraces at Ramat Rahel, Israel. J. Field Archaeol. 2012, 37, 192–208. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Meister, J.; Krause, J.; Müller-Neuhof, B.; Portillo, M.; Reimann, T.; Schütt, B. Desert agricultural systems at EBA Jawa (Jordan): Integrating archaeological and paleoenvironmental records. Quat. Int. 2017, 434, 33–50. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Avni, Y.; Porat, N.; Avni, G. Pre-farming environment and OSL chronology in the Negev Highlands, Israel. J. Arid Environ. 2012, 86, 12–27. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Avni, G.; Porat, N.; Avni, Y. Byzantine–Early Islamic agricultural systems in the Negev Highlands: Stages of development as interpreted through OSL dating. J. Field Archaeol. 2013, 38, 332–346. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gadot, Y.; Davidovich, U.; Avni, Y.; Avni, G.; Porat, N. The Formation of Terraced Landscapes in the Judean Highlands in Israel, and its Implications for Biblical Agricultural History. Hebr. Bible Anc. Isr. 2016, 5, 437–455. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Porat, N.; López, G.I.; Lensky, N.; Elinson, R.; Avni, Y.; Elgart-Sharon, Y.; Faershtein, G.; Gadot, Y. Using portable OSL reader to obtain a time scale for soil accumulation and erosion in archaeological terraces, the Judean Highlands, Israel. Quat. Geochronol. 2019, 49, 65–70. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stavi, I.; Ragolsky, G.; Haiman, M.; Porat, N. Ancient to recent-past runoff harvesting agriculture in the hyper-arid Arava Valley: OSL dating and insights. Holocene 2021, 31, 1047–1054. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Turner, S.; Kinnaird, T.; Varinlioğlu, G.; Şerifoğlu, T.; Koparal, E.; Demirciler, V.; Athanassoulis, D.; Ødegård, K.; Crow, J.; Jackson, M.; et al. Agricultural terraces in the Mediterranean: Intensive construction during the later Middle Ages revealed by landscape analysis with OSL profiling and dating. Antiquity 2021, 95, 773–790. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- French, C.; Taylor, S.; McLaughlin, R.; Cresswell, A.; Kinnaird, T.; Sanderson, D.; Stoddart, S.; Malone, C. A Neolithic palaeo-catena for the Xagħra Upper Coralline Limestone plateau of Gozo, Malta, and its implications for past soil development and land use. Catena 2018, 171, 337–358. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Singarayer, J.S.; Bailey, R.M. Further investigations of the quartz optically stimulated luminescence components using linear modulation. Radiat. Meas. 2003, 37, 451–458. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, B.; Li, S.H. Comparison of De estimates using the fast component and the medium component of quartz OSL. Radiat. Meas. 2006, 41, 125–136. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Olley, J.M.; Caitcheon, G.G.; Roberts, R.G. The origin of dose distributions in fluvial sediments, and the prospect of dating single grains from fluvial deposits using optically stimulated luminescence. Radiat. Meas. 1999, 30, 207–217. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rittenour, T.M. Luminescence dating of fluvial deposits: Applications to geomorphic, palaeoseismic and archaeological research. Boreas 2008, 37, 613–635. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bateman, M.D.; Boulter, C.H.; Carr, A.S.; Frederick, C.D.; Peter, D.; Wilder, M. Preserving the palaeoenvironmental record in drylands: Bioturbation and its significance for luminescence-derived chronologies. Sediment. Geol. 2007, 195, 5–19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nathan, R.P.; Thomas, P.J.; Jain, M.; Murray, A.S.; Rhodes, E.J. Environmental dose rate heterogeneity of beta radiation and its implications for luminescence dating: Monte Carlo modelling and experimental validation. Radiat. Meas. 2003, 37, 305–313. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guérin, G.; Christophe, C.; Philippe, A.; Murray, A.S.; Thomsen, K.J.; Tribolo, C.; Urbanová, P.; Jain, M.; Guibert, P.; Mercier, N.; et al. Absorbed dose, equivalent dose, measured dose rates, and implications for OSL age estimates: Introducing the Average Dose Model. Quat. Geochronol. 2017, 41, 163–173. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Galbraith, R.F.; Roberts, R.G.; Laslett, G.M.; Yoshida, H.; Olley, J.M. Optical dating of single and multiple grains of quartz from Jinmium rock shelter, northern Australia: Part I, experimental design and statistical models. Archaeometry 1999, 41, 339–364. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rodnight, H.; Duller, G.A.T.; Wintle, A.G.; Tooth, S. Assessing the reproducibility and accuracy of optical dating of fluvial deposits. Quat. Geochronol. 2006, 1, 109–120. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Arnold, L.J.; Roberts, R.G. Stochastic modelling of multi-grain equivalent dose (De) distributions: Implications for OSL dating of sediment mixtures. Quat. Geochronol. 2009, 4, 204–230. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Murray, A.; Arnold, L.J.; Buylaert, J.P.; Guérin, G.; Qin, J.; Singhvi, A.K.; Smedley, R.; Thomsen, K.J. Optically stimulated luminescence dating using quartz. Nat. Rev. Methods Prim. 2021, 1, 72. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fairclough, G.; Sarlov-Herlin, I.; Swanwick, C. (Eds.) Routledge Handbook of Landscape Character Assessment; Routledge: London, UK, 2018. [Google Scholar]
- Crow, J.; Turner, S. Silivri and the Thracian hinterland of Istanbul: An historic landscape. Anatol. Stud. 2009, 59, 167–182. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Turner, S.; Bolòs, J.; Kinnaird, T. Changes and continuities in a Mediterranean landscape: A new interdisciplinary approach to understanding historic character in western Catalonia. Landsc. Res. 2018, 43, 922–938. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Turner, S. Historic landscape characterisation: An archaeological approach to landscape heritage. In Routledge Handbook of Landscape Character Assessment; Fairclough, G., Sarlov-Herlin, I., Swanwick, C., Eds.; Routledge: London, UK, 2018; pp. 37–50. [Google Scholar]
- Dabaut, N.; Carrer, F. Historic Landscape Characterisation: Technical approaches beyond theory. Landscapes 2020, 21, 152–167. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rippon, S. Historic Landscape Analysis: Deciphering the Countryside; Council for British Archaeology: York, UK, 2005. [Google Scholar]
- Oosthuizen, S. Landscapes Decoded; University of Hertfordshire Press: Hertfordshire, UK, 2006. [Google Scholar]
- Doneus, M.; Neubauer, W.; Filzwieser, R.; Sevara, C. Stratigraphy from topography II. The practical application of the Harris Matrix for the GIS-based spatio-temporal archaeological interpretation of topographical data. Archaeol. Austriaca 2022, 106, 223–252. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brown, A.G.; Fallu, D.; Walsh, K.; Cucchiaro, S.; Tarolli, P.; Zhao, P.; Pears, B.R.; van Oost, K.; Snape, L.; Lang, A.; et al. Ending the Cinderella status of terraces and lynchets in Europe: The geomorphology of agricultural terraces and implications for ecosystem services and climate adaptation. Geomorphology 2021, 379, 107579. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Roberts, H.M.; Durcan, J.A.; Duller, G.A. Exploring procedures for the rapid assessment of optically stimulated luminescence range-finder ages. Radiat. Meas. 2009, 44, 582–587. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Durcan, J.A.; Roberts, H.M.; Duller, G.A.T.; Alizai, A.H. Testing the use of range-finder OSL dating to inform field sampling and laboratory processing strategies. Quat. Geochronol. 2010, 5, 86–90. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Roberts, H.M.; Duller, G.A. Standardised growth curves for optical dating of sediment using multiple-grain aliquots. Radiat. Meas. 2004, 38, 241–252. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Telfer, M.W.; Bateman, M.D.; Carr, A.S.; Chase, B.M. Testing the applicability of a standardized growth curve (SGC) for quartz OSL dating: Kalahari dunes, South African coastal dunes and Florida dune cordons. Quat. Geochronol. 2008, 3, 137–142. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Munyikwa, K.; Kinnaird, T.C.; Sanderson, D.C. The potential of portable luminescence readers in geomorphological investigations: A review. Earth Surf. Process. Landf. 2021, 46, 131–150. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Boyd, S.L.; Kinnaird, T.C.; Srivastava, A.; Whittaker, J.E.; Bates, C.R. Investigation of coastal environmental change at Ruddons Point, Fife, SE Scotland. Scott. J. Geol. 2022, 58, sjg2022-005. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kinnaird, T.; Bates, M.; Bateman, R.; Srivastava, A. Europe’s Lost Frontiers: Volume 1, Context and Methodology; Gaffney, V., Fitch, S., Eds.; Archaeopress: Oxford, UK, 2022; Volume 1, pp. 165–180. 15p. [Google Scholar]
- Sanderson, D.C.; Murphy, S. Using simple portable OSL measurements and laboratory characterisation to help understand complex and heterogeneous sediment sequences for luminescence dating. Quat. Geochronol. 2010, 5, 299–305. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stang, D.M.; Rhodes, E.J.; Heimsath, A.M. Assessing soil mixing processes and rates using a portable OSL-IRSL reader: Preliminary determinations. Quat. Geochronol. 2012, 10, 314–319. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vervust, S.; Kinnaird, T.; Herring, P.; Turner, S. Optically stimulated luminescence profiling and dating of earthworks: The creation and development of prehistoric field boundaries at Bosigran, Cornwall. Antiquity 2020, 94, 420–436. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Courty, M.A.; Goldberg, P.; Macphail, R. Soils and Micromorphology in Archaeology; Cambridge University Press: Cambridge, UK, 1989. [Google Scholar]
- Karkanas, P.; Goldberg, P. Reconstructing Archaeological Sites: Understanding the Geoarchaeological Matrix; John Wiley & Sons: Hoboken, NJ, USA, 2019. [Google Scholar]
- Tourloukis, V.; Karkanas, P.; Wallinga, J. Revisiting Kokkinopilos: Middle Pleistocene radiometric dates for stratified archaeological remains in Greece. J. Archaeol. Sci. 2015, 57, 355–369. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dakaris, S.I.; Higgs, E.S.; Hey, R.W.; Tippett, H.; Mellars, P. The climate, environment and industries of Stone Age Greece: Part I. Proc. Prehist. Soc. 1964, 30, 199–244. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Higgs, E.S.; Vita-Finzi, C. The climate, environment and industries of Stone Age Greece: Part II. In Proceedings of the Prehistoric Society; Cambridge University Press: Cambridge, UK, 1966; Volume 32, pp. 1–29. [Google Scholar]
- Van Andel, T.H.; Runnels, C.N. Karstic wetland dwellers of Middle Palaeolithic Epirus, Greece. J. Field Archaeol. 2005, 30, 367–384. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Karkanas, P.; Shahack-Gross, R.; Ayalon, A.; Bar-Matthews, M.; Barkai, R.; Frumkin, A.; Gopher, A.; Stiner, M.C. Evidence for habitual use of fire at the end of the Lower Paleolithic: Site-formation processes at Qesem Cave, Israel. J. Hum. Evol. 2007, 53, 197–212. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aldeias, V.; Goldberg, P.; Dibble, H.L.; El-Hajraoui, M. Deciphering site formation processes through soil micromorphology at Contrebandiers Cave, Morocco. J. Hum. Evol. 2014, 69, 8–30. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jacobs, Z.; Li, B.; Karkanas, P.; Tourloukis, V.; Thompson, N.; Panagopoulou, E.; Harvati, K. Optical dating of K-feldspar grains from Middle Pleistocene lacustrine sediment at Marathousa 1 (Greece). Quat. Int. 2018, 497, 170–177. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Karkanas, P.; Tourloukis, V.; Thompson, N.; Giusti, D.; Panagopoulou, E.; Harvati, K. Sedimentology and micromorphology of the Lower Palaeolithic lakeshore site Marathousa 1, Megalopolis basin, Greece. Quat. Int. 2018, 497, 123–136. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Carter, T.; Contreras, D.A.; Holcomb, J.; Mihailović, D.D.; Karkanas, P.; Guérin, G.; Taffin, N.; Athanasoulis, D.; Lahaye, C. Earliest occupation of the Central Aegean (Naxos), Greece: Implications for hominin and Homo sapiens’ behavior and dispersals. Sci. Adv. 2019, 5, eaax0997. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Connolly, R.; Jambrina-Enríquez, M.; Herrera-Herrera, A.V.; Vidal-Matutano, P.; Fagoaga, A.; Marquina-Blasco, R.; Marin-Monfort, M.D.; Ruiz-Sánchez, F.J.; Laplana, C.; Bailon, S.; et al. A multiproxy record of palaeoenvironmental conditions at the Middle Palaeolithic site of Abric del Pastor (Eastern Iberia). Quat. Sci. Rev. 2019, 225, 106023. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Spinapolice, E.E.; Zerboni, A.; Meyer, M.C.; Talamo, S.; Mariani, G.S.; Gliganic, L.A.; Buti, L.; Fusco, M.; Maiorano, M.P.; Silvestrini, S.; et al. Back to Uluzzo–archaeological, palaeoenvironmental and chronological context of the Mid–Upper Palaeolithic sequence at Uluzzo C Rock Shelter (Apulia, southern Italy). J. Quat. Sci. 2022, 37, 217–234. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schiegl, S.; Goldberg, P.; Bar-Yosef, O.; Weiner, S. Ash deposits in Hayonim and Kebara Caves, Israel: Macroscopic, microscopic and mineralogical observations, and their archaeological implications. J. Archaeol. Sci. 1996, 23, 763–781. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Weiner, S.; Schiegl, S.; Goldberg, P.; Bar-Yosef, O. Mineral assemblages in Kebara and Hayonim, Israel: Excavation strategies, bone preservation and wood ash remnants. Isr. J. Chem. 1995, 35, 143–154. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Davidson, D.A. Bioturbation in old arable soils: Quantitative evidence from soil micromorphology. J. Archaeol. Sci. 2002, 29, 1247–1253. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Goodman-Elgar, M. Evaluating soil resilience in long-term cultivation: A study of pre-Columbian terraces from the Paca Valley, Peru. J. Archaeol. Sci. 2008, 35, 3072–3086. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Boixadera, J.; Riera, S.; Vila, S.; Esteban, I.; Albert, R.M.; Llop, J.M.; Poch, R.M. Buried A horizons in old bench terraces in Les Garrigues (Catalonia). Catena 2016, 137, 635–650. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Deák, J.; Gebhardt, A.; Lewis, H.; Usai, M.R.; Lee, H. Soils disturbed by vegetation clearance and tillage. In Archaeological Soil and Sediment Micromorphology; Nicosia, C., Stoopes, G., Eds.; Wiley Blackwell: Hoboken, NJ, USA, 2017; pp. 233–264. [Google Scholar]
- Andlar, G.; Šrajer, F.; Trojanović, A. Classifying the Mediterranean terraced landscape: The case of Adriatic Croatia. Acta Geogr. Slov. 2017, 57, 111–129. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ziyadi, M.; Dahbi, A.; Aitlhaj, A.; El Ouahrani, A.; El Ouahidi, A.; Achtak, H. Terraced agroforestry systems in West Anti-Atlas (Morocco): Incidence of climate change and prospects for sustainable development. In Climate Change-Resilient Agriculture and Agroforestry; Springer: Cham, Germany, 2019; pp. 1–19. [Google Scholar]
- Brandolini, F.; Kinnaird, T.C.; Srivastava, A.; Turner, S. How landscape archaeology can inform future sustainable soil management. Sci. Rep. 2023, in press.
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).